1965:"The boundary of the land of India towards the north is Mount Taurus. It is not still called Taurus in this land; but Taurus begins from the sea over against Pamphylia and Lycia and Cilicia; and reaches as far as the Eastern Ocean, running right across Asia. But the mountain has different names in different places; in one, Parapamisus, in another Hemodus; elsewhere it is called Imaon and perhaps has all sorts of other names; but the Macedonians who fought with Alexander called it Caucasus; another Caucasus, that is, not the Scythian; so that the story ran that Alexander came even to the far side of the Caucasus. The western part of India is bounded by the river Indus right down to the ocean, where the river runs out by two mouths, not joined as are the five mouths of the Ister; but like those of the Nile, by which the Egyptian delta is formed; thus also the Indian delta is formed by the river Indus, not less than the Egyptian; and this in the Indian tongue is called Pattala. Towards the south this ocean bounds the land of India, and eastward the sea itself is the boundary. The southern part near Pattala and the mouths of the Indus were surveyed by Alexander and Macedonians and many Greeks; as for the eastern part, Alexander did not traverse this beyond the river Hyphasis. A few historians have described the parts which are this side of the Ganges and where are the mouths of the Ganges and the city of Palimbothra, the greatest Indian city on the Ganges.(...) The Indian rivers are greater than any others in Asia; greatest are the Ganges and the Indus, whence the land gets its name; each of these is greater than the Nile of Egypt and the Scythian Ister, even were these put together; my own idea is that even the Acesines is greater than the Ister and the Nile, where the Acesines having taken in the Hydaspes, Hydraotes, and Hyphasis, runs into the Indus, so that its breadth there becomes thirty stades. Possibly also other greater rivers run through the land of India."
911:
1528:), it has become a custom among them not to kill or attack . From west of the states Yuezhi and Gaofu, and south until the Western Sea, and east until the state of Panqi, all is the territory of Shendu. Shendu has several hundred separate towns, with a governor, and separate states which can be numbered in the tens, each with its own king. Although there are small differences among them, they all come under the general name of Shendu, and at this time all are subject to Yuezhi. Yuezhi have killed their kings and established a general in order to rule over their people. The land produces elephants, rhinoceros, tortoise shell, gold, silver, copper, iron, lead, and tin. It communicates to the west with
2736:: "Note finally that the letter H/η was originally used to mark word-initial aspiration... Since such aspiration was lost very early in the eastern Ionic-speaking area, the letter was recycled, being used first to denote the new, very open, long e-vowel ... and then to represent the inherited long e-vowel too, once these two sounds had merged. The use of H to represent open long e-vowels spread quite early to the central Ionic-speaking area and also to the Doric-speaking islands of the southern Aegean, where it doubled up both as the marker of aspiration and as a symbol for open long e-vowels."
922:
39:
173:
2271:
711:
4422:
4432:
2763:: "The early loss of aspiration is mainly a characteristic of Asia Minor (and also of the Aeolic and Doric of Asia Minor)...In Attica, however (and in some cases in Euboea, its colonies, and in the Ionic-speaking islands of the Aegean), the aspiration survived until later... During the second half of the fifth century BC, however, orthographic variation perhaps indicates that 'a change in the phonetic quality of was taking place' too."
1122:
2259:"The part of India beyond the Ganges extends in length as far as Cathay (China) and contains many provinces in which are found many notable things. As in the Kingdom of Kamul near Campichu (Cambodia)...And in Erguiul...In the Ava Mountains (Burma)..., and in the Salgatgu mountains...In Caindu...In the territory of Carajan..."
2500:: "Apparently the same territory was referred to as Hi(n)du(sh) in the Naqsh‐i‐Rustam inscription of Darius I as one of the countries in his empire. The terms Hindu and India ('Indoi) indicate an original indigenous expression like Sindhu. The name Sindhu could have been pronounced by the Persians as Hindu (replacing
396:
of the
Constitution, adopted in 1950, which states in English: "India, that is Bharat,..." Bharat, which was predominantly used in Hindi, was adopted as a self-ascribed alternative name by some people of the Indian subcontinent and the Republic of India.
2063:"The boundaries of Hindustan are marked on every side by natural features; e.g., the Himalayas, on the N.; the Patkoi Mountains, Tippera Hills, &c., on the N.E.; the Sea, on the E., S., and W.; and the Hala, and Sulaiman Mountains, on the N.W."
2205:"What shall I say? The greatness of this India is beyond description. But let this much suffice concerning India the Greater and the Less. Of India Tertia I will say this, that I have not indeed seen its many marvels, not having been there..."
1191:
countries before the introduction of the
English word "India". This alternate name is still used occasionally in Thailand, Malaysia, Java and Bali to describe the Indian Subcontinent. However, it also can refer to the whole continent of Asia.
2245:"Hindustan is described as enclosed on the east, west and south by the ocean, but Sarandip (Sri Lanka), Achin (Indonesia), Maluk (Indonesia) and Malagha (Malaysia) and a considerable number of islands are accounted for within its extent."
1524:. Its customs are the same as those of Yuezhi, and it is low, damp, and very hot. It borders a large river. The inhabitants ride on elephants in warfare; they are weaker than the Yuezhi. They practise the way of Futu (the
4012:
2137:"East of it (Hindistān) are the countries of China and Tibet; South of it, the Great Sea; west of it, the river Mihran (Indus); north of it, the country of Shaknan belonging to Vakhan and some parts of Tibet."
2637:: 'The Persians coined the name of Hindush after the current Sanskrit geographical name of Sindhu. Neither the Old Persian inscriptions, nor the Avesta make use of the word hindu in the sense of "river".'
2219:"And this same Thursday that the said Ambassadors arrived at this great River (the Oxus) they crossed to the other side. And the same day... came in the evening to a great city which is called Tenmit (
1109:
itself, entered the
English language in the 17th century. In the 19th century, the term as used in English referred to the Subcontinent. "Hindustan" was in use simultaneously with "India" during the
3233:: "The term Hindustan, which in the Naqsh-i-Rustam inscription of Shapur I denoted India on the lower Indus, and which later gradually began to denote more or less the whole of the subcontinent..."
1836:"Eastward of India lies a tract which is entirely sand. Indeed, of all the inhabitants of Asia, concerning whom anything is known, the Indians dwell nearest to the east and the rising of the Sun."
1877:"India then being four-sided in plan, the side which looks to the Orient and that to the South, the Great Sea compasseth; that towards the Arctic is divided by the mountain chain of Hēmōdus from
652:
gathering, which caused speculation on a name-change for the country. Such a change would need a constitutional amendment, meaning two-thirds of the vote in each of the two houses of parliament.
285:. Herodotus also generalised the term "Indian" from the people of lower Indus basin, to all the people living to the east of Persia, even though he had no knowledge of the geography of the land.
1881:, inhabited by that tribe of Scythians who are called Sakai; and on the fourth side, turned towards the West, the Indus marks the boundary, the biggest or nearly so of all rivers after the
146:
in Indian languages, though it has been in
Persian usage since at least the 3rd century CE while its earlier form "Hindush" was used as early as 6th century BCE. The term 'Hindu' was the
1993:; on three sides it is bounded by a great sea; on the north it is backed by snowy mountains. It is wide at the north and narrow at the south; its figure is that of a half-moon."
1907:"This (Brahmaputra) is the eastern boundary of Jambudvipa, its western boundary being the mouths of the Indus and its southern boundary being the Indian Ocean or Rama Sethu."
1322:"Tibet is inextricably linked to India through geography, history, culture, and spiritually, Tibetans refer to India as ‘Gyagar Phagpay Yul’ or ‘India the land of Aryas.’"
2588:, means "inhabitants of the lower Indus valley".... In this respect Sindhu is no tribal name at all. It denotes a geographical unit to which different tribes may belong."
1548:, literally "Five Indias"), because there were five geographical regions in India known to the Chinese: Central, Eastern, Western, Northern, and Southern India. The monk
95:"Bhārat" gained popularity in India during the nineteenth century. It is the shortened form of the term "Bhāratavarṣa" which is extensively used in the literature of the
2584:
means a stream, a river, and in particular the Indus river, but likewise it denotes the territory of the lower Indus valley, or modern Sind. Therefore, the appellation
2387:
appears upside-down at 6h (bottom) on the circular legend of the obverse side of the coin. The complete circular legend is "In the name of Allah, struck this dirham in
2074:
Writers throughout history, both Indian and of other nationalities have written about a 'Greater India', which
Indians have called either Akhand Bharat or Mahabharat.
2321:
1569:
from
Kuchean, though a very long time elapsed between that term's first use and its becoming the standard modern name for India in East Asian languages. Pronounced
910:
142:
and is also derived from the name of the river Sindhu. It gained popularity in India in the 11th century in
Islamic literature and became the common name for the
4481:
3134:
1632:
367:". The name "India" then came back to English usage from the 17th century onward, and may be due to the influence of Latin, or Spanish or Portuguese.
1948:
i.e. "The country (varṣam) that lies north of the ocean and south of the snowy mountains is called Bhāratam; there dwell the descendants of Bharat."
1927:
i.e. "The country (varṣam) that lies north of the ocean and south of the snowy mountains is called Bhāratam; there dwell the descendants of Bharat."
3645:
3594:
3048:
2667:: "The new satrapy, which received the name of Hindush, extended from the centre to the lower part of the Indus Valley, in present-day Pakistan."
1673:
3284:
2155:
in the north, to the Indian Ocean in the south; from Sehwan (on the west bank of the Indus) to the mountains on the east dividing from China."
