45:
53:
742:. As levels of PM10 decrease, related disease burden is also expected to decrease. Noise exposure and its associated disease burden is likely to increase to a level where the disease burden is similar to that of traffic accidents. The rough estimates do not provide a complete picture of the environmental health burden, because data are uncertain, not all environmental-health relationships are known, not all environmental factors have been included, and it was not possible to assess all potential health effects. The effects of a number of these assumptions were evaluated in an uncertainty analysis.
731:, air pollution is associated with respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, and exposure to certain forms of radiation can lead to the development of cancer. Quantification of the health impact of the environment was done by calculating DALYs for air pollution, noise, radon, UV, and indoor dampness for the period 1980 to 2020. In the Netherlands, 2–5% of the total disease burden in 2000 could be attributed to the effects of (short-term) exposure to air pollution, noise, radon, natural UV radiation, and
848:
resource needs. The choice of measures may also depend on individual and societal values. Measures that only consider premature death will omit the burden of living with a disease or disability, and measures that combine both in a single measure (i.e. DALYs) need to make a judgment to the significance of these measures compared to each other. Other metrics such as economic costs will not capture pain and suffering or other broader aspects of burden.
87:(DALYs). Both of these metrics quantify the number of years lost due to disability (YLDs), sometimes also known as years lost due to disease or years lived with disability/disease. One DALY can be thought of as one year of healthy life lost, and the overall disease burden can be thought of as a measure of the gap between current health status and the ideal health status (where the individual lives to
838:. These changes in the estimates of death and disease can partly be explained by the progress that has been achieved in some countries in improving access to WASH. For example, several large Asian countries (China, India, Indonesia) have managed to increase the "safely managed sanitation services" in their country from the year 2015 to 2020 by more than 10 percentage points.
808:
all DALYs globally." Of the four health outcomes studied, it was diarrheal disease that had the most striking correlation, namely the highest number of "attributable burden of disease": over 1 million deaths and 55 million DALYs from diarrheal diseases was linked with lack of WASH. Of these deaths, 564,000 deaths were linked to unsafe sanitation in particular.
706:, but it is possible to estimate a range of possible values the environmental disease burden may take based on different input parameters and assumptions. When more than one definition has to be made about a certain element in the assessment, multiple analyses can be run, using different sets of definitions.
689:
data, exposure-response relationships, and weighting factors that give an indication of the severity of a certain disorder. When information is missing or vague, experts will be consulted in order to decide which alternative data sources to use. An uncertainty analysis is carried out so as to analyze
619:
data to develop environmentally attributable fractions (EAFs) of mortality and morbidity for 85 categories of disease. In 2007, they released the first country-by-country analysis of the impact environmental factors had on health for its then 192 member states. These country estimates were the first
101:
in June 2015, low back pain and major depressive disorder were among the top ten causes of YLDs and were the cause of more health loss than diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and asthma combined. The study based on data from 188 countries, considered to be the largest and most detailed
856:
is most often directed at diseases with the highest DALYs, ignoring the fact that other diseases, despite having lower DALYs, are still major contributors to disease burden. Less-publicized diseases thus have little or no funding for health efforts. For example, maternal death (one of the top three
847:
There is no consensus on the best measures of the public's health. This may be due to the fact that measurements are used to accomplish diverse functions, such as population health assessment, evaluation of the effectiveness of interventions, formulation of health policies, and projection of future
807:
In 2023, WHO summarized the available data with the following key findings: "In 2019, use of safe WASH services could have prevented the loss of at least 1.4 million lives and 74 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) from four health outcomes. This represents 2.5% of all deaths and 2.9% of
698:
When estimating the environmental burden of disease, a number of potential sources of error may arise in the measure of exposure and exposure-risk relationship, assumptions made in applying the exposure or exposure-risk relationship to the relevant country, health statistics, and, if used, expert
829:
An earlier report by World Health
Organization which analyzed data up to 2016 had found higher values: "The WASH-attributable disease burden amounts to 3.3% of global deaths and 4.6% of global DALYs. Among children under 5 years, WASH-attributable deaths represent 13% of deaths and 12% of DALYs.
758:
developed by the WHO, EAFs developed by other researchers, and data from
Canadian public health institutions were used. Results showed a total of 10,000–25,000 deaths, with 78,000–194,000 hospitalizations; 600,000–1.5 million days spent in hospital; 1.1–1.8 million restricted activity days for
402:
In 2006, the WHO released a report which addressed the amount of global disease that could be prevented by reducing environmental risk factors. The report found that approximately one-fourth of the global disease burden and more than one-third of the burden among children was due to modifiable
138:
published in
November 2014, disorders in those aged 60 years and older represent "23% of the total global burden of disease" and leading contributors to disease burden in this group in 2014 were "cardiovascular diseases (30.3%), malignant neoplasms (15.1%), chronic respiratory diseases (9.5%),
815:
The connection between lack of WASH and burden of disease is primarily one of poverty and poor access in developing countries: "the WASH-attributable mortality rates were 42, 30, 4.4 and 3.7 deaths per 100 000 population in low-income, lower-middle income, upper-middle income and high-income
568:
The WHO developed a methodology to quantify the health of a population using summary measures, which combine information on mortality and non-fatal health outcomes. The measures quantify either health gaps or health expectancies; the most commonly used health summary measure is the DALY.
811:
Acute respiratory infections was the second largest cause of WASH-attributable burden of disease in 2019, followed by undernutrition and soil-transmitted helminthiases. The latter does not lead to such high death numbers (in comparison) but is fully connected to unsafe WASH; its
1776:
Wyper GM, Assuncao R, Fletcher E, Gourley M, Grant I, Haagsma JA, Hilderink H, Idavain J, Lesnik T, von der Lippe E, Majdan M, McCartney G, Santric-Milicevic M, Pallari E, Pires SM, Plass D, Porst M, Santos JV, de Haro Moro MT, Stockton DL, Devleesschauwer B (2021).
