2766:
1222:
2554:
2072:
2672:
the
Southern states were incorporated into the new regime. The Song dynasty adopted a distinctively Southern Chinese cultural outlook. The preserved cultural traditions of Southern Tang, Wu Yue and Later Shu were used to rebuild the cultural landscape of the north. Southern libraries were transported north, Southeastern architecture was promoted in the new capital, and Southeastern Buddhist icons, clergy and relics were concentrated in the new capital so as to reintegrate these traditions into the imperial culture. This was distinct from the five Northern dynasties, who never supported extended monastic lineage networks but instead typically sought to restrict them and draw on their economic and military resources.
2057:
202:
1280:(Chengde, Youzhou, Weibo) were able to maintain much greater autonomy from the central government in the aftermath of the An Lushan rebellion. With their administration under local military control, these provinces never submitted tax revenues, and governorships lapsed into hereditary succession. They engaged in occasional war with the central government, or against each other, and Youzhou seemed to conduct its own foreign policy. This meant that the culture of these northeastern provinces started diverging from the capital. Many of the elites in post-Tang China, including the future emperors of the Song dynasty, came from this region.
2694:
1435:
agricultural production and an entrepot for the other regions. The regions were economically interdependent. Sui and Tang's policies, while paying little attention to developing the South, gave the South room to innovate free of tight administrative controls. The dominant northern officials had been unwilling to serve in the South during the Tang, and so southerners were recruited by the Tang to serve in a local capacity under the "Southern
Selection" supplemental system. These southern officials became the administrative core of the Ten Kingdoms and later dominated the bureaucracy by the mid-Song.
2819:
2743:
35:
2594:
1447:
2483:
2717:
2833:
1748:
1990:
1797:
1933:
1862:
2539:. Because the Later Tang was in decline and Li Cunxu was killed in a revolt, Meng Zhixiang found the opportunity to reassert Shu's independence. Like the Former Shu, the capital was at Chengdu and it basically controlled the same territory as its predecessor. The kingdom was ruled well until forced to succumb to Song armies in 965.
1405:, sometimes dealt with each other on terms of diplomatic equality out of pragmatic concern. This concept of "sharing the Mandate of Heaven" as "sibling states" was the result of the brief balance of power. After the reunification of China by the Song dynasty, the Song embarked on a special effort to denounce such arrangements.
2772:
2585:, it eventually took over Yin, Min, and Chu, holding present-day southern Anhui, southern Jiangsu, much of Jiangxi, Hunan, and eastern Hubei at its height. The kingdom became nominally subordinate to the expanding Song in 961 and was invaded outright in 975, when it was formally absorbed into the Song dynasty.
2474:(the successor of the Tang in North China). Gao's successors claimed the title of King of Nanping after the fall of the Later Liang in 924. It was a small and weak kingdom, and thus tried to maintain good relations with each of the Five Dynasties. The kingdom fell to advancing armies of the Song in 963.
2806:
The Tang code of 737 was the basic statutory law for this period, together supplemental edicts and collections. The Later Liang promulgated a code in 909. This code was blamed for delays in the administration of justice and said to be excessively harsh with respect to economic crimes. The Later Tang,
2798:
In later tradition, the Five
Dynasties is viewed as a period of judicial abuse and excessive punishment. This view reflects both actual problems with the administration of justice and the bias of Confucian historians, who disapproved of the decentralization and militarization that characterized this
2671:
Several
Northern dynasties originated in the northeast, and centralisation of the north led to a migration of provincial elites into the capital, particularly northeasterners, creating a new metropolitan culture. After the unification of China by the Song dynasty, the culture, arts and literature of
2632:
The Song dynasty, established in 960, was determined to reunify China. Jingnan and Wuping
Jiedushi were swept away in 963, Later Shu in 965, Southern Han in 971, and Southern Tang in 975. Finally, Wuyue and Qingyuan Jiedushi gave up their land to Northern Song in 978, bringing all of southern China
2016:
to launch an assault on Later Zhou. Against the advice of
Minister Feng Dao, Chai Rong decided to lead his army against the incursion. When Chai Rong engaged Liu Chong at Gao Ping (in modern Jincheng), two of Chai's generals, Fan Aineng and He Hui, fled from the battlefield along with their troops.
1267:
and its successor the Song dynasty, and the demilitarisation of the provinces. Southern China, divided into several independent dynastic kingdoms, was more stable than the North which saw constant regime change. Consequently, the
Southern kingdoms were able to embark on trade, land reclamation, and
1262:
The historian Hugh Clark proposed a three-stage model of broad political trends during this time period. The first stage (880–910) consists of the period between the Huang Chao
Rebellion and the formal end of the Tang dynasty, which saw chaotic fighting between warlords who controlled approximately
1413:
The
Southern regimes generally had more stable and effective government during this period. Even the rulers of the Southern states were almost all military leaders from the North with their key officers and elite forces also hailing from the North since the bulk of the Tang army was based in the
1254:
independence from its authority. In the last decades of the Tang dynasty, they were not even appointed by the central court anymore, but developed hereditary systems, from father to son or from patron to protégé. They had their own armies rivaling the "palace armies" and amassed huge wealth, as
1430:
and the founder of
Southern Han was a southern tribal chief. The Southern kingdoms were founded by men of low social status who rose up through superior military ability, who were later scorned as "bandits" by future scholars. However, once established, these rulers took great pains to portray
2608:
Although more stable than northern China as a whole, southern China was also torn apart by warfare. Wu quarreled with its neighbours, a trend that continued as Wu was replaced with Southern Tang. In the 940s Min and Chu underwent internal crises which Southern Tang handily took advantage of,
1434:
The economies of each of the southern regions had prospered in the late Tang. Guangdong and Fujian were the sites of important port cities trading exotic goods, the middle Yangtze and Sichuan were centers of tea and porcelain production, and the Yangtze delta was a center of extremely high
2101:). Each court was a center of artistic excellence. The period is noted for the vitality of its poetry and for its economic prosperity. Commerce grew so quickly that there was a shortage of metallic currency. This was partly addressed by the creation of bank drafts, or "flying money" (
2802:
Other abuses included the use of severe torture. The Later Han was the most notorious dynasty in this regard. Suspects could be tortured to death with long knives and nails. The military officer in charge of security of the capital is said to have executed suspects without inquiry.
1201:
of the Central Plain crowned themselves emperor. During the 70-year period, there was near-constant warfare between the emerging kingdoms and the alliances they formed. All had the ultimate goal of controlling the Central Plain and establishing themselves as the Tang's successor.
1209:, which held out until Song conquered it in 979. For the next several centuries, although the Song controlled much of South China, they coexisted alongside the Liao dynasty, Jin dynasty, and various other regimes in China's north, until finally all of them were unified under the
1766:'s rebel army, he took on a crucial role in suppressing the Huang Chao Rebellion. For this function, he was awarded the Xuanwu Jiedushi title. Within a few years, he had consolidated his power by destroying neighbours and forcing the move of the imperial capital to
2765:
1295:), their personal staff, and the bureaucrats who served in the capitals of the Five dynasties. These families had risen to prominence due to the unraveling of central authority after the An Lushan Rebellion, despite lacking esteemed ancestry. The historian
1255:
testified by their sumptuous tombs. Due to the decline of Tang central authority after the An Lushan Rebellion, there was a growing tendency to superimpose large regional administrations over the old districts and prefectures that had been used since the
2624:
for many years after. With this, Southern Tang became the undisputedly most powerful regime in southern China. However, it was unable to defeat incursions by the Later Zhou between 956 and 958, and ceded all of its land north of the
2300:. Qian Liu was named the Prince of Yue by the Tang emperor in 902; the Prince of Wu was added in 904. After the fall of the Tang dynasty in 907, he declared himself king of Wuyue. Wuyue survived until the eighteenth year of the
2388:. Ma was named regional military governor by the Tang court in 896, and named himself the Prince of Chu with the fall of the Tang in 907. This status as the Prince of Chu was confirmed by the Southern Tang in 927. The
1263:
one or two prefectures each. The second stage (910–950) saw the various warlords stabilize and gain enough legitimacy to proclaim new dynasties. The third stage (950–979) saw the forceful reunification of China by the
2640:. The greater stability of the Ten Kingdoms, especially the longevity of Wuyue and Southern Han, would contribute to the development of distinct regional identities within China. The distinction was reinforced by the
2652:. Written from the northern viewpoint, these chronicles organized the history around the Five Dynasties (the north), presenting the Ten Kingdoms (the south) as illegitimate, self-absorbed and indulgent.
