1138:. When the eye is turned out (temporally) and horizontally, the function of the lateral rectus muscle is tested. When the eye is turned in (nasally) and horizontally, the function of the medial rectus muscle is being tested. When turning the eye down and in, the inferior rectus is contracting. When turning it up and in the superior rectus is contracting. Paradoxically, turning the eye up and out uses the inferior oblique muscle, and turning it down and out uses the superior oblique. All of these six movements can be tested by drawing a large "H" in the air with a finger or other object in front of a patient's face and having them follow the tip of the finger or object with their eyes without moving their head. Having them focus on the object as it is moved in toward their face in the midline will test
1227:
712:
usually triggered by the nearness of the target object. A "see-saw" movement, namely, one eye looking up and the other down, is possible, but not voluntarily; this effect is brought on by putting a prism in front of one eye, so the relevant image is apparently displaced. To avoid double vision from non-corresponding points, the eye with the prism must move up or down, following the image passing through the prism. Likewise conjugate torsion (rolling) on the anteroposterior axis (from the front to the back) can occur naturally, such as when one tips one's head to one shoulder; the torsion, in the opposite direction, keeps the image vertical.
444:
417:
1194:
427:
445:
1182:
326:
1206:
666:
1170:
1055:
443:
450:
1158:
510:, on the upper, nasal wall of the orbit. The muscle becomes tendinous about 10mm before it passes through the pulley, turning sharply across the orbit, and inserts on the lateral, posterior part of the globe. Thus, the superior oblique travels posteriorly for the last part of its path, going over the top of the eye. Due to its unique path, the superior oblique, when activated, pulls the eye downward and laterally.
1218:
436:
432:
517:, which originates at the lower front of the nasal orbital wall, passes inferiorly over the inferior rectus muscle on its path laterally and posteriorly, and inserts under the lateral rectus muscle on the lateral, posterior part of the globe. Thus, the inferior oblique pulls the eye upward and laterally.
621:
The nuclei or bodies of these nerves are found in the brain stem. The nuclei of the abducens and oculomotor nerves are connected. This is important in coordinating the motion of the lateral rectus in one eye and the medial action on the other. In one eye, in two antagonistic muscles, like the lateral
707:
Intermediate directions are controlled by simultaneous actions of multiple muscles. When one shifts the gaze horizontally, one eye will move laterally (toward the side) and the other will move medially (toward the midline). This may be neurally coordinated by the central nervous system, to make the
348:
must be precise and fast. This is seen in scenarios like reading, where the reader must shift gaze constantly. Although under voluntary control, most eye movement is accomplished without conscious effort. Precisely how the integration between voluntary and involuntary control of the eye occurs is a
711:
There are two main kinds of movement: conjugate movement (the eyes move in the same direction) and disjunctive (opposite directions). The former is typical when shifting gaze right or left, the latter is convergence of the two eyes on a near object. Disjunction can be performed voluntarily, but is
498:
Medial and lateral are relative terms. Medial indicates near the midline, and lateral describes a position away from the midline. Thus, the medial rectus is the muscle closest to the nose. The superior and inferior recti do not pull straight back on the eye, because both muscles also pull slightly
435:
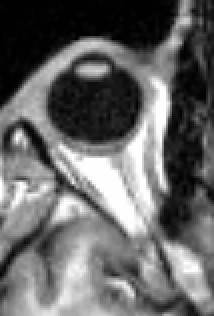
1089:). Lesions may also lead to inability to open the eye due to paralysis of the levator palpebrae muscle. Individuals suffering from a lesion to the oculomotor nerve may compensate by tilting their heads to alleviate symptoms due to paralysis of one or more of the eye muscles it controls.
698:
controlled by the abducens nerve (VI). This means the ability of the eye to look down and inwards is controlled by the trochlear nerve (IV), the ability to look outwards is controlled by the abducens nerve (VI), and all other movements are controlled by the oculomotor nerve (III).
1092:
Damage to the trochlear nerve (IV) can also cause double vision with the eye adducted and elevated. The result will be an eye which can not move downwards properly (especially downwards when in an inward position). This is due to impairment in the superior oblique muscle.
669:
The vestibulo-ocular reflex. A rotation of the head is detected, which triggers an inhibitory signal to the extraocular muscles on one side and an excitatory signal to the muscles on the other side. The result is a compensatory movement of the
424:
457:
423:
1145:
To evaluate for weakness or imbalance of the muscles, a penlight is shone directly on the corneas. Expected normal results of the corneal light reflex is when the penlight's reflection is located in the centre of both corneas, equally.
