880:: whenever a single input bit is complemented, each of the output bits changes with a 50% probability. The reason for this property is that selected subsets of the keyspace may have low variability. For the output to be uniformly distributed, a low amount of variability, even one bit, should translate into a high amount of variability (i.e. distribution over the tablespace) in the output. Each bit should change with a probability of 50% because, if some bits are reluctant to change, then the keys become clustered around those values. If the bits want to change too readily, then the mapping is approaching a fixed XOR function of a single bit. Standard tests for this property have been described in the literature. The relevance of the criterion to a multiplicative hash function is assessed here.
2528:
initialized at the start of the program. The random numbers could be any length, but 64 bits was natural due to the 64 squares on the board. A position was transcribed by cycling through the pieces in a position, indexing the corresponding random numbers (vacant spaces were not included in the calculation) and XORing them together (the starting value could be 0 (the identity value for XOR) or a random seed). The resulting value was reduced by modulo, folding, or some other operation to produce a hash table index. The original
Zobrist hash was stored in the table as the representation of the position.
2600:
addition is also a plausible alternative. The final operation would be a modulo, mask, or other function to reduce the word value to an index the size of the table. The weakness of this procedure is that information may cluster in the upper or lower bits of the bytes; this clustering will remain in the hashed result and cause more collisions than a proper randomizing hash. ASCII byte codes, for example, have an upper bit of 0, and printable strings do not use the first 32 byte codes, so the information (95 bytecodes) is clustered in the remaining bits in an unobvious manner.
154:
908:) by a constant can be inverted to become a multiplication by the word-size multiplicative-inverse of that constant. This can be done by the programmer, or by the compiler. Division can also be reduced directly into a series of shift-subtracts and shift-adds, though minimizing the number of such operations required is a daunting problem; the number of assembly instructions resulting may be more than a dozen and swamp the pipeline. If the architecture has
493:
57:
889:
indexable by the key-value would be very large and very sparse, but very fast. A hash function takes a finite amount of time to map a potentially large keyspace to a feasible amount of storage space searchable in a bounded amount of time regardless of the number of keys. In most applications, the hash function should be computable with minimum latency and secondarily in a minimum number of instructions.
1556:) and can be 10 times slower than multiplication. A second drawback is that it will not break up clustered keys. For example, the keys 123000, 456000, 789000, etc. modulo 1000 all map to the same address. This technique works well in practice because many key sets are sufficiently random already, and the probability that a key set will be cyclical by a large prime number is small.
2743:
example, a 128-bit word will hash only a 26-character alphabetic string (ignoring case) with a radix of 29; a printable ASCII string is limited to 9 characters using radix 97 and a 64-bit word. However, alphabetic keys are usually of modest length, because keys must be stored in the hash table. Numeric character strings are usually not a problem; 64 bits can count up to
339:
the item is added to the table there. If the hash code indexes a full slot, then some kind of collision resolution is required: the new item may be omitted (not added to the table), or replace the old item, or be added to the table in some other location by a specified procedure. That procedure depends on the structure of the hash table. In
1513:, so the hash code is taken as the middle 4 digits of the 17-digit number (ignoring the high digit) 8750. The mid-squares method produces a reasonable hash code if there is not a lot of leading or trailing zeros in the key. This is a variant of multiplicative hashing, but not as good because an arbitrary key is not a good multiplier.
4031:
implementation of the service and present solutions for avoiding single points of failure and guaranteeing a service with reasonable and stable delay. Guardtime AS has been operating a KSI Infrastructure for 5 years. We summarize how the KSI Infrastructure is built, and the lessons learned during the operational period of the service.
2641:
operations (e.g. multiplication by constant and bit-shifting). The final word, which may have unoccupied byte positions, is filled with zeros or a specified randomizing value before being folded into the hash. The accumulated hash code is reduced by a final modulo or other operation to yield an index into the table.
2591:
other pathologies in the key set. Such strategies may be effective as a custom hash function if the structure of the keys is such that either the middle, ends, or other fields are zero or some other invariant constant that does not differentiate the keys; then the invariant parts of the keys can be ignored.