2017:
At this critical moment, Chai Rong risked his life to break through the defense and crushed Liu's forces. After this campaign, Chai Rong consolidated his power. Between 956 and 958, forces of Later Zhou
1259:(221–206 BC). These administrations, known as circuit commissions, would become the boundaries of the later Southern regimes; many circuit commissioners became the emperors or kings of these states.
1283:
The administrations of the Five Dynasties and the early Song Dynasty shared a pattern of being disproportionately drawn from the families of military governors in northern and northwestern China (
1918:, marking the end of Later Jin. But while they had conquered vast regions of China, the Khitans were unable or unwilling to control those regions and retreated from them early in the next year.
1326:, the rebel defector turned warlord who ultimately ended the Tang dynasty. The rest of the Five Dynasties as well as the Song dynasty all emerged from a military organization originally led by
1914:
Not long after the founding of Later Jin, the Liao came to regard the emperor as a proxy ruler for China. In 943, the Khitans declared war and within three years seized the capital,
2675:
Although short, the period saw cultural innovations in different areas. Pottery saw the appearance of "white ceramics"/ In painting, the "varied landscape" of China was inspired by
1221:
1382:
served in the armies of Later Tang, Later Han, and Later Zhou. Zhao, also a professional soldier, rose through the ranks of the Later Zhou before seizing the throne in the
2446:
in 951. With the protection of the powerful Liao dynasty, the Northern Han maintained nominal independence until the Song dynasty wrested it from the Khitans in 979.
2093:
were generally concurrent, each controlling a specific geographical area. These were known as "The Ten Kingdoms" (in fact, some claimed the title of Emperor, such as
2866:
2397:
1807:
In the final years of the Tang dynasty, rival warlords declared independence in the provinces they governed—not all of which recognized the emperor's authority.
2029:
in defeat. In 959, Chai Rong attacked the Liao in an attempt to recover territories ceded during the Later Jin. After many victories, he succumbed to illness.
1431:
themselves as promoters of culture and economic development so as to legitimize their rule; many wooed former Tang courtiers to help administer their states.
1268:
infrastructure projects, laying the groundwork for the Song Dynasty economic boom. This economic shift to the south also led to a vast southward migration.
2519:. Wang was named military governor of western Sichuan by the Tang court in 891. The kingdom fell when his son surrendered in the face of an advance by the
2614:
1778:
a subordinate ruler. Three years later, he induced the boy emperor to abdicate in his favour. He then proclaimed himself emperor, thus beginning the
2693:
2288:
was the longest-lived (907–978) and among the most powerful of the southern states. Wuyue was known for its learning and culture. It was founded by
3942:
3826:
3809:
3335:
3638:
2888:
2799:
period. While Tang procedure called for delaying executions until appeals were exhausted, this was not generally the case in the Five Dynasties.
3947:
3972:
3898:
2008:
succeeded the throne and began a policy of expansion and reunification. One month after Chai Rong took the throne, Liu Chong, Emperor of
1827:
Empire in 911) in 915, and declared himself emperor in 923; within a few months, he brought down the Later Liang regime. Thus began the
2785:
2040:. This is the official end of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. During the next two decades, Zhao Kuangyin and his successor
1118:
1058:
2679:. It emphasized the sacredness of mountains as places between heaven and earth and depicted the natural world as a source of harmony.
3967:
3891:
2807:
Later Jin, and Later Zhou also produced recompilations. The Later Han was in power too briefly to make a mark on the legal system.
2648:
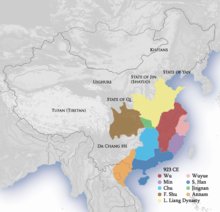
1155:, and more than a dozen concurrent dynastic states, collectively known as the Ten Kingdoms, were established elsewhere, mainly in
2396:, although Southern Tang rule of the region was temporary, as the next year former Chu military officers under the leadership of
2553:
1951:, establishing a third successive Shatuo reign. This was the shortest of the five dynasties. Following a coup in 951, General
3441:
3173:
3135:
3110:
3085:
1048:
2742:
1310:
The term "Five Dynasties" was coined by Song dynasty historians and reflects the view that the successive regimes based in
1197:
officials waned, but the key event was their recognition as sovereign by foreign powers. After the Tang collapsed, several
621:
611:
2071:
1872:
The Later Tang had a few years of relative calm, followed by unrest. In 934, Sichuan again asserted independence. In 936,
2636:
In common with other periods of fragmentation, the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period resulted in a division between
1090:
252:
3554:
3479:
3460:
3422:
3319:
3213:
242:
1422:
respectively, the founder of Min was a minor government staffer from Huainan, the founder of Wuyue was a 'rogue' from
1354:
was the son of a Shatuo commander in Li Keyong's army and became the son-in-law of the Later Tang general and emperor
3884:
3814:
3503:
3494:
3399:
3294:
3238:
3041:
3016:
2968:
2929:
2877:
2642:
2619:
1426:, the founder of Chu was (according to one source) a carpenter from Xuchang, the founder of Jingnan was a slave from
919:
2316:(909–945) was founded by Wang Shenzhi, who named himself the Prince of Min with its capital at Changle (present-day
2716:
3937:
3625:
2400:
seized the territory. In the waning years of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, the region was ruled by
2105:), as well as by certificates of deposit. Wood block printing became common during this period, 500 years before
673:
2056:
3952:
3932:
2856:
2578:
1136:
1111:
1063:
141:
45:
2462:, a former general of Liang. It was based in Jiangling and held two other districts southwest of present-day
1085:
1011:
946:
59:
3957:
3765:
3653:
3581:
2471:
1779:
1751:
1742:
1597:
1021:
2535:(935–965) is essentially a resurrection of the previous Shu state that had fallen a decade earlier to the
3977:
3962:
3927:
3770:
3718:
2637:
1175:
1073:
830:
211:
3376:, Cambridge University Press, 5 Mar 2015, McKnight, Brian, "Chapter 4: Chinese law and the legal system"
3339:
2320:). One of Shenzhi's sons proclaimed the independent state of Yin in the northeast of Min territory. The
2089:
Unlike the dynasties of northern China, which succeeded one another in rapid succession, the regimes of
3760:
3673:
3668:
3659:
2439:
1948:
1936:
1927:
1865:
1856:
1836:
1359:
1347:
1170:
in 960. In the following 19 years, Song gradually subdued the remaining states in South China, but the
1078:
2193:, viewing it as simply a continuation of Later Han. This era also coincided with the founding of the
1632:
1104:
1041:
1006:
579:
275:
185:
3603:
3057:
Robert M. Hartwell (1982). "Demographic, Political, and Social Transformations of China, 750–1550".
2985:
Robert M. Hartwell (1982). "Demographic, Political, and Social Transformations of China, 750–1550".
1811:
was the jiedushi for the Hedong circuit in present Shanxi, forming a polity called Jin (晉). His son
785:
3982:
2660:
The Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period turned away from the international cultural mood of the
2077:
1771:
775:
424:
3434:
Ten States, Five Dynasties, One Great Emperor: How Emperor Taizu Unified China in the Song Dynasty
3256:
1144:
3414:
3312:
Patrons and Patriarchs: Regional Rulers and Chan Monks during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms
3206:
Patrons and Patriarchs: Regional Rulers and Chan Monks during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms
2776:
1001:
3374:
The Cambridge History of China: Volume 5, The Five Dynasties and Sung China, 960–1279 AD, Part 2
2609:
destroying Min in 945 and Chu in 951. Remnants of Min and Chu, however, survived in the form of
3987:
3847:
3804:
2581:(Emperor Liezu) took the state over from within in 937. Expanding from the original domains of
2349:
2345:
2324:
took that territory after the Min asked for help. Despite declaring loyalty to the neighboring
2221:
1683:
1666:
1277:
1053:
1031:
1016:
502:
221:
1911:) to the Khitans. The rebellion succeeded, and Shi Jingtang became emperor in this same year.
2668:. Throughout the period, there was marked cultural and economic growth, rather than decline.
2499:(907–925) was founded after the fall of the Tang dynasty by Wang Jian, who held his court in
2205:
2037:
1394:
1232:
Towards the end of the Tang dynasty, the imperial government granted increased powers to the
1026:
443:
1835:. After reuniting much of northern China, in 924 Cunxu received the submission of Shaanxi's
3857:
2182:
1824:
1527:
1068:
281:
8:
3618:
2937:
2186:
2025:, the most powerful regime in southern China, which ceded all the territory north of the
1900:
1544:
1462:
1159:. It was a prolonged period of multiple political divisions in Chinese imperial history.
