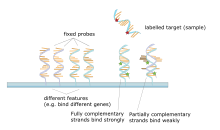1440:
which cluster together can enable the discovery of new groups that otherwise were not previously known to exist. During knowledge discovery analysis, various unsupervised classification techniques can be employed with DNA microarray data to identify novel clusters (classes) of arrays. This type of approach is not hypothesis-driven, but rather is based on iterative pattern recognition or statistical learning methods to find an "optimal" number of clusters in the data. Examples of unsupervised analyses methods include self-organizing maps, neural gas, k-means cluster analyses, hierarchical cluster analysis, Genomic Signal
Processing based clustering and model-based cluster analysis. For some of these methods the user also has to define a distance measure between pairs of objects. Although the Pearson correlation coefficient is usually employed, several other measures have been proposed and evaluated in the literature. The input data used in class discovery analyses are commonly based on lists of genes having high informativeness (low noise) based on low values of the coefficient of variation or high values of Shannon entropy, etc. The determination of the most likely or optimal number of clusters obtained from an unsupervised analysis is called cluster validity. Some commonly used metrics for cluster validity are the silhouette index, Davies-Bouldin index, Dunn's index, or Hubert's
767:, the arrays provide intensity data for each probe or probe set indicating a relative level of hybridization with the labeled target. However, they do not truly indicate abundance levels of a gene but rather relative abundance when compared to other samples or conditions when processed in the same experiment. Each RNA molecule encounters protocol and batch-specific bias during amplification, labeling, and hybridization phases of the experiment making comparisons between genes for the same microarray uninformative. The comparison of two conditions for the same gene requires two separate single-dye hybridizations. Several popular single-channel systems are the Affymetrix "Gene Chip", Illumina "Bead Chip", Agilent single-channel arrays, the Applied Microarrays "CodeLink" arrays, and the Eppendorf "DualChip & Silverquant". One strength of the single-dye system lies in the fact that an aberrant sample cannot affect the raw data derived from other samples, because each array chip is exposed to only one sample (as opposed to a two-color system in which a single low-quality sample may drastically impinge on overall data precision even if the other sample was of high quality). Another benefit is that data are more easily compared to arrays from different experiments as long as batch effects have been accounted for.
641:
resulting "grid" of probes represents the nucleic acid profiles of the prepared probes and is ready to receive complementary cDNA or cRNA "targets" derived from experimental or clinical samples. This technique is used by research scientists around the world to produce "in-house" printed microarrays in their own labs. These arrays may be easily customized for each experiment, because researchers can choose the probes and printing locations on the arrays, synthesize the probes in their own lab (or collaborating facility), and spot the arrays. They can then generate their own labeled samples for hybridization, hybridize the samples to the array, and finally scan the arrays with their own equipment. This provides a relatively low-cost microarray that may be customized for each study, and avoids the costs of purchasing often more expensive commercial arrays that may represent vast numbers of genes that are not of interest to the investigator. Publications exist which indicate in-house spotted microarrays may not provide the same level of sensitivity compared to commercial oligonucleotide arrays, possibly owing to the small batch sizes and reduced printing efficiencies when compared to industrial manufactures of oligo arrays.
1383:
990:
168:
181:
3966:
1726:
1712:
3978:
678:
128:
1271:
22:
164:
washing after hybridization. Total strength of the signal, from a spot (feature), depends upon the amount of target sample binding to the probes present on that spot. Microarrays use relative quantitation in which the intensity of a feature is compared to the intensity of the same feature under a different condition, and the identity of the feature is known by its position.
405:, genomic regions bound by a protein of interest can be isolated and used to probe a microarray to determine binding site occupancy. Unlike ChIP, DamID does not require antibodies but makes use of adenine methylation near the protein's binding sites to selectively amplify those regions, introduced by expressing minute amounts of protein of interest fused to bacterial
586:
652:. Although oligonucleotide probes are often used in "spotted" microarrays, the term "oligonucleotide array" most often refers to a specific technique of manufacturing. Oligonucleotide arrays are produced by printing short oligonucleotide sequences designed to represent a single gene or family of gene splice-variants by
669:
reaction takes place and the next set of probes are unmasked in preparation for a different nucleotide exposure. After many repetitions, the sequences of every probe become fully constructed. More recently, Maskless Array
Synthesis from NimbleGen Systems has combined flexibility with large numbers of probes.
1584:
technology, that enables a whole transcriptome shotgun approach to characterize and quantify gene expression. Unlike microarrays, which need a reference genome and transcriptome to be available before the microarray itself can be designed, RNA-Seq can also be used for new model organisms whose genome
1513:
Dimensional reduction: Analysts often reduce the number of dimensions (genes) prior to data analysis. This may involve linear approaches such as principal components analysis (PCA), or non-linear manifold learning (distance metric learning) using kernel PCA, diffusion maps, Laplacian eigenmaps, local
668:
synthesis (Affymetrix) on a silica substrate where light and light-sensitive masking agents are used to "build" a sequence one nucleotide at a time across the entire array. Each applicable probe is selectively "unmasked" prior to bathing the array in a solution of a single nucleotide, then a masking
1547:
that it is expected to detect is not trivial. Some mRNAs may cross-hybridize probes in the array that are supposed to detect another mRNA. In addition, mRNAs may experience amplification bias that is sequence or molecule-specific. Thirdly, probes that are designed to detect the mRNA of a particular
996:
Within the organisms, genes are transcribed and spliced to produce mature mRNA transcripts (red). The mRNA is extracted from the organism and reverse transcriptase is used to copy the mRNA into stable ds-cDNA (blue). In microarrays, the ds-cDNA is fragmented and fluorescently labelled (orange). The
545:
Multi-stranded DNA and RNA microarrays can be used to identify novel drugs that bind to these multi-stranded nucleic acid sequences. This approach can be used to discover new drugs and biologicals that have the ability to inhibit gene expression. These microarrays also allow for characterization of
1463:
Class prediction analysis: This approach, called supervised classification, establishes the basis for developing a predictive model into which future unknown test objects can be input in order to predict the most likely class membership of the test objects. Supervised analysis for class prediction
1439:
Class discovery analysis: This analytic approach, sometimes called unsupervised classification or knowledge discovery, tries to identify whether microarrays (objects, patients, mice, etc.) or genes cluster together in groups. Identifying naturally existing groups of objects (microarrays or genes)
1365:
as a requirement for the submission of papers incorporating microarray results. But MIAME does not describe the format for the information, so while many formats can support the MIAME requirements, as of 2007 no format permits verification of complete semantic compliance. The "MicroArray
Quality
1321:
There are three main elements to consider when designing a microarray experiment. First, replication of the biological samples is essential for drawing conclusions from the experiment. Second, technical replicates (e.g. two RNA samples obtained from each experimental unit) may help to quantitate
572:
Microarrays can be manufactured in different ways, depending on the number of probes under examination, costs, customization requirements, and the type of scientific question being asked. Arrays from commercial vendors may have as few as 10 probes or as many as 5 million or more micrometre-scale
536:
Left-handed double-stranded Z-DNA microarrays can be used to identify short sequences of the alternative Z-DNA structure located within longer stretches of right-handed B-DNA genes (e.g., transcriptional enhancement, recombination, RNA editing). The microarrays also allow for characterization of
163:
bonding between the two strands. After washing off non-specific bonding sequences, only strongly paired strands will remain hybridized. Fluorescently labeled target sequences that bind to a probe sequence generate a signal that depends on the hybridization conditions (such as temperature), and
527:
Right-handed double-stranded B-DNA microarrays can be used to characterize novel drugs and biologicals that can be employed to bind specific regions of immobilized, intact, double-stranded DNA. This approach can be used to inhibit gene expression. They also allow for characterization of their
715:
5 with a fluorescence emission wavelength of 670 nm (corresponding to the red part of the light spectrum). The two Cy-labeled cDNA samples are mixed and hybridized to a single microarray that is then scanned in a microarray scanner to visualize fluorescence of the two fluorophores after
640:
prior to deposition on the array surface and are then "spotted" onto glass. A common approach utilizes an array of fine pins or needles controlled by a robotic arm that is dipped into wells containing DNA probes and then depositing each probe at designated locations on the array surface. The
1326:
of the same extraction. Third, spots of each cDNA clone or oligonucleotide are present as replicates (at least duplicates) on the microarray slide, to provide a measure of technical precision in each hybridization. It is critical that information about the sample preparation and handling is
2011:
Hacia JG; Fan JB; Ryder O; Jin L; Edgemon K; Ghandour G; Mayer RA; Sun B; Hsie L; Robbins CM; Brody LC; Wang D; Lander ES; Lipshutz R; Fodor SP; Collins FS (1999). "Determination of ancestral alleles for human single-nucleotide polymorphisms using high-density oligonucleotide arrays".
735:
the hybridization measurements for the target probes. Although absolute levels of gene expression may be determined in the two-color array in rare instances, the relative differences in expression among different spots within a sample and between samples is the preferred method of
24:
28:
27:
23:
476:
for a gene. It is of intermediate density, or coverage, to a typical gene expression array (with 1–3 probes per gene) and a genomic tiling array (with hundreds or thousands of probes per gene). It is used to assay the expression of alternative splice forms of a gene.
115:-labeled targets to determine relative abundance of nucleic acid sequences in the target. The original nucleic acid arrays were macro arrays approximately 9 cm × 12 cm and the first computerized image based analysis was published in 1981. It was invented by
1877:
Adomas A; Heller G; Olson A; Osborne J; Karlsson M; Nahalkova J; Van Zyl L; Sederoff R; Stenlid J; Finlay R; Asiegbu FO (2008). "Comparative analysis of transcript abundance in Pinus sylvestris after challenge with a saprotrophic, pathogenic or mutualistic fungus".
38:
The video shows the process of extracting genotypes from a human spit sample using microarrays. Genotyping is a major use of DNA microarrays, but with some modifications they can also be used for other purposes such as measurement of gene expression and epigenetic
29:
1231:
The mixture is denatured and added to the pinholes of the microarray. The holes are sealed and the microarray hybridized, either in a hyb oven, where the microarray is mixed by rotation, or in a mixer, where the microarray is mixed by alternating pressure at the
587:
30:
31:
588:
664:) depending on the desired purpose; longer probes are more specific to individual target genes, shorter probes may be spotted in higher density across the array and are cheaper to manufacture. One technique used to produce oligonucleotide arrays include
2514:
Nuwaysir EF; Huang W; Albert TJ; Singh J; Nuwaysir K; Pitas A; Richmond T; Gorski T; Berg JP; Ballin J; McCormick M; Norton J; Pollock T; Sumwalt T; Butcher L; Porter D; Molla M; Hall C; Blattner F; Sussman MR; Wallace RL; Cerrina F; Green RD (2002).