1501:"Global, regional, and national burdens of ischemic heart disease and stroke attributable to exposure to long working hours for 194 countries, 2000–2016: A systematic analysis from the WHO/ILO Joint Estimates of the Work-related Burden of Disease and Injury"
1188:"Global, regional, and national burdens of ischemic heart disease and stroke attributable to exposure to long working hours for 194 countries, 2000–2016: A systematic analysis from the WHO/ILO Joint Estimates of the Work-related Burden of Disease and Injury"
608:(PM10), estimating the susceptible population, and combining these data with relevant dose-response relationships. A reduction of particulate matter levels in the air to recommended standards would cause a reduction of about 5,200 deaths, 4,700 respiratory
118:
to human health. These measures allow for comparison of disease burdens, and have also been used to forecast the possible impacts of health interventions. By 2014, DALYs per head were "40% higher in low-income and middle-income regions."
1030:"Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013"
816:
countries, respectively." The regions most affected are in the WHO Africa and South-East Asia regions. Here, between 66 and 76% of the diarrheal disease burden could be prevented if access to safe WASH services was provided.
102:
analysis to quantify levels, patterns, and trends in ill health and disability, concluded that "the proportion of disability-adjusted life years due to YLDs increased globally from 21.1% in 1990 to 31.2% in 2013." The
754:, so the magnitude of their contribution to Canada's total disease burden is not well understood. In order to give an initial estimate of the environmental burden of disease for four major categories of disease, the
653:
The total number of deaths, DALYs per capita, and the percentage of the national burden of disease attributable to the environment represent the disease burden that could be avoided by modifying the environment as a
1256:
Martin J Prince; Fan Wu; Yanfei Guo; Luis M Gutierrez
Robledo; Martin O'Donnell; Richard Sullivan; Salim Yusuf (2015). "The burden of disease in older people and implications for health policy and practice".
857:
killers in most poor countries) and pediatric respiratory and intestinal infections maintain a high disease burden, and safe pregnancy and the prevention of coughs in infants do not receive adequate funding.
851:
DALYs are a simplification of a complex reality, and therefore only give a crude indication of environmental health impact. Relying on DALYs may make donors take a narrow approach to health care programs.
587:
A dose-response relationship is a function of the exposure parameter assessed for the study population. Exposure distribution and dose-response relationships are combined to yield the study population's
576:
levels, is used to calculate the environmental burden of disease. This approach requires knowledge of the outcomes associated with the relevant risk factor, exposure levels and distribution in the
788:
The WHO has investigated which proportion of death and disease worldwide can be attributed to insufficient WASH services. In their analysis they focus on the following four health outcomes:
126:(WHO) has provided a set of detailed guidelines for measuring disease burden at the local or national level. In 2004, the health issue leading to the highest YLD for both men and women was
834:
could have been prevented in 2016 with adequate WASH." An even earlier study from 2002 had estimated even higher values, namely that up to 5 million people die each year from preventable
596:. The health impact distribution can then be converted into health summary measures, such as DALYs. Exposure-response relationships for a given risk factor are commonly obtained from
427:
attributed to environmental causes is also 12 times higher in developing countries. 85 out of the 102 major diseases and injuries classified by WHO were due to environmental factors.
341:
660:
Each country summary was broken down by the disease group, where the annual number of DALYs per capita attributable to environmental factors were calculated for each group.
771:
3.6–9.1 billion in costs each year due to respiratory disease, cardiovascular illness, cancer, and congenital conditions associated with adverse environmental exposures.
2720:
1330:"Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010"
2599:
1646:"Water, sanitation and hygiene: quantifying the health impact at national and local levels in countries with incomplete water supply and sanitation coverage"
999:
2136:
1380:
151:, conducted in 1990, quantified the health effects of more than 100 diseases and injuries for eight regions of the world, giving estimates of
2727:
2438:
1668:"The impact of worldwide, national and sub-national severity distributions in Burden of Disease studies: A case study of cancers in Scotland"
804:("Good Health and Wellbeing"): Indicator 3.9.2 reports on the "mortality rate attributed to unsafe water, sanitation, and lack of hygiene".
2303:
2225:
434:
was defined as "all the physical, chemical and biological factors external to a person, and all the related behaviours". The definition of
403:
environmental factors. The "environmentally-mediated" disease burden is much higher in developing countries, with the exception of certain
2273:
2066:
823:– which is the most extreme form of "lack of sanitation" – is a major factor in causing various diseases, most notably diarrhea and
2448:
170:
In 2004, the World Health
Organization calculated that 1.5 billion disability-adjusted life years were lost to disease and injury.
1499:
Pega, Frank; Nafradi, Balint; Momen, Natalie; Ujita, Yuka; Streicher, Kai; Prüss-Üstün, Annette; Technical
Advisory Group (2021).
2528:
1876:
866:
1991:
1974:
1964:
1727:"Prioritising the development of severity distributions in burden of disease studies for countries in the European region"
2443:
2152:
1301:
1009:
159:
by age, sex, and region. It also introduced the DALY as a new metric to quantify the burden of diseases, injuries, and
2166:"Worldwide burden of disease from exposure to second-hand smoke: a retrospective analysis of data from 192 countries"
208:
17:
2164:Öberg, Mattias; Jaakkola, Maritta S.; Woodward, Alistair; Peruga, Armando; Prüss-Ustün, Annette (26 November 2010).
2008:
Thacker, Stephen B; Stroup, Donna F; Carande-Kulis, Vilma; Marks, James S; Roy, Kakoli; Gerberding, Julie L (2006).
2543:
2283:
2218:
800:, and soil-transmitted helminthiases (STHs). These health outcomes are also included as an indicator for achieving
522:
2124:
1015:
2685:
2453:
2144:
482:
419:. Children have the highest death toll, with more than 4 million environmentally-caused deaths yearly, mostly in
2192:
1478:
163:. From 2000 to 2002, the 1990 study was updated to include a more extensive analysis using a framework known as
2649:
927:
801:
605:
533:
148:
44:
31:
1426:
2433:
2263:
1454:
928:"Preventing disease through healthy environments: Towards an estimate of the environmental burden of disease"
831:
781:
669:
The public health impacts of air pollution (annual means of PM10 and ozone), noise pollution, and radiation (
84:
2548:
2473:
2428:
1778:
1388:
2153:"National and regional story (Netherlands) – Environmental burden of disease in Europe: the EBoDE project"
2777:
2699:
2644:
2211:
2106:"Solar ultraviolet radiation: Assessing the environmental burden of disease at national and local levels"
793:
526:
249:
1906:"Open defecation and childhood stunting in India: an ecological analysis of new data from 112 districts"
1186:
Pega, Frank; Nafradi, Balint; Momen, Natalie; Ujita, Yuka; Streicher, Kai; Prüss-Üstün, Annette (2021).
