272:. The preform has a 1 inch by 1 inch round slug that stands up in the mold cavity. During the cycle, the operator loads the jig with slugs and places the jig over the mold. The preforms are released into the cavity of the mold when the slide tray is pulled. When the mold is opened, the lower platen lowers and the mold is hydraulically pushed out to the operator. The heat sheet (all molded parts from that cycle joined together by a parting line rind (flash)) is then placed in a transfer cart to be die cut.
265:
hydraulically closed to full pressure. The mold temperature is about 350 degrees. When the cycle ends (after about 3.5-4.0 minutes), the press opens and the mold is pulled out toward the operator. The operator opens the clam shell mold top and leans the top of the mold back against the press. Exposed is the bottle with the core still inside. While the bottle is still hot, the operator inserts prongs in between the bottle and the steel core and stretches the bottle at the neck to free it from the core.
605:
22:
196:
spoilers, as well as smaller more intricate parts. The material to be molded is positioned in the mold cavity and the heated platens are closed by a hydraulic ram. Bulk molding compound (BMC) or sheet molding compound (SMC), are conformed to the mold form by the applied pressure and heated until the curing reaction occurs. SMC feed material usually is cut to conform to the surface area of the mold. The mold is then cooled and the part removed.
611:
30:
51:
248:
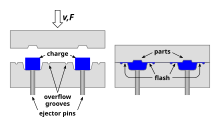
helps to reduce excess flash. Inserts, usually metallic, can also be molded with the plastic. As a side note, remember not to allow any undercuts on the shape, it will make ejection especially difficult. Thermoplastic matrices with an inherent indefinite shelf-life and shorter cycle molding times are widely used and examples are shown in Ref 3.
256:
Compression molding is one of the oldest manufacturing techniques for rubber molding. The process parameters include molding time, temperature, and pressure. Usually, a 300-400 ton clamp pressure is used. The typical mold is shaped like a clam shell with the bottom being the mold cavity. The molding
199:
Materials may be loaded into the mold either in the form of pellets or sheet, or the mold may be loaded from a plasticating extruder. Materials are heated above their melting points, formed and cooled. The more evenly the feed material is distributed over the mold surface, the less flow orientation
280:
Three types of molds used are the flash plunger-type, straight plunger-type, and the "landed" plunger-type molds. The flash type mold must have an accurate charge of plastic and produces a horizontal flash (excess material protruding from the mold). The straight plunger-type mold allows for some
264:
Compression molded water bottles are made from die-cut 3 inch by 6 inch sheets. One sheet is placed below a core and one sheet of equal size is placed above the core, and then the top of the mold is lowered by hand or by hoist to near shut. The mold is then pushed into the press, and the press is
247:
The use of thermoset plastic compounds characterizes this molding process from many of the other molding processes. These thermosets can be in either preform or granule shapes. Unlike some of the other processes we find that the materials are usually preheated and measured before molding. This
238:
Compression molding is a forming process in which a plastic material is placed directly into a heated metal mold then is softened by the heat and therefore forced to conform to the shape of the mold, as the mold closes. Once molding is completed excess Flash may be removed. Typically, compression
195:
Compression molding was first developed to manufacture composite parts for metal replacement applications, compression molding is typically used to make larger flat or moderately curved parts. This method of molding is greatly used in manufacturing automotive parts such as hoods, fenders, scoops,
148:
can also be compression molded with unidirectional tapes, woven fabrics, randomly oriented fiber mat or chopped strand. The advantage of compression molding is its ability to mold large, fairly intricate parts. Also, it is one of the lowest cost molding methods compared with other methods such as
168:
are produced and a smaller amount of fiber-length degradation is noticeable when compared to injection molding. Compression-molding is also suitable for ultra-large basic shape production in sizes beyond the capacity of extrusion techniques. Materials that are typically manufactured through
206:
Thermoplastic matrices are commonplace in mass production industries. One significant example are automotive applications where the leading technologies are long fibre reinforced thermoplastics (LFT) and glass fiber mat reinforced thermoplastics (GMT).
