693:
31:
422:
260:
791:. Among sharks, the heart consists of four parts arranged serially: blood flows into the most posterior part, the sinus venosus, and then to the atrium which moves it to the third part, the ventricle, before it reaches the conus anteriosus, which itself is connected to the ventral aorta. This is considered a primitive arrangement, and many vertebrates have condensed the atrium with the sinus venosus and the ventricle with the conus anteriosus.
1833:
632:. (3) The atrial contractions must be gentle enough so that the force of contraction does not exert significant back pressure that would impede venous flow. (4) The "let go" of the atria must be timed so that they relax before the start of ventricular contraction, to be able to accept venous flow without interruption.
779:
Many other animals, including mammals, also have four-chambered hearts, which have a similar function. Some animals (amphibians and reptiles) have a three-chambered heart, in which the blood from each atrium is mixed in the single ventricle before being pumped to the aorta. In these animals, the left
577:, which provides access to the left atrium; this connects the two chambers, which is essential for fetal blood circulation. At birth, when the first breath is taken fetal blood flow is reversed to travel through the lungs. The foramen ovale is no longer needed and it closes to leave a depression (the
445:
is characterized as being in one of four groups: windsock, cactus, cauliflower, and chicken wing. The LAA appears to "function as a decompression chamber during left ventricular systole and during other periods when left atrial pressure is high". It also modulates intravascular volume by secreting
619:
to the heart that would occur during ventricular systole if the veins ended at the inlet valves of the heart. In normal physiologic states, the output of the heart is pulsatile, and the venous inflow to the heart is continuous and non-pulsatile. But without functioning atria, venous flow becomes
623:
Atria have four essential characteristics that cause them to promote continuous venous flow. (1) There are no atrial inlet valves to interrupt blood flow during atrial systole. (2) The atrial systole contractions are incomplete and thus do not contract to the extent that would block flow from the
635:
By preventing the inertia of interrupted venous flow that would otherwise occur at each ventricular systole, atria allow approximately 75% more cardiac output than would otherwise occur. The fact that atrial contraction is 15% of the amount of the succeeding ventricular ejection has led to a
1700:"Images in cardiovascular medicine. The case of a disappearing left atrial appendage thrombus: direct visualization of left atrial thrombus migration, captured by echocardiography, in a patient with atrial fibrillation, resulting in a stroke"
802:, the ventricle is almost entirely divided by a septum, but retains an opening through which some mixing of blood occurs. In birds, mammals, and some other reptiles (alligators in particular) the partitioning of both chambers is complete.
636:
misplaced emphasis on their role in pumping up the ventricles (the so-called "atrial kick"), whereas the key benefit of atria is in preventing circulatory inertia and allowing uninterrupted venous flow to the heart.
599:
Within the fetal right atrium, blood from the inferior vena cava and the superior vena cava flow in separate streams to different locations in the heart; this has been reported to occur through the
365:(lat: auricula atrii dextra) is located at the front upper surface of the right atrium. Looking from the front, the right atrial appendage appears wedge-shaped or triangular. Its base surrounds the
270:
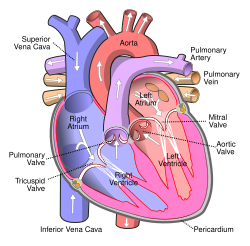
Humans have a four-chambered heart consisting of the right and left atrium, and the right and left ventricle. The atria are the two upper chambers which pump blood to the two lower ventricles.
238:
to move blood to the ventricles. Each atrium is roughly cube-shaped except for an ear-shaped projection called an atrial appendage, previously known as an auricle. All animals with a
624:
veins through the atria into the ventricles. During atrial systole, blood not only empties from the atria to the ventricles, but blood continues to flow uninterrupted from the
469:. The left atrial appendage can serve as an approach for mitral valve surgery. The body of the left atrial appendage is anterior to the left atrium and parallel to the left
465:
The left atrial appendage can be seen on a standard posteroanterior X-ray, where the lower level of the left hilum becomes concave. It can also be seen clearly using
130:
889:
1672:
584:
In some cases, the foramen ovale fails to close. This abnormality is present in approximately 25% of the general population. This is known as a
672:
results in the flow of blood in the reverse direction – from the left atrium to the right – which reduces cardiac output, potentially causing
102:
893:
2250:
539:
245:
The atrium was formerly called the 'auricle'. That term is still used to describe this chamber in some other animals, such as the
1865:
845:"Recording of blood pressure from the left auricle and the pulmonary veins in human subjects with interauricular septal defect"
481:, the left atrial appendage fibrillates rather than contracts resulting in blood stasis that predisposes to the formation of
1332:
Naksuk, Niyada; Padmanabhan, Deepak; Yogeswaran, Vidhushei; Asirvatham, Samuel J. (August 2016). "Left Atrial
Appendage".
