145:. A population exhibiting a weak Allee effect will possess a reduced per capita growth rate (directly related to individual fitness of the population) at lower population density or size. However, even at this low population size or density, the population will always exhibit a positive per capita growth rate. Meanwhile, a population exhibiting a strong Allee effect will have a critical population size or density under which the population growth rate becomes negative. Therefore, when the population density or size hits a number below this threshold, the population will be destined for extinction without any further aid. A strong Allee effect is often easier to demonstrate empirically using time series data, as one can pinpoint the population size or density at which per capita growth rate becomes negative.
240:
desirable than common species, prices for rare species can exceed high harvest costs. This phenomenon can create an "anthropogenic" Allee effect where rare species go extinct but common species are sustainably harvested. The anthropogenic Allee effect has become a standard approach for conceptualizing the threat of economic markets on endangered species. However, the original theory was posited using a one dimensional analysis of a two dimensional model. It turns out that a two dimensional analysis yields an Allee curve in human exploiter and biological population space and that this curve separating species destined to extinction vs persistence can be complicated. Even very high population sizes can potentially pass through the originally proposed Allee thresholds on predestined paths to extinction.
122:
285:). The Florida panther experienced a genetic bottleneck in the early 1990s where the population was reduced to ≈25 adult individuals. This reduction in genetic diversity was correlated with defects that include lower sperm quality, abnormal testosterone levels, cowlicks, and kinked tails. In response, a genetic rescue plan was put in motion and several female pumas from Texas were introduced into the Florida population. This action quickly led to the reduction in the prevalence of the defects previously associated with inbreeding depression. Although the timescale for this inbreeding depression is larger than of those more immediate Allee effects, it has significant implications on the long-term persistence of a species.
113:
cooperative hunting and the ability to more easily find mates, both influenced by population density, are component Allee effects, as they influence individual fitness of the population. At low population density, these component Allee effects would add up to produce an overall demographic Allee effect (increased fitness with higher population density). When population density reaches a high number, negative density dependence often offsets the component Allee effects through resource competition, thus erasing the demographic Allee effect. Allee effects might occur even at high population density for some species.
318:
colonization front simultaneously reduces the speed of colonization and enables a diversity of genes coming from the core of the population to remain on the front. The Allee effect also affects the spatial distribution of diversity. Whereas spatio-temporal models which do not include an Allee effect lead to a vertical pattern of genetic diversity (i.e., a strongly structured spatial distribution of genetic fractions), those including an Allee effect lead to a "horizontal pattern" of genetic diversity (i.e., an absence of genetic differentiation in space).
294:
increase the risk of population extinction. Whether or not demographic stochasticity can be considered a part of Allee effect is somewhat contentious however. The most current definition of Allee effect considers the correlation between population density and mean individual fitness. Therefore, random variation resulting from birth and death events would not be considered part of Allee effect as the increased risk of extinction is not a consequence of the changing fates of individuals within the population.
2515:
273:). While evolutionary theory states that expressed deleterious alleles should be purged through natural selection, purging would be most efficient only at eliminating alleles that are highly detrimental or harmful. Mildly deleterious alleles such as those that act later in life would be less likely to be removed by natural selection, and conversely, newly acquired beneficial mutations are more likely to be lost by random chance in smaller genetic pools than larger ones.
67:
1950s, a time when the field of ecology was heavily focused on the role of competition among and within species. The classical view of population dynamics stated that due to competition for resources, a population will experience a reduced overall growth rate at higher density and increased growth rate at lower density. In other words, individuals in a population would be better off when there are fewer individuals around due to a limited amount of resources (see
154:
individuals in the species. Examples of such cooperative behaviors include better mate finding, environmental conditioning, and group defense against predators. As these mechanisms are more-easily observable in the field, they tend to be more commonly associated with the Allee effect concept. Nevertheless, mechanisms of Allee effect that are less conspicuous such as
191:
Another possible benefit of aggregation is to protect against predation by group anti-predator behavior. Many species exhibit higher rates of predator vigilance behavior per individual at lower density. This increased vigilance might result in less time and energy spent on foraging, thus reducing the
224:
Environmental conditioning generally refers to the mechanism in which individuals work together in order to improve their immediate or future environment for the benefit of the species. This alteration could involve changes in both abiotic (temperature, turbulence, etc.) or biotic (toxins, hormones,
112:
The distinction between the two terms lies on the scale of the Allee effect: the presence of a demographic Allee effect suggests the presence of at least one component Allee effect, while the presence of a component Allee effect does not necessarily result in a demographic Allee effect. For example,
125:
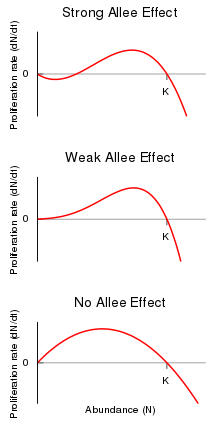
Allee effects are classified by the nature of density dependence at low densities. If the population shrinks for low densities, there is a strong Allee effect. If the proliferation rate is positive and increasing then there is a weak Allee effect. The null hypothesis is that proliferation rates are
894:
If the sub-populations are subject to different environmental variations (i.e. separated enough that a disaster could occur at one sub-population site without affecting the other sub-populations) but still allow individuals to travel between sub-populations, then the individual sub-populations are
239:
Classic economic theory predicts that human exploitation of a population is unlikely to result in species extinction because the escalating costs to find the last few individuals will exceed the fixed price one achieves by selling the individuals on the market. However, when rare species are more
317:
Recent results based on spatio-temporal models show that the Allee effect can also promote genetic diversity in expanding populations. These results counteract commonly held notions that the Allee effect possesses net adverse consequences. Reducing the growth rate of the individuals ahead of the
170:
Although numerous ecological mechanisms for Allee effects exist, the list of most commonly cited facilitative behaviors that contribute to Allee effects in the literature include: mate limitation, cooperative defense, cooperative feeding, and environmental conditioning. While these behaviors are
66:
have a greater survival rate when there are more individuals within the tank. This led him to conclude that aggregation can improve the survival rate of individuals, and that cooperation may be crucial in the overall evolution of social structure. The term "Allee principle" was introduced in the
297:
Meanwhile, when demographic stochasticity results in fluctuations of sex ratios, it arguably reduces the mean individual fitness as population declines. For example, a fluctuation in small population that causes a scarcity in one sex would in turn limit the access of mates for the opposite sex,
293:
Demographic stochasticity refers to variability in population growth arising from sampling random births and deaths in a population of finite size. In small populations, demographic stochasticity will decrease the population growth rate, causing an effect similar to the Allee effect, which will
814:
902:
of the population is detrimental to the population and increases extinction risk for the total population. In this case, the species receives none of the benefits of a small sub-population (loss of the sub-population is not catastrophic to the species as a whole) and all of the disadvantages
229:
present a potential case of such component Allee effects, where the density of spawning individuals can affect the survivability of the following generations. Spawning salmon carry marine nutrients they acquired from the ocean as they migrate to freshwater streams to reproduce, which in turn
153:
Due to its definition as the positive correlation between population density and average fitness, the mechanisms for which an Allee effect arises are therefore inherently tied to survival and reproduction. In general, these Allee effect mechanisms arise from cooperation or facilitation among
276:
Although the long-term population persistence of several species with low genetic variation has recently prompted debate on the generality of inbreeding depression, there are various empirical evidences for genetic Allee effects. One such case was observed in the endangered
230:
fertilize the surrounding habitat when they die, thus creating a more suitable habitat for the juveniles that would hatch in the following months. While compelling, this case of environmental conditioning by salmon has not been rigorously supported by empirical evidence.
84:
The generally accepted definition of Allee effect is positive density dependence, or the positive correlation between population density and individual fitness. It is sometimes referred to as "undercrowding" and it is analogous (or even considered synonymous by some) to
75:
is low. Individuals within a species often require the assistance of another individual for more than simple reproductive reasons in order to persist. The most obvious example of this is observed in animals that hunt for prey or defend against predators as a group.
178:
Mate limitation refers to the difficulty of finding a compatible and receptive mate for sexual reproduction at lower population size or density. This is generally a problem encountered by species that utilize passive reproduction and possess low mobility, such as
660:
After dividing both sides of the equation by the population size N, in the logistic growth the left hand side of the equation represents the per capita population growth rate, which is dependent on the population size N, and decreases with increasing
268:
throughout the population. Genetic variation within a species could range from beneficial to detrimental. Nevertheless, in a smaller sized gene pool, there is a higher chance of a stochastic event in which deleterious alleles become fixed
431:
171:
classified in separate categories, they can overlap and tend to be context dependent (will operate only under certain conditions – for example, cooperative defense will only be useful when there are predators or competitors present).
