1587:
reestablished some control over Epirus and
Thessaly. Throughout his reign, he was also able to work with competent administrators such as John Kantakouzenos who, along with many of the nobles, supported Andronikos during the civil war with Andronikos II. However, numerous reversals against Byzantium's enemies such as Serbia and the rising Ottomans at battles such as Pelekanon further drained the power Byzantium had in comparison to its neighbors. This would be a situation that would not be helped by his sudden death in the 1340s which resulted in a civil war between the regency of John V(a coalition of Anna of Savoy, Alexios Apokaukos and the patriarch of Constantinople, John XIV) and the nobility who promoted John Kantakouzenos as emperor. In addition, diplomacy became less useful, as Byzantium's enemies realized that the Emperor had not the military or even economic might to back his word. While there was a general decline in the Empire's fortunes, Andronikos III's death would be the
2413:
580:
2107:
891:
1566:, Serbian forces took five key forts from Byzantium in 1334 and forced it to recognize the new borders. Andronikos was then forced to recognize Serbian rule in Macedonia. In addition, Andronikos faced a further reversal when leading his army at Rousokastron where he was defeated by the Bulgarians under their leader Ivan Alexander. Nevertheless, Andronikos was able to bring back Epirus into the fold in 1341 through the use of diplomacy. The result was that while the Empire was reduced to its European territories, it had succeeded in bringing much of Greece under its control. Unfortunately for the newly expanded Byzantium,
83:
1668:, a nominal ally established by Andronikos III. The Regency of John V relied on Turkish mercenaries as well. However, Kantakouzenos began to draw support from the Ottoman Sultan Orhan, who wed Kantakouzenos' daughter in 1345. By 1347, Kantakouzenos had triumphed and entered Constantinople. However, in his hour of victory, he came to an accord with Anna and her son, John V: John V (now 15 years of age) and Kantakouzenos would rule as co-emperors, though John V would be the junior in this relationship. This unlikely partnership was not destined to last long.
1835:
619:
104:
555:
1149:
2622:
2253:. John VII was a favorite of Bayezid so Manuel II was in a dangerous position. He eventually sealed an agreement. However, the Ottoman Sultan became infuriated by Manuel II's attempts to reconcile his nephew John VII. Manuel was concerned that John VII might once again launch a coup against him so wished to end the threat diplomatically. Bayezid ordered Manuel's execution, but then reduced his furious response and instead demanded that Constantinople build another Mosque and that a colony of Turks be established.
2604:
who had been opened up to
Byzantium by the maritime expansions of Genoa and Venice came to appreciate their achievements, facilitating the Renaissance. As such these scholars found themselves in Italian institutions, expressing their Greco-Roman culture for pay. Immigration to Italy was made less attractive by the idea of abandoning the Orthodox faith to practice Catholicism. Nonetheless, a significant and increasing number of Greeks began travelling to Italy, first temporarily to Italian colonies such as
1470:
brother Manuel
Palaiologos had been accidentally murdered by Andronikos III's companions over a competitive love affair. His father (Michael IX), the son of Andronikos II, died of shock as a result of his son's death. Andronikos III did not take his disinheritance lightly — organizing an armed opposition, he succeeded in drawing support with promises of generous tax cuts, even beyond those enacted by Andronikos II. Andronikos II was powerless to stop the young usurper; he granted him
1296:
2233:
1512:
1603:
157:
2325:
2797:
5615:
2896:
2524:
167:
147:
1652:, sparked the civil conflict when he convinced the Empress that John V's rule was threatened by the ambitions of Kantakouzenos. In September 1341, while Kantakouzenos was in Thrace, Kalekas declared himself as regent and launched a vicious attack on Kantakouzenos, his supporters and family. In October, Anna ordered Kantakouzenos to resign his command. Kantakouzenos not only refused, but declared himself Emperor at
1071:
2398:
Manuel II Palaiologos re-established
Byzantium as a vassal of the Ottomans — 300,000 silver coins were to be paid to the Sultan on annual basis. That the Empire managed to accomplish this at its lowest ebb is remarkable. Nonetheless, until the 1450s, the Ottomans would not make any concerted efforts to overcome the walls of Constantinople, and the city retained a tenuous security for the next two decades.
1579:
2964:" that would cut a swathe through Asia Minor and allow Byzantine troops to re-occupy the empire's ancient heartlands. However, by the late 14th century, the Byzantine Empire did not possess sufficient resources for the task, and in any case such Western undertakings would have required Byzantium to submit to Rome. If the price for political freedom was religious freedom, certain emperors such as
1736:
2492:. Murad II was in no position to stop these troublesome westerners since he was overwhelmed with problems by easterners in Anatolia, the core of the Ottoman realm. Therefore, Murad hastily concluded a peace treaty in the Balkans. The Hungarians soon broke the treaty, but at Varna a hastily assembled Ottoman army crushed the Crusaders and left the Balkans at the mercy of Ottoman vengeance.
1461:, thereby further reducing Byzantium's military capability. While these solved some problems that Michael VIII had left for his son, it unraveled his father's attempts at restoring the power of the Byzantine Empire; where Michael VIII had attempted to deal with problems outside the Empire, Andronikos aimed to solve the internal problems resulting from his father's reign.
2218:, where he "donated" religious relics made of precious metals to them for their support. John refused to give up his right to rule as Emperor of Byzantium until his death in 1408. By then however, the Ottoman Sultan Bayezid had recognized Manuel II Palaiologos as co-emperor of Byzantium alongside his father John V, and finally, when John V died in 1391, as sole Emperor.
1775:
thinking of ways to stave off defeat. Amadeo returned to Europe via Rome and brought with him
Byzantine envoys. The Pope again was uninterested, but called for John V to visit him. In 1369, when the Ottomans finally captured Adrianople (though some sources indicate 1365), John V rushed to Rome and confessed his Catholic faith both privately and at a public spectacle.
1693:, one of the few islands in the Aegean still under Byzantine control, while Kantakouzenos made his son Matthew co-emperor. John V would not give up so easy however, and in 1354 Ottoman troops began crossing over into Thrace in his support. The citizens of Constantinople became gripped with fear and in November of that same year, John V launched a successful coup with
2981:
severely weakened the empire from within, leaving it disastrously exposed to outside attack. Furthermore, the empire's military system had become increasingly disorganised and chaotic, following the demise of the theme system in the 11th–13th centuries. The result was persistent failure and defeat on every frontier.
2177:, useless. Again, prison break became the next event with John V and Manuel escaping Constantinople, offering the Ottoman Sultan higher tribute than normally paid, in return for help in taking over Constantinople. Andronikos IV, having been beaten yet again, evaded capture and slipped into the Genoese district of
1440:
2984:
Byzantium could only lose and decline for so long before it destroyed her; by the late 14th century, the situation had become so severe that
Byzantium surrendered her political independence. By the mid 15th century, restoring both the religious and the political freedom of Byzantium was ultimately an
2971:
The proximate cause of the problem lay in
Byzantium's numerous enemies, who combined during the course of the 14th century to overwhelm what remained of the empire's core territories. With each passing decade, the Byzantine Empire became weaker and lost more land. There were fewer resources available
1003:
in 1243. The
Palaiologoi were engaged on several fronts, often continually, while the empire's supply of food and manpower dwindled. In this period, the Byzantine Empire found itself continually at war, both civil and interstate, with most interstate conflicts being with other Christian empires. Most
2603:
Despite much chaos in the Empire, the
Byzantines experienced a revival in culture and art within their domain. Towards the 14th century, as the Empire entered into a phase of terminal crisis, such achievements became less valued. All was not lost for these seemingly rejected scholars — many in Italy
2561:
Mehmed II assembled a huge army to assail
Constantinople's landward walls — some sources suggest 80,000 soldiers, while others suggest figures as high as 100,000 or even 200,000, including camp followers. A major feature of the Ottoman army was its high-quality artillery. Among others, it featured a
2495:
John VIII died in 1448. His reign lasted two decades. His achievement was the continued survival of the Empire. Yet Byzantium was now hanging by a thread. With insufficient military manpower for its own defense, an economy ruined by years of warfare, a depopulated capital, and insufficient territory
2381:
The Byzantines were the first to make a move when John VIII and his advisors made a risky decision by inciting a rebellion within the Ottoman Sultanate. In August 1421, they backed a man named Mustafa who claimed to be a long lost son of Bayezid the Thunderbolt. In Europe, Mustafa's rebellion worked
2261:
Manuel's next steps were bold and seemingly foolish — not only did he refuse to pay the Sultan tribute, he refused to answer the Sultan's messages and Bayezid set about laying siege to Constantinople. In 1394, his siege began and would continue for eight years. Manuel II realized that while the city
2193:
With Thessalonica surrendering in 1387 and his position rather hopeless, Manuel returned to John V and, with the Sultan's assent, began making conciliatory offers to his father. John V realized that accepting his second son back would cause his grandson to rebel in turn, and therefore he simply kept
1774:
arrived at and seized the fortress of Gallipoli from the Ottomans and handed it back to the Byzantines, hoping that this would stem the tide of Turkish emigration into Thrace. However, the Turks had by now firmly established themselves in Thrace. Amadeo and John spent much time between 1367 and 1369
1758:
and Michael VIII, John V now turned to the Pope and offered the promise of a Union of the two Churches in the hopes of receiving military assistance. As a guarantee of compliance, John V offered his son, Manuel. In the past, Byzantium's cry for assistance were answered with mixed results — pillaging
1586:
Although ultimately unsuccessful, the reign of Andronikos III was one of the last bright spots in Byzantine history, as the Empire's position was becoming increasingly precarious. Andronikos was able to score some successes in his life as he campaigned vigorously against the Genoese with success and
1469:
Andronikos II's policies were not successful in dealing with Byzantium's external problems; however, it would be threats from within the Empire that led to his abdication — in 1320 Andronikos III, the young (in his twenties) grandson of Andronikos II was disinherited by the Emperor. Andronikos III's
1448:
Andronikos II ordered the Union of the Orthodox and Catholic Churches to be canceled, a move which pleased many. But he also ordered drastic reductions in the military, and effectively disbanded the navy, which his father had worked hard to build up. As a result, tax reductions throughout the Empire
1382:
Unlike his father, Andronikos II recognized the gravity of the situation in Asia Minor, and tried to drive out the Turks, utilizing a variety of methods. His first action was to move his court to Asia Minor, where he could better oversee the construction of fortifications and raise troop morale. His
1326:
and the ostensible union of the two Churches did little to avert Catholic aggression, while at the same time the Orthodox population, led by large parts of the priesthood, denounced Michael VIII as a traitor. His death in 1282 came as a relief to many, and his body was denied an Orthodox funeral, as
1260:
arranged a pact, whereby Charles would receive land in the East in return for assisting a new military expedition to Constantinople. A delay on Charles' end meant that Michael VIII was given enough time to negotiate a union between the Church of Rome and that of Constantinople in 1274, thus removing
2579:
Constantine's rule is hard to assess due to the shortness of his reign. As a Despot, he had shown ability, but the fall of the Empire to the Turks was by his time inevitable, no matter how able and energetic an Emperor sat on the throne. What is most remembered of him is the stubborn defence of his
2443:
1391. John VIII was still hopeful that he could emulate his Father's success and more. Like his predecessors, his attempts were in vain. And just like his predecessors, he relied too heavily on a Pope not willing to give, but only take; take that is, the Church of a wretched state surrounded by the
1718:
The lands ravaged and depopulated by the civil war were filled up by arriving Turks who colonised the land through a mixture of conquest and trade. The result was that Byzantium's power was undermined beyond all recovery — two hundred years ago Byzantium could rely on the people living in the lands
1684:
Kantakouzenos had a son, Matthew Kantakouzenos — and any hope of keeping peace between John V and Matthew became more remote as the two grew older and more independent. John V wed Kantakouzenos' daughter, thus becoming his son in law, in a move designed to bind the two families, but it was destined
1491:
Andronikos II attempted to solve Byzantium's internal problems more than his father had. The solutions he chose however had severe repercussions. They undermined the military and financial basis of the state, and the disasters suffered by his foreign policy failures further worsened the situation.
2189:
and Epirus, thus "expanding" the Empire, at least nominally, and thereby catching the Ottoman Sultan's attention. Murad I besieged Thessalonica in 1383, beginning a siege that would last until 1387. Meanwhile, Andronikos IV died and his son, John VII, began quarreling with his grandfather, John V.