257:
press looked a lot like a ladle filled vertical press used for casting aluminum. Compression molding uses preforms made by an extruder and wink cutter (in which two blades meet at the center to cut the extrudate to length) or a roller die and
281:
inaccuracy in the charge of plastic and produces a vertical flash. The landed plunger type mold must have an accurate charge of plastic, and no flash is produced. Further details are explained in Ref 3.
129:
are maintained until the molding material has cured; this process is known as compression molding method and in case of rubber it is also known as 'Vulcanisation'. The process employs thermosetting
188:
Compression molding is commonly utilized by product development engineers seeking cost effective rubber and silicone parts. Manufacturers of low volume compression molded components include
1212:
936:
404:
Todd, Robert H., Dell K. Allen, and Leo Alting. Manufacturing
Processes Reference Guide. New York: Industrial P, Incorporated, 1993 on page 219-220....
121:
cavity. The mold is closed with a top force or plug member, pressure is applied to force the material into contact with all mold areas, while
203:
Compression molding is also widely used to produce sandwich structures that incorporate a core material such as a honeycomb or polymer foam.
189:
929:
812:
1271:
1222:
1191:
79:
922:
429:
97:
914:
454:
157:; moreover it wastes relatively little material, giving it an advantage when working with expensive compounds.
1207:
1186:
1083:
837:
1261:
1181:
335:
1254:
1176:
992:
589:
1313:
519:
494:
140:
Compression molding is a high-volume, high-pressure method suitable for molding complex, high-strength
1294:
1028:
827:
652:
469:
459:
178:
66:
210:
In compression molding there are six important considerations that an engineer should bear in mind:
1098:
1088:
950:
637:
584:
474:
379:
258:
160:
However, compression molding often provides poor product consistency and difficulty in controlling
688:
579:
564:
544:
1103:
981:
736:
464:
422:
1283:
987:
632:
38:
310:
1003:
998:
971:
889:
229:
Designing the mold for rapid cooling after the material has been compressed into the mold.
8:
1133:
894:
817:
683:
357:
1148:
1066:
807:
781:
751:
711:
693:
642:
594:
574:
117:
in which the molding material, generally preheated, is first placed in an open, heated
1278:
1244:
1164:
976:
798:
716:
415:
154:
118:
114:
61:
1169:
864:
766:
741:
673:
539:
534:
479:
150:
944:
1033:
1019:
884:
771:
761:
529:
1062:
874:
776:
647:
290:
1307:
1249:
1056:
842:
832:
822:
726:
627:
549:
499:
161:
145:
226:
Predicting the required force, to ensure that shot attains the proper shape.
869:
859:
721:
668:
569:
514:
489:
169:
compression molding include: Polyester fiberglass resin systems (SMC/BMC),
1115:
604:
1052:
1024:
959:
879:
678:
559:
554:
72:
1128:
756:
746:
217:
Determining the minimum amount of energy required to heat the material.
141:
21:
1217:
1123:
1093:
963:
524:
509:
484:
269:
165:
1138:
126:
610:
1266:
1143:
1044:
946:
438:
174:
170:
34:
29:
134:
130:
133:
in a partially cured stage, either in the form of granules,
504:
407:
220:
Determining the minimum time required to heat the material.
182:
122:
268:
The preforms for compression molded golf ball centers are
164:, and it is not suitable for some types of parts. Fewer
25:
Compression molding - simplified diagram of the process
275:
1305:
223:Determining the appropriate heating technique.
930:
423:
239:molding machines open along a vertical axis.
937:
923:
430:
416:
242:
214:Determining the proper amount of material.
98:Learn how and when to remove this message
28:
20:
1306:
520:Polyethylene terephthalate (PET, PETE)
918:
460:Cross-linked polyethylene (PEX, XLPE)
455:Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)
411:
336:"Introduction to Compression Molding"
233:
200:occurs during the compression stage.
1272:List of environmental health hazards
1192:List of environmental health hazards
251:
44:
276:Typical tools and geometry produced
144:reinforcements. Advanced composite
13:
1077:Miscellaneous additives incl. PHCs
14:
1325:
609:
603:
495:Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT)
470:Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA)
49:
475:Poly(ethyl methacrylate) (PEMA)
398:
380:"What is Compression Moulding?"