541:. Each rectus muscle receives blood from two anterior ciliary arteries, except for the lateral rectus muscle, which receives blood from only one. The exact number and arrangement of these ciliary arteries may vary. Branches of the
499:
medially. This posterior medial angle causes the eye to roll with contraction of either the superior rectus muscle or the inferior rectus muscle. The extent of rolling in the recti is less than the oblique, and opposite from it.
428:
433:
1226:
739:
Below is a table of each extraocular muscle and their innervation, origins and insertions, and the primary actions of the muscles (the secondary and tertiary actions are also included, where applicable).
642:. There are three centers of growth that are important in the development of the eye, and each is associated with a nerve. Hence the subsequent nerve supply (innervation) of the eye muscles is from three
425:
364:, and this can be a voluntary or involuntary action. The other six extraocular muscles are involved in movements of the eye; these are the four recti (straight) muscles, and two oblique muscles.
29:
448:
506:
muscle originates at the back of the orbit (a little closer to the medial rectus, though medial to it), getting rounder as it courses forward to a rigid, cartilaginous pulley, called the
454:
422:
421:
451:
426:
452:
1417:
1181:
495:: the four recti muscles. The four recti muscles attach directly to the front half of the eye (anterior to the eye's equator), and are named after their straight paths.
449:
431:
1058:
The oculomotor (III), troclear (IV) and abducens (VI) nerves supply the muscle of the eye. Damage will affect the movement of the eye in various ways, shown here.
646:. The development of the extraocular muscles is dependent on the normal development of the eye socket, while the formation of the ligament is fully independent.
622:
and medial recti, contraction of one leads to inhibition of the other. Muscles show small degrees of activity even when resting, keeping the muscles taut. This "
453:
429:
223:
434:
708:
eyes move together and almost involuntarily. This is a key factor in the study of strabismus, namely, the inability of the eyes to be directed to one point.
1096:
Damage to the abducens nerve (VI) can also result in double vision. This is due to impairment in the lateral rectus muscle, supplied by the abducens nerve.
420:
446:
439:
438:
1169:
455:
1193:
475:
in the orbit. The extraocular muscle pulley system is fundamental to the movement of the eye muscles, in particular also to ensure conformity to
456:
442:
1265:
1070:) because the movements of the eyes are not synchronized. Abnormalities of visual movement may also be seen on examination, such as jittering (
199:
440:
441:
731:
that stabilizes gaze when the head is moved. The reflex involves compensatory eye movements driven by inhibitory and excitatory signals.
1134:
The initial clinical examination of the extraoccular eye muscles is done by examining the movement of the globe of the eye through the
1896:
715:
The muscles show little inertia - a shutdown of one muscle is not due to checking of the antagonist, so the motion is not ballistic.
1532:
Demer JL (March 2004). "Pivotal role of orbital connective tissues in binocular alignment and strabismus: the
Friedenwald lecture".
437:
430:
479:. Certain diseases of the pulleys (heterotopy, instability, and hindrance of the pulleys) cause particular patterns of incomitant
1681:
Talley, Nicholas J.; O'Connor, Simon (2018). "Chapter 32. The neurological examination: general signs and the cranial nerves".
471:
The movements of the extraocular muscles take place under the influence of a system of extraocular muscle pulleys, soft tissue
2213:
1835:
1777:
1747:
86:
66:
1255:
2022:
970:
885:
844:
776:
447:
357:
280:
1715:
388:. The recti muscles are all of almost equal length of around 40 mm but the lengths of their associated tendons differ.
416:
1802:
1690:
1622:
1077:
Damage to the oculomotor nerve (III) can cause double vision and inability to coordinate the movements of both eyes (
2170:
1432:"Normal Anatomy and Anomalies of the Rectus Extraocular Muscles in Human: A Review of the Recent Data and Findings"
1863:
2187:
290:. The actions of the six muscles responsible for eye movement depend on the position of the eye at the time of
1889:
218:
1319:
1997:
1006:
936:
507:
334:
1793:
Lewis SL, Heitkemper MM, Dirkson SR, O'Brien PG, Bucher L, Barry MA, Goldsworthy S, Goodridge D (2010).
1157:
491:
Four of the extraocular muscles have their origin in the back of the orbit in a fibrous ring called the
2218:
1232:
Schematic demonstrating the actions and cranial nerve innervation (in subscript) of extraocular muscles
1187:
Dissection showing origins of right ocular muscles, and nerves entering by the superior orbital fissure
302:
230:
153:
2100:
2032:
1260:
1129:
538:
463:
are shown in this image of the left eye (lateral view). Click on the structures for more information.