2013:), on the W. and S. by the countries of Islām and on the N. by the Chinese Empire... The length of the land of the Hind from the government of
843:
3676:
Hodu is the biblical name for India (Esther 1:1), which is derived from the
Persian word Hindu, a name for the region around the Indus River
1689:
to emphasise the religious aspect of their travels, though most of their contemporaries (even fellow
Buddhist pilgrims) adopted the name
4387:
3416:
1069:
1432:
traditionally used this term and its related forms to designate India as their "heavenly centre", referring to the sacred origins of
3621:"Esther 1:1 This is what happened during the time of Xerxes, the Xerxes who ruled over 127 provinces stretching from India to Cush"
3099:
4336:
828:
3805:
3779:
A History of
Civilization in Ancient India, Based on Sanskrit Literature. In Three Volumes. Volume 3. Buddhist and Pauranik Ages
882:
879:
873:
738:
735:
729:
3074:
870:
726:
2045:"Hind is surrounded on the East by Chín and Máchín, on the West by Sind (Baluchistan) and Kábul and on the South by the Sea."
3957:
3937:
3821:
3794:
3390:
3207:
3005:
2837:
2784:
2757:
2730:
2688:
2562:
2494:
2465:
876:
867:
732:
723:
267:
who explored the Indus river for the Persian emperor probably took over the Persian name and passed it into Greek. The terms
569:
The country that lies north of the ocean and south of the snowy mountains is called Bhāratam there dwell the descendants of
4061:
2191:) and contains 8 great Kingdoms... Abash is a very great province and you must know that it constitutes the Middle India."
1248:
i.e. land of noble, holy, enlightened & superior people who are the source of spiritual enlightenment. Tibetan scholar
2223:) and this used to belong to India Minor, but now belongs to the empire of Samarkand, having been conquered by Tamurbec."
617:
are still excluded. Some other Puranic passages refer to the same Bhārata people, who are described as the descendants of
470:. The term is a verbal noun of the Sanskrit root bhr-, "to bear/to carry", with a literal meaning of to be maintained (of
4397:
2959:
899:
763:
393:
4018:
4466:
3547:
3978:
3813:
3786:
3763:
3718:
3516:
3491:
3462:
3157:
2969:
2661:
2617:
2326:
4476:
4311:
3778:
2183:) and it contains 13 great kingdoms... India the Lesser extends from the Province of Champa to Mutfili (i.e. from
1001:
Emperor Babur of the Mughal Empire said, "On the East, the South, and the West it is bounded by the Great Ocean."
4461:
302:
denoted the region beyond the Indus. Alexander's companions were aware of at least India up to the Ganges delta (
207:
4356:
3361:
3173:
3021:
1459:
1317:
634:
The use of Bharat often has political overtones, appealing to a certain cultural conception of India. In 2023,
3671:
1092:, the term Hindustan has recently come to mean the Republic of India. The same is the case with Arabic, where
371:
3598:
2794:
as a collective name for all the peoples living east of Persia. This was also a significant development over
1202:
Both Gyagar ("White expanse", analogous to the names Gyanak for China and Gyaser for Russia) and Phagyul are
128:
1665:
2568:: "In early Indian sources Sindhu denoted the mighty Indus river and also a territory on the lower Indus."
684:(first century BCE), where it applies only to a restrained area of northern India, namely the part of the
4456:
3577:
2361:
3649:
2530:
2029:, is about 4 months and its breadth from the Indian Ocean to the country of Kannūj about three months."
590:) had the best qualities and it was because of him that this land by the people is called Bhāratavarṣa"
150:
adaption of "Sindhu". "Hindustan" is still commonly used in the subcontinent to refer to the modern day
3341:
3049:"Opinion: It's not just about its colonial past. Here's what India's possible name change is all about"
1332:
609:(200 BCE to 300 CE), a larger region of North India is encompassed by the term Bharat, but much of the
17:
4471:
4146:
2381:
2234:
946:
937:
692:. The inscription clearly mentions Bharat was named after Bharata, the son of first Jain tirthankar
4392:
4078:
4054:
3692:
3432:
1158:
853:) was used for the lower Indus basin. The name was also known as far as the Achaemenid province of
3535:
3531:
1504:
A detailed account of Tianzhu is given in the "Xiyu Zhuan" (Record of the Western Regions) in the
4351:
4256:
3131:
1637:
1290:, which originally developed around 200 BCE or 300 BCE and about 600 CE, describes India as the "
677:
642:
417:
30:
3755:
2773:
Arora, Udai Prakash (2005), "Ideas of India in Ancient Greek Literature", in Irfan Habib (ed.),
1561:
The name Tianzhu and its Sino-Xenic cognates were eventually replaced by terms derived from the
2933:
2795:
1683:
who travelled to India for pilgrimages to Buddhist historical sites, continued to use the name
405:
104:
3999:
3927:
3337:
3320:
3300:
3245:, p. 553: "Among the countries that fell before Shapur I the area in question appears as
3195:
2934:"S'RÎMAD BHÂGAVATAM : "The Story of the Fortunate One" : Third revised version 2012"
2678:
2651:
2516:) and the Greeks would have transformed the latter as Indo‐ (Indoi, Latin Indica, India) with
2439:
115:(Land of the Aryans). At first the name Bhāratavarṣa referred only to the western part of the
4361:
3945:
3929:
Alexander's Campaigns in Sind and Baluchistan and the Siege of the Brahmin Town of Harmatelia
3382:
An Anthology of Chinese Discourse on Translation: From Earliest Times to the Buddhist Project
3324:
3304:
3242:
2875:
2418:
2018:
622:
3925:
2995:
2807:
2634:
2577:
2455:
1025:('History of India'). It occurs intermittently in usage within India, such as in the phrase
921:
4306:
4271:
4226:
3704:
1312:
799:
759:
358:
330:
196:
3379:
Cheung, Martha Pui Yiu (2014) . "Zan Ning (919–1001 CE), To Translate Means to Exchange".
1175:'berry island') was used in ancient scriptures as a name of India before the term
8:
4376:
4196:
4191:
4086:
4047:
3316:
2703:
2351:
2279:
1717:
1437:
1425:
1305:
1249:
1170:
289:
278:
155:
120:
43:
1451:
4316:
4291:
4206:
4186:
4136:
4106:
4096:
3748:
1678:
1509:
1287:
1244:
1226:
or holy centre) for India. Since at least 13th century, several influential indigenous
949:
635:
475:
264:
2676:
4431:
4402:
4281:
4276:
4156:
4028:
3974:
3953:
3933:
3817:
3809:
3790:
3782:
3759:
3714:
3512:
3487:
3458:
3386:
3203:
3153:
3107:
3001:
2965:
2833:
2780:
2753:
2726:
2684:
2657:
2613:
2558:
2490:
2461:
2131:
1257:
1203:
1149:
1099:
587:
570:
541:
505:
167:
151:
124:
65:, is also used commonly when Indians speak among themselves. The usage of "Bhārat", "
2009:"As for the land of the Hind it is bounded on the East by the Persian Sea (i.e. the
504:
This realm of Bharat, which has been referred to as Bhāratavarṣa in puranas - after
4346:
4296:
4251:
4231:
4221:
4121:
2304:
2176:
2110:
1982:
1580:
1491:
1366:
1207:
1134:
1061:
969:
791:
777:
529:
334:
96:
53:
has two principal official short names, each of which is historically significant,
2798:, who had used this term in a strict sense for the groups dwelling in Sindh only."
1655:
4321:
4236:
4216:
4101:
4091:
3947:
3380:
3226:
3222:
3147:
2827:
2823:
2774:
2747:
2720:
2680:
Luwian Identities: Culture, Language and Religion Between Anatolia and the Aegean
2607:
2552:
2548:
2484:
2480:
1748:
1737:
1415:
1355:
1073:
1006:
3433:"China and the Ancient Mediterranean World: A Survey of Ancient Chinese Sources"
3405:
1411:
4366:
4301:
4266:
4201:
4181:
4171:
4131:
4116:
4111:
4007:
4003:
3832:
3075:"'India' or 'Bharat'? A G-20 dinner invite sparks rumors of a national rebrand"
2052:
1847:
1753:
1562:
1338:
1227:
1188:
1034:
959:
638:
610:
413:
342:
338:
112:
89:
77:
3835:, The Vishnu Purana, translated by Horace Hayman Wilson, , at sacred-texts.com
3336:
Jianbian Joacuo (translated by Liang Yanjun, Wu Chunxiao and Song Xin), 2019,
2853:
2175:"India the Greater is that which extends from Maabar to Kesmacoran (i.e. from
1668:, was not completely displaced until the early 20th century: scholars such as
1341:. He continues to advocate the revival of India's ancient wisdom based on the
4450:
4425:
4407:
4326:
4286:
4261:
4241:
4176:
4151:
4141:
4126:
4032:
3995:
3111:
2435:
2356:
2188:
1939:
1918:
1762:
1622:
1180:
1130:
1077:
945:, "In India") on an Umayyad coin minted in India, from the time of the first
693:
645:
583:
537:
521:
517:
509:
189:
3555:
1621:) had been found occasionally in 18th and early 19th-century works, such as
1145:
848:
258:
248:
38:
4246:
4211:
4166:
4161:
4070:
2346:
2341:
2239:
2010:
1901:
1271:
1110:
1054:
593:
525:
401:
377:
116:
100:
3509:
Seeking Sakyamuni: South Asia in the Formation of Modern Japanese Buddhism
72:
The name "India" is originally derived from the name of the river Sindhu (
4435:
3966:
3191:
2331:
2270:
2184:
2114:
1872:
1791:
1787:
1669:
1627:
1589:) in Chinese, it was first used by the seventh-century monk and traveler
812:
627:
614:
597:
533:
444:
307:
299:
238:
230:
177:
172:
147:
85:
73:
710:
3582:
3357:
2336:
2170:
1475:
1429:
1391:
1324:
820:
605:
303:
282:
1068:, and from that into northern Indian languages, from the 11th century
3620:
2791:
2414:
2100:
2040:
1990:
1861:
who reigned from Hodu (India) to Cush (Ethiopia) over 127 provinces"
1858:
1854:
1831:
1766:
1456:
705:
681:
618:
513:
494:
489:. This term also means "one who is engaged in search for knowledge".