611:
In human physiology, the atria facilitate circulation primarily by allowing uninterrupted venous flow to the heart during
519:
then spreads across both atria causing them to contract, forcing the blood they hold into their corresponding ventricles.
1812:
1682:
1926:
1621:(video produced by University of Arizona Biomedical Communications; demonstration of atrial effect begings at 13:43).
1443:
939:
511:(SA node) is located in the posterior aspect of the right atrium, next to the superior vena cava. This is a group of
369:. The right atrial appendage is a pouch-like extension of the right atrium and is covered by a trabecula network of
1921:
798:, the oxygenated and deoxygenated blood is mixed in the ventricle before being pumped out to the body's organs; in
720:
546:
490:
651:
when a drop in atrial pressure (which indicates a drop in blood volume) is detected. This triggers a release of
732:
466:
723:
may be performed at the time of any open-heart surgery to prevent future clot formation within the appendage.
696:
CT scan of the chest showing a thrombus in the left atrial appendage (left: axial plane, right: coronal plane)
963:
752:
125:
692:
281:. As the atria do not have valves at their inlets, a venous pulsation is normal, and can be detected in the
1837:
844:
758:
455:
377:
separates the right atrium from the left atrium; this is marked by a depression in the right atrium – the
2328:
2105:
1858:
1699:
983:"A comprehensive review of the anatomical variations in the right atrium and their clinical significance"
473:. The left pulmonary artery passes posterosuperiorly and is separated from the atrial appendage by the
451:
794:
With the advent of lungs came a partitioning of the atrium into two parts divided by a septum. Among
2129:
1240:
Radakovic D, Penov K, Lazarus M, Madrahimov N, Hamouda K, Schimmer C, Leyh RG, Bening C (June 2023).
527:
502:
239:
1438:(6th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 145.
1035:
2398:
516:
309:. The sinus venarum is the adult remnant of the sinus venosus and it surrounds the openings of the
85:
549:
is partly responsible for venous drainage; it derives from the embryonic left superior vena cava.
2109:
2022:
1990:
1978:
1802:
640:
286:
1022:
301:, which act as a boundary inside the atrium and the smooth-walled part of the right atrium, the
2347:
2125:
2097:
2089:
1851:
1102:
Edgerton JR (2020). "Current State of
Surgical Left Atrial Appendage Exclusion: How and When".
811:
334:
330:
198:
137:
109:
97:
565:
begins to be formed as one chamber, which over the following two weeks becomes divided by the
2270:
2175:
2143:
2017:
1936:
1657:
981:
Shereen, Rafik; Lee, Sang; Salandy, Sonja; Roberts, Wallisa; Loukas, Marios (November 2019).
574:
523:
350:
215:
787:, the circulatory system is very simple: a two-chambered heart including one atrium and one
2372:
2265:
2201:
2121:
2093:
2040:
1941:
681:
669:
589:
578:
410:
378:
223:
1618:
251:. Auricles in this modern terminology are distinguished by having thicker muscular walls.
8:
2323:
1906:
1293:"Mitral valve reoperation through the left atrial appendage in a patient with mesocardia"
1242:"The completeness of the left atrial appendage amputation during routine cardiac surgery"
701:
558:
478:
447:
168:
1268:
1241:
2367:
2335:
1995:
1968:
1916:
1780:
1498:
1463:
1416:
1357:
1166:
1141:
1079:
1052:
1004:
823:
742:
612:
570:
421:
386:
374:
366:
326:
322:
190:
61:
30:
1716:
1521:
Ashrafian H (July 2006). "The Coanda effect and preferential right atrial streaming".
1480:
1309:
1292:
908:
708:
have a tendency to form in the left atrial appendage. The clots may dislodge (forming
2377:
2305:
2255:
2101:
2000:
1985:
1973:
1901:
1896:
1808:
1784:
1772:
1721:
1678:
1601:
1597:
1538:
1503:
1485:
1439:
1420:
1408:
1349:
1314:
1273:
1201:
1171:
1119:
1084:
1008:
945:
935:
864:
860:
788:
747:
629:
512:
474:
370:
294:
290:
194:
1361:
716:
damage to the brain, kidneys, or other organs supplied by the systemic circulation.
2139:
2035:
2005:
1762:
1752:
1711:
1593:
1530:
1493:
1475:
1398:
1388:
1341:
1304:
1263:
1253:
1161:
1153:
1111:
1074:
1064:
994:
856:
818:
562:
346:
600:
2285:
2280:
2260:
2133:
2117:
2113:
1911:
1641:
1555:
1142:"Left atrial appendage: structure, function, and role in thromboembolism: Review"
1053:"A review of the LARIAT device: insights from the cumulative clinical experience"
774:
673:
508:
398:
342:
298:
214:
There are two atria in the human heart – the left atrium receives blood from the
205:
90:
1345:
2242:
2183:
2165:
2079:
1258:
1193:
1115:
999:
982:
737:
677:
470:
459:
429:
High in the upper part of the left atrium is a muscular ear-shaped pouch – the
382:
338:
159:
1069:
780:
atrium still serves the purpose of collecting blood from the pulmonary veins.
