616:
305:
298:
785:
allowing it to efficiently handle graphs with thousands of nodes. The vf2 algorithm has been widely used in various applications, such as pattern recognition, computer vision, and bioinformatics. While it has a worst-case exponential time complexity, it performs well in practice for many types of graphs.
780:
can be used to heuristically test for graph isomorphism. If the test fails the two input graphs are guaranteed to be non-isomorphic. If the test succeeds the graphs may or may not be isomorphic. There are generalizations of the test algorithm that are guaranteed to detect isomorphisms, however their
482:
The formal notion of "isomorphism", e.g., of "graph isomorphism", captures the informal notion that some objects have "the same structure" if one ignores individual distinctions of "atomic" components of objects in question. Whenever individuality of "atomic" components (vertices and edges, for
681:
While graph isomorphism may be studied in a classical mathematical way, as exemplified by the
Whitney theorem, it is recognized that it is a problem to be tackled with an algorithmic approach. The computational problem of determining whether two finite graphs are isomorphic is called the graph
784:
Another well-known algorithm for graph isomorphism is the vf2 algorithm, developed by
Cordella et al. in 2001. The vf2 algorithm is a depth-first search algorithm that tries to build an isomorphism between two graphs incrementally. It uses a set of feasibility rules to prune the search space,
473:
is the number of the vertices of the graph, used only to uniquely identify the vertices. In such cases two labeled graphs are sometimes said to be isomorphic if the corresponding underlying unlabeled graphs are isomorphic (otherwise the definition of isomorphism would be trivial).
427:
Under another definition, an isomorphism is an edge-preserving vertex bijection which preserves equivalence classes of labels, i.e., vertices with equivalent (e.g., the same) labels are mapped onto the vertices with equivalent labels and vice versa; same with edge labels.
408:
graphs. However, the notion of isomorphism may be applied to all other variants of the notion of graph, by adding the requirements to preserve the corresponding additional elements of structure: arc directions, edge weights, etc., with the following exception.
499:
and so on. The isomorphism relation may also be defined for all these generalizations of graphs: the isomorphism bijection must preserve the elements of structure which define the object type in question:
483:
graphs) is important for correct representation of whatever is modeled by graphs, the model is refined by imposing additional restrictions on the structure, and other mathematical objects are used:
596:
99:
227:
458:
graph with the two vertices labelled with 1 and 2 has a single automorphism under the first definition, but under the second definition there are two auto-morphisms.
456:
182:
153:
759:
complexity bound instead. He restored the original claim five days later. As of 2024, the full journal version of Babai's paper has not yet been published.
266:
of graphs. The question of whether graph isomorphism can be determined in polynomial time is a major unsolved problem in computer science, known as the
1231:
743:, a mathematician and computer scientist at the University of Chicago, claimed to have proven that the graph isomorphism problem is solvable in
527:, then all graphs in its isomorphism class also have exactly one cycle. On the other hand, in the common case when the vertices of a graph are (
752:
1031:
777:
1206:
1019:
Dirk L. Vertigan, Geoffrey P. Whittle: A 2-Isomorphism
Theorem for Hypergraphs. J. Comb. Theory, Ser. B 71(2): 215–230. 1997.
940:
882:
545:
188:. This kind of bijection is commonly described as "edge-preserving bijection", in accordance with the general notion of
829:
1274:
961:
867:
610:
1179:
Huang, Ningyuan Teresa; Villar, Soledad (2021). "A Short
Tutorial on the Weisfeiler-Lehman Test and Its Variants".
748:
705:
769:
The main areas of research for the problem are design of fast algorithms and theoretical investigations of its
424:
Under one definition, an isomorphism is a vertex bijection which is both edge-preserving and label-preserving.
1261:
763:
694:
26:
1143:
Proceedings of the
International Congress of Mathematicians—Rio de Janeiro 2018. Vol. IV. Invited lectures
54:
619:
The exception to
Whitney's theorem: these two graphs are not isomorphic but have isomorphic line graphs.