273:
In a hash table, a hash function takes a key as an input, which is associated with a datum or record and used to identify it to the data storage and retrieval application. The keys may be fixed-length, like an integer, or variable-length, like a name. In some cases, the key is the datum itself. The
3006:
Worst case results for a hash function can be assessed two ways: theoretical and practical. The theoretical worst case is the probability that all keys map to a single slot. The practical worst case is the expected longest probe sequence (hash function + collision resolution method). This analysis
2599:
The paradigmatic example of folding by characters is to add up the integer values of all the characters in the string. A better idea is to multiply the hash total by a constant, typically a sizable prime number, before adding in the next character, ignoring overflow. Using exclusive-or instead of
2547:
A hash function can be designed to exploit existing entropy in the keys. If the keys have leading or trailing zeros, or particular fields that are unused, always zero or some other constant, or generally vary little, then masking out only the volatile bits and hashing on those will provide a better
1328:
In some applications, the input data may contain features that are irrelevant for comparison purposes. For example, when looking up a personal name, it may be desirable to ignore the distinction between upper and lower case letters. For such data, one must use a hash function that is compatible with
2531:
Later, the method was extended to hashing integers by representing each byte in each of 4 possible positions in the word by a unique 32-bit random number. Thus, a table of 2×4 random numbers is constructed. A 32-bit hashed integer is transcribed by successively indexing the table with the value of
2307:
Multiplicative hashing is susceptible to a "common mistake" that leads to poor diffusion—higher-value input bits do not affect lower-value output bits. A transmutation on the input which shifts the span of retained top bits down and XORs or ADDs them to the key before the multiplication step
888:
In data storage and retrieval applications, the use of a hash function is a trade-off between search time and data storage space. If search time were unbounded, then a very compact unordered linear list would be the best medium; if storage space were unbounded, then a randomly accessible structure
681:
function of the number of keys to be mapped versus the number of table slots that they are mapped into. Finding a perfect hash function over more than a very small set of keys is usually computationally infeasible; the resulting function is likely to be more computationally complex than a standard
616:
Hash tables often contain only a small subset of the valid inputs. For instance, a club membership list may contain only a hundred or so member names, out of the very large set of all possible names. In these cases, the uniformity criterion should hold for almost all typical subsets of entries that
2742:
is usually a prime number large enough to hold the number of different characters in the character set of potential keys. Radix conversion hashing of strings minimizes the number of collisions. Available data sizes may restrict the maximum length of string that can be hashed with this method. For
2590:
characters of a string along with the length, or form a word-size hash from the middle 4 characters of a string. This saves iterating over the (potentially long) string, but hash functions that do not hash on all characters of a string can readily become linear due to redundancies, clustering, or
338:
to store and retrieve data items or data records. The hash function translates the key associated with each datum or record into a hash code, which is used to index the hash table. When an item is to be added to the table, the hash code may index an empty slot (also called a bucket), in which case
1443:
If the keys are uniformly or sufficiently uniformly distributed over the key space, so that the key values are essentially random, then they may be considered to be already "hashed". In this case, any number of any bits in the key may be extracted and collated as an index into the hash table. For
1103:
It is often desirable that the output of a hash function have fixed size (but see below). If, for example, the output is constrained to 32-bit integer values, then the hash values can be used to index into an array. Such hashing is commonly used to accelerate data searches. Producing fixed-length
214:
Hash functions and their associated hash tables are used in data storage and retrieval applications to access data in a small and nearly constant time per retrieval. They require an amount of storage space only fractionally greater than the total space required for the data or records themselves.
2527:
Zobrist hashing was originally introduced as a means of compactly representing chess positions in computer game-playing programs. A unique random number was assigned to represent each type of piece (six each for black and white) on each space of the board. Thus a table of 64×12 such numbers is
315:
key sets, and poorly designed hash functions can result in access times approaching linear in the number of items in the table. Hash functions can be designed to give the best worst-case performance, good performance under high table loading factors, and in special cases, perfect (collisionless)
2640:
Modern microprocessors will allow for much faster processing if 8-bit character strings are not hashed by processing one character at a time, but by interpreting the string as an array of 32-bit or 64-bit integers and hashing/accumulating these "wide word" integer values by means of arithmetic
1468:
is the table size, and using a parity-preserving bitwise operation such as ADD or XOR to combine the sections, followed by a mask or shifts to trim off any excess bits at the high or low end. For example, for a table size of 15 bits and a 64-bit key value of 0x0123456789ABCDEF, there are five
972:
If keys are being hashed repeatedly, and the hash function is costly, then computing time can be saved by precomputing the hash codes and storing them with the keys. Matching hash codes almost certainly means that the keys are identical. This technique is used for the transposition table in
4030:
Keyless
Signatures Infrastructure (KSI) is a globally distributed system for providing time-stamping and server-supported digital signature services. Global per-second hash trees are created and their root hash values published. We discuss some service quality issues that arise in practical
1014:
is the number of distinct hash values desired—independently of the two keys. Universal hashing ensures (in a probabilistic sense) that the hash function application will behave as well as if it were using a random function, for any distribution of the input data. It will, however, have more
1104:
output from variable-length input can be accomplished by breaking the input data into chunks of specific size. Hash functions used for data searches use some arithmetic expression that iteratively processes chunks of the input (such as the characters in a string) to produce the hash value.
