293:
140:
413:
43:
2067:
741:, a hormone produced by the duodenal "S cells" in response to the stomach chyme containing high hydrogen atom concentration (high acidity), is released into the blood stream; upon return to the digestive tract, secretion decreases gastric emptying, increases secretion of the pancreatic ductal cells, as well as stimulating pancreatic acinar cells to release their zymogenic juice.
747:(CCK) is a unique peptide released by the duodenal "I cells" in response to chyme containing high fat or protein content. Unlike secretin, which is an endocrine hormone, CCK actually works via stimulation of a neuronal circuit, the end-result of which is stimulation of the acinar cells to release their content. CCK also increases gallbladder contraction, resulting in
802:
Cholecystokinin (CCK) is a unique peptide released by the duodenal "I cells" in response to chyme containing high fat or protein content. Unlike secretin, which is an endocrine hormone, CCK actually works via stimulation of a neuronal circuit, the end-result of which is stimulation of the acinar
599:
to produce their bicarbonate-rich secretions, in what is in essence a bio-feedback mechanism; highly acidic stomach chyme entering the duodenum stimulates duodenal cells called "S cells" to produce the hormone secretin and release to the bloodstream. Secretin having entered the blood eventually
340:
Complex food substances that are eaten must be broken down into simple, soluble, and diffusible substances before they can be absorbed. In the oral cavity, salivary glands secrete an array of enzymes and substances that aid in digestion and also disinfection. They include the following:
577:), to control glucose metabolism, and also to secrete digestive / exocrinic pancreatic juice, which is secreted eventually via the pancreatic duct into the duodenum. Digestive or exocrine function of pancreas is as significant to the maintenance of health as its endocrine function.
733:
The pancreas's exocrine function owes part of its notable reliability to biofeedback mechanisms controlling secretion of the juice. The following significant pancreatic biofeedback mechanisms are essential to the maintenance of pancreatic juice balance/production:
1217:
811:, which is the sphincter that regulates flow through the ampulla of Vater. CCK also decreases gastric activity and decreases gastric emptying, thereby giving more time to the pancreatic juices to neutralize the acidity of the gastric chyme.
481:. The stomach plays a major role in digestion, both in a mechanical sense by mixing and crushing the food, and also in an enzymatic sense, by digesting it. The following are enzymes produced by the stomach and their respective function:
1044:
358:: Carbohydrate digestion also initiates in the mouth. Amylase, produced by the salivary glands, breaks complex carbohydrates, mainly cooked starch, to smaller chains, or even simple sugars. It is sometimes referred to as
542:
occurring during digestion in the human adult, with gastric lipase contributing the most of the two acidic lipases. In neonates, acidic lipases are much more important, providing up to 50% of total lipolytic
867:: This is a significant enzyme that converts lactose into glucose and galactose. A majority of Middle-Eastern and Asian populations lack this enzyme. This enzyme also decreases with age. As such
835:
enzymes whose function is to further break down the chyme released from the stomach into absorbable particles. These enzymes are absorbed whilst peristalsis occurs. Some of these enzymes include:
1088:
Freund, Matthias; Graus, Dorothea; Fleischmann, Andreas; Gilbert, Kadeem J; Lin, Qianshi; Renner, Tanya; Stigloher, Christian; Albert, Victor A; Hedrich, Rainer; Fukushima, Kenji (2022-05-23).
368:: Considering that food contains more than just essential nutrients, e.g. bacteria or viruses, the lysozyme offers a limited and non-specific, yet beneficial antiseptic function in digestion.
154:, which follows the mechanical process of digestion. Food consists of macromolecules of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats that need to be broken down chemically by digestive enzymes in the
803:
cells to release their content. CCK also increases gallbladder contraction, causing release of pre-stored bile into the cystic duct, and eventually into the common bile duct and via the
759:
and eventually the duodenum. Bile of course helps absorption of the fat by emulsifying it, increasing its absorptive surface. Bile is made by the liver, but is stored in the gallbladder.
775:
is a hormone produced by the mucosal cells of the duodenum and also the "delta cells" of the pancreas. Somatostatin has a major inhibitory effect, including on pancreatic production.
1309:
Morino, P; Mascagni, F; McDonald, A; Hökfelt, T (1994). "Cholecystokinin corticostriatal pathway in the rat: Evidence for bilateral origin from medial prefrontal cortical areas".