123:
1882:
1869:
953:
904:
533:, a main branch of the ophthalmic artery. Additional branches of the ophthalmic artery include the
306:
287:
182:
1205:
2004:
1992:
1481:
Demer JL (April 2002). "The orbital pulley system: a revolution in concepts of orbital anatomy".
1030:
994:
965:
921:
863:
724:
691:
401:
397:
350:
310:
272:
268:
1870:
Animations of extraocular cranial nerve and muscle function and damage (University of
Liverpool)
1977:
1972:
1344:
Kels, Barry D.; Grzybowski, Andrzej; Grant-Kels, Jane M. (March 2015). "Human ocular anatomy".
1243:
880:
839:
385:
373:
206:
194:
1982:
1638:
Westheimer G, McKee SP (July 1975). "Visual acuity in the presence of retinal-image motion".
892:
851:
816:
806:
783:
695:
492:
377:
330:
71:
37:
1987:
1647:
1490:
771:
381:
372:
The four recti muscles are named according to their relative positions of attachment – the
41:
8:
2110:
2085:
999:
958:
828:
542:
119:
1821:
1651:
1494:
2192:
2105:
2077:
1595:
1514:
1502:
1458:
1431:
1357:
635:
529:. This is done either directly or indirectly, as in the lateral rectus muscle, via the
314:
291:
2137:
2090:
2057:
1831:
1824:
1798:
1773:
1743:
1711:
1686:
1663:
1618:
1587:
1549:
1506:
1463:
1388:
1361:
1294:
1175:
Figure showing the mode of innervation of the Recti medialis and lateralis of the eye
1107:
526:
256:
111:
1599:
1518:
2127:
2122:
2027:
1655:
1579:
1541:
1498:
1453:
1443:
1353:
1113:
1011:
675:
534:
476:
267:
and other animals. Six of the extraocular muscles, the four recti muscles, and the
138:
2047:
2042:
2037:
1906:
1125:
1082:
926:
679:
665:
530:
341:
187:
142:
115:
1380:
1286:
1142:, or the eyes' ability to turn inward simultaneously to focus on a near object.
28:
2177:
2095:
1929:
1852:
1063:
989:
977:
948:
909:
868:
811:
683:
643:
298:
146:
75:
2207:
2117:
2067:
1954:
1949:
1939:
1591:
1583:
1016:
931:
211:
79:
59:
2132:
1944:
1924:
1659:
1553:
1510:
1467:
1448:
1392:
1365:
1298:
1036:
1021:
687:
660:
345:
325:
276:
91:
54:
1667:
1320:"Extrinsic eye muscle definition and meaning | Collins English Dictionary"
2165:
1545:
749:
639:
626:" activity is brought on by discharges of the motor nerve to the muscle.
623:
1066:
may affect the movement of the eye. Damage may result in double vision (
483:. Defective pulley functions can be improved by surgical interventions.
2182:
1874:
1078:
480:
1054:
690:. The oculomotor nerve controls all muscles of the eye except for the
236:
1910:
1857:
1822:
Eldra Pearl
Solomon; Richard R. Schmidt; Peter James Adragna (1990).
1250:
1199:
View of the orbit from the front, with nerves and extraocular muscles
1099:
1086:
1071:
982:
941:
914:
897:
873:
856:
821:
795:
788:
264:
1742:(5. ed.). Appleton and Lange: McGraw Hill. pp. 1533–1549.
1067:
329:
Lateral and anterior views of the extraocular muscles also showing
33:
2158:
2153:
2062:
2052:
1934:
1792:
353:
plays an important role in the involuntary movement of the eye.
2014:
1025:
728:
525:
The extraocular muscles are supplied mainly by branches of the
472:
361:
349:
subject of continuing research. It is known, however, that the
284:
106:
95:
1217:
1116:
is weakness or paralysis of one or more extraocular muscles.
344:
provides sharp vision, the eye must move to follow a target.
170:
133:
1285:
Shumway, Caleb L.; Motlagh, Mahsaw; Wade, Matthew (2022).
1418:
Encyclopædia
Britannica 2006 Ultimate Reference Suite DVD
545:
supply the inferior rectus and inferior oblique muscles.
260:
99:
1379:
Ludwig, Parker E.; Aslam, Sanah; Czyz, Craig N. (2024).
1343:
1685:(8th ed.). Chatswood: Elsevier. pp. 500–539.
1772:. Philadelphia, Pa.: Saunders Elsevier. p. 78.
638:(part of the ligaments) and the fatty tissue of the
1823:
1680:
1284:
1617:(2nd ed., rev. and enl. ed.). London: Pion.
1287:"Anatomy, Head and Neck, Eye Extraocular Muscles"
2205:
1710:(3rd ed.). Edinburgh: Mosby. p. 1303.