1464:
involves use of techniques such as linear regression, k-nearest neighbor, learning vector quantization, decision tree analysis, random forests, naive Bayes, logistic regression, kernel regression, artificial neural networks, support vector machines,
2411:
Bammler T, Beyer RP; Consortium, Members of the
Toxicogenomics Research; Kerr, X; Jing, LX; Lapidus, S; Lasarev, DA; Paules, RS; Li, JL; Phillips, SO (2005). "Standardizing global gene expression analysis between laboratories and across platforms".
1244:
The raw data is normalized; the simplest normalization method is to subtract background intensity and scale so that the total intensities of the features of the two channels are equal, or to use the intensity of a reference gene to calculate the
26:
119:. An example of its application is in SNPs arrays for polymorphisms in cardiovascular diseases, cancer, pathogens and GWAS analysis. It is also used for the identification of structural variations and the measurement of gene expression.
1526:
Microarray data may require further processing aimed at reducing the dimensionality of the data to aid comprehension and more focused analysis. Other methods permit analysis of data consisting of a low number of biological or technical
590:
1624:: an experimental design paradigm especially suited to the two-colour array system, in which a condition chosen as control (such as healthy tissue or state) is compared to an altered condition (such as a diseased tissue or state).
1480:. Input data for class prediction are usually based on filtered lists of genes which are predictive of class, determined using classical hypothesis tests (next section), Gini diversity index, or information gain (entropy).
510:
Genome tiling arrays consist of overlapping probes designed to densely represent a genomic region of interest, sometimes as large as an entire human chromosome. The purpose is to empirically detect expression of
1522:
is widely used for identifying co-expression modules and intramodular hub genes. Modules may corresponds to cell types or pathways. Highly connected intramodular hubs best represent their respective modules.
226:
The alternative bead array is a collection of microscopic polystyrene beads, each with a specific probe and a ratio of two or more dyes, which do not interfere with the fluorescent dyes used on the target
1517:
Network-based methods: Statistical methods that take the underlying structure of gene networks into account, representing either associative or causative interactions or dependencies among gene products.
1184:
in two-channel experiments; for a dye flip, a second slide is used, with the labels swapped (the sample that was labeled with Cy3 in the first slide is labeled with Cy5, and vice versa). In this example,
1413:
of the data. Normalization methods may be suited to specific platforms and, in the case of commercial platforms, the analysis may be proprietary. Algorithms that affect statistical analysis include:
2984:
Ben Gal, I.; Shani, A.; Gohr, A.; Grau, J.; Arviv, S.; Shmilovici, A.; Posch, S.; Grosse, I. (2005). "Identification of transcription factor binding sites with variable-order
Bayesian networks".
196:
The traditional solid-phase array is a collection of orderly microscopic "spots", called features, each with thousands of identical and specific probes attached to a solid surface, such as
1001:
across the array indicates the abundance of a predetermined set of sequences. These sequences are typically specifically chosen to report on genes of interest within the organism's genome.
2350:
J Biochem
Biophys Methods. 2000 Mar 16;42(3):105–10. DNA-printing: utilization of a standard inkjet printer for the transfer of nucleic acids to solid supports. Goldmann T, Gonzalez JS.
2295:
25:
3982:
1370:(FDA) to develop standards and quality control metrics which will eventually allow the use of MicroArray data in drug discovery, clinical practice and regulatory decision-making. The
289:, and developmental stages on gene expression. For example, microarray-based gene expression profiling can be used to identify genes whose expression is changed in response to
3163:
Wouters L; Gõhlmann HW; Bijnens L; Kass SU; Molenberghs G; Lewi PJ (2003). "Graphical exploration of gene expression data: a comparative study of three multivariate methods".
2060:
Gagna, Claude E.; Lambert, W. Clark (1 May 2009). "Novel multistranded, alternative, plasmid and helical transitional DNA and RNA microarrays: implications for therapeutics".
589:
481:
have a different design, employing probes designed to detect each individual exon for known or predicted genes, and can be used for detecting different splicing isoforms.
790:
samples need to be compared: then the number of experiments required using the two channel arrays quickly becomes unfeasible, unless a sample is used as a reference.
1424:
Data processing: background subtraction (based on global or local background), determination of spot intensities and intensity ratios, visualisation of data (e.g. see
950:
1842:
Taub, Floyd (1983). "Laboratory methods: Sequential comparative hybridizations analyzed by computerized image processing can identify and quantitate regulated RNAs".
1458:
1221:
724:
beam of a defined wavelength. Relative intensities of each fluorophore may then be used in ratio-based analysis to identify up-regulated and down-regulated genes.
1564:), and curation efforts associated with the datasets require specialized databases to store the data. A number of open-source data warehousing solutions, such as
977:
1009:
which includes details for a particular case to better explain DNA microarray experiments, while listing modifications for RNA or other alternative experiments.
500:
microarrays. The oligo design strategy enables combined measurements of chimeric transcript junctions with exon-wise measurements of individual fusion partners.
1417:
Image analysis: gridding, spot recognition of the scanned image (segmentation algorithm), removal or marking of poor-quality and low-intensity features (called
1282:
The advent of inexpensive microarray experiments created several specific bioinformatics challenges: the multiple levels of replication in experimental design (
906:
885:
788:
1339:
Microarray data is difficult to exchange due to the lack of standardization in platform fabrication, assay protocols, and analysis methods. This presents an
1139:
The labeling can be direct (not used) or indirect (requires a coupling stage). For two-channel arrays, the coupling stage occurs before hybridization, using
468:
3306:
Mortazavi, Ali; Brian A Williams; Kenneth McCue; Lorian
Schaeffer; Barbara Wold (July 2008). "Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq".
1065:
1663:: an instrument used to detect and quantify the intensity of fluorescence of spots on a microarray slide, by selectively exciting fluorophores with a
1506:. These methods assess statistical power based on the variation present in the data and the number of experimental replicates, and can help minimize
1962:"Comparative genomics using Candida albicans DNA microarrays reveals absence and divergence of virulence-associated genes in Candida dubliniensis"
4580:
1792:
1483:
Hypothesis-driven statistical analysis: Identification of statistically significant changes in gene expression are commonly identified using the
1114:
microarrays ligate an oligonucleotide to the purified small RNA (isolated with a fractionator), which is then reverse transcribed and amplified.
308:
3467:
1177:
contains amine groups). The aminoallyl group is an amine group on a long linker attached to the nucleobase, which reacts with a reactive dye.
4464:
1560:
Microarray data was found to be more useful when compared to other similar datasets. The sheer volume of data, specialized formats (such as
1169:)) are added enzymatically in a low ratio to normal nucleotides, typically resulting in 1 every 60 bases. The aaDNA is then purified with a
2729:
478:
396:
3458:
3544:
2299:
656:
this sequence directly onto the array surface instead of depositing intact sequences. Sequences may be longer (60-mer probes such as the
3507:
3257:
Barbosa-Morais, N. L.; Dunning, M. J.; Samarajiwa, S. A.; Darot, J. F. J.; Ritchie, M. E.; Lynch, A. G.; Tavare, S. (18 November 2009).
699:
with cDNA prepared from two samples to be compared (e.g. diseased tissue versus healthy tissue) and that are labeled with two different
2108:
Gagna, Claude E.; Clark
Lambert, W. (1 March 2007). "Cell biology, chemogenomics and chemoproteomics – application to drug discovery".
1386:
1080:
1238:
The microarray is dried and scanned by a machine that uses a laser to excite the dye and measures the emission levels with a detector.
753:
3476:
4016:
3026:
Yuk Fai Leung and Duccio
Cavalieri, Fundamentals of cDNA microarray data analysis. Trends in Genetics Vol.19 No.11 November 2003.
2974:
Bolshakova N, Azuaje F (2003) Cluster validation techniques for genome expression data, Signal
Processing, Vol. 83, pp. 825–833.
1072:) which isolates most RNA (whereas column methods have a cut off of 200 nucleotides) and if done correctly has a better purity.
192:
Many types of arrays exist and the broadest distinction is whether they are spatially arranged on a surface or on coded beads:
1213:
4595:
3147:
2899:
2607:"Expression ratio evaluation in two-colour microarray experiments is significantly improved by correcting image misalignment"
1519:
3496:
711:
3, which has a fluorescence emission wavelength of 570 nm (corresponding to the green part of the light spectrum), and
605:
Microarrays can be fabricated using a variety of technologies, including printing with fine-pointed pins onto glass slides,
1787:
3569:
1314:
Due to the biological complexity of gene expression, the considerations of experimental design that are discussed in the
1170:
148:
3449:
327:
3888:
3591:
2838:
1745:
1604:
3218:"Local-pooled-error test for identifying differentially expressed genes with a small number of replicated microarrays"
1913:
Pollack JR; Perou CM; Alizadeh AA; Eisen MB; Pergamenschikov A; Williams CF; Jeffrey SS; Botstein D; Brown PO (1999).
1318:
article are of critical importance if statistically and biologically valid conclusions are to be drawn from the data.
3880:
3820:
1690:
298:
232:
96:
1572:, have been created for the specific purpose of integrating diverse biological datasets, and also support analysis.
1241:
The image is gridded with a template and the intensities of each feature (composed of several pixels) is quantified.
1117:
The label is added either during the reverse transcription step, or following amplification if it is performed. The
107:) under high-stringency conditions. Probe-target hybridization is usually detected and quantified by detection of
4489:
4285:
3942:
3825:
3537:
3420:
2914:
De Souto M et al. (2008) Clustering cancer gene expression data: a comparative study, BMC Bioinformatics, 9(497).
1327:
discussed, in order to help identify the independent units in the experiment and to avoid inflated estimates of
2273:
Rasheed, Awais; Hao, Yuanfeng; Xia, Xianchun; Khan, Awais; Xu, Yunbi; Varshney, Rajeev K.; He, Zhonghu (2017).
1762:
1405:
Microarray data sets are commonly very large, and analytical precision is influenced by a number of variables.
1394:
1374:
has developed standards for the representation of gene expression experiment results and relevant annotations.