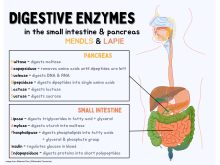
614:) that, once present in the small bowel, become activated and perform their major digestive functions by breaking down proteins, fat, and DNA/RNA. Acinar cells are stimulated by
526:
mucosa of the stomach. It has a pH level of 3–6. Gastric lipase, together with lingual lipase, comprise the two acidic lipases. These lipases, unlike alkaline lipases (such as
504:. Protein digestion, therefore, primarily starts in the stomach, unlike carbohydrate and lipids, which start their digestion in the mouth (however, trace amounts of the enzyme
913:. The absorption of the needed nutrients are usually more efficient than in other plants. Digestive enzymes independently came about in carnivorous plants and animals.
595:), which acts to neutralize the acidity of the stomach chyme entering duodenum through the pylorus. Ductal cells of the pancreas are stimulated by the hormone
2012:
618:(CCK), which is a hormone/neurotransmitter produced by the intestinal cells (I cells) in the duodenum. CCK stimulates production of the pancreatic zymogens.
496:. Pepsinogen is then activated by the stomach acid into its active form, pepsin. Pepsin breaks down the protein in the food into smaller particles, such as
1872:
872:
569:
Pancreas is both an endocrine and an exocrine gland, in that it functions to produce endocrinic hormones released into the circulatory system (such as
600:
comes into contact with the pancreatic ductal cells, stimulating them to produce their bicarbonate-rich juice. Secretin also inhibits production of
1612:
871:
is often a common abdominal complaint in the Middle-Eastern, Asian, and older populations, manifesting with bloating, abdominal pain, and
1479:
1632:
107:
79:
765:(GIP) is produced by the mucosal duodenal cells in response to chyme containing high amounts of carbohydrate, proteins, and
379:: These glands produce a secretion rich in water, electrolytes, and enzymes. A great example of a serous oral gland is the
897:
and in some plants small animals. In some plants, the leaf collapses on the prey to increase contact, others have a small
1605:
86:
308:, the main sites of digestion are the mouth, stomach, and small intestine. Digestive enzymes are secreted by different
1385:
Carnivory of Byblis revisited - A simple method for enzyme testing on carnivorous plants, by
Hartmeyer, Siegfried 1997
1590:
727:
460:
434:
126:
60:
17:
814:
Gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP): This peptide decreases gastric motility and is produced by duodenal mucosal cells.
442:
1352:
93:
1472:
1396:
1275:
723:
563:
31:
1598:
438:
64:
562:"Pancreatic enzyme" and "pancrease" redirect to this discussion of endogenous forms. For exogenous forms, see
75:
1832:
820:: This substance increases gastro-intestinal motility via specialized receptors called "motilin receptors".
488:
is the main gastric enzyme. It is produced by the stomach cells called "chief cells" in its inactive form
625:, composed of the secretions of both ductal and acinar cells, contains the following digestive enzymes:
2057:
1465:
762:
193:
Digestive enzymes are found in the digestive tracts of animals (including humans) and in the tracts of
646:, which is an inactive (zymogenic) protease that, once activated by duodenal enterokinase, turns into
1747:
1732:
1629:
423:
636:, breaks down proteins at the basic amino acids. Trypsinogen is activated via the duodenal enzyme
604:
by "G cells", and also stimulates acinar cells of the pancreas to produce their pancreatic enzyme.
2022:
1987:
1982:
427:
53:
1145:
714:
which are alpha-linked glucose polymers. Humans lack the cellulases to digest the carbohydrate
305:
301:
187:
100:
1977:
1827:
182:. Once in the stomach further mechanical churning takes place mixing the food with secreted
1967:
651:
580:
Two of the population of cells in the pancreatic parenchyma make up its digestive enzymes:
394:, and include sublingual and submandibular glands. Their secretion is mucinous and high in
170:, before being able to be absorbed into the bloodstream. Initial breakdown is achieved by
8:
1867:
1857:
1674:
1669:
868:
372:
Of note is the diversity of the salivary glands. There are two types of salivary glands:
352:
digestion initiates in the mouth. Lingual lipase starts the digestion of the lipids/fats.