233:
3867:
3231:
China during the Tang-Song Interregnum, 878–978: New Approaches to the Southern Kingdoms
1899:
in his rebellion. In return for their aid, Shi Jingtang promised annual tribute and the
3714:
3130:. Amherst, NY: Cambria Press. pp. 2, 5–6, 8, 11–12, 115, 118, 122, 233, 247, 248.
2700:
2217:
2106:
1832:
1775:
1661:
1644:
1148:
1036:
216:
163:
155:
3550:
3521:
3513:
3499:
3475:
3456:
3437:
3418:
3395:
3315:
3290:
3262:
3234:
3209:
3169:
3131:
3106:
3081:
3037:
3012:
2964:
2925:
2851:
2610:
2582:
2574:
2018:
1712:
1319:
964:
532:
512:
287:
125:
117:
34:
1331:
3799:
3794:
2846:
2296:). It was based mostly in modern Zhejiang province but also held parts of southern
2213:
2209:
1567:
1536:
1466:
1402:
643:
201:
193:
82:
3105:. University of California, Berkeley: Cambridge University Press. pp. 72–73.
2177:
Only ten are traditionally listed, hence the era's name. Some historians, such as
3369:
3284:
2958:
2919:
2733:
1383:
1191:
independent long before 907 as the late Tang dynasty's control over its numerous
3611:
3080:. University of California, Berkeley: Cambridge University Press. p. 100.
2894:
2883:
2838:
2272:). The kingdom fell in 937 when it was taken from within by the founder of the
1246:
rebellions weakened the imperial government, and by the early 10th century the
545:
462:
103:
2963:. Translated by Richard L. Davis. Columbia University Press. pp. lv–lxv.
2264:
military governor in 892. The capital was initially at Guangling (present-day
3921:
3821:
3739:
3546:
2626:
2570:
2548:
2488:
2401:
2389:
2321:
2273:
2225:
2164:
2033:
2022:
1892:
1816:
1580:
1553:
1515:
1398:
1379:
1300:
335:
302:
3411:
A Portrait of Five Dynasties China: From the Memoirs of Wang Renyu (880–956)
2921:
A Portrait of Five Dynasties China: From the Memoirs of Wang Renyu (880–956)
3905:
3862:
3852:
3744:
3724:
3595:
3591:
3574:
2871:
2861:
2824:
2665:
2664:
and appears as a transition towards the solidified national culture of the
2661:
2597:
2593:
2419:
2413:
2337:
2301:
2261:
2198:
2194:
2190:
2170:
2140:
2082:
2045:
2041:
2013:
2009:
1968:
1896:
1873:
1678:
1649:
1576:
1397:
of ancient China, remarking that none of the rulers could be described as "
1375:
1351:
1296:
1210:
1206:
1171:
1167:
1163:
910:
886:
873:
860:
804:
763:
701:
415:
405:
382:
89:
3789:
3529:
2459:
2313:
2257:
2128:
2090:
1956:
1944:
1700:
1604:
1571:
1549:
1511:
1476:
1455:
1363:
1256:
1179:
1156:
817:
688:
522:
490:
477:
311:
3392:
From Warhorses to Ploughshares: The Later Tang Reign of Emperor Mingzong
1366:
was a Shatuo officer under Li Siyuan and Shi Jintang. The father of the
3699:
3678:
3663:
3489:
3270:
2752:
2562:
2536:
2520:
2496:
2443:
2392:
absorbed the state in 951 and moved the royal family to its capital in
2146:
2094:
1993:
1984:
1960:
1840:
1800:
1791:
1763:
1717:
1695:
1532:
1506:
1446:
1390:
1367:
1335:
1264:
1243:
569:
358:
2352:, was named regional governor by the Tang court. The kingdom included
3734:
3633:
2781:
2723:
2532:
2353:
2341:
2229:
2152:
2098:
2064:
2005:
1964:
1947:
entered the imperial capital in 947 and proclaimed the advent of the
1877:
1808:
1674:
1670:
1563:
1490:
1355:
1343:
1315:
1239:
1152:
134:
1393:(1619–1692) wrote that this period could be compared to the earlier
3498:. (transl. Richard L. Davis). New York: Columbia University Press.
2727:
2482:
2381:
2293:
2289:
2265:
1884:
1820:
1812:
1721:
1704:
1636:
1619:
1615:
1611:
1494:
1480:
1450:
Map of warlords ("jiedushi") in 902, before the end of Tang dynasty
1427:
1423:
1346:, who was the main military rival to Zhu Wen in the late Tang. The
1339:
1234:
1187:
3729:
3694:
2516:
2504:
2500:
2455:
2393:
2385:
2357:
2297:
2269:
2253:
2245:
2241:
2178:
2158:
2116:
2026:
2001:
1972:
1967:, a member of the Later Han imperial family, established a rival
1952:
1915:
1908:
1888:
1844:
1767:
1759:
1725:
1708:
1691:
1687:
1589:
1585:
1540:
1523:
1519:
1498:
1419:
1415:
1374:
fought in Li Keyong's army and Guo served under Liu Zhiyuan. The
1371:
1323:
1311:
1304:
1292:
1198:
1193:
1162:
Traditionally, the era is seen as beginning with the fall of the
712:
563:
557:
3543:
Power and Politics in Tenth-Century China: The Former Shu Regime
3166:
Power and politics in tenth-century China: the Former Shu regime
3154:(1977), "Chapter IX: The Epoch of the Second Division of China."
3128:
Power and politics in tenth-century China: the Former Shu regime
2044:
defeated the other remaining regimes in South China, conquering
1770:, which was within his region of influence. In 904, he executed
3842:
3704:
3534:
The Structure of Power in North China During the Five Dynasties
2975:
The information was taken from Richard L. Davis's introduction.
2676:
2423:
2377:
2373:
2361:
2317:
2134:
1881:
1828:
1657:
1653:
1628:
1502:
1327:
1288:
3338:. Museum of Chinese Art and Ethnography, Parma. Archived from
1747:
1401:". The Five Dynasties' rulers, despite claiming the status of
3709:
3011:. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. pp. 127–128.
2601:
2558:
2512:
2508:
2467:
2463:
2325:
2285:
2249:
2122:
1989:
1904:
1819:
fiercely fought the regime forces to conquer northern China;
1796:
1640:
1623:
1593:
1557:
1484:
1470:
1284:
1174:
still remained in China's north (eventually succeeded by the
3193:. The Chinese University of Hong Kong Press. pp. 51–78.
2036:
staged a coup and took the throne for himself, founding the
1932:
1861:
1414:
North. The founders of Wu and Former Shu were 'rogues' from
1205:
The last of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms regimes was
1823:
succeeded. He defeated Liu Shouguang (who had proclaimed a
1299:
argued that many of these military families, including the
3518:
Empire of Min: A South China Kingdom of the Tenth Century
2328:, the Southern Tang finished its conquest of Min in 945.
160:
146:
3289:. Britannica Educational Publishing. 2011. p. 245.
1880:, the fourth emperor of the Later Tang. Shi Jingtang, a
1166:
in 907 and reaching its climax with the founding of the
2588:
2304:, when Qian Shu surrendered to the expanding dynasty.
122:
108:
94:
2814:
1228:
by Anonymous, Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period
929:
851:
731:
664:
594:
468:
3034:
The Destruction of the Medieval Chinese Aristocracy
2684:
Art from the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period
1975:and requested Khitan aid to defeat the Later Zhou.
1386:in 960, which ended the era of the Five Dynasties.
1358:, who was himself an adopted son of Li Keyong. The
1143:) was an era of political upheaval and division in
3512:
3056:
2984:
2867:Family trees of the emperors of the Five Dynasties
2449:
2422:was based in the traditional Shatuo stronghold of
2404:. In 963, the region was annexed by Song dynasty.
39:The Later Liang (yellow) and contemporary kingdoms
3450:
3389:
1330:whose commanders replaced each other in frequent
1322:. The first of the Five Dynasties was founded by
1182:was eventually established in China's northwest.
3919:
3314:. University of Hawaii Press. pp. 116–124.
2364:. It was finally conquered by the Song dynasty.
3431:
3408:
3100:
3075:
3031:
2889:Timeline of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms
2418:Though considered one of the ten kingdoms, the
3309:
3208:. University of Hawaii Press. pp. 20–21.
3203:
3036:. Harvard University Press. pp. 151–184.
3006:
2917:
2048:in 979, starting the Song dynasty era in 982.
3619:
3163:
3125:
2633:under the control of the central government.