615:. By being partially empty and distensible, atria prevent the interruption of
2392:
2275:
1800:
1489:
927:
592:. It is mostly unproblematic, although it can be associated with paradoxical
566:
306:
227:
118:
114:
1698:
Parekh A, Jaladi R, Sharma S, Van Decker WA, Ezekowitz MD (September 2006).
1534:
1433:
2191:
2187:
2179:
2085:
1776:
1767:
1725:
1542:
1507:
1412:
1403:
1353:
1318:
1277:
1205:
1175:
1123:
1088:
949:
868:
648:
644:
593:
402:
282:
201:
56:
1757:
1741:"Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion during Cardiac Surgery to Prevent Stroke"
1740:
1605:
1393:
1377:"Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion during Cardiac Surgery to Prevent Stroke"
1376:
2315:
2297:
2232:
2224:
2171:
2075:
2065:
2012:
1578:
1157:
705:
652:
489:
risk, surgeons may choose to close it during open-heart surgery, using a
313:
and the coronary sinus. Attached to each atrium is an atrial appendage.
310:
274:
263:
219:
208:
143:
2340:
2155:
1843:
770:
278:
1576:
397:
The left atrium receives the oxygenated blood from the left and right
259:
182:
1331:
639:
Also of importance in maintaining the blood flow are the presence of
620:
pulsatile, and the overall circulation rate decreases significantly.
438:
273:
The right atrium and ventricle are often referred to together as the
932:
Clinical
Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations
930:. In Walker, H. Kenneth; Hall, W. Dallas; Hurst, J. Willis (eds.).
713:
482:
247:
231:
1738:
1374:
515:
which spontaneously depolarize to create an action potential. The
1290:
442:
235:
321:
The right atrium receives and holds deoxygenated blood from the
1832:
1239:
799:
709:
486:
341:, which it then sends down to the right ventricle through the
2197:
1875:
1630:
406:
186:
73:
49:
1697:
1644:
The Gross
Physiology of the Cardiovascular System (2nd ed.)
795:
784:
625:
616:
1801:
Doris R. Helms; Carl W. Helms; Robert J. Kosinski (1997).
1291:
Guhathakurta S, Kurian VM, Manmohan G, Cherian KM (2004).
405:(left atrioventricular valve) for pumping out through the
1434:
Keith L. Moore; Arthur F. Dalley; Anne M.R. Agur (2010).
980:
530:. This is located between the atria and the ventricles.
1677:(7th revised ed.). Cengage Learning. p. 567.
1192:
Arora, Yingyot; Jozsa, Felix; Soos, Michael P. (2023),
1572:
1570:
1568:
437:) (lat: auricula atrii sinistra), which has a tubular
266:
anatomy, right ventricle seen on right of illustration
1660:. Robert M. Anderson. 1999 – via Google Books.
401:, which it pumps to the left ventricle (through the
1804:
Biology in the
Laboratory: With BioBytes 3.1 CD-ROM
1658:"The Gross Physiology of the Cardiovascular System"
1565:
687:
1050:
719:In those with uncontrollable atrial fibrillation,
1796:
1794:
1558:The Gross Physiology of the Cardiovascular System
2390:
1577:Anderson R.M.; Fritz J.M.; O'Hare J.E. (1967).
1200:, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing,
928:"The Jugular Venous Pressure and Pulse Contour"
909:"Jugular Venous Pressure: Causes and Prognosis"
569:into the left atrium and the right atrium. The
462:, where they enter into the blood circulation.
218:, and the right atrium receives blood from the
1791:
1631:Discussion of atrial effect in text Chapter 1.
1579:"The Mechanical Nature of the Heart as a Pump"
1194:"Anatomy, Thorax, Heart Left Atrial Appendage"
1191:
1046:
1044:
855:(2). American Journal of Physiology: 267–271.
849:American Journal of Physiology. Legacy Content
704:, mitral valve disease, and other conditions,
1859:
1015:
1691:
1457:
1455:
1284:
1095:
193:. The blood in the atria is pumped into the
1520:
1139:
1135:
1133:
1101:
1041:
726:
277:, and the left atrium and ventricle as the
230:, the atria receive blood while relaxed in
1866:
1852:
1739:Whitlock, Richard P.; et al. (2021).
1375:Whitlock, Richard P.; et al. (2021).
892:. American Heart Association. 8 May 2020.
538:The left atrium is supplied mainly by the
425:Left atrial appendage shown at upper right
29:
1766:
1756:
1715:
1497:
1479:
1452:
1402:
1392:
1308:
1267:
1257:
1233:
1165:
1078:
1068:
998:
975:
973:
925:
356:
1873:
1670:
1130:
1051:Srivastava MC, See VY, Price MJ (2015).