1193:
1438:
1411:
1334:
1122:
707:
607:
519:
1620:
1365:
807:
into the second anatomic position of the duodenum. CCK also decreases the tone of the
1849:
1443:
1326:
1322:
1127:
1109:
917:
808:
674:
632:, which is an inactive(zymogenic) protease that, once activated in the duodenum into
550:
527:
329:
194:
1338:
1242:
190:. Most of the enzymatic activity, and hence absorption takes place in the duodenum.
2087:
1529:
1433:
1423:
1318:
1117:
1101:
987:
827:
of the pancreas. Its main function is to inhibit a variety of secretory mechanisms.
804:
756:
657:
643:
622:
209:
332:
plant-specific digestive enzymes are used to break down their captured organisms.
2071:
1882:
1877:
1649:
1625:
1509:
744:
683:
660:, which is a protease that takes off the terminal amino acid group from a protein
615:
325:
186:. Digestive gastric enzymes take part in some of the chemical process needed for
1026:
1287:
930:
to break down the food. These plants do not have digestive juices, but use the
852:
844:
511:
345:
313:
265:
198:
1412:"Discovery of digestive enzymes in carnivorous plants with focus on proteases"
30:
This article is about the naturally produced enzymes. For the medication, see
2081:
2027:
1900:
1889:
1621:
1113:
1105:
931:
898:
840:
688:
678:
523:
355:
317:
1169:
1089:
1070:
1923:
1817:
1659:
1564:
1519:
1447:
1131:
965:
832:
772:
722:
Some of the preceding endogenous enzymes have pharmaceutical counterparts (
647:
637:
584:
376:
277:
253:
183:
1330:
1299:
Brown, Thomas A. "Rapid Review
Physiology." Mosby Elsevier, 1st Ed. p. 244
1265:
Brown, Thomas A. "Rapid Review
Physiology." Mosby Elsevier, 1st Ed. p. 235
823:
somatostatin: This hormone is produced by duodenal mucosa and also by the
292:
2042:
2037:
1686:
1535:
977:
922:
905:. Then digestion fluids are used to digest the prey to get at the needed
848:
824:
766:
752:
629:
588:
546:
501:
391:
387:
281:
610:: Mainly responsible for production of the inactive pancreatic enzymes (
2004:
1946:
1727:
1722:
1702:
1496:
1428:
1194:"Proteolytic enzyme | Description, Types, & Functions | Britannica"
971:
942:
910:
539:
505:
489:
245:
217:
1376:
The Uptake of
Digestion Products by Drosera, by Chandler, Graeme, 1978
508:, which catabolises certain protein, is found in saliva in the mouth).
2032:
2018:
1837:
1717:
1707:
1146:"Enzymes: What Are Enzymes, Pancreas, Digestion & Liver Function"
992:
953:
715:
531:
395:
233:
151:
1457:
538:
for optimal enzymatic activity. Acidic lipases make up 30% of lipid
412:
143:
Diagram of the digestive enzymes in the small intestine and pancreas
139:
42:
1918:
1913:
1862:
1712:
1697:
1664:
1524:
949:
927:
906:
792:
785:
738:
711:
694:
664:
611:
596:
574:
535:
365:
321:
309:
273:
241:
229:
202:
167:
163:
1972:
1962:
1908:
1822:
1654:
1579:
1573:
1514:
1005:
878:
864:
858:
817:
668:
633:
601:
570:
497:
493:
474:
380:
359:
269:
249:
237:
171:
159:
831:
Throughout the lining of the small intestine there are numerous
1999:
1941:
1554:
1504:
902:
894:
796:
702:
698:
515:
485:
257:
213:
179:
175:
1394:
McPherson, S., A. Wistuba, A. Fleischmann & J. Nerz 2011.
893:
In carnivorous plants, digestive enzymes and acids break down
2008:
1994:
1933:
1807:
1802:
1797:
1792:
1787:
1782:
1545:
1308:
1087:
983:
349:
261:
197:, where they aid in the digestion of food, as well as inside
155:
1290:. San Rafael (CA): Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences; 2010
1170:"Lipase | Fat-digesting, Pancreatic, Lipolytic | Britannica"
1777:
1772:
1767:
1762:
1757:
1752:
1742:
1737:
748:
795:: This is an endocrine hormone produced by the duodenal "
225:
221:
855:
that convert peptones and polypeptides into amino acids.
769:. Main function of GIP is to decrease gastric emptying.