838:Category:Plastics applications
585:Styrene maleic anhydride (SMA)
580:Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC)
565:Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
372:
350:
328:
303:
1:
545:Poly(p-phenylene oxide) (PPO)
296:
1262:Persistent organic pollutant
1223:Toxic Substances Control Act
1182:Persistent organic pollutant
465:Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA)
437:
137:-like masses, or preforms.
7:
1255:Great Pacific garbage patch
1177:Great Pacific garbage patch
590:Styrene-acrylonitrile (SAN)
505:Polyetheretherketone (PEEK)
284:
69:. The specific problem is:
10:
1330:
1218:Japan Toxic Substances Law
1013:Miscellaneous plasticizers
311:"Moulding | Walker Rubber"
192:, 3D, STYS, and Aero MFG.
181:(PPS), and many grades of
1292:
1237:
1213:European REACH regulation
1208:California Proposition 65
1200:
1157:
1114:
1076:
1043:
1012:
958:
951:polyhalogenated compounds
907:
852:
828:High-performance plastics
797:
790:
702:
661:
653:High-performance plastics
618:
601:
445:
179:Poly(p-phenylene sulfide)
638:Fibre-reinforced plastic
575:Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
689:Biodegradable additives
243:Process characteristics
1104:Perfluorooctanoic acid
540:Polyphenyl ether (PPE)
535:Polyoxymethylene (POM)
480:Polyacrylic acid (PAA)
382:. Coventive Composites
42:
26:
1284:Biodegradable plastic
633:Thermosetting polymer
530:Polylactic acid (PLA)
32:
24:
1295:Identification codes
895:Foam food containers
818:Engineering plastics
80:improve this article
65:to meet Knowledge's
1134:Endocrine disruptor
732:Compression molding
684:Polymer stabilizers
111:Compression molding
33:Compression molded
1149:Polymer fume fever
808:Commodity plastics
782:Rotational molding
752:Fiberglass molding
712:Injection moulding
694:Filler (materials)
643:Corrugated plastic
595:Tritan copolyester
550:Polypropylene (PP)
500:Polycarbonate (PC)
234:Process definition
43:
27:
1314:Molding processes
1301:
1300:
1279:Plastic recycling
1245:Plastic pollution
1231:
1230:
1165:Plastic pollution
945:Health issues of
903:
902:
799:Plastics industry
717:Plastic extrusion
570:Polyurethane (PU)
560:Polysulfone (PES)
515:Polyethylene (PE)
490:Polybutylene (PB)
315:Walker Rubber Ltd
252:Process schematic
155:injection molding
108:
107:
100:
67:quality standards
58:This article may
37:boots before the
16:Method of molding
1321:
1170:Rubber pollution
1020:Organophosphates
939:
932:
925:
916:
915:
795:
794:
767:Filament winding
742:Transfer molding
669:Polymer additive
613:
607:
555:Polystyrene (PS)
432:
425:
418:
409:
408:
392:
391:
389:
387:
376:
370:
369:
367:
365:
358:"DKM-DH Machine"
354:
348:
347:
345:
343:
332:
326:
325:
323:
321:
307:
151:transfer molding
103:
96:
92:
89:
83:
53:
52:
45:
1329:
1328:
1324:
1323:
1322:
1320:
1319:
1318:
1304:
1303:
1302:
1297:
1288:
1233:
1232:
1227:
1196:
1153:
1110:
1072:
1039:
1008:
954:
943:
909:
899:
848:
786:
772:Solvent bonding
762:Plastic welding
704:
698:
657:
620:
614:
608:
599:
510:Polyester (PEs)
447:
441:
436:
401:
396:
395:
385:
383:
378:
377:
373:
363:
361:
356:
355:
351:
341:
339:
334:
333:
329:
319:
317:
309:
308:
304:
299:
287:
278:
254:
245:
236:
113:is a method of
104:
93:
87:
84:
77:
54:
50:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1327:
1317:
1316:
1299:
1298:
1293:
1290:
1289:
1287:
1286:
1281:
1276:
1275:
1274:
1269:
1264:
1259:
1258:
1257:
1241:
1239:
1235:
1234:
1229:
1228:
1226:
1225:
1220:
1215:
1210:
1204:
1202:
1198:
1197:
1195:
1194:
1189:
1184:
1179:
1174:
1173:
1172:
1161:
1159:
1155:
1154:
1152:
1151:
1146:
1141:
1136:
1131:
1126:
1120:
1118:
1112:
1111:
1109:
1108:
1107:
1106:
1096:
1091:
1086:
1080:
1078:
1074:
1073:
1071:
1070:
1063:Vinyl chloride
1060:
1057:Polycarbonates
1049:
1047:
1041:
1040:
1038:
1037:
1031:
1022:
1016:
1014:
1010:
1009:
1007:
1006:
1001:
996:
990:
985:
979:
974:
968:
966:
956:
955:
942:
941:
934:
927:
919:
913:
911:
905:
904:
901:
900:
898:
897:
892:
887:
882:
877:
872:
870:Packaging film
867:
862:
856:
854:
853:Specific goods
850:
849:
847:
846:
840:
835:
830:
825:
820:
815:
810:
804:
802:
792:
788:
787:
785:
784:
779:
777:Vacuum forming
774:
769:
764:
759:
754:
749:
744:
739:
734:
729:
724:
719:
714:
708:
706:
700:
699:
697:
696:
691:
686:
681:
676:
671:
665:
663:
659:
658:
656:
655:
650:
648:Polymeric foam
645:
640:
635:
630:
624:
622:
616:
615:
602:
600:
598:
597:
592:
587:
582:
577:
572:
567:
562:
557:
552:
547:
542:
537:
532:
527:
525:Polyimide (PI)
522:
517:
512:
507:
502:
497:
492:
487:
485:Polyamide (PA)
482:
477:
472:
467:
462:
457:
451:
449:
443:
442:
435:
434:
427:
420:
412:
406:
405:
400:
397:
394:
393:
371:
349:
327:
301:
300:
298:
295:
294:
293:
291:Matrix molding
286:
283:
277:
274:
253:
250:
244:
241:
235:
232:
231:
230:
227:
224:
221:
218:
215:
146:thermoplastics
106:
105:
57:
55:
48:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1326:
1315:
1312:
1311:
1309:
1296:
1291:
1285:
1282:
1280:
1277:
1273:
1270:
1268:
1265:
1263:
1260:
1256:
1253:
1252:
1251:
1250:Garbage patch
1248:
1247:
1246:
1243:
1242:
1240:
1236:
1224:
1221:
1219:
1216:
1214:
1211:
1209:
1206:
1205:
1203:
1199:
1193:
1190:
1188:
1185:
1183:
1180:
1178:
1175:
1171:
1168:
1167:
1166:
1163:
1162:
1160:
1156:
1150:
1147:
1145:
1142:
1140:
1137:
1135:
1132:
1130:
1127:
1125:
1122:
1121:
1119:
1117:
1116:Health issues
1113:
1105:
1102:
1101:
1100:
1097:
1095:
1092:
1090:
1087:
1085:
1082:
1081:
1079:
1075:
1068:
1064:
1061:
1058:
1054:
1051:
1050:
1048:
1046:
1042:
1035:
1032:
1030:
1026:
1023:
1021:
1018:
1017:
1015:
1011:
1005:
1002:
1000:
997:
994:
991:
989:
986:
983:
980:
978:
975:
973:
970:
969:
967:
965:
961:
957:
952:
948:
940:
935:
933:
928:
926:
921:
920:
917:
912:
906:
896:
893:
891:
890:Shopping bags
888:
886:
883:
881:
878:
876:
873:
871:
868:
866:
863:
861:
858:
857:
855:
851:
845:(Agriculture)
844:
843:Plasticulture
841:
839:
836:
834:
831:
829:
826:
824:
823:Geosynthetics
821:
819:
816:
814:
811:
809:
806:
805:
803:
800:
796:
793:
789:
783:
780:
778:
775:
773:
770:
768:
765:
763:
760:
758:
755:
753:
750:
748:
745:
743:
740:
738:
735:
733:
730:
728:
727:Thermoforming
725:
723:
720:
718:
715:
713:
710:
709:
707:
701:
695:
692:
690:
687:
685:
682:
680:
677:
675:
672:
670:
667:
666:
664:
660:
654:
651:
649:
646:
644:
641:
639:
636:
634:
631:
629:
628:Thermoplastic
626:
625:
623:
617:
612:
606:
596:
593:
591:
588:
586:
583:
581:
578:
576:
573:
571:
568:
566:
563:
561:
558:
556:
553:
551:
548:
546:
543:
541:
538:
536:
533:
531:
528:
526:
523:
521:
518:
516:
513:
511:
508:
506:
503:
501:
498:
496:
493:
491:
488:
486:
483:
481:
478:
476:
473:
471:
468:
466:
463:
461:
458:
456:
453:
452:
450:
444:
440:
433:
428:
426:
421:
419:
414:
413:
410:
403:
402:
381:
375:
359:
353:
337:
331:
316:
312:
306:
302:
292:
289:
288:
282:
273:
271:
266:
262:
260:
249:
240:
228:
225:
222:
219:
216:
213:
212:
211:
208:
204:
201:
197:
193:
191:
186:
184:
180:
176:
172:
167:
163:
158:
156:
152:
147:
143:
138:
136:
132:
128:
124:
120:
116:
112:
102:
99:
91:
88:February 2020
81:
76:
74:
68:
64:
63:
56:
47:
46:
40:
36:
31:
23:
19:
960:Plasticizers
908:Environment
860:Blister pack
813:Construction
731:
722:Blow molding
399:Bibliography
384:. Retrieved
374:
362:. Retrieved
352:
340:. Retrieved
330:
318:. Retrieved
314:
305:
279:
267:
263:
255:
246:
237:
209:
205:
202:
198:
194:
187:
159:
139:
110:
109:
94:
85:
78:Please help
70:
59:
41:are removed.
18:
1201:Regulations
1053:Bisphenol A
737:Calendering
679:Plasticizer
619:Mechanical
82:if you can.
73:readability
1129:Carcinogen
1094:Organotins
964:Phthalates
910:and health
757:Pultrusion
747:Laminating
705:processing
386:October 1,
297:References
259:die cutter
166:knit lines
142:fiberglass
1158:Pollution
1124:Teratogen
1055:(BPA, in
703:Plastics
674:Colorants
662:Additives
446:Chemical
342:March 19,
190:PrintForm
1308:Category
1139:Diabetes
1045:Monomers
1025:Adipates
947:plastics
801:segments
791:Products
439:Plastics
338:. eFunda
285:See also
270:extruded
162:flashing
127:pressure
60:require
1267:Dioxins
1187:Dioxins
1144:Obesity
885:Cutlery
875:Bottles
364:July 9,
320:May 19,
115:molding
62:cleanup
39:flashes
984:(BBzP)
953:(PHCs)
865:Chairs
833:Nurdle
175:Vespel
171:Torlon
131:resins
35:rubber
1238:Waste
1084:PBDEs
995:(DOP)
621:types
448:types
360:. DKM
135:putty
71:poor
1099:PFCs
1089:PCBs
1065:(in
1029:DEHA
1004:DINP
999:DIDP
993:DEHP
988:DIHP
972:DIBP
949:and
880:Bags
388:2018
366:2023
344:2013
322:2021
183:PEEK
153:and
125:and
123:heat
119:mold
1067:PVC
1034:DOA
982:BBP
977:DBP
185:.
1310::
962::
313:.
261:.
177:,
173:,
1069:)
1059:)
1036:)
1027:(
938:e
931:t
924:v
431:e
424:t
417:v
390:.
368:.
346:.
324:.
101:)
95:(
90:)
86:(
75:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.