293:
274:
268:
200:
181:
143:
81:
66:
3243:
Ray & Chattopadhyaya, A Sourcebook of Indian Civilization (2000)
2746:
Panayotou, A. (2007), "Ionic and Attic", in A.-F. Christidis (ed.),
1262:
449:
he who conquers the whole of Bhāratavarṣa is celebrated as a samrāṭa
257:
conquered Sindh in about 516 BCE, upon which the Persian equivalent
3872:
Kitab Muruj Al-dahab Al-Masudi. El-Masudis Historical Encyclopaedia
2152:
2004:
1976:
1896:
1780:
1775:
1590:
1549:
1433:
1299:
1028:
991:
987:
824:
803:
254:
221:
69:", or "India" depends on the context and language of conversation.
1516:
The state of Tianzhu: Also named Shendu, it lies several thousand
1390:
and is used since ancient times in China and its peripheries. Its
976:) was added, indicative of a country or region, forming the name
2749:
A History of Ancient Greek: From the Beginnings to Late Antiquity
2705:
Herodotus, with an English Translation by A. D. Godley, Volume II
2388:
2022:
1878:
1342:
1279:
1275:
931:
689:
432:
409:
108:
1320:, often referred to as the Tibetan Government-in-Exile, asserts
1266:(buddhist monastery), and the ancient Tibetans applied the term
352:
346:
324:
29:"Bharat (term)" redirects here. For other uses of "Bharat", see
4039:
3345:
3200:
The Varied Facets of History: Essays in Honour of Aniruddha Ray
2808:
Eggermont, Alexander's Campaigns in Sind and Baluchistan (1975)
2635:
Eggermont, Alexander's Campaigns in Sind and Baluchistan (1975)
2578:
Eggermont, Alexander's Campaigns in Sind and Baluchistan (1975)
2220:
2180:
2014:
1960:
1805:
Some historical definitions prior to 1500 are presented below.
1758:
1529:
1525:
1521:
1407:
1138:
1121:
1065:
685:
459:
320:
135:
893:
384:, is unrelated, but has sometimes been erroneously connected.
3808:, Dr. N.N. Kher & Jaideep Aggarwal, Pitambar Publishing,
3319:(translated by Thupten Jinpa and Donald S. Lopez Jr.), 2014,
3271:
2286:
2274:
The name and logo of state-owned petroleum companies of India
2026:
1382:) is one of several Chinese transliterations of the Sanskrit
1337:"refers to himself the ‘Son of India’ and a true follower of
1283:
1106:
1085:
1081:
854:
816:
751:
234:
139:
50:
3846:
A smaller manual of modern geography. Physical and political
3710:
The Vishnu Purana: A System of Hindu Mythology and Tradition
3455:
Other Routes: 1500 Years of African and Asian Travel Writing
3301:
The Holy Land Reborn: Pilgrimage and the Tibetan Reinvention
3268:
Memoirs of Zahir-ad-Din Muhammad Babur: Emperor of Hindustan
2069:
2059:
A Smaller Manual of Modern Geography. Physical and Political
1179:
became widespread. It might be an indirect reference to the
3946:
Ray, Niharranjan; Chattopadhyaya, Brajadulal, eds. (2000),
3417:
How the Japan-India alliance could redraw the political map
1882:
1328:
1230:
1089:
471:
467:
381:
3848:
By John Richardson (Vicar of St. Mary's Hospital, Ilford.)
2725:(Second ed.), John Wiley & Sons, pp. 27–28,
2109:"The Hindu nation (Al-Hind) extends from the mountains of
831:
in about 516 BCE, upon which the Achaemenid equivalent of
362:
2677:
Mouton, Alice; Rutherford, Ian; Yakubovich, Ilya (2013),
1376:
649:
586:) begot a hundred sons that were exactly like him... He (
3994:
3511:. University of Chicago Press. pp. 12–13, 114–115.
2457:
Indography: Writing the "Indian" in Early Modern England
1210:
authors and pilgrims used the ethnogeographic referents
582:
The Bhagavat Puran mentions (Canto 5, Chapter 4) - "He (
281:/h/ was probably due to the dialects of Greek spoken in
273:
for the Indus river as well as "an Indian" are found in
3257:
respectively in the three languages mentioned above ."
2997:
Studies in the Geography of Ancient and Medieval India
2829:
Nationhood and Statehood in India: A historical survey
2554:
Nationhood and Statehood in India: A historical survey
2486:
Nationhood and Statehood in India: A historical survey
1690:
1684:
1659:
1643:
1594:
1163:
1080:
periods called their Indian dominion, centered around
832:
806:
427:
appears in the official Sanskrit name of the country,
242:
224:
123:. In 1949, it was adopted as an official name for the
3727:
3040:
1769:
had been described as King ruling 127 provinces from
1570:
1270:
mainly to the northern and central India region from
977:
963:
785:
771:
3073:
Press, SHEIKH SAALIQ Associated (8 September 2023).
2878:: "India that is Bharat shall be a Union of States."
2645:
2643:
2021:
and Bodha and the rest of Sind, till thou comest to
1724:
was used in classical Chinese much like the English
1699:
1233:& authors also started to refer to India as the
1093:
1010:
345:, the name was, under French influence, replaced by
263:
was used for the province at the lower Indus basin.
2993:
2630:
2628:
2278:The official names as set down in article 1 of the
1042:
4011:
3747:
2907:, Delhi: Motilal Banarsidass, pp. ff. 8 p. 40
2854:"'India, that is Bharat…': One Country, Two Names"
435:, which refer to the land that comprises India as
310:included in India the southern peninsula as well.
3754:. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p.
3286:Inscriptions of Asoka. New Edition by E. Hultzsch
2722:Greek: A History of the Language and its Speakers
2640:
1664:, which was heavily associated with the image of
962:, probably from the first century CE, the suffix
596:(or Bhārat Kṣētra) is a term used in some of the
99:. "Bhāratavarṣa" is derived from the name of the
4448:
3321:Grains of Gold: Tales of a Cosmopolitan Traveler
2625:
1711:
1419:
564:varṣaṃ tad bhārataṃ nāma bhāratī yatra santatiḥ.
439:and uses this term to distinguish it from other
392:Bharat is another name of India, as set down in
3338:降边嘉措著, 梁艳君, 吴春晓 A study of Tibetan epic Gesar
2779:, Munshiram Manoharlal Publishers, p. 47,
2571:
2431:
2429:
1912:Between first century BCE and ninth century CE
3781:, Romesh Chunder Dutt, Publisher Elibron.com,
3713:. Cambridge: Read Country Books. p. xii.
3578:Brown–Driver–Briggs Hebrew and English Lexicon
2851:
2845:
1944:"उत्तरं यत्समुद्रस्य हिमाद्रेश्चैव दक्षिणम् ।
1923:"उत्तरं यत्समुद्रस्य हिमाद्रेश्चैव दक्षिणम् ।
1649:
1616:
1610:
1604:
1395:
1021:) for India, for example, in the 11th-century
562:
557:Uttaraṃ yat samudrasya himādreścaiva dakṣiṇam.
555:
4055:
3482:in Pre-Modern Japan". In Sen, -Tansen (ed.).
3364:, published: Jan 2018, accessed: 19 Dec 2022.
2896:
2858:South Asia Multidisciplinary Academic Journal
1584:
1553:
1543:
1537:
1485:
1479:
1469:
1463:
1444:
1370:
1360:
431:. The name is derived from the ancient Hindu
3874:By 'Abu-l-Hasan 'Ali ibn al-Husain al-Masudi
3486:. ISEAS–Yusof Ishak Institute. p. 262.
3228:The Foreign Names of the Indian Subcontinent
2818:
2816:
2708:, London: William Heinemann, 1921, III.97–99
2653:A Political History of the Achaemenid Empire
2426:
1705:
1401:
1016:
935:
660:The earliest recorded use of Bhārata-varṣa (
119:, but was later more broadly applied to the
4482:Lists of country names in various languages
3885:Journal of Ancient Indian History, Volume 9
3478:Rambelli, Fabio (2014). "The Idea of India
2752:, Cambridge University Press, p. 410,
2606:", in Mary Boyce; Ilya Gershevitch (eds.),
2296:
2290:
1084:, "Hindustan". In contemporary Persian and
1048:
1026:
661:
314:
212:
4062:
4048:
4019:The Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition
3231:, Place Names Society of India, p. 46
3152:. Routledge & Kegan Paul. p. 10.
3145:
2117:) as far as et-Tubbet (Tibetan Plateau.)"
1946:वर्षं तद् भारतं नाम भारती यत्र संततिः ।।"
1925:वर्षं तद् भारतं नाम भारती यत्र संततिः ।।"
1797:. It is thus cognate with the term India.
1187:was the historical term for India in many
655:
648:used the Bharat name in connection with a
3926:Eggermont, Pierre Herman Leonard (1975),
3910:The Mapping of Power in Renaissance Italy
3374:
3372:
3370:
3221:
2958:Dikshitar, Ramachandra (1 January 1993).
2957:
2892:, Delhi: Motilal Banarsidass, p. 131
2822:
2813:
2776:India — Studies in the History of an Idea
2745:
2649:
2547:
2479:
2070:Historical definitions of a Greater India
233:as well as the lower Indus basin (modern
3477:
2902:
2887:
2881:
2874:Article 1 of the English version of the
2718:
2269:
1720:. Similar to Hindu and Sindhu, the term
1292:Gyagar: The Kingdom of Buddhist Doctrine
1120:
709:
497:name for India, is also a derivation of
412:as one of the original community of the
171:
84:(5th century BCE). The term appeared in
37:
3973:. Wiesbaden: Otto Harrassowitz Verlag.
3100:"Will India change its name to Bharat?"