902:
2415:
2308:
2105:
819:
Most of the diseases resulting from lack of sanitation have a direct relation to poverty. For example,
581:
80:
52:
30:"Global burden of disease" redirects here. For the research program that measures disease burden, see
2787:
2751:
2678:
2538:
2423:
2165:
2116:
127:
123:
1001:
Assessing the environmental burden of disease at national and local levels: Introduction and methods
2706:
2619:
2604:
2478:
1645:
1570:
962:
593:
404:
115:
56:
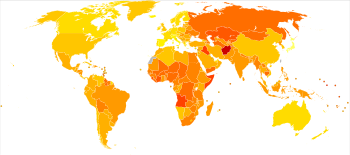
Burden of non-communicable diseases, worldwide in 2004, measured in disability-adjusted life years
2508:
2258:
1592:
597:
279:
48:
Burden of all infectious diseases, worldwide in 2004, measured in disability-adjusted life years
2782:
2772:
2734:
2563:
2298:
2177:
1593:"Second-hand smoke: Assessing the environmental burden of disease at national and local levels"
735:
in houses. The percentage can increase to up to 13% due to uncertainty, assuming no threshold.
408:
304:
1004:. WHO Environmental Burden of Disease Series. Vol. 1. Geneva: World Health Organization.
612:, and 13,500,000 days of restricted activity per year, for a total population of 4.7 million.
2692:
2654:
871:
557:
465:
38:
1864:
Burden of disease attributable to unsafe drinking-water, sanitation and hygiene, 2019 update
2318:
1917:
1679:
1512:
1199:
1099:
835:
707:
420:
107:
1405:
8:
2553:
1627:
882:
703:
488:
416:
2007:
1921:
1863:
1683:
1644:
Fewtrell, Lorna; Prüss-Üstün, Annette; Bos, Robert; Gore, Fiona; Bartram, Jamie (2007).
1516:
1203:
1103:
2634:
2594:
2579:
2533:
2498:
2468:
2253:
2234:
2042:
2009:
1940:
1905:
1816:
1803:
1753:
1726:
1702:
1667:
1543:
1500:
1354:
1329:
1282:
1255:
1230:
1187:
1122:
1087:
1054:
1029:
774:
681:
in the case of mortality) × severity (varying from 0 for perfect health to 1 for death)
632:
609:
495:
456:
2178:"The Global Burden of Disease study and applications in water, sanitation and hygiene"
1345:
1270:
1045:
2671:
2523:
2518:
2394:
2359:
2334:
2248:
2081:
2047:
2029:
1970:
1945:
1820:
1808:
1758:
1707:
1548:
1530:
1359:
1274:
1235:
1217:
1168:
1127:
1059:
1005:
711:
621:
551:
516:
470:
424:
738:
Among the investigated factors, long-term PM10 exposure have the greatest impact on
2713:
2364:
2354:
2293:
2037:
2021:
1935:
1925:
1798:
1790:
1748:
1738:
1697:
1687:
1590:
1538:
1520:
1349:
1341:
1286:
1266:
1225:
1207:
1158:
1117:
1107:
1049:
1041:
714:
can help determine which sources of uncertainty affect the final results the most.
673:
and UV), can be quantified using DALYs. For each disease, a DALY is calculated as:
577:
447:
345:
1997:(Report). Pacific Institute for Studies in Development, Environment, and Security.
1779:"The increasing significance of disease severity in a burden of disease framework"
2483:
2458:
2278:
1930:
1692:
1571:"Quantification of the disease burden attributable to environmental risk factors"
1525:
1212:
820:
768:
751:
728:
678:
631:
This presents the yearly burden, expressed in deaths and DALYs, attributable to:
616:
601:
461:
337:
1591:Öberg, M.; Jaakkola, M.S.; Prüss-Üstün, A.; Schweizer, C.; Woodward, A. (2010).
677:
DALYs = number of people with the disease × duration of the disease (or loss of
139:
musculoskeletal diseases (7.5%), and neurological and mental disorders (6.6%)."
2639:
2629:
2614:
2584:
2558:
2503:
2349:
2313:
2176:
Prüss, Annette; Havelaar, Arie (2001). Fewtrell, Lorna; Bartram, Jamie (eds.).
2025:
797:
615:
In 2002, the WHO estimated the global environmental burden of disease by using
156:
72:
68:
64:
1794:
1743:
2766:
2609:
2589:
2513:
2085:
2033:
1628:"Trends in the environmental burden of disease in the Netherlands, 1980–2020"
1534:
1221:
824:
739:
308:
131:
1725:
Wyper GM, Grant I, Fletcher E, Chalmers N, McCartney G, Stockton DL (2020).
2488:
2410:
2384:
2379:
2369:
2344:
2051:
1949:
1812:
1762:
1711:
1568:
1552:
1363:
1278:
1239:
1172:
1131:
1112:
1063:
764:
220:
152:
1088:"Dealing with uncertainties in environmental burden of disease assessment"
998:
Prüss-Üstün, Annette; Mathers, C.; Corvalán, Carlos; Woodward, A. (2003).
2463:
2288:
1163:
1146:
853:
452:
160:
1866:. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2023. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
2339:
686:
640:
636:
545:
537:
507:
476:
412:
114:
is defined as the number of deaths and DALYs that can be attributed to
97:
92:
2389:
2203:
1838:
573:
76:
1455:"Standard DALYs (3% discounting, age weights): WHO subregions (YLL)"
1086:
Knol AB, Petersen AC, van der Sluijs JP, Lebret E (1 January 2009).
775:
Burden of disease attributable to lack of water, sanitation, hygiene
2624:
2493:
2374:
1992:
Dirty Water: Estimated Deaths from Water-Related
Diseases 2000–2020
789:
732:
443:
275:
212:
997:
961:
Kay, David; Prüss, Annette; Corvalán, Carlos (23–24 August 2000).
502:
Certain environmental factors were excluded from this definition:
2193:"The WHO guides on assessing the environmental burden of disease"
644:
224:
88:
1666:
Wyper GM, Grant I, Fletcher E, McCartney G, Stockton DL (2019).