677:
that degrades triglycerides into two fatty acids and a
208:
Digestive enzymes are classified based on their target
1069:
Heda, Rajiv; Toro, Fadi; Tombazzi, Claudio R. (2024).
2055:
205:, where they function to maintain cellular survival.
1045:"22.10C: Digestive Processes of the Small Intestine"
654:. Chymotrypsinogen can also be activated by trypsin.
784:The following enzymes/hormones are produced in the
300:Digestive enzymes are found throughout much of the
67:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
1243:"Pancreatic nucleases - Big Chemical Encyclopedia"
799:" in response to the acidity of the gastric chyme.
2079:
1218:"3.3: Digestion and Absorption of Carbohydrates"
1068:
1024:
1025:Patricia, Justin J.; Dhamoon, Amit S. (2024).
296:Table of the different major digestive enzymes
1606:
1473:
1400:. Redfern Natural History Productions, Poole.
1388:
1090:"The digestive systems of carnivorous plants"
881:: converts sucrose into glucose and fructose.
1410:Ravee, R.; Goh, H. H.; Goh, Hoe-Han (2018).
1409:
937:Some carnivorous plants digestive enzymes:
441:. Unsourced material may be challenged and
1613:
1599:
1480:
1466:
1437:
1427:
1121:
461:Learn how and when to remove this message
127:Learn how and when to remove this message
291:
138:
1353:"Small Intestinal Brush Border Enzymes"
1018:
726:) that are administered to people with
718:which is a beta-linked glucose polymer.
587:: Mainly responsible for production of
174:(mastication) and the use of digestive
14:
2080:
1626:serine proteases/serine endopeptidases
926:do not use digestive enzymes, but use
1594:
1487:
1461:
473:The enzymes that are secreted in the
386:Mixed glands: These glands have both
150:take part in the chemical process of
1277:"Exocrine Secretion of the Pancreas"
439:adding citations to reliable sources
406:
65:adding citations to reliable sources
36:
1062:
24:
650:and breaks down proteins at their
25:
2099:
728:exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
697:that degrade nucleic acids, like
2065:
1366:carnivorousplants.org, digestion
861:: converts maltose into glucose.
411:
41:
1403:
1397:Sarraceniaceae of South America
1379:
1370:
1359:
1345:
1302:
1293:
1280:
1268:
1259:
564:Pancreatic enzymes (medication)
52:needs additional citations for
32:Pancreatic enzymes (medication)
1235:
1210:
1186:
1162:
1138:
1081:
1037:
514:: Gastric lipase is an acidic
324:, and secretory glands in the
13:
1:
1838:Urinary plasminogen activator
1011:
640:into its active form trypsin.
1833:Tissue plasminogen activator
1323:10.1016/0306-4522(94)90297-6
710:that breaks down starch and
7:
999:
779:
557:
10:
2104:
763:Gastric inhibitory peptide
561:
402:
29:
1955:
1932:
1924:Proteinase 3/Myeloblastin
1898:
1848:
1685:
1640:
1563:
1544:
1495:
888:
667:that degrade the protein
320:, secretory cells in the
1077:. StatPearls Publishing.
1033:. StatPearls Publishing.