2951:
400:Bharat is derived from the name of the
14:
4449:
3965:
3733:
3703:
3525:
3506:
3378:
3367:
3289:(in Sanskrit). 1925. pp. 169–171.
3022:"How Hindu is India's foreign policy?"
2832:, Regency Publications, pp. 3–4,
2597:
2453:
4043:
3745:
3672:"TARNEGOL HODU, A BIRD CALLED TURKEY"
3452:
3426:
3424:
3190:
3072:
3047:Singh, Akanksha (20 September 2023).
3046:
2772:
2410:
2408:
2105:Muruj adh-dhahab wa ma'adin al-jawhar
1195:
986:in the Naqsh-e-Rustam inscription of
466:, which was originally an epithet of
42:The geographic region containing the
3648:. Hanefesh Community. Archived from
3406:An Invitation to Indian Architecture
3351:
3330:
3310:
3293:
2917:
2612:, Lund Humphries, pp. 447–450,
2460:, Palgrave Macmillan US, p. 8,
2322:Origin of the names of Indian states
2265:
1593:. In Japanese for example, the name
676:) in a geographical sense is in the
88:by the 9th century and reemerged in
3949:A Sourcebook of Indian Civilization
3646:"The Book of Esther - Kids Version"
3125:
2905:Ancient Indian Historical Tradition
2890:Ancient Indian Historical Tradition
2557:, Regency Publications, p. 3,
2489:, Regency Publications, p. 3,
2441:Political Violence in Ancient India
1989:, the Five Indies) is about 90,000
1800:
1741:
1532:and (so) has the exotica of Da Qin.
1296:Gyagar: The Kingdom of Aru Medicine
1053:), the Standard Hindi name for the
1017:
973:
795:
781:
699:
544:(50,41), all using the designation
111:as one of the principal peoples of
24:
3988:
3430:
3421:
3139:
3000:. Motilal Banarsidass. p. 3.
2852:Clémentin-Ojha, Catherine (2014).
2790:: "The term 'Indians' was used by
2405:
1853:"Now it took place in the days of
1779:. The term seemingly derives from
443:s or continents. For example, the
25:
4493:
3174:"Susa, Statue of Darius – Livius"
2151:"The whole country of Hind, from
982:. Thus, Sindh was referred to as
481:is cognate with the English verb
416:and notably participating in the
363:
220:The name derives ultimately from
4430:
4421:
4420:
4069:
3385:. Routledge. pp. 179, 181.
3196:"Hindi/Hindwī in Medieval Times"
1751:name for India mentioned in the
1658:). However, the use of the name
1536:Tianzhu was also referred to as
920:
909:
134:"Hindustān" meaning Land of the
3919:
3902:
3890:
3877:
3864:
3861:By University of Calcutta, 1950
3851:
3838:
3833:VISHŃU PURÁŃA, BOOK II, CHAP. I
3826:
3799:
3772:
3739:
3697:
3681:
3664:
3638:
3613:
3587:
3570:
3540:
3500:
3471:
3446:
3410:
3399:
3277:
3260:
3236:
3215:
3184:
3166:
3092:
3066:
3014:
2987:
2978:
2926:
2911:
2868:
2801:
2766:
2739:
2712:
2696:
2670:
2375:
1060:Both the names were current in
138:is another common name for the
4388:British Indian Ocean Territory
3806:A Text Book of Social Sciences
3362:Central Tibetan Administration
2591:
2541:
2523:
2473:
2447:
2391:in the year seven and ninety."
1915:Bhāratavarṣ (realm of Bhārat)
1698:India is nowadays also called
1544:
1486:
1470:
1318:Central Tibetan Administration
524:(2,1,31), Vayu Puran (33,52),
277:'s Geography. The loss of the
13:
1:
3431:Yu, Taishan (November 2013).
3202:, Primus Books, p. 105,
2609:W. B. Henning memorial volume
2598:Thieme, P. (1970), "Sanskrit
2531:"Etymology of the Name India"
2398:
1654:, a translation of a work by
1497:, another transliteration of
1116:
995:
520:. This has been mentioned in
211:), via Latin transliteration
3457:. Signal Books. p. 36.
2994:Dineschandra Sircar (1971).
2964:. Motilal Banarsidass Publ.
894:
849:
551:The Vishnu Purana mentions:
294:
269:
259:
249:
229:, which was the name of the
201:
144:northern Indian subcontinent
7:
3899:By Abū al-Faz̤l ibn Mubārak
3750:An Introduction to Hinduism
3507:Jaffee, Richard M. (2019).
2719:Horrocks, Geoffrey (2009),
2362:Renaming of cities in India
2314:
2297:
1786:, "great river", i.e., the
1700:
1691:
1685:
1666:India as a land of Buddhism
1660:
1644:
1595:
1571:
1554:
1538:
1480:
1464:
1445:
1402:
1396:
1361:
1313:The Kingdom of Golden Vases
1252:explains that Tibetan word
1164:
1094:
1043:
1011:
1005:was notably adapted in the
978:
964:
833:
807:
786:
772:
408:, who are mentioned in the
243:
225:
10:
4498:
3897:The Ain i Akbari, Volume 3
3342:Liaoning Normal University
3198:, in Aniruddha Ray (ed.),
3146:Yar-Shater, Ehsan (1982).
2918:Jain, Champat Rai (1929).
2535:World History Encyclopedia
1981:"The circumference of 五印 (
1765:. In Esther, 1:1 and 8:9,
1552:also referred to India as
1428:. Devout Buddhists in the
1353:
1349:
1335:(shishya or disciple) and
859:
842:
715:
703:
603:In the Sanskrit epic, the
512:. He is described to be a
206:
165:
28:
4467:Cultural history of India
4416:
4375:
4335:
4077:
3689:Chanakya and Chandragupta
3223:Mukherjee, Bratindra Nath
2824:Mukherjee, Bratindra Nath
2650:Dandamaev, M. A. (1989),
2549:Mukherjee, Bratindra Nath
2481:Mukherjee, Bratindra Nath
2420:Rethinking Hindu Identity
2291:
2025:and thence passest on to
1706:
1650:
1617:
1611:
1605:
1585:
1478:(Book of the Later Han).
1450:
1371:
1206:names for India. Ancient
1153:
1105:"Hindustan", as the term
1049:
1038:
936:
387:
188:The English term is from
107:who are mentioned in the
76:) and has been in use in
4137:East Timor (Timor-Leste)
3693:A. S. Panchapakesa Ayyar
2903:Pargiter, F. F. (1922),
2888:Pargiter, F. F. (1922),
2368:
2327:List of regions of India
2216:Ruy González de Clavijo
2202:Friar Jordanus Catalani
1474:), which is used in the
380:)", also a term for the
161:
4477:Names of places in Asia
4398:Cocos (Keeling) Islands
4027:. Leiden: E. J. Brill.
3132:National Museum of Iran
2938:Ia801005.us.archive.org
2423:(Routledge: 2014), p.11
1731:
1378:
1009:as the definitive form
678:Hathigumpha inscription
656:Epigraphical references
418:Battle of the Ten Kings
353:
347:
325:
195:(cf. Megasthenes' work
31:Bharat (disambiguation)
4462:Country name etymology
3932:, Peeters Publishers,
3453:Khair, Tabish (2006).
3274:(Emperor of Hindustan)
2656:, Brill, p. 147,
2275:
2235:Abu'l-Fazl ibn Mubarak
1712:
1534:
1420:
1375:originally pronounced
1256:comes from the Indian
1142:
1027:
767:
576:—Vishnu Purana (2,3,1)
563:
556:
451:(Vayu Puran 45, 86)."
315:
213:
185:
46:
3746:Flood, Gavin (1996).
3325:University of Chicago
3305:University of Chicago
3149:Encyclopaedia Iranica
2984:D.N. Jha (2014), p.11
2876:Constitution of India
2415:Dwijendra Narayan Jha
2273:
1514:
1327:reveres India as the
1306:The Kingdom of Pearls
1124:
857:where it was written
713:
184:'s view of the world.
175:
166:Further information:
92:in the 17th century.
41:
4312:United Arab Emirates
3952:, Orient Blackswan,
3548:"THE BOOK OF ESTHER"
3484:Buddhism Across Asia
3440:Sino-Platonic Papers
2920:The Practical Dharma
1455:), which appears in
1443:Other forms include
1098:is the name for the
1072:: the rulers in the
760:Egyptian hieroglyphs
359:Early Modern English
331:Old English language
237:, in Pakistan). The
176:India was the lower
131:along with "India".
129:Constituent Assembly
4339:limited recognition
3674:. 26 October 2015.
2454:Harris, J. (2012),
2352:Bharat chakravartin
2280:Indian constitution
1757:part of the Jewish
1481:Yìntèjiā or Indəkka
1438:Indian subcontinent
1216:Gyagar to the south
758:"India" written in
121:Indian subcontinent
44:Indian subcontinent
4457:Toponyms for India
3299:Toni Huber, 2008,
2537:. 13 January 2011.
2276:
2163:India the Greater
1615:, or occasionally
1331:with Tibet as its
1288:Epic of King Gesar
1196:Gyagar and Phagyul
1143:
1133:) in the Sahasram
950:Muhammad ibn Qasim
900:Statue of Darius I
768:
764:Statue of Darius I
454:The Sanskrit word
337:'s translation of
323:(2nd century CE).