420:
243:) that may or may not be translated into proteins. The process of measuring gene expression via cDNA is called
4401:
4378:
3947:
3937:
3924:
2410:
1049:
364:
356:
4575:
4234:
3564:
2566:"A DNA microarray system for analyzing complex DNA samples using two-color fluorescent probe hybridization"
1740:
1367:
1322:
precision. The biological replicates include independent RNA extractions. Technical replicates may be two
4009:
3485:
3439:
2291:
1695:
1473:
1013:
The two samples to be compared (pairwise comparison) are grown/acquired. In this example treated sample (
363:) allowing the determination of protein binding site occupancy throughout the genome. Example protein to
3259:"A re-annotation pipeline for Illumina BeadArrays: improving the interpretation of gene expression data"
1323:
427:
within or between populations. Several applications of microarrays make use of SNP detection, including
3970:
3530:
1410:
1197:
732:
136:
4305:
1382:
285:
levels of thousands of genes are simultaneously monitored to study the effects of certain treatments,
4265:
4186:
4076:
2889:
1507:
1118:
1099:
1076:
1041:
682:
653:
637:
629:
621:
338:
303:
Assessing genome content in different cells or closely related organisms, as originally described by
278:
268:
3513:
PNAS Commentary: Discovery of Principles of Nature from Mathematical Modeling of DNA Microarray Data
3177:
293:
or other organisms by comparing gene expression in infected to that in uninfected cells or tissues.
4590:
4565:
4534:
4166:
2792:
1528:
1354:
projects are trying to ease the exchange and analysis of data produced with non-proprietary chips:
1328:
1133:
388:
4570:
4529:
4396:
4270:
3609:
1821:
1628:
1535:
of genes with similar expression levels in an effort to compensate for insufficient replication.
1477:
1162:
376:
2830:
2768:
147:
The core principle behind microarrays is hybridization between two DNA strands, the property of
4002:
3172:
2274:
1657:: reciprocal labelling of DNA targets with the two dyes to account for dye bias in experiments.
1618:: a group of spots, typically made in one print round; several subarrays/ blocks form an array.
1549:
1201:
1166:
648:, the probes are short sequences designed to match parts of the sequence of known or predicted
609:
using pre-made masks, photolithography using dynamic micromirror devices, ink-jet printing, or
599:
448:
436:
372:
1468:, and supervised neural gas. In addition, various metaheuristic methods are employed, such as
912:
4338:
4146:
3768:
3763:
3705:
3619:
2517:"Gene Expression Analysis Using Oligonucleotide Arrays Produced by Maskless Photolithography"
1495:
1443:
1432:
normalization of intensity ratios, and segmentation into different copy number regions using
1095:
240:
1361:) checklist helps define the level of detail that should exist and is being adopted by many
1102:
amplification. The RNA is reverse transcribed with either polyT primers (which amplify only
564:
at early stages to lower the number of unneeded seedlings tried out in breeding operations.
4600:
4494:
4368:
4280:
4116:
4106:
3868:
3725:
3574:
3517:
2468:
2362:"POSaM: a fast, flexible, open-source, inkjet oligonucleotide synthesizer and microarrayer"
1811:
1767:
1499:
1315:
1150:
1087:). If the material is of acceptable quality and sufficient quantity is present (e.g., >1
1033:
516:
497:
460:
248:
223:). Thousands of these features can be placed in known locations on a single DNA microarray.
55:) is a collection of microscopic DNA spots attached to a solid surface. Scientists use DNA
4406:
1091:, although the required amount varies by microarray platform), the experiment can proceed.
8:
4514:
4441:
4436:
4358:
4333:
4300:
4161:
3737:
3732:
3710:
3656:
2605:
Tang T; François N; Glatigny A; Agier N; Mucchielli MH; Aggerbeck L; Delacroix H (2007).
1121:
labeling is dependent on the microarray; e.g. if the label is added with the RT mix, the
956:
745:
352:
312:
77:
2804:
2472:
1257:
and RMA (robust multichip analysis) for Affymetrix chips (single-channel, silicon chip,
1125:
is antisense and the microarray probe is sense, except in the case of negative controls.
542:
Multi-stranded DNA microarrays (triplex-DNA microarrays and quadruplex-DNA microarrays)
4421:
4343:
4091:
4081:
3512:
3394:
3361:
3339:
3283:
3258:
3198:
3064:
3037:
2952:
2925:
2860:
2760:
2437:
2333:
2250:
2217:
2193:
2160:
2141:
2037:
1942:
1782:
1532:
1465:
1400:
1362:
891:
870:
773:
649:
557:
3305:
3115:
3088:
2541:
2516:
2388:
2361:
2275:"Crop Breeding Chips and Genotyping Platforms: Progress, Challenges, and Perspectives"
1235:
After an overnight hybridization, all nonspecific binding is washed off (SDS and SSC).
731:. The degree of hybridization between the spike-ins and the control probes is used to
4499:
4469:
4426:
4363:
4348:
4260:
4151:
3909:
3553:
3399:
3381:
3343:
3331:
3323:
3288:
3239:
3190:
3186:
3143:
3120:
3069:
3009:
3001:
2957:
2895:
2865:
2752:
2710:
2669:
2628:
2587:
2546:
2496:
2491:
2456:
2441:
2429:
2393:
2325:
2317:
2255:
2237:
2198:
2180:
2133:
2125:
2085:
2077:
2029:
1993:
1934:
1895:
1859:
1731:
1469:
1351:
696:
665:
444:
384:
112:
3434:
3234:
3217:
3202:
3089:"Sample size for detecting differentially expressed genes in microarray experiments"
2997:
2764:
2623:
2606:
2337:
2145:
2041:
1158:
4290:
4275:
4045:
3389:
3373:
3315:
3278:
3270:
3229:
3182:
3110:
3100:
3059:
3049:
2993:
2947:
2937:
2855:
2847:
2744:
2700:
2659:
2618:
2577:
2536:
2528:
2486:
2476:
2421:
2383:
2373:
2307:
2245:
2229:
2188:
2172:
2117:
2069:
2021:
1983:
1973:
1926:
1887:
1851:
1503:
1429:
1409:
challenges include taking into account effects of background noise and appropriate
1340:
1254:
1181:
1157:); for single-channel arrays, the coupling stage occurs after hybridization, using
997:
labelled fragments bind to an ordered array of complementary oligonucleotides, and
610:
606:
472:
design uses probes specific to the expected or potential splice sites of predicted
304:
159:. A high number of complementary base pairs in a nucleotide sequence means tighter
116:
3038:"Evaluation of gene-expression clustering via mutual information distance measure"
1946:
727:
Oligonucleotide microarrays often carry control probes designed to hybridize with
4484:
4479:
4328:
4224:
4201:
4196:
4181:
4176:
4171:
4131:
4101:
3873:
3599:
2282:
2176:
1816:
1684:: a small area on an array slide that contains picomoles of specific DNA samples.
1671:
1492:
452:
406:
282:
244:
87:
60:
1891:
4446:
4411:
3855:
3815:
2942:
2926:"On the selection of appropriate distances for gene expression data clustering"
2312:
1717:
1433:
1344:
1060:
or regulation studies. In this example total RNA is isolated (both nuclear and
2705:
2688:
1914:
740:
for the two-color system. Examples of providers for such microarrays includes
4559:
4353:
4310:
4216:
4191:
4086:
3914:
3805:
3720:
3385:
3327:
3005:
2714:
2689:"The challenges of gene expression microarrays for the study of human cancer"
2673:
2321:
2241:
2184:
2129:
2121:
2081:
1806:
1797:
737:
717:
152:
4156:
3491:
3054:
2664:
2647:
2481:
2378:
1180:
A form of replicate known as a dye flip can be performed to control for dye
989:
167:
4585:
4519:
4474:
4431:
4121:
4096:
4050:
3850:
3758:
3753:
3403:
3335:
3292:
3243:
3194:
3124:
3105:
3073:
3013:
2961:
2869:
2851:
2756:
2632:
2550:
2433:
2397:
2329:
2259:
2202:
2137:
2089:
2033:
1997:
1938:
1899:
1855:
1776:
1633:
1608:
spatially arranged in a two dimensional grid, arranged in columns and rows.
1371:
1146:
1084:
1053:
1025:
1018:
1014:
728:
704:
505:
360:
346:
160:
2591:
2500:
2161:"Triplex technology in studies of DNA damage, DNA repair, and mutagenesis"
1978:
1961:
1863:
770:
One channel microarray may be the only choice in some situations. Suppose
4544:
4509:
4229:
4111:
3932:
3661:
3274:
2233:
1801:
1652:
1637:
1348:
1274:
Gene expression values from microarray experiments can be represented as
1225:
1129:
1057:
998:
749:
700:
486:
380:
108:
72:
3459:
Micro Scale Products and Services for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
2831:"Generalized Methods and Solvers for Piecewise Constant Signals: Part I"
2457:"Light-generated oligonucleotide arrays for rapid DNA sequence analysis"
1915:"Genome-wide analysis of DNA copy-number changes using cDNA microarrays"
1580:
Advances in massively parallel sequencing has led to the development of
180:
4539:
4504:
4373:
4141:
4136:
3994:
3688:
3683:
3678:
3319:
2582:
2565:
2455:
Pease AC; Solas D; Sullivan EJ; Cronin MT; Holmes CP; Fodor SP (1994).
1514:
linear embedding, locally preserving projections, and Sammon's mapping.
1406:
1186:
1140:
661:
428:
330:
156:
151:
nucleic acid sequences to specifically pair with each other by forming
64:
56:
2532:
2073:
1357:
For example, the "Minimum Information About a Microarray Experiment" (
3715:
2425:
1988:
1912:
1565:
1061:
414:
359:), these fragments can be then hybridized to a microarray (such as a
334:
290:
3522:
3377:
3256:
3162:
1960:
Moran G; Stokes C; Thewes S; Hube B; Coleman DC; Sullivan D (2004).
677:
496:
from cancer specimens. The principle behind this is building on the
4524:
4295:
4071:
4066:
3778:
3773:
3666:
2748:
2454:
2303:
1757:
1711:
1668:
1286:); the number of platforms and independent groups and data format (
1275:
1111:
561:
440:
432:
368:
323:
Small microarrays to check IDs of organisms in food and feed (like
3504: – a free web-server for online microarray analysis
2513:
1930:
1725:
1498:
methods tailored to microarray data sets, which take into account
1165:. The modified nucleotides (usually in a ratio of 1 aaUTP: 4 TTP (
4244:
3884:
3859:
3834:
3830:
3810:
3623:
3216:
Jain N; Thatte J; Braciale T; Ley K; O'Connell M; Lee JK (2003).