2873:
As the Empire descended into chaos, it could not spare any finances in its efforts to defend its borders. Study in the fields of science and mathematics naturally disappeared from the minds of those whose lands were raided and seized. It was due to this lack of patronage that led many scholars to
2869:
in order to survive. The most important source was from the Imperial court, especially before the destructive civil wars that were characterized by Andronikos III and his son John V. Other sources were from minor courts, from the wealthy, and from the Church, if not from individual Church clergy,
2397:
Manuel II was now out of tricks to save the erroneous rule of his son, John VIII. In September 1423, Thessalonika was surrendered to the Venetians, no doubt hoping to draw in the Western Powers into a new crusade and, if not, at least their wealth would enable them to defend it. In February 1424,
1426:
in Spain and now, for an extraordinarily high price, they drove the Turks back in Asia Minor. Once again, these successes were nullified when their leader, Roger de Flor, was assassinated on his way to meet Andronikos; the Catalans then revolted against imperial authority, and began pillaging and
2514:
Constantine's reign was short; from 1448 (some sources say 1449) until 1453. Constantine XI, like many of his predecessors who took the Union between Eastern and Western Christendom seriously, lived as a Catholic. Not much is known of his reign, except that he died with his soldiers in the final
1614:
swept through its diminished lands. The first outbreak occurred in 1347, and between the 1360s and 1420s, eight further outbreaks of plague are recorded. Cities were full of social unrest between the corrupt wealthy (who had been exploiting the tax system for their own benefit) and the countless
1211:
were all strengthened against a possible new expedition by the Latin West. Many hospitals, hospices, markets, baths, streets and churches were built, some with private patronage. Even a new Mosque was built to compensate for the one burnt during the Fourth Crusade. These attempts were costly and
2570:
engineer who had originally offered his services to Constantine, who rejected them for lack of money. After the rejection of terms of surrender by Constantine, the siege began on April 2, 1453, with Ottoman cannon firing from April 6. The defenders were few, but the mighty walls allowed them to
2240:
Manuel II's reign saw another temporary respite for the Byzantines. For an Empire in such trouble, he succeeded in retaking some territory and held it to the end of his reign. His limited success largely came through the resurrection of Mongol Power in the East and the great friendship achieved
2336:
considerably changed the mood within Constantinople. The rewards reaped by the Empire were outstanding considering that only a short time had passed since the city (and possibly the Empire itself) stood on the brink of destruction. John VII appeared to have achieved numerous other benefits for
2156:
and the two worked towards fomenting revolution in their peoples. Consequently, both the Byzantine and Ottoman rulers were facing their sons and as a result, coordinated efforts were made to defeat both. John V had his eldest son, Andronikos IV, along with the latter's son, John VII, partially
2980:
However, the most serious problems arose from the internal political and military organisation of the empire. The empire's political system, based as it was around an autocratic and semi-divine emperor who exercised absolute power, had become obsolete, while the civil wars the system produced
2571:
withstand the siege for some time. Finally however, on May 29, the Ottomans achieved a breach, and the city fell. Constantine XI charged at the oncoming Ottoman army; the last Roman Emperor died fighting, and since his body was never recognized, is assumed to have been buried in a mass grave.
1279:
For the remainder of his life, Michael campaigned to drive the Latins out of Greece and the Balkans, and secure his position versus the Bulgarians. He was largely successful, regaining several islands in the Aegean, and establishing a foothold in the Peloponnese, that would grow to become the
1677:
1335:
Michael VIII was a very energetic, ambitious and capable emperor who had enlarged and preserved the Empire and had once again made Byzantium a power to be reckoned with in the region. His army, however, was still small, and diplomacy was relied upon more than ever. An extortionate tax system
2976:
and Arabs), by the later 14th century the empire no longer possessed any significant territories (such as Asia Minor) to form the basis of a recovery. As a result, many attempts at driving back the Ottomans and Bulgarians failed, while the lack of territory, revenue and manpower meant that
2762:. As a result, Persian tables were used more often, even if in conjunction with Ptolemy's. The acceptance of Arab astronomy was made harder by the fact that it had to be translated, and only entered through "lowlier social channels", namely by men who travelled between Constantinople and
1659:
There were not nearly enough troops to defend Byzantium's borders at the time and there certainly was not enough for the two factions to split; consequently, foreigner mercenaries were brought in. Kantakouzenos hired Turks and Serbs — his main supply of Turkish mercenaries came from the
1318:
army, and while it was not as effective, it was just as burdensome on the treasury. The result was that heavy taxes were levied on the peasantry, something that the Ottomans would later use to their advantage, winning over these poverty-stricken peasants with promises of lower taxes.
2292:
The seemingly insurmountable pressure was ultimately relieved as a result of events in Anatolia. Bayezid, his position in Europe secure, turned his attentions to Anatolia and attempted to bring the various Turcoman tribes under formal Ottoman control. These actions greatly offended
2629:
The Fourth Crusade saw the destruction of many homes in Constantinople and much of the city on fire. It is difficult to determine what books were burned in the libraries of Constantinople, though one can only imagine that few would be available today were it not for the works of
2337:
Byzantium. The first was a non-aggression treaty between the local Christian powers (who were also free from Ottoman servitude), meaning that the disasters of Andronikos III's later rule would not be repeated. Next were a treaty between Byzantium and the successor of Bayezid,
1366:
in 1282 and raids against Macedonia were launched throughout the 1290s. Byzantine counter-attacks failed to stop these, and as a result Andronikos was forced to resort to diplomacy, marrying his 5-year-old daughter to the Serbian King and ceding a number of forts from
2472:, not only at the terms at which the Byzantine Church had to stoop to, but also at the non-existent aid to Byzantium. One can safely say that the most notable effect of the Union was the increased resentment between Byzantium's populace and the Imperial government.
2164:
Unfortunately for John V, Andronikos IV and his son John VII escaped. With Genoan and Turkish aid, they returned to Constantinople and succeeded in overthrowing John V, imprisoning him and Manuel. In exchange for Ottoman aid, Andronikos IV handed the fortress of
1593:
for the Empire — his 10-year-old son was led by a regency that was torn apart in dynastic rivalries which led to the Second Palaiologan Civil War and the recognition of John Kantakouzenos as emperor and a catastrophe from which Byzantium would never recover.
1336:
supported his ambitious and successful foreign policies of expansion, as well as his numerous bribes and gifts to various potentates. He had put Byzantium on the road of recovery, but his achievements were still perilously fragile, as events would soon show.
1623:— the fortress of Gallipoli was destroyed in 1354 by such an earthquake and the Ottoman Turks lost no time in taking it and establishing a bridgehead in Europe. Meanwhile, the Serbs continued pressing south, removing any nominal Imperial control in Epirus.
2612:
before returning to Byzantium, then as the Empire began to fail horribly, in more permanent manner. The Fall of Constantinople was marked by large numbers of Greek refugees escaping Turkic rule into Europe via Italy and thus accelerating the Renaissance.
2369:
Manuel II Palaiologos was 70 years of age in 1421 and believed that the time had come for him to retire and give his eldest son, John VIII, the opportunity to rule with a more aggressive manner than he had done so. At the same time, a far less restrained
2390:, the latter falling in 1430. Murad II was unable to take Constantinople by force. Nonetheless, the situation in the Capital was dire enough for Manuel II to come out of retirement and incite yet another rebellion in Asia Minor under Murad II's brother,
2181:
with his family and hostages. John V, only interested in securing his throne and stability, came to conclude a pact with Andronikos IV in 1381, recognizing him as heir with John VII as heir apparent, thus removing Manuel from the line of succession.
2382:
well and he gathered some support. However, in August 1422, Murad II had this rebellion crushed and Mustafa received the traditional execution (hanging) shortly after, something any rebel would have expected. Murad II was enraged and had an
1140:. Palaiologos was a leading noble of military standing and the main figure of the regency of John IV, who had used this role to propel himself to the throne, and set the stage for his becoming sole Emperor of the restored Byzantine Empire.
2788:
Such works, while being non-Christian and in many cases non-Hellenistic, were cultivated by the Greek Orthodox ecclesiastics. Both Choniades and Metochites established themselves in the Greek Orthodox Church; the former becoming Bishop of
1482:
Despite the calamities of the civil war, Andronikos III was about to revitalise the Empire. Although Asia Minor was at this point destined to fall to the Turks, it had been in a worse position in 1091 and yet still recovered by Byzantium.
1387:, was an able commander, campaigning with some success against the Turks in the Meander Valley. Unfortunately Byzantium was robbed of his services when he staged an unsuccessful coup, leading to his blinding. Next Andronikos sent his son,
2847:
Others went so far as to suggest that Byzantium would not live forever — a fundamental belief for every subject of the Byzantine Orthodox Church. Metochites did not see Byzantine civilization as superior to others and even considered the
2209:
John VII's rebellion succeeded initially, taking Constantinople from John V, but Manuel countered by rousing the rest of the empire and its few remaining military assets and turned them against John VII. Manuel also received aid from the
1656:, allegedly to protect John V's rule from Kalekas. Whether or not Kantakouzenos wished to be Emperor is not known, but the provocative actions of the Patriarch forced Kantakouzenos to fight to retain his power and started the civil war.
1519:
The rule of Andronikos III is characterized as the last genuine attempt to restore Byzantine fortunes. His attempts came close to fruition, but the many hostile neighbors of Byzantium eventually took their toll on an Empire in decline.
1478:
in 1321, the title of co-emperor in 1322, and after a small war where the Bulgarians and Serbians played the two sides against each other, Andronikos II was forced to abdicate and retire as a monk to a monastery, where he died in 1332.
2553:
succeeded his father Murad. Upon his succession to the throne, he received a demand by Constantine XI for subsidies, coupled with a threat to rebel if these were not met. Mehmed II responded with these bold declarations by building a
2360:
had emerged as the victor. However, the Byzantines had made sure to support the victor and Mehmed I did not forget the kindness of the Byzantines and was able to "control" his Turk subjects from expanding into Byzantine territory.
2864:
Philosophers had to find ways of bringing food to the table. The most common occupation in the Byzantine Empire would have either been agriculturally-based or, earlier in the Empire, trade-based. In contrast, philosophers needed
1313:
Michael VIII's foreign policy relied heavily on diplomacy; nevertheless, his construction projects and military campaigns against the remaining Latins were extensive as well as expensive; the Nicaean army was modeled around the
2394:. Initial rebel success, including a siege of Bursa was too much for Murad II to ignore so the siege of Constantinople was lifted to deal with this threat, and to the Byzantines' greatest despair, dealt with it successfully.
2774:, who acquainted themselves with this science. By the mid 14th century, when Byzantium was overwhelmed with troubles, the tables of Ptolemy were deemed by professionals as inadequate and slowly abandoned for Persian tables.
1523:
His first concern was that of Asia Minor. Nicaea, until 1261 the capital of the Empire, was under siege by Ottoman Turks. In the summer of 1329, Andronikos III launched a relief attempt which culminated in a defeat at the
1299:
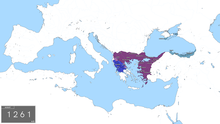
Middle East c. 1263 KEY: Lighter red - Byzantine Empire; Dark red and magenta - other Greek states; Light green - Turkic lands; Dark green - Ottoman domain by the 1300s, dotted line indicates conquests up to 1326; Yellow
2496:
to provide a basis for recovery, the Empire's position was becoming untenable. John was severely constrained by his circumstances, and proved unable to improve the fortunes of the state. He was succeeded by his brother
1688:
In 1353, Kantakouzenos was still hopeful that peace would be maintained, but in that year, John V launched a military attack on Matthew, thereby re-igniting the civil war. John V was demoted and exiled to the island of
1709:
sometime between 1361 and 1383, though other sources indicate 1391 a possible date. At 25 years, John V had managed to establish himself firmly as ruler of the Empire, at the cost of bleeding out all its resources.
1198:
and their successors, the Latin Empire, had done much to reduce Byzantium's finest city to an underpopulated wreck. Michael VIII began the task of restoring many monasteries, public buildings and defence works. The
1443:
Andronikos II's debasement of the Byzantine currency, along with his co-rule with his father, his son and his grandson as well as his own sole rule, resulted in the minting of several different coins during his
1284:. The downside however was that Michael's efforts in the West absorbed most of the Empire's manpower and resources, and neglected the Asian provinces, where a new and fateful threat was rising: the beylik of
2824:. His works on computational astronomy using Hebrew and Persian tables were overshadowed by the neo-pagan beliefs he adopted in his old age. He proclaimed his belief in the "Seven Wise Men", the message of
1704:
was his brother-in-law, he was able to obtain troops from him, but had barely begun his campaign when he was captured in the summer of 1356. He was forced to renounce his claims in 1357 and exiled to the
1532:
or the other few remaining forts in Asia Minor suffer the same fate, Andronikos III sought to pay off the Ottomans with tribute — the Ottomans did not stop at this and seized Nicomedia as well in 1337.
2304:
Manuel, who was still in Europe, arrived in 1403 to a welcoming sight — Constantinople free from Ottoman siege. John VII had remained loyal, handing back control of the capital to Manuel. In addition,
2708:. As the Empire's borders shrunk, so too had its cultural diversity. By the late 13th century, the Empire consisted almost exclusively of traditionally Greek territory (inhabited by Greeks since
1178:
had already been taken by Nicaea in 1246. Following the capture of Constantinople, Michael ordered the blinding of John IV in December 1261, so as to become sole emperor. As a result, Patriarch
2972:
to deal with the Empire's opponents. Her power base was consequently ruined. While the empire had experienced difficulties before (in the 8th century much of Byzantium's lands were occupied by
2960:, there were high hopes that the Turks would be driven out of Europe. The Byzantines that pinned their dreams of restoration on the West had hoped that they could reap the benefits of another "
1536:
Despite this, Andronikos III scored a few successes in the Aegean: in 1329, Chios was recovered, and in 1335, Andronikos arranged an alliance involving financial indemnities with the Turkic
1719:
of Anatolia, Greece, Macedonia and several large islands like Cyprus and Crete. Now the population under its control was limited to the few remaining cities in Byzantine possession, namely
3784:
1882:
666:
2353:. The importance of the latter should not be underestimated as these would serve in the future as refuge for any seeking to escape Ottoman expansion, even if only as a temporary refuge.
1786:
In 1371, the Serbs mustered their strength and prepared to launch an attack to drive back the Turks from Thrace. In a crushing victory, the Ottomans annihilated the Serbian army at the
2301:
Bayezid in 1402 near Ankara. The defeat caused a panic amongst the Turks in Anatolia, who frantically began crossing over to Europe, with the assistance of Venetian and Genoese ships.
2135:
919:
1746:
now had to face the serious threat the Ottomans posed to Byzantium. In the 1360s, the Turks continued to drive through Thrace, taking Byzantine, Bulgarian and Serbian settlements.