842:
691:
647:in the atria, which send signals to the
573:has an opening in the right atrium, the
420:
416:
258:
1674:Human physiology: From cells to systems
663:
2391:
2126:moderator band/septomarginal trabecula
970:
1847:
1461:
1224:
1187:
1185:
441:structure. LAA anatomy as seen in a
35:Front view of heart showing the atria
906:
496:
1647:See "Chapter 1: Normal Physiology."
1562:See "Chapter 1: Normal Physiology."
676:, and in severe or untreated cases
174:
13:
1619:The Determinants of Cardiac Output
1182:
896:from the original on 20 June 2010.
289:. Internally, there are the rough
14:
2410:
1825:
1717:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.617886
1481:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.524371
1464:"Patent Foramen Ovale and Stroke"
1140:Al-Saady NM; et al. (1999).
1104:Cardiac Electrophysiology Clinics
987:Translational Research in Anatomy
890:"Roles of Your Four Heart Valves"
628:right through the atria into the
526:(AV node) is another node in the
1831:
1334:JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology
907:Tidy, Colin (20 December 2021).
861:10.1152/ajplegacy.1947.150.2.267
764:
688:Left atrial appendage thrombosis
467:transesophageal echocardiography
452:atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
345:, which in turn sends it to the
1745:New England Journal of Medicine
1732:
1664:
1650:
1635:
1624:
1612:
1549:
1514:
1427:
1381:New England Journal of Medicine
1368:
1325:
1218:
721:left atrial appendage occlusion
547:oblique vein of the left atrium
540:left circumflex coronary artery
533:
491:left atrial appendage occlusion
456:brain natriuretic peptide (BNP)
316:
1029:
956:
919:
900:
882:
836:
733:Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
552:
392:
1:
1807:. W. H. Freeman. p. 36.
1297:Texas Heart Institute Journal
829:
753:Multifocal atrial tachycardia
305:, which are derived from the
189:that receives blood from the
1598:10.1016/0002-8703(67)90313-4
1246:BMC Cardiovascular Disorders
1036:Human heart anatomy diagram.
775:Amphibian § Circulation
759:Premature atrial contraction
658:
254:
7:
2329:sternopericardial ligaments
2106:valve of inferior vena cava
1671:Sherwood, Lauralee (2008).
1436:Clinically oriented anatomy
1346:10.1016/j.jacep.2016.06.006
1225:Corne; et al. (2002).
926:Applefeld, Mark M. (1990).
805:
606:
10:
2415:
1927:posterior interventricular
1259:10.1186/s12872-023-03330-8
1116:10.1016/j.ccep.2019.10.001
1000:10.1016/j.tria.2019.100046
809:
768:
542:, and its small branches.
500:
242:have at least one atrium.
2360:
2341:epicardium/visceral layer
2314:
2296:
2241:
2223:
2216:
2154:
2130:crista supraventricularis
2064:
2057:
2031:
1959:
1952:
1922:anterior interventricular
1889:
1882:
1070:10.1186/s40064-015-1289-8
643:. These are low-pressure
528:cardiac conduction system
503:Cardiac conduction system
485:. Because of consequent
240:closed circulatory system
136:
124:
108:
96:
84:
72:
67:
55:
45:
40:
28:
23:
1229:. Churchill Livingstone.
1038:Retrieved on 2010-07-02.
1023:"Structure of the Heart"
727:Functional abnormalities
517:cardiac action potential
2110:valve of coronary sinus
2023:atrioventricular septum
1991:interventricular septum
1535:10.1378/chest.130.1.300
771:Fish § Circulation
641:atrial volume receptors
287:jugular venous pressure
16:Part of the human heart
2348:fold of left vena cava
2098:limbus of fossa ovalis
1586:American Heart Journal
964:"Embryo Images Online"
812:anatomical terminology
697:
581:) in the atrial wall.
561:at about two weeks, a
426:
363:right atrial appendage
357:Right atrial appendage
335:smallest cardiac veins
331:anterior cardiac veins
267:
173:'entry hall';
163:
138:Anatomical terminology
2144:pulmonary circulation
1758:10.1056/NEJMoa2101897
1394:10.1056/NEJMoa2101897
1227:Chest X-Ray Made Easy
712:), which may lead to
695:
524:atrioventricular node
431:left atrial appendage
424:
417:Left atrial appendage
351:pulmonary circulation
262:
216:pulmonary circulation
2373:Coronary circulation
2202:systemic circulation
2041:intervenous tubercle
1840:at Wikimedia Commons
1158:10.1136/hrt.82.5.547
843:Cournand, A (1947).