215:
Hashing is a computationally- and storage-space-efficient form of data access that avoids the non-constant access time of ordered and unordered lists and structured trees, and the often-exponential storage requirements of direct access of state spaces of large or variable-length keys.
892:
Computational complexity varies with the number of instructions required and latency of individual instructions, with the simplest being the bitwise methods (folding), followed by the multiplicative methods, and the most complex (slowest) are the division-based methods.
1112:
In many applications, the range of hash values may be different for each run of the program or may change along the same run (for instance, when a hash table needs to be expanded). In those situations, one needs a hash function which takes two parameters—the input data
3765:
343:, each slot is the head of a linked list or chain, and items that collide at the slot are added to the chain. Chains may be kept in random order and searched linearly, or in serial order, or as a self-ordering list by frequency to speed up access. In
316:
mapping of keys into hash codes. Implementation is based on parity-preserving bit operations (XOR and ADD), multiply, or divide. A necessary adjunct to the hash function is a collision-resolution method that employs an auxiliary data structure like
3157:
is a 7-bit character encoding, although it is often stored in 8-bit bytes with the highest-order bit always clear (zero). Therefore, for plain ASCII, the bytes have only 2 = 128 valid values, and the character translation table has only this many
2524:, is a method for constructing universal families of hash functions by combining table lookup with XOR operations. This algorithm has proven to be very fast and of high quality for hashing purposes (especially hashing of integer-number keys).
602:—pairs of inputs that are mapped to the same hash value—increases. If some hash values are more likely to occur than others, then a larger fraction of the lookup operations will have to search through a larger set of colliding table entries.
2532:
each byte of the plain text integer and XORing the loaded values together (again, the starting value can be the identity value or a random seed). The natural extension to 64-bit integers is by use of a table of 2×8 64-bit random numbers.
1095:) is still a valid hash function when used within a single run, but if the values are persisted (for example, written to disk), they can no longer be treated as valid hash values, since in the next run the random value might differ.
359:
until an open slot is located or the entire table is probed (overflow). Searching for the item follows the same procedure until the item is located, an open slot is found, or the entire table has been searched (item not in table).
3072:
offers a natural analogy with its non-technical meaning (to chop up or make a mess out of something), given how hash functions scramble their input data to derive their output. In his research for the precise origin of the term,
4059:
pHash is an open source software library released under the GPLv3 license that implements several perceptual hashing algorithms, and provides a C-like API to use those functions in your own programs. pHash itself is written in
1395:, one can use the binary encoding of each character, interpreted as an integer, to index a table that gives the alternative form of that character ("A" for "a", "8" for "8", etc.). If each character is stored in 8 bits (as in
843:
2342:
of consecutive keys with respect to any block of bits in the key. Consecutive keys within the high bits or low bits of the key (or some other field) are relatively common. The multipliers for various word lengths are:
896:
Because collisions should be infrequent, and cause a marginal delay but are otherwise harmless, it is usually preferable to choose a faster hash function over one that needs more computation but saves a few collisions.
1079:
or the time of day. It also excludes functions that depend on the memory address of the object being hashed, because the address may change during execution (as may happen on systems that use certain methods of
1333:
criterion being used: that is, any two inputs that are considered equivalent must yield the same hash value. This can be accomplished by normalizing the input before hashing it, as by upper-casing all letters.
1203:
When the hash function is used to store values in a hash table that outlives the run of the program, and the hash table needs to be expanded or shrunk, the hash table is referred to as a dynamic hash table.
1342:
There are several common algorithms for hashing integers. The method giving the best distribution is data-dependent. One of the simplest and most common methods in practice is the modulo division method.
372:
for large data sets stored in slow media. A cache is generally simpler than a hashed search table, since any collision can be resolved by discarding or writing back the older of the two colliding items.
2548:
and possibly faster hash function. Selected divisors or multipliers in the division and multiplicative schemes may make more uniform hash functions if the keys are cyclic or have other redundancies.
3085:
appears to have been the first to use the concept of a hash function in a memo dated
January 1953, the term itself did not appear in published literature until the late 1960s, in Herbert Hellerman's
253:. Although the concepts overlap to some extent, each one has its own uses and requirements and is designed and optimized differently. The hash function differs from these concepts mainly in terms of
671:
In special cases when the keys are known in advance and the key set is static, a hash function can be found that achieves absolute (or collisionless) uniformity. Such a hash function is said to be
1984:
218:
Use of hash functions relies on statistical properties of key and function interaction: worst-case behavior is intolerably bad but rare, and average-case behavior can be nearly optimal (minimal
1292:
to compute the hash function, and it becomes a function of the previous keys that have been inserted. Several algorithms that preserve the uniformity property but require time proportional to
3251:
594:
A good hash function should map the expected inputs as evenly as possible over its output range. That is, every hash value in the output range should be generated with roughly the same
2933:, which are designed to have significantly different hashes for even minor differences. Fuzzy hashing has been used to identify malware and has potential for other applications, like
2623:
back into the low byte of the cumulative quantity. The result is a word-size hash code to which a modulo or other reducing operation can be applied to produce the final hash index.