1035:
and a few other isolated exclaves, which only nominally recognized the Emperor as their lord. Nonetheless, Byzantine diplomacy, political intrigue and the invasion of Anatolia by
2917:
1770:, and her nephew (being John V's cousin) was concerned for the safety of his Greek counterpart. Sailing from Venice in June 1366 with dreams of initiating yet another Crusade,
1615:
landless peasants burdened by the demands of the government. Religious controversy, the cancer of Byzantium in the 7th and 8th centuries, once again emerged in the form of the
1570:(ruling Serbia from 1331) decided to take these lands as well from Byzantium. The death of Andronikos III and the resulting chaos left the Empire in no position to fight back.
4494:
1763:
had been largely beneficial and no doubt John V envisioned a repeat of such a Crusade. This time, however, the Papacy was unmoved by the calamity facing the Byzantine Empire.
2198:. Eventually, John VII did rebel against his grandfather — news of Manuel's arrival at Constantinople and John V's reconciliation talks with him prompted John VII to head to
2541:
before his ascension to the throne. From this position, he had continued the aggressive policies of his father and his brothers against the Ottomans and their vassals, the
1727:. The immigration of Turks would be decisive in the survival of the Empire as it gave her most dire enemy, the Ottomans, a new power base, not in Asia but now in Europe.
1610:
The Byzantine Empire entered into a new era of decay in 1341. The Empire was ravaged by multiple serious disasters — alongside wars and civil wars, renewed epidemics of
1562:
In Europe, Andronikos III had mixed results; Thessaly returned to Imperial rule in 1333, but Serbia once again began expanding southwards: led by the Byzantine renegade
1268:. The Greek Church was excommunicated, and Charles was given renewed papal support for the invasion of Constantinople. In order to counter this, Michael VIII subsidized
541:
2273:
The situation was dire; so much so that John VII, Manuel's dire opponent, was left in charge of Constantinople. He made one grand tour of Europe in 1399, stopping at
2270:, Bayezid force-marched his army to a stunning yet costly victory. Thousands were killed, but now Bayezid was able to turn his armies fully against Constantinople.
1232:
invasions in ca. 1240. As a result, the greatest threat to Byzantium was not the Muslims but their Christian counterparts in the West — Michael VIII knew that the
2374:, son of Mehmed I, came to the Ottoman throne in May of that year. With two men uninterested in diplomacy on the thrones of Byzantium and the Ottoman Sultanate,
981:
had begun conducting raids and expanding into Byzantine territory in Asia Minor by 1263, just two years after the enthronement of the first Palaiologos emperor
5647:
2738:', instead of Romans. This enthusiasm for the glorious past, contained elements that were also present in the movement that led to the creation of the modern
4727:
2882:, who between them had travelled to Florence, Pavia, Rome, Padua and Milan. The end of the Byzantine Empire coincided with the beginning of the Renaissance.
2771:
2185:
Naturally, Manuel felt betrayed by this move which demoted him from co-emperor. Returning to Thessalonica in 1382, he rebelled and established his rule over
2128:
912:
3670:
Raybaud, L. P. (1968) Le gouvernement et l’administration centrale de l’empire Byzantin sous les premiers Paléologues (1258-1354). Paris, pp. 202–206
2646:. New editions of poets, such as Hesiod and Pindar, were made and their metric systems were reconstructed with competence. They wrote about such works as
2580:
city against the odds, and his death in battle, through which he entered popular legend. Despite his Catholic confession, he is viewed as a saint by many
2148:
John V's rule was an unhappy one, resulting in his vassalage to Murad I. However, it must have been even worse when his eldest son and heir to the throne
5642:
1121:, a Turkic force was repelled and an earlier assault on Nicaea led to the death of the Seljuk Sultan. In the west, the Latins were unable to expand into
1778:
Nevertheless, in 1371 John V returned empty-handed, having humiliated himself and done nothing to improve the deteriorating situation in the Balkans.
3707:
2121:
905:
3633:
Bentley, Jerry H., and Herb F. Ziegler. Traditions & Encounters a Global Perspective on the Past. 3rd ed. Vol. 1. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2006.
2289:; in England, he was well received and treated to a jousting tournament. However, Manuel was unable to secure any help from Western Christendom.
5603:
3858:
3663:
1937:
1834:
721:
618:
5667:
5662:
5657:
5291:
3868:
3801:
1947:
1896:
731:
680:
3816:
3811:
2968:
were willing to pay it. In the long run though, the Byzantines were not prepared to surrender their ancient customs and beliefs willingly.
2705:
1911:
1906:
1449:
were possible, earning him greater popularity while seriously undermining Byzantium's abilities to deal with its opponents. He debased the
695:
690:
2312:
as a gesture of goodwill and in an effort to curry favour at a time the Ottoman Empire was weakened by the war with Timur and effectively
4892:
3878:
3853:
1957:
1932:
741:
716:
1619:
controversy, which eventually became a doctrine of the Eastern Orthodox church. There were numerous earthquakes, destroying Byzantium's
5243:
5226:
3883:
3863:
2416:
1962:
1942:
746:
726:
3189:
Shepherd, William R. "The Byzantine Empire in 1265." Perry–Castañeda Library. 1926. University of Texas Libraries. June 15, 2007. See
2266:. At first, the situation was not so dire — a massive counter-attack by the West was to be launched as the Crusade of Nicopolis. In a
4942:
4788:
4760:
4404:
4396:
3873:
3806:
1952:
1901:
736:
685:
3281:
Editors of Britannica, editor. "Andronicus III Palaeologus", Encyclopædia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, inc., June 11, 2018,
1697:
aid. Kantakouzenos now abdicated and retired to a monastery, where he would write his memoirs and thoughts until his death in 1383.
5138:
4499:
2484:
began launching successful campaigns against the Turks in Serbia, leading to the Serbian Despot and the Albanian resistance leader
1817:
601:
1074:
After 1204, the Byzantine Empire was partitioned into various successor states, with the Latin Empire in control of Constantinople
4987:
3636:
1427:
raiding cities in Thrace, leaving Asia Minor open to Turkish incursions. After this, Andronikos turned to diplomacy, asking the
1292:. Nevertheless, the border was kept relatively secure, and no significant losses occurred in Asia Minor during Michael's reign.
1212:
crippling taxes were placed on the peasantry. Nonetheless, the city grew new cultural and diplomatic contacts, notably with the
5467:
4992:
2488:
into direct opposition with their former masters. This led to one of the last great Crusades of a united Western Christendom —
2452:
Uniting the Church of Byzantium with that of Rome was a simple matter, since all the bargaining chips were in the hands of the
1179:
5672:
5391:
4151:
4144:
3700:
3507:
3190:
3014:
2079:
1700:
Matthew Kantakouzenos, no doubt disappointed with his father's failure, continued to resist John V. Since the Ottoman Sultan
863:
3680:
2297:, leader of the Timurid Empire, who saw Anatolia as within his sphere of influence. In response, Timur invaded Anatolia and
5143:
5002:
4290:
2464:
dispute arose from semantic confusion. Few on Byzantium's side were impressed with the Union between 1438 and 1439 held in
1807:
1642:
1632:
1183:
1023:
The loss of land in the East to the Turks and in the West to the Bulgarians coincided with two disastrous civil wars, the
4134:
2956:
The end of the Byzantine Empire did not seem inevitable to contemporaries. As late as 1444, a mere nine years before the
2712:). Consequently, this Greek culture soon came to dominate the Empire and the works of the Classical age such as those of
1359:
5472:
4885:
3123:
135:
2816:
Not all thinkers were welcome in Byzantium. Some who opened their minds to other beliefs would have strayed from the "
2412:
1090:, and Trebizond, with a multitude of Frankish and Latin possessions occupying the remainder, nominally subject to the
5573:
4139:
3559:
3535:
3029:
2943:
2480:
In the late 1440s, the Ottomans experienced difficulty in bringing their Christian vassals in the Balkans into line.
1162:
In 1261, while the bulk of the Latin Empire's military forces were absent from Constantinople, the Byzantine General
1055:
940:
dynasty in the period between 1261 and 1453, from the restoration of Byzantine rule to Constantinople by the usurper
2925:
1050:
However, the Palaiologan period witnessed a renewed flourishing in art and the letters, in what has been called the
4636:
3693:
103:
2727:
who characterized the interest in Science and Mathematics at the time. Astronomy was also a field of interest, as
1276:, a revolt that overthrew the Angevin King of Sicily and installed Peter III of Aragon as King of Sicily in 1281.
82:
5608:
5430:
3962:
3730:
3024:
2045:
1826:
829:
610:
5578:
5568:
5440:
5361:
5179:
5047:
4619:
4563:
4484:
4351:
3615:
2921:
2731:
illustrates with his proposal to modify the calendar before changes were put in place by the Gregorian reform.
2383:
1492:
Dissatisfaction from his failure, his old age and a "reckless grandson" culminated in his enforced abdication.
2152:
rebelled against his father in 1373. Curiously, this rebellion coincided with the rebellion of Murad I's son,
1680:
Byzantine coins showing John V and his co-emperor & guide Kantakouzenos during their peaceful co-existence
1213:
5435:
5425:
5340:
5095:
4880:
3009:
3004:
4315:
2241:
between Manuel II and Mehmed I. However, he lived long enough to see his son undo much of his achievements.
5652:
5509:
5477:
5381:
5090:
5062:
4870:
4409:
3019:
2387:
483:
88:
5233:
4875:
4722:
4479:
4230:
2999:
2994:
2734:
Moreover, some prominent personalities also proposed the change of the Imperial title to 'Emperor of the
1701:
1301:
1102:
was initially the strongest of the three Greek states, the Nicaeans succeeded in taking back the city of
999:
zeal, the prospect of economic gain, and the desire to seek refuge from the Mongols after the disastrous
3580:
John Joseph Saunders, The History of the Mongol Conquests, (University of Pennsylvania Press, 1971), 79.
2460:
head of the Byzantine Church ordered the Byzantine Church to accept Papal primacy and declared that the
1031:
which allowed the Turks to occupy the peninsula. By 1380, the Byzantine Empire consisted of the capital
5553:
5499:
5238:
5110:
5100:
4800:
4680:
4558:
4489:
4377:
4346:
4189:
4129:
1501:
458:
354:
299:
989:, which had formed the very heart of the shrinking empire, was systematically lost to numerous Turkic
5413:
4937:
4793:
4578:
4469:
4356:
3574:
Madden, Thomas F. Crusades the Illustrated History. 1st ed. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan P, 2005
2149:
2059:
1345:
1129:
against Bulgaria was a challenge that kept the Latins occupied for the duration of the Latin Empire.
843:
390:
330:
4712:
4464:
3951:
3830:
2906:
2170:
2026:
1916:
1157:
1137:
1118:
982:
941:
810:
700:
318:
186:
3282:
2341:
who was in Asia Minor, confirming Byzantium's freedom from paying tribute. The Empire also gained
5618:
5042:
4768:
4588:
4474:
2910:
2263:
2203:
2111:
1858:
1384:
1323:
1208:
1095:
1051:
1005:
1000:
895:
642:
5543:
5133:
4975:
4419:
4225:
4199:
4194:
3967:
3943:
3939:
3906:
2957:
2532:
2375:
2050:
2038:
2016:
1992:
1724:
1563:
1281:
1272:'s attempts to seize Sicily from Charles. Michael's efforts paid off with the outbreak of the
1163:
1040:
953:
834:
822:
800:
776:
500:
342:
247:
37:
3551:
2558:
on the European side of the Bosporus in order to better control traffic through the Bosporus.
5261:
5115:
4305:
4215:
4179:
4064:
3794:
3789:
2581:
2407:
2356:
Bayezid's sons lost no time fighting each other for their father's shattered realm. By 1413,
2227:
2158:
1890:
1886:
1350:
Andronikos II was the son of Michael VIII. He ascended the throne in 1282, at the age of 24.
1315:
674:
670:
446:
434:
378:
260:
243:
1431:
of Persia to send troops to attack the Turks, but negotiations for such an alliance failed.
1148:
5504:
5487:
5308:
5067:
5032:
4915:
4852:
4847:
4382:
4325:
2856:
as more enlightened in some aspects, such as morality, than his Christian co-religionists.
2631:
2338:
2309:
412:
3681:
Byzantine & Christian Museum, The Palaiologan period: The final flowering of Byzantium
1637:
John V, ten years old at his ascension, was guided by a regency consisting of his mother,
1358:
Andronikos II was tied down with events in the West and the East. The Serbians under King
8:
4414:
4330:
4320:
4184:
3947:
3935:
3822:
2973:
2837:
2801:
2782:
2758:'s tables for calculations. However, these proved to be inaccurate when compared to Arab
2728:
2709:
2677:
2635:
2538:
2333:
2313:
2286:
2267:
2211:
2021:
2012:
1525:
1269:
1264:
Unfortunately for Michael VIII, the new union was seen as a fake by Clement's successor,
1099:
1087:
1059:
1044:
1017:
805:
796:
182:
178:
109:
2704:
In the past, at its full height, the Byzantine Empire was composed of many territories,
1997:
1039:
allowed Byzantium to survive until 1453. The last remnants of the Byzantine Empire, the
781:
5492:
5482:
5356:
5027:
4910:
4827:
4690:
4042:
4022:
4002:
3992:
3758:
3657:
3604:
2879:
1771:
1755:
1743:
1245:
1233:
1094:
at Constantinople. In addition, the disintegration of the Byzantine Empire allowed the
366:
233:
223:
5614:
5548:
5453:
5386:
5366:
5334:
5266:
5253:
5174:
5169:
4920:
4685:
4535:
4054:
4007:
3997:
3987:
3611:
3555:
3531:
3503:
2875:
2817:
2767:
2262:
could endure a half-hearted blockade, it did not have the military assets to man the
2084:
1787:
1694:
1649:
1400:
1171:
868:
292:
265:
5418:
5211:
5159:
5105:
5072:
5022:
4815:
4805:
4583:
4271:
4163:
4086:
4069:
4047:
4032:
4017:
3931:
3716:
2643:
2567:
2489:
2298:
2007:
1273:
1225:
1133:
1098:, the Serbs, and the various Turcoman emirates of Anatolia to make gains. Although
1083:
933:
791:
546:
282:
1589:
1203:, looted in the Crusade of 1204, was refurbished to Greek Orthodox tradition. The
5563:
5396:
5376:
5371:
5326:
5316:
5276:
5271:
5221:
5216:
4997:
4603:
4520:
4515:
4255:
4245:
4081:
4075:
4059:
4037:
4027:
4012:
3641:
3624:
Parker, Geoffrey. Compact History of the World. 4th ed. London: Times Books, 2005
3495:
2693:
2639:
2625:
Classical literature that was studied included mythical figures such as Dionysus.