694:controlled by the trochlear nerve (IV), and the
1637:
1570:Ahmed HU (2002). "A case of mistaken muscles".
1378:
419:
340:Since only a small part of the eye called the
1890:
1770:Netter's head and neck anatomy for dentistry
1412:
1410:
1408:
1406:
1404:
1402:
1866:at the University of Michigan Health System
1705:
1631:
1565:
1563:
1525:
1474:
1266:Sherrington's law of reciprocal innervation
634:The extraocular muscles develop along with
1897:
1883:
1416:"eye, human."Encyclopædia Britannica from
1797:. Toronto: Elsevier Canada. p. 464.
1763:
1761:
1759:
1733:
1731:
1729:
1727:
1612:
1457:
1447:
1399:
718:
486:
411:
1904:
1560:
1053:
1049:
702:
664:
415:
324:
1429:
986:(posterior, inferior, lateral surface)
945:(posterior, superior, lateral surface)
2206:
1767:
1756:
1737:
1724:
1674:
1423:
1312:
1278:
1878:
1706:Yanoff, Myron; Duker, Jay S. (2008).
1569:
1531:
1480:
1381:"Anatomy, Head and Neck: Eye Muscles"
1163:Nerves of the orbit. Seen from above.
360:is responsible for raising the upper
587:Levator palpebrae superioris muscle
2023:Levator palpebrae superioris muscle
128:superior and inferior orbital veins
13:
1815:
1795:Medical-Surgical Nursing in Canada
1503:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb02805.x
1358:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2014.10.006
391:
16:Seven extrinsic muscles of the eye
14:
2230:
1845:
1256:Hering's law of equal innervation
1860:- "Extraocular Muscles, Actions"
1225:
1216:
1204:
1192:
1180:
1168:
1156:
407:
396:The two oblique muscles are the
367:
27:
1830:. Saunders College Publishing.
1786:
1699:
1606:
654:
548:
520:
2188:Suspensory ligament of eyeball
1826:Human anatomy & physiology
1613:Carpenter, Roger H.S. (1988).
1372:
1337:
1119:
629:
158:
1:
1436:BioMed Research International
1271:
901:(anterior, inferior surface)
860:(anterior, superior surface)
2214:Muscles of the head and neck
1998:Trochlea of superior oblique
1740:Principles of neural science
1534:Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci
1007:Levator palpebrae superioris
825:(anterior, lateral surface)
358:levator palpebrae superioris
320:
281:levator palpebrae superioris
7:
1237:
792:(anterior, medial surface)
649:
176:musculi externi bulbi oculi
10:
2235:
1241:
1149:
1136:six cardinal eye movements
1123:
658:
414:
303:pupillary sphincter muscle
231:Anatomical terms of muscle
2146:
2101:Accessory lacrimal glands
2076:
2033:Medial palpebral ligament
2013:
1963:
1917:
1387:. StatPearls Publishing.
1324:www.collinsdictionary.com
1293:. StatPearls Publishing.
1130:Cranial nerve examination
1081:), also eyelid drooping (
563:
539:anterior ciliary arteries
229:
217:
205:
193:
181:
169:
164:
152:
132:
124:anterior ciliary arteries
105:
85:
65:
53:
48:
26:
21:
1738:Kandel, Eric R. (2013).
1584:10.1136/bmj.324.7343.962
734:
601:Superior oblique muscle
581:Inferior oblique muscle
537:, which branch into the
311:intrinsic ocular muscles
307:pupillary dilator muscle
279:. The other muscle, the
273:inferior oblique muscles
253:extrinsic ocular muscles
2005:Inferior oblique muscle
1993:Superior oblique muscle
725:vestibulo-ocular reflex
692:superior oblique muscle
575:Inferior rectus muscle
573:Superior rectus muscle
513:The last muscle is the
402:superior oblique muscle
398:inferior oblique muscle
351:vestibulo-ocular reflex
1978:Inferior rectus muscle
1973:Superior rectus muscle
1660:10.1364/josa.65.000847
1346:Clinics in Dermatology
1261:Park's three-step test
1244:anatomical terminology
1085:) and pupil dilation (
1059:
719:Compensatory movements
671:
615:Lateral rectus muscle
487:Origins and insertions
464:
386:inferior rectus muscle
374:superior rectus muscle
337:
1983:Lateral rectus muscle
1768:Norton, Neil (2007).