2576:, characteristic of the language. For such data, it is prudent to use a hash function that depends on all characters of the string—and depends on each character in a different way.
3021:
worries about adversarial attack on real time systems, Gonnet has shown that the probability of such a case is "ridiculously small". His representation was that the probability of
1552:. This gives good results over a large number of key sets. A significant drawback of division hashing is that division is microprogrammed on most modern architectures (including
1023:
A hash function that allows only certain table sizes or strings only up to a certain length, or cannot accept a seed (i.e. allow double hashing) is less useful than one that does.
3998:
Buldas, Ahto; Kroonmaa, Andres; Laanoja, Risto (2013). "Keyless
Signatures' Infrastructure: How to Build Global Distributed Hash-Trees". In Riis, Nielson H.; Gollmann, D. (eds.).
1091:
adds the feature that hash functions make use of a randomized seed that is generated once when the Python process starts in addition to the input to be hashed. The Python hash (
3488:
1435:
entries), etc. Invalid data values (such as the country code "xx" or the ZIP code 00000) may be left undefined in the table or mapped to some appropriate "null" value.
613:
in any sense. A good randomizing function is (barring computational efficiency concerns) generally a good choice as a hash function, but the converse need not be true.
698:. This test is a goodness-of-fit measure: it is the actual distribution of items in buckets versus the expected (or uniform) distribution of items. The formula is
1039:: Minor input changes result in a random-looking output alteration, known as the diffusion property. Thus, hash functions are valuable for key derivation functions.
177:
of arbitrary size to fixed-size values, though there are some hash functions that support variable-length output. The values returned by a hash function are called
4195:
1052:
Password storage: The password's hash value does not expose any password details, emphasizing the importance of securely storing hashed passwords on the server.
1075:
of the data to be hashed, in the mathematical sense of the term. This requirement excludes hash functions that depend on external variable parameters, such as
1045:(MACs): Through the integration of a confidential key with the input data, hash functions can generate MACs ensuring the genuineness of the data, such as in
1351:
If the data to be hashed is small enough, then one can use the data itself (reinterpreted as an integer) as the hashed value. The cost of computing this
2890:(in all fairness, the worst case here is gravely pathological: both the text string and substring are composed of a repeated single character, such as
1477:
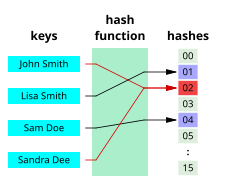
A mid-squares hash code is produced by squaring the input and extracting an appropriate number of middle digits or bits. For example, if the input is
924:
to not be a power of 2 and still not have to perform any remainder or division operation, as these computations are sometimes costly. For example, let
2619:. This hash function offsets the bytes 4 bits before adding them together. When the quantity wraps, the high 4 bits are shifted out and if non-zero,
682:
hash function and provides only a marginal advantage over a function with good statistical properties that yields a minimum number of collisions. See
2736:. It can be used directly as the hash code, or a hash function applied to it to map the potentially large value to the hash table size. The value of
1282:
are examples of dynamic hash functions that execute in constant time but relax the property of uniformity to achieve the minimal movement property.
703:
3811:
873:
A ratio within one confidence interval (such as 0.95 to 1.05) is indicative that the hash function evaluated has an expected uniform distribution.
2985:
of a small change in input value creating a drastic change in output value. Perceptual hash functions are widely used in finding cases of online
876:
Hash functions can have some technical properties that make it more likely that they will have a uniform distribution when applied. One is the
2158:
will get large, or both, for the scheme to be computationally feasible. Therefore, it is more suited to hardware or microcode implementation.
2653:
character string representing a decimal number is converted to a numeric quantity for computing, a variable-length string can be converted as
303:
A good hash function satisfies two basic properties: it should be very fast to compute, and it should minimize duplication of output values (
4188:
2616:
1207:
A hash function that will relocate the minimum number of records when the table is resized is desirable. What is needed is a hash function
3858:
1564:
Algebraic coding is a variant of the division method of hashing which uses division by a polynomial modulo 2 instead of an integer to map
2626:
Today, especially with the advent of 64-bit word sizes, much more efficient variable-length string hashing by word chunks is available.
