106:
1033:). The reason is that the Emperor, as "fons nobilitatium," had the power to create new princes, counts and barons of the Empire, a power which he began to use more frequently. The existing princes, counts and barons were obviously loath to see the value of their title diminished. The members of the Diet complained and, after 1582, it became the rule that such new princes and counts would not of right have a seat at the Diet. Furthermore, in 1653 the Electoral Capitulation included strict rules on the process by which the Emperor could create new states of the Empire. In particular, any new member had to possess an
1014:, the Imperial Diet. In the late 16th c., the multiplication of votes due to territorial fragmentation led to reforms. After the Diet held at Augsburg in 1582, the list of votes remained fixed, notwithstanding further territorial divisions. Furthermore, the right to vote became attached to a land, rather than to a person or family (of course, land was inheritable within families). A member of the Diet with seat and vote (individual or shared) was called a
76:. This page does not directly contain the list but discusses the format of the various lists and offers some background to understand the complex organisation of the Holy Roman Empire. The lists themselves can be accessed via the alphabetical navigation box below; each letter will lead the reader to a page on which states of the Empire that began with that letter are listed.
30:
942:; as a bishop, he exercised the spiritual duties of an ordinary bishop over his diocese, which was always larger than his Hochstift. Prince-bishops had seat and voice on the Ecclesiastical Bench of the College of Ruling Princes of the Imperial Diet. Nearly all the bishops of the Holy Roman Empire outside the Habsburg lands were prince-bishops.
1804:
1138:
The three were "usually" related, in that the sovereign of a territory was a state of the Empire, and a state of the Empire usually had sovereignty over an immediate territory; but there were exceptions both ways. Various authors emphasized one or a combination of these elements. Thus, Runde (1791)
1004:
provides an excellent overview on what an Estate (or State) of the Empire is. For his purpose, the author deals only with the hereditary territorial rulers but it should be remembered that the
Estates also included a substantial number of non-hereditary territorial rulers such as the ecclesiastical
1093:
In principle, the possession of a territory was a pre-condition for admission in the Diet. However, in the second half of the 18th century a number of counts sat on the counts' benches without any such territory. They were called "personalists" because they had been admitted on a personal basis
1813:
1146:
Using the second, slightly broader concept, at the end of the 18th century the high nobility consisted of those families which had seat and vote at the
Imperial Diet, with title of either prince or count (the last baronial family died out in 1775), numbering about 25 princely
904:: any ruling Prince whose territory is a member of the Holy Roman Empire (not only German-speaking countries, but also many bordering and extensive neighbouring regions) and entitled to a voting seat (or in a collective voting unit, such as a Grafenbank) in the Imperial Diet.
1101:
Possession of a large immediate territory was a condition for entry, but not a condition for remaining in the Diet. It happened that territories became subjected to another state of the Empire, thus losing immediate status; yet the owner remained in the
878:). It refers to the large number of nearly sovereign small and medium-sized secular and ecclesiastical principalities and free imperial cities, some of which were little larger than a single town or the surrounding grounds of the monastery of an
1845:
Wember, Heinz. "Die
Genealogie (Genealogy) von Montfort: Bludenz, Bregenz, Feldkirch, Heiligenberg, Herrenberg, Langenargen, Pfullendorf, Rheinegg, Rothenfels, Sargans, Tettnang, Tosters, Tübingen, Vaduz, Wasserburg, Werdenberg, Zollern".
918:): an abbot or abbess with the rank of prince. Prince-abbots (but not prince-abbesses) had a seat and vote on the Ecclesiastical Bench of the College of Ruling Princes of the Imperial Diet, where they sat alongside the prince-bishops.
1139:
required all three; Pütter emphasized sovereignty; Gönner and Leist emphasized seat and vote at the Diet. Among 19th century authors, the main division was between those who required all three criteria, and those who considered
786:): an entity in the Holy Roman Empire with a vote in the Imperial Diet. Several states had no seats in the Empire, while some officials (such as the Hereditary Usher) were non-voting members; neither qualified as Imperial States.
1727:
1009:
The special status of these families manifested itself in the constitution of the Empire as it evolved in the 16th c. To the status of territorial ruler corresponded a seat and vote in one of the colleges of the
762:): a regional grouping of states of the Holy Roman Empire, primarily for the purpose of organising a common defence and of collecting imperial taxes, but also as a means of organisation within the Imperial Diet.
90:
While any such list could never be definitive, the list attempts to be as comprehensive as possible. It is sorted alphabetically and split into separate articles linked below. There is also a separate
621:
818:) was a privileged feudal and political status, a form of statehood within the Holy Roman Empire. The ruler of an immediate city, abbey or territory had no overlord other than the
1106:
Consequently, whereas, in the 16th century, it was fairly easy to say who was in the upper nobility and who wasn't, it had become more difficult by the turn of the 19th century.