670:atrial septal defect
664:Atrial septal defect
590:atrial septal defect
586:patent foramen ovale
448:natriuretic peptides
411:systemic circulation
224:systemic circulation
181:) is one of the two
2324:fibrous pericardium
702:atrial fibrillation
613:ventricular systole
479:atrial fibrillation
234:, then contract in
2368:Circulatory system
2336:serous pericardium
2298:Pericardial cavity
1996:trabeculae carneae
1969:interatrial septum
1462:Homma, S. (2005).
824:Left atrial volume
810:This article uses
743:Atrial tachycardia
698:
571:interatrial septum
427:
375:interatrial septum
367:superior vena cava
327:inferior vena cava
323:superior vena cava
268:
191:circulatory system
62:Circulatory system
2386:
2385:
2378:Coronary arteries
2356:
2355:
2306:pericardial sinus
2266:Bachmann's bundle
2256:cardiac pacemaker
2251:Conduction system
2212:
2211:
2102:crista terminalis
2053:
2052:
2049:
2048:
2001:chordae tendineae
1974:pectinate muscles
1836:Media related to
1751:(22): 2081–2091.
1387:(22): 2081–2091.
748:Sinus tachycardia
700:In patients with
497:Conduction system
371:pectinate muscles
295:crista terminalis
291:pectinate muscles
172:
152:
151:
147:
2406:
2221:
2220:
2176:atrial appendage
2140:pulmonary artery
2090:atrial appendage
2062:
2061:
2036:cardiac skeleton
2006:papillary muscle
1957:
1956:
1887:
1886:
1868:
1861:
1854:
1845:
1844:
1835:
1819:
1818:
1798:
1789:
1788:
1770:
1760:
1736:
1730:
1729:
1719:
1710:(13): e513–514.
1695:
1689:
1688:
1668:
1662:
1661:
1654:
1648:
1639:
1633:
1628:
1622:
1616:
1610:
1609:
1583:
1574:
1563:
1560:(2nd ed., 2012).
1553:
1547:
1546:
1518:
1512:
1511:
1501:
1483:
1474:(7): 1063–1072.
1459:
1450:
1449:
1431:
1425:
1424:
1406:
1396:
1372:
1366:
1365:
1329:
1323:
1322:
1312:
1288:
1282:
1281:
1271:
1261:
1237:
1231:
1230:
1222:
1216:
1215:
1214:
1212:
1189:
1180:
1179:
1169:
1137:
1128:
1127:
1099:
1093:
1092:
1082:
1072:
1048:
1039:
1033:
1027:
1026:
1019:
1013:
1012:
1002:
977:
968:
967:
960:
954:
953:
934:. Butterworths.
923:
917:
916:
904:
898:
897:
886:
880:
879:
877:
875:
840:
819:Atrial syncytium
668:In an adult, an
563:primitive atrium
475:transverse sinus
381:. The atria are
347:pulmonary artery
199:atrioventricular
195:heart ventricles
176:
167:
144:edit on Wikidata
141:
131:7099 85574, 7099
33:
21:
20:
2414:
2413:
2409:
2408:
2407:
2405:
2404:
2403:
2399:Cardiac anatomy
2389:
2388:
2387:
2382:
2352:
2310:
2292:
2286:Purkinje fibers
2281:bundle branches
2237:
2208:
2166:pulmonary veins
2150:
2134:pulmonary valve
2118:right ventricle
2114:tricuspid valve
2045:
2027:
1979:terminal sulcus
1948:
1878:
1874:Anatomy of the
1872:
1828:
1823:
1822:
1815:
1799:
1792:
1737:
1733:
1696:
1692:
1685:
1669:
1665:
1656:
1655:
1651:
1640:
1636:
1629:
1625:
1617:
1613:
1581:
1575:
1566:
1554:
1550:
1519:
1515:
1460:
1453:
1446:
1432:
1428:
1373:
1369:
1330:
1326:
1289:
1285:
1238:
1234:
1223:
1219:
1210:
1208:
1190:
1183:
1138:
1131:
1100:
1096:
1049:
1042:
1034:
1030:
1021:
1020:
1016:
978:
971:
962:
961:
957:
942:
924:
920:
905:
901:
888:
887:
883:
873:
871:
841:
837:
832:
815:
808:
777:
767:
755:– several types
729:
690:
674:cardiac failure
666:
661:
609:
555:
536:
513:pacemaker cells
509:sinoatrial node
505:
499:
471:pulmonary veins
419:
399:pulmonary veins
395:
359:
343:tricuspid valve
319:
257:
148:
36:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2412:
2402:
2401:
2384:
2383:
2381:
2380:
2375:
2370:
2364:
2362:
2358:
2357:
2354:
2353:
2351:
2350:
2345:
2344:
2343:
2333:
2332:
2331:
2320:
2318:
2312:
2311:
2309:
2308:
2302:
2300:
2294:
2293:
2291:
2290:
2289:
2288:
2283:
2278:
2273:
2268:
2263:
2258:
2247:
2245:
2239:
2238:
2236:
2235:
2229:
2227:
2218:
2214:
2213:
2210:
2209:
2207:
2206:
2184:left ventricle
2160:
2158:
2152:
2151:
2149:
2148:
2080:coronary sinus
2070:
2068:
2059:
2055:
2054:
2051:
2050:
2047:
2046:
2044:
2043:
2038:
2032:
2029:
2028:
2026:
2025:
2020:
2015:
2010:
2009:
2008:
2003:
1998:
1993:
1983:
1982:
1981:
1976:
1971:
1960:
1954:
1950:
1949:
1947:
1946:
1945:
1944:
1939:
1931:
1930:
1929:
1924:
1919:
1914:
1904:
1899:
1893:
1891:
1884:
1880:
1879:
1871:
1870:
1863:
1856:
1848:
1842:
1841:
1827:
1826:External links
1824:
1821:
1820:
1814:978-0716731467
1813:
1790:
1731:
1690:
1684:978-0495391845
1683:
1663:
1649:
1642:Anderson, RM.