1085:
1299:
963:"Methodology for assessment of Environmental burden of disease"
760:
600:. For example, the disease burden of outdoor air pollution for
371:
312:
1427:"Standard DALYs (3% discounting, age weights): WHO subregions"
755:
650:
Total environmental burden of disease for the relevant country
763:; 8000–24,000 new cases of cancer; 500–2,500 babies with low
670:
1775:
812:"population-attributable fraction" is estimated to be 100%.
106:
is defined as the number of DALYs that can be attributed to
2163:
1665:
876:
647:. Results are calculated using the exposure-based approach.
216:
1724:
1643:
1633:. National Institute of Public Health and the Environment.
1147:"Environmental pollution and the global burden of disease"
79:, or other indicators. It is often quantified in terms of
628:
Environmental burden of disease for selected risk factors
572:
The exposure-based approach, which measures exposure via
1969:. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization (WHO).
782:
WASH § WASH-attributable burden of diseases and injuries
1962:
624:. The country estimates were divided into three parts:
187:
2600:
Existential risk from artificial general intelligence
1578:
Programme on quantifying environmental health impacts
1498:
1185:
903:"WHO | Metrics: Disability-Adjusted Life Year (DALY)"
2420:
1569:
664:
180:
1479:"What is the environment in the context of health?"
925:
702:Generally, it is not possible to estimate a formal
604:, was calculated by measuring the concentration of
1903:
1839:"Study: Environmental burden of disease in Canada"
1381:"About the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) project"
2137:"Metrics: Population Attributable Fraction (PAF)"
1564:
1562:
993:
991:
989:
987:
985:
983:
981:
979:
2764:
2141:Health statistics and health information systems
2129:Health statistics and health information systems
1836:
1385:Health statistics and health information systems
960:
2185:Water Quality: Guidelines, Standards and Health
2125:"Metrics: Disability-Adjusted Life Year (DALY)"
1400:
1398:
970:ISEE session on environmental burden of disease
926:Prüss-Üstün, Annette; Corvalán, Carlos (2006).
494:Individual behaviors, such as hand-washing and
2439:Centre for Enabling EA Learning & Research
1626:Knol, A.B.; Staatsen, B.A.M. (8 August 2005).
1559:
1462:Disease and injury regional estimates for 2004
1434:Disease and injury regional estimates for 2004
1302:"Disease incidence, prevalence and disability"
976:
830:Worldwide, 1.9 million deaths and 123 million
639:use; outdoor air pollution; and unsafe water,
207:Infectious and parasitic diseases, especially
2728:Superintelligence: Paths, Dangers, Strategies
2219:
2175:
1321:
1251:
1249:
2304:Psychological barriers to effective altruism
1625:
1473:
1471:
1395:
750:Exposure to environmental hazards may cause
430:To measure the environmental health impact,
2143:. World Health Organization. Archived from
1869:
1858:
1856:
1854:
1852:
1850:
1848:
1387:. World Health Organization. Archived from
1375:
1373:
620:step to assist governments in carrying out
2274:Distributional cost-effectiveness analysis
2226:
2212:
1963:Johnston R, Prüss-Ustün A, Wolf J (2019).
1832:
1830:
1769:
1718:
1659:
1653:WHO Environmental Burden of Disease Series
1637:
1421:
1419:
1417:
1415:
1246:
1022:
491:, including exposure to long working hours
397:
2041:
1939:
1929:
1802:
1752:
1742:
1701:
1691:
1621:
1619:
1617:
1542:
1524:
1468:
1449:
1447:
1445:
1443:
1353:
1229:
1211:
1162:
1121:
1111:
1053:
2449:Centre for the Study of Existential Risk
1956:
1845:
1370:
1300:World Health Organization (WHO) (2004).
1081:
1079:
1077:
1075:
1073:
935:Quantifying environmental health impacts
657:Environmental burden by disease category
95:). According to an article published in
51:
43:
2529:Machine Intelligence Research Institute
2064:
1827:
1584:
1412:
956:
954:
952:
950:
948:
946:
944:
14:
2765:
2233:
2113:Environmental burden of disease series
1989:
1614:
1600:Environmental Burden of Disease Series
1486:Environmental burden of disease series
1440:
1144:
867:Climate change and infectious diseases
690:the effects of different assumptions.
2207:
1904:Spears D, Ghosh A, Cumming O (2013).
1783:Scandinavian Journal of Public Health
1070:
2159:. European Environment Agency (EEA).
1837:Wigmore, Cameron (2 November 2007).
941:
442:Air, soil, and water pollution with
202:Percent of all DALYs, US and Canada
199:Percent of all YPLLs, US and Canada
2444:Center for High Impact Philanthropy
1327:
24:
2065:Garrett, Laurie (1 January 2007).
722:
498:due to unsafe water or dirty hands
209:lower respiratory tract infections
165:comparative risk factor assessment
25:
2799:
2103:
665:Implementation and interpretation
2284:Equal consideration of interests
2080:(January/February 2007): 14–38.
2067:"The Challenge of Global Health"
780:This section is an excerpt from
592:, usually expressed in terms of
104:environmental burden of disease
2686:Famine, Affluence, and Morality
2454:Development Media International
2058:
2010:"Measuring the Public's Health"
2001:
1983:
1897:
1492:
1293:
879:(water, sanitation and hygiene)
112:work-related burden of disease
2650:Risk of astronomical suffering
1877:"Call to action on sanitation"
1179:
1145:Briggs, D. (1 December 2003).
1138:
1040:(9995): 743–800. 8 June 2015.
919:
895:
802:Sustainable Development Goal 3
693:
606:atmospheric particulate matter
563:
85:disability-adjusted life years
32:Global Burden of Disease Study
13:
1:
2434:Centre for Effective Altruism
2264:Disability-adjusted life year
1346:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2
1271:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61347-7
1046:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60692-4
888:
196:Percent of all DALYs, Europe
193:Percent of all YPLLs, Europe
142:
134:. According to an article in
2549:Raising for Effective Giving
2474:Future of Humanity Institute
2198:. World Health Organization.
2171:. World Health Organization.
2131:. World Health Organization.
1931:10.1371/journal.pone.0073784
1693:10.1371/journal.pone.0221026
1655:. World Health Organization.
1580:. World Health Organization.