2924:
Jaskowiak, Pablo A; Campello, Ricardo JGB; Costa, Ivan G (2014).
2604:
2025:
1772:
1750:
1581:
1569:
1425:
1250:
1246:
1209:
1205:
1154:
1143:
1045:
741:
712:
708:
657:
424:
286:
208:
205:
201:
52:
2687:
Tinker, Anna V.; Boussioutas, Alex; Bowtell, David D.L. (2006).
1876:
4320:
4126:
3695:
3673:
3480:
3471:
3462:
3453:
3359:
1484:
1249:
for all of the intensities. More sophisticated methods include
1069:
351:
DNA sequences bound to a particular protein can be isolated by
16:
Collection of microscopic DNA spots attached to a solid surface
4239:
4206:
4040:
4025:
3897:
3501:
3215:
3035:
1959:
1664:
1561:
1488:
1358:
1217:
1106:) or random primers (which amplify all RNA, most of which is
721:
595:
197:
185:
68:
1088:
127:
3700:
3360:
Wang, Zhong; Mark Gerstein; Michael Snyder (January 2009).
3137:
1552:
information that is incorrectly associated with that gene.
1544:
1295:
1174:
1122:
1107:
1103:
633:
625:
553:
512:
473:
402:
274:
236:
100:
92:
2730:"Fundamentals of experimental design for cDNA microarrays"
2507:
2010:
1270:
546:
their structure under different environmental conditions.
537:
their structure under different environmental conditions.
3613:
3603:
1302:); the sheer volume of data and the ability to share it (
1037:
1029:
576:
560:
applications. In the future they could be used to screen
324:
48:
2686:
2563:
672:
492:
A fusion gene microarray can detect fusion transcripts,
2159:
Mukherjee, Anirban; Vasquez, Karen M. (1 August 2011).
1531:; for example, the Local Pooled Error (LPE) test pools
519:
which may not have been previously known or predicted.
2923:
2218:"G-quadruplexes and their regulatory roles in biology"
1196:
The labeled samples are then mixed with a proprietary
63:
levels of large numbers of genes simultaneously or to
3086:
1446:
1366:
Control (MAQC) Project" is being conducted by the US
959:
915:
894:
873:
776:
103:
or cRNA (also called anti-sense RNA) sample (called
67:
multiple regions of a genome. Each DNA spot contains
3140:
Analysis of Microarray Data A Network-Based Approach
2983:
1707:
1066:
guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction
528:
structure under different environmental conditions.
439:
to disease, identifying drug-candidates, evaluating
3362:"RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics"
2404:
2216:Rhodes, Daniela; Lipps, Hans J. (15 October 2015).
1189:-UTP is present in the reverse-transcribed mixture.
2266:
2107:
1452:
971:
944:
900:
879:
782:
2887:
2828:
2272:
1636:output recorded in the scanner for an individual
1265:
994:Examples of levels of application of microarrays.
231:DNA microarrays can be used to detect DNA (as in
4557:
2977:
2793:NCTR Center for Toxicoinformatics – MAQC Project
2158:
2448:
2103:
2101:
2099:
2055:
2053:
2051:
1793:Methylation specific oligonucleotide microarray
1428:), and log-transformation of ratios, global or
748:with their DualChip platform for colorimetric
660:design) or shorter (25-mer probes produced by
4465:Conservation and restoration of glass objects
4010:
3538:
3299:
2557:
1906:
1775:dyes, such as Cy3 and Cy5, are commonly used
1075:The purified RNA is analysed for quality (by
707:dyes commonly used for cDNA labeling include
171:The steps required in a microarray experiment
3477:Online Services for Gene Expression Analysis
2096:
2059:
2048:
1870:
1520:Weighted gene co-expression network analysis
188:is shown at bottom left for size comparison.
3355:
3353:
3138:Emmert-Streib, F. & Dehmer, M. (2008).
3029:
2883:
2881:
2879:
2648:"Eukaryotic and prokaryotic gene structure"
2598:
2215:
2004:
1953:
1575:
4017:
4003:
3545:
3531:
3036:Priness I.; Maimon O.; Ben-Gal I. (2007).
2891:Classification Analysis of DNA Microarrays
2645:
1387:National Center for Toxicological Research
1290:); the statistical treatment of the data (
752:labeling, and TeleChem International with
552:Specialised arrays tailored to particular
3468:Products and Services for Gene Expression
3393:
3282:
3233:
3176:
3114:
3104:
3063:
3053:
2951:
2941:
2859:
2727:
2704:
2663:
2622:
2581:
2540:
2490:
2480:
2387:
2377:
2359:
2311:
2249:
2192:
1987:
1977:
1278:to visualize the result of data analysis.
4024:
3492:PLoS Biology Primer: Microarray Analysis
3350:
2876:
1381:
1283:
1269:
1079:) and quantity (for example, by using a
988:
806:two channel microarray (with reference)
676:
584:
337:for disease detection, mostly combining
179:
166:
131:Hybridization of the target to the probe
126:
20:
1173:(using a phosphate buffer solution, as
142:
75:) of a specific DNA sequence, known as
36:How to use a microarray for genotyping.
4581:Glass coating and surface modification
4558:
3131:
1667:and measuring the fluorescence with a
1309:
95:or other DNA element that are used to
3998:
3552:
3526:
2564:Shalon D; Smith SJ; Brown PO (1996).
1543:The relation between a probe and the
1472:, covariance matrix self-adaptation,
1303:
1216:, salmon sperm DNA, calf thymus DNA,
1094:The labeled product is generated via
1028:of interest is purified: this can be
984:
673:Two-channel vs. one-channel detection
556:are becoming increasingly popular in
347:Chromatin immunoprecipitation on Chip
91:). These can be a short section of a
2646:Shafee, Thomas; Lowe, Rohan (2017).
1841:
1788:Significance analysis of microarrays
1287:
1261:synthesized short oligonucleotides).
999:measurement of fluorescent intensity
594:A DNA microarray being printed by a
3977:
3080:
1835:
1555:
1044:, or DNA/RNA bound to a particular
235:), or detect RNA (most commonly as
13:
3087:Wei C; Li J; Bumgarner RE (2004).
2839:Proceedings of the Royal Society A
2829:Little, M.A.; Jones, N.S. (2011).
1746:Serial analysis of gene expression
1447:
1389:scientist reviews microarray data.
1334:
1291:
533:Double-stranded Z-DNA microarrays
524:Double-stranded B-DNA microarrays
14:
4612:
3821:Post-transcriptional modification
3518:DNA microarray virtual experiment
3414:
1691:Glossary of gene expression terms
299:Comparative genomic hybridization
233:comparative genomic hybridization
175:
3976:
3965:
3964:
3497:Rundown of microarray technology
3187:10.1111/j.0006-341X.2003.00130.x
2110:Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery
1724:
1710:
1377:
447:mutations in cancers, assessing
4535:Radioactive waste vitrification
4490:Glass fiber reinforced concrete
3826:Post-translational modification
3250:
3209:
3156:
3020:
2968:
2917:
2908:
2822:
2805:"Prosigna | Prosigna algorithm"
2797:
2786:
2721:
2680:
2639:
2360:Lausted C; et al. (2004).
2353:
2344:
1548:gene may be relying on genomic
1299:
1149:(aminoallyl-UTP, or aaUTP) and
744:with their Dual-Mode platform,
681:Diagram of typical dual-colour
3508:Microarray – How does it work?
2209:
2152:
1763:Microarray analysis techniques
1687:For other relevant terms see:
1395:Microarray analysis techniques
1266:Microarrays and bioinformatics
1200:solution which can consist of
931:
919:
567:
421:single nucleotide polymorphism
1:
4402:Chemically strengthened glass
3948:Post-translational regulation
3235:10.1093/bioinformatics/btg264
2998:10.1093/bioinformatics/bti410
2624:10.1093/bioinformatics/btm399
1828:
1538:
1298:transcript that it measures (
1294:); mapping each probe to the
1153:amino-reactive dyes (such as
407:DNA adenine methyltransferase
4596:Molecular biology techniques
4235:Glass-ceramic-to-metal seals
3896:High-throughput technique ("
3440:Resources in other libraries
2177:10.1016/j.biochi.2011.04.001
1741:Transcriptomics technologies
1640:and can even be ultraviolet.
1585:has not been sequenced yet.
1368:Food and Drug Administration
1212:, a blocking agent (such as
1098:and followed by an optional
632:products that correspond to
443:mutations in individuals or
122:
7:
3774:Functional biology/medicine
1703:
1696:Protocol (natural sciences)
1588:
1474:particle swarm optimization
1255:loess and lowess regression
646:oligonucleotide microarrays
517:alternatively spliced forms
375:(PRC2:Suz12, PRC1:YY1) and
371:, H3K4me2, H3K9me3, etc.),
367:are histone modifications (
341:and microarray technology.
10:
4617:
2943:10.1186/1471-2105-15-S2-S2
2888:Peterson, Leif E. (2013).
2313:10.1016/j.molp.2017.06.008
1398:
1392:
761:single-channel microarrays
613:on microelectrode arrays.
260:Application or technology
140:
137:Nucleic acid hybridization
134:
4455:
4387:
4319:
4266:Chemical vapor deposition
4253:
4215:
4187:Ultra low expansion glass
4077:Borophosphosilicate glass
4059:
4033:
3960:
3923:
3843:
3798:
3791:
3746:
3633:
3590:
3583:
3560:
3435:Resources in your library
2706:10.1016/j.ccr.2006.05.001
1892:10.1093/treephys/28.6.885
1508:type I and type II errors
1077:capillary electrophoresis
1042:comparative hybridization
1007:DNA microarray experiment
279:gene expression profiling
269:Gene expression profiling
143:§ A typical protocol
4505:Glass-reinforced plastic
4167:Sodium hexametaphosphate
2122:10.1517/17460441.2.3.381
1576:Alternative technologies
1329:statistical significance
1132:; only one machine uses
1017:) and untreated sample (
1005:This is an example of a
945:{\displaystyle i(i-1)/2}
184:Two Affymetrix chips. A
47:(also commonly known as
4397:Anti-reflective coating
4271:Glass batch calculation
4152:Photochromic lens glass
3055:10.1186/1471-2105-8-111
2894:. John Wiley and Sons.