2621:
2584:, and many legends were created about the ultimate fate of the last Constantine.
2542:
2461:
2346:
1690:
1407:
1392:
1257:
212:
3577:
Mango, Cyril. The Oxford History of Byzantium. 1st ed. New York: Oxford UP, 2002
2555:
2169:
over to the Ottomans, thus rendering the only genuine European aid, provided by
5401:
5281:
5014:
4773:
4667:
4653:
4452:
4156:
3911:
2509:
2497:
2453:
2350:
2094:
2089:
1978:
1739:
Byzantium (in red) in 1369, after the Ottomans conquered the city of Adrianople
1620:
1611:
1195:
1114:
1110:
1103:
1079:
1032:
1009:
974:
961:
957:
949:
878:
873:
762:
573:
504:
199:
60:
1216:. Both had common enemies; Latin aggression, and later on, the Ottoman Turks.
5636:
5321:
5198:
5164:
4902:
4837:
4810:
4695:
4310:
4250:
3523:
3034:
2961:
2391:
2074:
1790:, and in its aftermath, many surviving lords submitted to the Ottoman Sultan
1767:
1760:
1638:
1567:
1415:
1253:
858:
238:
2836:
was burnt by the Patriarch of Constantinople. Plethon's ashes repose in the
5082:
5057:
5037:
4842:
4820:
4675:
3923:
3918:
3752:
2965:
2681:
2305:
1987:
1982:
1852:
1766:
Fortunately for John V, he had other European connections — his mother was
1720:
1653:
1241:
1204:
1200:
1175:
1091:
1013:
966:
945:
771:
766:
636:
560:
487:
3685:
3627:
Turnbull, Stephen. The Ottoman Empire 1326 – 1699. New York: Osprey, 2003.
2523:
2153:
1136:, a boy of 10 years. However, John IV was overshadowed by his co-emperor,
5583:
5558:
5052:
4862:
4629:
4235:
4220:
2751:
2598:
2342:
2232:
1511:
1295:
1024:
937:
269:
228:
3464:
The Crusades: Islam and Christianity in the Struggle for World Supremacy
2161:, the second son of John V, was made co-emperor and heir to the throne.
1602:
1439:
1082:, the Byzantine Empire had fractured into the Greek successor-states of
156:
4857:
4717:
4707:
4540:
4530:
4240:
2717:
2668:
2485:
2431:
2324:
1798:
from the defeated Serbs, John V swore allegiance as a vassal to Murad.
1582:
The Byzantine Empire in 1340 a year before the death of Andronikos III.
1451:
1411:
1388:
978:
3594:
Midway Through the Plunge: John Cantacuzenus and the Fall of Byzantium
2796:
2349:. As an added bonus, Imperial authority was asserted over a number of
2157:
blinded, while Murad I defeated his son, Savci, and had him executed.
5406:
5286:
4778:
4646:
4593:
4525:
2866:
2825:
2820:", as the Byzantines would have seen it. One such example is that of
2778:
2759:
2713:
2659:
2655:
2550:
2420:
2250:
2166:
1877:
1671:
1616:
1529:
1428:
1419:
1396:
1265:
1028:
661:
128:
44:
2895:
4932:
4832:
4783:
4641:
4573:
4361:
2829:
2735:
2724:
2685:
2673:
2546:
2469:
2425:
2371:
2357:
2186:
1548:
1540:
1475:
1376:
1122:
986:
3637:
Historical Dynamics in a Time of Crisis: Late Byzantium, 1204–1453
3630:
Haldon, John. Byzantium at War 600 – 1453. New York: Osprey, 2000.
1735:
1676:
1665:
5298:
5184:
5125:
4624:
4598:
4276:
2977:
Byzantium's armies became increasingly obsolete and outnumbered.
2849:
2821:
2763:
2755:
2647:
2481:
2465:
2236:
Byzantium in 1389. Thrace was lost in the previous three decades.
1791:
1556:
1457:
1285:
996:
277:
166:
146:
1597:
1379:
as a "dowry". Nonetheless, the Serbs continued their expansion.
1372:
4927:
4702:
4568:
3283:
https://www.britannica.com/biography/Andronicus-III-Palaeologus
2853:
2841:
2805:
2790:
2739:
2689:
2651:
2609:
2274:
2215:
2195:
2178:
1795:
1552:
1471:
1422:, these hardy mercenaries were used to skirmishing against the
1363:
1249:
1237:
1229:
1167:
1126:
1070:
2249:
Manuel II's first priority was to establish an agreement with
1578:
995:, whose raids evolved into conquering expeditions inspired by
3650:
The Byzantine provincial administration under the Palaiologoi
2809:
2605:
2563:
2500:. The new emperor would be Byzantium's last sovereign ruler.
2294:
2282:
2278:
2199:
2174:
1706:
1641:, John VI Kantakouzenos and the Patriarch of Constantinople (
1423:
1368:
1289:
1036:
991:
218:
122:
29:
2439:
Manuel II's final years saw his gains wasted and the Empire
1723:
and Constantinople and the surrounding countryside, and the
5206:
2785:
published his thoughts using Persian and Ptolemaic tables.
2592:
2423:(1438). The legend reads, in Greek: "John the Palaiologos,
2256:
1537:
1528:
on June 10, and in 1331, the city fell. Not wishing to see
1182:
excommunicated Michael, but he was deposed and replaced by
1838:
Territorial development of the Byzantine Empire (330–1453)
622:
Territorial development of the Byzantine Empire (330–1453)
2345:
and coastal land of the Black Sea from Constantinople to
1801:
1661:
1544:
2676:
and the Greek Anthology of epigrams. Works assembled by
1166:
used the opportunity to seize the city with 600 troops.
1113:
was successful in holding its own against its Latin and
973:
From the start, the regime faced numerous problems. The
2832:. Consequently, his work on a modified Greek Pantheon,
1794:. Byzantium was in no better position and after taking
1339:
2874:
flee to the West. Remarkable travels were recorded by
2781:
were translated into Greek as early as 1309. In 1352,
2742:
state, in 1830, after four centuries of Ottoman rule.
1143:
2745:
1515:
Byzantium at the beginning of Andronikos III's reign.
1455:
currency and heavily taxed the military elite of the
970:, this period is known as the late Byzantine Empire.
3644:, Great Ages of Man Byzantium, Time-Life Books, 1975
3177:
Battle a Visual Journey Through 5000 Years of Combat
3056:
2793:and the latter the head of the Patriarchal school.
2706:
stretching from modern-day Iraq to modern-day Spain
2221:
1244:in Constantinople. The situation became worse when
1240:would no doubt launch another attempt to establish
3603:
3484:(2nd ed.). London: Penguin. pp. 365–371.
3466:(2nd ed.). London: Robinson. pp. 234–35.
1672:Reign and fall of John VI Kantakouzenos, 1347–1357
1406:Not giving up, Andronikos hired the 6,500 strong "
3552:History of the Byzantine Empire, 324-1453, Vol. 2
2654:. Countless works are also included, such as the
2587:
2527:Constantine XI depicted in semi-classical armour.
1759:Crusaders would sack both friend and foe but the
1261:papal support for an invasion of Constantinople.
5634:
1189:
3601:
2800:Plethon's final resting place was moved to the
2518:
2444:Ottomans, soon-to-be Christendom's direst foe.
2319:
4076:Spain (Iberian Peninsula and Balearic Islands)
3502:. Cambridge University Press. pp. 79–80.
3488:
2616:
1781:
1228:was in chaos and decentralized ever since the
5648:States and territories disestablished in 1453
3701:
2777:Despite this, Persian works such as those on
2285:, Paris and London, where he met the English
2129:
1626:
1598:The rise and fall of Kantakouzenos, 1341–1357
1395:to attack the Turks who were laying siege to
913:
16:Period of Byzantine history from 1261 to 1453
3610:. New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art.
2364:
1495:
3715:
3448:
3446:
3427:
3425:
3423:
3421:
3411:
3409:
3407:
3405:
3395:
3393:
3391:
3389:
3387:
3377:
3375:
3373:
3371:
3361:
3359:
3357:
3355:
3353:
3351:
3349:
3347:
3337:
3335:
3333:
3323:
3321:
3319:
3300:
3298:
3296:
3294:
3292:
3290:
3268:
3266:
3264:
3262:
3260:
3258:
3256:
3246:
3244:
3242:
3240:
3238:
3236:
3234:
3224:
3222:
3220:
3218:
3208:
3206:
3204:
3202:
3200:
3198:
3109:
3107:
3083:
2924:. Unsourced material may be challenged and
1464:
1132:In 1261, the Empire of Nicaea was ruled by
52:
5643:States and territories established in 1261
3708:
3694:
3662:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
3647:
3590:
3516:
3152:
3150:
3148:
3146:
3144:
3134:
3132:
3097:
3095:
3076:
3074:
3072:
3070:
3068:
2870:although only bishops had such resources.
2417:Medal of the Emperor John VIII Palaiologos
2136:
2122:
920:
906:
165:
155:
145:
3528:Constantinople 1453: The end of Byzantium
3179:. London: Dorling Kindersley. p. 93.
3159:
2944:Learn how and when to remove this message
2206:, to seek aid in order to topple John V.
130:Basileus Basileōn, Basileuōn Basileuontōn
124:Βασιλεὺς Βασιλέων, Βασιλεύων Βασιλευόντων
3494:
3443:
3418:
3402:
3384:
3368:
3344:
3330:
3316:
3307:
3287:
3253:
3231:
3215:
3195:
3104:
2795:
2720:were meticulously copied and annotated.
2620:
2593:Second Byzantine/Palaiologan Renaissance
2522:
2411:
2323:
2257:Rebellion; Byzantium survives, 1394–1402
2231:
1734:
1675:
1601:
1577:
1510:
1438:
1362:had begun invading the Balkans and took
1294:
1147:
1069:
150:
4964:
3522:
3461:
3168:
3141:
3129:
3092:
3065:
3047:
2401:
1327:a result of his policies towards Rome.
5635:
3606:Byzantium: faith and power (1261–1557)
3479:
2545:, but had been forced to back down by
1802:Third Palaiologan Civil War, 1373–1379
1713:
1648:The Patriarch, aided by the ambitious
5532:
4963:
4748:
4440:
4107:
3728:
3689:
3475:
3473:
3174:
3015:Byzantium under the Justinian Dynasty
2308:was handed back to the Byzantines by
1058:to the West also helped to spark the
5668:15th century in the Byzantine Empire
5663:14th century in the Byzantine Empire
5658:13th century in the Byzantine Empire
4749:
2922:adding citations to reliable sources
2889:
2244:
2202:and then to the new Ottoman Sultan,
1730:
1340:Andronikos II Palaiologos, 1282–1328
4451:
2562:number of "super-cannons" built by
1749:
1506:
1353:
1308:
1144:Michael VIII Palaiologos, 1261–1282
13:
3584:
3550:Aleksandr Aleksandrovich Vasiliev
3470:
2746:Persian science enters, circa 1300
2699:
2447:
2328:Manuel II lived to 75 years of age
1833:
1434:
617:
14:
5684:
5574:Greek scholars in the Renaissance
3674:
3554:. Univ of Wisconsin Press, 1952,
3530:. Osprey Publishing. p. 13.
3030:Family tree of Byzantine emperors
2684:can be found in the libraries of
2503:
2419:during his visit to Florence, by
1606:Byzantine Empire in the year 1350
1219:
944:following its recapture from the
5613:
3500:The Fall of Constantinople, 1453
3122:Lowe, Steven, and Martin Baker.
2894:
2222:Manuel II Palaiologos, 1391–1420
2105:
1808:Byzantine civil war of 1373–1379
1633:Byzantine civil war of 1341–1347
889:
578:
553:
539:
136:King of Kings, Ruling Over Kings
102:
81:
3963:Decline of the Byzantine Empire
3785:Constantinian–Valentinianic era
3544:
3482:Byzantium: The Decline and Fall
3455:
3434:
3275:
3183:
3037:dynasty and related family tree
3025:Byzantium under the Macedonians
2885:
2672:, edits and "rediscoveries" on
2046:Decline of the Byzantine Empire
1883:Constantinian–Valentinianic era
1827:History of the Byzantine Empire
1056:migration of Byzantine scholars
830:Decline of the Byzantine Empire
667:Constantinian–Valentinianic era
611:History of the Byzantine Empire
5048:Great Palace of Constantinople
4789:Patriarchate of Constantinople
4108:
3116:
2588:Learning under the Palaiologoi
1399:, but they were beaten at the
1004:commonly, these comprised the
960:. Together with the preceding
1:
3568:
3010:Byzantium under the Isaurians
3005:Byzantium under the Heraclian
2723:Notable philosophers include
2574:
1190:Restoration of Constantinople
1065:
1027:, and the 1354 earthquake at
90:
5673:Fall of the Byzantine Empire
5510:University of Constantinople
5091:Arch of Galerius and Rotunda
4441:
4241:Chartoularios tou vestiariou
3930:Byzantine successor states (
3480:Norwich, John Julius (199).