1526:10.1016/j.envint.2021.106595
1488:. World Health Organization.
1464:. World Health Organization.
1436:. World Health Organization.
1408:. World Health Organization.
1309:The Global Burden of Disease
1213:10.1016/j.envint.2021.106595
937:. World Health Organization.
842:
794:acute respiratory infections
415:disease burden is larger in
7:
2700:Living High and Letting Die
2645:Neglected tropical diseases
2157:National and regional story
1602:. World Health Organization
860:
717:
582:dose-response relationships
527:human-caused climate change
250:Neuropsychiatric conditions
81:quality-adjusted life years
10:
2804:
2416:Against Malaria Foundation
2309:Quality-adjusted life year
2096:
2026:10.1177/003335490612100107
1966:Safer Water, Better Health
1406:"Global burden of disease"
825:intestinal worm infections
779:
590:health impact distribution
36:
29:
2752:Effective Altruism Global
2744:
2679:The End of Animal Farming
2663:
2572:
2539:Nuclear Threat Initiative
2424:Animal Charity Evaluators
2403:
2327:
2241:
2187:. London: IWA Publishing.
2117:World Health Organization
1795:10.1177/14034948211024478
1744:10.1186/s13690-019-0385-6
1731:Archives of Public Health
1505:Environment International
1192:Environment International
745:
485:and ecosystem degradation
483:Human-made climate change
475:Agricultural methods and
405:non-communicable diseases
201:
198:
195:
192:
185:
178:
175:
124:World Health Organization
116:occupational risk factors
2707:The Most Good You Can Do
2620:Intensive animal farming
2605:Global catastrophic risk
2479:Future of Life Institute
1151:British Medical Bulletin
149:global burden of disease
37:Not to be confused with
2509:The Good Food Institute
2259:Demandingness objection
1328:Vos, T (Dec 15, 2012).
685:Necessary data include
598:epidemiological studies
411:and cancers, where the
409:cardiovascular diseases
398:Modifiable risk factors
305:Cardiovascular diseases
280:motor vehicle accidents
147:The first study on the
2735:What We Owe the Future
2564:Wild Animal Initiative
2299:Moral circle expansion
1113:10.1186/1476-069X-8-21
466:electromagnetic fields
436:modifiable environment
57:
49:
2693:The Life You Can Save
2655:Wild animal suffering
2147:on November 14, 2008.
2014:Public Health Reports
558:ultraviolet radiation
542:Outdoor air pollution
534:airborne particulates
252:, such as depression
108:environmental factors
55:
47:
39:Environmental disease
2319:Venture philanthropy
1391:on October 27, 2008.
1092:Environmental Health
872:Vectorborne diseases
633:indoor air pollution
548:and hygiene problems
421:developing countries
91:without disease and
2554:Sentience Institute
1922:2013PLoSO...873784S
1684:2019PLoSO..1421026W
1517:2021EnInt.15406595P
1204:2021EnInt.15406595P
1104:2009EnvHe...8...21K
883:Waterborne diseases
836:waterborne diseases
704:confidence interval
610:hospital admissions
584:of the pollutants.
417:developed countries
128:unipolar depression
63:is the impact of a
2778:Health informatics
2635:Malaria prevention
2595:Economic stability
2580:Biotechnology risk
2534:Malaria Consortium
2499:Giving What We Can
2469:Fistula Foundation
2254:Charity assessment
2235:Effective altruism
1164:10.1093/bmb/ldg019
506:Indoor smoke from
496:food contamination
489:Occupational risks
457:ionizing radiation
130:; in 2010, it was
58:
50:
27:Impact of diseases
2760:
2759:
2672:Doing Good Better
2544:Open Philanthropy
2524:Mercy for Animals
2519:The Humane League
2395:Eliezer Yudkowsky
2360:William MacAskill
2335:Sam Bankman-Fried
2249:Aid effectiveness
1990:Gleick P (2002).
1976:978-92-4-151689-1
1340:(9859): 2163–96.
1018:on June 12, 2005.
759:individuals with
712:decision analyses
622:preventive action
552:Second-hand smoke
471:Built environment
448:biological agents
425:infant death rate
395:
394:
176:Disease category
110:. Similarly, the
18:Burden of disease
16:(Redirected from
2795:
2788:Health economics
2714:Practical Ethics
2365:Dustin Moskovitz
2355:Holden Karnofsky
2294:Marginal utility
2228:
2221:
2214:
2205:
2204:
2199:
2197:
2188:
2182:
2172:
2170:
2160:
2148:
2132:
2120:
2115:. Vol. 17.
2110:
2090:
2089:
2071:
2062:
2056:
2055:
2045:
2005:
1999:
1998:
1996:
1987:
1981:
1980:
1960:
1954:
1953:
1943:
1933:
1901:
1895:
1894:
1892:
1890:
1881:
1873:
1867:
1860:
1843:
1842:
1834:
1825:
1824:
1806:
1773:
1767:
1766:
1756:
1746:
1722:
1716:
1715:
1705:
1695:
1663:
1657:
1656:
1650:
1641:
1635:
1634:
1632:
1623:
1612:
1611:
1609:
1607:
1597:
1588:
1582:
1581:
1575:
1566:
1557:
1556:
1546:
1528:
1496:
1490:
1489:
1483:
1475:
1466:
1465:
1459:
1451:
1438:
1437:
1431:
1423:
1410:
1409:
1402:
1393:
1392:
1377:
1368:
1367:
1357:
1325:
1319:
1318:
1316:
1315:
1306:
1297:
1291:
1290:
1265:(9967): 549–62.
1253:
1244:
1243:
1233:
1215:
1183:
1177:
1176:
1166:
1142:
1136:
1135:
1125:
1115:
1083:
1068:
1067:
1057:
1026:
1020:
1019:
1014:. Archived from
995:
974:
973:
967:
958:
939:
938:
932:
923:
917:
916:
914:
913:
899:
757:
752:chronic diseases
578:study population
346:infant mortality
189:
182:
173:
172:
21:
2803:
2802:
2798:
2797:
2796:
2794:
2793:
2792:
2763:
2762:
2761:
2756:
2740:
2659:
2625:Land use reform
2568:
2484:Founders Pledge
2459:Evidence Action
2399:
2323:
2279:Earning to give
2237:
2232:
2202:
2195:
2191:
2180:
2168:
2151:
2135:
2123:
2108:
2099:
2094:
2093:
2074:Foreign Affairs
2069:
2063:
2059:
2006:
2002:
1994:
1988:
1984:
1977:
1961:
1957:
1902:
1898:
1888:
1886:
1879:
1875:
1874:
1870:
1861:
1846:
1835:
1828:
1774:
1770:
1723:
1719:
1678:(8): e0221026.