335:
287:
1027:"Physiology, Digestion"
671:and some other proteins
1978:Proprotein convertases
1106:10.1093/plphys/kiac232
306:human digestive system
302:gastrointestinal tract
297:
201:, especially in their
144:
1828:Plasminogen activator
1288:The Exocrine Pancreas
884:Other disaccharidases
295:
142:
1968:Prolyl endopeptidase
1071:"Physiology, Pepsin"
652:aromatic amino acids
435:improve this section
61:improve this article
1222:Medicine LibreTexts
1049:Medicine LibreTexts
869:lactose intolerance
520:gastric chief cells
1429:10.7717/peerj.4914
1198:www.britannica.com
1174:www.britannica.com
918:carnivorous plants
751:squeezed into the
724:pancreatic enzymes
708:Pancreatic amylase
530:), do not require
330:carnivorous plants
298:
195:carnivorous plants
145:
76:"Digestive enzyme"
2053:
2052:
1850:Complement system
1642:Digestive enzymes
1588:
1587:
1489:Digestive enzymes
988:organic compounds
809:sphincter of Oddi
675:Pancreatic lipase
551:cysteine protease
528:pancreatic lipase
471:
470:
463:
312:glands including
148:Digestive enzymes
137:
136:
129:
111:
18:Digestive enzymes
16:(Redirected from
2095:
2070:
2069:
2068:
2061:
1615:
1608:
1601:
1592:
1591:
1530:Carboxypeptidase
1482:
1475:
1468:
1459:
1458:
1452:
1451:
1441:
1431:
1407:
1401:
1392:
1386:
1383:
1377:
1374:
1368:
1363:
1357:
1356:
1349:
1343:
1342:
1306:
1300:
1297:
1291:
1284:
1278:
1272:
1266:
1263:
1257:
1256:
1254:
1253:
1239:
1233:
1232:
1230:
1229:
1214:
1208:
1207:
1205:
1204:
1190:
1184:
1183:
1181:
1180:
1166:
1160:
1159:
1157:
1156:
1150:Cleveland Clinic
1142:
1136:
1135:
1125:
1094:Plant Physiology
1085:
1079:
1078:
1066:
1060:
1059:
1057:
1056:
1041:
1035:
1034:
1022:
962:Nucleases enzyme
959:Proteases enzyme
873:osmotic diarrhea
805:ampulla of Vater
757:common bile duct
658:Carboxypeptidase
644:Chymotrypsinogen
623:Pancreatic juice
518:secreted by the
466:
459:
455:
452:
446:
415:
407:
356:Salivary amylase
132:
125:
121:
118:
112:
110:
69:
45:
37:
27:Class of enzymes
21:
2103:
2102:
2098:
2097:
2096:
2094:
2093:
2092:
2078:
2077:
2076:
2066:
2064:
2056:
2054:
2049:
1951:
1928:
1894:
1844:
1681:
1650:Enteropeptidase
1636:
1619:
1589:
1584:
1559:
1540:
1510:Enteropeptidase
1491:
1486:
1456:
1455:
1408:
1404:
1393:
1389:
1384:
1380:
1375:
1371:
1364:
1360:
1351:
1350:
1346:
1307:
1303:
1298:
1294:
1285:
1281:
1273:
1269:
1264:
1260:
1251:
1249:
1241:
1240:
1236:
1227:
1225:
1216:
1215:
1211:
1202:
1200:
1192:
1191:
1187:
1178:
1176:
1168:
1167:
1163:
1154:
1152:
1144:
1143:
1139:
1086:
1082:
1067:
1063:
1054:
1052:
1043:
1042:
1038:
1023:
1019:
1014:
1002:
891:
853:aminopeptidases
782:
745:Cholecystokinin
684:Sterol esterase
616:cholecystokinin
594:
567:
560:
479:gastric enzymes
467:
456:
450:
447:
432:
416:
405:
338:
326:small intestine
314:salivary glands
290:
133:
122:
116:
113:
70:
68:
58:
46:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2101:
2091:
2090:
2075:
2074:
2051:
2050:
2048:
2047:
2046:
2045:
2040:
2030:
2025:
2016:
2002:
1997:
1992:
1991:
1990:
1985:
1975:
1970:
1965:
1959:
1957:
1953:
1952:
1950:
1949:
1944:
1938:
1936:
1930:
1929:
1927:
1926:
1921:
1916:
1911:
1905:
1903:
1896:
1895:
1893:
1892:
1887:
1886:
1885:
1880:
1870:
1865:
1860:
1854:
1852:
1846:
1845:
1843:
1842:
1841:
1840:
1835:
1825:
1813:
1812:
1811:
1810:
1805:
1800:
1795:
1790:
1785:
1780:
1775:
1770:
1765:
1760:
1755:
1750:
1745:
1740:
1735:
1725:
1720:
1715:
1710:
1705:
1700:
1691:
1689:
1683:
1682:
1680:
1679:
1678:
1677:
1672:
1662:
1657:
1652:
1646:
1644:
1638:
1637:
1622:Endopeptidases
1618:
1617:
1610:
1603:
1595:
1586:
1585:
1583:
1582:
1576:
1569:
1567:
1561:
1560:
1558:
1557:
1550:
1548:
1542:
1541:
1539:
1538:
1533:
1527:
1522:
1517:
1512:
1507:
1501:
1499:
1493:
1492:
1485:
1484:
1477:
1470:
1462:
1454:
1453:
1402:
1387:
1378:
1369:
1358:
1344:
1301:
1292:
1279:
1267:
1258:
1247:chempedia.info
1234:
1209:
1185:
1161:
1137:
1080:
1061:
1036:
1016:
1015:
1013:
1010:
1009:
1008:
1001:
998:
997:
996:
990:
981:
975:
969:
963:
960:
957:
947:
890:
887:
886:
885:
882:
876:
862:
856:
845:endopeptidases
829:
828:
821:
815:
812:
800:
781:
778:
777:
776:
770:
760:
742:
720:
719:
705:
691:
686:
681:
672:
661:
655:
641:
620:
619:
605:
592:
559:
556:
555:
554:
544:
512:Gastric lipase
509:
500:fragments and
469:
468:
419:
417:
410:
404:
401:
400:
399:
384:
370:
369:
363:
353:
346:Lingual lipase
337:
334:
318:gastric glands
289:
286:
135:
134:
49:
47:
40:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2100:
2089:
2086:
2085:
2083:
2073:
2063:
2062:
2059:
2044:
2041:
2039:
2036:
2035:
2034:
2031:
2029:
2028:Streptokinase
2026:
2024:
2020:
2017:
2014:
2010:
2006:
2003:
2001:
1998:
1996:
1993:
1989:
1986:
1984:
1981:
1980:
1979:
1976:
1974:
1971:
1969:
1966:
1964:
1961:
1960:
1958:
1954:
1948:
1945:
1943:
1940:
1939:
1937:
1935:
1931:
1925:
1922:
1920:
1917:
1915:
1912:
1910:
1907:
1906:
1904:
1902:
1901:immune system
1897:
1891:
1890:C3-convertase
1888:
1884:
1881:
1879:
1876:
1875:
1874:
1871:
1869:
1866:
1864:
1861:
1859:
1856:
1855:
1853:
1851:
1847:
1839:
1836:
1834:
1831:
1830:
1829:
1826:
1824:
1821:
1819:
1815:
1814:
1809:
1806:
1804:
1801:
1799:
1796:
1794:
1791:
1789:
1786:
1784:
1781:
1779:
1776:
1774:
1771:
1769:
1766:
1764:
1761:
1759:
1756:
1754:
1751:
1749:
1746:
1744:
1741:
1739:
1736:
1734:
1731:
1730:
1729:
1726:
1724:
1721:
1719:
1716:
1714:
1711:
1709:
1706:
1704:
1701:
1699:
1696:
1693:
1692:
1690:
1688:
1684:
1676:
1673:
1671:
1668:
1667:
1666:
1663:
1661:
1658:
1656:
1653:
1651:
1648:
1647:
1645:
1643:
1639:
1634:
1631:
1627:
1623:
1616:
1611:
1609:
1604:
1602:
1597:
1596:
1593:
1581:
1577:
1575:
1571:
1570:
1568:
1566:
1565:Carbohydrates
1562:
1556:
1552:
1551:
1549:
1547:
1543:
1537:
1534:
1531:
1528:
1526:
1523:
1521:
1518:
1516:
1513:
1511:
1508:
1506:
1503:
1502:
1500:
1498:
1494:
1490:
1483:
1478:
1476:
1471:
1469:
1464:
1463:
1460:
1449:
1445:
1440:
1435:
1430:
1425:
1421:
1417:
1413:
1406:
1399:
1398:
1391:
1382:
1373:
1367:
1362:
1354:
1348:
1340:
1336:
1332:
1328:
1324:
1320:
1317:(4): 939–52.
1316:
1312:
1305:
1296:
1289:
1283:
1276:
1271:
1262:
1248:
1244:
1238:
1223:
1219:
1213:
1199:
1195:
1189:
1175:
1171:
1165:
1151:
1147:
1141:
1133:
1129:
1124:
1119:
1115:
1111:
1107:
1103:
1099:
1095:
1091:
1084:
1076:
1072:
1065:
1050:
1046:
1040:
1032:
1028:
1021:
1017:
1007:
1004:
1003:
994:
991:
989:
985:
982:
979:
976:
973:
970:
967:
964:
961:
958:
955:
951:
948:
946:
944:
940:
939:
938:
935:
934:of the prey.