3062:John Joseph Saunders, pp. 79
3020:Byzantium under the Komnenoi
2859:
2519:Defiance, defence and defeat
2320:Ottoman Interregnum, 1402–13
484:Reconquest of Constantinople
129:
45:
7:
5180:Saint Catherine's Monastery
4236:Chartoularios tou sakelliou
4231:Logothetes tou stratiotikou
3729:
3000:Byzantium under the Doukids
2995:Byzantium under the Angeloi
2988:
2617:Restoration of the Classics
2486:George Kastrioti Skanderbeg
2384:army sent to Constantinople
2112:Byzantine Empire portal
2004:Byzantine successor states
1782:Ottoman vassalage of John V
1573:
1486:
1288:, who by 1263 had captured
1047:, fell shortly afterwards.
896:Byzantine Empire portal
788:Byzantine successor states
10:
5689:
5569:Neo-Byzantine architecture
5533:
4190:Comes sacrarum largitionum
3462:Hindley, Geoffrey (2004).
2596:
2530:
2515:fight for Constantinople.
2507:
2405:
2225:
1805:
1630:
1627:The civil war of 1341–1347
1551:, and was able to recover
1502:Andronikos III Palaiologos
1499:
1343:
1155:
1152:Hyperpyron of Michael VIII
123:
30:
5596:
5539:
5528:
5449:
5349:
5307:
5252:
5197:
5152:
5139:Sant'Apollinare in Classe
5124:
5081:
5013:
4983:
4974:
4970:
4959:
4901:
4759:
4755:
4744:
4666:
4612:
4551:
4508:
4460:
4447:
4436:
4395:
4370:
4339:
4298:
4289:
4264:
4208:
4172:
4125:
4118:
4114:
4103:
3976:
3892:
3839:
3770:
3741:
3737:
3724:
3126:21 Feb. 1992. 29 May 2007
2812:by his Italian disciples.
2365:Resumption of hostilities
2150:Andronikos IV Palaiologos
1496:Andronikos III, 1328–1341
1346:Andronikos II Palaiologos
1330:
518:
514:
497:
480:
476:
468:
464:
452:
440:
428:
418:
406:
396:
384:
372:
360:
348:
336:
324:
312:
308:
298:
288:
276:
256:
205:
195:
142:
118:
77:
72:
21:
4713:Droungarios of the Fleet
3602:Evans, Helen C. (2004).
3041:
2666:, Nonnus of Panaopolis'
2475:
2456:West. John VIII, as the
1925:Middle period (717–1204)
1465:Civil War and abdication
1158:Michael VIII Palaiologos
1138:Michael VIII Palaiologos
1119:Battle of Meander Valley
1052:Palaiologian Renaissance
942:Michael VIII Palaiologos
709:Middle period (717–1204)
187:Principality of Theodoro
171:Byzantine Empire in 1453
161:Byzantine Empire in 1341
151:Byzantine Empire in 1261
5227:Early Byzantine mosaics
4589:Domestic of the Schools
3648:Maksimović, L. (1988).
2656:tragedians of Sophocles
2537:Constantine XI was the
2264:walls of Constantinople
2204:Bayezid the Thunderbolt
1971:Late period (1204–1453)
1385:Alexios Philanthropenos
1324:Second Council of Lyons
1304:; Purple - Latin states
1209:walls of Constantinople
1106:from the Latin Empire.
1006:Second Bulgarian Empire
755:Late period (1204–1453)
5544:Byzantine commonwealth
4306:Praetorian prefectures
4226:Logothetes tou genikou
4200:Quaestor sacri palatii
4195:Comes rerum privatarum
3968:Fall of Constantinople
3907:Sack of Constantinople
2958:Fall of Constantinople
2813:
2626:
2533:Fall of Constantinople
2528:
2436:
2334:defeat of the Ottomans
2329:
2237:
2051:Fall of Constantinople
2039:Despotate of the Morea
1993:Principality of Achaea
1870:Early period (330–717)
1839:
1754:Like his predecessors
1740:
1725:Despotate of the Morea
1681:
1607:
1583:
1564:Syrgiannes Palaiologos
1516:
1445:
1360:Stefan Uroš II Milutin
1305:
1282:Despotate of the Morea
1164:Alexios Strategopoulos
1153:
1075:
1041:Despotate of the Morea
1012:, the remnants of the
954:Fall of Constantinople
835:Fall of Constantinople
823:Despotate of the Morea
777:Principality of Achaea
654:Early period (330–717)
623:
501:Fall of Constantinople
248:South Slavic languages
185:in light blue and the
53:
5244:Komnenian renaissance
5239:Macedonian period art
5144:Sant'Apollinare Nuovo
5116:Walls of Thessaloniki
4216:Logothetes tou dromou
3831:Twenty Years' Anarchy
3795:Valentinianic dynasty
3790:Constantinian dynasty
2799:
2624:
2597:Further information:
2526:
2508:Further information:
2415:
2408:John VIII Palaiologos
2406:Further information:
2327:
2235:
2228:Manuel II Palaiologos
2226:Further information:
1917:Twenty Years' Anarchy
1891:Valentinianic dynasty
1887:Constantinian dynasty
1837:
1738:
1679:
1605:
1581:
1514:
1442:
1391:, and the Heteriarch
1298:
1151:
1073:
964:and the contemporary
701:Twenty Years' Anarchy
675:Valentinianic dynasty
671:Constantinian dynasty
621:
244:Old Anatolian Turkish
206:Common languages
5441:Units of measurement
5175:Panagia Gorgoepikoos
5068:Pammakaristos Church
4916:Corpus Juris Civilis
4867:Missionary activity
4326:Exarchate of Ravenna
4152:Imperial bureaucracy
3597:. Byzantine Emporia.
3175:Grant, R.G. (2005).
2918:improve this section
2766:. Such men included
2680:at the Monastery of
2632:Demetrius Triclinius
2402:John VIII takes over
948:, founded after the
5653:Palaiologos dynasty
4965:Culture and society
4828:Ecumenical councils
4331:Exarchate of Africa
4321:Quaestura exercitus
4185:Magister officiorum
4180:Praetorian prefects
3823:Byzantine Dark Ages
3591:Duval, Ben (2019).
3089:Madden, pp. 110–113
2838:Tempio Malatestiano
2802:Tempio Malatestiano
2783:Theodore Metochites
2772:George Chrysokokkes
2729:Nicephorus Gregoras
2678:Theodore Metochites
2636:Manuel Moschopoulos
2539:Despot of the Morea
2212:Knights of St. John
2194:Manuel in exile in
1714:Turkish immigration
1526:Battle of Pelekanon
1418:. Originating from
1270:Peter III of Aragon
1060:Italian Renaissance
1045:Empire of Trebizond
1018:Knights Hospitaller
183:Empire of Trebizond
179:Despotate of Epirus
5382:Flags and insignia
5028:Baths of Zeuxippus
4911:Codex Theodosianus
4801:Oriental Orthodoxy
3759:Later Roman Empire
2985:impossible cause.
2880:Manuel Chrysoloras
2814:
2627:
2529:
2437:
2330:
2238:
1840:
1772:Amadeo VI of Savoy
1756:Alexios I Komnenos
1744:John V Palaiologos
1741:
1682:
1608:
1584:
1517:
1446:
1306:
1256:in 1266. In 1267,
1246:Charles I of Anjou
1154:
1117:opponents. At the
1076:
1001:Battle of Köse Dağ
952:(1204), up to the
624:
181:in dark blue, the
5630:
5629:
5592:
5591:
5549:Byzantine studies
5524:
5523:
5520:
5519:
5335:Alexander Romance
5193:
5192:
5170:Nea Moni of Chios
5033:Blachernae Palace
4955:
4954:
4951:
4950:
4921:Code of Justinian
4769:Eastern Orthodoxy
4740:
4739:
4736:
4735:
4662:
4661:
4536:Scholae Palatinae
4432:
4431:
4428:
4427:
4397:Foreign relations
4391:
4390:
4285:
4284:
4099:
4098:
4095:
4094:
3898:(1204–1453)
3509:978-0-521-39832-9
3124:"Seljuks of Rum".
2954:
2953:
2946:
2876:John Argyropoulos
2818:one true Religion
2770:and his follower
2768:Gregory Choniades
2245:Vassalage to 1394
2146:
2145:
1788:Battle of Maritsa
1731:John V, 1354–1391
1650:Alexios Apokaukos
1559:from the Latins.
1401:Battle of Bapheus
936:was ruled by the
930:
929:
594:
593:
590:
589:
586:
585:
566:
565:
454:• 1448–1453
442:• 1425–1448
430:• 1391–1425
420:• 1390–1391
398:• 1379–1390
386:• 1376–1379
374:• 1347–1354
362:• 1341–1376
350:• 1328–1341
338:• 1295–1320
326:• 1282–1328
314:• 1261–1282
293:Absolute monarchy
266:Roman Catholicism
263:(Predominantly),
190:
46:Basileía Rhōmaíōn
5680:
5617:
5530:
5529:
5473:Imperial Library
5419:Byzantine Greeks
5160:Daphni Monastery
5111:Panagia Chalkeon
5106:Hagios Demetrios
5073:Prison of Anemas
5023:Basilica Cistern
4981:
4980:
4972:
4971:
4961:
4960:
4816:West Syriac Rite
4806:Alexandrian Rite
4757:
4756:
4750:Religion and law
4746:
4745:
4681:Maritime themata
4637:Palaiologan army
4490:Military manuals
4458:
4457:
4449:
4448:
4438:
4437:
4296:
4295:
4272:Megas logothetes
4123:
4122:
4116:
4115:
4105:
4104:
3978:By modern region
3899:
3846:
3845:(717–1204)
3777:
3739:
3738:
3726:
3725:
3717:Byzantine Empire
3710:
3703:
3696:
3687:
3686:
3667:
3661:
3653:
3621:
3609:
3598:
3563:
3548:
3542:
3541:
3520:
3514:
3513:
3496:Runciman, Steven
3492:
3486:
3485:
3477:
3468:
3467:
3459:
3453:
3450:
3441:
3438:
3432:
3429:
3416:
3413:
3400:
3397:
3382:
3379:
3366:
3363:
3342:
3339:
3328:
3325:
3314:
3311:
3305:
3302:
3285:
3279:
3273:
3270:
3251:
3248:
3229:
3226:
3213:
3210:
3193:
3187:
3181:
3180:
3172:
3166:
3163:
3157:
3154:
3139:
3136:
3127:
3120:
3114:
3111:
3102:
3099:
3090:
3087:
3081:
3078:
3063:
3060:
3054:
3051:
2949:
2942:
2938:
2935:
2929:
2898:
2890:
2696:and even Paris.
2644:Maximos Planudes
2490:Crusade of Varna
2378:was inevitable.
2138:
2131:
2124:
2110:
2109:
2108:
1812:
1811:
1750:Plea to the West
1643:John XIV Kalekas
1274:Sicilian Vespers
1226:Sultanate of Rum
1207:harbour and the
1134:John IV Laskaris
1125:; consolidating
934:Byzantine Empire
922:
915:
908:
894:
893:
892:
596:
595:
582:
581:
570:
569:
557:
556:
547:Empire of Nicaea
543:
542:
536:
535:
520:
519:
176:
172:
169:
162:
159:
152:
149:
132:
126:
125:
106:
95:
92:
85:
64:
56:
54:Imperium Romanum
49:
48:
41:
33:
32:
31:Βασιλεία Ῥωμαίων
23:Byzantine Empire
19:
18:
5688:
5687:
5683:
5682:
5681:
5679:
5678:
5677:
5633:
5632:
5631:
5626:
5623:
5588:
5564:Cyrillic script
5535:
5516:
5461:
5445:
5345:
5327:Digenes Akritas
5303:
5248:
5189:
5153:Other locations
5148:
5120:
5077:
5009:
4998:Cross-in-square
4966:
4947:
4897:
4751:
4732:
4658:
4608:
4604:Varangian Guard
4547:
4521:East Roman army
4516:Late Roman army
4504:
4443:
4424:
4387:
4366:
4335:
4281:
4260:
4256:Epi ton deeseon
4246:Epi tou eidikou
4204:
4168:
4110:
4091:
4078:
3981:
3979:
3972:
3958:Palaiologan era
3900:
3897:
3888:
3859:Nikephorian era
3847:
3844:
3835:
3778:
3776:(330–717)
3775:
3766:
3746:
3733:
3720:
3714:
3677:
3655:
3654:
3642:Philip Sherrard
3618:
3587:
3585:Further reading
3571:
3566:
3549:
3545:
3538:
3521:
3517:
3510:
3493:
3489:
3478:
3471:
3460:
3456:
3451:
3444:
3439:
3435:
3430:
3419:
3414:
3403:
3398:
3385:
3380:
3369:
3364:
3345:
3340:
3331:
3326:
3317:
3312:
3308:
3303:
3288:
3280:
3276:
3271:
3254:
3249:
3232:
3227:
3216:
3211:
3196:
3188:
3184:
3173:
3169:
3164:
3160:
3155:
3142:
3137:
3130:
3121:
3117:
3112:
3105:
3100:
3093:
3088:
3084:
3079:
3066:
3061:
3057:
3052:
3048:
3044:
2991:
2950:
2939:
2933:
2930:
2915:
2899:
2888:
2862:
2754:had to rely on
2748:
2702:
2700:Greek Byzantium
2640:Thomas Magister
2619:
2601:
2595:
2590:
2577:
2543:Duchy of Athens
2535:
2521:
2512:
2506:
2478:
2450:
2448:Union with Rome
2441:status quo ante
2435:of the Romans".