252:'s role in the evolutionary potential of a species, this could in turn result in an observable Allee effect. As a species' population becomes smaller, its gene pool will be reduced in size as well. One possible outcome from this
678:
895:
more likely to go extinct than the total population. In the case of a catastrophic event decreasing numbers at a sub-population, individuals from another sub-population site may be able to repopulate the area.
919:
Clumping results due to individuals aggregating in response to: local habitat or landscape differences, daily and seasonal weather changes, reproductive processes, or as the result of social attractions.
608:
881:
183:, plants and sessile invertebrates. For example, wind-pollinated plants would have a lower fitness in sparse populations due to the lower likelihood of pollen successfully landing on a conspecific.
314:
Demographic and mathematical studies demonstrate that the existence of an Allee effect can reduce the speed of range expansion of a population and can even prevent biological invasions.
530:
498:
466:
1434:
Holden, Matthew H.; McDonald-Madden, Eve (2017-09-21). "High prices for rare species can drive large populations extinct: the anthropogenic Allee effect revisited".
332:
1960:
Tobin PC, Whitmire SL, Johnson DN, Bjørnstad ON, Liebhold AM (2007). "Invasion speed is affected by geographic variation in the strength of Allee effects".
809:{\displaystyle {\frac {\partial N}{\partial t}}=D{\frac {\partial ^{2}N}{\partial x^{2}}}+rN\left({\frac {N}{A}}-1\right)\left(1-{\frac {N}{K}}\right),}
2857:
1670:
1240:
Mooring MS, Fitzpatrick TA, Nishihira TT, Reisig DD (2004). Hall (ed.). "Vigilance, predation risk, and the Allee effect in desert bighorn sheep".
665:
throughout the entire range of population sizes. In contrast, when there is an Allee effect the per-capita growth rate increases with increasing
3637:
2890:
4452:
3781:
2298:
898:
If all sub-populations are subject to the same environmental variations (i.e. if a disaster affected one, it would affect them all) then
3851:
2247:
541:
2292:
1565:"Albatrosses, eagles and newts, Oh My!: exceptions to the prevailing paradigm concerning genetic diversity and population viability?"
3423:
1816:
Bessa-Gomes C, Legendre S, Clobert J (2004). "Allee effects, mating systems and the extinction risk in populations with two sexes".
1370:
Courchamp, Franck; Angulo, Elena; Rivalan, Philippe; Hall, Richard J.; Signoret, Laetitia; Bull, Leigh; Meinard, Yves (2006-11-28).
3388:
204:. The confusion effect that this herding behavior would have on predators will be more effective when more individuals are present.
2546:
2309:
2238:
835:
3861:
3589:
2726:
1332:
spp.) runs and consumer fitness: growth and energy storage in stream-dwelling salmonids increase with salmon spawner density".
2465:
2259:
958:
672:
Spatio-temporal models can take Allee effect into account as well. A simple example is given by the reaction-diffusion model
298:
decreasing the fitness of the individuals within the population. This type of Allee effect will likely be more prevalent in
68:
3866:
4054:
2276:
212:
Certain species also require group foraging in order to survive. As an example, species that hunt in packs, such as the
3807:
3630:
3471:
2883:
2475:
2362:
1275:
Clutton-Brock TH, Gaynor D, McIlrath GM, MacColl AD, Kansky R, Chadwick P, Manser M, Skinner JD, Brotherton PN (1999).
974:
Allee WC, Bowen E (1932). "Studies in animal aggregations: mass protection against colloidal silver among goldfishes".
121:
1604:
Johnson, WE; Onorato, DP; Roelke, MW; Land, ED; Cunningham, M; Belden, RC; McBride, R; Jansen, D; et al. (2010).
3143:
2668:
1690:
1547:
58:
Although the concept of Allee effect had no title at the time, it was first described in the 1930s by its namesake,
3604:
1851:
Engen S, Lande R, Saether BE (2003). "Demographic stochasticity and Allee effects in populations with two sexes".
3886:
3599:
3466:
3178:
2565:
192:
fitness of an individual living in smaller groups. One striking example of such shared vigilance is exhibited by
1253:
911:
and increased vulnerability to environmental instability) and the population would survive better unfragmented.
105:
is the positive relationship between any measurable component of individual fitness and population density. The
4271:
4144:
2011:
Johnson DM, Liebhold AM, Tobin PC, Bjørnstad ON (2006). "Allee effects and pulsed invasion by the gypsy moth".
4317:
3916:
3871:
3623:
2876:
3403:
1696:
4442:
3749:
2436:
2387:
4106:
2997:
2683:
2636:
2286:
4171:
3891:
3378:
3095:
2992:
2392:
2067:"Success rate of a biological invasion in terms of the spatial distribution of the founding population"
141:
The distinction between the two terms is based on whether or not the population in question exhibits a
93:. Listed below are a few significant subcategories of the Allee effect used in the ecology literature.
4352:
3964:
3856:
3714:
3699:
3694:
3373:
3085:
2570:
2541:
2441:
2379:
2333:
2302:
1922:
71:). However, the concept of the Allee effect introduced the idea that the reverse holds true when the
2868:
891:
When a population is made up of small sub-populations additional factors to the Allee effect arise.
4342:
4337:
4307:
4111:
3574:
3456:
2721:
899:
3615:
3246:
1682:
4186:
4049:
3959:
3827:
3709:
3679:
3536:
3501:
3221:
3188:
3163:
2802:
2587:
1495:
Frankham R (1996). "Relationship of genetic variation to population size in wildlife- a review".
503:
471:
439:
2195:
4332:
4276:
4211:
4074:
4009:
3944:
3506:
3294:
3002:
2982:
2822:
2482:
2355:
1763:(November 1998). "Demographic Stochasticity and Allee Effect on a Scale with Isotropic Noise".
426:{\displaystyle {\frac {dN}{dt}}=-rN\left(1-{\frac {N}{A}}\right)\left(1-{\frac {N}{K}}\right),}
196:. Meanwhile, other species move in synchrony to confuse and avoid predators such as schools of
41:
1717:
Lande R (1998). "Demographic stochasticity and Allee effect on a scale with isotropic noise".
4236:
4181:
4044:
4029:
3812:
3769:
3759:
3754:
3511:
3491:
3347:
3337:
3279:
3274:
3110:
2962:
2631:
2536:
2232:
2066:
827:
261:
253:
155:
109:
is the positive relationship between the overall individual fitness and population density.
4362:
4327:
4322:
4246:
4241:
4196:
4094:
4064:
4059:
3911:
3774:
3764:
3309:
3148:
2937:
2842:
2807:
2645:
2592:
2499:
2327:
2131:
2020:
1969:
1895:
1860:
1825:
1726:
1617:
1576:
1504:
1453:
1341:
1292:
1194:
1133:
1124:
Berec L, Angulo E, Courchamp F (2007). "Multiple Allee effects and population management".
1087:
1033:
983:
142:
8:
4412:
4387:
4251:
4221:
4166:
4079:
3969:
3954:
3901:
3734:
3669:
3551:
3481:
3413:
3012:
2852:
2827:
2817:
2407:
627:
2655:
2135:
2024:
1973:
1899:
1864:
1829:
1730:
1621:
1580:
1516:
1508:
1457:
1345:
1296:
1198:
1137:
1091:
1037:
987:
4423:
4372:
4367:
4176:
4139:
3881:
3837:
3802:
3659:
3584:
3486:
3418:
3408:
3342:
3289:
3100:
3045:
3007:
2932:
2832:
2693:
2688:
2154:
2119:
2097:
2044:
1993:
1790:
1742:
1651:
1638:
1605:
1520:
1477:
1443:
1406:
1371:
1310:
1257:
1103:
1057:
1049:
72:
59:
53:
1217:
1178:
4447:
4312:
4281:
4069:
3896:
3704:
3569:
3546:
3284:
3060:
2972:
2957:
2942:
2922:
2797:
2716:
2703:
2663:
2504:
2348:
2255:
2159:
2089:
2036:
1985:
1981:
1942:
1938:
1837:
1782:
1686:
1655:
1643:
1589:
1564:
1543:
1469:
1411:
1393:
1305:
1276:
1222:
1159:
1078:
Kramer AM, Dennis B, Liebhold AM, Drake JM (2009). "The evidence for Allee effects".
954:
908:
637:
533:
326:
A simple mathematical example of an Allee effect is given by the cubic growth model.