1615:Movements of the eyes
1057:
1050:Clinical significance
893:Common tendinous ring
852:Common tendinous ring
817:Common tendinous ring
784:Common tendinous ring
703:Movement coordination
696:lateral rectus muscle
668:
578:Medial rectus muscle
493:common tendinous ring
459:
378:lateral rectus muscle
331:common tendinous ring
328:
309:sometimes are called
72:Common tendinous ring
38:lateral rectus muscle
1988:Medial rectus muscle
1683:Clinical examination
1546:10.1167/iovs.03-0464
1483:Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci
1449:10.1155/2019/8909162
382:medial rectus muscle
42:medial rectus muscle
2086:Lacrimal canaliculi
1864:Atlas image: eye_13
1652:1975JOSA...65..847W
1495:2002NYASA.956...17D
1430:Haładaj, R (2019).
1211:Extraocular muscles
543:infraorbital artery
461:Extraocular muscles
315:intraocular muscles
277:movement of the eye
249:extraocular muscles
120:infraorbital artery
22:Extraocular muscles
2078:Lacrimal apparatus
1540:(3): 729–38, 728.
1242:This article uses
1106:is a condition of
1060:
672:
640:eye socket (orbit)
465:
338:
292:muscle contraction
2219:Human eye anatomy
2201:
2200:
2171:Plica semilunaris
2138:Nasolacrimal duct
2091:Lacrimal caruncle
2058:Palpebral fissure
1837:978-0-03-011914-9
1779:978-1-929007-88-2
1749:978-0-07-139011-8
1047:
1046:
973:(inferior branch)
971:Oculomotor nerve
888:(inferior branch)
886:Oculomotor nerve
847:(superior branch)
845:Oculomotor nerve
779:(inferior branch)
777:Oculomotor nerve
763:Secondary action
619:
618:
564:Oculomotor nerve
527:ophthalmic artery
469:
468:
257:extrinsic muscles
245:
244:
240:
112:Ophthalmic artery
2226:
2128:Lacrimal punctum
2123:Lacrimal papilla
2111:Ciaccio's glands
1899:
1892:
1885:
1876:
1875:
1841:
1829:
1809:
1808:
1790:
1784:
1783:
1765:
1754:
1753:
1735:
1722:
1721:
1703:
1697:
1696:
1678:
1672:
1671:
1635:
1629:
1628:
1610:
1604:
1603:
1567:
1558:
1557:
1529:
1523:
1522:
1478:
1472:
1471:
1461:
1451:
1427:
1421:
1414:
1397:
1396:
1376:
1370:
1369:
1341:
1335:
1334:
1332:
1330:
1316:
1310:
1309:
1307:
1305:
1282:
1229:
1220:
1208:
1196:
1184:
1172:
1160:
1114:Ophthalmoparesis
1012:Oculomotor nerve
966:Inferior oblique
922:Superior oblique
766:Tertiary action
743:
742:
686:(VI) coordinate
676:oculomotor nerve
611:
597:
592:Trochlear nerve
569:
553:
552:
535:ciliary arteries
515:inferior oblique
504:superior oblique
412:
255:, are the seven
237:edit on Wikidata
234:
31:
19:
18:
2234:
2233:
2229:
2228:
2227:
2225:
2224:
2223:
2204:
2203:
2202:
2197:
2193:Tenon's capsule
2142:
2106:Krause's glands
2072:
2043:Meibomian gland
2038:Epicanthic fold
2009:
1959:
1913:
1903:
1848:
1838:
1818:
1816:Further reading
1813:
1812:
1805:
1791:
1787:
1780:
1766:
1757:
1750:
1736:
1725:
1718:
1704:
1700:
1693:
1679:
1675:
1636:
1632:
1625:
1611:
1607:
1568:
1561:
1530:
1526:
1479:
1475:
1428:
1424:
1415:
1400:
1377:
1373:
1342:
1338:
1328:
1326:
1318:
1317:
1313:
1303:
1301:
1283:
1279:
1274:
1251:ALS#Late stages
1247:
1240:
1233:
1230:
1221:
1212:
1209:
1200:
1197:
1188:
1185:
1176:
1173:
1164:
1161:
1152:
1132:
1126:Eye examination
1122:
1108:diminshed sight
1052:
985:
972:
944:
934:
927:Trochlear nerve
900:
887:
881:Inferior rectus
859:
846:
840:Superior rectus
824:
791:
778:
760:Primary action
737:
721:
705:
680:trochlear nerve
663:
657:
652:
636:Tenon's capsule
632:
609:
607:
606:Abducens nerve
595:
593:
567:
565:
551:
531:lacrimal artery
523:
489:
458:
410:
394:
392:Oblique muscles
370:
323:
241:
127:
116:lacrimal artery
44:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2232:
2222:
2221:
2216:
2199:
2198:
2196:
2195:
2190:
2185:
2180:
2178:Orbital septum
2175:
2174:
2173:
2163:
2162:
2161:
2150:
2148:
2144:
2143:
2141:
2140:
2135:
2130:
2125:
2120:
2115:
2114:
2113:
2108:
2098:
2096:Lacrimal gland
2093:
2088:
2082:
2080:
2074:
2073:
2071:
2070:
2065:
2060:
2055:
2050:
2048:Ciliary glands
2045:
2040:
2035:
2030:
2025:
2019:
2017:
2011:
2010:
2008:
2007:
2002:
2001:
2000:
1990:
1985:
1980:
1975:
1969:
1967:
1961:
1960:
1958:
1957:
1952:
1947:
1942:
1937:
1935:Maxillary bone
1932:
1930:Zygomatic bone
1927:
1921:
1919:
1915:
1914:
1902:
1901:
1894:
1887:
1879:
1873:
1872:
1867:
1861:
1847:
1846:External links
1844:
1843:
1842:
1836:
1817:
1814:
1811:
1810:
1803:
1785:
1778:
1755:
1748:
1723:
1717:978-0323057516
1716:
1698:
1691:
1673:
1630:
1623:
1605:
1559:
1524:
1473:
1422:
1398:
1371:
1352:(2): 140–146.