1084:
799:
511:
inherent to the structures of graphs themselves from properties associated with graph representations:
1314:
1266:
834:
804:
676:
267:
1181:
ICASSP 2021 - 2021 IEEE International
Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP)
647:
117:
770:
690:
516:
206:
907:
1309:
861:
744:
729:
484:
956:
1284:
1150:
1120:
1058:
Cho, Adrian (November 10, 2015), "Mathematician claims breakthrough in complexity theory",
756:
733:
524:
434:
249:
158:
129:
8:
713:
920:
1319:
1212:
1184:
1124:
1002:
809:
794:
698:
501:
253:
238:
755:. In January 2017, Babai briefly retracted the quasi-polynomiality claim and stated a
1288:
1270:
1216:
1202:
1198:
1060:
1044:
936:
740:
262:
257:
1128:
975:
Whitney, Hassler (January 1932). "Congruent Graphs and the
Connectivity of Graphs".
747:. He published preliminary versions of these results in the proceedings of the 2016
461:
The second definition is assumed in certain situations when graphs are endowed with
1256:
1194:
1108:
1065:
1040:
992:
984:
928:
843:
508:
229:. In the case when the isomorphism is a mapping of a graph onto itself, i.e., when
1164:
1141:
Babai, László (2018), "Group, graphs, algorithms: the graph isomorphism problem",
1105:
STOC'16—Proceedings of the 48th Annual ACM SIGACT Symposium on Theory of
Computing
1280:
1146:
1116:
1089:
887:
709:
686:
628:
717:
643:
520:
405:
399:
124:
997:
1303:
1292:
1252:
615:
512:
492:
488:
418:
402:
274:
1236:
3rd IAPR-TC15 Workshop on Graph-based
Representations in Pattern Recognition
1112:
1069:
697:(verification of equivalence of various representations of the design of an
273:
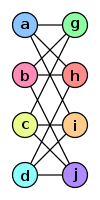
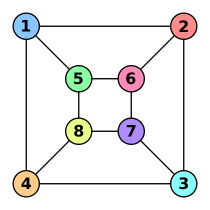
The two graphs shown below are isomorphic, despite their different looking
20:
1265:. Series of Books in the Mathematical Sciences (1st ed.). New York:
721:
496:
196:
189:
932:
1006:
927:. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Vol. 3984. pp. 422–431.
664:
632:
631:, states that two connected graphs are isomorphic if and only if their
1262:
Computers and Intractability: A Guide to the Theory of NP-Completeness
304:
297:
38:
1103:
Babai, László (2016), "Graph isomorphism in quasipolynomial time ",
988:
847:
1189:
1029:
Schöning, Uwe (1988). "Graph isomorphism is in the low hierarchy".
921:"Efficient Method to Perform Isomorphism Testing of Labeled Graphs"
732:. It is however known that if the problem is NP-complete then the
773:, both for the general problem and for special classes of graphs.
704:
The graph isomorphism problem is one of few standard problems in
663:
as their line graph. The Whitney graph theorem can be extended to
532:
504:, labels, vertex/edge colors, the root of the rooted tree, etc.
712:, but not known to belong to either of its well-known (and, if
724:. It is one of only two, out of 12 total, problems listed in
1230:
Cordella, L. P.; Foggia, P.; Sansone, C.; Vento, M. (2001).
507:
The notion of "graph isomorphism" allows us to distinguish
1229:
237:
are one and the same graph, the isomorphism is called an
1145:, World Sci. Publ., Hackensack, NJ, pp. 3319–3336,
260:. A set of graphs isomorphic to each other is called an
925:
Computational Science and Its Applications - ICCSA 2006
919:
Hsieh, Shu-Ming; Hsu, Chiun-Chieh; Hsu, Li-Fu (2006).
591:{\displaystyle \sum _{v\in V(G)}v\cdot {\text{deg }}v}
199:
exists between two graphs, then the graphs are called
728:
whose complexity remains unresolved, the other being
548:
437:
398:
In the above definition, graphs are understood to be
209:
161:
132:
57:
670:
590:
450:
221:
176:
147:
93:
1232:"An Improved Algorithm for Matching Large Graphs"
1301:
412:
523:, etc. For example, if a graph has exactly one
16:Bijection between the vertex set of two graphs
685:Its practical applications include primarily
421:, two definitions of isomorphism are in use.
1251:
957:"Measuring the Similarity of Labeled Graphs"
725:
693:(identification of chemical compounds), and
601:may be different for two isomorphic graphs.