2433:
2427:
2292:, who set up his capital at Xifu (modern-day
1112:
64:
50:
3899:Spring and Autumn Annals of the Ten Kingdoms
3540:
3469:
3528:
3365:
3363:
3361:
3359:
3357:
3188:
2913:
2911:
3626:
3612:
3488:
3253:
3228:
3168:. Amherst, NY: Cambria Press. p. 82.
2956:
2384:. The kingdom held Hunan and northeastern
2268:) and later moved to Jinling (present-day
1119:
1105:
33:
2204:Other regimes during this period include
3892:Historical Records of the Five Dynasties
3495:Historical Records of the Five Dynasties
3354:
2960:Historical Records of the Five Dynasties
2908:
2592:
2552:
2481:
2244:(902–937) was established in modern-day
2070:
2055:
1988:
1931:
1860:
1839:kingdom, and in 925 Cunxu conquered the
1795:
1746:
1736:
1445:
1220:
3943:10th-century disestablishments in China
3453:China's Southern Tang Dynasty (937–976)
2952:
2950:
2503:. The kingdom held most of present-day
1978:
1943:To fill the power vacuum, the jiedushi
1831:Later Tang—the first in a long line of
1785:
1438:
1238:, the regional military governors. The
3920:
3635:Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period
3255:
2924:. Oxford University Press. p. 8.
1921:
1850:
1133:Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period
162:
124:
3607:
3002:
3000:
2573:(937–975) was the successor state of
2454:The smallest of the southern states,
1758:During the Tang dynasty, the warlord
1151:quickly succeeded one another in the
3948:10th-century establishments in China
2947:
2589:Transitions between the Ten Kingdoms
1959:, was enthroned, thus beginning the
1774:and made Zhaozong's 13-year-old son
3973:Former countries in Chinese history
1843:, a regime that had been set up in
1303:, were of mixed Han Chinese-Turkic-
1276:According to Nicholas Tackett, the
16:Period of Chinese history (907–979)
13:
3383:
3059:Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies
2997:
2987:Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies
14:
3999:
3885:Old History of the Five Dynasties
3564:
3336:"Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms"
3103:The Origins of the Chinese Nation
3078:The Origins of the Chinese Nation
2878:Old History of the Five Dynasties
2857:Conquest of Southern Tang by Song
1731:
3474:. The Chinese University Press.
2831:
2817:
2764:
2741:
2715:
2692:
2542:
2470:. Gao was in the service of the
2432:), formerly known as Liu Chong (
200:
3968:Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms
3472:Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms
3328:
3303:
3277:
3247:
3233:. Routledge. pp. 101–103.
3222:
3197:
3191:Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms
3182:
3157:
3144:
2450:Jingnan (also known as Nanping)
2407:
2331:
2051:
161:
147:
24:Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms
3394:. Hong Kong University Press.
3119:
3094:
3069:
3050:
3025:
3009:A Companion to Chinese History
2978:
2434:
2428:
1140:
1059:Science and technology history
123:
109:
95:
65:
51:
1:
2901:
2704:
2477:
2426:. It was founded by Liu Min (
1216:
429:
388:
364:
341:
317:
258:
3582:Dynasties in Chinese history
3536:. Stanford University Press.
2526:
2442:fell to the Han Chinese-led
1743:Later Liang (Five Dynasties)
7:
2810:
2699:Painting by Chinese artist
2638:northern and southern China
1762:was originally a member of
1342:, the son of Shatuo leader
10:
4004:
3470:Lorge, Peter, ed. (2011).
3451:Kurz, Johannes L. (2011).
3390:Davis, Richard L. (2015).
2936:Dudbridge actually quotes
2655:
2546:
2458:(924–963), was founded by
2411:
2235:
2181:, count eleven, including
1982:
1928:Later Han (Five Dynasties)
1925:
1857:Later Jin (Five Dynasties)
1854:
1789:
1740:
3876:
3835:
3779:
3753:
3688:Ten Kingdoms (Ten States)
3687:
3646:
3588:
3579:
3571:
3269:(in Chinese) – via
2492:by Li Sheng (fl. 908–925)
2376:(927–951) was founded by
2367:
2340:(917–971) was founded in
933:
855:
735:
668:
598:
472:
175:
154:
140:
133:
116:
102:
88:
81:
76:
72:
58:
44:
32:
28:
23:
3432:Hung, Hing Ming (2014).
3409:Dudbridge, Glen (2013).
3261:
3101:Nicolas Tackett (2017).
3076:Nicolas Tackett (2017).
3032:Nicolas Tackett (2014).
2847:Annam (Chinese province)
2511:, and parts of southern
2279:
2004:in 954, his adopted son
1772:Emperor Zhaozong of Tang
1543:province), precursor to
1408:
1278:three provinces of Hebei
1271:
46:Traditional Chinese
3415:Oxford University Press
3310:Benjamin Brose (2015).
3204:Benjamin Brose (2015).
3007:Michael Szonyi (2017).
2918:Glen Dudbridge (2013).
2777:Early Snow on the River
2112:The Ten Kingdoms were:
60:Simplified Chinese
3938:10th-century conflicts
3848:Ganzhou Uyghur Kingdom
3164:Wang, Hongjie (2011).
3126:Wang, Hongjie (2011).
2793:
2605:
2566:
2493:
2307:
2222:Ganzhou Uyghur Kingdom
2197:in the north, and the
2086:
2068:
1997:
1940:
1869:
1804:
1755:
1451:
1229:
1147:from 907 to 979. Five
3953:10th century in China
3933:960 disestablishments
3541:Wang Hongjie (2011).
3436:. Algora Publishing.
2596:
2557:A painting depicting
2556:
2485:
2074:
2059:
2038:Northern Song dynasty
1992:
1935:
1864:
1799:
1750:
1737:Later Liang (907–923)
1535:at Fengxiang (modern
1449:
1395:Warring States period
1224:
1185:Many states had been
924:(mainland, 1912–1949)
3783:independent entities
3286:The Culture of China
3189:Peter Lorge (2011).
2380:with the capital at
2256:. It was founded by
2032:In 960, the general
1979:Later Zhou (951–960)
1786:Later Tang (923–936)
1588:at Bianzhou (modern
1479:at Dingzhou (modern
1465:at Zhenzhou (modern
1301:Song imperial family
3958:Civil wars in China
3372:, Denis Twitchett,
3229:Hugh Clark (2021).
3150:Eberhard, Wolfram,
2957:Xiu Ouyang (2004).
2000:After the death of
1922:Later Han (947–951)
1901:Sixteen Prefectures
1891:, was aided by the
1851:Later Jin (937–947)
1673:(modern Guangzhou,
1389:The Qing historian
3978:Geography of China
3963:Dynasties of China
3928:907 establishments
3836:Neighboring states
3514:Schafer, Edward H.
3462:-9780415454964
3342:on 5 February 2018
3152:A History of China
2606:
2567:
2494:
2212:, Wuping Circuit,
2201:in the southwest.
2107:Johannes Gutenberg
2087:
2069:
1998:
1941:
1870:
1833:conquest dynasties
1805:
1776:Emperor Ai of Tang
1756:
1707:(modern Yangzhou,
1618:(modern Hangzhou,
1452:
1318:and possessed the
1265:Later Zhou dynasty
1230:
939:
749:Five Dynasties and
741:
676:Southern dynasties
604:
503:Chu–Han Contention
3915:
3914:
3602:
3601:
3589:Succeeded by
3522:Tuttle Publishing
3443:978-1-62894-072-5
3175:978-1-60497-764-6
3137:978-1-60497-764-6
3112:978-1-316-64748-6
3087:978-1-316-64748-6
2852:Chinese sovereign
2780:(五代南唐 趙幹 江行初雪圖);
2749:A Literary Garden
2611:Qingyuan Jiedushi
2076:Summer Palace of
1903:(modern northern
1876:rebelled against
1690:(modern Chengdu,
1552:at Weibo (modern
1501:(modern Taiyuan,
1320:Mandate of Heaven
1314:, controlled the
1129:
1128:
1086:Transport history
1012:Education history
984:
983:
979:
978:
965:Republic of China
947:People's Republic
920:Republic of China
899:
898:
848:
847:
843:
842:
728:
727:
661:
660:
656:
655:
592:
591:
495:(206 BC – 220 AD)
425:Spring and Autumn
288:Liao civilization
179:
178:
171:
170:
142:Yale Romanization
83:Standard Mandarin
3995:
3858:Tibetan kingdoms
3818:
3800:Qingyuan Circuit
3628:
3621:
3614:
3605:
3604:
3572:Preceded by
3569:
3568:
3560:
3537:
3525:
3509:
3485:
3466:
3447:
3428:
3405:
3377:
3367:
3352:
3351:
3349:
3347:
3332:
3326:
3325:
3307:
3301:
3300:
3281:
3275:
3274:
3268:
3259:
3254:Zizhi Tongjian.