1309:
698:
898:
through annexation by a larger state. A mediatized lord lost most of his power over his former territory, but retained his title and most of his personal privileges.
796:): a city formally responsible to the emperor only – as opposed to the majority of cities in the Empire, which belonged to the territory of one of the many princes (
1609:
Austrian
Federal Ministry for Education, Science and Culture. "aeiou: The Annotable, Elektronic, Interactive, Osterreich (Austria), Universal Information System".
1819:
1663:
Hilkens, Bob (2000). "States and
Regents of the World: An Alphabetical Listing of States and Territories and their Regents in the 19th and 20th Centuries". [
1089:
Thus it would seem that having seat and vote in the
Reichstag would be a clear criterion for belonging to the Hochadel. But there were further complications:
1086:
Only the first two groups were part of the
Hochadel. Those in the third group were titular counts and princes but in no way accepted as part of the Hochadel.
888:
is
Military alliance and mutual assistance strengthened the position of imperial cities, especially during the interregnum period of the 13th to 14th century.
984:
the attributes of "statehood" (right to mint coins, holding markets and fairs, entering into treaties and pacts, appointment of civil officials, etc.); and
63:
periods and was generally ruled by a German-speaking
Emperor. The states that composed the Empire, while enjoying a form of territorial authority called
72:
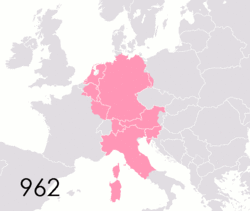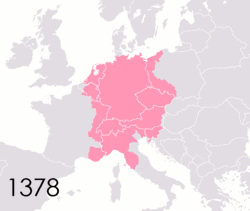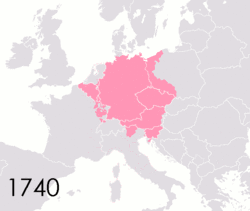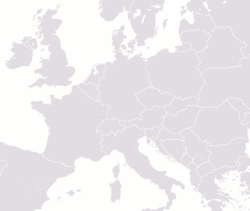
In the 18th century, the Holy Roman Empire consisted of approximately 1,800 such territories, the majority being tiny estates owned by the families of
1818:
Höckmann, Thomas (2006). "Territorial arrangement of North Rhine-Westphalia 1789". (Translation from the original in German through Google Search).
1952:
1616:
17:
800:) of the Empire, such as dukes or prince-bishops. Free cities also had independent representation in the Imperial Diet of the Holy Roman Empire.
1732:
Reitwiesner, William Addams (1998). "One of the major questions about the
Mediatized Houses is the word 'Mediatized'. What does it mean?".
1664:
1801:
1709:
975:
the territorial development of the different states or polities (acquisition or loss of possessions, union of rulers or dynasties, etc.);
380:
375:
370:
365:
360:
355:
350:
345:
340:
335:
330:
325:
320:
315:
310:
305:
300:
295:
290:
285:
280:
275:
270:
265:
240:
229:
224:
219:
214:
209:
204:
199:
194:
189:
184:
179:
174:
169:
164:
159:
154:
149:
144:
139:
134:
129:
124:
119:
1766:
1021:
At some point (Abt 1911, 103 n2 cites various possible dates, from the turn of the 16th c. to 1653 to the 18th c.), the definition of
822:
and the Imperial Diet. Immediate states had the right to collect taxes and tolls themselves, and held juridical rights (including the
1488:
95:
69:
that granted them many attributes of sovereignty, were never fully sovereign states in the sense that term is understood presently.
1947:
1840:
1782:
1604:
1690:
772:): the parliament of the Holy Roman Empire. The same name was used in the North German Confederation and in Germany until 1945.
1760:
1733:
523:
1671:
1715:
1679:
1493:
1286:
956:): a member of the electoral college of the Holy Roman Empire, having the function of electing the Holy Roman Emperors.
711:
1847:
1232:
1218:
870:
is a German word mostly used to describe the territorial fragmentation in Germany and neighboring regions during the
765:
404:
1834:
1825:
844:
to give the disintegrating Holy Roman Empire a new structure, commonly referred to as Imperial Reform (in German:
1885:
1272:
1558:
Mißheiraten in den deutschen Fürstenhäusern unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der standesherrlichen Familien
245:
91:
978:
the royal or noble dynasties, including their various branches, which ruled over territories or polities;
1665:
https://web.archive.org/web/20091027065258/http://www.geocities.com/CapitolHill/Rotunda/2209/index.html
1378:
1821:. (Excellent articles and links about the States of the Holy Roman Empire). Retrieved June 26, 2006.