1336:
1311:
1276:
1275:
1273:
1270:
1269:
1268:
1263:
1258:
1253:
1239:
1236:
1235:
1234:
1231:
1224:
1222:
1215:
1213:
1210:
1203:
1201:
1198:
1191:
1189:
1186:
1179:
1177:
1174:
1167:
1165:
1162:
1155:
1151:
1148:
1121:
1118:
1102:also known as
1064:cranial nerves
1062:Damage to the
1051:
1048:
1045:
1044:
1042:
1040:
1028:
1019:
1014:
1009:
1003:
1002:
997:
992:
990:Excyclotorsion
987:
980:
978:Maxillary bone
975:
968:
962:
961:
956:
951:
949:Incyclotorsion
946:
939:
929:
924:
918:
917:
912:
910:Excyclotorsion
907:
902:
895:
890:
883:
877:
876:
871:
869:Incyclotorsion
866:
861:
854:
849:
842:
836:
835:
833:
831:
826:
819:
814:
812:Abducens nerve
809:
807:Lateral rectus
803:
802:
800:
798:
793:
786:
781:
774:
768:
767:
764:
761:
758:
755:
752:
747:
736:
733:
720:
717:
704:
701:
684:abducens nerve
659:Main article:
656:
653:
651:
648:
644:cranial nerves
631:
628:
617:
616:
613:
603:
602:
599:
589:
588:
584:
583:
571:
561:
560:
557:
556:Cranial nerve
550:
547:
522:
519:
488:
485:
467:
466:
409:
406:
393:
390:
369:
366:
322:
319:
299:ciliary muscle
243:
242:
233:
227:
226:
221:
215:
214:
209:
203:
202:
197:
191:
190:
185:
179:
178:
173:
167:
166:
162:
161:
156:
150:
149:
147:abducens nerve
136:
130:
129:
109:
103:
102:
89:
83:
82:
69:
63:
62:
57:
51:
50:
46:
45:
32:
24:
23:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2231:
2220:
2217:
2215:
2212:
2211:
2209:
2194:
2191:
2189:
2186:
2184:
2181:
2179:
2176:
2172:
2169:
2168:
2167:
2164:
2160:
2157:
2156:
2155:
2152:
2151:
2149:
2145:
2139:
2136:
2134:
2131:
2129:
2126:
2124:
2121:
2119:
2118:Lacrimal lake
2116:
2112:
2109:
2107:
2104:
2103:
2102:
2099:
2097:
2094:
2092:
2089:
2087:
2084:
2083:
2081:
2079:
2075:
2069:
2068:Gland of Zeis
2066:
2064:
2061:
2059:
2056:
2054:
2051:
2049:
2046:
2044:
2041:
2039:
2036:
2034:
2031:
2029:
2026:
2024:
2021:
2020:
2018:
2016:
2012:
2006:
2003:
1999:
1996:
1995:
1994:
1991:
1989:
1986:
1984:
1981:
1979:
1976:
1974:
1971:
1970:
1968:
1966:
1962:
1956:
1955:Lacrimal bone
1953:
1951:
1950:Palatine bone
1948:
1946:
1943:
1941:
1940:Sphenoid bone
1938:
1936:
1933:
1931:
1928:
1926:
1923:
1922:
1920:
1916:
1912:
1908:
1900:
1895:
1893:
1888:
1886:
1881:
1880:
1877:
1871:
1868:
1865:
1862:
1859:
1855:
1854:
1850:
1849:
1839:
1833:
1828:
1827:
1820:
1819:
1806:
1804:9781897422014
1800:
1796:
1789:
1781:
1775:
1771:
1764:
1762:
1760:
1751:
1745:
1741:
1734:
1732:
1730:
1728:
1719:
1713:
1709:
1708:Ophthalmology
1702:
1694:
1692:9780729542869
1688:
1684:
1677:
1669:
1665:
1661:
1657:
1653:
1649:
1646:(7): 847–50.