265:
249:
32:
2101:
1314:
1261:
1107:
1061:
248:
Declines in population size can result in a loss of genetic diversity, and owing to
4266:
4129:
4121:
4039:
3921:
3906:
3842:
3822:
3739:
3729:
3724:
3689:
3521:
3461:
3332:
3133:
3075:
2987:
2947:
2678:
2626:
2609:
2531:
2523:
2149:
2139:
2081:
2048:
2028:
1997:
1977:
1934:
1903:
1886:
Lewis MA, Kareiva P (1993). "Allee dynamics and the spread of invading organisms".
1868:
1833:
1798:
1774:
1734:
1678:
1633:
1625:
1584:
1524:
1512:
1481:
1461:
1401:
1383:
1349:
1328:
Rinella DJ, Wipfli MS, Stricker CA, Heintz RA, Rinella MJ (2012). "Pacific salmon (
1300:
1249:
1212:
1202:
1149:
1141:
1095:
1041:
991:
884:
213:
4402:
4261:
4231:
4226:
4216:
4149:
4134:
4014:
3994:
3876:
3744:
3650:
3541:
3451:
3393:
2977:
2903:
2494:
2371:
2313:
2177:
1765:
1388:
278:
90:
28:
216:, would not be able to locate and capture prey as efficiently in smaller groups.
4382:
4206:
4159:
4089:
4084:
3979:
3846:
3719:
3526:
3516:
3496:
3299:
3264:
3203:
3080:
3035:
2927:
2837:
2771:
2748:
2582:
2577:
2560:
2553:
2446:
1465:
1179:"Pollen limitation causes an Allee effect in a wind-pollinated invasive grass (
1145:
1024:
Stephens PA, Sutherland WJ, Freckleton RP (1999). "What is the Allee effect?".
226:
2514:
2252:
Marine conservation biology: the science of maintaining the sea's biodiversity
2085:
1099:
134:
is a demographic Allee effect with a critical population size or density. The
4436:
4407:
3383:
3357:
3314:
3304:
3259:
3226:
3118:
2952:
2907:
2711:
2453:
2424:
2402:
1786:
1760:
1397:
270:
264:. This overall fitness decrease of a species is caused by an accumulation of
257:
138:
is a demographic Allee effect without a critical population size or density.
2144:
1629:
1207:
4392:
4377:
4034:
4004:
3949:
3832:
3797:
3173:
2766:
2756:
2733:
2614:
2182:
2163:
2093:
2040:
1989:
1907:
1647:
1473:
1415:
1226:
1163:
995:
1946:
1802:
3684:
3231:
3193:
3168:
3158:
3123:
3070:
3050:
2812:
2761:
2602:
2458:
86:
2032:
4397:
3974:
3939:
3579:
3531:
3476:
3446:
3352:
3269:
3213:
3090:
3040:
2619:
2597:
2282:
1794:
1746:
1154:
1053:
904:
37:
1353:
4302:
4256:
3984:
3428:
3398:
3198:
3153:
3128:
3065:
3055:
3030:
3022:
2967:
2898:
2847:
2487:
1372:"Rarity Value and Species Extinction: The Anthropogenic Allee Effect"
201:
159:
2120:"Allee effect promotes diversity in traveling waves of colonization"
1872:
1778:
1738:
1045:
4357:
4286:
3817:
3645:
3324:
3236:
3183:
3138:
2776:
2738:
2470:
2412:
1448:
303:
299:
197:
180:
63:
62:. Through experimental studies, Allee was able to demonstrate that
1274:
4347:
4154:
4024:
4019:
3646:
3594:
3254:
2899:
2397:
2323:
1239:
193:
24:
1277:"Predation, group size and mortality in a cooperative mongoose,
603:{\displaystyle {\frac {dN}{dt}}=rN\left(1-{\frac {N}{K}}\right)}
256:
is a reduction in fitness of the species through the process of
2431:
2673:
2010:
1959:
1920:
1542:. Baltimore, Maryland, USA: Johns Hopkins University Press.
1023:
2419:
2340:
1925:(1993). "Waves of extinction from sterile insect release".
1669:
Lande, Russell; Engen, Steinar; SÆther, Bernt-Erik (2003).
1327:
1254:
10.2193/0022-541X(2004)068[0519:VPRATA]2.0.CO;2
2124:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the USA
1815:
1675:
Stochastic
Population Dynamics in Ecology and Conservation
1369:
1176:
876:{\displaystyle {\frac {\partial ^{2}}{\partial x^{2}}}={}}
96:
2223:
Allee WC, Emerson AE, Park O, Park T, Schmidt KP (1949).
1077:
309:
2308:
Stephens, PA, Sutherland, WJ and
Freckleton, RP (1999).
1603:
2322:, 185–90, at Evolutionary Biology Group, Department of
2117:
948:
1433:
1177:
Davis HG, Taylor CM, Lambrinos JG, Strong DR (2004).
838:
681:
544:
506:
474:
442:
335:
2222:
1123:
436:
where the population has a negative growth rate for
2193:
2858:Task allocation and partitioning of social insects
2064:
1334:Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences
914:
875:
808:
602:
524:
492:
460:
425:
2330:. Updated 22 November 2005. Retrieved 19 May 2008
2194:Traill LW, Brook BW, Bradshaw CJ (6 March 2010).
1850:
4434:
1668:
116:
2118:Roques L, Garnier J, Hamel F, Klein EK (2012).
1187:Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
221:Environmental conditioning / habitat alteration
1119:
1117:
3631:
2884:
2356:
1759:
1671:"Demographic and environmental stochasticity"
2245:
1885:
1606:"Genetic restoration of the Florida panther"
1013:. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA: Saunders.
288:
1114:
3852:Latitudinal gradients in species diversity
3638:
3624:
2891:
2877:
2363:
2349:
1494:
973:
949:Courchamp F, Berec J, Gascoigne J (2008).
2153:
2143:
1683:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780198525257.003.0001
1637:
1588:
1537:
1447:
1405:
1387:
1304:
1216:
1206:
1153:
951:Allee effects in ecology and conservation
126:positive but decreasing at low densities.
47:
3750:Predator–prey (Lotka–Volterra) equations
3389:Tritrophic interactions in plant defense
2113:
2111:
2060:
2058:
1073:
1071:
120:
3782:Random generalized Lotka–Volterra model
1562:
1008:
944:
942:
940:
938:
936:
934:
932:
165:
97:Component vs. demographic Allee effects
27:characterized by a correlation between
4435:
3590:Herbivore adaptations to plant defense
669:over some range of population sizes .
321:
310:Effects on range-expanding populations
3619:
2872:
2466:Patterns of self-organization in ants
2344:
2310:"What is the Allee effect?" (summary)
2108:
2065:Garnier J, Roques L, Hamel F (2012).
2055:
1716:
1429:
1427:
1425:
1365:
1363:
1068:
953:. New York: Oxford University Press.
656:= rate of increase of the population.
243:
4453:Mathematical and theoretical biology
3605:Predator avoidance in schooling fish
1540:Population genetics: a concise guide
929:
4055:Intermediate disturbance hypothesis
2299:Warner College of Natural Resources
2237:: CS1 maint: untitled periodical (
1517:10.1046/j.1523-1739.1996.10061500.x
162:bias should be considered as well.
143:critical population size or density
31:or density and the mean individual
13:
3808:Ecological effects of biodiversity
2476:symmetry breaking of escaping ants
2216:
1422:
1360:
852:
842:
726:
712:
693:
685:
468:, and a positive growth rate for
14:
4464:
3144:Generalist and specialist species
2269:
1126:Trends in Ecology & Evolution
3867:Occupancy–abundance relationship
2513:
2196:"Minimum viable population size"
2074:Bulletin of Mathematical Biology
1982:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2006.00991.x
1838:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2004.00632.x
1590:10.1111/j.1469-1795.2010.00353.x
1306:10.1046/j.1365-2656.1999.00317.x
532:). This is a departure from the
234:
16:Population phenomenon in biology
3887:Relative abundance distribution
3600:Plant defense against herbivory
3467:Competitive exclusion principle
3179:Mesopredator release hypothesis
2278:Underpopulation (Allee) effects
2187:
2170:
2004:
1953:
1914:
1879:
1844:
1809:
1753:
1710:
1662:
1597:
1556:
1531:
1488:
1321:
976:Journal of Experimental Zoology
915:Allee principles of aggregation
3472:Consumer–resource interactions
1888:Theoretical Population Biology
1436:Journal of Theoretical Biology
1268:
1242:Journal of Wildlife Management
1233:
1170:
1017:
1002:
967:
44:) of a population or species.
1:
4318:Biological data visualization
4145:Environmental niche modelling
3872:Population viability analysis
2248:"The Allee Effect in the Sea"
2246:Norse EA, Crowder LB (2005).
923:
225:etc.) environmental factors.