2652:WikiJournal of Medicine
2482:10.1073/pnas.91.11.5022
2379:10.1186/gb-2004-5-8-r58
1822:Whole genome sequencing
1478:ant colony optimization
1453:{\displaystyle \Gamma }
1128:The label is typically
802:two channel microarray
799:one-channel microarray
693:two-channel microarrays
389:transcription landscape
377:trithorax-group protein
3263:Nucleic Acids Research
3106:10.1186/1471-2164-5-87
2852:10.1098/rspa.2010.0671
2728:Churchill, GA (2002).
2222:Nucleic Acids Research
1856:10.1089/dna.1983.2.309
1454:
1390:
1279:
1167:thymidine triphosphate
1002:
973:
946:
902:
881:
784:
685:
628:or small fragments of
602:
600:University of Delaware
449:loss of heterozygosity
373:Polycomb-group protein
254:Applications include:
189:
172:
155:between complementary
132:
40:
4530:Prince Rupert's drops
4379:Transparent materials
4339:Gradient-index optics
4147:Phosphosilicate glass
3769:Developmental biology
3764:Computational biology
2665:10.15347/wjm/2017.002
2300:Shanghai Inst Bio Sci
1979:10.1099/mic.0.27221-0
1455:
1385:
1273:
1096:reverse transcription
992:
974:
947:
903:
882:
785:
765:one-color microarrays
689:Two-color microarrays
683:microarray experiment
680:
593:
241:reverse transcription
211:(commonly known as a
183:
170:
157:nucleotide base pairs
141:Further information:
130:
34:
4495:Glass ionomer cement
4369:Photosensitive glass
4296:Liquidus temperature
4117:Fluorosilicate glass
3943:Post-transcriptional
3486:Microarray Animation
1972:(Pt 10): 3363–3382.
1812:Phenotype microarray
1768:Microarray databases
1500:multiple comparisons
1444:
1316:expression profiling
1034:expression profiling
957:
913:
892:
871:
774:
498:alternative splicing
461:Alternative splicing
435:analysis, measuring
381:epigenetic landscape
379:(Ash1) to study the
333:in cell culture, or
307:, Jonathan Pollack,
249:expression profiling
4576:Genetics techniques
4515:Glass-to-metal seal
4437:Self-cleaning glass
4359:Optical lens design
3738:Histone methylation
2846:(2135): 3088–3114.
2473:1994PNAS...91.5022P
1602:is a collection of
1533:standard deviations
1310:Experimental design
1284:Experimental design
1222:Denhardt's solution
972:{\displaystyle i-1}
650:open reading frames
618:spotted microarrays
469:exon junction array
353:immunoprecipitating
245:expression analysis
4500:Glass microspheres
4422:Hydrogen darkening
4344:Hydrogen darkening
4092:Chalcogenide glass
4082:Borosilicate glass
3320:10.1038/nmeth.1226
3275:10.1093/nar/gkp942
3042:BMC Bioinformatics
2930:BMC Bioinformatics
2583:10.1101/gr.6.7.639
2296:Chin Soc Plant Bio
2234:10.1093/nar/gkv862
1783:Gene chip analysis
1470:genetic algorithms
1466:mixture of experts
1450:
1401:Gene chip analysis
1391:
1280:
1083:or NanoPhotometer
1050:immunoprecipitated
1003:
985:A typical protocol
969:
942:
898:
877:
796:number of samples
780:
686:
603:
581:synthesised arrays
558:molecular breeding
311:and colleagues at
190:
173:
133:
41:
4553:
4552:
4470:Glass-coated wire
4442:sol–gel technique
4427:Insulated glazing
4364:Photochromic lens
4349:Optical amplifier
4301:sol–gel technique
3992:
3991:
3971:Molecular biology
3956:
3955:
3910:Mass spectrometry
3787:
3786:
3554:Molecular biology
3421:Library resources
3228:(15): 1945–1951.
3149:978-3-527-31822-3
2992:(11): 2657–2666.
2901:978-0-470-17081-6
2617:(20): 2686–2691.
2533:10.1101/gr.362402
2527:(11): 1749–1755.
2467:(11): 5022–5026.
2228:(18): 8627–8637.
2074:10.2217/pgs.09.27
1732:Technology portal
1496:Mann–Whitney test
982:
981:
901:{\displaystyle i}
880:{\displaystyle i}
783:{\displaystyle i}
666:photolithographic
636:. The probes are
620:, the probes are
591:
550:
549:
385:RNA polymerase II
365:immunoprecipitate
113:chemiluminescence
32:
4608:
4291:Ion implantation
4046:Glass transition
4019:
4012:
4005:
3996:
3995:
3980:
3979:
3968:
3967:
3901:
3796:
3795:
3649:
3644:
3588:
3587:
3547:
3540:
3533:
3524:
3523:
3408:
3407:
3397:
3357:
3348:
3347:
3303:
3297:
3296:
3286:
3254:
3248:
3247:
3237:
3213:
3207:
3206:
3180:
3171:(4): 1131–1139.
3160:
3154:
3153:
3135:
3129:
3128:
3118:
3108:
3084:
3078:
3077:
3067:
3057:
3033:
3027:
3024:
3018:
3017:
2981:
2975:
2972:
2966:
2965:
2955:
2945:
2921:
2915:
2912:
2906:
2905:
2885:
2874:
2873:
2863:
2835:
2826:
2820:
2819:
2817:
2815:
2801:
2795:
2790:
2784:
2783:
2781:
2779:
2773:
2767:. Archived from
2734:
2725:
2719:
2718:
2708:
2684:
2678:
2677:
2667:
2643:
2637:
2636:
2626:
2602:
2596:
2595:
2585:
2561:
2555:
2554:
2544:
2511:
2505:
2504:
2494:
2484:
2452:
2446:
2445:
2426:10.1038/nmeth754
2408:
2402:
2401:
2391:
2381:
2357:
2351:
2348:
2342:
2341:
2315:
2279:
2270:
2264:
2263:
2253:
2213:
2207:
2206:
2196:
2171:(8): 1197–1208.
2156:
2150:
2149:
2105:
2094:
2093:
2062:Pharmacogenomics
2057:
2046:
2045:
2008:
2002:
2001:
1991:
1981:
1957:
1951:
1950:
1910:
1904:
1903:
1874:
1868:
1867:
1839:
1779:with microarrays
1734:
1729:
1728:
1720:
1715:
1714:
1556:Data warehousing
1510:in the analyses.
1504:cluster analysis
1459:
1457:
1456:
1451:
1341:interoperability
1304:Data warehousing
978:
976:
975:
970:
951:
949:
948:
943:
938:
907:
905:
904:
899:
886:
884:
883:
878:
793:
792:
789:
787:
786:
781:
622:oligonucleotides
611:electrochemistry
607:photolithography
592:
257:
256:
117:Patrick O. Brown
33:
4616:
4615:
4611:
4610:
4609:
4607:
4606:
4605:
4591:Microtechnology
4566:Gene expression
4556:
4555:
4554:
4549:
4485:Glass electrode
4480:Glass databases
4457:
4451:
4389:
4383:
4315:
4249:
4225:Bioactive glass
4211:
4197:Vitreous enamel
4182:Thoriated glass
4177:Tellurite glass
4162:Soda–lime glass
4132:Gold ruby glass
4102:Cranberry glass
4055:
4029:
4023:
3993:
3988:
3952:
3925:Gene regulation
3919:
3895:
3856:Model organisms
3839:
3816:Cell signalling
3783:
3742:
3647:
3642:
3629:
3600:DNA replication
3579:
3556:
3551:
3502:ArrayMining.net
3450:Gene Expression
3446:
3445:
3444:
3429:
3428:
3426:DNA microarrays
3424:
3417:
3412:
3411:
3378:10.1038/nrg2484
3358:
3351:
3304:
3300:
3255:
3251:
3214:
3210:
3178:10.1.1.730.3670
3161:
3157:
3150:
3136:
3132:
3085:
3081:
3034:
3030:
3025:
3021:
2982:
2978:
2973:
2969:
2936:(Suppl 2): S2.