1645:
1641:
1634:
1626:
1624:0-85086-109-8
1620:
1616:
1609:
1601:
1597:
1593:
1589:
1585:
1581:
1578:(7343): 962.
1577:
1573:
1566:
1564:
1555:
1551:
1547:
1543:
1539:
1535:
1528:
1520:
1516:
1512:
1508:
1504:
1500:
1496:
1492:
1488:
1484:
1477:
1469:
1465:
1460:
1455:
1450:
1445:
1441:
1437:
1433:
1426:
1419:
1413:
1411:
1409:
1407:
1405:
1403:
1394:
1390:
1386:
1382:
1375:
1367:
1363:
1359:
1355:
1351:
1347:
1340:
1325:
1321:
1315:
1300:
1296:
1292:
1288:
1281:
1277:
1267:
1264:
1262:
1259:
1257:
1254:
1252:
1249:
1248:
1245:
1228:
1223:
1219:
1214:
1207:
1202:
1195:
1190:
1183:
1178:
1171:
1166:
1159:
1154:
1153:
1147:
1143:
1141:
1137:
1131:
1127:
1117:
1115:
1111:
1109:
1105:
1101:
1097:
1094:
1090:
1088:
1084:
1080:
1075:
1073:
1069:
1065:
1056:
1043:
1041:
1039:
1038:
1032:
1029:
1027:
1023:
1020:
1018:
1017:Sphenoid bone
1015:
1013:
1010:
1008:
1005:
1004:
1001:
998:
996:
993:
991:
988:
984:
981:
979:
976:
974:
969:
967:
964:
963:
960:
957:
955:
952:
950:
947:
943:
940:
938:
933:
932:Sphenoid bone
930:
928:
925:
923:
920:
919:
916:
913:
911:
908:
906:
903:
899:
896:
894:
891:
889:
884:
882:
879:
878:
875:
872:
870:
867:
865:
862:
858:
855:
853:
850:
848:
843:
841:
838:
837:
834:
832:
830:
827:
823:
820:
818:
815:
813:
810:
808:
805:
804:
801:
799:
797:
794:
790:
787:
785:
782:
780:
775:
773:
772:Medial rectus
770:
769:
765:
762:
759:
756:
753:
751:
748:
745:
744:
741:
732:
730:
726:
716:
713:
709:
700:
697:
693:
689:
685:
681:
677:
667:
662:
647:
645:
641:
637:
627:
625:
614:
605:
604:
600:
591:
590:
586:
585:
582:
579:
576:
572:
562:
558:
555:
554:
546:
544:
540:
536:
532:
528:
518:
516:
511:
509:
505:
500:
496:
494:
484:
482:
478:
477:Listing's law
474:
462:
418:
413:
408:Pulley system
405:
403:
399:
389:
387:
383:
379:
375:
368:Recti muscles
365:
363:
359:
354:
352:
347:
346:Eye movements
343:
336:
332:
327:
318:
316:
312:
308:
304:
300:
295:
293:
289:
286:
282:
278:
274:
270:
266:
262:
258:
254:
250:
238:
232:
228:
225:
222:
220:
216:
213:
210:
208:
204:
201:
198:
196:
192:
189:
186:
184:
180:
177:
174:
172:
168:
163:
160:
157:
155:
151:
148:
144:
140:
137:
135:
131:
125:
121:
117:
113:
110:
108:
104:
101:
97:
93:
90:
88:
84:
81:
80:sphenoid bone
77:
73:
70:
68:
64:
61:
60:Visual system
58:
56:
52:
47:
43:
39:
35:
30:
25:
20:
2133:Lacrimal sac
1964:
1945:Ethmoid bone
1925:Frontal bone
1851:
1825:
1794:
1788:
1769:
1739:
1707:
1701:
1682:
1676:
1643:
1640:J Opt Soc Am
1639:
1633:
1614:
1608:
1575:
1571:
1537:
1533:
1527:
1489:(1): 17–32.
1486:
1482:
1476:
1439:
1435:
1425:
1384:
1374:
1349:
1345:
1339:
1327:. Retrieved
1323:
1314:
1302:. Retrieved
1290:
1280:
1144:
1139:
1135:
1133:
1112:
1110:in one eye.