148:
117:Strong vs. weak Allee effects
79:
3803:Density-dependent inhibition
2437:Mixed-species foraging flock
2388:Agent-based model in biology
2370:
2225:Principles of Animal Ecology
1939:10.1016/0025-5564(93)90067-K
1389:10.1371/journal.pbio.0040415
7:
4272:Liebig's law of the minimum
4107:Resource selection function
2998:Metabolic theory of ecology
2684:Particle swarm optimization
2287:Washington State University
2202:. The Encyclopedia of Earth
525:{\displaystyle 0<A<K}
493:{\displaystyle A<N<K}
461:{\displaystyle 0<N<A}
10:
4469:
4172:Niche apportionment models
3892:Relative species abundance
3096:Primary nutritional groups
2993:List of feeding behaviours
2393:Collective animal behavior
2335:Classics: the Allee effect
1466:10.1016/j.jtbi.2017.06.019
1146:10.1016/j.tree.2006.12.002
628:intrinsic rate of increase
51:
4421:
4353:Ecosystem based fisheries
4295:
4195:
4120:
3993:
3965:Interspecific competition
3930:
3857:Minimum viable population
3790:
3715:Maximum sustainable yield
3700:Intraspecific competition
3695:Effective population size
3658:
3575:Anti-predator adaptations
3560:
3439:
3366:
3323:
3245:
3212:
3109:
3086:Photosynthetic efficiency
3021:
2915:
2785:
2747:
2702:
2654:
2522:
2511:
2378:
2303:Colorado State University
2086:10.1007/s11538-011-9694-9
1538:Gillespie, J. H. (2004).
1285:Journal of Animal Ecology
1100:10.1007/s10144-009-0152-6
289:Demographic stochasticity
4343:Ecological stoichiometry
4308:Alternative stable state
2722:Self-propelled particles
2305:. Retrieved 19 May 2008.
2289:. Retrieved 19 May 2008.
1927:Mathematical Biosciences
534:logistic growth equation
107:demographic Allee effect
4187:Ontogenetic niche shift
4050:Ideal free distribution
3960:Ecological facilitation
3710:Malthusian growth model
3680:Consumer-resource model
3537:Paradox of the plankton
3502:Energy systems language
3222:Chemoorganoheterotrophy
3189:Optimal foraging theory
3164:Heterotrophic nutrition
2803:Collective intelligence
2669:Ant colony optimization
2145:10.1073/pnas.1201695109
1630:10.1126/science.1192891
1208:10.1073/pnas.0405230101
1011:Fundamentals of Ecology
4333:Ecological forecasting
4277:Marginal value theorem
4075:Landscape epidemiology
4010:Cross-boundary subsidy
3945:Biological interaction
3295:Microbial intelligence
2983:Green world hypothesis
2823:Microbial intelligence
2483:Shoaling and schooling
1908:10.1006/tpbi.1993.1007
996:10.1002/jez.1400610202
877:
810:
604:
526:
494:
462:
427:
127:
103:component Allee effect
48:History and background
42:population growth rate
4338:Ecological humanities
4237:Ecological energetics
4182:Niche differentiation
4045:Habitat fragmentation
3813:Ecological extinction
3760:Small population size
3512:Feed conversion ratio
3492:Ecological succession
3424:San Francisco Estuary
3338:Ecological efficiency
3280:Microbial cooperation
2275:Berryman, AA (1997).
2178:Essentials of Ecology
1181:Spartina alterniflora
878:
828:diffusion coefficient
811:
646:= critical point; and
605:
527:
495:
463:
428:
266:deleterious mutations
262:inbreeding depression
156:inbreeding depression
124:
4363:Evolutionary ecology
4328:Ecological footprint
4323:Ecological economics
4247:Ecological threshold
4242:Ecological indicator
4112:Source–sink dynamics
4065:Land change modeling
4060:Insular biogeography
3912:Species distribution
3651:Modelling ecosystems
3310:Microbial metabolism
3149:Intraguild predation
2938:Biogeochemical cycle
2904:Modelling ecosystems
2843:Spatial organization
2808:Decentralised system
2646:Sea turtle migration
2500:Swarming (honey bee)
2328:University of Oxford
1497:Conservation Biology
907:depression, loss of
836:
679:
542:
504:
472:
440:
333:
166:Ecological mechanism
4443:Population dynamics
4413:Theoretical ecology
4388:Natural environment
4252:Ecosystem diversity
4222:Ecological collapse
4212:Bateman's principle
4167:Limiting similarity
4080:Landscape limnology
3902:Species homogeneity
3740:Population modeling
3735:Population dynamics
3552:Trophic state index
2818:Group size measures
2380:Biological swarming
2136:2012PNAS..109.8828R
2033:10.1038/nature05242
2025:2006Natur.444..361J
1974:2007EcolL..10...36T
1923:van den Driessche P
1900:1993TPBio..43..141L
1865:2003Ecol...84.2378E
1830:2004EcolL...7..802B
1731:1998Oikos..83..353L
1622:2010Sci...329.1641J
1616:(5999): 1641–1645.
1581:2010AnCon..13..448R
1569:Animal Conservation
1509:1996ConBi..10.1500F
1458:2017JThBi.429..170H
1346:2012CJFAS..69Q..73R
1297:1999JAnEc..68..672C
1199:2004PNAS..10113804D
1193:(38): 13804–13807.
1138:2007TEcoE..22..185B
1092:2009PopEc..51..341K
1038:1999Oikos..87..185S
988:1932JEZ....61..185A
322:Mathematical models
283:Puma concolor coryi
209:Cooperative feeding
188:Cooperative defense
132:strong Allee effect
35:(often measured as
23:is a phenomenon in
4424:Outline of ecology
4373:Industrial ecology
4368:Functional ecology
4232:Ecological deficit
4177:Niche construction
4140:Ecosystem engineer
3917:Species–area curve
3838:Introduced species
3653:: Other components
3585:Deimatic behaviour
3487:Ecological network
3419:North Pacific Gyre
3404:hydrothermal vents
3343:Ecological pyramid
3290:Microbial food web
3101:Primary production
3046:Foundation species
2833:Predator satiation
2694:Swarm (simulation)
2689:Swarm intelligence
2664:Agent-based models
2495:Swarming behaviour
1279:Suricata suricatta
1080:Population Ecology
873:
806:
620:= population size;
600:
522:
490:
458:
423:
254:genetic bottleneck
244:Genetic mechanisms
128:
89:" in the field of
73:population density
60:Warder Clyde Allee
54:Warder Clyde Allee
4430:
4429:
4313:Balance of nature
4070:Landscape ecology
3955:Community ecology
3897:Species diversity
3833:Indicator species
3828:Gradient analysis
3705:Logistic function
3613:
3612:
3570:Animal coloration
3547:Trophic mutualism
3285:Microbial ecology
3076:Photoheterotrophs
3061:Myco-heterotrophy
2973:Ecosystem ecology
2958:Carrying capacity
2923:Abiotic component
2866:
2865:
2853:Military swarming
2798:Animal navigation
2717:Collective motion
2704:Collective motion
2571:reverse migration
2505:Swarming motility
2261:978-1-55963-662-9
2019:(7117): 361–363.
1677:. pp. 1–24.
1354:10.1139/f2011-133
960:978-0-19-956755-3
909:genetic diversity
866:
796:
764:
740:
700:
638:carrying capacity
593:
563:
413:
387:
354:
250:genetic variation
214:African wild dogs
136:weak Allee effect
4460:
4130:Ecological niche
4102:selection theory
3922:Umbrella species
3907:Species richness
3843:Invasive species
3823:Flagship species
3730:Population cycle
3725:Overexploitation
3690:Ecological yield
3640:
3633:
3626:
3617:
3616:
3522:Mesotrophic soil
3462:Climax community
3394:Marine food webs
3333:Biomagnification
3134:Chemoorganotroph
2988:Keystone species
2948:Biotic component
2893:
2886:
2879:
2870:
2869:
2679:Crowd simulation
2656:Swarm algorithms
2627:Insect migration
2532:Animal migration
2524:Animal migration
2517:
2442:Mobbing behavior
2365:
2358:
2351:
2342:
2341:
2265:
2254:. Island Press.
2242:
2236:
2228:
2211:
2210:
2208:
2207:
2191:
2185:
2174:
2168:
2167:
2157:
2147:
2115:
2106:
2105:
2071:
2062:
2053:
2052:
2008:
2002:
2001:
1957:
1951:
1950:
1918:
1912:
1911:
1883:
1877:
1876:
1859:(9): 2378–2386.
1848:
1842:
1841:
1813:
1807:
1806:
1757:
1751:
1750:
1714:
1708:
1707:
1705:
1704:
1695:. Archived from
1666:
1660:
1659:
1641:
1601:
1595:
1594:
1592:
1563:Reed DH (2010).