2922:
2918:
2913:
2909:
2902:
2886:
2877:
2833:
2827:
2823:
2813:
2811:
2803:
2802:
2798:
2791:
2787:
2777:
2775:
2771:
2737:Nature Genetics
2732:
2726:
2722:
2685:
2681:
2644:
2640:
2603:
2599:
2562:
2558:
2512:
2508:
2453:
2449:
2409:
2405:
2358:
2354:
2349:
2345:
2283:Molecular Plant
2277:
2271:
2267:
2214:
2210:
2157:
2153:
2106:
2097:
2058:
2049:
2009:
2005:
1958:
1954:
1911:
1907:
1875:
1871:
1840:
1836:
1831:
1826:
1817:Systems biology
1730:
1723:
1716:
1709:
1706:
1672:photomultiplier
1669:filter (optics)
1591:
1578:
1558:
1541:
1493:Bayesian method
1445:
1442:
1441:
1403:
1397:
1380:
1337:
1335:Standardization
1312:
1288:Standardization
1268:
1210:dextran sulfate
987:
958:
955:
954:
934:
914:
911:
910:
893:
890:
889:
872:
869:
868:
775:
772:
771:
675:
585:
583:
570:
453:genetic linkage
401:Analogously to
281:experiment the
178:
145:
139:
125:
111:-, silver-, or
59:to measure the
21:
17:
12:
11:
5:
4614:
4604:
4603:
4598:
4593:
4588:
4583:
4578:
4573:
4571:Bioinformatics
4568:
4551:
4550:
4548:
4547:
4542:
4537:
4532:
4527:
4522:
4517:
4512:
4507:
4502:
4497:
4492:
4487:
4482:
4477:
4472:
4467:
4461:
4459:
4453:
4452:
4450:
4449:
4447:Tempered glass
4444:
4439:
4434:
4429:
4424:
4419:
4417:DNA microarray
4414:
4412:Dealkalization
4409:
4404:
4399:
4393:
4391:
4385:
4384:
4382:
4381:
4376:
4371:
4366:
4361:
4356:
4351:
4346:
4341:
4336:
4331:
4325:
4323:
4317:
4316:
4314:
4313:
4308:
4303:
4298:
4293:
4288:
4286:Glass modeling
4283:
4278:
4273:
4268:
4263:
4257:
4255:
4251:
4250:
4248:
4247:
4242:
4237:
4232:
4227:
4221:
4219:
4217:Glass-ceramics
4213:
4212:
4210:
4209:
4204:
4199:
4194:
4189:
4184:
4179:
4174:
4169:
4164:
4159:
4157:Silicate glass
4154:
4149:
4144:
4139:
4134:
4129:
4124:
4119:
4114:
4109:
4104:
4099:
4094:
4089:
4084:
4079:
4074:
4069:
4063:
4061:
4057:
4056:
4054:
4053:
4048:
4043:
4037:
4035:
4031:
4030:
4028:science topics
4022:
4021:
4014:
4007:
3999:
3990:
3989:
3987:
3986:
3974:
3961:
3958:
3957:
3954:
3953:
3951:
3950:
3945:
3940:
3935:
3929:
3927:
3921:
3920:
3918:
3917:
3912:
3907:
3905:DNA microarray
3902:
3892:
3891:
3878:
3877:
3876:
3871:
3863:
3853:
3847:
3845:
3841:
3840:
3838:
3837:
3828:
3823:
3818:
3813:
3808:
3802:
3800:
3793:
3789:
3788:
3785:
3784:
3782:
3781:
3776:
3771:
3766:
3761:
3756:
3750:
3748:
3744:
3743:
3741:
3740:
3735:
3730:
3729:
3728:
3723:
3713:
3708:
3703:
3698:
3693:
3692:
3691:
3686:
3681:
3671:
3670:
3669:
3664:
3653:
3652:
3651:
3650:
3645:
3637:
3635:
3631:
3630:
3628:
3627:
3617:
3607:
3596:
3594:
3585:
3581:
3580:
3578:
3577:
3572:
3567:
3561:
3558:
3557:
3550:
3549:
3542:
3535:
3527:
3521:
3520:
3515:
3510:
3505:
3499:
3494:
3489:
3483:
3474:
3465:
3456:
3443:
3442:
3437:
3431:
3430:
3419:
3418:
3416:
3415:External links
3413:
3410:
3409:
3349:
3314:(7): 621–628.
3298:
3249:
3222:Bioinformatics
3208:
3155:
3148:
3130:
3079:
3028:
3019:
2986:Bioinformatics
2976:
2967:
2916:
2907:
2900:
2875:
2821:
2796:
2785:
2749:10.1038/ng1031
2739:. supplement.
2720:
2699:(5): 333–339.
2679:
2638:
2611:Bioinformatics
2597:
2576:(7): 639–645.
2556:
2506:
2447:
2420:(5): 351–356.
2403:
2366:Genome Biology
2352:
2343:
2306:): 1047–1064.
2265:
2208:
2151:
2116:(3): 381–401.
2095:
2068:(5): 895–914.
2047:
2020:(2): 164–167.
2003:
1952:
1905:
1886:(6): 885–897.
1869:
1850:(4): 309–327.
1833:
1832:
1830:
1827:
1825:
1824:
1819:
1814:
1809:
1804:
1795:
1790:
1785:
1780:
1770:
1765:
1760:
1755:
1754:
1753:
1748:
1737:
1736:
1735:
1721:
1718:Biology portal
1705:
1702:
1701:
1700:
1699:
1698:
1693:
1685:
1675:
1658:
1641:
1625:
1619:
1609:
1590:
1587:
1577:
1574:
1557:
1554:
1540:
1537:
1524:
1523:
1515:
1511:
1481:
1461:
1449:
1437:
1434:step detection
1422:
1393:Main article:
1379:
1376:
1345:bioinformatics
1336:
1333:
1311:
1308:
1267:
1264:
1263:
1262:
1242:
1239:
1236:
1233:
1229:
1194:
1193:
1192:
1191:
1190:
1137:
1126:
1092:
1073:
1022:
986:
983:
980:
979:
968:
965:
962:
952:
941:
937:
933:
930:
927:
924:
921:
918:
908:
897:
887:
876:
865:
864:
861:
858:
855:
851:
850:
847:
844:
841:
837:
836:
833:
830:
827:
823:
822:
819:
816:
813:
809:
808:
803:
800:
797:
779:
695:are typically
674:
671:
582:
575:
569:
566:
548:
547:
543:
539:
538:
534:
530:
529:
525:
521:
520:
508:
502:
501:
490:
483:
482:
464:
457:
456:
437:predisposition
417:
411:
410:
399:
393:
392:
355:that protein (
349:
343:
342:
321:
317:
316:
301:
295:
294:
271:
265:
264:
261:
229:
228:
224:
177:
176:Uses and types
174:
153:hydrogen bonds
135:Main article:
124:
121:
45:DNA microarray
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
4613:
4602:
4599:
4597:
4594:
4592:
4589:
4587:
4584:
4582:
4579:
4577:
4574:
4572:
4569:
4567:
4564:
4563:
4561:
4546:
4543:
4541:
4538:
4536:
4533:
4531:
4528:
4526:
4523:
4521:
4518:
4516:
4513:
4511:
4508:
4506:
4503:
4501:
4498:
4496:
4493:
4491:
4488:
4486:
4483:
4481:
4478:
4476:
4473:
4471:
4468:
4466:
4463:
4462:
4460:
4454:
4448:
4445:
4443:
4440:
4438:
4435:
4433:
4430:
4428:
4425:
4423:
4420:
4418:
4415:
4413:
4410:
4408:
4405:
4403:
4400:
4398:
4395:
4394:
4392:
4386:
4380:
4377:
4375:
4372:
4370:
4367:
4365:
4362:
4360:
4357:
4355:
4354:Optical fiber
4352:
4350:
4347:
4345:
4342:
4340:
4337:
4335:
4332:
4330:
4327:
4326:
4324:
4322:
4318:
4312:
4311:Vitrification
4309:
4307:
4304:
4302:
4299:
4297:
4294:
4292:
4289:
4287:
4284:
4282:
4281:Glass melting
4279:
4277:
4276:Glass forming
4274:
4272:
4269:
4267:
4264:
4262:
4259:
4258:
4256:
4252:
4246:
4243:
4241:
4238:
4236:
4233:
4231:
4228:
4226:
4223:
4222:
4220:
4218:
4214:
4208:
4205:
4203:
4200:
4198:
4195:
4193:
4192:Uranium glass
4190:
4188:
4185:
4183:
4180:
4178:
4175:
4173:
4172:Soluble glass
4170:
4168:
4165:
4163:
4160:
4158:
4155:
4153:
4150:
4148:
4145:
4143:
4140:
4138:
4135:
4133:
4130:
4128:
4125:
4123:
4120:
4118:
4115:
4113:
4110:
4108:
4105:
4103:
4100:
4098:
4095:
4093:
4090:
4088:
4087:Ceramic glaze
4085:
4083:
4080:
4078:
4075:
4073:
4070:
4068:
4065:
4064:
4062:
4058:
4052:
4049:
4047:
4044:
4042:
4039:
4038:
4036:
4032:
4027:
4020:
4015:
4013:
4008:
4006:
4001:
4000:
3997:
3985:
3984:
3975:
3973:
3972:
3963:
3962:
3959:
3949:
3946:
3944:
3941:
3939:
3936:
3934:
3931:
3930:
3928:
3926:
3922:
3916:
3915:Lab-on-a-chip
3913:
3911:
3908:
3906:
3903:
3899:
3894:
3893:
3890:
3889:Radioactivity
3886:
3882:
3879:
3875:
3872:
3870:
3867:
3866:
3864:
3861:
3857:
3854:
3852:
3849:
3848:
3846:
3842:
3836:
3832:
3829:
3827:
3824:
3822:
3819:
3817:
3814:
3812:
3809:
3807:
3806:Cultured meat
3804:
3803:
3801:
3797:
3794:
3790:
3780:
3777:
3775:
3772:
3770:
3767:
3765:
3762:
3760:
3757:
3755:
3752:
3751:
3749:
3745:
3739:
3736:
3734:
3731:
3727:
3726:trp repressor
3724:
3722:
3721:lac repressor
3719:
3718:
3717:
3714:
3712:
3709:
3707:
3704:
3702:
3699:
3697:
3694:
3690:
3687:
3685:
3682:
3680:
3677:
3676:
3675:
3672:
3668:
3665:
3663:
3660:
3659:
3658:
3655:
3654:
3646:
3641:
3640:
3639:
3638:
3636:
3632:
3625:
3621:
3618:
3615:
3611:
3610:Transcription
3608:
3605:
3601:
3598:
3597:
3595:
3593:
3592:Central dogma
3589:
3586:
3582:
3576:
3573:
3571:
3568:
3566:
3563:
3562:
3559:
3555:
3548:
3543:
3541:
3536:
3534:
3529:
3528:
3525:
3519:
3516:
3514:
3511:
3509:
3506:
3503:
3500:
3498:
3495:
3493:
3490:
3487:
3484:
3482:
3478:
3475:
3473:
3469:
3466:
3464:
3460:
3457:
3455:
3451:
3448:
3447:
3441:
3438:
3436:
3433:
3432:
3427:
3422:
3405:
3401:
3396:
3391:
3387:
3383:
3379:
3375:
3371:
3367:
3366:Nat Rev Genet
3363:
3356:
3354:
3345:
3341:
3337:
3333:
3329:
3325:
3321:
3317:
3313:
3309:
3302:
3294:
3290:
3285:
3280:
3276:
3272:
3268:
3264:
3260:
3253:
3245:
3241:
3236:
3231:
3227:
3223:
3219:
3212:
3204:
3200:
3196:
3192:
3188:
3184:
3179:
3174:
3170:
3166:
3159:
3151:
3145:
3142:. Wiley-VCH.