3251:
3245:
3244:
3226:
3220:
3219:
3201:
3195:
3194:
3186:
3180:
3179:
3161:
3155:
3148:
3142:
3141:
3123:
3117:
3116:
3098:
3092:
3091:
3073:
3067:
3066:
3054:
3048:
3047:
3029:
3023:
3022:
3004:
2995:
2994:
2982:
2976:
2974:
2954:
2945:
2935:
2915:
2841:
2836:
2835:
2834:
2827:
2822:
2821:
2820:
2768:
2745:
2719:
2709:
2706:
2696:
2623:
2437:
2436:
2431:
2430:
2214:Qingyuan Circuit
2208:, Yiwu Circuit,
1711:), precursor to
1694:), precursor to
1677:), precursor to
1660:), precursor to
1656:(modern Fuzhou,
1643:), precursor to
1622:), precursor to
1596:), precursor to
1537:Fengxiang County
1526:), precursor to
1505:), precursor to
1467:Zhengding County
1378:of Song founder
1142:
1121:
1114:
1107:
1049:Military history
1007:Economic history
995:Related articles
972:
954:
936:
935:
931:
930:
925:
892:
879:
866:
853:
852:
836:
823:
810:
791:
781:
769:
756:
738:
737:
733:
732:
717:
707:
694:
681:
666:
665:
649:
644:Sixteen Kingdoms
627:
617:
601:
600:
596:
595:
585:
551:
538:
528:
518:
508:
496:
483:
470:
469:
448:
440:
438:
434:
431:
421:
411:
399:
397:
393:
390:
375:
373:
369:
366:
352:
350:
346:
343:
328:
326:
322:
319:
269:
267:
263:
260:
204:
194:History of China
181:
180:
167:
166:
165:
150:
149:
129:
128:
127:
112:
111:
98:
97:
74:
73:
68:
67:
54:
53:
37:
21:
20:
4003:
4002:
3998:
3997:
3996:
3994:
3993:
3992:
3983:Historical eras
3918:
3917:
3916:
3911:
3872:
3831:
3812:
3805:Jinghai Circuit
3795:Dingnan Circuit
3775:
3749:
3683:
3642:
3632:
3598:
3594:
3585:
3577:
3567:
3557:
3506:
3482:
3463:
3444:
3425:
3402:
3386:
3384:Further reading
3381:
3380:
3370:John W. Chaffee
3368:
3355:
3345:
3343:
3334:
3333:
3329:
3322:
3308:
3304:
3297:
3283:
3282:
3278:
3252:
3248:
3241:
3227:
3223:
3216:
3202:
3198:
3187:
3183:
3176:
3162:
3158:
3149:
3145:
3138:
3124:
3120:
3113:
3099:
3095:
3088:
3074:
3070:
3055:
3051:
3044:
3030:
3026:
3019:
3005:
2998:
2983:
2979:
2971:
2955:
2948:
2942:Ennin's Travels
2932:
2916:
2909:
2904:
2837:
2832:
2830:
2823:
2818:
2816:
2813:
2796:
2791:
2790:
2789:
2774:
2769:
2760:
2759:
2758:
2755:
2746:
2737:
2720:
2711:
2707:
2697:
2686:
2685:
2658:
2617:
2615:Wuping Jiedushi
2600:'s conquest of
2591:
2551:
2545:
2529:
2480:
2452:
2416:
2410:
2370:
2348:. His brother,
2334:
2310:
2282:
2260:, who became a
2238:
2210:Dingnan Circuit
2054:
1987:
1981:
1930:
1924:
1859:
1853:
1794:
1788:
1745:
1739:
1734:
1724:, precursor to
1570:, precursor to
1568:Dingnan circuit
1444:
1411:
1384:Chenqiao Mutiny
1338:was founded by
1274:
1219:
1149:dynastic states
1125:
1096:
1095:
1091:Women's history
997:
996:
987:
986:
985:
980:
975:
970:
968:
957:
952:
948:
928:
923:
914:
913:
902:
901:
900:
895:
890:
882:
877:
869:
864:
850:
849:
844:
839:
834:
826:
821:
813:
808:
800:
794:
789:
779:
767:
759:
754:
750:
730:
729:
724:
715:
705:
697:
692:
684:
679:
675:
663:
662:
657:
652:
647:
639:
636:
630:
625:
615:
593:
588:
583:
575:
549:
541:
536:
526:
517:(202 BC – 9 AD)
516:
506:
494:
486:
481:
466:
465:
454:
453:
446:
436:
432:
427:
419:
409:
395:
391:
386:
378:
371:
367:
362:
348:
344:
339:
331:
324:
320:
315:
306:
305:
294:
293:
265:
261:
256:
248:
237:
236:
148:Ng doi sap gwok
110:Wu tai shih kuo
40:
17:
12:
11:
5:
4001:
3991:
3990:
3985:
3980:
3975:
3970:
3965:
3960:
3955:
3950:
3945:
3940:
3935:
3930:
3913:
3912:
3910:
3909:
3902:
3895:
3888:
3880:
3878:
3874:
3873:
3871:
3870:
3865:
3860:
3855:
3850:
3845:
3839:
3837:
3833:
3832:
3830:
3829:
3827:Lulong Circuit
3824:
3819:
3810:Wuping Circuit
3807:
3802:
3797:
3792:
3786:
3784:
3777:
3776:
3774:
3773:
3768:
3763:
3757:
3755:
3751:
3750:
3748:
3747:
3742:
3737:
3732:
3727:
3722:
3712:
3707:
3702:
3697:
3691:
3689:
3685:
3684:
3682:
3681:
3676:
3671:
3666:
3656:
3650:
3648:
3647:Five Dynasties
3644:
3643:
3631:
3630:
3623:
3616:
3608:
3600:
3599:
3590:
3587:
3578:
3573:
3566:
3565:External links
3563:
3562:
3561:
3556:978-1604977646
3555:
3538:
3526:
3510:
3504:
3486:
3481:978-9629964184
3480:
3467:
3461:
3448:
3442:
3429:
3424:978-0199670680
3423:
3406:
3400:
3385:
3382:
3379:
3378:
3353:
3327:
3321:978-0824857240
3320:
3302:
3295:
3276:
3246:
3239:
3221:
3215:978-0824857240
3214:
3196:
3181:
3174:
3156:
3143:
3136:
3118:
3111:
3093:
3086:
3068:
3049:
3042:
3024:
3017:
2996:
2977:
2969:
2946:
2930:
2906:
2905:
2903:
2900:
2899:
2898:
2895:Zizhi Tongjian
2891:
2886:
2884:Tibetan Empire
2881:
2874:
2869:
2864:
2859:
2854:
2849:
2843:
2842:
2839:History portal
2828:
2812:
2809:
2795:
2792:
2771:
2770:
2763:
2762:
2761:
2757:
2756:
2747:
2740:
2738:
2721:
2714:
2712:
2698:
2691:
2688:
2687:
2683:
2682:
2681:
2657:
2654:
2590:
2587:
2547:Main article:
2544:
2541:
2528:
2525:
2479:
2476:
2451:
2448:
2412:Main article:
2409:
2406:
2369:
2366:
2333:
2330:
2309:
2306:
2281:
2278:
2237:
2234:
2175:
2174:
2168:
2162:
2156:
2150:
2144:
2138:
2132:
2126:
2120:
2053:
2050:
2012:, allied with
1983:Main article:
1980:
1977:
1926:Main article:
1923:
1920:
1855:Main article:
1852:
1849:
1790:Main article:
1787:
1784:
1741:Main article:
1738:
1735:
1733:
1732:Five Dynasties
1730:
1729:
1728:
1715:
1698:
1681:
1664:
1647:
1626:
1601:
1600:
1583:
1574:
1561:
1547:
1530:
1509:
1488:
1474:
1443:
1437:
1410:
1407:
1273:
1270:
1242:(755–763) and
1226:Palace Banquet
1218:
1215:
1145:Imperial China
1127:
1126:
1124:
1123:
1116:
1109:
1101:
1098:
1097:
1094:
1093:
1088:
1083:
1082:
1081:
1076:
1071:
1066:
1056:
1051:
1046:
1045:
1044:
1034:
1029:
1024:
1022:Jewish history
1019:
1014:
1009:
1004:
998:
994:
993:
992:
989:
988:
982:
981:
977:
976:
974:
973:
960:
958:
956:
955:
953:(1949–present)