2498:. The last two values given above are rounded (up and down, respectively) by more than 1/2 of a least-significant bit to achieve this.
3506:
Wagner, Urs; Lugrin, Thomas (2023), Mulder, Valentin; Mermoud, Alain; Lenders, Vincent; Tellenbach, Bernhard (eds.), "Hash
Functions",
4181:
2233:; it should be large, and its binary representation a random mix of 1s and 0s. An important practical special case occurs when
652:, then very few buckets should have more than one or two records. A small number of collisions is virtually inevitable, even if
2304:
this translates into a single integer multiplication and right-shift, making it one of the fastest hash functions to compute.
4128:
4015:
3975:
3891:
3704:
3525:
3375:
1081:
557:
121:
2286:
is done by default in low-level programming languages and integer division by a power of 2 is simply a right-shift, so, in
1164:. When this approach is used, the hash function must be chosen so that the result has fairly uniform distribution between
1026:
A hash function is applicable in a variety of situations. Particularly within cryptography, notable applications include:
529:
93:
2815:. The straightforward solution, which is to extract such a substring at every character position in the text and compute
1919:
38:
2993:
because of the ability to have a correlation between hashes so similar data can be found (for instance with a differing
3576:
3429:
2564:, or mail messages—their distribution is usually very uneven, with complicated dependencies. For example, text in any
1181:
that may occur in the application. Depending on the function, the remainder may be uniform only for certain values of
3842:
3734:
3687:
576:
536:
140:
100:
1033:: Identical hash values for different files imply equality, providing a reliable means to detect file modifications.
598:. The reason for this last requirement is that the cost of hashing-based methods goes up sharply as the number of
3170:
258:
4163:
3445:
Castro, Julio Cesar
Hernandez; et al. (3 February 2005). "The strict avalanche criterion randomness test".
1364:
The meaning of "small enough" depends on the size of the type that is used as the hashed value. For example, in
1001:
among a family of such functions, in such a way that the probability of a collision of any two distinct keys is
1076:
543:
514:
510:
107:
78:
74:
17:
2762:
1088:
935:
3782:
3144:
This is useful in cases where keys are devised by a malicious agent, for example in pursuit of a DOS attack.
2906:, designed to avoid collisions in 8-bit character strings, but other suitable hash functions are also used.
2338:(approximately 1.618). A property of this multiplier is that it uniformly distributes over the table space,
4373:
4343:
4328:
2926:
2615:
in the 1970s, was originally designed for hashing identifiers into compiler symbol tables as given in the
525:
89:
2978:
2930:
1365:
1042:
262:
694:
When testing a hash function, the uniformity of the distribution of hash values can be evaluated by the
44:
This article is about a computer programming construct. For other meanings of "hash" and "hashing", see
4447:
4398:
4272:
4262:
4242:
2837:, one can use the technique of rolling hash to compute all those hashes with an effort proportional to
2768:
877:
312:
3916:
3625:
1469:
sections consisting of 0x4DEF, 0x1357, 0x159E, 0x091A, and 0x0. Adding yields 0x7FFE, a 15-bit value.
1015:
collisions than perfect hashing and may require more operations than a special-purpose hash function.
4277:
3540:
2635:
3952:
1071:—for a given input value, it must always generate the same hash value. In other words, it must be a
4167:
4157:
3717:
3119:
2539:, meaning that every 3-tuple of keys is equally likely to be mapped to any 3-tuple of hash values.
2287:
476:
308:
293:
274:
output is a hash code used to index a hash table holding the data or records, or pointers to them.
4442:
4416:
4378:
3870:
3104:
2970:
2962:
2958:
1068:
1036:
503:
453:
411:
234:
67:
4222:
4099:
3712:
3639:
3297:. 2015 International Conference on Advances in Computer Engineering and Applications (ICACEA).
3109:
3099:
2986:
2521:
1317:
1072:
441:
392:
311:
for their effectiveness, reducing access time to nearly constant. High table loading factors,
242:
170:
3867:"Forensic Malware Analysis: The Value of Fuzzy Hashing Algorithms in Identifying Similarities"
3392:
2494:
The multiplier should be odd, so the least significant bit of the output is invertible modulo
4282:
4252:
3007:
considers uniform hashing, that is, any key will map to any particular slot with probability
2569:
1358:
673:
388:
292:
Scramble the bits of the key so that the resulting values are uniformly distributed over the
246:
45:
4393:
4368:
4313:
3363:
2934:
1330:
992:
550:
457:
114:
4153:
3651:, Tech. Rep. 88, Madison, Wisconsin: Computer Sciences Department, University of Wisconsin
973:
game-playing programs, which stores a 64-bit hashed representation of the board position.