1634:
1623:
1611:
1564:
1556:Anderson, RM.
1548:
1513:
1451:
1444:
1426:
1367:
1340:(4): 403–412.
1324:
1303:(3): 316–318.
1283:
1232:
1217:
1181:
1152:(5): 547–554.
1129:
1110:(1): 109–115.
1094:
1040:
1028:
1014:
969:
955:
940:
918:
899:
881:
834:
833:
831:
828:
827:
826:
821:
807:
804:
766:
763:
762:
761:
756:
750:
745:
740:
738:Atrial flutter
735:
728:
725:
689:
686:
678:cardiac arrest
665:
662:
660:
657:
608:
605:
554:
551:
535:
532:
501:Main article:
498:
495:
460:coronary sinus
418:
415:
394:
391:
358:
355:
339:coronary sinus
318:
315:
256:
253:
183:upper chambers
150:
149:
140:
134:
133:
128:
122:
121:
112:
106:
105:
100:
94:
93:
88:
82:
81:
76:
70:
69:
65:
64:
59:
53:
52:
47:
43:
42:
38:
37:
34:
26:
25:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2411:
2400:
2397:
2396:
2394:
2379:
2376:
2374:
2371:
2369:
2366:
2365:
2363:
2359:
2349:
2346:
2342:
2339:
2338:
2337:
2334:
2330:
2327:
2326:
2325:
2322:
2321:
2319:
2317:
2313:
2307:
2304:
2303:
2301:
2299:
2295:
2287:
2284:
2282:
2279:
2277:
2276:bundle of His
2274:
2272:
2269:
2267:
2264:
2262:
2259:
2257:
2254:
2253:
2252:
2249:
2248:
2246:
2244:
2240:
2234:
2231:
2230:
2228:
2226:
2222:
2219:
2215:
2205:
2203:
2199:
2193:
2189:
2185:
2181:
2177:
2173:
2169:
2167:
2162:
2161:
2159:
2157:
2153:
2147:
2145:
2141:
2135:
2131:
2127:
2123:
2119:
2115:
2111:
2107:
2103:
2099:
2095:
2091:
2087:
2083:
2081:
2077:
2072:
2071:
2069:
2067:
2063:
2060:
2056:
2042:
2039:
2037:
2034:
2033:
2030:
2024:
2021:
2019:
2016:
2014:
2011:
2007:
2004:
2002:
1999:
1997:
1994:
1992:
1989:
1988:
1987:
1984:
1980:
1977:
1975:
1972:
1970:
1967:
1966:
1965:
1962:
1961:
1958:
1955:
1951:
1943:
1940:
1938:
1935:
1934:
1932:
1928:
1925:
1923:
1920:
1918:
1915:
1913:
1910:
1909:
1908:
1905:
1903:
1900:
1898:
1895:
1894:
1892:
1888:
1885:
1881:
1877:
1869:
1864:
1862:
1857:
1855:
1850:
1849:
1846:
1839:
1834:
1830:
1829:
1816:
1810:
1806:
1805:
1797:
1795:
1786:
1782:
1778:
1774:
1769:
1768:10044/1/89235
1764:
1759:
1754:
1750:
1746:
1742:
1735:
1727:
1723:
1718:
1713:
1709:
1705:
1701:
1694:
1686:
1680:
1676:
1675:
1667:
1659:
1653:
1646:
1645:
1638:
1632:
1627:
1620:
1615:
1607:
1603:
1599:
1595:
1592:(1): 92–105.