2410:
2404:
2388:to Thessalonika
2367:
2322:
2310:Prince Suleyman
2259:
2247:
2230:
2224:
2142:
2106:
2104:
2099:
2034:Palaiologan era
1938:Nikephorian era
1821:
1810:
1804:
1784:
1752:
1733:
1716:
1674:
1635:
1629:
1600:
1576:
1509:
1504:
1498:
1489:
1467:
1437:
1435:Domestic policy
1408:Catalan Company
1393:George Mouzalon
1356:
1348:
1342:
1333:
1311:
1258:Pope Clement IV
1222:
1192:
1160:
1146:
1068:
926:
890:
888:
883:
818:Palaiologan era
722:Nikephorian era
605:
579:
554:
540:
507:
490:
455:
443:
431:
421:
409:
399:
387:
375:
363:
351:
339:
327:
315:
283:Byzantine Greek
264:
261:Greek Orthodoxy
252:
191:
174:
173:
170:
163:
160:
153:
133:
127:
114:
113:
112:
110:Byzantine eagle
107:
99:
98:
93:
86:
68:
67:
58:
43:
42:
35:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
5686:
5676:
5675:
5670:
5665:
5660:
5655:
5650:
5645:
5628:
5627:
5625:
5624:
5622:
5621:
5611:
5606:
5600:
5597:
5594:
5593:
5590:
5589:
5587:
5586:
5581:
5576:
5571:
5566:
5561:
5556:
5551:
5546:
5540:
5537:
5536:
5526:
5525:
5522:
5521:
5518:
5517:
5515:
5514:
5513:
5512:
5502:
5497:
5496:
5495:
5485:
5480:
5475:
5470:
5464:
5462:
5460:
5459:
5456:
5450:
5447:
5446:
5444:
5443:
5438:
5433:
5428:
5423:
5422:
5421:
5411:
5410:
5409:
5404:
5394:
5389:
5384:
5379:
5374:
5369:
5364:
5359:
5353:
5351:
5347:
5346:
5344:
5343:
5338:
5331:
5330:
5329:
5319:
5313:
5311:
5305:
5304:
5302:
5301:
5296:
5295:
5294:
5289:
5284:
5274:
5269:
5264:
5258:
5256:
5250:
5249:
5247:
5246:
5241:
5236:
5231:
5230:
5229:
5219:
5214:
5209:
5203:
5201:
5195:
5194:
5191:
5190:
5188:
5187:
5182:
5177:
5172:
5167:
5162:
5156:
5154:
5150:
5149:
5147:
5146:
5141:
5136:
5130:
5128:
5122:
5121:
5119:
5118:
5113:
5108:
5103:
5098:
5096:Byzantine Bath
5093:
5087:
5085:
5079:
5078:
5076:
5075:
5070:
5065:
5060:
5055:
5050:
5045:
5040:
5035:
5030:
5025:
5019:
5017:
5015:Constantinople
5011:
5010:
5008:
5007:
5006:
5005:
5000:
4990:
4984:
4978:
4968:
4967:
4957:
4956:
4953:
4952:
4949:
4948:
4946:
4945:
4940:
4935:
4930:
4925:
4924:
4923:
4913:
4907:
4905:
4899:
4898:
4896:
4895:
4890:
4889:
4888:
4883:
4878:
4873:
4865:
4860:
4855:
4850:
4845:
4840:
4835:
4830:
4825:
4824:
4823:
4818:
4813:
4808:
4798:
4797:
4796:
4791:
4786:
4781:
4776:
4774:Byzantine Rite
4765:
4763:
4753:
4752:
4742:
4741:
4738:
4737:
4734:
4733:
4731:
4730:
4725:
4720:
4715:
4710:
4705:
4700:
4699:
4698:
4693:
4688:
4678:
4672:
4670:
4664:
4663:
4660:
4659:
4657:
4656:
4654:Grand domestic
4651:
4650:
4649:
4644:
4634:
4633:
4632:
4627:
4620:Komnenian army
4616:
4614:
4610:
4609:
4607:
4606:
4601:
4596:
4591:
4586:
4581:
4576:
4571:
4566:
4561:
4555:
4553:
4549:
4548:
4546:
4545:
4544:
4543:
4538:
4533:
4528:
4518:
4512:
4510:
4506:
4505:
4503:
4502:
4497:
4495:Military units
4492:
4487:
4482:
4477:
4472:
4467:
4465:Battle tactics
4461:
4455:
4445:
4444:
4434:
4433:
4430:
4429:
4426:
4425:
4423:
4422:
4417:
4412:
4407:
4401:
4399:
4393:
4392:
4389:
4388:
4386:
4385:
4380:
4374:
4372:
4368:
4367:
4365:
4364:
4359:
4354:
4349:
4343:
4341:
4337:
4336:
4334:
4333:
4328:
4323:
4318:
4313:
4308:
4302:
4300:
4293:
4287:
4286:
4283:
4282:
4280:
4279:
4274:
4268:
4266:
4262:
4261:
4259:
4258:
4253:
4248:
4243:
4238:
4233:
4228:
4223:
4218:
4212:
4210:
4206:
4205:
4203:
4202:
4197:
4192:
4187:
4182:
4176:
4174:
4170:
4169:
4167:
4166:
4161:
4160:
4159:
4157:Medieval Greek
4149:
4148:
4147:
4142:
4137:
4126:
4120:
4112:
4111:
4101:
4100:
4097:
4096:
4093:
4092:
4090:
4089:
4084:
4079:
4074:
4072:
4067:
4062:
4057:
4052:
4051:
4050:
4045:
4035:
4030:
4025:
4020:
4015:
4010:
4005:
4000:
3995:
3990:
3984:
3982:
3977:
3974:
3973:
3971:
3970:
3965:
3960:
3955:
3928:
3927:
3926:
3916:
3915:
3914:
3912:Fourth Crusade
3903:
3901:
3893:
3890:
3889:
3887:
3886:
3881:
3876:
3871:
3869:Macedonian era
3866:
3861:
3856:
3850:
3848:
3840:
3837:
3836:
3834:
3833:
3828:
3827:
3826:
3814:
3809:
3804:
3802:Theodosian era
3799:
3798:
3797:
3792:
3781:
3779:
3771:
3768:
3767:
3765:
3764:
3763:
3762:
3749:
3747:
3742:
3735:
3734:
3722:
3721:
3713:
3712:
3705:
3698:
3690:
3684:
3683:
3676:
3675:External links
3673:
3672:
3671:
3668:
3645:
3639:
3634:
3631:
3628:
3625:
3622:
3616:
3599:
3586:
3583:
3582:
3581:
3578:
3575:
3570:
3567:
3565:
3564:
3543:
3536:
3524:Nicolle, David
3515:
3508:
3487:
3469:
3454:
3442:
3433:
3417:
3401:
3383:
3367:
3343:
3329:
3315:
3306:
3286:
3274:
3252:
3230:
3214:
3194:
3182:
3167:
3165:Madden, p. 162
3158:
3140:
3128:
3115:
3113:Madden, p. 179
3103:
3091:
3082:
3064:
3055:
3045:
3043:
3040:
3039:
3038:
3032:
3027:
3022:
3017:
3012:
3007:
3002:
2997:
2990:
2987:
2952:
2951:
2902:
2900:
2893:
2887:
2884:
2861:
2858:
2747:
2744:
2701:
2698:
2618:
2615:
2594:
2591:
2589:
2586:
2576:
2573:
2531:Main article:
2520:
2517:
2510:Constantine XI
2505:
2504:Constantine XI
2502:
2498:Constantine XI
2477:
2474:
2454:Roman Catholic
2449:
2446:
2403:
2400:
2366:
2363:
2351:Aegean Islands
2321:
2318:
2268:titanic battle
2258:
2255:
2246:
2243:
2223:
2220:
2144:
2143:
2141:
2140:
2133:
2126:
2118:
2115:
2114:
2101:
2100:
2098:
2097:
2092:
2087:
2082:
2077:
2071:
2068:
2067:
2063:
2062:
2056:
2055:
2054:
2053:
2048:
2043:
2042:
2041:
2031:
2030:
2029:
2024:
2019:
2010:
2002:
2001:
2000:
1995:
1990:
1979:Fourth Crusade
1973:
1972:
1968:
1967:
1966:
1965:
1960:
1955:
1950:
1948:Macedonian era
1945:
1940:
1935:
1927:
1926:
1922:
1921:
1920:
1919:
1914:
1909:
1904:
1899:
1897:Theodosian era
1894:
1880:
1872:
1871:
1867:
1866:
1865:
1864:
1863:
1862:
1847:
1846:
1842:
1841:
1830:
1829:
1823:
1822:
1815:
1806:Main article:
1803:
1800:
1783:
1780:
1751:
1748:
1732:
1729:
1715:
1712:
1673:
1670:
1631:Main article:
1628:
1625:
1621:infrastructure
1612:bubonic plague
1599:
1596:
1575:
1572:
1541:Bahud-din Umur
1508:
1507:Foreign policy
1505:
1500:Main article:
1497:
1494:
1488:
1485:
1466:
1463:
1436:
1433:
1355:
1354:Foreign policy
1352:
1344:Main article:
1341:
1338:
1332:
1329:
1310:
1309:Foreign policy
1307:
1221:
1220:Foreign policy
1218:
1196:Fourth Crusade
1191:
1188:
1156:Main article:
1145:
1142:
1111:Nicaean Empire
1104:Constantinople
1092:Latin Emperors
1080:Fourth Crusade
1078:Following the
1067:
1064:
1033:Constantinople
1010:Serbian Empire
962:Nicaean Empire
958:Ottoman Empire
950:Fourth Crusade
928:
927:
925:
924:
917:
910:
902:
899:
898:
885:
884:
882:
881:
876:
871:
866:
861:
855:
852:
851:
847:
846:
840:
839:
838:
837:
832:
827:
826:
825:
815:
814:
813:
808:
803:
794:
786:
785:
784:
779:
774:
763:Fourth Crusade
757:
756:
752:
751:
750:
749:
744:
739:
734:
732:Macedonian era
729:
724:
719:
711:
710:
706:
705:
704:
703:
698:
693:
688:
683:
681:Theodosian era
678:
664:
656:
655:
651:
650:
649:
648:
647:
646:
631:
630:
626:
625:
614:
613:
607:
606:
599:
592:
591:
588:
587:
584:
583:
576:
574:Ottoman Empire
567:
564:
563:
558:
550:
549:
544:
532:
531:
526:
516:
515:
512:
511:
508:
498:
495:
494:
491:
481:
478:
477:
474:
473:
470:
466:
465:
462:
461:
459:Constantine XI
456:
453:
450:
449:
444:
441:
438:
437:
432:
429:
426:
425:
422:
419:
416:
415:
410:
407:
404:
403:
400:
397:
394:
393:
388:
385:
382:
381:
376:
373:
370:
369:
364:
361:
358:
357:
355:Andronikos III
352:
349:
346:
345:
340:
337:
334:
333:
328:
325:
322:
321:
316:
313:
310:
309:
306:
305:
302:
296:
295:
290:
286:
285:
280:
274:
273:
258:
254:
253:
251:
250:
241:
236:
231:
226:
221:
216:
209:
207:
203:
202:
200:Constantinople
197:
193:
192:
175:
164:
154:
144:
143:
140:
139:
116:
115:
108:
101:
100:
87:
80:
79:
78:
75:
74:
70:
69:
66:
65:
50:
26:
25:
22:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
5685:
5674:
5671:
5669:
5666:
5664:
5661:
5659:
5656:
5654:
5651:
5649:
5646:
5644:
5641:
5640:
5638:
5620:
5616:
5612:
5610:
5607:
5605:
5602:
5601:
5599:
5598:
5595:
5585:
5582:
5580:
5577:
5575:
5572:
5570:
5567:
5565:
5562:
5560:
5557:
5555:
5552:
5550:
5547:
5545:
5542:
5541:
5538:
5531:
5527:
5511:
5508:
5507:
5506:
5503:
5501:
5498:
5494:
5491:
5490:
5489:
5486:
5484:
5481:
5479:
5476:
5474:
5471:
5469:
5468:Encyclopedias
5466:
5465:
5463:
5457:
5455:
5452:
5451:
5448:
5442:
5439:
5437:
5434:
5432:
5429:
5427:
5424:
5420:
5417:
5416:
5415:
5412:
5408:
5405:
5403:
5400:
5399:
5398:
5395:
5393:
5392:Hellenization
5390:
5388:
5385:
5383:
5380:
5378:
5375:
5373:
5370:
5368:
5365:
5363:
5360:
5358:
5355:
5354:
5352:
5350:Everyday life
5348:
5342:
5339:
5337:
5336:
5332:
5328:
5325:
5324:
5323:
5322:Acritic songs
5320:
5318:
5315:
5314:
5312:
5310:
5306:
5300:
5297:
5293:
5290:
5288:
5285:
5283:
5280:
5279:
5278:
5275:
5273:
5270:
5268:
5265:
5263:
5260:
5259:
5257:
5255:
5251:
5245:
5242:
5240:
5237:
5235:
5232:
5228:
5225:
5224:
5223:
5220:
5218:
5215:
5213:
5210:
5208:
5205:
5204:
5202:
5200:
5196:
5186:
5183:
5181:
5178:
5176:
5173:
5171:
5168:
5166:
5165:Hosios Loukas
5163:
5161:
5158:
5157:
5155:
5151:
5145:
5142:
5140:
5137:
5135:
5132:
5131:
5129:
5127:
5123:
5117:
5114:
5112:
5109:
5107:
5104:
5102:
5099:
5097:
5094:
5092:
5089:
5088:
5086:
5084:
5080:
5074:
5071:
5069:
5066:
5064:
5061:
5059:
5056:
5054:
5051:
5049:
5046:
5044:
5041:
5039:
5036:
5034:
5031:
5029:
5026:
5024:
5021:
5020:
5018:
5016:
5012:
5004:
5001:
4999:
4996:
4995:
4994:
4991:
4989:
4986:
4985:
4982:
4979:
4977:
4973:
4969:
4962:
4958:
4944:
4941:
4939:
4936:
4934:
4931:
4929:
4926:
4922:
4919:
4918:
4917:
4914:
4912:
4909:
4908:
4906:
4904:
4900:
4894:
4891:
4887:
4884:
4882:
4879:
4877:
4874:
4872:
4869:
4868:
4866:
4864:
4861:
4859:
4856:
4854:
4851:
4849:
4846:
4844:
4841:
4839:
4838:Monophysitism
4836:
4834:
4831:
4829:
4826:
4822:
4819:
4817:
4814:
4812:
4811:Armenian Rite
4809:
4807:
4804:
4803:
4802:
4799:
4795:
4792:
4790:
4787:
4785:
4782:
4780:
4777:
4775:
4772:
4771:
4770:
4767:
4766:
4764:
4762:
4758:
4754:
4747:
4743:
4729:
4728:Naval battles
4726:
4724:
4721:
4719:
4716:
4714:
4711:
4709:
4706:
4704:
4701:
4697:
4694:
4692:
4689:
4687:
4684:
4683:
4682:
4679:
4677:
4674:
4673:
4671:
4669:
4665:
4655:
4652:
4648:
4645:
4643:
4640:
4639:
4638:
4635:
4631:
4628:
4626:
4623:
4622:
4621:
4618:
4617:
4615:
4611:
4605:
4602:
4600:
4597:
4595:
4592:
4590:
4587:
4585:
4582:
4580:
4577:
4575:
4572:
4570:
4567:
4565:
4562:
4560:
4557:
4556:
4554:
4550:
4542:
4539:
4537:
4534:
4532:
4529:
4527:
4524:
4523:
4522:
4519:
4517:
4514:
4513:
4511:
4507:
4501:
4498:
4496:
4493:
4491:
4488:
4486:
4483:
4481:
4478:
4476:
4473:
4471:
4468:
4466:
4463:
4462:
4459:
4456:
4454:
4450:
4446:
4439:
4435:
4421:
4418:
4416:
4413:
4411:
4408:
4406:
4403:
4402:
4400:
4398:
4394:
4384:
4381:
4379:
4376:
4375:
4373:
4369:
4363:
4360:
4358:
4355:
4353:
4350:
4348:
4345:
4344:
4342:
4338:
4332:
4329:
4327:
4324:
4322:
4319:
4317:
4314:
4312:
4309:
4307:
4304:
4303:
4301:
4297:
4294:
4292:
4288:
4278:
4275:
4273:
4270:
4269:
4267:
4263:
4257:
4254:
4252:
4251:Protasekretis
4249:
4247:
4244:
4242:
4239:
4237:
4234:
4232:
4229:
4227:
4224:
4222:
4219:
4217:
4214:
4213:
4211:
4207:
4201:
4198:
4196:
4193:
4191:
4188:
4186:
4183:
4181:
4178:
4177:
4175:
4171:
4165:
4162:
4158:
4155:
4154:
4153:
4150:
4146:
4143:
4141:
4138:
4136:
4133:
4132:
4131:
4128:
4127:
4124:
4121:
4117:
4113:
4106:
4102:
4088:
4085:
4083:
4080:
4077:
4073:
4071:
4068:
4066:
4063:
4061:
4058:
4056:
4053:
4049:
4046:
4044:
4041:
4040:
4039:
4036:
4034:
4031:
4029:
4026:
4024:
4021:
4019:
4016:
4014:
4011:
4009:
4006:
4004:
4001:
3999:
3996:
3994:
3991:
3989:
3986:
3985:
3983:
3975:
3969:
3966:
3964:
3961:
3959:
3956:
3953:
3949:
3945:
3941:
3937:
3933:
3929:
3925:
3922:
3921:
3920:
3917:
3913:
3910:
3909:
3908:
3905:
3904:
3902:
3896:
3891:
3885:
3882:
3880:
3879:Komnenian era
3877:
3875:
3872:
3870:
3867:
3865:
3862:
3860:
3857:
3855:
3852:
3851:
3849:
3843:
3838:
3832:
3829:
3824:
3820:
3819:
3818:
3817:Heraclian era
3815:
3813:
3812:Justinian era
3810:
3808:
3805:
3803:
3800:
3796:
3793:
3791:
3788:
3787:
3786:
3783:
3782:
3780:
3774:
3769:
3761:
3760:
3756:
3755:
3754:
3751:
3750:
3748:
3745:
3740:
3736:
3732:
3727:
3723:
3718:
3711:
3706:
3704:
3699:
3697:
3692:
3691:
3688:
3682:
3679:
3678:
3669:
3665:
3659:
3651:
3646:
3643:
3640:
3638:
3635:
3632:
3629:
3626:
3623:
3619:
3613:
3608:
3607:
3600:
3596:
3593:
3589:
3588:
3579:
3576:
3573:
3572:
3561:
3560:9780299809263
3557:
3553:
3547:
3539:
3537:1-84176-091-9
3533:
3529:
3525:
3519:
3511:
3505:
3501:
3497:
3491:
3483:
3476:
3474:
3465:
3458:
3452:Mango, p. 274
3449:
3447:
3440:Mango, p. 264
3437:
3431:Mango, p. 273
3428:
3426:
3424:
3422:
3415:Mango, p. 272
3412:
3410:
3408:
3406:
3399:Mango, p. 271
3396:
3394:
3392:
3390:
3388:
3381:Mango, p. 270
3378:
3376:
3374:
3372:
3365:Mango, p. 269
3362:
3360:
3358:
3356:
3354:
3352:
3350:
3348:
3341:Mango, p. 268
3338:
3336:
3334:
3327:Mango, p. 267
3324:
3322:
3320:
3313:Mango, p. 266
3310:
3304:Mango, p. 265
3301:
3299:
3297:
3295:
3293:
3291:
3284:
3278:
3272:Mango, p. 263
3269:
3267:
3265:
3263:
3261:
3259:
3257:
3250:Mango, p. 262
3247:
3245:
3243:
3241:
3239:
3237:
3235:
3228:Mango, p. 261
3225:
3223:
3221:
3219:
3212:Mango, p. 260
3209:
3207:
3205:
3203:
3201:
3199:
3191:
3186:
3178:
3171:
3162:
3156:Mango, p. 258
3153:
3151:
3149:
3147:
3145:
3138:Mango, p. 257
3135:
3133:
3125:
3119:
3110:
3108:
3101:Mango, p. 256
3098:
3096:
3086:
3080:Mango, p. 254
3077:
3075:
3073:
3071:
3069:
3059:
3053:Mango, p. 255
3050:
3046:
3036:
3035:Kantakouzenos
3033:
3031:
3028:
3026:
3023:
3021:
3018:
3016:
3013:
3011:
3008:
3006:
3003:
3001:
2998:
2996:
2993:
2992:
2986:
2982:
2978:
2975:
2969:
2967:
2963:
2962:First Crusade
2959:
2948:
2945:
2937:
2927:
2923:
2919:
2913:
2912:
2908:
2903:This section
2901:
2897:
2892:
2891:
2883:
2881:
2877:
2871:
2868:
2857:
2855:
2851:
2845:
2843:
2839:
2835:
2831:
2827:
2823:
2819:
2811:
2807:
2803:
2798:
2794:
2792:
2786:
2784:
2780:
2775:
2773:
2769:
2765:
2761:
2757:
2753:
2750:At the time,
2743:
2741:
2737:
2732:
2730:
2726:
2721:
2719:
2715:
2711:
2707:
2697:
2695:
2691:
2687:
2683:
2679:
2675:
2671:
2670:
2665:
2661:
2657:
2653:
2649:
2645:
2641:
2637:
2633:
2623:
2614:
2611:
2607:
2600:
2585:
2583:
2572:
2569:
2565:
2559:
2557:
2552:
2548:
2544:
2540:
2534:
2525:
2516:
2511:
2501:
2499:
2493:
2491:
2487:
2483:
2473:
2471:
2467:
2463:
2459:
2455:
2445:
2442:
2434:
2433:
2428:
2427:
2422:
2418:
2414:
2409:
2399:
2395:
2393:
2392:Kucuk Mustafa
2389:
2385:
2379:
2377:
2373:
2362:
2359:
2354:
2352:
2348:
2344:
2340:
2335:
2326:
2317:
2315:
2311:
2307:
2302:
2300:
2296:
2290:
2288:
2287:King Henry IV
2284:
2280:
2276:
2271:
2269:
2265:
2254:
2252:
2242:
2234:
2229:
2219:
2217:
2214:stationed at
2213:
2207:
2205:
2201:
2197:
2191:
2188:
2183:
2180:
2176:
2172:
2168:
2162:
2160:
2155:
2151:
2139:
2134:
2132:
2127:
2125:
2120:
2119:
2117:
2116:
2113:
2103:
2102:
2096:
2093:
2091:
2088:
2086:
2083:
2081:
2078:
2076:
2073:
2072:
2070:
2069:
2065:
2064:
2061:
2058:
2057:
2052:
2049:
2047:
2044:
2040:
2037:
2036:
2035:
2032:
2028:
2025:
2023:
2020:
2018:
2014:
2011:
2009:
2006:
2005:
2003:
1999:
1996:
1994:
1991:
1989:
1986:
1985:
1984:
1980:
1977:
1976:
1975:
1974:
1970:
1969:
1964:
1961:
1959:
1958:Komnenian era
1956:
1954:
1951:
1949:
1946:
1944:
1941:
1939:
1936:
1934:
1931:
1930:
1929:
1928:
1924:
1923:
1918:
1915:
1913:
1912:Heraclian era
1910:
1908:
1907:Justinian era
1905:
1903:
1900:
1898:
1895:
1892:
1888:
1884:
1881:
1879:
1878:Tetrarchy era
1876:
1875:
1874:
1873:
1869:
1868:
1861:
1860:
1856:
1855:
1854:
1851:
1850:
1849:
1848:
1844:
1843:
1836:
1832:
1831:
1828:
1825:
1824:
1819:
1814:
1813:
1809:
1799:
1797:
1793:
1789:
1779:
1776:
1773:
1769:
1768:Anna of Savoy
1764:
1762:
1761:First Crusade
1757:
1747:
1745:
1737:
1728:
1726:
1722:
1711:
1708:
1703:
1698:
1696:
1692:
1686:
1678:
1669:
1667:
1663:
1657:
1655:
1654:Didymoteichon
1651:
1646:
1644:
1640:
1639:Anna of Savoy
1634:
1624:
1622:
1618:
1613:
1604:
1595:
1592:
1591:
1590:coup de grâce
1580:
1571:
1569:
1568:Stephen Dusan
1565:
1560:
1558:
1554:
1550:
1546:
1542:
1539:
1534:
1531:
1527:
1521:
1513:
1503:
1493:
1484:
1480:
1477:
1473:
1462:
1460:
1459:
1454:
1453:
1441:
1432:
1430:
1425:
1421:
1417:
1416:Roger de Flor
1413:
1409:
1404:
1402:
1398:
1394:
1390:
1386:
1380:
1378:
1374:
1370:
1365:
1361:
1351:
1347:
1337:
1328:
1325:
1320:
1317:
1303:
1297:
1293:
1291:
1287:
1283:
1277:
1275:
1271:
1267:
1262:
1259:
1255:
1254:Hohenstaufens
1251:
1247:
1243:
1239:
1235:
1231:
1227:
1217:
1215:
1210:
1206:
1202:
1197:
1187:
1185:
1181:
1177:
1173:
1169:
1165:
1159:
1150:
1141:
1139:
1135:
1130:
1128:
1124:
1120:
1116:
1112:
1107:
1105:
1101:
1097:
1093:
1089:
1085:
1081:
1072:
1063:
1061:
1057:
1053:
1048:
1046:
1042:
1038:
1034:
1030:
1026:
1021:
1019:
1016:and even the
1015:
1011:
1007:
1002:
998:
994:
993:
988:
984:
980:
976:
971:
969:
968:
963:
959:
955:
951:
947:
943:
939:
935:
923:
918:
916:
911:
909:
904:
903:
901:
900:
897:
887:
886:
880:
877:
875:
872:
870:
867:
865:
862:
860:
857:
856:
854:
853:
849:
848:
845:
842:
841:
836:
833:
831:
828:
824:
821:
820:
819:
816:
812:
809:
807:
804:
802:
798:
795:
793:
790:
789:
787:
783:
780:
778:
775:
773:
770:
769:
768:
764:
761:
760:
759:
758:
754:
753:
748:
745:
743:
742:Komnenian era
740:
738:
735:
733:
730:
728:
725:
723:
720:
718:
715:
714:
713:
712:
708:
707:
702:
699:
697:
696:Heraclian era
694:
692:
691:Justinian era
689:
687:
684:
682:
679:
676:
672:
668:
665:
663:
662:Tetrarchy era
660:
659:
658:
657:
653:
652:
645:
644:
640:
639:
638:
635:
634:
633:
632:
628:
627:
620:
616:
615:
612:
609:
608:
603:
598:
597:
577:
575:
572:
571:
568:
562:
559:
552:
551:
548:
545:
538:
537:
534:
533:
530:
527:
525:
522:
521:
517:
513:
509:
506:
502:
496:
492:
489:
485:
479:
475:
471:
467:
463:
460:
457:
451:
448:
445:
439:
436:
433:
427:
423:
417:
414:
411:
405:
401:
395:
392:
391:Andronikos IV
389:
383:
380:
377:
371:
368:
365:
359:
356:
353:
347:
344:
341:
335:
332:
331:Andronikos II
329:
323:
320:
317:
311:
307:
303:
301:
297:
294:
291:
287:
284:
281:
279:
275:
271:
267:
262:
259:
255:
249:
245:
242:
240:
239:Old Bulgarian
237:
235:
232:
230:
227:
225:
222:
220:
217:
214:
211:
210:
208:
204:
201:
198:
194:
188:
184:
180:
168:
158:
148:
141:
137:
131:
121:
117:
111:
105:
97:
84:
76:
71:
62:
55:
51:
47:
39:
38:Ancient Greek
28:
27:
20:
5333:
5101:Hagia Sophia
5083:Thessalonica
5058:Hagia Sophia
5038:Chora Church
4976:Architecture
4853:Great Schism
4843:Paulicianism
4821:Miaphysitism
4676:Karabisianoi
3980:or territory
3957:
3940:Thessalonica
3924:Latin Empire
3919:Frankokratia
3894:
3854:Isaurian era
3841:
3772:
3757:
3753:Roman Empire
3743:
3652:. Amsterdam.