265:Scylax of Caryanda
186:
47:
4444:
4443:
4381:other territories
3959:978-81-250-1871-1
3939:978-90-6186-037-2
3822:978-81-209-1466-7
3795:978-0-543-92939-6
3392:978-1-317-63928-2
3209:978-93-80607-16-0
3079:Los Angeles Times
3028:. 18 January 2024
3007:978-81-208-0690-0
2839:978-81-87498-26-1
2786:978-81-215-1152-0
2759:978-0-521-83307-3
2732:978-1-4443-1892-0
2690:978-90-04-25341-4
2564:978-81-87498-26-1
2496:978-81-87498-26-1
2467:978-1-137-09076-8
2266:Republic of India
2263:
2262:
2067:
2066:
2057:John Richardson,
2017:, the country of
1710:) in Korean, and
1490:) comes from the
1258:sanskrit language
1183:. The derivative
1174:
1162:
1100:Republic of India
1070:Islamic conquests
947:Governor of Sindh
890:
889:
886:
885:
756:
746:
745:
742:
741:
168:India (Herodotus)
152:Republic of India
140:Republic of India
125:Republic of India
61:. A third name,
51:Republic of India
16:(Redirected from
4489:
4472:Culture of India
4434:
4424:
4423:
4393:Christmas Island
4079:Sovereign states
4064:
4057:
4050:
4041:
4040:
4036:
4015:
3984:
3962:
3942:
3913:
3906:
3900:
3894:
3888:
3881:
3875:
3868:
3862:
3855:
3849:
3842:
3836:
3830:
3824:
3803:
3797:
3776:
3770:
3769:
3753:
3743:
3737:
3731:
3725:
3724:
3701:
3695:
3685:
3679:
3678:
3668:
3662:
3661:
3659:
3657:
3652:on 12 March 2014
3642:
3636:
3635:
3633:
3631:
3617:
3611:
3610:
3608:
3606:
3597:. Archived from
3591:
3585:
3574:
3568:
3567:
3565:
3563:
3554:. Archived from
3544:
3538:
3529:
3523:
3522:
3504:
3498:
3497:
3475:
3469:
3468:
3450:
3444:
3443:
3437:
3428:
3419:
3414:
3408:
3403:
3397:
3396:
3376:
3365:
3355:
3349:
3334:
3328:
3314:
3308:
3297:
3291:
3290:
3281:
3275:
3264:
3258:
3240:
3234:
3232:
3219:
3213:
3212:
3188:
3182:
3181:
3170:
3164:
3163:
3143:
3137:
3129:
3123:
3122:
3120:
3118:
3096:
3090:
3089:
3087:
3085:
3070:
3064:
3063:
3061:
3059:
3044:
3038:
3037:
3035:
3033:
3018:
3012:
3011:
2991:
2985:
2982:
2976:
2975:
2961:The Gupta Polity
2955:
2949:
2948:
2946:
2944:
2930:
2924:
2923:
2915:
2909:
2908:
2900:
2894:
2893:
2885:
2879:
2872:
2866:
2865:
2849:
2843:
2842:
2820:
2811:
2810:, pp. 13–14
2805:
2799:
2789:
2770:
2764:
2762:
2743:
2737:
2735:
2716:
2710:
2709:
2700:
2694:
2693:
2674:
2668:
2666:
2647:
2638:
2632:
2623:
2622:
2602:and Old Iranian
2595:
2589:
2580:, p. 145: "
2575:
2569:
2567:
2545:
2539:
2538:
2527:
2521:
2499:
2477:
2471:
2470:
2451:
2445:
2433:
2424:
2412:
2392:
2379:
2300:
2294:
2293:
2165:India the Minor
2113:and of es-Sind (
2077:
2076:
1933:100 CE or later
1808:
1807:
1801:Historical names
1743:
1715:
1709:
1708:
1703:
1694:
1688:
1682:
1663:
1653:
1652:
1647:
1641:
1633:Yamamura Saisuke
1620:
1619:
1614:
1613:
1608:
1607:
1602:
1600:
1599:
1588:
1587:
1578:
1576:
1575:
1558:or "Five Inds".
1557:
1547:
1546:
1541:
1489:
1488:
1483:
1473:
1472:
1467:
1454:
1448:
1423:
1405:
1399:
1381:
1374:
1373:
1364:
1208:Tibetan Buddhist
1169:
1167:
1157:
1155:
1141:, circa 250 BCE.
1135:Minor Rock Edict
1097:
1052:
1051:
1046:
1040:
1032:
1020:
1019:
1014:
997:
981:
975:
967:
941:
940:
924:
913:
902:, circa 500 BCE.
897:
891:
864:
863:
860:
852:
846:
836:
829:the Indus valley
810:
797:
789:
783:
775:
766:, circa 500 BCE.
748:
720:
719:
716:
700:Hind / Hindustan
675:
672:
669:
666:
663:
566:
559:
542:Markanday Purana
530:Brahmanda Purana
429:Bhārat Gaṇarājya
423:The designation
366:
365:
357:, which entered
356:
350:
333:and was used in
328:
318:
297:
272:
262:
252:
246:
228:
216:
210:
204:
97:native religions
21:
4497:
4496:
4492:
4491:
4490:
4488:
4487:
4486:
4447:
4446:
4445:
4440:
4412:
4380:
4371:
4352:Northern Cyprus
4338:
4331:
4073:
4068:
4010:, eds. (1971).
3991:
3989:Further reading
3981:
3960:
3940:
3922:
3917:
3916:
3907:
3903:
3895:
3891:
3882:
3878:
3869:
3865:
3859:Calcutta Review
3856:
3852:
3843:
3839:
3831:
3827:
3804:
3800:
3777:
3773:
3766:
3744:
3740:
3732:
3728:
3721:
3702:
3698:
3686:
3682:
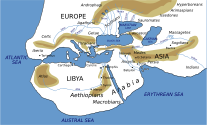
3670:
3669:
3665:
3655:
3653:
3644:
3643:
3639:
3629:
3627:
3619:
3618:
3614:
3604:
3602:
3601:on 28 June 2012
3595:"Hobson-Jobson"
3593:
3592:
3588:
3575:
3571:
3561:
3559:
3558:on 4 March 2016
3552:Uskojaelama.net
3546:
3545:
3541:
3530:
3526:
3519:
3505:
3501:
3494:
3476:
3472:
3465:
3451:
3447:
3435:
3429:
3422:
3415:
3411:
3404:
3400:
3393:
3377:
3368:
3358:Thank you India
3356:
3352:
3335:
3331:
3327:Press, p.73-74.
3315:
3311:
3307:Press, p.74-80.
3298:
3294:
3283:
3282:
3278:
3265:
3261:
3241:
3237:
3220:
3216:
3210:
3189:
3185:
3172:
3171:
3167:
3160:
3144:
3140:
3130:
3126:
3116:
3114:
3098:
3097:
3093:
3083:
3081:
3071:
3067:
3057:
3055:
3045:
3041:
3031:
3029:
3020:
3019:
3015:
3008:
2992:
2988:
2983:
2979:
2972:
2956:
2952:
2942:
2940:
2932:
2931:
2927:
2916:
2912:
2901:
2897:
2886:
2882:
2873:
2869:
2850:
2846:
2840:
2821:
2814:
2806:
2802:
2787:
2771:
2767:
2760:
2744:
2740:
2733:
2717:
2713:
2702:
2701:
2697:
2691:
2675:
2671:
2664:
2648:
2641:
2633:
2626:
2620:
2596:
2592:
2576:
2572:
2565:
2546:
2542:
2529:
2528:
2524:
2497:
2478:
2474:
2468:
2452:
2448:
2434:
2427:
2413:
2406:
2401:
2396:
2395:
2380:
2376:
2371:
2366:
2317:
2268:
2237:
2166:
2164:
2129:
2103:
2072:
1947:
1926:
1899:
1841:c. 400–300 BCE
1803:
1749:Biblical Hebrew
1734:
1676:
1635:
1597:
1596:
1573:
1572:
1358:
1356:Tianzhu (India)
1352:
1198:
1189:Southeast Asian
1119:
1074:Delhi Sultanate
1007:Arabic language
956:
955:
954:
953:
927:
926:
925:
916:
915:
914:
903:
858:
757:
747:
708:
702:
673:
671:Bharat mainland
670:
667:
664:
658:
390:
288:By the time of
170:
164:
117:Gangetic Valley
34:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
4495:
4485:
4484:
4479:
4474:
4469:
4464:
4459:
4442:
4441:
4439:
4438:
4428:
4417:
4414:
4413:
4411:
4410:
4405:
4400:
4395:
4390:
4384:
4382:
4373:
4372:
4370:
4369:
4364:
4359:
4354:
4349:
4343:
4341:
4333:
4332:
4330:
4329:
4324:
4319:
4314:
4309:
4304:
4299:
4294:
4289:
4284:
4279:
4274:
4269:
4264:
4259:
4254:
4249:
4244:
4239:
4234:
4229:
4224:
4219:
4214:
4209:
4204:
4199:
4194:
4189:
4184:
4179:
4174:
4169:
4164:
4159:
4154:
4149:
4144:
4139:
4134:
4129:
4124:
4119:
4114:
4109:
4104:
4099:
4094:
4089:
4083:
4081:
4075:
4074:
4067:
4066:
4059:
4052:
4044:
4038:
4037:
3990:
3987:
3986:
3985:
3979:
3963:
3958:
3943:
3938:
3921:
3918:
3915:
3914:
3901:
3889:
3887:By D.C. Sircar
3876:
3863:
3850:
3837:
3825:
3798:
3771:
3764:
3738:
3736:, p. 249.
3726:
3719:
3696:
3680:
3663:
3637:
3612:
3586:
3569:
3539:
3524:
3517:
3499:
3492:
3470:
3463:
3445:
3442:(242): 73, 77.