1664:
1660:
1648:
1642:
1638:
1630:
1624:
1615:
1605:
1603:
1595:
1589:
1585:
1573:
1567:
1560:
1497:
1493:
1481:
1477:
1476:
1469:
1457:
1453:
1452:
1441:
1429:
1425:
1424:
1413:
1404:
1403:
1396:
1379:
1378:
1371:
1326:
1322:
1313:
1311:
1304:
1298:
1294:
1254:
1247:
1184:
1180:
1143:
1139:
1084:
1071:
1028:
1027:
1023:
1012:
996:
977:
965:
959:
942:
930:
924:
920:
911:
909:
901:
900:
896:
891:
863:
845:
840:
839:
821:open defecation
785:
777:
748:
729:the Netherlands
725:
723:The Netherlands
720:
696:
679:life expectancy
667:
617:risk assessment
602:Santiago, Chile
566:
525:(as opposed to
400:
338:Premature birth
186:Percent of all
179:Percent of all
145:
132:lower back pain
67:as measured by
42:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2801:
2791:
2790:
2785:
2780:
2775:
2758:
2757:
2755:
2754:
2748:
2746:
2742:
2741:
2739:
2738:
2731:
2724:
2717:
2710:
2703:
2696:
2689:
2682:
2675:
2667:
2665:
2661:
2660:
2658:
2657:
2652:
2647:
2642:
2640:Mass deworming
2637:
2632:
2630:Life extension
2627:
2622:
2617:
2615:Global poverty
2612:
2607:
2602:
2597:
2592:
2587:
2585:Climate change
2582:
2576:
2574:
2570:
2569:
2567:
2566:
2561:
2559:Unlimit Health
2556:
2551:
2546:
2541:
2536:
2531:
2526:
2521:
2516:
2511:
2506:
2504:Good Food Fund
2501:
2496:
2491:
2486:
2481:
2476:
2471:
2466:
2461:
2456:
2451:
2446:
2441:
2436:
2431:
2426:
2421:
2418:
2413:
2407:
2405:
2401:
2400:
2398:
2397:
2392:
2387:
2382:
2377:
2372:
2367:
2362:
2357:
2352:
2350:Hilary Greaves
2347:
2342:
2337:
2331:
2329:
2325:
2324:
2322:
2321:
2316:
2314:Utilitarianism
2311:
2306:
2301:
2296:
2291:
2286:
2281:
2276:
2271:
2269:Disease burden
2266:
2261:
2256:
2251:
2245:
2243:
2239:
2238:
2231:
2230:
2223:
2216:
2208:
2201:
2200:
2189:
2173:
2161:
2149:
2133:
2121:
2104:Lucas, Robyn.
2100:
2098:
2095:
2092:
2091:
2057:
2000:
1982:
1975:
1955:
1896:
1884:United Nations
1868:
1844:
1826:
1789:(2): 296–300.
1768:
1717:
1658:
1636:
1613:
1583:
1558:
1491:
1467:
1439:
1411:
1394:
1369:
1320:
1292:
1245:
1178:
1137:
1069:
1021:
1011:978-9241546201
1010:
975:
940:
918:
893:
892:
890:
887:
886:
885:
880:
874:
869:
862:
859:
844:
841:
798:undernutrition
786:
778:
776:
773:
747:
744:
724:
721:
719:
716:
695:
692:
683:
682:
666:
663:
662:
661:
658:
655:
651:
648:
629:
565:
562:
561:
560:
554:
549:
543:
540:
530:
523:climate change
519:
514:
511:
500:
499:
492:
486:
480:
473:
468:
459:
450:
399:
396:
393:
392:
389:
386:
383:
380:
377:
374:
368:
367:
364:
361:
358:
355:
352:
349:
334:
333:
330:
327:
324:
321:
318:
315:
307:, principally
301:
300:
297:
294:
291:
288:
285:
282:
272:
271:
268:
265:
262:
259:
256:
253:
246:
245:
242:
239:
236:
233:
230:
227:
204:
203:
200:
197:
194:
191:
184:
177:
144:
141:
69:financial cost
65:health problem
61:Disease burden
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2800:
2789:
2786:
2784:
2783:Public health
2781:
2779:
2776:
2774:
2773:Global health
2771:
2770:
2768:
2753:
2750:
2749:
2747:
2743:
2737:
2736:
2732:
2730:
2729:
2725:
2723:
2722:
2721:The Precipice
2718:
2716:
2715:
2711:
2709:
2708:
2704:
2702:
2701:
2697:
2695:
2694:
2690:
2688:
2687:
2683:
2681:
2680:
2676:
2674:
2673:
2669:
2668:
2666:
2662:
2656:
2653:
2651:
2648:
2646:
2643:
2641:
2638:
2636:
2633:
2631:
2628:
2626:
2623:
2621:
2618:
2616:
2613:
2611:
2610:Global health
2608:
2606:
2603:
2601:
2598:
2596:
2593:
2591:
2590:Cultured meat
2588:
2586:
2583:
2581:
2578:
2577:
2575:
2571:
2565:
2562:
2560:
2557:
2555:
2552:
2550:
2547:
2545:
2542:
2540:
2537:
2535:
2532:
2530:
2527:
2525:
2522:
2520:
2517:
2515:
2514:Good Ventures
2512:
2510:
2507:
2505:
2502:
2500:
2497:
2495:
2492:
2490:
2487:
2485:
2482:
2480:
2477:
2475:
2472:
2470:
2467:
2465:
2462:
2460:
2457:
2455:
2452:
2450:
2447:
2445:
2442:
2440:
2437:
2435:
2432:
2430:
2429:Animal Ethics
2427:
2425:
2422:
2419:
2417:
2414:
2412:
2409:
2408:
2406:
2404:Organizations
2402:
2396:
2393:
2391:
2388:
2386:
2383:
2381:
2378:
2376:
2373:
2371:
2368:
2366:
2363:
2361:
2358:
2356:
2353:
2351:
2348:
2346:
2343:
2341:
2338:
2336:
2333:
2332:
2330:
2326:
2320:
2317:
2315:
2312:
2310:
2307:
2305:
2302:
2300:
2297:
2295:
2292:
2290:
2287:
2285:
2282:
2280:
2277:
2275:
2272:
2270:
2267:
2265:
2262:
2260:
2257:
2255:
2252:
2250:
2247:
2246:
2244:
2240:
2236:
2229:
2224:
2222:
2217:
2215:
2210:
2209:
2206:
2194:
2190:
2186:
2179:
2174:
2167:
2162:
2158:
2154:
2150:
2146:
2142:
2138:
2134:
2130:
2126:
2122:
2118:
2114:
2107:
2102:
2101:
2087:
2083:
2079:
2075:
2068:
2061:
2053:
2049:
2044:
2039:
2035:
2031:
2027:
2023:
2019:
2015:
2011:
2004:
1993:
1986:
1978:
1972:
1968:
1967:
1959:
1951:
1947:
1942:
1937:
1932:
1927:
1923:
1919:
1916:(9): e73784.