1942:
1907:
1544:
981:
the transmission of succession rights (marriage, female succession, conquest, cession, pledge, etc.);
257:
1252:
1098:), and some jurists did not consider them to be part of the upper nobility (e.g., Pütter 1795, 143).
55:
The Holy Roman Empire was a complex political entity that existed in central Europe for most of the
1438:
1398:
1393:
1236:
1222:
484:
253:
1676:
Kane, Ed (2000). "Castle Directory: Alphabetical Listing of German Castles and Fortifications".
1738:
Rozn, Val (1999–2003). "The German Reigning Houses: Titles, territories, regnal chronologies".
1333:
879:
249:
1413:
1204:
1831:
1697:
1316:
744:, literally 'Imperial Abbot' or 'Abbot of the Empire'. A monastery with similar status was a
1475:
1403:
1262:
1210:
635:
Note that in the "Circle" column, "n/a" denotes a state that had ceased to exist before the
1744:
Rozn, Val (2002). "The Imperial Nobility and the Constitution of the Holy Roman Empire".
1653:
Graz, Thomas. "Thomas's Glassware Tour to Central Europe: Old Glasses from Old Europe" in
1343:
1338:
901:
891:
875:
837:
564:
52:, as well as many other feudal entities such as lordships, sous-fiefs, and allodial fiefs.
1721:
987:
the size of territory and population of the various polities whenever these are available.
8:
1458:
1383:
1353:
1242:
1186:
60:
1714:"Milestones in Pomeranian History, with particular attention to Lauenburg and Buetow".
1869:
Höckmann, Thomas (2006). "Historical maps – Germany at the end of the 18th century".
1113:
895:
819:
803:
789:
735:
611:
583:
545:
49:
1800:
Bursik, Heinrich (1998). "Die Herrschaft Hohenberg und die Markgrafschaft Burgau".
1408:
1358:
1348:
1321:
871:
504:
468:
105:
85:
44:
34:
1703:
1756:
1648:
1642:
1453:
1448:
1443:
1304:
1289:
1052:
families that were part of the Diet in 1582: the "old princely" and "old comital" (
885:
100:
1059:
families who were admitted to the Diet between 1582 and 1803: the "new princely" (
1911:
1830:
Ortwein, Friedrich J. "Die Herren zu Rappoltstein" (The Lords of Rappoltstein)".
1683:
1425:
1363:
833:
775:
751:
636:
449:
429:
393:
73:
1875:
Westermann, Großer Atlass zu Weltgeschichte (in German; exquisite detailed maps)
1745:
1388:
1373:
1368:
1228:
1176:
959:
945:
866:
851:
841:
727:
602:
438:
1852:
1658:
1470:
102:
1936:
1922:
1890:
1776:
1677:
1637:
Dotor, Santiago (2004). "Historical Flags (Schleswig-Holstein, Germany)" in
1200:
921:
830:, immediacy corresponded to a semi-independence with a far-reaching autonomy.
649:
457:
1917:
1870:
1824:"Mittelalterliche Genealogie im Deutschen Reich bis zum Ende der Staufer".
1751:
1632:
907:
691:
65:
1788:
1534:
Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, 1989
962:: the transfer of property from ecclesiastical to civil possession or use.
1005:
states (prince-bishoprics and imperial abbeys) and free imperial cities.
56:
1622:
1213:(from 1207, as Bishopric of Riga until 1255, subjugated directly to the
1810:
1726:
Principality of Liechtenstein. "Liechtenstein at a Glance: History".
930:
862:): an entity in the Holy Roman Empire with a vote in the Imperial Diet.
572:
1603:
The Arenberg Archives and Cultural Centre. "The Dukes of Arenberg".
1514:
Reich and Nation, The Holy Roman Empire as Idea and Reality, 1763–1806
1857:
939:
740:
721:
715:
677:
531:
1214:
684:
591:
493:
48:
includes any territory ruled by an authority that had been granted
1898:(On ruling families and polities in present-day Republic of Italy)
1739:
1165:
The following lists are going to be included into the table above.
1927:
1266:
1256:
656:
403:
The "Bench" column shows where the state was represented in the
1276:
1246:
553:
512:
441:, the exclusive elite formally electing the Holy Roman Emperor
1765:
Sainty, Guy Stair. "The Knights of Saint John in Germany".
1231:(secularized 16th century, secularized and subjugated to the
670:
663:
534:
1895:
1750:
Rozn, Val (2002). "The Last Years of the Ancient Empire".
1217:
in 1215, again from 1225, secularized and subjugated to the
701:) (Imperial abbacy, a monastery enjoying Imperial immediacy)
1282:
826:, 'high' justice including capital punishment) themselves.