3141:
3134:
3126:
3122:
3117:
3112:
3107:
3102:
3098:
3094:
3090:
3083:
3075:
3071:
3066:
3061:
3056:
3051:
3047:
3043:
3039:
3032:
3023:
3015:
3011:
3007:
3003:
2999:
2995:
2991:
2987:
2980:
2971:
2963:
2959:
2954:
2949:
2944:
2939:
2935:
2931:
2927:
2920:
2911:
2903:
2897:
2893:
2892:
2884:
2882:
2880:
2871:
2867:
2862:
2857:
2853:
2849:
2845:
2841:
2840:
2832:
2825:
2810:
2806:
2800:
2794:
2789:
2774:on 8 May 2005
2770:
2766:
2762:
2758:
2754:
2750:
2746:
2742:
2738:
2731:
2724:
2716:
2712:
2707:
2702:
2698:
2694:
2690:
2683:
2675:
2671:
2666:
2661:
2657:
2653:
2649:
2642:
2634:
2630:
2625:
2620:
2616:
2612:
2608:
2601:
2593:
2589:
2584:
2579:
2575:
2571:
2567:
2560:
2552:
2548:
2543:
2538:
2534:
2530:
2526:
2522:
2518:
2510:
2502:
2498:
2493:
2488:
2483:
2478:
2474:
2470:
2466:
2462:
2458:
2451:
2443:
2439:
2435:
2431:
2427:
2423:
2419:
2415:
2407:
2399:
2395:
2390:
2385:
2380:
2375:
2371:
2367:
2363:
2356:
2347:
2339:
2335:
2331:
2327:
2323:
2319:
2314:
2309:
2305:
2301:
2297:
2293:
2292:Chin Acad Sci
2289:
2285:
2284:
2276:
2269:
2261:
2257:
2252:
2247:
2243:
2239:
2235:
2231:
2227:
2223:
2219:
2212:
2204:
2200:
2195:
2190:
2186:
2182:
2178:
2174:
2170:
2166:
2162:
2155:
2147:
2143:
2139:
2135:
2131:
2127:
2123:
2119:
2115:
2111:
2104:
2102:
2100:
2091:
2087:
2083:
2079:
2075:
2071:
2067:
2063:
2056:
2054:
2052:
2043:
2039:
2035:
2031:
2027:
2023:
2019:
2015:
2007:
1999:
1995:
1990:
1985:
1980:
1975:
1971:
1967:
1963:
1956:
1948:
1944:
1940:
1936:
1932:
1931:10.1038/12640
1928:
1924:
1920:
1916:
1909:
1901:
1897:
1893:
1889:
1885:
1881:
1873:
1865:
1861:
1857:
1853:
1849:
1845:
1838:
1834:
1823:
1820:
1818:
1815:
1813:
1810:
1808:
1807:Pathogenomics
1805:
1803:
1799:
1798:Microfluidics
1796:
1794:
1791:
1789:
1786:
1784:
1781:
1778:
1774:
1771:
1769:
1766:
1764:
1761:
1759:
1756:
1752:
1749:
1747:
1744:
1743:
1742:
1739:
1738:
1733:
1727:
1722:
1719:
1713:
1708:
1697:
1694:
1692:
1689:
1688:
1686:
1683:
1679:
1676:
1673:
1670:
1666:
1662:
1659:
1656:
1654:
1649:
1645:
1642:
1639:
1635:
1631:
1630:
1626:
1623:
1620:
1617:
1613:
1610:
1607:
1606:
1601:
1597:
1593:
1592:
1586:
1583:
1573:
1571:
1567:
1563:
1553:
1551:
1546:
1536:
1534:
1530:
1521:
1516:
1512:
1509:
1505:
1501:
1497:
1494:
1490:
1486:
1482:
1479:
1475:
1471:
1467:
1462:
1438:
1435:
1431:
1427:
1423:
1420:
1416:
1415:
1414:
1412:
1411:normalization
1408:
1402:
1396:
1388:
1384:
1378:Data analysis
1375:
1373:
1369:
1364:
1360:
1355:
1353:
1350:
1346:
1342:
1332:
1330:
1325:
1319:
1317:
1307:
1305:
1301:
1297:
1293:
1292:Data analysis
1289:
1285:
1277:
1272:
1260:
1256:
1252:
1248:
1243:
1240:
1237:
1234:
1230:
1227:
1223:
1220:, or PolyT),
1219:
1215:
1211:
1207:
1203:
1199:
1198:hybridization
1195:
1188:
1183:
1179:
1178:
1176:
1172:
1168:
1164:
1160:
1156:
1152:
1148:
1145:
1142:
1138:
1135:
1131:
1127:
1124:
1120:
1116:
1115:
1113:
1109:
1105:
1101:
1097:
1093:
1090:
1086:
1082:
1078:
1074:
1071:
1067:
1063:
1059:
1055:
1051:
1047:
1043:
1039:
1035:
1031:
1027:
1023:
1020:
1016:
1012:
1011:
1010:
1008:
1000:
995:
991:
966:
963:
960:
953:
939:
935:
928:
925:
922:
916:
909:
895:
888:
874:
867:
866:
862:
859:
856:
853:
852:
848:
845:
842:
839:
838:
834:
831:
828:
825:
824:
820:
817:
814:
811:
810:
807:
804:
801:
798:
795:
794:
791:
777:
768:
766:
762:
757:
755:
751:
747:
743:
739:
738:data analysis
734:
730:
729:RNA spike-ins
725:
723:
719:
714:
710:
706:
702:
698:
694:
690:
684:
679:
670:
667:
663:
659:
655:
651:
647:
642:
639:
635:
631:
627:
623:
619:
614:
612:
608:
601:
597:
580:
574:
565:
563:
559:
555:
544:
541:
540:
535:
532:
531:
526:
523:
522:
518:
514:
509:
507:
504:
503:
499:
495:
491:
488:
485:
484:
480:
475:
471:
470:
465:
462:
459:
458:
454:
450:
446:
442:
438:
434:
430:
426:
422:
418:
416:
415:SNP detection
413:
412:
408:
404:
400:
398:
395:
394:
390:
387:to study the
386:
382:
378:
374:
370:
366:
362:
358:
354:
350:
348:
345:
344:
340:
336:
332:
328:
326:
322:
319:
318:
314:
310:
306:
305:Patrick Brown
302:
300:
297:
296:
292:
288:
284:
280:
276:
272:
270:
267:
266:
262:
259:
258:
255:
252:
250:
246:
242:
238:
234:
225:
222:
218:
214:
210:
207:
203:
199:
195:
194:
193:
187:
182:
169:
165:
162:
158:
154:
150:
149:complementary
144:
138:
129:
120:
118:
114:
110:
106:
102:
98:
94:
90:
89:
84:
80:
79:
74:
70:
66:
62:
58:
54:
50:
46:
37:
19:
4520:Porous glass
4475:Safety glass
4432:Porous glass
4416:
4390:modification
4202:Wood's glass
4122:Fused quartz
4097:Cobalt glass
4051:Supercooling
3981:
3969:
3904:
3881:Fluorescence
3869:Nucleic acid
3860:C57BL/6 mice
3851:Cell culture
3759:Biochemistry
3754:Cell biology
3425:
3372:(1): 57–63.
3369:
3365:
3311:
3307:
3301:
3266:
3262:
3252:
3225:
3221:
3211:
3168:
3164:
3158:
3139:
3133:
3096:
3093:BMC Genomics
3092:
3082:
3045:
3041:
3031:
3022:
2989:
2985:
2979:
2970:
2933:
2929:
2919:
2910:
2890:
2843:
2837:
2824:
2812:. Retrieved
2809:prosigna.com
2808:
2799:
2788:
2776:. Retrieved
2769:the original
2740:
2736:
2723:
2696:
2692:
2682:
2655:
2651:
2641:
2614:
2610:
2600:
2573:
2569:
2559:
2524:
2520:
2509:
2464:
2460:
2450:
2417:
2413:
2406:
2369:
2365:
2355:
2346:
2287:
2281:
2268:
2225:
2221:
2211:
2168:
2164:
2154:
2113:
2109:
2065:
2061:
2026:10.1038/9674
2017:
2013:
2006:
1969:
1966:Microbiology
1965:
1955:
1925:(1): 41–46.
1922:
1918:
1908:
1883:
1880:Tree Physiol
1879:
1872:
1847:
1843:
1837:
1777:fluorophores
1681:
1677:
1660:
1651:
1647:
1643:
1634:fluorescence
1627:
1622:Case/control
1621:
1615:
1611:
1603:
1599:
1595:
1579:
1559:
1542:
1525:
1418:
1404:
1372:MGED Society
1356:
1338:
1320:
1313:
1281:
1258:
1163:streptavidin
1161:and labeled
1155:cyanine dyes
1147:triphosphate
1085:spectrometer
1054:ChIP-on-chip
1026:nucleic acid
1006:
1004:
993:
805:
769:
764:
760:
758:
726:
701:fluorophores
692:
688:
687:
654:synthesizing
645:
643:
617:
615:
604:
578:
577:Spotted vs.
571:
551:
506:Tiling array
493:
487:Fusion genes
467:
419:Identifying
361:tiling array
309:Ash Alizadeh
253:
230:
220:
216:
212:
191:
161:non-covalent
146:
104:
86:
82:
76:
44:
42:
35:
18:
4601:Microarrays
4545:Glass fiber
4510:Glass cloth
4254:Preparation
4230:CorningWare
4112:Flint glass
4107:Crown glass
4060:Formulation
3983:WikiProject
3792:Engineering
3747:Linked life
3662:Pribnow box
3620:Translation
3308:Nat Methods
2778:12 December
2693:Cancer Cell
2414:Nat Methods
1802:lab-on-chip
1638:fluorophore
1436:algorithms.
1407:Statistical
1352:open-source
1349:grass-roots
1343:problem in
1134:radiolabels
1130:fluorescent
1062:cytoplasmic
750:Silverquant
705:Fluorescent
638:synthesized
568:Fabrication
513:transcripts
489:microarray
479:Exon arrays
213:genome chip
109:fluorophore
57:microarrays
4560:Categories
4540:Windshield
4374:Refraction
4334:Dispersion
4142:Milk glass
4137:Lead glass
3933:Epigenetic
3844:Techniques
3706:Terminator
3689:trp operon
3684:lac operon
3679:gal operon
3269:(3): e17.
3165:Biometrics
3048:(1): 111.
2570:Genome Res
2521:Genome Res
2372:(8): R58.
1829:References
1539:Annotation
1529:replicates
1460:statistic.
1399:See also:
1347:. Various
1300:Annotation
1187:aminoallyl
1141:aminoallyl
1058:epigenetic
718:excitation
697:hybridized
662:Affymetrix
463:detection
455:analysis.
429:genotyping
331:mycoplasms
283:expression
221:gene array
61:expression
4407:Corrosion
4306:Viscosity
4261:Annealing
3858:(such as
3716:Repressor
3386:1471-0056
3344:205418589
3328:1548-7091
3173:CiteSeerX
3006:1367-4803
2743:: 490–5.