1560:
1554:
1553:
1535:
1529:
1528:
1503:(6): 1500–1508.
1492:
1486:
1485:
1451:
1431:
1420:
1419:
1409:
1391:
1367:
1358:
1357:
1325:
1319:
1318:
1308:
1272:
1266:
1265:
1237:
1231:
1230:
1220:
1210:
1174:
1168:
1167:
1157:
1121:
1112:
1111:
1075:
1066:
1065:
1021:
1015:
1014:
1009:Odum EP (1953).
1006:
1000:
999:
971:
965:
964:
946:
885:Laplace operator
883:one-dimensional
882:
880:
879:
874:
872:
867:
865:
864:
863:
850:
849:
840:
815:
813:
812:
807:
802:
798:
797:
789:
776:
772:
765:
757:
741:
739:
738:
737:
724:
720:
719:
709:
701:
699:
691:
683:
609:
607:
606:
601:
599:
595:
594:
586:
564:
562:
554:
546:
531:
529:
528:
523:
499:
497:
496:
491:
467:
465:
464:
459:
432:
430:
429:
424:
419:
415:
414:
406:
393:
389:
388:
380:
355:
353:
345:
337:
91:fishery sciences
4468:
4467:
4463:
4462:
4461:
4459:
4458:
4457:
4433:
4432:
4431:
4426:
4417:
4403:Systems ecology
4291:
4262:Extinction debt
4227:Ecological debt
4217:Bioluminescence
4198:
4191:
4160:marine habitats
4135:Ecological trap
4116:
3996:
3989:
3932:
3926:
3882:Rapoport's rule
3877:Priority effect
3818:Endemic species
3786:
3745:Population size
3661:
3654:
3644:
3614:
3609:
3562:
3556:
3542:Trophic cascade
3452:Bioaccumulation
3435:
3362:
3319:
3241:
3208:
3105:
3017:
2978:Ecosystem model
2911:
2897:
2867:
2862:
2781:
2743:
2698:
2650:
2518:
2509:
2374:
2369:
2272:
2262:
2230:
2229:
2219:
2217:Further reading
2214:
2205:
2203:
2192:
2188:
2175:
2171:
2130:(23): 8828–33.
2116:
2109:
2069:
2063:
2056:
2009:
2005:
1962:Ecology Letters
1958:
1954:
1919:
1915:
1884:
1880:
1873:10.1890/02-0123
1849:
1845:
1818:Ecology Letters
1814:
1810:
1779:10.2307/3546849
1758:
1754:
1739:10.2307/3546849
1715:
1711:
1702:
1700:
1693:
1667:
1663:
1602:
1598:
1561:
1557:
1550:
1536:
1532:
1493:
1489:
1432:
1423:
1368:
1361:
1326:
1322:
1273:
1269:
1238:
1234:
1175:
1171:
1122:
1115:
1076:
1069:
1046:10.2307/3547011
1022:
1018:
1007:
1003:
972:
968:
961:
947:
930:
926:
917:
871:
859:
855:
851:
845:
841:
839:
837:
834:
833:
788:
781:
777:
756:
755:
751:
733:
729:
725:
715:
711:
710:
708:
692:
684:
682:
680:
677:
676:
585:
578:
574:
555:
547:
545:
543:
540:
539:
505:
502:
501:
473:
470:
469:
441:
438:
437:
405:
398:
394:
379:
372:
368:
346:
338:
336:
334:
331:
330:
324:
312:
291:
279:Florida panther
246:
237:
175:Mate limitation
168:
151:
119:
99:
82:
69:logistic growth
56:
50:
29:population size
17:
12:
11:
5:
4466:
4456:
4455:
4450:
4445:
4428:
4427:
4422:
4419:
4418:
4416:
4415:
4410:
4405:
4400:
4395:
4390:
4385:
4383:Microecosystem
4380:
4375:
4370:
4365:
4360:
4355:
4350:
4345:
4340:
4335:
4330:
4325:
4320:
4315:
4310:
4305:
4299:
4297:
4293:
4292:
4290:
4289:
4284:
4282:Thorson's rule
4279:
4274:
4269:
4264:
4259:
4254:
4249:
4244:
4239:
4234:
4229:
4224:
4219:
4214:
4209:
4207:Assembly rules
4203:
4201:
4193:
4192:
4190:
4189:
4184:
4179:
4174:
4169:
4164:
4163:
4162:
4152:
4147:
4142:
4137:
4132:
4126:
4124:
4118:
4117:
4115:
4114:
4109:
4104:
4092:
4090:Patch dynamics
4087:
4085:Metapopulation
4082:
4077:
4072:
4067:
4062:
4057:
4052:
4047:
4042:
4037:
4032:
4027:
4022:
4017:
4012:
4007:
4001:
3999:
3991:
3990:
3988:
3987:
3982:
3980:Storage effect
3977:
3972:
3967:
3962:
3957:
3952:
3947:
3942:
3936:
3934:
3928:
3927:
3925:
3924:
3919:
3914:
3909:
3904:
3899:
3894:
3889:
3884:
3879:
3874:
3869:
3864:
3862:Neutral theory
3859:
3854:
3849:
3847:Native species
3840:
3835:
3830:
3825:
3820:
3815:
3810:
3805:
3800:
3794:
3792:
3788:
3787:
3785:
3784:
3779:
3778:
3777:
3772:
3762:
3757:
3752:
3747:
3742:
3737:
3732:
3727:
3722:
3720:Overpopulation
3717:
3712:
3707:
3702:
3697:
3692:
3687:
3682:
3677:
3672:
3666:
3664:
3656:
3655:
3643:
3642:
3635:
3628:
3620:
3611:
3610:
3608:
3607:
3602:
3597:
3592:
3587:
3582:
3577:
3572:
3566:
3564:
3558:
3557:
3555:
3554:
3549:
3544:
3539:
3534:
3529:
3527:Nutrient cycle
3524:
3519:
3517:Feeding frenzy
3514:
3509:
3504:
3499:
3497:Energy quality
3494:
3489:
3484:
3479:
3474:
3469:
3464:
3459:
3457:Cascade effect
3454:
3449:
3443:
3441:
3437:
3436:
3434:
3433:
3432:
3431:
3426:
3421:
3416:
3411:
3406:
3401:
3391:
3386:
3381:
3376:
3370:
3368:
3364:
3363:
3361:
3360:
3355:
3350:
3345:
3340:
3335:
3329:
3327:
3321:
3320:
3318:
3317:
3312:
3307:
3302:
3300:Microbial loop
3297:
3292:
3287:
3282:
3277:
3272:
3267:
3265:Lithoautotroph
3262:
3257:
3251:
3249:
3247:Microorganisms
3243:
3242:
3240:
3239:
3234:
3229:
3224:
3218:
3216:
3210:
3209:
3207:
3206:
3204:Prey switching
3201:
3196:
3191:
3186:
3181:
3176:
3171:
3166:
3161:
3156:
3151:
3146:
3141:
3136:
3131:
3126:
3121:
3115:
3113:
3107:
3106:
3104:
3103:
3098:
3093:
3088:
3083:
3081:Photosynthesis
3078:
3073:
3068:
3063:
3058:
3053:
3048:
3043:
3038:
3036:Chemosynthesis
3033:
3027:
3025:
3019:
3018:
3016:
3015:
3010:
3005:
3000:
2995:
2990:
2985:
2980:
2975:
2970:
2965:
2960:
2955:
2950:
2945:
2940:
2935:
2930:
2928:Abiotic stress
2925:
2919:
2917:
2913:
2912:
2896:
2895:
2888:
2881:
2873:
2864:
2863:
2861:
2860:
2855:
2850:
2845:
2840:
2838:Quorum sensing
2835:
2830:
2825:
2820:
2815:
2810:
2805:
2800:
2795:
2789:
2787:
2786:Related topics
2783:
2782:
2780:
2779:
2774:
2772:Swarm robotics
2769:
2764:
2759:
2753:
2751:
2749:Swarm robotics
2745:
2744:
2742:
2741:
2736:
2731:
2730:
2729:
2719:
2714:
2708:
2706:
2700:
2699:
2697:
2696:
2691:
2686:
2681:
2676:
2671:
2666:
2660:
2658:
2652:
2651:
2649:
2648:
2643:
2642:
2641:
2640:
2639:
2624:
2623:
2622:
2617:
2607:
2606:
2605:
2600:
2595:
2590:
2583:Fish migration
2580:
2578:Cell migration
2575:
2574:
2573:
2568:
2561:Bird migration
2558:
2557:
2556:
2554:coded wire tag
2551:
2550:
2549:
2539:
2528:
2526:
2520:
2519:
2512:
2510:
2508:
2507:
2502:
2497:
2492:
2491:
2490:
2480:
2479:
2478:
2473:
2463:
2462:
2461:
2451:
2450:
2449:
2447:feeding frenzy
2439:
2434:
2429:
2428:
2427:
2417:
2416:
2415:
2410:
2400:
2395:
2390:
2384:
2382:
2376:
2375:
2368:
2367:
2360:
2353:
2345:
2339:
2338:
2331:
2306:
2290:
2271:
2270:External links
2268:
2267:
2266:
2260:
2243:
2218:
2215:
2213:
2212:
2200:Ecology Theory
2186:
2169:
2107:
2080:(2): 453–473.