933:
929:
925:
924:
919:
914:
912:
908:
904:
901:of digestive
900:
896:
883:
880:
877:
874:
870:
866:
863:
860:
857:
854:
850:
846:
842:
841:exopeptidases
838:
837:
836:
834:
826:
822:
819:
816:
813:
810:
806:
801:
798:
794:
791:
790:
789:
787:
774:
771:
768:
764:
761:
758:
754:
750:
746:
743:
740:
737:
736:
735:
731:
729:
725:
717:
713:
709:
706:
704:
700:
696:
692:
690:
689:Phospholipase
687:
685:
682:
680:
679:monoglyceride
676:
673:
670:
666:
662:
659:
656:
653:
649:
645:
642:
639:
635:
631:
628:
627:
626:
624:
617:
613:
609:
606:
603:
598:
590:
586:
583:
582:
581:
578:
576:
572:
565:
552:
548:
545:
541:
537:
533:
529:
525:
521:
517:
513:
510:
507:
503:
499:
495:
492:, which is a
491:
487:
484:
483:
482:
480:
476:
465:
462:
454:
451:December 2016
444:
440:
436:
430:
429:
425:
420:This section
418:
414:
409:
408:
397:
393:
389:
385:
382:
378:
377:Serous glands
375:
374:
373:
367:
364:
361:
357:
354:
351:
347:
344:
343:
342:
333:
331:
327:
323:
319:
315:
311:
307:
303:
294:
285:
283:
279:
278:nucleic acids
275:
271:
267:
266:simple sugars
263:
259:
255:
254:carbohydrates
251:
247:
243:
239:
235:
231:
227:
223:
219:
215:
211:
206:
204:
200:
196:
191:
189:
185:
181:
177:
173:
169:
165:
161:
157:
153:
149:
141:
131:
128:
120:
117:December 2016
109:
106:
102:
99:
95:
92:
88:
85:
81:
78: –
77:
73:
72:Find sources:
66:
62:
56:
55:
50:This article
48:
44:
39:
38:
33:
19:
1818:fibrinolysis
1816:
1694:
1660:Chymotrypsin
1641:
1520:Chymotrypsin
1488:
1419:
1415:
1405:
1395:
1390:
1381:
1372:
1361:
1347:
1314:
1311:Neuroscience
1310:
1304:
1295:
1282:
1270:
1261:
1250:. Retrieved
1246:
1237:
1226:. Retrieved
1224:. 2017-06-14
1221:
1212:
1201:. Retrieved
1197:
1188:
1177:. Retrieved
1173:
1164:
1153:. Retrieved
1149:
1140:
1100:(1): 44–59.
1097:
1093:
1083:
1074:
1064:
1053:. Retrieved
1051:. 2018-07-22
1048:
1039:
1030:
1020:
966:Phosphatases
941:
936:
921:
915:
892:
833:brush border
830:
783:
773:Somatostatin
732:
721:
648:chymotrypsin
638:enterokinase
621:
608:Acinar cells
585:Ductal cells
579:
568:
478:
472:
457:
448:
433:Please help
421:
392:mucous cells
388:serous cells
371:
339:
299:
207:
192:
184:gastric acid
147:
146:
123:
114:
104:
97:
90:
83:
71:
59:Please help
54:verification
51:
1723:Factor XIIa
1703:Factor VIIa
1687:Coagulation
1578:Pancreatic
1536:Nepenthesin
1497:Amino acids
1286:Pandol SJ.
978:Peroxidases
923:Heliamphora
849:dipeptidase
825:delta cells
767:fatty acids
753:cystic duct
630:Trypsinogen
589:bicarbonate
547:Cathepsin F
502:amino acids
282:nucleotides
246:amino acids
240:into small
218:fatty acids
2005:Subtilisin
1947:Batroxobin
1728:Kallikrein
1718:Factor XIa
1708:Factor IXa
1675:Pancreatic
1670:Neutrophil
1274:Bowen, R.
1252:2023-08-14
1228:2023-08-14
1203:2023-08-14
1179:2023-08-14
1155:2023-08-14
1075:StatPearls
1055:2023-08-14
1031:StatPearls
1012:References
972:Glucanases
943:Hydrolytic
911:phosphorus
847:including
540:hydrolysis
506:kallikrein
490:pepsinogen
328:. In some
234:peptidases
210:substrates
188:absorption
87:newspapers
2033:Cathepsin
2019:Sedolisin
1995:Prostasin
1713:Factor Xa
1422:: e4914.
1114:0032-0889
993:Chitinase
954:hydrolase
920:like the
716:cellulose
695:nucleases
665:elastases
543:activity.