476:
Secular Bench of the Council of Princes (individual voice)
1901:
1720:
Pantel, Mike (2000). "The History of Baden-Wurttemberg".
1696:"Lippe(-Detmold): Chronology of Lippe" in Genealogy.net.
1143:
to be the sole criterion (Hohler, Klüber, Zoepf, Rehm).
1610:
1419:
1298:
1902:
HIS DATA: Historische Herrscher der Territorien (Adel)
1693:. Retrieved July 9, 2006 (Updated February 25, 2007).
29:
1787:
Voss, Hans Peter. "History of Schleswig Holstein".
1615:"Austrian and German Mediatized Houses, 1871–1919".
1285:(from 1581, in effect in 1582, incorporated into the
991:
1627:
Cahoon, Benjamin M. (2000–2006). "Europe Index" in
1070:families or individuals who received the title of
1702:Martinsson, Örjan. "Historical Atlas: Europe".
1934:
629:Swabian Bench of the Council of Imperial Cities
1858:List of states of the Holy Roman Empire of 1521
938:). As a prince, he was the temporal ruler of a
1923:Regional Research in German-speaking Countries
1647:"Freiburg's History for Pedestrians" (2006).
1545:Unequal and Morganatic Marriages in German Law
1002:Unequal and Morganatic Marriages in German Law
724:: the territory ruled by a bishop as a prince.
1812:. For Google-translated English version, see
460:of the Council of Princes (individual voice)
1000:The following excerpt from François Velde's
96:participants in the Imperial Diet as of 1792
971:The "Notes" column shows, in capsule form,
414:
381:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (Z)
376:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (W)
371:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (V)
366:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (U)
361:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (T)
356:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (S)
351:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (R)
346:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (Q)
341:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (P)
336:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (O)
331:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (N)
326:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (M)
321:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (L)
316:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (K)
311:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (J)
306:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (I)
301:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (H)
296:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (G)
291:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (F)
286:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (E)
281:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (D)
276:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (C)
271:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (B)
266:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire (A)
644:Other abbreviations used in the list are:
1896:Genealogie delle Dinastie Nobili Italiane
1863:
1809:"Das Fürstenhaus Bentheim-Tecklenburg".
1803:. For Google-translated English version
1586:. Göttingen : Schneider, 1803. §32.
1560:. Heidelberg, 1911. Carl Winter. (Diss.)
1516:, Indiana University Press, 1980, p. 4-5.
1489:List of Imperial Diet participants (1792)
1953:Lists of states in the Holy Roman Empire
1886:Carantha: History of Slovenia-Carantania
1621:"Braunschweig – Brunswick. A history".
1169:
28:
1547:. 2004–2007. Retrieved 2012 October 09.
1194:
111:List of states in the Holy Roman Empire
14:
1935:
1327:
1130:a seat and vote at the Imperial Diet (
705:
1794:
1573:. Landshut : Krüll, 1804. §74.
1464:
1432:
1420:Territories of new princely families
1299:Territories of old princely families
836:: In 1495, an attempt was made at a
1584:Lehrbuch des Teutschen Staatsrechts
1048:Thus a distinction emerged between
24:
1592:
1494:List of historic states of Germany
1045:by his peers (princes or counts).
712:Feudalism in the Holy Roman Empire
79:
25:
1964:
1879:
1670:"History of the House of Sayn".
1639:FOTW: Flags of the World Web Site
1082:but were not admitted to the Diet
874:(especially after the end of the
1853:List of imperial circles of 1532
1159:
666:) (sometimes also called county)
610:Rhenish Bench of the Council of
104:
1948:States of the Holy Roman Empire
1273:Roman Catholic Diocese of Reval
1109:Three concepts came into play:
966:
18:States of the Holy Roman Empire
1576:
1563:
1550:
1537:
1528:
1519:
1506:
1428:, held Friedberg-Scheer (1754)
1275:(from 1521, incorporated into
1123:sovereignty over a territory (
1025:became congruent with being a
515:prelates (Council of Princes)
392:The "Circle" column shows the
13:
1:
1833:. (For English translation:
1708:"Medieval German Counties".
1597:
1500:
816:reichsfrei, reichsunmittelbar
400:) that the state belonged to.
1918:Internet Medieval Sourcebook
1836:). Retrieved June 25, 2006.
594:counts (Council of Princes)
575:counts (Council of Princes)
556:counts (Council of Princes)
92:list of Free Imperial Cities
33:Historical evolution of the
7:
1872:. Retrieved June 26, 2006.
1849:. Retrieved June 23, 2006.
1827:. Retrieved June 23, 2006.
1815:. Retrieved July 11, 2006.