8:
4403:
4388:
4333:
3124:
2608:
2573:
2311:
unsigned hash(unsigned K) { K ^= K >> (w-m); return (a*K) >> (w-m); }
2143:
modulo 2. If follows that the corresponding hash function will map keys with fewer than
3367:
347:, the table is probed starting from the occupied slot in a specified manner, usually by
4421:
4323:
4318:
4232:
3897:
3740:
3466:
3418:
2954:
2948:
2507:
1421:
1283:
677:. There is no algorithmic way of constructing such a function—searching for one is a
4383:
4227:
4124:
4021:
4011:
3971:
3887:
3838:
3827:
Proceedings of the Eighth ACM Conference on Data and
Application Security and Privacy
3730:
3683:
3572:
3521:
3425:
3371:
2994:
2990:
2903:
2604:
1353:
1055:
1030:
982:
909:
683:
472:
445:
437:
399:
369:
352:
238:
3901:
3643:
3470:
1521:
A standard technique is to use a modulo function on the key, by selecting a divisor
1128:
A common solution is to compute a fixed hash function with a very large range (say,
900:
Division-based implementations can be of particular concern because the division is
4363:
4348:
4170:) Latest Trends on Computers, Vol.2, pp. 483–489, CSCC Conference, Corfu, 2010
4003:
4002:. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Vol. 8208. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer.
3963:
3924:
3879:
3830:
3793:
3744:
3722:
3605:
3511:
3458:
3298:
2982:
2565:
2557:
2535:
This kind of function has some nice theoretical properties, one of which is called
2319:
2226:
1388:
1157:
1143:
905:
901:
695:
665:
461:
449:
174:
3323:
4338:
4173:
4123:(2. ed., 6. printing, newly updated and rev. ed.). Boston : Addison-Wesley.
4007:
3462:
3078:
2511:
912:
465:
286:
3516:
3302:
1448:
least significant bits and use the result as an index into a hash table of size
1387:
Other types of data can also use this hashing scheme. For example, when mapping
617:
may be found in the table, not just for the global set of all possible entries.
4204:
4080:
3929:
3883:
3866:
3819:
3726:
3679:
3671:
3359:
3292:
2974:
1396:
1279:
1275:
1198:
384:
356:
348:
304:
254:
219:
158:
3917:"Identifying almost identical files using context triggered piecewise hashing"
3610:
3593:
945:
that is uniform on the interval . A hash function uniform on the interval is
838:{\displaystyle {\frac {\sum _{j=0}^{m-1}(b_{j})(b_{j}+1)/2}{(n/2m)(n+2m-1)}},}
153:
4436:
4308:
4147:
4025:
2922:
2916:
1087:
The determinism is in the context of the reuse of the function. For example,
3834:
3797:
2166:
Unique permutation hashing has a guaranteed best worst-case insertion time.
4303:
4267:
4237:
4116:
4072:
3351:
3074:
3018:
2756:
2620:
2335:
1818:
1811:
1192:
1161:
956:
407:
377:
282:
1544:. The table size is usually a power of 2. This gives a distribution from
4257:
1400:
1392:
595:
381:
335:
317:
299:
Map the key values into ones less than or equal to the size of the table.
285:-length or less) values, by folding them by words or other units using a
230:
4247:
3967:
3667:
3663:
2966:
2857:
2339:
2322:
hashing is a form of multiplicative hashing in which the multiplier is
1460:
A folding hash code is produced by dividing the input into sections of
1188:
632:
table slots, then the probability of a bucket receiving many more than
517: in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
329:
199:
1376:
objects can simply use the value directly, whereas the 64-bit integer
265:
are used in cybersecurity to secure sensitive data such as passwords.
4208:
4164:
Hash
Function Construction for Textual and Geometrical Data Retrieval
3416:
Menezes, Alfred J.; van
Oorschot, Paul C.; Vanstone, Scott A (1996).
3114:
2784:
2612:
2252:
1424:
like "us" or "za" to country names (26 = 676 table entries), 5-digit
678:
420:
226:
157:
A hash function that maps names to integers from 0 to 15. There is a
4096:
Expected Length of the
Longest Probe Sequence in Hash Code Searching
3818:
Pagani, Fabio; Dell'Amico, Matteo; Balzarotti, Davide (2018-03-13).