2054:
2003:
1952:
1933:(2): 221–247.
1913:
1894:(2): 141–158.
1878:
1843:
1824:(9): 802–812.
1808:
1752:
1725:(2): 353–358.
1709:
1691:
1661:
1596:
1575:(5): 448–457.
1555:
1548:
1530:
1487:
1421:
1359:
1320:
1291:(4): 672–683.
1267:
1248:(3): 519–532.
1232:
1169:
1132:(4): 185–191.
1113:
1086:(3): 341–354.
1067:
1032:(1): 185–190.
1016:
1001:
982:(2): 185–207.
966:
959:
927:
925:
922:
916:
913:
889:
888:
870:
862:
858:
854:
848:
844:
831:
817:
816:
805:
801:
795:
792:
787:
784:
780:
775:
771:
768:
763:
760:
754:
750:
747:
744:
736:
732:
728:
723:
718:
714:
707:
704:
698:
695:
690:
687:
658:
657:
647:
641:
631:
621:
611:
610:
598:
592:
589:
584:
581:
577:
573:
570:
567:
561:
558:
553:
550:
521:
518:
515:
512:
509:
489:
486:
483:
480:
477:
457:
454:
451:
448:
445:
434:
433:
422:
418:
412:
409:
404:
401:
397:
392:
386:
383:
378:
375:
371:
367:
364:
361:
358:
352:
349:
344:
341:
323:
320:
311:
308:
290:
287:
245:
242:
236:
233:
232:
231:
227:Pacific salmon
222:
218:
217:
210:
206:
205:
200:and flocks of
189:
185:
184:
176:
167:
164:
150:
147:
118:
115:
98:
95:
81:
78:
52:Main article:
49:
46:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
4465:
4454:
4451:
4449:
4446:
4444:
4441:
4440:
4438:
4425:
4420:
4414:
4411:
4409:
4408:Urban ecology
4406:
4404:
4401:
4399:
4396:
4394:
4391:
4389:
4386:
4384:
4381:
4379:
4376:
4374:
4371:
4369:
4366:
4364:
4361:
4359:
4356:
4354:
4351:
4349:
4346:
4344:
4341:
4339:
4336:
4334:
4331:
4329:
4326:
4324:
4321:
4319:
4316:
4314:
4311:
4309:
4306:
4304:
4301:
4300:
4298:
4294:
4288:
4285:
4283:
4280:
4278:
4275:
4273:
4270:
4268:
4267:Kleiber's law
4265:
4263:
4260:
4258:
4255:
4253:
4250:
4248:
4245:
4243:
4240:
4238:
4235:
4233:
4230:
4228:
4225:
4223:
4220:
4218:
4215:
4213:
4210:
4208:
4205:
4204:
4202:
4200:
4194:
4188:
4185:
4183:
4180:
4178:
4175:
4173:
4170:
4168:
4165:
4161:
4158:
4157:
4156:
4153:
4151:
4148:
4146:
4143:
4141:
4138:
4136:
4133:
4131:
4128:
4127:
4125:
4123:
4119:
4113:
4110:
4108:
4105:
4103:
4101:
4097:
4093:
4091:
4088:
4086:
4083:
4081:
4078:
4076:
4073:
4071:
4068:
4066:
4063:
4061:
4058:
4056:
4053:
4051:
4048:
4046:
4043:
4041:
4040:Foster's rule
4038:
4036:
4033:
4031:
4028:
4026:
4023:
4021:
4018:
4016:
4013:
4011:
4008:
4006:
4003:
4002:
4000:
3998:
3992:
3986:
3983:
3981:
3978:
3976:
3973:
3971:
3968:
3966:
3963:
3961:
3958:
3956:
3953:
3951:
3948:
3946:
3943:
3941:
3938:
3937:
3935:
3929:
3923:
3920:
3918:
3915:
3913:
3910:
3908:
3905:
3903:
3900:
3898:
3895:
3893:
3890:
3888:
3885:
3883:
3880:
3878:
3875:
3873:
3870:
3868:
3865:
3863:
3860:
3858:
3855:
3853:
3850:
3848:
3844:
3841:
3839:
3836:
3834:
3831:
3829:
3826:
3824:
3821:
3819:
3816:
3814:
3811:
3809:
3806:
3804:
3801:
3799:
3796:
3795:
3793:
3789:
3783:
3780:
3776:
3773:
3771:
3768:
3767:
3766:
3763:
3761:
3758:
3756:
3753:
3751:
3748:
3746:
3743:
3741:
3738:
3736:
3733:
3731:
3728:
3726:
3723:
3721:
3718:
3716:
3713:
3711:
3708:
3706:
3703:
3701:
3698:
3696:
3693:
3691:
3688:
3686:
3683:
3681:
3678:
3676:
3673:
3671:
3668:
3667:
3665:
3663:
3657:
3652:
3648:
3641:
3636:
3634:
3629:
3627:
3622:
3621:
3618:
3606:
3603:
3601:
3598:
3596:
3593:
3591:
3588:
3586:
3583:
3581:
3578:
3576:
3573:
3571:
3568:
3567:
3565:
3559:
3553:
3550:
3548:
3545:
3543:
3540:
3538:
3535:
3533:
3530:
3528:
3525:
3523:
3520:
3518:
3515:
3513:
3510:
3508:
3505:
3503:
3500:
3498:
3495:
3493:
3490:
3488:
3485:
3483:
3480:
3478:
3475:
3473:
3470:
3468:
3465:
3463:
3460:
3458:
3455:
3453:
3450:
3448:
3445:
3444:
3442:
3438:
3430:
3427:
3425:
3422:
3420:
3417:
3415:
3412:
3410:
3407:
3405:
3402:
3400:
3397:
3396:
3395:
3392:
3390:
3387:
3385:
3382:
3380:
3377:
3375:
3372:
3371:
3369:
3365:
3359:
3358:Trophic level
3356:
3354:
3351:
3349:
3346:
3344:
3341:
3339:
3336:
3334:
3331:
3330:
3328:
3326:
3322:
3316:
3315:Phage ecology
3313:
3311:
3308:
3306:
3305:Microbial mat
3303:
3301:
3298:
3296:
3293:
3291:
3288:
3286:
3283:
3281:
3278:
3276:
3273:
3271:
3268:
3266:
3263:
3261:
3260:Bacteriophage
3258:
3256:
3253:
3252:
3250:
3248:
3244:
3238:
3235:
3233:
3230:
3228:
3227:Decomposition
3225:
3223:
3220:
3219:
3217:
3215:
3211:
3205:
3202:
3200:
3197:
3195:
3192:
3190:
3187:
3185:
3182:
3180:
3177:
3175:
3174:Mesopredators
3172:
3170:
3167:
3165:
3162:
3160:
3157:
3155:
3152:
3150:
3147:
3145:
3142:
3140:
3137:
3135:
3132:
3130:
3127:
3125:
3122:
3120:
3119:Apex predator
3117:
3116:
3114:
3112:
3108:
3102:
3099:
3097:
3094:
3092:
3089:
3087:
3084:
3082:
3079:
3077:
3074:
3072:
3069:
3067:
3064:
3062:
3059:
3057:
3054:
3052:
3049:
3047:
3044:
3042:
3039:
3037:
3034:
3032:
3029:
3028:
3026:
3024:
3020:
3014:
3011:
3009:
3006:
3004:
3001:
2999:
2996:
2994:
2991:
2989:
2986:
2984:
2981:
2979:
2976:
2974:
2971:
2969:
2966:
2964:
2961:
2959:
2956:
2954:
2953:Biotic stress
2951:
2949:
2946:
2944:
2941:
2939:
2936:
2934:
2931:
2929:
2926:
2924:
2921:
2920:
2918:
2914:
2909:
2905:
2901:
2894:
2889:
2887:
2882:
2880:
2875:
2874:
2871:
2859:
2856:
2854:
2851:
2849:
2846:
2844:
2841:
2839:
2836:
2834:
2831:
2829:
2826:
2824:
2821:
2819:
2816:
2814:
2811:
2809:
2806:
2804:
2801:
2799:
2796:
2794:
2791:
2790:
2788:
2784:
2778:
2775:
2773:
2770:
2768:
2765:
2763:
2760:
2758:
2755:
2754:
2752:
2750:
2746:
2740:
2737:
2735:
2732:
2728:
2725:
2724:
2723:
2720:
2718:
2715:
2713:
2712:Active matter
2710:
2709:
2707:
2705:
2701:
2695:
2692:
2690:
2687:
2685:
2682:
2680:
2677:
2675:
2672:
2670:
2667:
2665:
2662:
2661:
2659:
2657:
2653:
2647:
2644:
2638:
2635:
2634:
2633:
2630:
2629:
2628:
2625:
2621:
2618:
2616:
2613:
2612:
2611:
2608:
2604:
2601:
2599:
2596:
2594:
2591:
2589:
2588:diel vertical
2586:
2585:
2584:
2581:
2579:
2576:
2572:
2569:
2567:
2564:
2563:
2562:
2559:
2555:
2552:
2548:
2545:
2544:
2543:
2540:
2538:
2535:
2534:
2533:
2530:
2529:
2527:
2525:
2521:
2516:
2506:
2503:
2501:
2498:
2496:
2493:
2489:
2486:
2485:
2484:
2481:
2477:
2474:
2472:
2469:
2468:
2467:
2464:
2460:
2457:
2456:
2455:
2452:
2448:
2445:
2444:
2443:
2440:
2438:
2435:
2433:
2430:
2426:
2425:herd behavior
2423:
2422:
2421:
2418:
2414:
2411:
2409:
2406:
2405:
2404:
2401:
2399:
2396:
2394:
2391:
2389:
2386:
2385:
2383:
2381:
2377:
2373:
2366:
2361:
2359:
2354:
2352:
2347:
2346:
2343:
2337:
2336:
2332:
2329:
2325:
2321:
2317:
2316:
2311:
2307:
2304:
2300:
2296:
2295:
2291:
2288:
2284:
2280:
2279:
2274:
2273:
2263:
2257:
2253:
2249:
2244:
2240:
2234:
2226:
2221:
2220:
2201:
2197:
2190:
2184:
2180:
2179:
2173:
2165:
2161:
2156:
2151:
2146:
2141:
2137:
2133:
2129:
2125:
2121:
2114:
2112:
2103:
2099:
2095:
2091:
2087:
2083:
2079:
2075:
2068:
2061:
2059:
2050:
2046:
2042:
2038:
2034:
2030:
2026:
2022:
2018:
2014:
2007:
1999:
1995:
1991:
1987:
1983:
1979:
1975:
1971:
1967:
1963:
1956:
1948:
1944:
1940:
1936:
1932:
1928:
1924:
1917:
1909:
1905:
1901:
1897:
1893:
1889:
1882:
1874:
1870:
1866:
1862:
1858:
1854:
1847:
1839:
1835:
1831:
1827:
1823:
1819:
1812:
1804:
1800:
1796:
1792:
1788:
1784:
1780:
1776:
1772:
1768:
1767:
1762:
1761:Russell Lande
1756:
1748:
1744:
1740:
1736:
1732:
1728:
1724:
1720:
1713:
1699:on 2018-11-27
1698:
1694:
1692:9780198525257
1688:
1684:
1680:
1676:
1672:
1665:
1657:
1653:
1649:
1645:
1640:
1635:
1631:
1627:
1623:
1619:
1615:
1611:
1607:
1600:
1591:
1586:
1582:
1578:
1574:
1570:
1566:
1559:
1551:
1549:0-8018-8008-4
1545:
1541:
1534:
1526:
1522:
1518:
1514:
1510:
1506:
1502:
1498:
1491:
1483:
1479:
1475:
1471:
1467:
1463:
1459:
1455:
1450:
1445:
1441:
1437:
1430:
1428:
1426:
1417:
1413:
1408:
1403:
1399:
1395:
1390:
1385:
1381:
1377:
1373:
1366:
1364:
1355:
1351:
1347:
1343:
1339:
1335:
1331:
1324:
1316:
1312:
1307:
1302:
1298:
1294:
1290:
1286:
1282:
1280:
1271:
1263:
1259:
1255:
1251:
1247:
1243:
1236:
1228:
1224:
1219:
1214:
1209:
1204:
1200:
1196:
1192:
1188:
1184:
1182:
1173:
1165:
1161:
1156:
1151:
1147:
1143:
1139:
1135:
1131:
1127:
1120:
1118:
1109:
1105:
1101:
1097:
1093:
1089:
1085:
1081:
1074:
1072:
1063:
1059:
1055:
1051:
1047:
1043:
1039:
1035:
1031:
1027:
1020:
1012:
1005:
997:
993:
989:
985:
981:
977:
970:
962:
956:
952:
945:
943:
941:
939:
937:
935:
933:
928:
921:
912:
910:
906:
901:
900:fragmentation
896:
892:
886:
868:
860:
856:
846:
832:
829:
825:
822:
821:
820:
803:
799:
793:
790:
785:
782:
778:
773:
769:
766:
761:
758:
752:
748:
745:
742:
734:
730:
721:
716:
705:
702:
696:
688:
675:
674:
673:
670:
668:
664:
655:
651:
648:
645:
642:
639:
635:
632:
629:
625:
622:
619:
616:
615:
614:
596:
590:
587:
582:
579:
575:
571:
568:
565:
559:
556:
551:
548:
538:
537:
536:
535:
519:
516:
513:
510:
507:
487:
484:
481:
478:
475:
455:
452:
449:
446:
443:
420:
416:
410:
407:
402:
399:
395:
390:
384:
381:
376:
373:
369:
365:
362:
359:
356:
350:
347:
342:
339:
329:
328:
327:
319:
315:
307:
305:
302:species than
301:
295:
286:
284:
280:
274:
272:
271:genetic drift
267:
263:
260:, as well as
259:
258:genetic drift
255:
251:
241:
235:Human induced
228:
223:
220:
219:
215:
211:
208:
207:
203:
199:
195:
190:
187:
186:
182:
177:
174:
173:
172:
163:
161:
157:
146:
144:
139:
137:
133:
123:
114:
110:
108:
104:
94:
92:
88:
77:
74:
70:
65:
61:
55:
45:
43:
40:
39:
34:
30:
26:
22:
4393:Regime shift
4378:Macroecology
4099:
4095:
4035:Edge effects
4005:Biogeography
3950:Commensalism
3798:Biodiversity
3675:Allee effect
3674:
3414:kelp forests
3367:Example webs
3232:Detritivores
3071:Organotrophs
3051:Kinetotrophs
3003:Productivity
2793:Allee effect
2792:
2767:Nanorobotics
2757:Ant robotics
2734:Vicsek model
2334:
2319:
2314:
2294:Allee effect
2293:
2285:Department,
2277:
2251:
2233:cite journal
2224:
2204:. Retrieved
2199:
2189:
2183:Google Books
2176:
2172:
2127:
2123:
2077:
2073:
2016:
2012:
2006:
1968:(1): 36–43.
1965:
1961:
1955:
1930:
1926:
1916:
1891:
1887:
1881:
1856:
1852:
1846:
1821:
1817:
1811:
1770:
1764:
1755:
1722:
1718:
1712:
1701:. Retrieved
1697:the original
1674:
1664:
1613:
1609:
1599:
1572:
1568:
1558:
1539:
1533:
1500:
1496:
1490:
1439:
1435:
1382:(12): e415.
1379:
1376:PLOS Biology
1375:
1340:(1): 73–84.
1337:
1333:
1330:Oncorhynchus
1329:
1323:
1288:
1284:
1278:
1270:
1245:
1241:
1235:
1190:
1186:
1180:
1172:
1129:
1125:
1083:
1079:
1029:
1025:
1019:
1010:
1004:
979:
975:
969:
950:
918:
897:
893:
890:
823:
818:
671:
666:
662:
659:
653:
649:
643:
633:
623:
617:
612:
435:
325:
316:
313:
296:
292:
282:
275:
247:
238:
169:
152:
140:
135:
131:
129:
111:
106:
102:
100:
83:
57:
36:
21:Allee effect
20:
18:
4030:Disturbance
3933:interaction
3755:Recruitment
3685:Depensation
3477:Copiotrophs
3348:Energy flow
3270:Lithotrophy
3214:Decomposers
3194:Planktivore
3169:Insectivore
3159:Heterotroph
3124:Bacterivore
3091:Phototrophs
3041:Chemotrophs
3013:Restoration
2963:Competition
2813:Eusociality
2762:Microbotics
2632:butterflies
2603:sardine run
2537:altitudinal
2459:pack hunter
1442:: 170–180.