3420:
3409:
3398:
3391:
3366:
3350:
3329:
3309:
3292:
3276:
3259:
3235:
3214:
3208:
3183:
3178:www.livius.org
3165:
3158:
3138:
3124:
3091:
3065:
3039:
3013:
3006:
2986:
2977:
2970:
2950:
2925:
2910:
2895:
2880:
2867:
2844:
2838:
2812:
2800:
2785:
2765:
2758:
2738:
2731:
2711:
2695:
2689:
2669:
2662:
2639:
2624:
2618:
2600:sindu-/Sindhu-
2590:
2570:
2563:
2540:
2522:
2495:
2472:
2466:
2446:
2425:
2403:
2402:
2400:
2397:
2394:
2393:
2373:
2372:
2370:
2367:
2365:
2364:
2359:
2354:
2349:
2344:
2339:
2334:
2329:
2324:
2318:
2316:
2313:
2312:
2311:
2302:
2267:
2264:
2261:
2260:
2257:
2256:Ignazio Danti
2254:
2251:
2247:
2246:
2243:
2232:
2229:
2225:
2224:
2217:
2214:
2211:
2207:
2206:
2203:
2200:
2197:
2193:
2192:
2173:
2168:
2161:
2157:
2156:
2149:
2146:
2143:
2139:
2138:
2135:
2132:Hudud al-'Alam
2128:Author Unknown
2126:
2123:
2119:
2118:
2107:
2098:
2095:
2091:
2090:
2087:
2084:
2081:
2071:
2068:
2065:
2064:
2061:
2055:
2050:
2047:
2046:
2043:
2038:
2035:
2031:
2030:
2007:
2002:
1999:
1995:
1994:
1983:Modern Chinese
1979:
1974:
1971:
1967:
1966:
1963:
1958:
1955:
1951:
1950:
1942:
1937:
1934:
1930:
1929:
1921:
1916:
1913:
1909:
1908:
1905:
1894:
1891:
1887:
1886:
1875:
1870:
1867:
1863:
1862:
1851:
1848:Book of Esther
1845:
1842:
1838:
1837:
1834:
1829:
1826:
1822:
1821:
1818:
1815:
1812:
1802:
1799:
1761:and Christian
1754:Book of Esther
1733:
1730:
1565:borrowing of *
1563:Middle Chinese
1354:Main article:
1351:
1348:
1339:Mahatma Gandhi
1197:
1194:
1118:
1115:
1044:Hind Mahāsāgar
1023:Tarikh Al-Hind
960:middle Persian
929:
928:
919:
918:
917:
908:
907:
906:
905:
904:
888:
887:
884:
883:
880:
877:
874:
871:
868:
769:
744:
743:
740:
739:
736:
733:
730:
727:
724:
714:
704:Main article:
701:
698:
657:
654:
643:Prime Minister
639:Droupadi Murmu
580:
579:
578:
577:
567:
560:
462:derivation of
389:
386:
343:Middle English
339:Paulus Orosius
241:equivalent of
163:
160:
90:Modern English
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
4494:
4483:
4480:
4478:
4475:
4473:
4470:
4468:
4465:
4463:
4460:
4458:
4455:
4454:
4452:
4437:
4433:
4429:
4427:
4419:
4418:
4415:
4409:
4406:
4404:
4401:
4399:
4396:
4394:
4391:
4389:
4386:
4385:
4383:
4378:
4374:
4368:
4365:
4363:
4362:South Ossetia
4360:
4358:
4355:
4353:
4350:
4348:
4345:
4344:
4342:
4340:
4334:
4328:
4325:
4323:
4320:
4318:
4315:
4313:
4310:
4308:
4305:
4303:
4300:
4298:
4295:
4293:
4290:
4288:
4285:
4283:
4280:
4278:
4275:
4273:
4270:
4268:
4265:
4263:
4260:
4258:
4255:
4253:
4250:
4248:
4245:
4243:
4240:
4238:
4235:
4233:
4230:
4228:
4225:
4223:
4220:
4218:
4215:
4213:
4210:
4208:
4205:
4203:
4200:
4198:
4195:
4193:
4190:
4188:
4185:
4183:
4180:
4178:
4175:
4173:
4170:
4168:
4165:
4163:
4160:
4158:
4155:
4153:
4150:
4148:
4145:
4143:
4140:
4138:
4135:
4133:
4130:
4128:
4125:
4123:
4120:
4118:
4115:
4113:
4110:
4108:
4105:
4103:
4100:
4098:
4095:
4093:
4090:
4088:
4085:
4084:
4082:
4080:
4076:
4072:
4071:Name of Asia
4065:
4060:
4058:
4053:
4051:
4046:
4045:
4042:
4034:
4030:
4026:
4022:
4020:
4014:
4009:
4005:
4001:
4000:Ménage, V. L.
3997:
3993:
3992:
3982:
3980:3-447-02522-0
3976:
3972:
3968:
3964:
3961:
3955:
3951:
3950:
3944:
3941:
3935:
3931:
3930:
3924:
3923:
3912:By Mark Rosen
3911:
3905:
3898:
3893:
3886:
3880:
3873:
3867:
3860:
3854:
3847:
3841:
3834:
3829:
3823:
3819:
3815:
3814:81-209-1466-X
3811:
3807:
3802:
3796:
3792:
3788:
3787:0-543-92939-6
3784:
3780:
3775:
3767:
3765:0-521-43878-0
3761:
3757:
3752:
3751:
3742:
3735:
3730:
3722:
3720:1-84664-664-2
3716:
3712:
3709:
3706:
3705:Wilson, H. H.
3700:
3694:
3690:
3684:
3677:
3673:
3667:
3651:
3647:
3641:
3626:
3622:
3616:
3600:
3596:
3590:
3584:
3580:
3579:
3573:
3557:
3553:
3549:
3543:
3537:
3533:
3528:
3520:
3518:9780226391151
3514:
3510:
3503:
3495:
3493:9789814519328
3489:
3485:
3481:
3474:
3466:
3464:9781904955115
3460:
3456:
3449:
3441:
3434:
3427:
3425:
3418:
3413:
3407:
3402:
3394:
3388:
3384:
3383:
3375:
3373:
3371:
3363:
3359:
3354:
3347:
3343:
3339:
3333:
3326:
3322:
3318:
3317:Gendun Chopel
3313:
3306:
3302:
3296:
3288:
3287:
3280:
3273:
3269:
3263:
3256:
3252:
3248:
3244:
3239:
3230:
3229:
3224:
3218:
3211:
3205:
3201:
3197:
3193:
3187:
3179:
3175:
3169:
3161:
3159:9780933273955
3155:
3151:
3150:
3142:
3136:
3133:
3128:
3113:
3109:
3105:
3104:The Economist
3101:
3095:
3080:
3076:
3069:
3054:
3050:
3043:
3027:
3026:The Economist
3023:
3017:
3009:
3003:
2999:
2998:
2990:
2981:
2973:
2971:9788120810242
2967:
2963:
2962:
2954:
2939:
2935:
2929:
2922:. p. 92.
2921:
2914:
2906:
2899:
2891:
2884:
2877:
2871:
2863:
2859:
2855:
2848:
2841:
2835:
2831:
2830:
2825:
2819:
2817:
2809:
2804:
2797:
2793:
2788:
2782:
2778:
2777:
2769:
2761:
2755:
2751:
2750:
2742:
2734:
2728:
2724:
2723:
2715:
2707:
2706:
2699:
2692:
2686:
2682:
2681:
2673:
2665:
2663:90-04-09172-6
2659:
2655:
2654:
2646:
2644:
2636:
2631:
2629:
2621:
2619:9780853312550
2615:
2611:
2610:
2605:
2604:hindu-/Hindu-
2601:
2594:
2587:
2583:
2579:
2574:
2566:
2560:
2556:
2555:
2550:
2544:
2536:
2532:
2526:
2519:
2515:
2511:
2507:
2503:
2498:
2492:
2488:
2487:
2482:
2476:
2469:
2463:
2459:
2458:
2450:
2443:
2442:
2437:
2436:Upinder Singh
2432:
2430:
2422:
2421:
2416:
2411:
2409:
2404:
2390:
2386:
2383:
2378:
2374:
2363:
2360:
2358:
2357:Akhand Bharat
2355:
2353:
2350:
2348:
2345:
2343:
2340:
2338:
2335:
2333:
2330:
2328:
2325:
2323:
2320:
2319:
2310:
2306:
2303:
2299:
2288:
2285:
2284:
2283:
2281:
2272:
2258:
2255:
2252:
2250:16th century
2249:
2248:
2244:
2242:
2241:
2236:
2233:
2230:
2227:
2226:
2222:
2218:
2215:
2212:
2209:
2208:
2204:
2201:
2198:
2195:
2194:
2190:
2189:Krishna Delta
2186:
2182:
2178:
2174:
2172:
2169:
2167:Middle India
2162:
2159:
2158:
2154:
2150:
2148:Hasan Nizāmī
2147:
2144:
2141:
2140:
2136:
2134:
2133:
2127:
2124:
2121:
2120:
2116:
2112:
2108:
2106:
2102:
2099:
2096:
2093:
2092:
2088:
2085:
2082:
2079:
2078:
2075:
2062:
2060:
2056:
2054:
2051:
2049:
2048:
2044:
2042:
2039:
2036:
2033:
2032:
2028:
2024:
2020:
2016:
2012:
2008:
2006:
2003:
2000:
1997:
1996:
1992:
1988:
1984:
1980:
1978:
1975:
1972:
1969:
1968:
1964:
1962:
1959:
1957:Indoi, Indou
1956:
1953:
1952:
1949:
1943:
1941:
1940:Vishnu Purana
1938:
1935:
1932:
1931:
1928:
1922:
1920:
1919:Vishnu Purana
1917:
1914:
1911:
1910:
1906:
1904:
1903:
1898:
1895:
1892:
1889:
1888:
1884:
1880:
1876:
1874:
1871:
1869:India/Indikē
1868:
1865:
1864:
1860:
1856:
1852:
1849:
1846:
1843:
1840:
1839:
1835:
1833:
1830:
1827:
1824:
1823:
1819:
1816:
1813:
1810:
1809:
1806:
1798:
1796:
1793:
1789:
1785:
1782:
1778:
1777:
1772:
1768:
1764:
1763:Old Testament
1760:
1756:
1755:
1750:
1746:
1739:
1729:
1727:
1723:
1719:
1714:
1702:
1696:
1693:
1687:
1680:
1675:
1674:Seki Seisetsu
1671:
1667:
1662:
1657:
1656:Johann Hübner
1646:
1639:
1634:
1630:
1629:
1624:
1623:Arai Hakuseki
1601:
1592:
1582:
1577:
1568:
1564:
1559:
1556:
1551:
1540:
1533:
1531:
1527:
1523:
1520:southeast of
1519:
1513:
1511:
1507:
1502:
1500:
1496:
1493:
1482:
1477:
1466:
1462:. Another is
1461:
1458:
1453:
1447:
1441:
1439:
1435:
1431:
1427:
1422:
1417:
1413:
1409:
1404:
1400:in Japanese,
1398:
1393:
1389:
1385:
1380:
1368:
1363:
1357:
1347:
1346:
1344:
1340:
1334:
1330:
1326:
1323:
1319:
1315:
1314:
1308:
1307:
1301:
1297:
1293:
1289:
1285:
1281:
1277:
1273:
1269:
1265:
1264:
1259:
1255:
1251:
1250:Gendun Chopel
1247:
1246:
1240:
1236:
1232:
1229:
1225:
1221:
1217:
1213:
1209:
1205:
1200:
1193:
1190:
1186:
1182:
1181:Insular India
1178:
1172:
1166:
1160:
1151:
1147:
1140:
1136:
1132:
1131:Brahmi script
1129:for "India" (
1128:
1123:
1114:
1112:
1108:
1103:
1101:
1096:
1091:
1087:
1083:
1079:
1075:
1071:
1067:
1063:
1058:
1056:
1050:हिन्द महासागर
1045:
1036:
1031:
1030:
1024:
1013:
1008:
1004:
999:
993:
989:
985:
980:
971:
966:
961:
951:
948:
944:
939:
933:
923:
912:
901:
896:
881:
878:
875:
872:
869:
866:
865:
862:
861:
856:
851:
845:
840:
835:
830:
826:
822:
818:
814:
809:
805:
801:
793:
788:
779:
774:
765:
761:
755:
753:
737:
734:
731:
728:
725:
722:
721:
718:
717:
712:
707:
697:
695:
694:Rishabhanatha
691:
687:
683:
679:
653:
651:
647:
646:Narendra Modi
644:
640:
637:
632:
630:
629:
624:
620:
616:
612:
608:
607:
601:
599:
595:
591:
589:
585:
575:
574:
572:
568:
565:
561:
558:
554:
553:
552:
549:
547:
543:
539:
536:(107,11–12),
535:
531:
527:
523:
522:Vishnu Purana
519:
518:Solar dynasty
515:
511:
508:, the son of
507:
502:
500:
496:
492:
488:
484:
480:
477:
473:
469:
465:
461:
457:
452:
450:
446:
442:
438:
434:
430:
426:
421:
419:
415:
411:
407:
403:
398:
395:
385:
383:
379:
375:
374:
368:
360:
355:
349:
344:
340:
336:
332:
329:was known in
327:
322:
317:
311:
309:
305:
301:
296:
291:
286:
284:
280:
276:
271:
266:
261:
256:
251:
245:
240:
236:
232:
227:
223:
218:
215:
209:
203:
198:
194:
191:
183:
179:
174:
169:
159:
157:
153:
149:
145:
141:
137:
132:
130:
126:
122:
118:
114:
110:
106:
102:
98:
93:
91:
87:
83:
79:
75:
70:
68:
64:
60:
56:
52:
45:
40:
36:
32:
27:
19:
4377:Dependencies
4307:Turkmenistan
4272:Saudi Arabia
4024:
4017:
3970:
3967:Rocher, Ludo
3948:
3928:
3920:Bibliography
3909:
3904:
3896:
3892:
3884:
3879:
3871:
3866:
3858:
3853:
3845:
3840:
3828:
3801:
3774:
3749:
3741:
3729:
3711:
3708:
3699:
3688:
3683:
3675:
3666:
3654:. Retrieved
3650:the original
3640:
3628:. Retrieved
3625:Biblehub.com
3624:
3615:
3603:. Retrieved
3599:the original
3589:
3576:
3572:
3560:. Retrieved
3556:the original
3551:
3542:
3527:
3508:
3502:
3483:
3479:
3473:
3454:
3448:
3439:
3412:
3401:
3381:
3353:
3332:
3312:
3295:
3285:
3279:
3267:
3262:
3254:
3250:
3246:
3238:
3227:
3217:
3199:
3192:Habib, Irfan
3186:
3177:
3168:
3148:
3141:
3127:
3115:. Retrieved
3103:
3094:
3082:. Retrieved
3078:
3068:
3058:21 September
3056:. Retrieved
3052:
3042:
3030:. Retrieved
3025:
3016:
2996:
2989:
2980:
2960:
2953:
2941:. Retrieved
2937:
2928:
2919:
2913:
2904:
2898:
2889:
2883:
2870:
2861:
2857:
2847:
2828:
2803:
2775:
2768:
2748:
2741:
2721:
2714:
2704:
2698:
2679:
2672:
2652:
2608:
2603:
2599:
2593:
2585:
2581:
2573:
2553:
2543:
2534:
2525:
2517:
2513:
2509:
2505:
2501:
2485:
2475:
2456:
2449:
2440:
2419:
2384:
2377:
2347:Sapta Sindhu
2342:Bharat Khand
2308:
2277:
2240:Ain-i-Akbari
2238:
2213:India Minor
2130:
2104:
2073:
2058:
2011:Indian Ocean
1986:
1973:Five Indies
1945:
1924:
1902:Arthashastra
1900:
1804:
1794:
1783:
1774:
1770:
1752:
1744:
1735:
1725:
1721:
1697:
1626:
1566:
1560:
1535:
1517:
1515:
1508:compiled by
1505:
1503:
1498:
1494:
1442:
1387:
1386:via Persian
1383:
1359:
1336:
1321:
1310:
1303:
1295:
1291:
1267:
1261:
1253:
1243:the land of
1242:
1238:
1237:, short for
1234:
1224:central land
1223:
1219:
1215:
1211:
1201:
1199:
1184:
1176:
1144:
1126:
1104:
1059:
1055:Indian Ocean
1022:
1002:
1000:
983:
957:
942:
838:
798:) came from
749:
659:
633:
626:
604:
602:
594:Bharat Khand
592:
581:
550:
546:Bhāratavarṣa
545:
540:(37,57) and
538:Skand Purana
526:Linga Purana
516:born in the
503:
498:
490:
486:
482:
478:
463:
455:
453:
448:
440:
437:Bhāratavarṣa
436:
428:
424:
422:
399:
391:
372:
369:
312:
287:
219:
192:
187:
133:
94:
71:
62:
58:
54:
48:
35:
26:
4436:Asia portal
4337:States with
4257:Philippines
4197:South Korea
4192:North Korea
4087:Afghanistan
4023:Volume III:
4008:Schacht, J.
4004:Pellat, Ch.
3971:The Purāṇas
3734:Rocher 1986
2520:dropped..."
2185:Cochinchina
2115:Baluchistan
2089:Definition
1893:Jambudvīpa
1873:Megasthenes
1866:c. 300 BCE
1825:c. 440 BCE
1820:Definition
1792:Old Persian
1788:Indus River
1773:(India) to
1677: [
1670:Soyen Shaku
1636: [
1631:(1713) and
1628:Sairan Igen
1512:(398–445):
1457:Sima Qian's
1394:reading is
1379:qʰl'iːn tuɡ
1345:tradition."
1185:Jambu Dwipa
1165:Jambu-dvīpa
1127:Jambudīpasi
1111:British era
813:Indus River
628:Mahabharata
615:South India
598:Hindu texts
534:Agni Purana
532:(14,5,62),
528:(1,47,23),
445:Vayu Purana
335:King Alfred
319:is used by
308:Megasthenes
300:Koine Greek
239:Old Persian
231:Indus River
148:Old Persian
86:Old English
74:Indus River
4451:Categories
4317:Uzbekistan
4292:Tajikistan
4207:Kyrgyzstan
4187:Kazakhstan
4107:Bangladesh
4097:Azerbaijan
3532:Esther 1:1
3032:24 January
2586:Saindhavah
2399:References
2337:Indosphere
2231:Hindustān
2177:Coromandel
2171:Marco Polo
2125:Hindistān
1718:Vietnamese
1506:Hou Hanshu
1476:Hou Hanshu
1430:Sinosphere
1426:Vietnamese
1421:Thiên Trúc
1392:Sino-Xenic
1325:Dalai Lama
1241:, meaning
1220:Madhyadesa
1154:जम्बुद्वीप
1146:Jambudvīpa
1117:Jambudvīpa
952:in 715 CE.
930:The name "
895:H-n-d-wꜣ-y
850:H-i-du-u-š
844:𐏃𐎡𐎯𐎢𐏁
827:conquered
821:Achaemenid
800:Indo-Aryan
770:The words
606:Mahabharat
485:and Latin
404:community
376:"drop (of
306:). Later,
304:Gangaridai
283:Asia Minor
158:speakers.
156:Hindustani
18:Epic India
4403:Hong Kong
4357:Palestine
4282:Sri Lanka
4277:Singapore
4157:Indonesia
4033:495469525
3996:Lewis, B.
3630:10 August
3562:10 August
3480:(Tenjiku)
3112:0013-0613
2943:10 August
2796:Hekataios
2792:Herodotus
2683:, BRILL,
2253:Indostān
2101:Al-Masudi
2053:Hindustan
2041:Al-Biruni
1936:Bhāratam
1859:Ahasuerus
1855:Ahasuerus
1832:Herodotus
1767:Ahasuerus
1747:) is the
1695:by then.