492:
197:. The values are usually used to index a fixed-size table called a
56:
4045:"pHash.org: Home of pHash, the open source perceptual hash library"
3454:
1425:
31:
2929:, but not exactly the same, as other data. This is in contrast to
2902:="AAA"). The hash function used for the algorithm is usually the
4358:
1784:
or fewer non-zero coefficients, then keys which share fewer than
1404:
1286:
uses a dynamic hash function that requires space proportional to
1092:
418:. The table is often an array with two or more indices (called a
37:"Hash code" redirects here. For the programming competition, see
460:
in a set of points, similar shapes in a list of shapes, similar
3409:
2650:
2293:
unsigned hash(unsigned K) { return (a*K) >> (w-m); }
406:. In these applications, the set of all inputs is some sort of
250:
4121:
The Art of Computer Programming, Vol. 3, Sorting and Searching
4077:
The Art of Computer Programming, Vol. 3, Sorting and Searching
3865:
Sarantinos, Nikolaos; Benzaïd, Chafika; Arabiat, Omar (2016).
3817:
3356:
The Art of Computer Programming, Vol. 3, Sorting and Searching
1316:
A hash function with minimal movement is especially useful in
277:
A hash function may be considered to perform three functions:
3774:
3154:
2693:
1368:, the hash code is a 32-bit integer. Thus the 32-bit integer
433:
432:, and similar names), and the hash function returns an index
30:"hashlink" redirects here. For the Haxe virtual machine, see
2821:
separately, requires a number of operations proportional to
1199:
Variable range with minimal movement (dynamic hash function)
915:, then the multiply-by-inverse is likely a better approach.
320:, or systematic probing of the table to find an empty slot.
4287:
3991:
3489:"Fibonacci Hashing: The Optimization that the World Forgot"
3444:
3415:
1046:
955:. We can replace the division by a (possibly faster) right
4036:
3261:
Knuth conveniently leaves the proof of this to the reader.
1058:: Message hashes are signed rather than the whole message.
3960:
2013 Fourth Cybercrime and Trustworthy Computing Workshop
3082:
2561:
1553:
1357:
hash function is effectively zero. This hash function is
1084:), although sometimes rehashing of the item is possible.
203:. Use of a hash function to index a hash table is called
4044:
3864:
3089:, even though it was already widespread jargon by then.
1684:. The remainder using polynomial arithmetic modulo 2 is
281:
Convert variable-length keys into fixed-length (usually
225:
Hash functions are related to (and often confused with)
2925:, also known as similarity hashing, is a technique for
642:
records should be vanishingly small. In particular, if
3645:
A New Hashing Method with Application for Game Playing
2977:
of the multimedia are similar. This is in contrast to
2308:
corrects for this. The resulting function looks like:
1403:), the table has only 2 = 256 entries; in the case of
3997:
3951:
Oliver, Jonathan; Cheng, Chun; Chen, Yanggui (2013).
3705:"Performance in Practice of String Hashing Functions"
3592:
Dolev, Shlomi; Lahiani, Limor; Haviv, Yinnon (2013).
3562:
3560:
3510:, Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, pp. 21–24,
3508:
Trends in Data Protection and Encryption Technologies
3173:
2584:
Simplistic hash functions may add the first and last
1922:
706:
3908:
1525:
which is a prime number close to the table size, so
3482:
3480:
3294:
Hash_RC6 — Variable length Hash algorithm using RC6
3291:Aggarwal, Kirti; Verma, Harsh K. (March 19, 2015).
2556:When the data values are long (or variable-length)
1979:{\displaystyle P(x)=\prod _{j\in S}(x-\alpha ^{j})}
1444:example, a simple hash function might mask off the
410:, and the hashing function can be interpreted as a
81:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
4203:
3944:
3557:
3417:
3245:
1978:
1361:, as it maps each input to a distinct hash value.
837:
376:Hash functions are an essential ingredient of the
3591:
2793:-character string by advancing a window of width
2174:Standard multiplicative hashing uses the formula
4434:
3702:
3477:
3014:, a characteristic of universal hash functions.
2730:as the characters of the input string of length
2225:is an appropriately chosen value that should be
2117:is any nonzero polynomial modulo 2 with at most
2001:are computed in this field. Then the degree of
1234:is the number of allowed hash values) such that
307:). Hash functions rely on generating favorable
3950:
2853:is the number of occurrences of the substring.
2551:
3709:Database Systems for Advanced Applications '97
3662:
4189:
4111:
4109:
3290:
2282:. This is special because arithmetic modulo
2161:
1337:
904:on nearly all chip architectures. Division (
605:This criterion only requires the value to be
3829:. New York, NY, USA: ACM. pp. 354–365.