1915:
1911:
1907:
1900:
1885:
1878:
1872:
1865:
1859:
1857:
1855:
1853:
1851:
1849:
1840:
1833:
1831:
1822:
1818:
1814:
1810:
1805:
1800:
1796:
1792:
1788:
1784:
1780:
1772:
1764:
1760:
1755:
1750:
1745:
1740:
1736:
1732:
1728:
1721:
1713:
1709:
1704:
1699:
1694:
1689:
1685:
1681:
1677:
1673:
1669:
1662:
1654:
1647:
1640:
1629:
1622:
1620:
1618:
1601:
1594:
1587:
1579:
1572:
1565:
1563:
1554:
1550:
1545:
1540:
1536:
1532:
1527:
1522:
1518:
1514:
1510:
1506:
1502:
1495:
1487:
1480:
1474:
1472:
1463:
1456:
1450:
1448:
1446:
1444:
1435:
1428:
1422:
1420:
1418:
1416:
1407:
1401:
1399:
1390:
1386:
1382:
1376:
1374:
1365:
1361:
1356:
1351:
1347:
1343:
1339:
1335:
1331:
1324:
1310:
1303:
1296:
1288:
1284:
1280:
1276:
1272:
1268:
1264:
1260:
1252:
1250:
1241:
1237:
1232:
1227:
1223:
1219:
1214:
1209:
1205:
1201:
1197:
1193:
1189:
1182:
1174:
1170:
1165:
1160:
1156:
1152:
1148:
1141:
1133:
1129:
1124:
1119:
1114:
1109:
1105:
1101:
1097:
1093:
1089:
1082:
1080:
1078:
1076:
1074:
1065:
1061:
1056:
1051:
1047:
1043:
1039:
1035:
1031:
1025:
1017:
1013:
1007:
1003:
1002:
994:
992:
990:
988:
986:
984:
982:
980:
971:
964:
957:
955:
953:
951:
949:
947:
945:
936:
929:
922:
908:
904:
898:
894:
884:
881:
878:
875:
873:
870:
868:
865:
864:
858:
855:
849:
837:
833:
828:
826:
822:
817:
813:
809:
805:
803:
799:
795:
791:
783:
772:
770:
766:
765:birth weights
762:
753:
743:
741:
740:public health
736:
734:
730:
715:
713:
709:
705:
700:
691:
688:
680:
676:
675:
674:
672:
659:
656:
652:
649:
646:
642:
638:
634:
630:
627:
626:
625:
623:
618:
613:
611:
607:
603:
599:
595:
591:
585:
583:
579:
575:
570:
559:
555:
553:
550:
547:
544:
541:
539:
535:
532:Occupational
531:
528:
524:
520:
518:
515:
512:
509:
505:
504:
503:
497:
493:
490:
487:
484:
481:
478:
474:
472:
469:
467:
463:
460:
458:
454:
451:
449:
445:
441:
440:
439:
437:
433:
428:
426:
422:
418:
414:
410:
406:
390:
387:
384:
381:
378:
375:
373:
370:
369:
365:
362:
359:
356:
353:
350:
347:
343:
339:
336:
335:
331:
328:
325:
322:
319:
316:
314:
310:
309:heart attacks
306:
303:
302:
298:
295:
292:
289:
286:
283:
281:
278:, especially
277:
274:
273:
269:
266:
263:
260:
257:
254:
251:
248:
247:
243:
240:
237:
234:
231:
228:
226:
222:
218:
214:
210:
206:
205:
174:
171:
168:
166:
162:
158:
154:
150:
140:
137:
133:
129:
125:
120:
117:
113:
109:
105:
100:
99:
94:
90:
86:
82:
78:
74:
70:
66:
62:
54:
46:
40:
33:
19:
2733:
2726:
2719:
2712:
2705:
2698:
2691:
2684:
2677:
2670:
2489:GiveDirectly
2411:80,000 Hours
2385:Peter Singer
2380:Derek Parfit
2370:Yew-Kwang Ng
2345:Nick Bostrom
2268:
2184:
2156:
2145:the original
2140:
2128:
2112:
2077:
2073:
2060:
2020:(1): 14–22.
2017:
2013:
2003:
1985:
1965:
1958:
1913:
1909:
1899:
1887:. Retrieved
1883:
1871:
1786:
1782:
1771:
1734:
1730:
1720:
1675:
1671:
1661:
1652:
1639:
1604:. Retrieved
1599:
1586:
1577:
1508:
1504:
1494:
1485:
1461:
1433:
1389:the original
1384:
1337:
1333:
1323:
1312:. Retrieved
1308:
1295:
1262:
1258:
1195:
1191:
1181:
1154:
1150:
1140:
1095:
1091:
1037:
1033:
1024:
1016:the original
1000:
969:
934:
921:
910:. Retrieved
906:
897:
850:
846:
818:
814:
810:
806:
787:
749:
737:
726:
701:
697:
684:
668:
614:
589:
586:
571:
567:
501:
435:
431:
429:
401:
221:tuberculosis
190:, worldwide
183:, worldwide
169:
164:
161:risk factors
146:
135:
121:
111:
103:
96:
60:
59:
2573:Focus areas
2464:Faunalytics
2328:Key figures
2289:Longtermism
1862:WHO (2023)
1157:(1): 1–24.