942:
940:
934:
927:
926:
915:
909:
908:
907:
904:
903:
897:
896:
894:
893:
881:
880:
868:
867:
856:
846:
845:
841:
840:
838:
837:
827:
824:
814:
811:
801:
797:
795:
793:
792:
782:
771:
770:
758:
757:
744:
742:
736:
726:
725:
723:
722:
721:
720:
719:
718:
696:
695:
683:
682:
669:
659:
658:
654:
653:
651:
650:
640:
637:
633:
631:
629:
628:
618:
607:
605:
599:
590:
589:
587:
586:
574:
573:
553:
552:
546:Three Kingdoms
540:
539:
529:
519:
509:
498:
497:
485:
484:
473:
467:
461:
460:
459:
456:
455:
452:
451:
450:
449:
444:Warring States
441:
412:
401:
400:
377:
376:
354:
353:
349: 1046 BC
330:
329:
325: 1600 BC
307:
301:
300:
299:
296:
295:
292:
291:
271:
270:
266: 2000 BC
247:
246:
238:
232:
231:
230:
227:
226:
225:
224:
222:Historiography
219:
214:
206:
205:
197:
196:
190:
189:
177:
176:
173:
172:
169:
168:
158:
152:
151:
144:
138:
137:
135:Yue: Cantonese
131:
130:
120:
114:
113:
106:
100:
99:
96:Wǔ dài shí guó
92:
86:
85:
79:
78:
77:Transcriptions
70:
69:
62:
56:
55:
48:
42:
41:
38:
30:
29:
26:
25:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
4000:
3989:
3988:Medieval Asia
3986:
3984:
3981:
3979:
3976:
3974:
3971:
3969:
3966:
3964:
3961:
3959:
3956:
3954:
3951:
3949:
3946:
3944:
3941:
3939:
3936:
3934:
3931:
3929:
3926:
3925:
3923:
3908:
3907:
3903:
3901:
3900:
3896:
3894:
3893:
3889:
3887:
3886:
3882:
3881:
3879:
3875:
3869:
3866:
3864:
3861:
3859:
3856:
3854:
3851:
3849:
3846:
3844:
3841:
3840:
3838:
3834:
3828:
3825:
3823:
3822:Guiyi Circuit
3820:
3816:
3811:
3808:
3806:
3803:
3801:
3798:
3796:
3793:
3791:
3788:
3787:
3785:
3782:
3778:
3772:
3769:
3767:
3764:
3762:
3759:
3758:
3756:
3752:
3746:
3743:
3741:
3740:Southern Tang
3738:
3736:
3733:
3731:
3728:
3726:
3723:
3720:
3716:
3713:
3711:
3708:
3706:
3703:
3701:
3698:
3696:
3693:
3692:
3690:
3686:
3680:
3677:
3675:
3672:
3670:
3667:
3665:
3661:
3657:
3655:
3652:
3651:
3649:
3645:
3640:
3636:
3629:
3624:
3622:
3617:
3615:
3610:
3609:
3606:
3597:
3593:
3584:
3583:
3576:
3570:
3558:
3552:
3548:
3547:Cambria Press
3544:
3539:
3535:
3531:
3527:
3523:
3519:
3515:
3511:
3507:
3505:0-231-12826-6
3501:
3497:
3496:
3491:
3487:
3483:
3477:
3473:
3468:
3464:
3458:
3455:. Routledge.
3454:
3449:
3445:
3439:
3435:
3430:
3426:
3420:
3416:
3412:
3407:
3403:
3401:9789888208104
3397:
3393:
3388:
3387:
3375:
3371:
3366:
3364:
3362:
3360:
3358:
3341:
3337:
3331:
3323:
3317:
3313:
3306:
3298:
3296:9781615301836
3292:
3288:
3287:
3280:
3272:
3267:
3265:
3258:
3250:
3242:
3240:9781000426397
3236:
3232:
3225:
3217:
3211:
3207:
3200:
3192:
3185:
3177:
3171:
3167:
3160:
3153:
3147:
3139:
3133:
3129:
3122:
3114:
3108:
3104:
3097:
3089:
3083:
3079:
3072:
3065:(2): 405–408.
3064:
3060:
3053:
3045:
3043:9780674492059
3039:
3035:
3028:
3020:
3018:9781118624548
3014:
3010:
3003:
3001:
2992:
2988:
2981:
2972:
2970:9780231128278
2966:
2962:
2961:
2953:
2951:
2943:
2939:
2933:
2931:9780191749537
2927:
2923:
2922:
2914:
2912:
2907:
2897:
2896:
2892:
2890:
2887:
2885:
2882:
2880:
2879:
2875:
2873:
2870:
2868:
2865:
2863:
2860:
2858:
2855:
2853:
2850:
2848:
2845:
2844:
2840:
2829:
2826:
2815:
2808:
2804:
2800:
2787:
2783:
2779:
2778:
2773:
2767:
2754:
2750:
2744:
2739:
2735:
2731:
2729:
2725:
2718:
2713:
2702:
2695:
2690:
2689:
2680:
2678:
2673:
2669:
2667:
2663:
2653:
2651:
2650:
2645:
2644:
2639:
2634:
2630:
2628:
2627:Yangtze River
2621:
2616:
2612:
2603:
2599:
2595:
2586:
2584:
2580:
2576:
2572:
2571:Southern Tang
2565:(fl. 942–961)
2564:
2560:
2555:
2550:
2549:Southern Tang
2543:Southern Tang
2540:
2538:
2534:
2524:
2522:
2518:
2514:
2510:
2506:
2502:
2498:
2491:
2490:
2489:Yueyang Tower
2484:
2475:
2473:
2469:
2465:
2461:
2457:
2447:
2445:
2441:
2438:), after the
2425:
2421:
2415:
2405:
2403:
2402:Zhou Xingfeng
2399:
2395:
2391:
2390:Southern Tang
2387:
2383:
2379:
2375:
2365:
2363:
2359:
2355:
2351:
2347:
2343:
2339:
2329:
2327:
2323:
2322:Southern Tang
2319:
2315:
2305:
2303:
2299:
2295:
2291:
2287:
2277:
2275:
2274:Southern Tang
2271:
2267:
2263:
2259:
2255:
2251:
2247:
2243:
2233:
2231:
2227:
2226:Guiyi Circuit
2223:
2219:
2215:
2211:
2207:
2202:
2200:
2196:
2192:
2188:
2184:
2180:
2172:
2169:
2166:
2165:Southern Tang
2163:
2160:
2157:
2154:
2151:
2148:
2145:
2142:
2139:
2136:
2133:
2130:
2127:
2124:
2121:
2118:
2115:
2114:
2113:
2110:
2108:
2104:
2100:
2096:
2092:
2084:
2080:
2079:
2073:
2066:
2062:
2058:
2049:
2047:
2043:
2039:
2035:
2034:Zhao Kuangyin
2030:
2028:
2024:
2023:Southern Tang
2020:
2015:
2011:
2007:
2003:
1995:
1991:
1986:
1976:
1974:
1970:
1966:
1962:
1958:
1954:
1950:
1946:
1938:
1934:
1929:
1919:
1917:
1912:
1910:
1906:
1902:
1898:
1894:
1890:
1886:
1883:
1879:
1875:
1867:
1863:
1858:
1848:
1846:
1842:
1838:
1834:
1830:
1826:
1822:
1818:
1817:Liu Shouguang
1814:
1810:
1802:
1798:
1793:
1783:
1781:
1777:
1773:
1769:
1765:
1761:
1753:
1749:
1744:
1727:
1723:
1719:
1716:
1714:
1710:
1706:
1702:
1699:
1697:
1693:
1689:
1685:
1682:
1680:
1676:
1672:
1668:
1665:
1663:
1659:
1655:
1651:
1648:
1646:
1642:
1638:
1634:
1630:
1627:
1625:
1621:
1617:
1613:
1610:
1609:
1608:
1607:
1606:
1599:
1595:
1591:
1587:
1584:
1582:
1578:
1575:
1573:
1569:
1565:
1562:
1559:
1555:
1554:Daming County
1551:
1548:
1546:
1542:
1538:
1534:
1531:
1529:
1525:
1521:
1517:
1516:Liu Shouguang
1513:
1510:
1508:
1504:
1500:
1496:
1492:
1489:
1486:
1482:
1478:
1475:
1472:
1468:
1464:
1461:
1460:
1459:
1458:
1457:
1448:
1442:
1436:
1432:
1429:
1425:
1421:
1417:
1406:
1404:
1400:
1399:Son of Heaven
1396:
1392:
1387:
1385:
1381:
1380:Zhao Kuangyin
1377:
1373:
1369:
1365:
1361:
1357:
1353:
1349:
1345:
1341:
1337:
1333:
1329:
1325:
1321:
1317:
1316:Central Plain
1313:
1308:
1306:
1302:
1298:
1294:
1290:
1286:
1281:
1279:
1269:
1266:
1260:
1258:
1253:
1249:
1245:
1241:
1237:
1236:
1227:
1223:
1214:
1212:
1208:
1203:
1200:
1196:
1195:
1190:
1189:
1183:
1181:
1177:
1173:
1169:
1165:
1160:
1158:
1154:
1153:Central Plain
1150:
1146:
1138:
1134:
1122:
1117:
1115:
1110:
1108:
1103:
1102:
1100:
1099:
1092:
1089:
1087:
1084:
1080:
1077:
1075:
1072:
1070:
1067:
1065:
1062:
1061:
1060:
1057:
1055:
1054:Naval history
1052:
1050:
1047:
1043:
1040:
1039:
1038:
1037:Music history
1035:
1033:
1032:Media history
1030:
1028:
1025:
1023:
1020:
1018:
1017:Legal history
1015:
1013:
1010:
1008:
1005:
1003:
1000:
999:
991:
990:
971:1949–present)
967:
966:
962:
961:
959:
951:
950:
944:
943:
941:
938:
937:
932:
922:
921:
917:
916:
912:
906:
905:
889:
888:
884:
883:
876:
875:
871:
870:
863:
862:
858:
857:
854:
833:
832:
828:
825:
820:
819:
815:
812:
807:
806:
802:
799:
798:
796:
788:
787:
786:Southern Song
783:
778:
777:
776:Northern Song
773:
772:
766:
765:
761:
760:
753:
752:
746:
745:
743:
740:
739:
734:
714:
711:
710:
709:
708:
704:
703:
699:
698:
691:
690:
686:
685:
678:
677:
671:
670:
667:
646:
645:
641:
638:
635:
634:
632:
624:
623:
619:
614:
613:
609:
608:
606:
603:
602:
597:
582:
581:
577:
576:
572:
571:
566:
565:
560:
559:
555:
554:
548:
547:
543:
542:
535:
534:
530:
525:
524:
520:
515:
514:
510:
505:
504:
500:
499:
493:
492:
488:
487:
480:
479:
475:
474:
471:
464:
458:
457:
445:
442:
437: 476 BC
426:
423:
422:
418:
417:
413:
410:(1046–771 BC)
408:
407:
403:
402:
396: 256 BC
385:
384:
380:
379:
361:
360:
356:
355:
338:
337:
333:
332:
314:
313:
309:
308:
304:
298:
297:
290:
289:
284:
283:
278:
277:
273:
272:
255:
254:
250:
249:
245:
244:
240:
239:
235:
229:
228:
223:
220:
218:
215:
213:
210:
209:
208:
207:
203:
199:
198:
195:
192:
191:
187:
183:
182:
174:
164:
159:
157:
153:
145:
143:
139:
136:
132:
126:
121:
119:
115:
107:
105:
101:
93:
91:
87:
84:
80:
75:
71:
63:
61:
57:
49:
47:
43:
36:
31:
27:
22:
19:
3906:Wudai Huiyao
3904:
3897:
3890:
3883:
3853:Liao dynasty
3790:Yiwu Circuit
3780:
3754:Other states
3745:Northern Han
3725:Southern Han
3634:
3596:Liao dynasty
3592:Song dynasty
3580:
3575:Tang dynasty
3542:
3533:
3517:
3493:
3471:
3452:
3433:
3410:
3391:
3373:
3344:. Retrieved
3340:the original
3330:
3311:
3305:
3285:
3279:
3263:
3257:"卷291"
3249:
3230:
3224:
3205:
3199:
3190:
3184:
3165:
3159:
3151:
3146:
3127:
3121:
3102:
3096:
3077:
3071:
3062:
3058:
3052:
3033:
3027:
3008:
2990:
2986:
2980:
2959:
2941:
2920:
2893:
2876:
2872:Liao dynasty
2862:Dali Kingdom
2825:China portal
2805:
2801:
2797:
2784:painting by
2775:
2748:
2722:
2674:
2670:
2666:Song dynasty
2662:Tang dynasty
2659:
2647:
2641:
2635:
2631:
2607:
2598:Song dynasty
2568:
2530:
2495:
2487:
2453:
2420:Northern Han
2417:
2414:Northern Han
2408:Northern Han
2371:
2338:Southern Han
2335:
2332:Southern Han
2311:
2302:Song dynasty
2283:
2262:Tang dynasty
2239:
2203:
2199:Dali Kingdom
2195:Liao dynasty
2191:Northern Han
2189:but not the
2176:
2171:Northern Han
2141:Southern Han
2111:
2102:
2088:
2083:Guo Zhongshu
2078:Emperor Ming
2075:
2060:
2052:Ten Kingdoms
2046:Northern Han
2042:Zhao Kuangyi
2031:
2014:Liao dynasty
2010:Northern Han
1999:
1969:Northern Han
1942:
1913:
1897:Liao dynasty
1874:Shi Jingtang
1871:
1806:
1757:
1679:Southern Han
1650:Wang Shenzhi
1603:
1602:
1577:Zhang Yichao
1454:
1453:
1440:
1439:Significant
1433:
1412:
1388:
1352:Shi Jingtang
1328:Shatuo Turks
1309:
1297:Deng Xiaonan
1282:
1275:
1261:
1251:
1247:
1233:
1231:
1225:
1211:Yuan dynasty
1207:Northern Han
1204:
1192:
1186:
1184:
1172:Liao dynasty
1168:Song dynasty
1164:Tang dynasty
1161:
1132:
1130:
1027:LGBT history
963:
945:
918:
885:
872:
859:
829:
816:
803:
784:
774:
762:
751:Ten Kingdoms
748:
747:
700:
687:
674:Northern and
672:
642:
620:
610:
578:
568:
562:
556:
550:(220–280 AD)
544:
531:
521:
511:
507:(206–202 BC)
501:
489:
482:(221–207 BC)
476:
447:(475–221 BC)
420:(771–256 BC)
416:Eastern Zhou
414:
406:Western Zhou
404:
381:
357:
334:
310:
286:
280:
274:
251:
241:
90:Hanyu Pinyin
18:
3813: [
3654:Later Liang
3530:Wang Gungwu
2649:New History
2643:Old History
2618: [
2561:players by
2472:Later Liang
2460:Gao Jichang
2258:Yang Xingmi
2091:South China
2081:(明皇避暑宮) by
1963:. However,
1957:Han Chinese
1945:Liu Zhiyuan
1780:Later Liang
1752:Later Liang
1701:Yang Xingmi
1605:South China
1598:Later Liang
1572:Western Xia
1550:Luo Shaowei
1512:Liu Rengong
1477:Wang Chuzhi
1456:North China
1364:Liu Zhiyuan
1332:coup d'état
1257:Qin dynasty
1180:Western Xia
1178:), and the
1176:Jin dynasty
1157:South China
1074:Discoveries
1069:Cartography
1064:Archaeology
1002:Art history
891:(1644–1912)
878:(1368–1644)
865:(1271–1368)
835:(1115–1234)
822:(1038–1227)
818:Western Xia
790:(1127–1279)
622:Eastern Jin
612:Western Jin
537:(25–220 AD)
533:Eastern Han
513:Western Han
392: 1046
372: 1046
368: 1250
345: 1600
321: 2070
262: 8500
243:Paleolithic
234:Prehistoric
3922:Categories
3700:Former Shu
3679:Later Zhou
3664:Later Tang
3490:Ouyang Xiu
3346:4 February
3271:Wikisource
2938:Reischauer
2902:References
2753:Zhou Wenju
2708: 919
2563:Zhou Wenju
2537:Later Tang
2521:Later Tang
2507:, western
2497:Former Shu
2478:Former Shu
2444:Later Zhou
2147:Former Shu
2109:'s press.
2095:Former Shu
1994:Later Zhou
1985:Later Zhou
1971:regime in
1961:Later Zhou
1841:Former Shu
1801:Later Tang
1792:Later Tang
1764:Huang Chao
1718:Gao Jixing
1696:Former Shu
1533:Li Maozhen
1507:Later Tang
1391:Wang Fuzhi
1368:Later Zhou
1336:Later Tang
1307:ancestry.