3649:
3605:
3595:
3592:
3546:
3527:
3518:
3499:
3490:
3481:
3463:
3457:
3436:
3309:
3277:
3185:
3176:
3170:
3161:
3118:
3085:
3058:
3049:
2983:
2979:
2970:
2966:Michael VIII
2955:
2940:
2931:
2916:Please help
2904:
2872:
2863:
2846:
2833:
2815:
2787:
2776:
2752:astrologists
2749:
2733:
2722:
2703:
2667:
2663:
2662:, Ptolemy's
2628:
2602:
2578:
2560:
2536:
2513:
2494:
2479:
2457:
2451:
2440:
2438:
2430:
2424:
2396:
2380:
2368:
2355:
2331:
2314:split in two
2306:Thessalonica
2303:
2291:
2272:
2260:
2248:
2239:
2208:
2192:
2184:
2163:
2147:
2033:
2017:Thessalonica
1988:Latin Empire
1933:Isaurian era
1857:
1853:Roman Empire
1785:
1777:
1765:
1753:
1742:
1721:Thessalonica
1717:
1699:
1687:
1683:
1658:
1647:
1636:
1609:
1588:
1585:
1561:
1535:
1522:
1518:
1490:
1481:
1468:
1456:
1450:
1447:
1405:
1381:
1357:
1349:
1334:
1321:
1312:
1278:
1263:
1223:
1205:Kontoskalion
1201:Hagia Sophia
1193:
1176:Thessalonica
1161:
1131:
1108:
1077:
1049:
1022:
1014:Latin Empire
990:
983:Michael VIII
972:
967:Frankokratia
965:
946:Latin Empire
931:
817:
801:Thessalonica
772:Latin Empire
717:Isaurian era
641:
637:Roman Empire
561:Latin Empire
529:Succeeded by
528:
523:
408:• 1390
319:Michael VIII
120:Motto:
119:
5584:Megali Idea
5559:Byzantinism
5262:Agriculture
5053:Hagia Irene
4886:Kievan Rus'
4863:Mount Athos
4686:Cibyrrhaeot
4630:Vestiaritai
4485:Mercenaries
4362:Catepanates
4221:Sakellarios
4140:Family tree
4065:Mesopotamia
3884:Angelid era
3864:Amorian era
2599:Renaissance
2549:. In 1451,
2343:Mount Athos
1963:Angelid era
1943:Amorian era
1458:pronoiarioi
1025:Black Death
938:Palaiologos
747:Angelid era
727:Amorian era
524:Preceded by
270:Sunni Islam
229:Old Catalan
134:(English: "
94: 1350
5637:Categories
5579:Third Rome
5505:University
5488:Philosophy
5478:Inventions
5341:Historians
5309:Literature
5292:Varangians
5134:San Vitale
5063:Hippodrome
5043:City Walls
4943:Mutilation
4938:Hexabiblos
4858:Bogomilism
4848:Iconoclasm
4718:Megas doux
4708:Greek fire
4691:Aegean Sea
4564:Kleisourai
4541:Excubitors
4531:Bucellarii
4383:Despotates
4352:Kleisourai
4291:Provincial
4135:Coronation
4109:Governance
3874:Doukid era
3807:Leonid era
3617:1588391132
3569:References
2886:Conclusion
2718:Theocritus
2669:Dionysiaca
2575:Conclusion
2432:autokrator
2080:Government
1983:Latin rule
1953:Doukid era
1902:Leonid era
1452:hyperpyron
1412:Almogavars
1389:Michael IX
1248:conquered
1242:Latin rule
1096:Bulgarians
1066:Background
979:Asia Minor
864:Government
767:Latin rule
737:Doukid era
686:Leonid era
343:Michael IX
289:Government
278:Demonym(s)
272:(Minority)
246:and other
215:(official)
189:in violet.
5407:Octoechos
5287:Silk Road
4779:Hesychasm
4647:Paramonai
4594:Hetaireia
4526:Foederati
4415:Diplomacy
4410:Diplomats
4316:Provinces
4145:Empresses
3948:Trebizond
3744:Preceding
3658:cite book
2905:does not
2867:patronage
2860:Patronage
2826:Zoroaster
2779:astrolabe
2764:Trebizond
2760:astronomy
2714:Sophocles
2710:Antiquity
2664:Geography
2660:Euripides
2568:Hungarian
2551:Mehmed II
2421:Pisanello
2251:Bayezid I
2167:Gallipoli
2154:Savcı Bey
2022:Trebizond
1845:Preceding
1685:to fail.
1617:Hesychasm
1530:Nicomedia
1429:Ilkhanids
1420:Catalonia
1414:, led by
1403:in 1302.
1397:Nicomedia
1383:General,
1316:Komnenian
1266:Martin IV
1252:from the
1234:Venetians
1214:Mamelukes
1172:Macedonia
1029:Gallipoli
806:Trebizond
629:Preceding
486:from the
447:John VIII
435:Manuel II
257:Religion
234:Aromanian
73:1261–1453
5500:Scholars
5493:Rhetoric
5483:Medicine
5458:Learning
5357:Calendar
5234:Painters
4933:Basilika
4871:Bulgaria
4833:Arianism
4784:Hayhurum
4761:Religion
4723:Admirals
4642:Allagion
4574:Droungos
4480:Generals
4442:Military
4405:Treaties
4311:Dioceses
4130:Emperors
4043:Sardinia
4023:Dalmatia
4003:Bulgaria
3993:Anatolia
3952:Theodoro
3946: /
3942: /
3934: /
3562:, p. 582
3526:(2000).
3498:(1990).
2989:See also
2934:May 2019
2834:The Laws
2830:Fatalism
2736:Hellenes
2725:Planudes
2686:Istanbul
2674:Plutarch
2582:Orthodox
2556:fortress
2547:Murad II
2470:Florence
2462:Filioque
2458:de facto
2426:basileus
2372:Murad II
2358:Mehmed I
2339:Süleyman
2299:defeated
2187:Thessaly
2066:By topic
2060:Timeline
2027:Theodoro
1859:Dominate
1818:a series
1816:Part of
1476:appanage
1377:Strumica
1236:and the
1184:Joseph I
1180:Arsenios
1123:Anatolia
1043:and the
987:Anatolia
850:By topic
844:Timeline
811:Theodoro
643:Dominate
602:a series
600:Part of
505:Ottomans
413:John VII
224:Armenian
5609:Outline
5554:Museums
5454:Science
5431:Slavery
5387:Gardens
5367:Cuisine
5299:Dynatoi
5267:Coinage
5254:Economy
5222:Mosaics
5185:Mystras
5126:Ravenna
4988:Secular
4876:Moravia
4625:Pronoia
4599:Akritai
4584:Tagmata
4559:Themata
4500:Revolts
4470:Battles
4378:Kephale
4347:Themata
4277:Mesazon
4119:Central
4055:Maghreb
4008:Corsica
3998:Armenia
3988:Albania
3731:History
2926:removed
2911:sources
2850:infidel
2822:Plethon
2756:Ptolemy
2694:Vatican
2648:Scholia
2482:Hungary
2466:Ferrara
2085:Economy
1792:Murad I
1691:Tenedos
1557:Phocaea
1302:Cilicia
1286:Osman I
997:Islamic
956:to the
869:Economy
503:to the
499:•
482:•
469:History
379:John VI
300:Emperor
196:Capital
5619:Portal
5534:Impact
5414:People
5362:Cities
5212:Enamel
4993:Sacred
4928:Ecloga
4794:Saints
4703:Dromon
4579:Bandon
4569:Tourma
4552:Middle
4475:Beacon
4357:Bandon
4340:Middle
4209:Middle
4164:Senate
4087:Thrace
4070:Serbia
4048:Sicily
4033:Greece
4018:Cyprus
3936:Epirus
3932:Nicaea
3842:Middle
3719:topics
3614:
3558:
3534:
3506:
2854:Tatars
2842:Rimini
2806:Rimini
2791:Tabriz
2692:, the
2690:Oxford
2652:Pindar
2610:Cyprus
2275:Venice
2216:Rhodes
2196:Lemnos
2179:Galata
2171:Amadeo
2159:Manuel
2013:Epirus
2008:Nicaea
1998:others
1820:on the
1796:Serres
1695:Genoan
1574:Legacy
1553:Lesbos
1487:Legacy
1474:as an
1472:Thrace
1444:reign.
1364:Skopje
1331:Legacy
1250:Sicily
1238:Franks
1230:Mongol
1168:Thrace
1127:Thrace
1115:Seljuk
1100:Epirus
1088:Epirus
1084:Nicaea
1054:. The
1008:, the
992:ghazis
797:Epirus
792:Nicaea
782:others
604:on the
488:Latins
472:
424:John V
402:John V
367:John V
304:
89:Flag (
57:
34:
5604:Index
5436:Death
5426:Women
5397:Music
5377:Dress
5372:Dance
5317:Novel
5277:Trade
5272:Mints
5217:Glass
5207:Icons
5003:Domes
4881:Serbs
4696:Samos
4509:Early
4299:Early
4173:Early
4082:Syria
4060:Malta
4038:Italy
4028:Egypt
4013:Crete
3944:Morea
3773:Early
3042:Notes
2974:Avars
2810:Italy
2740:Greek
2682:Chora
2606:Crete
2564:Orban
2476:Varna
2347:Varna
2295:Timur
2283:Milan
2279:Padua
2200:Genoa
2175:Savoy
1707:Morea
1702:Orhan
1666:Aydın
1549:Aydın
1424:Moors
1410:" of
1369:Ohrid
1290:Sogut
1037:Timur
975:Turks
219:Latin
213:Greek
61:Latin
5402:Lyra
5282:silk
4893:Jews
4668:Navy
4613:Late
4453:Army
4420:Wars
4371:Late
4265:Late
3895:Late
3664:link
3612:ISBN
3556:ISBN
3532:ISBN
3504:ISBN
2909:any
2907:cite
2878:and
2828:and
2716:and
2658:and
2650:and
2642:and
2566:, a
2468:and
2429:and
2386:and
2332:The
2095:Navy
2090:Army
1981:and
1555:and
1538:Emir
1373:Stip
1322:The
1224:The
1194:The
1174:and
1109:The
932:The
879:Navy
874:Army
765:and
510:1453
493:1261
268:and
177:The
5199:Art
4903:Law
2920:by
2840:of
2804:in
2608:or
2376:war
2173:of
2075:Art
1664:of
1662:Bey
1645:).
1547:of
1545:Bey
1375:to
1371:to
977:of
859:Art
5639::
3660:}}
3656:{{
3472:^
3445:^
3420:^
3404:^
3386:^
3370:^
3346:^
3332:^
3318:^
3289:^
3255:^
3233:^
3217:^
3197:^
3143:^
3131:^
3106:^
3094:^
3067:^
2852:"
2844:.
2808:,
2688:,
2638:,
2634:,
2316:.
2281:,
2277:,
1889:–
1543:,
1186:.
1170:,
1086:,
1062:.
1020:.
985:.
673:–
138:")
91:c.
3954:)
3950:–
3938:–
3825:"
3821:"
3709:e
3702:t
3695:v
3666:)
3620:.
3540:.
3512:.
3192:.
2947:)
2941:(
2936:)
2932:(
2928:.
2914:.
2848:"
2137:e
2130:t
2123:v
2015:/
1893:)
1885:(
1300:-
921:e
914:t
907:v
799:/
677:)
669:(
96:)
63:)
59:(
40:)
36:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.