854:Foreign aid
708:Sensitivity
694:Uncertainty
564:Methodology
538:carcinogens
453:Ultraviolet
432:environment
83:(QALYs) or
2767:Categories
2664:Literature
2340:Liv Boeree
1606:January 2,
1511:: 106595.
1314:2009-01-30
1259:The Lancet
1198:: 106595.
1034:The Lancet
972:. Buffalo.
912:2020-01-02
889:References
699:opinions.
687:prevalence
641:sanitation
637:solid fuel
546:Sanitation
508:solid fuel
477:irrigation
438:included:
413:per capita
407:, such as
340:and other
143:Statistics
136:The Lancet
98:The Lancet
93:disability
2390:Cari Tuna
2086:0015-7120
2034:0033-3549
1889:15 August
1821:235713060
1535:0160-4120
1222:0160-4120
1098:(1): 21.
843:Criticism
594:incidence
574:pollutant
444:chemicals
342:perinatal
157:mortality
153:morbidity
77:morbidity
73:mortality
2494:GiveWell
2375:Toby Ord
2242:Concepts
2052:16416694
1950:24066070
1910:PLOS ONE
1813:34213383
1763:31921418
1737:(3): 3.
1712:31398232
1672:PLOS ONE
1553:34011457
1364:23245607
1279:25468153
1240:34011457
1173:14757707
1132:19400963
1064:26063472
861:See also
790:diarrhea
733:dampness
718:Examples
521:Natural
344:deaths (
276:Injuries
213:diarrhea
2097:Sources
2043:1497799
1941:3774764
1918:Bibcode
1804:9969303
1754:6950931
1703:6688784
1680:Bibcode
1544:8204267
1513:Bibcode
1355:6350784
1287:1598103
1231:8204267
1200:Bibcode
1123:2684742
1100:Bibcode
1055:4561509
645:hygiene
517:Mercury
479:schemes
225:malaria
89:old age
2745:Events
2084:
2050:
2040:
2032:
1973:
1948:
1938:
1819:
1811:
1801:
1761:
1751:
1710:
1700:
1551:
1541:
1533:
1362:
1352:
1334:Lancet
1285:
1277:
1238:
1228:
1220:
1171:
1130:
1120:
1062:
1052:
1008:
767:; and
761:asthma
746:Canada
654:whole.
643:, and
580:, and
556:Solar
423:. The
372:Cancer
313:stroke
223:, and
2196:(PDF)
2181:(PDF)
2169:(PDF)
2109:(PDF)
2070:(PDF)
1995:(PDF)
1880:(PDF)
1817:S2CID
1649:(PDF)
1631:(PDF)
1596:(PDF)
1574:(PDF)
1482:(PDF)
1458:(XLS)
1430:(XLS)
1305:(PDF)
1283:S2CID
966:(PDF)
931:(PDF)
832:DALYs
671:radon
635:from
462:Noise
188:DALYs
181:YPLLs
2082:ISSN
2048:PMID
2030:ISSN
1971:ISBN
1946:PMID
1891:2014
1809:PMID
1759:PMID
1708:PMID
1608:2019
1549:PMID
1531:ISSN
1360:PMID
1275:PMID
1236:PMID
1218:ISSN
1169:PMID
1128:PMID
1060:PMID
1006:ISBN
877:WASH
710:and
513:Lead
464:and
455:and
391:13%
388:25%
385:11%
382:19%
351:11%
332:14%
329:26%
326:23%
323:35%
320:10%
317:14%
311:and
299:10%
296:18%
293:13%
290:18%
287:12%
284:14%
270:28%
264:19%
258:13%
232:26%
229:37%
217:AIDS
155:and
122:The
2038:PMC
2022:doi
2018:121
1936:PMC
1926:doi
1799:PMC
1791:doi
1749:PMC
1739:doi
1698:PMC
1688:doi
1539:PMC
1521:doi
1509:154
1350:PMC
1342:doi
1338:380
1267:doi
1263:385
1226:PMC
1208:doi
1196:154
1159:doi
1118:PMC
1108:doi
1050:PMC
1042:doi
1038:386
907:WHO
769:C$
756:EAF
727:In
536:or
510:use
446:or
379:5%
376:8%
366:2%
363:3%
360:2%
357:4%
354:8%
267:5%
261:3%
255:2%
244:3%
241:5%
238:6%
235:9%
2769::
2183:.
2155:.
2139:.
2127:.
2111:.
2078:86
2076:.
2072:.
2046:.
2036:.
2028:.
2016:.
2012:.
1944:.
1934:.
1924:.
1912:.
1908:.
1882:.
1847:^
1829:^
1815:.
1807:.
1797:.
1787:51
1785:.
1781:.
1757:.
1747:.
1735:78
1733:.
1729:.
1706:.
1696:.
1686:.
1676:14
1674:.
1670:.
1651:.
1616:^
1598:.
1576:.
1561:^
1547:.
1537:.
1529:.
1519:.
1507:.
1503:.
1484:.
1470:^
1460:.
1442:^
1432:.
1414:^
1397:^
1383:.
1372:^
1358:.
1348:.
1336:.
1332:.
1307:.
1281:.
1273:.
1261:.
1248:^
1234:.
1224:.
1216:.
1206:.
1194:.
1190:.
1167:.
1155:68
1153:.
1149:.
1126:.
1116:.
1106:.
1094:.
1090:.
1072:^
1058:.
1048:.
1036:.
1032:.
978:^
968:.
943:^
933:.
905:.
827:.
796:,
792:,
348:)
219:,
215:,
211:,
167:.
75:,
71:,
2227:e
2220:t
2213:v
2119:.
2088:.
2054:.
2024::
1979:.
1952:.
1928::
1920::
1914:8
1893:.
1841:.
1823:.
1793::
1765:.
1741::
1714:.
1690::
1682::
1610:.
1555:.
1523::
1515::
1366:.
1344::
1317:.
1289:.
1269::
1242:.
1210::
1202::
1175:.
1161::
1134:.
1110::
1102::
1096:8
1066:.
1044::
915:.
784:.
529:)
41:.
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.