465:commonly taken from the integer range 1,...,
1178:
1085:"Landmark Algorithm Breaks 30-Year Impasse"
918:
883:"Landmark Algorithm Breaks 30-Year Impasse"
955:Pierre-Antoine Champin, Christine Solnon,
1188:
1082:
996:
880:
656:, which are not isomorphic but both have
635:are isomorphic, with a single exception:
1028:
753:International Congress of Mathematicians
614:
252:on graphs and as such it partitions the
192:being a structure-preserving bijection.
1032:Journal of Computer and System Sciences
974:
778:Weisfeiler Leman graph isomorphism test
1302:
1083:Klarreich, Erica (December 14, 2015),
1162:
1140:
1102:
827:
94:{\displaystyle f\colon V(G)\to V(H)}
1107:, ACM, New York, pp. 684–697,
1057:
13:
604:
14:
1331:
1163:Babai, László (January 9, 2017),
962:Lecture Notes in Computer Science
625:Whitney graph isomorphism theorem
611:Whitney graph isomorphism theorem
1199:10.1109/ICASSP39728.2021.9413523
749:Symposium on Theory of Computing
671:Recognition of graph isomorphism
303:
296:
1223:
1172:
1156:
1134:
1096:
1076:
977:American Journal of Mathematics
881:Klarreich, Erica (2015-12-14).
830:"The Graph Isomorphism Problem"
706:computational complexity theory
1051:
1022:
1013:
968:
949:
912:
901:
874:
821:
766:, is known to be NP-complete.
569:
563:
171:
165:
142:
136:
88:
82:
76:
73:
67:
1:
1245:
866:: CS1 maint: date and year (
736:collapses to a finite level.
477:
413:Isomorphism of labeled graphs
393:
1045:10.1016/0022-0000(88)90010-4
828:Grohe, Martin (2020-11-01).
764:subgraph isomorphism problem
695:electronic design automation
309:
7:
788:
646:on three vertices, and the
104:such that any two vertices
41:between the vertex sets of
10:
1336:
800:Graph automorphism problem
726:Garey & Johnson (1979)
674:
608:
517:data structures for graphs
1267:W. H. Freeman and Company
835:Communications of the ACM
805:Graph isomorphism problem
781:run time is exponential.
677:Graph isomorphism problem
268:graph isomorphism problem
222:{\displaystyle G\simeq H}
1166:Graph isomorphism update
815:
771:computational complexity
762:Its generalization, the
648:complete bipartite graph
248:Graph isomorphism is an
1113:10.1145/2897518.2897542
1070:10.1126/science.aad7416
1183:. pp. 8533–8537.
691:mathematical chemistry
620:
592:
539:, then the expression
452:
223:
178:
149:
95:
965:, vol. 2689, pp 80–95
745:quasi-polynomial time
730:integer factorization
716:, disjoint) subsets:
682:isomorphism problem.
618:
593:
453:
451:{\displaystyle K_{2}}
224:
179:
150:
96:
757:sub-exponential time
734:polynomial hierarchy
546:
435:
250:equivalence relation
207:
177:{\displaystyle f(v)}
159:
148:{\displaystyle f(u)}
130:
55:
933:10.1007/11751649_46
258:equivalence classes
256:of all graphs into
998:10338.dmlcz/101067
810:Graph canonization
795:Graph homomorphism
751:, and of the 2018
739:In November 2015,
699:electronic circuit
621:
588:
573:
448:
219:
174:
145:
91:
1257:Johnson, David S.
1253:Garey, Michael R.
1208:978-1-7281-7605-5
942:978-3-540-34079-9
583:
549:
431:For example, the
391:
390:
263:isomorphism class
1327:
1315:Graph algorithms
1296:
1240:
1239:
1227:
1221:
1220:
1192:
1176:
1170:
1169:
1160:
1154:
1153:
1138:
1132:
1131:
1100:
1094:
1093:
1080:
1074:
1072:
1055:
1049:
1048:
1026:
1020:
1017:
1011:
1010:
1000:
972:
966:
953:
947:
946:
916:
910:
905:
899:
898:
896:
895:
878:
872:
871:
865:
857:
855:
854:
825:
714:P ≠ NP
597:
595:
594:
589:
584:
581:
572:
509:graph properties
457:
455:
454:
449:
447:
446:
307:
300:
291:between G and H
280:
279:
228:
226:
225:
220:
184:are adjacent in
183:
181:
180:
175:
154:
152:
151:
146:
100:
98:
97:
92:
1335:
1334:
1330:
1329:
1328:
1326:
1325:
1324:
1300:
1299:
1277:
1248:
1243:
1228:
1224:
1209:
1177:
1173:
1161:
1157:
1139:
1135:
1101:
1097:
1090:Quanta Magazine
1081:
1077:
1056:
1052:
1027:
1023:
1018:
1014:
989:10.2307/2371086
973:
969:
954:
950:
943:
917:
913:
906:
902:
893:
891:
888:Quanta Magazine
879:
875:
859:
858:
852:
850:
848:10.1145/3372123
842:(11): 128–134.