1591:
1587:
1580:
1573:
1571:
1569:
1561:
1559:
1552:
1544:
1540:
1536:
1532:
1528:
1524:
1517:
1509:
1505:
1500:
1495:
1491:
1487:
1482:
1477:
1473:
1469:
1465:
1458:
1456:
1447:
1445:9780781775250
1441:
1437:
1430:
1422:
1418:
1414:
1410:
1405:
1404:10044/1/89235
1400:
1395:
1390:
1386:
1382:
1378:
1371:
1363:
1359:
1355:
1351:
1347:
1343:
1339:
1335:
1328:
1320:
1316:
1311:
1306:
1302:
1298:
1294:
1287:
1279:
1275:
1270:
1265:
1260:
1255:
1251:
1247:
1243:
1236:
1228:
1221:
1207:
1203:
1199:
1195:
1188:
1186:
1177:
1173:
1168:
1163:
1159:
1155:
1151:
1147:
1143:
1136:
1134:
1125:
1121:
1117:
1113:
1109:
1105:
1098:
1090:
1086:
1081:
1076:
1071:
1066:
1062:
1058:
1054:
1047:
1045:
1037:
1032:
1024:
1018:
1010:
1006:
1001:
996:
992:
988:
984:
976:
974:
965:
959:
951:
947:
943:
941:9780409900774
937:
933:
929:
922:
914:
910:
903:
895:
891:
885:
870:
866:
862:
858:
854:
850:
846:
839:
835:
825:
822:
820:
817:
816:
813:
803:
801:
797:
792:
790:
786:
781:
776:
772:
765:Other animals
760:
757:
754:
751:
749:
746:
744:
741:
739:
736:
734:
731:
730:
724:
722:
717:
715:
711:
707:
703:
694:
685:
683:
679:
675:
671:
656:
654:
650:
646:
645:baroreceptors
642:
637:
633:
631:
627:
621:
618:
614:
604:
602:
601:Coandă effect
597:
595:
591:
587:
582:
580:
576:
575:foramen ovale
572:
568:
567:septum primum
564:
560:
559:embryogenesis
550:
548:
543:
541:
531:
529:
525:
520:
518:
514:
510:
504:
494:
492:
488:
484:
480:
476:
472:
468:
463:
461:
457:
453:
449:
444:
440:
436:
432:
423:
414:
412:
408:
404:
400:
390:
388:
384:
380:
376:
372:
368:
364:
354:
352:
348:
344:
340:
336:
332:
328:
324:
314:
312:
308:
307:sinus venosus
304:
303:sinus venarum
300:
296:
292:
288:
284:
280:
276:
271:
265:
261:
252:
250:
249:
243:
241:
237:
233:
229:
228:cardiac cycle
226:. During the
225:
221:
217:
212:
210:
207:
203:
200:
196:
192:
188:
184:
180:
170:
165:
161:
157:
145:
139:
135:
132:
129:
127:
123:
120:
116:
113:
111:
107:
104:
101:
99:
95:
92:
89:
87:
83:
80:
77:
75:
71:
66:
63:
60:
58:
54:
51:
48:
44:
39:
32:
27:
22:
19:
2361:Blood supply
2233:heart valves
2195:
2192:aortic sinus
2188:aortic valve
2180:mitral valve
2163:
2137:
2122:infundibulum
2094:fossa ovalis
2086:right atrium
2073:
1963:
1803:
1748:
1744:
1734:
1707:
1703:
1693:
1673:
1666:
1652:
1643:
1637:
1626:
1614:
1589:
1585:
1557:
1551:
1526:
1522:
1516:
1471:
1467:
1435:
1429:
1384:
1380:
1370:
1337:
1333:
1327:
1300:
1296:
1286:
1249:
1245:
1235:
1226:
1220:
1209:, retrieved
1197:
1149:
1145:
1107:
1103:
1097:
1060:
1057:SpringerPlus
1056:
1031:
1017:
990:
986:
958:
931:
921:
912:
902:
884:
872:. Retrieved
852:
848:
838:
793:
782:
778:
718:
699:
682:sudden death
667:
649:hypothalamus
638:
634:
622:
610:
598:
596:and stroke.
594:embolization
585:
583:
579:fossa ovalis
556:
544:
537:
534:Blood supply
521:
506:
464:
439:trabeculated
434:
430:
428:
403:mitral valve
396:
379:fossa ovalis
362:
360:
320:
317:Right atrium
302:
283:jugular vein
272:
269:
246:
244:
213:
209:heart valves
197:through the
178:
155:
153:
103:A12.1.00.017
78:
18:
2316:Pericardium
2225:Endocardium
2172:left atrium
2076:venae cavae
2066:Right heart
1917:interatrial
1838:Heart atria
1704:Circulation
1468:Circulation
706:blood clots
653:vasopressin
617:venous flow
553:Development
493:procedure.
483:blood clots
393:Left atrium
383:depolarised
311:venae cavae
275:right heart
264:Right heart
220:venae cavae
68:Identifiers
2243:Myocardium
2156:Left heart
1986:ventricles
1529:(1): 300.
1252:(1): 308.
1211:24 October
1198:StatPearls
993:: 100046.