1103:
1098:
1095:
1091:
1076:
1061:
1037:upper eyelid
1034:
1033:/retraction
1022:Tarsal plate
738:
722:
714:
710:
706:
688:eye movement
673:
661:Eye movement
655:Eye movement
633:
620:
580:
577:
574:
549:Nerve supply
524:
521:Blood supply
514:
512:
503:
501:
497:
490:
470:
460:
395:
371:
355:
339:
296:
252:
248:
246:
200:A04.1.01.001
175:
92:Tarsal plate
2166:Conjunctiva
1442:: 8909162.
1140:convergence
1120:Examination
750:Innervation
630:Development
333:origin and
283:, controls
165:Identifiers
2208:Categories
2183:Periorbita
1385:StatPearls
1304:12 January
1291:StatPearls
1272:References
1124:See also:
1079:strabismus
954:Depression
905:Depression
757:Insertion
481:strabismus
275:, control
139:Oculomotor
1858:eMedicine
1853:neuro/637
1592:0959-8138
1100:Amblyopia
1087:mydriasis
1072:nystagmus
1031:Elevation
1024:of upper
1000:Abduction
995:Elevation
959:Abduction
915:Adduction
874:Adduction
864:Elevation
829:Abduction
796:Adduction
682:(IV) and
321:Structure
288:elevation
159:See table
143:trochlear
94:of upper
87:Insertion
76:maxillary
1600:71166629
1554:14985282
1519:28173133
1511:11960790
1468:31976329
1393:29262013
1366:25704934
1299:30137849
1238:See also
1104:lazy eye
1068:diplopia
937:Trochlea
935:via the
650:Function
508:trochlea
400:and the
335:trochlea
269:superior
36:showing
34:MRI scan
2159:Unibrow
2154:Eyebrow
2063:Canthus
2053:Eyelash
1965:Muscles
1909:of the
1668:1142031
1648:Bibcode
1491:Bibcode
1459:6954479
1150:Gallery
1035:of the
754:Origin
746:Muscle
678:(III),
559:Muscle
473:pulleys
259:of the
188:D009801
154:Actions
49:Details
2028:Tarsus
2015:Eyelid
1834:
1801:
1776:
1746:
1714:
1689:
1666:
1621:
1598:
1590:
1552:
1517:
1509:
1466:
1456:
1391:
1364:
1297:
1083:ptosis
1026:eyelid
729:reflex
568:N. III
384:, and
362:eyelid
285:eyelid
265:humans
107:Artery
96:eyelid
67:Origin
55:System
2147:Other
1918:Bones
1907:orbit
1596:S2CID
1515:S2CID
1329:7 May
735:Table
727:is a
670:eyes.
624:tonic
610:N. VI
596:N. IV
342:fovea
251:, or
235:[
224:49033
171:Latin
134:Nerve
1905:The
1832:ISBN
1799:ISBN
1774:ISBN
1744:ISBN
1712:ISBN
1687:ISBN
1664:PMID
1619:ISBN
1588:ISSN
1550:PMID
1507:PMID
1464:PMID
1440:2019
1420:2009
1389:PMID
1362:PMID
1331:2021
1306:2022
1295:PMID
1128:and
723:The
674:The
502:The
356:The
305:and
297:The
271:and
247:The
212:2041
195:TA98
183:MeSH
145:and
78:and
40:and
1911:eye
1856:at
1656:doi
1580:doi
1576:324
1572:BMJ
1542:doi
1499:doi
1487:956
1454:PMC
1444:doi
1354:doi
1074:).
983:Eye
942:Eye
898:Eye
857:Eye
822:Eye
789:Eye
313:or
263:in
261:eye
219:FMA
207:TA2
100:eye
2210::
1758:^
1726:^
1662:.
1654:.
1644:65
1642:.
1594:.
1586:.
1574:.
1562:^
1548:.
1538:45
1536:.
1513:.
1505:.
1497:.
1485:.
1462:.
1452:.
1438:.
1434:.
1401:^
1383:.
1360:.
1350:33
1348:.
1322:.
1289:.
612:)
598:)
570:)
404:.
380:,
376:,
317:.
301:,
294:.
141:,
126:,
122:,
118:,
114:,
98:,
74:,
1898:e
1891:t
1884:v
1840:.
1807:.
1782:.
1752:.
1720:.
1695:.
1670:.
1658::
1650::
1627:.
1602:.
1582::
1556:.
1544::
1521:.
1501::
1493::
1470:.
1446::
1395:.
1368:.
1356::
1333:.
1308:.
1246:.
608:(
594:(
566:(
239:]
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.