1784:. Retrieved June 22, 2006.
1778:. Retrieved June 25, 2006.
1762:. Retrieved June 23, 2006.
1759:. "European Royal Houses".
1747:. Retrieved July 16, 2006.
1729:. Retrieved June 25, 2006.
1723:. Retrieved June 25, 2006.
1717:. Retrieved June 26, 2006.
1705:. Retrieved July 14, 2006.
1699:. Retrieved June 25, 2006.
1686:. Retrieved July 28, 2006.
1673:. Retrieved July 13, 2006.
1660:. Retrieved June 20, 2006.
1650:. Retrieved June 26, 2006.
1612:. Retrieved June 23, 2006.
1606:. Retrieved June 26, 2006.
1569:Gönner, Nikolaus Thaddäus.
1482:
1054:altfürstliche, altgräfliche
928:): a bishop with the rank,
10:
1969:
1842:. Retrieved July 8, 2006.
1806:. Retrieved July 9, 2006.
1790:. Retrieved July 3, 2006.
1781:"Sovereigns in Germany".
1768:. Retrieved July 1, 2006.
1753:. Retrieved June 24, 2006
1741:. Retrieved June 9, 2006.
1735:. Retrieved July 1, 2006.
1711:. Retrieved July 9, 2006.
1682:February 19, 2012, at the
1644:. Retrieved July 3, 2006.
1624:. Retrieved July 6, 2006.
1618:. Retrieved July 4, 2006.
1310:Holstein-Gottorp-Oldenburg
709:
83:
37:overlaid on modern borders
1891:The Catholic Encyclopedia
1582:Leist, Justus Christoph.
1245:(from 1225, conquered by
524:Lower Rhenish-Westphalian
420:
417:
1667:Retrieved June 27, 2006.
1237:Grand Duchy of Lithuania
1223:Grand Duchy of Lithuania
1190:1793: Council of Princes
1182:1793: Council of Princes
1180:1529: College of Princes
1018:or state of the Empire.
485:Electoral Rhenish Circle
1910:April 27, 2006, at the
1864:Maps and illustrations
1771:"Schaumburg-Lippe" in
1253:Bishopric of Ösel-Wiek
1205:Livonian Confederation
1157:
992:Estate of the Empire (
386:
43:list of states in the
38:
1914:(English translation)
1571:Teutsches Staatsrecht
1476:Old Swiss Confederacy
1263:Bishopric of Courland
1211:Archbishopric of Riga
1170:Ecclesiastical orders
1118:Reichsunmittelbarkeit
1007:
948:or electoral prince (
812:Reichsunmittelbarkeit
710:Further information:
537:(Council of Princes)
496:(Council of Princes)
84:Further information:
32:
1839:"Die Reichsstände".
1525:Gagliardo, p. 12-13.
1265:(from 1521, sold to
1255:(from 1228, sold to
1195:Livonian territories
1041:size, and had to be
914:) or prince-abbess (
902:Prince of the Empire
246:Free Imperial Cities
1689:The History Files:
1655:German History Ring
1459:Schmalkaldic League
1328:Italian territories
1317:Holstein-Glückstadt
1243:Bishopric of Dorpat
1063:and "new comital" (
706:Definition of terms
1795:In other languages
1691:Kingdoms of Europe
1629:WorldStatesmen.org
1151:) and 80 comital (
896:imperial immediacy
820:Holy Roman Emperor
804:Imperial immediacy
790:Imperial Free City
736:imperial immediacy
50:imperial immediacy
39:
1757:Sainty, Guy Stair
1634:. June 26, 2006.