1539:Wǔtiānzhú
1403:Cheonchuk
1239:Phags yul
1159:romanized
1125:The name
984:Hindustān
979:Hindūstān
898:) on the
837:, viz., "
706:Hindustan
682:Kharavela
636:President
619:Dushyanta
514:Kshatriya
495:Esperanto
414:Āryāvarta
394:Article 1
370:Sanskrit
290:Alexander
275:Herodotus
182:Herodotus
180:basin in
113:Aryavarta
103:tribe of
82:Herodotus
67:Hindustān
63:Hindustan
4426:Category
4347:Abkhazia
4297:Thailand
4252:Pakistan
4232:Mongolia
4227:Maldives
4222:Malaysia
4122:Cambodia
3969:(1986).
3707:(2006).
3583:BibleHub
3348:, China.
3225:(1989),
3194:(2011),
2826:(2001),
2551:(2001),
2483:(2001),
2385:Bil'Hind
2315:See also
2196:c. 1328
2153:Peshawar
2122:982–983
2111:Khorasan
2097:Al-Hind
2034:c. 1020
2005:Istakhri
1977:Xuanzang
1897:Chanakya
1890:200 BCE
1850:(Bible)
1781:Sanskrit
1776:Ethiopia
1591:Xuanzang
1550:Xuanzang
1434:Buddhism
1311:Gyagar:
1309:" and "
1304:Gyagar:
1300:ayurveda
1282:(modern
1274:(modern
1150:Sanskrit
1041:) or in
1039:जय हिन्द
1029:Jai Hind
998:262 CE.
992:Shapur I
990:emperor
988:Sassanid
943:Bil'Hind
934:" (here
825:Darius I
823:emperor
804:Sanskrit
688:west of
680:of King
584:Rishabha
510:Rishabha
406:Bharatas
279:aspirate
255:Darius I
222:Sanskrit
105:Bharatas
4322:Vietnam
4237:Myanmar
4217:Lebanon
4147:Georgia
4102:Bahrain
4092:Armenia
3883:P. 187
3870:P. 177
3844:P. 146
3687:P. 247
3656:25 June
3605:28 June
3266:P. 310
2444:, p.253
2389:al-Hind
2305:English
2187:to the
2086:Source
2023:Kannauj
2019:Mansūra
1998:c. 950
1970:c. 650
1954:c. 140
1879:Scythia
1817:Source
1686:Tenjiku
1661:Tenjiku
1645:Indoshi
1581:Chinese
1492:Kuchean
1436:in the
1397:Tenjiku
1367:Chinese
1362:Tiānzhú
1350:Tianzhu
1343:Nalanda
1316:". The
1286:). The
1280:Magadha
1276:Haryana
1235:Phagyul
1228:Tibetan
1204:Tibetan
1173:
1161::
1095:al-Hind
1062:Persian
1012:Al-Hind
970:Persian
932:al-Hind
839:Hindush
819:). The
815:or its
792:Persian
778:Persian
762:on the
750:H-n-d-w
690:Magadha
665:
625:in the
623:Bharata
621:'s son
588:Bharata
571:Bharata
506:Bharata
499:Bhārata
483:to bear
474:). The
464:Bharata
456:Bhārata
433:Puranas
410:Rigveda
127:by the
109:Rigveda
4367:Taiwan
4302:Turkey
4267:Russia
4202:Kuwait
4182:Jordan
4172:Israel
4132:Cyprus
4117:Brunei
4112:Bhutan
4031:
4025:H–Iram
4013:"Hind"
4006:&
3977:
3956:
3936:
3857:P. 45
3820:
3812:
3793:
3785:
3762:
3717:
3515:
3490:
3461:
3389:
3346:Dalian
3247:Hndstn
3206:
3156:
3135:notice
3117:2 July
3110:
3084:2 July
3004:
2968:
2836:
2783:
2756:
2729:
2687:
2660:
2616:
2582:Sindhu
2561:
2493:
2464:
2382:بالهند
2332:Sindhu
2298:Bhārat
2221:Termez
2199:India
2181:Mekran
2015:Mokrān
1987:Wǔ Yìn
1961:Arrian
1857:, the
1828:India
1795:Hiñd°u
1790:, via
1784:Sindhu
1759:Tanakh
1742:הֹדּוּ
1738:Hebrew
1736:Hodu (
1555:Wǔ Yìn
1530:Da Qin
1526:Buddha
1522:Yuezhi
1510:Fan Ye
1495:Indaka
1465:Tiāndǔ
1446:Juāndú
1418:, and
1416:Korean
1408:Hangul
1384:Sindhu
1268:Geysar
1263:vihāra
1254:gyagar
1212:Gyagar
1177:Bhārat
1139:Ashoka
1078:Mughal
1066:Arabic
938:بالهند
834:Sindhu
817:region
808:Sindhu
784:) and
686:Ganges
611:Deccan
493:, the
491:Barato
460:vrddhi
447:says "
425:Bharat
388:Bharat
321:Lucian
313:Latin
260:Hinduš
244:Síndhu
226:Sindhu
197:Indica
193:Indikē
136:Hindus
80:since
59:Bharat
4408:Macau
4327:Yemen
4287:Syria
4262:Qatar
4242:Nepal
4177:Japan
4152:India
4142:Egypt
4127:China
3908:P. 3
3436:(PDF)
3272:Babur
3255:Hindy
3251:India
2369:Notes
2309:India
2287:Hindi
2282:are:
2228:1590
2210:1404
2160:1298
2145:Hind
2142:1205
2083:Name
2080:Year
2037:Hind
2027:Tibet
2001:Hind
1844:Hodû
1814:Name
1811:Year
1713:Ấn Độ
1681:]
1640:]
1574:Yìndù
1567:yentu
1499:Hindu
1460:Shiji
1414:) in
1388:Hindu
1377:*
1333:chela
1284:Bihar
1278:) to
1260:word
1245:aryas
1231:lamas
1107:Hindu
1086:Hindi
1082:Delhi
1035:Hindi
1018:الهند
965:-stān
855:Egypt
811:(the
773:Hindū
458:is a
441:varṣa
402:Vedic
364:Indie
341:. In
326:India
316:India
295:Indía
270:Indos
250:Hindu
235:Sindh
214:India
208:Ἰνδία
202:Indía
199:) or
190:Greek
178:Indus
162:India
101:Vedic
78:Greek
55:India
4247:Oman
4212:Laos
4167:Iraq
4162:Iran
4029:OCLC
3975:ISBN
3954:ISBN
3934:ISBN
3818:ISBN
3810:ISBN
3791:ISBN
3783:ISBN
3760:ISBN
3715:ISBN
3658:2020
3632:2017
3607:2012
3564:2017
3534:and
3513:ISBN
3488:ISBN
3459:ISBN
3387:ISBN
3253:and
3204:ISBN
3154:ISBN
3119:2024
3108:ISSN
3086:2024
3060:2023
3034:2024
3002:ISBN
2966:ISBN
2945:2017
2834:ISBN
2781:ISBN
2754:ISBN
2727:ISBN
2685:ISBN
2658:ISBN
2614:ISBN
2559:ISBN
2508:and
2491:ISBN
2462:ISBN
2292:भारत
2094:944
1883:Nile
1771:Hodu
1745:Hodû
1732:Hodu
1701:Indo
1692:Indo
1672:and
1598:Indo
1329:guru
1302:), "
1294:", "
1272:Kuru
1218:and
1171:lit.
1090:Urdu
1076:and
1064:and
1003:Hind
974:ستان
787:Hind
782:هندو
662:lit.
641:and
613:and
487:ferō
476:root
472:fire
468:Agni
382:Moon
378:Soma
373:indu
361:as "
354:Inde
348:Ynde
247:was
57:and
49:The
4379:and
3756:111
3691:By
3581:at
3536:8:9
3270:By
3053:CNN
2512:by
2504:by
2179:to
1885:."
1726:Ind
1722:Yin
1716:in
1651:印度志
1642:'s
1625:'s
1606:インド
1545:五天竺
1487:印特伽
1424:in
1298:" (
1214:or
1137:of
994:in
958:In
841:" (
796:هند
650:G20
479:bhr
420:.
351:or
298:in
154:by
4453::
4021:.
4016:.
4002:;
3998:;
3816:,
3789:,
3758:.
3623:.
3550:.
3438:.
3423:^
3369:^
3360:,
3344:,
3340:,
3323:,
3303:,
3249:,
3176:.
3106:.
3102:.
3077:.
3051:.
3024:.
2936:.
2862:10
2860:.
2856:.
2815:^
2642:^
2627:^
2533:.
2510:dh
2438:,
2428:^
2417:,
2407:^
2307::
2289::
1991:li
1985::
1740::
1728:.
1707:인도
1679:ja
1638:ja
1618:印土
1612:印度
1609:,
1586:印度
1583::
1518:li
1501:.
1471:天篤
1452:身毒
1440:.
1412:천축
1410::
1372:天竺
1369::
1168:,
1156:,
1152::
1113:.
1102:.
1057:.
1037::
996:c.
972::
847:,
794::
780::
754:-y
696:.
631:.
600:.
573:.
548:.
501:.
292:,
253:.
217:.
4063:e
4056:t
4049:v
4035:.
3983:.
3768:.
3723:.
3660:.
3634:.
3609:.
3566:.
3521:.
3496:.
3467:.
3395:.
3180:.
3162:.
3121:.
3088:.
3062:.
3036:.
3010:.
2974:.
2947:.
2864:.
2518:h
2514:d
2506:h
2502:s
2301:)
2295:(
1704:(
1648:(
1603:(
1579:(
1542:(
1484:(
1468:(
1449:(
1406:(
1365:(
1222:(
1148:(
1088:-
1047:(
1033:(
1015:(
968:(
892:(
802:/
790:(
776:(
752:Ꜣ
674:'
668:'
205:(
33:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.