826:
822:
818:
791:
687:cheminformatics
679:
673:
662:
655:
641:
629:Hassler Whitney
613:
607:
605:Whitney theorem
580:
553:
547:
544:
543:
521:graph labelings
480:
442:
438:
436:
433:
432:
415:
396:
290:
208:
205:
204:
203:and denoted as
160:
157:
156:
131:
128:
127:
56:
53:
52:
25:isomorphism of
17:
12:
11:
5:
1333:
1323:
1322:
1317:
1312:
1298:
1297:
1275:
1247:
1244:
1242:
1241:
1222:
1207:
1171:
1155:
1133:
1095:
1075:
1050:
1039:(3): 312–323.
1021:
1012:
983:(1): 150–168.
967:
948:
941:
911:
900:
873:
819:
817:
814:
813:
812:
807:
802:
797:
790:
787:
675:Main article:
672:
669:
660:
653:
644:complete graph
639:
609:Main article:
606:
603:
599:
598:
587:
579:
576:
571:
568:
565:
562:
559:
556:
552:
513:graph drawings
493:colored graphs
489:labeled graphs
479:
476:
445:
441:
419:labeled graphs
414:
411:
395:
392:
389:
388:
308:
301:
293:
292:
289:An isomorphism
287:
284:
218:
215:
212:
173:
170:
167:
164:
144:
141:
138:
135:
125:if and only if
102:
101:
90:
87:
84:
81:
78:
75:
72:
69:
66:
63:
60:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1332:
1321:
1318:
1316:
1313:
1311:
1308:
1307:
1305:
1294:
1290:
1286:
1282:
1278:
1276:9780716710455
1272:
1268:
1264:
1263:
1258:
1254:
1250:
1249:
1237:
1233:
1226:
1218:
1214:
1210:
1204:
1200:
1196:
1191:
1186:
1182:
1175:
1168:
1167:
1159:
1152:
1148:
1144:
1137:
1130:
1126:
1122:
1118:
1114:
1110:
1106:
1099:
1092:
1091:
1086:
1079:
1071:
1067:
1063:
1062:
1054:
1046:
1042:
1038:
1034:
1033:
1025:
1016:
1008:
1004:
999:
994:
990:
986:
982:
978:
971:
964:
963:
958:
952:
944:
938:
934:
930:
926:
922:
915:
909:
904:
890:
889:
884:
877:
869:
863:
849:
845:
841:
837:
836:
831:
824:
820:
811:
808:
806:
803:
801:
798:
796:
793:
792:
786:
782:
779:
774:
772:
767:
765:
760:
758:
754:
750:
746:
742:
737:
735:
731:
727:
723:
719:
715:
711:
708:belonging to
707:
702:
700:
696:
692:
688:
683:
678:
668:
666:
659:
652:
649:
645:
638:
634:
630:
626:
617:
612:
602:
585:
577:
574:
566:
560:
557:
554:
550:
542:
541:
540:
538:
534:
530:
526:
522:
518:
514:
510:
505:
503:
498:
494:
490:
486:
475:
472:
468:
464:
463:unique labels
459:
443:
439:
429:
425:
422:
420:
410:
407:
404:
401:
387:
385:
381:
377:
375:
371:
367:
365:
361:
357:
355:
351:
347:
345:
341:
337:
335:
331:
327:
325:
321:
316:
312:
306:
302:
299:
295:
294:
288:
285:
282:
281:
278:
276:
271:
269:
265:
264:
259:
255:
251:
246:
244:
240:
236:
232:
216:
213:
210:
202:
198:
193:
191:
187:
168:
162:
139:
133:
126:
123:
119:
115:
111:
107:
85:
79:
70:
64:
61:
58:
51:
50:
49:
48:
44:
40:
36:
32:
29:
28:
22:
1310:Graph theory
1260:
1235:
1225:
1180:
1174:
1165:
1158:
1142:
1136:
1104:
1098:
1088:
1078:
1059:
1053:
1036:
1030:
1024:
1015:
980:
976:
970:
960:
951:
924:
914:
903:
892:. Retrieved
886:
876:
862:cite journal
851:. Retrieved
839:
833:
823:
783:
775:
768:
761:
741:László Babai
738:
703:
684:
680:
657:
650:
636:
624:
622:
600:
536:
528:
506:
497:rooted trees
481:
470:
466:
462:
460:
430:
426:
423:
416:
406:non-weighted
397:
383:
379:
378:
373:
369:
368:
363:
359:
358:
353:
349:
348:
343:
339:
338:
333:
329:
328:
323:
319:
318:
314:
310:
272:
261:
247:
242:
239:automorphism
234:
230:
200:
194:
185:
121:
113:
109:
105:
103:
46:
42:
34:
30:
24:
21:graph theory
18:
722:NP-complete
665:hypergraphs
633:line graphs
627:, shown by
529:represented
403:non-labeled
197:isomorphism
190:isomorphism
1304:Categories
1246:References
1238:: 149–159.
1190:2201.07083
894:2023-03-06
853:2023-03-06
478:Motivation
400:undirected
394:Variations
201:isomorphic
1320:Morphisms
1293:247570676
1217:235780517
582:deg
578:⋅
558:∈
551:∑
535:1, 2,...
214:≃
77:→
62::
39:bijection
1259:(1979).
1129:17118954
789:See also
533:integers
531:by) the
485:digraphs
469:, where
286:Graph H
283:Graph G
275:drawings
118:adjacent
1285:0519066
1151:3966534
1121:3536606
1061:Science
1007:2371086
1291:
1283:
1273:
1215:
1205:
1149:
1127:
1119:
1005:
939:
642:, the
386:) = 7
376:) = 4
366:) = 2
356:) = 5
346:) = 3
336:) = 8
326:) = 6
317:) = 1
195:If an
27:graphs
1213:S2CID
1185:arXiv
1125:S2CID
1003:JSTOR
959:in:
908:p.424
816:Notes
525:cycle
254:class
37:is a
23:, an
1289:OCLC
1271:ISBN
1203:ISBN
937:ISBN
868:link
776:The
720:and
623:The
502:arcs
417:For
233:and
155:and
116:are
108:and
45:and
33:and
1195:doi
1109:doi
1066:doi
1041:doi
993:hdl
985:doi
929:doi
844:doi
701:).
654:1,3
241:of
120:in
112:of
19:In
1306::
1287:.
1281:MR
1279:.
1269:.
1255:;
1234:.
1211:.
1201:.
1193:.
1147:MR
1123:,
1117:MR
1115:,
1087:,
1064:,
1037:37
1035:.
1001:.
991:.
981:54
979:.
935:.
923:.
885:.
864:}}
860:{{
840:63
838:.
832:.
710:NP
689:,
667:.
519:,
515:,
495:,
491:,
487:,
277:.
270:.
245:.
1295:.
1219:.
1197::
1187::
1111::
1073:.
1068::
1047:.
1043::
1009:.
995::
987::
945:.
931::
897:.
870:)
856:.
846::
718:P
661:3
658:K
651:K
640:3
637:K
586:v
575:v
570:)
567:G
564:(
561:V
555:v
537:N
471:n
467:n
444:2
440:K
384:j
382:(
380:f
374:i
372:(
370:f
364:h
362:(
360:f
354:g
352:(
350:f
344:d
342:(
340:f
334:c
332:(
330:f
324:b
322:(
320:f
315:a
313:(
311:f
243:G
235:H
231:G
217:H
211:G
186:H
172:)
169:v
166:(
163:f
143:)
140:u
137:(
134:f
122:G
114:G
110:v
106:u
89:)
86:H
83:(
80:V
74:)
71:G
68:(
65:V
59:f
47:H
43:G
35:H
31:G
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.