532:bile acid
422:does not
396:viscosity
304:. In the
274:nucleases
230:proteases
203:lysosomes
152:digestion
2082:Category
2072:Medicine
1934:Venombin
1919:Tryptase
1914:Granzyme
1868:Factor I
1863:Factor D
1858:Factor B
1698:Thrombin
1695:factors:
1665:Elastase
1572:Gastric
1553:Gastric
1525:Elastase
1448:29888132
1339:32097183
1132:35604105
1000:See also
950:Esterase
928:bacteria
907:nitrates
839:Various
793:secretin
786:duodenum
780:Duodenum
739:Secretin
712:glycogen
693:Several
663:Several
612:zymogens
597:secretin
575:glucagon
558:Pancreas
536:colipase
366:Lysozyme
322:pancreas
310:exocrine
268:such as
256:such as
250:amylases
242:peptides
238:proteins
168:duodenum
164:pancreas
2088:Enzymes
1973:Pronase
1963:Acrosin
1909:Chymase
1823:Plasmin
1655:Trypsin
1580:amylase
1574:amylase
1515:Trypsin
1439:5993016
1331:7520138
1123:9434158
1006:Erepsin
945:process
895:insects
879:Sucrase
865:Lactase
859:Maltase
818:motilin
797:S cells
669:elastin
634:trypsin
602:gastrin
571:insulin
549:: is a
522:in the
498:peptide
494:zymogen
475:stomach
443:removed
428:sources
403:Stomach
381:parotid
360:ptyalin
270:glucose
214:lipases
176:enzymes
172:chewing
160:stomach
101:scholar
2058:Portal
2000:Reelin
1942:Ancrod
1899:Other
1633:3.4.21
1555:lipase
1546:Lipids
1505:Pepsin
1446:
1436:
1337:
1329:
1130:
1120:
1112:
995:enzyme
980:enzyme
974:enzyme
968:enzyme
956:enzyme
903:liquid
899:vessel
889:Plants
703:RNAase
699:DNAase
573:, and
524:fundic
516:lipase
486:Pepsin
383:gland.
276:split
272:, and
262:sugars
258:starch
252:split
236:split
216:split
180:saliva
166:, and
103:
96:
89:
82:
74:
2009:Furin
1956:Other
1883:MASP2
1878:MASP1
1808:KLK15
1803:KLK14
1798:KLK13
1793:KLK12
1788:KLK11
1783:KLK10
1416:PeerJ
1335:S2CID
984:Ureas
916:Some
350:Lipid
336:Mouth
288:Types
280:into
264:into
220:into
199:cells
156:mouth
108:JSTOR
94:books
2023:TPP1
1873:MASP
1778:KLK9
1773:KLK8
1768:KLK7
1763:KLK6
1758:KLK5
1753:KLK4
1748:KLK3
1743:KLK2
1738:KLK1
1532:A, B
1444:PMID
1327:PMID
1128:PMID
1110:ISSN
909:and
851:and
843:and
749:bile
701:and
591:(HCO
477:are
426:any
424:cite
390:and
260:and
244:and
232:and
226:oils
224:and
222:fats
80:news
2013:S1P
1733:PSA
1434:PMC
1424:doi
1319:doi
1118:PMC
1102:doi
1098:190
986:an
932:rot
534:or
437:by
178:of
63:by
2084::
1630:EC
1624::
1442:.
1432:.
1418:.
1414:.
1333:.
1325:.
1315:59
1313:.
1245:.
1220:.
1196:.
1172:.
1148:.
1126:.
1116:.
1108:.
1096:.
1092:.
1073:.
1047:.
1029:.
952:a
788::
755:,
730:.
348::
316:,
284:.
248:;
228:;
212::
162:,
158:,
2060::
2043:G
2038:A
2021:/
2015:4
2011:/
2007:/
1988:2
1983:1
1820::
1635:)
1628:(
1614:e
1607:t
1600:v
1481:e
1474:t
1467:v
1450:.
1426::
1420:6
1355:.
1341:.
1321::
1255:.
1231:.
1206:.
1182:.
1158:.
1134:.
1104::
1058:.
875:.
593:3
566:.
553:.
464:)
458:(
453:)
449:(
445:.
431:.
398:.
362:.
130:)
124:(
119:)
115:(
105:·
98:·
91:·
84:·
57:.
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.