1250:commanded
1244:Huang Chao
1217:Background
1079:Inventions
809:(916–1125)
780:(960–1127)
768:(960–1279)
435: – c.
433: 770
394: – c.
370: – c.
359:Late Shang
347: – c.
323: – c.
264: – c.
104:Wade–Giles
3877:Histories
3735:Later Shu
3674:Later Han
3669:Later Jin
3492:(2004) .
2993:(2): 397.
2782:shan shui
2736:(886–974)
2724:Butterfly
2604:(960–979)
2533:Later Shu
2527:Later Shu
2440:Later Han
2354:Guangdong
2342:Guangzhou
2230:Xiliangfu
2173:(951–979)
2167:(937–976)
2161:(924–963)
2155:(934–965)
2153:Later Shu
2149:(907–925)
2143:(917–971)
2137:(907–951)
2131:(909–945)
2125:(907–978)
2119:(907–937)
2099:Later Shu
2085:(929–977)
2067:(932–962)
2065:Dong Yuan
2061:Riverbank
2019:conquered
2006:Chai Rong
1996:in 951 AD
1965:Liu Chong
1949:Later Han
1939:in 949 AD
1937:Later Han
1878:Li Congke
1868:in 939 AD
1866:Later Jin
1809:Li Keyong
1803:in 926 AD
1754:in 907 AD
1684:Wang Jian
1675:Guangdong
1671:Guangzhou
1564:Li Sigong
1560:province)
1491:Li Keyong
1473:province)
1463:Wang Rong
1360:Later Han
1356:Li Siyuan
1348:Later Jin
1344:Li Keyong
1240:An Lushan
755:(907–979)
716:(690–705)
706:(618–907)
693:(581–618)
680:(420–589)
648:(304–439)
626:(317–420)
616:(266–316)
584:(266–420)
527:(9–23 AD)
253:Neolithic
217:Dynasties
3868:Đại Việt
3781:De facto
3639:Timeline
3586:907–960
3532:(1963).
3516:(1954).
2811:See also
2786:Zhao Gan
2728:Wisteria
2701:Li Cheng
2646:and the
2523:in 925.
2382:Changsha
2294:Hangzhou
2290:Qian Liu
2266:Yangzhou
2021:much of
1885:jiedushi
1821:Li Cunxu
1813:Li Cunxu
1722:Jingzhou
1705:Yangzhou
1637:Changsha
1635:(modern
1620:Zhejiang
1616:Hangzhou
1612:Qian Liu
1522:(modern
1495:Li Cunxu
1481:Dingzhou
1441:jiedushi
1428:Shanzhou
1424:Hangzhou
1370:founder
1362:founder
1350:founder
1340:Li Cunxu
1252:de facto
1248:jiedushi
1235:jiedushi
1199:warlords
1188:de facto
1042:Timeline
969:(Taiwan,
949:of China
463:Imperial
212:Timeline
186:a series
184:Part of
3730:Jingnan
3264:zh:資治通鑑
2730:Flowers
2656:Culture
2579:Li Bian
2517:Shaanxi
2505:Sichuan
2501:Chengdu
2456:Jingnan
2398:Liu Yan
2394:Nanjing
2386:Guangxi
2358:Guangxi
2350:Liu Yin
2346:Liu Yan
2298:Jiangsu
2270:Nanjing
2254:Jiangxi
2246:Jiangsu
2242:Yang Wu
2236:Yang Wu
2179:Bo Yang
2159:Jingnan
2117:Yang Wu
2103:feiqian
2027:Yangtze
2002:Guo Wei
1973:Taiyuan
1953:Guo Wei
1916:Kaifeng
1909:Beijing
1889:Taiyuan
1845:Sichuan
1768:Luoyang
1760:Zhu Wen
1726:Jingnan
1709:Jiangsu
1692:Sichuan
1688:Chengdu
1667:Liu Yin
1633:Tanzhou
1590:Kaifeng
1586:Zhu Wen
1541:Shaanxi
1524:Beijing
1520:Youzhou
1499:Taiyuan
1420:Xuchang
1416:Huainan
1403:emperor
1372:Guo Wei
1324:Zhu Wen
1312:Kaifeng
1305:Kumo Xi
1293:Shaanxi
1194:fanzhen
1137:Chinese
713:Wu Zhou
303:Ancient
282:Yangtze
3843:Balhae
3553:
3502:
3478:
3459:
3440:
3421:
3398:
3318:
3293:
3266:
3237:
3212:
3172:
3134:
3109:
3084:
3040:
3015:
2967:
2928:
2677:Taoism
2424:Shanxi
2378:Ma Yin
2374:Ma Chu
2368:Ma Chu
2362:Hainan
2360:, and
2318:Fuzhou
2252:, and
2135:Ma Chu
1893:Khitan
1882:Shatuo
1829:Shatuo
1658:Fujian
1654:Fuzhou
1629:Ma Yin
1503:Shanxi
1376:father
1334:. The
1289:Shanxi
1139::
911:Modern
567:, and
285:, and
276:Yellow
188:on the
3817:]
3710:Wuyue
2751:, by
2734:Xu Xi
2732:, by
2710:–967)
2622:]
2602:China
2559:weiqi
2513:Gansu
2509:Hubei
2468:Hubei
2464:Wuhan
2326:Wuyue
2286:Wuyue
2280:Wuyue
2250:Anhui
2123:Wuyue
1905:Hebei
1895:-led
1887:from
1641:Hunan
1624:Wuyue
1594:Henan
1581:Guiyi
1558:Hebei
1485:Hebei
1471:Hebei
1409:South
1285:Hebei
1272:North
336:Shang
3863:Dali
3766:Zhao
3662:) /
3551:ISBN
3500:ISBN
3476:ISBN
3457:ISBN
3438:ISBN
3419:ISBN
3396:ISBN
3348:2018
3316:ISBN
3291:ISBN
3235:ISBN
3210:ISBN
3170:ISBN
3132:ISBN
3107:ISBN
3082:ISBN
3038:ISBN
3013:ISBN
2965:ISBN
2926:ISBN
2726:and
2613:and
2569:The
2531:The
2515:and
2486:The
2372:The
2336:The
2312:The
2284:The
2240:The
2228:and
2206:Zhao
2185:and
2097:and
1955:, a
1907:and
1815:and
1514:and
1493:and
1418:and
1141:五代十國
1131:The
887:Qing
874:Ming
861:Yuan
805:Liao
764:Song
702:Tang
383:Zhou
66:五代十国
52:五代十國
3771:Yan
3719:Yin
3717:/ (
3715:Min
3705:Chu
3660:Jin
2940:'s
2794:Law
2577:as
2466:in
2344:by
2314:Min
2308:Min
2218:Yin
2183:Yan
2129:Min
2063:by
1825:Yan
1720:at
1703:at
1686:at
1669:at
1662:Min
1652:at
1645:Chu
1631:at
1614:at
1579:at
1566:at
1528:Yan
1518:at
1497:at
831:Jin
689:Sui
580:Jin
564:Shu
558:Wei
523:Xin
491:Han
478:Qin
374:BC)
312:Xia
156:IPA
118:IPA
3924::
3815:zh
3761:Qi
3695:Wu
3549:.
3545:.
3520:.
3417:.
3413:.
3356:^
3260:.
3063:42
3061:.
2999:^
2991:42
2989:.
2949:^
2910:^
2705:c.
2629:.
2620:zh
2583:Wu
2575:Wu
2435:劉崇
2429:劉旻
2356:,
2276:.
2248:,
2232:.
2224:,
2220:,
2216:,
2187:Qi
1847:.
1837:Qi
1782:.
1713:Wu
1639:,
1592:,
1556:,
1545:Qi
1539:,
1483:,
1469:,
1291:,
1287:,
1213:.
570:Wu
561:,
430:c.
389:c.
365:c.
342:c.
318:c.
279:,
259:c.
3721:)
3658:(
3641:)
3637:(
3627:e
3620:t
3613:v
3559:.
3524:.
3508:.
3484:.
3465:.
3446:.
3427:.
3404:.
3350:.
3324:.
3299:.
3273:.
3243:.
3218:.
3178:.
3140:.
3115:.
3090:.
3046:.
3021:.
2973:.
2944:.
2934:.
2788:.
2703:(
1487:)
1135:(
1120:e
1113:t
1106:v
439:)
428:(
398:)
387:(
363:(
351:)
340:(
327:)
316:(
268:)
257:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.