830:References
769:See also:
630:ventricles
293:, and the
279:left heart
1785:234747730
1490:0009-7322
1421:234747730
1009:202002161
789:ventricle
659:Disorders
458:into the
450:, namely
255:Structure
206:tricuspid
2393:Category
2058:Chambers
1953:Internal
1933:borders
1912:coronary
1777:33999547
1726:17000914
1543:16840419
1508:16103257
1413:33999547
1362:46891270
1354:29759858
1319:15562857
1278:37340354
1269:10283164
1206:31985999
1176:10525506
1124:32067640
1089:26405642
950:21250143
894:Archived
874:20 March
869:20258383
806:See also
783:In most
714:ischemic
607:Function
337:and the
248:Mollusca
232:diastole
2271:AV node
2261:SA node
1890:Surface
1883:General
1606:6016029
1499:3723385
1167:1760793
1080:4574041
1063:: 522.
913:Patient
800:turtles
557:During
443:CT scan
387:calcium
285:as the
236:systole
222:of the
185:in the
171:
91:D006325
46:Part of
41:Details
2217:Layers
2132:), →
2013:valves
1811:
1783:
1775:
1724:
1681:
1604:
1541:
1506:
1496:
1488:
1442:
1419:
1411:
1360:
1352:
1317:
1310:521780
1307:
1276:
1266:
1204:
1174:
1164:
1122:
1087:
1077:
1007:
948:
938:
867:
773:, and
710:emboli
487:stroke
454:, and
373:. The
202:mitral
164:ātrium
156:atrium
79:atrium
57:System
24:Atrium
2198:aorta
2178:) →
2018:cusps
1964:atria
1937:right
1907:sulci
1876:heart
1781:S2CID
1582:(PDF)
1523:Chest
1417:S2CID
1358:S2CID
1146:Heart
1005:S2CID
796:frogs
626:veins
588:, an
477:. In
407:aorta
187:heart
179:atria
160:Latin
142:[
74:Latin
50:Heart
2200:and
2194:) →
2142:and
2112:) →
1942:left
1902:apex
1897:base
1809:ISBN
1773:PMID
1722:PMID
1679:ISBN
1602:PMID
1539:PMID
1504:PMID
1486:ISSN
1440:ISBN
1409:PMID
1350:PMID
1315:PMID
1274:PMID
1213:2023
1202:PMID
1172:PMID
1120:PMID
1085:PMID
979:>
946:PMID
936:ISBN
876:2022
865:PMID
785:fish
680:and
545:The
522:The
507:The
409:for
361:The
349:for
204:and
169:lit.
154:The
119:4054
115:4022
98:TA98
86:MeSH
1763:hdl
1753:doi
1749:384
1712:doi
1708:114
1594:doi
1531:doi
1527:130
1494:PMC
1476:doi
1472:112
1399:hdl
1389:doi
1385:384
1342:doi
1305:PMC
1264:PMC
1254:doi
1162:PMC
1154:doi
1112:doi
1075:PMC
1065:doi
995:doi
857:doi
853:150
435:LAA
385:by
299:His
297:of
175:pl.
126:FMA
110:TA2
2395::
2186:→
2182:→
2170:→
2136:→
2128:,
2124:,
2116:→
2108:,
2104:,
2100:,
2096:,
2092:,
2084:→
2078:,
1793:^
1779:.
1771:.
1761:.
1747:.
1743:.
1720:.
1706:.
1702:.
1600:.
1590:73
1588:.
1584:.
1567:^
1537:.
1525:.
1502:.
1492:.
1484:.
1470:.
1466:.
1454:^
1415:.
1407:.
1397:.
1383:.
1379:.
1356:.
1348:.
1336:.
1313:.
1301:31
1299:.
1295:.
1272:.
1262:.
1250:23
1248:.
1244:.
1196:,
1184:^
1170:.
1160:.
1150:82
1148:.
1144:.
1132:^
1118:.
1108:12
1106:.
1083:.
1073:.
1059:.
1055:.
1043:^
1003:.
991:17
989:.
985:.
972:^
944:.
911:.
863:.
851:.
847:.
684:.
655:.
603:.
413:.
389:.
353:.
333:,
329:,
325:,
211:.
177::
166:,
162::
117:,
2204:)
2196:(
2190:(
2174:(
2168:)
2164:(
2146:)
2138:(
2120:(
2088:(
2082:)
2074:(
1867:e
1860:t
1853:v
1817:.
1787:.
1765::
1755::
1728:.
1714::
1687:.
1608:.
1596::
1545:.
1533::
1510:.
1478::
1448:.
1423:.
1401::
1391::
1364:.
1344::
1338:2
1321:.
1280:.
1256::
1178:.
1156::
1126:.
1114::
1091:.
1067::
1061:4
1025:.
1011:.
997::
966:.
952:.
915:.
878:.
859::
814:.
433:(
158:(
146:]
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.