1155:10261/45491
87:depensation
4437:Categories
4398:Sexecology
3975:Parasitism
3940:Antibiosis
3775:Resistance
3770:Resilience
3660:Population
3580:Camouflage
3532:Oligotroph
3447:Ascendency
3409:intertidal
3399:cold seeps
3353:Food chain
3154:Herbivores
3129:Carnivores
3056:Mixotrophs
3031:Autotrophs
2910:components
2727:clustering
2620:philopatry
2598:salmon run
2593:Lessepsian
2283:Entomology
2206:2012-08-12
1921:Lewis MA,
1773:(2): 353.
1703:2017-10-11
1449:1703.06736
924:References
905:inbreeding
500:(assuming
304:polygynous
300:monogamous
149:Mechanisms
80:Definition
38:per capita
4303:Allometry
4257:Emergence
3985:Symbiosis
3970:Mutualism
3765:Stability
3670:Abundance
3482:Dominance
3440:Processes
3429:tide pool
3325:Food webs
3199:Predation
3184:Omnivores
3111:Consumers
3066:Mycotroph
3023:Producers
2968:Ecosystem
2933:Behaviour
2848:Stigmergy
2828:Mutualism
2488:bait ball
1803:Q56486427
1787:0030-1299
1656:206527881
1398:1545-7885
853:∂
843:∂
786:−
767:−
727:∂
713:∂
694:∂
686:∂
583:−
403:−
377:−
360:−
306:species.
202:starlings
160:sex ratio
4448:Ethology
4358:Endolith
4287:Xerosere
4199:networks
4015:Ecocline
3561:Defense,
3237:Detritus
3139:Foraging
3008:Resource
2777:Symbrion
2739:BIO-LGCA
2542:tracking
2471:ant mill
2413:sort sol
2408:flocking
2372:Swarming
2164:22611189
2102:23554577
2094:21972031
2041:17108964
1990:17204115
1799:Wikidata
1648:20929847
1474:28669883
1416:17132047
1315:51855211
1262:53981797
1227:15317944
1164:17175060
1108:36920194
1062:54663313
198:sardines
194:meerkats
181:plankton
64:goldfish
4348:Ecopath
4155:Habitat
4025:Ecotype
4020:Ecotone
3997:ecology
3995:Spatial
3931:Species
3791:Species
3662:ecology
3647:Ecology
3595:Mimicry
3563:counter
3507:f-ratio
3255:Archaea
2943:Biomass
2916:General
2908:Trophic
2900:Ecology
2637:monarch
2566:flyways
2547:history
2398:Droving
2324:Zoology
2155:3384151
2132:Bibcode
2049:4432173
2021:Bibcode
1998:6027336
1970:Bibcode
1947:8369600
1896:Bibcode
1861:Bibcode
1853:Ecology
1826:Bibcode
1795:3546849
1747:3546849
1727:Bibcode
1639:6993177
1618:Bibcode
1610:Science
1577:Bibcode
1525:6088451
1505:Bibcode
1482:4877874
1454:Bibcode
1407:1661683
1342:Bibcode
1293:Bibcode
1195:Bibcode
1134:Bibcode
1088:Bibcode
1054:3547011
1034:Bibcode
984:Bibcode
33:fitness
25:biology
3379:Rivers
3275:Marine
2610:Homing
2432:Locust
2258:
2162:
2152:
2100:
2092:
2047:
2039:
2013:Nature
1996:
1988:
1945:
1801:
1793:
1785:
1745:
1689:
1654:
1646:
1636:
1546:
1523:
1480:
1472:
1414:
1404:
1396:
1313:
1260:
1225:
1218:518837
1215:
1162:
1106:
1060:
1052:
957:
819:where
613:where
4296:Other
4197:Other
4150:Guild
4122:Niche
3374:Lakes
2674:Boids
2615:natal
2403:Flock
2315:Oikos
2098:S2CID
2070:(PDF)
2045:S2CID
1994:S2CID
1791:JSTOR
1766:Oikos
1743:JSTOR
1719:Oikos
1652:S2CID
1521:S2CID
1478:S2CID
1444:arXiv
1311:S2CID
1258:S2CID
1104:S2CID
1058:S2CID
1050:JSTOR
1026:Oikos
3384:Soil
2454:Pack
2420:Herd
2256:ISBN
2239:link
2160:PMID
2090:PMID
2037:PMID
1986:PMID
1943:PMID
1783:ISSN
1687:ISBN
1644:PMID
1544:ISBN
1470:PMID
1412:PMID
1394:ISSN
1223:PMID
1160:PMID
955:ISBN
517:<
511:<
485:<
479:<
453:<
447:<
158:and
130:The
101:The
19:The
2181:at
2150:PMC
2140:doi
2128:109
2082:doi
2029:doi
2017:444
1978:doi
1935:doi
1931:116
1904:doi
1869:doi
1834:doi
1775:doi
1735:doi
1679:doi
1634:PMC
1626:doi
1614:329
1585:doi
1513:doi
1462:doi
1440:429
1402:PMC
1384:doi
1350:doi
1301:doi
1250:doi
1213:PMC
1203:doi
1191:101
1150:hdl
1142:doi
1096:doi
1042:doi
992:doi
4439::
3845:/
3649::
2906::
2902::
2326:,
2320:87
2318:,
2312:,
2301:,
2297:,
2281:,
2250:.
2235:}}
2231:{{
2198:.
2158:.
2148:.
2138:.
2126:.
2122:.
2110:^
2096:.
2088:.
2078:74
2076:.
2072:.
2057:^
2043:.
2035:.
2027:.
2015:.
1992:.
1984:.
1976:.
1966:10
1964:.
1941:.
1929:.
1902:.
1892:43
1890:.
1867:.
1857:84
1855:.
1832:.
1820:.
1797:.
1789:.
1781:.
1771:83
1769:.
1741:.
1733:.
1723:83
1721:.
1685:.
1673:.
1650:.
1642:.
1632:.
1624:.
1612:.
1608:.
1583:.
1573:13
1571:.
1567:.
1519:.
1511:.
1501:10
1499:.
1476:.
1468:.
1460:.
1452:.
1438:.
1424:^
1410:.
1400:.
1392:.
1378:.
1374:.
1362:^
1348:.
1338:69
1336:.
1309:.
1299:.
1289:68
1287:.
1283:.
1256:.
1246:68
1244:.
1221:.
1211:.
1201:.
1189:.
1185:.
1183:)"
1158:.
1148:.
1140:.
1130:22
1128:.
1116:^
1102:.
1094:.
1084:51
1082:.
1070:^
1056:.
1048:.
1040:.
1030:87
1028:.
990:.
980:61
978:.
931:^
826:=
654:dt
650:dN
636:=
626:=
4100:K
4098:/
4096:r
3639:e
3632:t
3625:v
2892:e
2885:t
2878:v
2364:e
2357:t
2350:v
2264:.
2241:)
2227:.
2209:.
2166:.
2142::
2134::
2104:.
2084::
2051:.
2031::
2023::
2000:.
1980::
1972::
1949:.
1937::
1910:.
1906::
1898::
1875:.
1871::
1863::
1840:.
1836::
1828::
1822:7
1805:.
1777::
1749:.
1737::
1729::
1706:.
1681::
1658:.
1628::
1620::
1593:.
1587::
1579::
1552:.
1527:.
1515::
1507::
1484:.
1464::
1456::
1446::
1418:.
1386::
1380:4
1356:.
1352::
1344::
1317:.
1303::
1295::
1281:"
1264:.
1252::
1229:.
1205::
1197::
1166:.
1152::
1144::
1136::
1110:.
1098::
1090::
1064:.
1044::
1036::
998:.
994::
986::
963:.
903:(
887:.
869:=
861:2
857:x
847:2
830:;
824:D
804:,
800:)
794:K
791:N
783:1
779:(
774:)
770:1
762:A
759:N
753:(
749:N
746:r
743:+
735:2
731:x
722:N
717:2
706:D
703:=
697:t
689:N
667:N
663:N
652:/
644:A
640:;
634:K
630:;
624:r
618:N
597:)
591:K
588:N
580:1
576:(
572:N
569:r
566:=
560:t
557:d
552:N
549:d
520:K
514:A
508:0
488:K
482:N
476:A
456:A
450:N
444:0
421:,
417:)
411:K
408:N
400:1
396:(
391:)
385:A
382:N
374:1
370:(
366:N
363:r
357:=
351:t
348:d
343:N
340:d
281:(
269:(
85:"
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.