1465:Political leagues
1433:Religious leagues
1379:Modena and Reggio
1322:Ernestine duchies
1287:Polish–Lithuanian
1233:Kingdom of Poland
1219:Kingdom of Poland
1187:Order of St. John
1141:Reichsstandschaft
1132:Reichsstandschaft
876:Thirty Years' War
872:Holy Roman Empire
794:freie Reichsstadt
738:. Its head was a
734:): an abbey with
633:
632:
258:Imperial Villages
86:Holy Roman Empire
45:Holy Roman Empire
35:Holy Roman Empire
16:(Redirected from
1960:
1943:German feudalism
1587:
1580:
1574:
1567:
1561:
1554:
1548:
1543:François Velde:
1541:
1535:
1532:
1526:
1523:
1517:
1510:
1454:Protestant Union
1449:League of Torgau
1444:Heilbronn League
1305:Holstein-Gottorp
1290:Duchy of Livonia
886:League of cities
415:
254:Imperial Knights
109:
108:
74:Imperial Knights
21:
1968:
1967:
1963:
1962:
1961:
1959:
1958:
1957:
1933:
1932:
1928:World Statesmen
1912:Wayback Machine
1882:
1866:
1797:
1684:Wayback Machine
1600:
1595:
1593:Further reading
1590:
1581:
1577:
1568:
1564:
1555:
1551:
1542:
1538:
1533:
1529:
1524:
1520:
1512:Gagliardo, G.,
1511:
1507:
1503:
1485:
1467:
1439:Catholic League
1435:
1426:Thurn und Taxis
1422:
1330:
1301:
1197:
1189:
1181:
1179:
1172:
1162:
1061:neufürstliche)
1031:reichsständisch
998:
969:
894:is the loss of
840:in the city of
834:Imperial Reform
776:Imperial Estate
752:Imperial Circle
718:
708:
612:Imperial Cities
458:Spiritual Bench
394:Imperial Circle
389:
262:
261:
260:
250:Imperial abbeys
114:
103:
88:
82:
80:Table of states
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1966:
1956:
1955:
1950:
1945:
1931:
1930:
1925:
1920:
1915:
1905:
1899:
1893:
1888:
1881:
1880:External links
1878:
1877:
1876:
1873:
1865:
1862:
1861:
1860:
1855:
1850:
1843:
1837:
1828:
1822:
1816:
1807:
1796:
1793:
1792:
1791:
1785:
1779:
1769:
1763:
1754:
1748:
1742:
1736:
1730:
1724:
1718:
1712:
1706:
1700:
1694:
1687:
1674:
1668:
1661:
1651:
1645:
1635:
1625:
1619:
1613:
1607:
1599:
1596:
1594:
1591:
1589:
1588:
1575:
1562:
1549:
1536:
1527:
1518:
1504:
1502:
1499:
1498:
1497:
1491:
1484:
1481:
1480:
1479:
1473:
1466:
1463:
1462:
1461:
1456:
1451:
1446:
1441:
1434:
1431:
1430:
1429:
1421:
1418:
1417:
1416:
1411:
1406:
1401:
1396:
1391:
1386:
1381:
1376:
1371:
1366:
1361:
1356:
1351:
1346:
1341:
1336:
1329:
1326:
1325:
1324:
1319:
1314:
1313:
1312:
1300:
1297:
1296:
1295:
1294:
1293:
1280:
1270:
1260:
1250:
1240:
1229:Livonian Order
1226:
1196:
1193:
1192:
1191:
1183:
1177:Teutonic Order
1171:
1168:
1161:
1158:
1136:
1135:
1128:
1121:
1104:
1103:
1099:
1084:
1083:
1072:Reichsfreiherr
1068:
1057:
997:
990:
989:
988:
985:
982:
979:
976:
968:
965:
964:
963:
960:Secularization
957:
946:Prince-elector
943:
919:
905:
899:
889:
883:
880:Imperial abbey
867:Kleinstaaterei
863:
852:Imperial State
849:
831:
808:Reichsfreiheit
801:
787:
773:
763:
749:
728:Imperial Abbey
725:
707:
704:
703:
702:
695:
688:
681:
674:
667:
660:
653:
631:
630:
627:
624:
619:
615:
614:
608:
605:
600:
596:
595:
589:
586:
581:
577:
576:
570:
567:
562:
558:
557:
551:
548:
543:
539:
538:
529:
526:
521:
517:
516:
510:
507:
502:
498:
497:
490:
487:
482:
478:
477:
474:
471:
466:
462:
461:
455:
452:
447:
443:
442:
435:
432:
427:
423:
422:
419:
413:
412:
401:
388:
385:
384:
383:
378:
373:
368:
363:
358:
353:
348:
343:
338:
333:
328:
323:
318:
313:
308:
303:
298:
293:
288:
283:
278:
273:
268:
244:
243:
238:
235:
232:
227:
222:
217:
212:
207:
202:
197:
192:
187:
182:
177:
172:
167:
162:
157:
152:
147:
142:
137:
132:
127:
122:
116:
115:
113:
101:
94:and a list of
81:
78:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1965:
1954:
1951:
1949:
1946:
1944:
1941:
1940:
1938:
1929:
1926:
1924:
1921:
1919:
1916:
1913:
1909:
1906:
1903:
1900:
1897:
1894:
1892:
1889:
1887:
1884:
1883:
1874:
1871:
1868:
1867:
1859:
1856:
1854:
1851:
1848:
1844:
1841:
1838:
1835:
1832:
1829:
1826:
1823:
1820:
1817:
1814:
1811:
1808:
1805:
1802:
1799:
1798:
1789:
1786:
1783:
1780:
1777:
1774:
1773:Genealogy.net
1770:
1767:
1764:
1761:
1758:
1755:
1752:
1749:
1746:
1743:
1740:
1737:
1734:
1731:
1728:
1725:
1722:
1719:
1716:
1713:
1710:
1707:
1704:
1701:
1698:
1695:
1692:
1688:
1685:
1681:
1678:
1675:
1672:
1669:
1666:
1662:
1659:
1656:
1652:
1649:
1646:
1643:
1640:
1636:
1633:
1630:
1626:
1623:
1620:
1617:
1614:
1611:
1608:
1605:
1602:
1601:
1585:
1579:
1572:
1566:
1559:
1553:
1546:
1540:
1531:
1522:
1515:
1509:
1505:
1495:
1492:
1490:
1487:
1486:
1477:
1474:
1472:
1469:
1468:
1460:
1457:
1455:
1452:
1450:
1447:
1445:
1442:
1440:
1437:
1436:
1427:
1424:
1423:
1415:
1412:
1410:
1407:
1405:
1402:
1400:
1397:
1395:
1392:
1390:
1387:
1385:
1382:
1380:
1377:
1375:
1372:
1370:
1367:
1365:
1362:
1360:
1357:
1355:
1352:
1350:
1347:
1345:
1342:
1340:
1337:
1335:
1332:
1331:
1323:
1320:
1318:
1315:
1311:
1308:
1307:
1306:
1303:
1302:
1291:
1288:
1284:
1281:
1278:
1274:
1271:
1268:
1264:
1261:
1258:
1254:
1251:
1248:
1244:
1241:
1238:
1234:
1230:
1227:
1224:
1220:
1216:
1212:
1209:
1208:
1206:
1202:
1201:Terra Mariana
1199:
1198:
1188:
1184:
1178:
1174:
1173:
1167:
1166:
1160:Grouped lists
1156:
1154:
1150:
1144:
1142:
1133:
1129:
1126:
1122:
1119:
1115:
1112:
1111:
1110:
1107:
1100:
1097:
1092:
1091:
1090:
1087:
1081:
1077:
1073:
1069:
1066:
1062:
1058:
1055:
1051:
1050:
1049:
1046:
1044:
1040:
1037:territory of
1036:
1032:
1028:
1024:
1019:
1017:
1013:
1006:
1003:
995:
986:
983:
980:
977:
974:
973:
972:
961:
958:
955:
951:
947:
944:
941:
937:
934:, of prince (
933:
932:
927:
923:
922:Prince-bishop
920:
917:
913:
909:
906:
903:
900:
897:
893:
892:Mediatization
890:
887:
884:
881:
877:
873:
869:
868:
864:
861:
857:
853:
850:
847:
843:
839:
835:
832:
829:
825:
821:
817:
814:; adjectives
813:
809:
805:
802:
799:
795:
791:
788:
785:
781:
777:
774:
771:
767:
766:Imperial Diet
764:
761:
757:
753:
750:
747:
746:Reichskloster
743:
742:
737:
733:
729:
726:
723:
720:
719:
717:
713:
700:
696:
693:
689:
686:
682:
679:
675:
672:
668:
665:
661:
658:
654:
651:
650:Archbishopric
647:
646:
645:
642:
640:
639:
628:
625:
623:
622:"Circle-free"
620:
617:
616:
613:
609:
606:
604:
601:
598:
597:
593:
590:
587:
585:
582:
579:
578:
574:
571:
568:
566:
565:Upper Rhenish
563:
560:
559:
555:
552:
549:
547:
544:
541:
540:
536:
533:
530:
527:
525:
522:
519:
518:
514:
511:
508:
506:
503:
500:
499:
495:
491:
488:
486:
483:
480:
479:
475:
472:
470:
467:
464:
463:
459:
456:
453:
451:
448:
445:
444:
440:
436:
433:
431:
428:
425:
424:
416:
410:
406:
405:Imperial Diet
402:
399:
395:
391:
390:
382:
379:
377:
374:
372:
369:
367:
364:
362:
359:
357:
354:
352:
349:
347:
344:
342:
339:
337:
334:
332:
329:
327:
324:
322:
319:
317:
314:
312:
309:
307:
304:
302:
299:
297:
294:
292:
289:
287:
284:
282:
279:
277:
274:
272:
269:
267:
264:
263:
259:
255:
251:
247:
242:
239:
236:
233:
231:
228:
226:
223:
221:
218:
216:
213:
211:
208:
206:
203:
201:
198:
196:
193:
191:
188:
186:
183:
181:
178:
176:
173:
171:
168:
166:
163:
161:
158:
156:
153:
151:
148:
146:
143:
141:
138:
136:
133:
131:
128:
126:
123:
121:
118:
117:
112:
107:
99:
97:
93:
87:
77:
75:
70:
68:
67:
62:
58:
53:
51:
47:
46:
36:
31:
27:
19:
1772:
1654:
1638:
1628:
1583:
1578:
1570:
1565:
1557:
1556:Abt, Emil.