2715:1535-6108
2674:2002-4436
2442:195368323
2322:1674-2052
2242:1362-4962
2185:1638-6183
2165:Biochimie
2130:1746-0441
2082:1744-8042
2014:Nat Genet
1989:2262/6097
1919:Nat Genet
1566:InterMine
1448:Γ
1276:heat maps
1232:pinholes.
1226:formamine
1214:Cot-1 DNA
1182:artifacts
1048:which is
964:−
926:−
746:Eppendorf
733:normalize
562:seedlings
335:pathogens
291:pathogens
263:Synopsis
227:sequence.
123:Principle
97:hybridize
83:reporters
69:picomoles
4525:Pre-preg
4329:Achromat
4072:Bioglass
4067:AgInSbTe
3865:Methods
3799:Concepts
3779:Genetics
3733:Silencer
3711:Enhancer
3667:TATA box
3657:Promoter
3648:Heredity
3584:Overview
3575:Glossary
3488:1Lec.com
3404:19015660
3336:18516045
3293:19923232
3244:14555628
3203:16248921
3195:14969494
3125:15533245
3074:17397530
3014:15797905
2962:24564555
2870:22003312
2765:15412245
2757:12454643
2633:17698492
2551:12421762
2434:15846362
2398:15287980
2338:33780984
2330:28669791
2304:Elsevier
2260:26350216
2203:21501652
2146:41959328
2138:23484648
2090:19450135
2042:41718227
2034:10369258
1998:15470115
1939:10471496
1900:18381269
1758:MAGIChip
1704:See also
1655:reversal
1648:dye swap
1644:Dye flip
1616:subarray
1605:features
1589:Glossary
1419:flagging
1363:journals
1324:aliquots
1081:NanoDrop
573:probes.
441:germline
433:forensic
369:H3K27me3
313:Stanford
287:diseases
217:DNA chip
65:genotype
51:chip or
39:markers.
4456:Diverse
4388:Surface
4245:Zerodur
3938:Genetic
3885:Pigment
3874:Protein
3835:Wet lab
3831:Dry lab
3811:Mitosis
3643:Genetic
3634:Element
3624:protein
3565:History
3395:2949280
3284:2817484
3065:1858704
2953:4072854
2861:3191861
2814:22 June
2592:8796352
2501:8197176
2469:Bibcode
2251:4605312
2194:3545518
1864:6198132
1773:Cyanine
1751:RNA-Seq
1682:feature
1674:system.
1661:Scanner
1629:Channel
1582:RNA-Seq
1570:BioMart
1426:MA plot
1259:in situ
1251:z-ratio
1247:t-value
1144:uridine
1046:protein
1019:control
754:Arrayit
742:Agilent
720:with a
658:Agilent
598:at the
579:in situ
445:somatic
425:alleles
320:GeneID
209:biochip
206:silicon
202:plastic
53:biochip
4458:topics
4321:Optics
4127:GeSbTe
4034:Basics
3898:-omics
3887:&
3696:Intron
3674:Operon
3481:Curlie
3472:Curlie
3463:Curlie
3454:Curlie
3423:about
3402:
3392:
3384:
3342:
3334:
3326:
3291:
3281:
3242:
3201:
3193:
3175:
3146:
3123:
3116:533874
3113:
3099:: 87.
3072:
3062:
3012:
3004:
2960:
2950:
2898:
2868:
2858:
2763:
2755:
2713:
2672:
2631:
2590:
2549:
2542:187555
2539:
2499:
2489:
2440:
2432:
2396:
2389:507883
2386:
2336:
2328:
2320:
2258:
2248:
2240:
2201:
2191:
2183:
2144:
2136:
2128:
2088:
2080:
2040:
2032:
1996:
1947:997032
1945:
1937:
1898:
1862:
1632:: the
1485:t-test
1476:, and
1171:column
1159:biotin
1070:Trizol
1068:(e.g.
1056:) for
423:among
273:In an
239:after
105:target
88:oligos
78:probes
4240:Macor
4207:ZBLAN
4041:Glass
4026:Glass
3570:Index
3340:S2CID
3199:S2CID
2834:(PDF)
2772:(PDF)
2761:S2CID
2733:(PDF)
2658:(1).
2492:43922
2438:S2CID
2334:S2CID
2290:(8).
2278:(PDF)
2142:S2CID
2038:S2CID
1943:S2CID
1665:laser
1653:fluor
1612:Block
1600:slide
1596:array
1562:MIAME
1489:ANOVA
1430:local
1359:MIAME
1224:, or
1218:PolyA
1119:sense
1112:miRNA
1064:) by
722:laser
634:mRNAs
596:robot
554:crops
474:exons
451:, or
397:DamID
198:glass
186:match
73:moles
3701:Exon
3400:PMID
3382:ISSN
3332:PMID
3324:ISSN
3289:PMID
3240:PMID
3191:PMID
3144:ISBN
3121:PMID
3070:PMID
3010:PMID
3002:ISSN
2958:PMID
2896:ISBN
2866:PMID
2816:2017
2780:2013
2753:PMID
2711:ISSN
2670:ISSN
2629:PMID
2588:PMID
2547:PMID
2497:PMID
2461:PNAS
2430:PMID
2394:PMID
2326:PMID
2318:ISSN
2256:PMID
2238:ISSN
2199:PMID
2181:ISSN
2134:PMID
2126:ISSN
2086:PMID
2078:ISSN
2030:PMID
1994:PMID
1935:PMID
1896:PMID
1860:PMID
1678:Spot
1568:and
1545:mRNA
1296:mRNA
1175:Tris
1123:cDNA
1108:rRNA
1104:mRNA
1040:for
1032:for
1024:The
1015:case
626:cDNA
494:e.g.
403:ChIP
357:ChIP
275:mRNA
237:cDNA
101:cDNA
93:gene
81:(or
71:(10
4586:DNA
3614:RNA
3604:DNA
3479:at
3470:at
3461:at
3452:at
3390:PMC
3374:doi
3316:doi
3279:PMC
3271:doi
3230:doi
3183:doi
3111:PMC
3101:doi
3060:PMC
3050:doi
2994:doi
2948:PMC
2938:doi
2856:PMC
2848:doi
2844:467
2745:doi
2701:doi
2660:doi
2619:doi
2578:doi
2537:PMC
2529:doi
2487:PMC
2477:doi
2422:doi
2384:PMC
2374:doi
2308:doi
2246:PMC
2230:doi
2189:PMC
2173:doi
2118:doi
2070:doi
2022:doi
1984:hdl
1974:doi
1970:150
1927:doi
1888:doi
1852:doi
1844:DNA
1800:or
1680:or
1650:or
1646:or
1614:or
1598:or
1594:An
1550:EST
1502:or
1306:).
1206:SSC
1202:SDS
1151:NHS
1110:).
1100:PCR
1038:DNA
1030:RNA
763:or
759:In
691:or
644:In
630:PCR
616:In
515:or
466:An
383:or
339:PCR
329:),
325:GMO
277:or
247:or
219:or
204:or
85:or
49:DNA
4562::
3900:")
3883:,
3833:/
3398:.
3388:.
3380:.
3370:10
3368:.
3364:.
3352:^
3338:.
3330:.
3322:.
3310:.
3287:.
3277:.
3267:38
3265:.
3261:.
3238:.
3226:19
3224:.
3220:.
3197:.
3189:.
3181:.
3169:59
3167:.
3119:.
3109:.
3095:.
3091:.
3068:.
3058:.
3044:.
3040:.
3008:.
3000:.
2990:21
2988:.
2956:.
2946:.
2934:15
2932:.
2928:.
2878:^
2864:.
2854:.
2842:.
2836:.
2807:.
2759:.
2751:.
2741:32
2735:.
2709:.
2695:.
2691:.
2668:.
2654:.
2650:.
2627:.
2615:23
2613:.
2609:.
2586:.
2572:.
2568:.
2545:.
2535:.
2525:12
2523:.
2519:.
2495:.
2485:.
2475:.
2465:91
2463:.
2459:.
2436:.
2428:.
2416:.
2392:.
2382:.
2368:.
2364:.
2332:.
2324:.
2316:.
2288:10
2286:.
2280:.
2254:.
2244:.
2236:.
2226:43
2224:.
2220:.
2197:.
2187:.
2179:.
2169:93
2167:.
2163:.
2140:.
2132:.
2124:.
2112:.
2098:^
2084:.
2076:.
2066:10
2064:.
2050:^
2036:.
2028:.
2018:22
2016:.
1992:.
1982:.
1968:.
1964:.
1941:.
1933:.
1923:23
1921:.
1917:.
1894:.
1884:28
1882:.
1858:.
1846:.
1491:,
1487:,
1421:).
1331:.
1253:,
1208:,
1204:,
1089:μg
1036:,
1021:).
863:3
860:6
857:4
854:4
849:2
846:3
843:3
840:3
835:1
832:1
829:2
826:2
821:1
818:1
815:1
812:1
756:.
713:Cy
709:Cy
703:.
624:,
431:,
409:.
391:.
315:.
251:.
215:,
200:,
99:a
43:A
4018:e
4011:t
4004:v
3862:)
3626:)
3622:(
3616:)
3612:(
3606:)
3602:(
3546:e
3539:t
3532:v
3406:.
3376::
3346:.
3318::
3312:5
3295:.
3273::
3246:.
3232::
3205:.
3185::
3152:.
3127:.
3103::
3097:5
3076:.
3052::
3046:8
3016:.
2996::
2964:.
2940::
2904:.
2872:.
2850::
2818:.
2782:.
2747::
2717:.
2703::
2697:9
2676:.
2662::
2656:4
2635:.
2621::
2594:.
2580::
2574:6
2553:.
2531::
2503:.
2479::
2471::
2444:.
2424::
2418:2
2400:.
2376::
2370:5
2340:.
2310::
2302:(
2298:+
2294:+
2262:.
2232::
2205:.
2175::
2148:.
2120::
2114:2
2092:.
2072::
2044:.
2024::
2000:.
1986::
1976::
1949:.
1929::
1902:.
1890::
1866:.
1854::
1848:2
1228:.
1136:.
1052:(
967:1
961:i
940:2
936:/
932:)
929:1
923:i
920:(
917:i
896:i
875:i
778:i
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.