1552:
1539:
1530:
1521:
1513:
1508:
1496:(after 1815)
1478:(until 1648)
1207:from 1435):
1164:
1163:
1152:
1148:
1145:
1140:
1137:
1131:
1125:Landeshoheit
1124:
1117:
1108:
1105:
1095:
1088:
1085:
1079:
1075:
1071:
1065:neugräfliche
1064:
1060:
1053:
1047:
1042:
1038:
1034:
1030:
1029:(adjective:
1026:
1022:
1020:
1016:Reichsstand,
1015:
1011:
1008:
1001:
999:
993:
970:
967:Notes column
953:
949:
935:
929:
926:Fürstbischof
925:
915:
911:
908:Prince-abbot
865:
860:Reichsstände
859:
855:
846:Reichsreform
845:
827:
823:
815:
811:
807:
797:
793:
784:Reichsstände
783:
779:
769:
760:Reichskreise
759:
755:
745:
739:
731:
692:Principality
678:Landgraviate
643:
638:Reichsreform
637:
634:
408:
397:
110:
89:
71:
66:Landeshoheit
64:
61:early modern
54:
42:
40:
26:
1471:Fürstenbund
1155:) families.
1096:ad personam
1080:Reichsfürst
1027:Reichsstand
994:Reichsstand
856:Reichsstand
824:Blutgericht
780:Reichsstand
756:Reichskreis
732:Reichsabtei
699:Reichsabtei
685:Margraviate
584:Upper Saxon
573:Westphalian
546:Lower Saxon
437:Council of
398:Reichskreis
1937:Categories
1598:In English
1501:References
1384:Montferrat
1149:fürstliche
1076:Reichsgraf
1067:) families
1056:) families
1039:sufficient
954:Kurfürsten
931:ex officio
532:Franconian
505:Franconian
469:Burgundian
1354:Guastalla
1153:gräfliche
1114:immediacy
1035:immediate
1012:Reichstag
940:Hochstift
858:, plural
782:, plural
770:Reichstag
758:, plural
741:Reichsabt
722:Hochstift
716:Lehnsmann
664:Countship
657:Bishopric
561:Upp Rhin
520:Low Rhen
409:Reichstag
1908:Archived
1904:(German)
1680:Archived
1483:See also
1399:Piombino
1394:Piedmont
1344:Florence
1292:in 1581)
1279:in 1561)
1269:in 1560)
1259:in 1560)
1249:in 1558)
1239:in 1561)
1225:in 1561)
1215:Holy See
1043:accepted
1023:Hochadel
950:Kurfürst
916:Äbtissin
912:Fürstabt
828:De facto
592:Wetterau
580:Upp Sax
542:Low Sax
494:prelates
492:Rhenish
481:El Rhin
450:Bavarian
439:Electors
430:Austrian
421:Benches
418:Circles
57:medieval
1414:Tuscany
1404:Saluzzo
1334:Carrara
1267:Denmark
1257:Denmark
798:Fürsten
603:Swabian
554:Swabian
513:Swabian
1364:Mantua
1339:Finale
1277:Sweden
1247:Russia
952:, pl.
683:Mrg. (
676:Ldg. (
648:Abp. (
535:counts
501:Franc
1409:Siena
1389:Parma
1374:Milan
1369:Massa
1359:Lucca
1349:Genoa
1203:(the
1102:Diet.
936:Fürst
842:Worms
690:Pr. (
671:Duchy
662:Co. (
655:Bp. (
618:None
599:Swab
465:Burg
426:Aust
41:This
1283:Riga
1235:and
1221:and
1185:The
1175:The
838:Diet
714:and
697:RA (
669:D. (
446:Bav
59:and
1775:.
1657:.
1641:.
1631:.
1078:or
810:or
626:SW
607:RH
588:WT
569:WE
550:SC
528:FC
509:SP
489:RP
473:PR
454:EC
434:EL
387:Key
1939::
1134:).
1127:),
1120:),
1074:,
848:).
641:.
411:).
256:,
252:,
248:,
98:.
1147:(
1116:(
1094:(
996:)
924:(
910:(
882:.
854:(
806:(
792:(
778:(
768:(
754:(
748:.
730:(
694:)
687:)
680:)
673:)
659:)
652:)
407:(
396:(
241:Z
237:Y
234:X
230:W
225:V
220:U
215:T
210:S
205:R
200:Q
195:P
190:O
185:N
180:M
175:L
170:K
165:J
160:I
155:H
150:G
145:F
140:E
135:D
130:C
125:B
120:A
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.