3541:"3. Data model — Python 3.6.1 documentation"
3505:
3346:
3344:
3342:
3340:
3240:
3180:
2856:The most familiar algorithm of this type is
2516:Tabulation hashing, more generally known as
2037:is a root, it follows that the coefficients
444:, and many other disciplines, to solve many
334:Hash functions are used in conjunction with
3676:Compilers: Principles, Techniques and Tools
3393:"Understanding CPU caching and performance"
3246:{\displaystyle S=\{1,2,3,4,5,6,8,10,12,9\}}
2644:
2542:
161:between keys "John Smith" and "Sandra Dee".
27:Mapping arbitrary data to fixed-size values
4196:
4182:
4106:
3780:
3703:Ramakrishna, M. V.; Zobel, Justin (1997).
1879:be the smallest set of integers such that
1407:characters, the table would have 17 × 2 =
689:
3928:
3923:. 3, Supplement (September 2006): 91–97.
3716:
3609:
3567:Sedgewick, Robert (2002). "14. Hashing".
3566:
3515:
3337:
2169:
1346:
577:Learn how and when to remove this message
141:Learn how and when to remove this message
3914:
3486:
2937:and detecting multiple versions of code.
2636:Universal hashing § Hashing strings
2568:has highly non-uniform distributions of
1438:
152:
3638:
3447:Mathematics and Computers in Simulation
2860:with best and average case performance
471:Hash tables are also used to implement
398:A special case of hashing is known as
14:
4435:
4093:
3390:
2747:, or 19 decimal digits with radix 10.
2629:
1420:The same technique can be used to map
368:Hash functions are also used to build
4177:
4115:
4098:(Technical report). Ontario, Canada:
4071:
4042:
3350:
2831:. However, with the proper choice of
2290:, for example, this function becomes
2255:. In this case, this formula becomes
1323:
4043:Klinger, Evan; Starkweather, David.
3626:"CS 3110 Lecture 21: Hash functions"
2799:characters along the string, where
2594:
2314:
1788:bits are guaranteed to not collide.
620:In other words, if a typical set of
515:adding citations to reliable sources
486:
436:. This principle is widely used in
79:adding citations to reliable sources
50:
3953:"TLSH -- A Locality Sensitive Hash"
3628:. Section "Multiplicative hashing".
2961:that produces a snippet, hash, or
2692:. This is simply a polynomial in a
1806:(the last of which is a divisor of
1559:
1516:
363:
39:Hash Code (programming competition)
24:
3783:"NIST Special Publication 800-168"
3087:Digital Computer System Principles
2941:
2771:, one can compute a hash function
2579:
2501:
2147:bits in common to unique indices.
1644:can be regarded as the polynomial
25:
4459:
4141:
3872:2016 IEEE Trustcom/BigDataSE/ISPA
3763:
3711:. DASFAA 1997. pp. 215–224.
3167:For example, for n=15, k=4, t=6,
3033:keys mapping to a single slot is
2969:. A perceptual hash is a type of
2649:Analogous to the way an ASCII or
2603:The classic approach, dubbed the
2213:, which produces a hash value in
2150:The usual outcome is that either
1494:, then squaring the key produces
1107:
866:is the number of items in bucket
3487:Sharupke, Malte (16 June 2018).
3420:Handbook of Applied Cryptography
2947:This section is an excerpt from
2915:This section is an excerpt from
1872:. The derivation is as follows:
1098:
1062:
1018:
491:
387:that is used to test whether an
259:non-cryptographic hash functions
55:
4148:Calculate hash of a given value
4087:
4065:
4000:Secure IT Systems. NordSec 2013
3757:
3696:
3656:
3632:
3618:
3585:
3533:
3358:. Reading, MA., United States:
3264:
3255:
3161:
3147:
2750:
2330:is the machine word length and
1077:pseudo-random number generators
976:
502:needs additional citations for
66:needs additional citations for
3781:Breitinger, Frank (May 2014).
3571:(3 ed.). Addison Wesley.
3499:
3438:
3384:
3316:
3284:
3138:
2927:detecting data that is similar
2767:In some applications, such as
1990:and where the coefficients of
1973:
1954:
1932:
1926:
1810:) and is constructed from the
1472:
855:is the number of buckets, and
826:
805:
802:
785:
772:
753:
750:
737:
323:
13:
1:
4154:The Goulburn Hashing Function
3904:. 10.1109/TrustCom.2016.0274.
3820:"Beyond Precision and Recall"
3324:"NIST Glossary — hash digest"
3277:
2909:
2763:Linear congruential generator
2077:, so they are all 0 or 1. If
995:that selects a hash function
936:pseudorandom number generator
883:
589:
482:
414:of that space into a grid of
4008:10.1007/978-3-642-41488-6_21
3598:Theoretical Computer Science
3594:"Unique permutation hashing"
3463:10.1016/j.matcom.2004.09.001
2931:cryptographic hash functions
2552:Hashing variable-length data
1228:is the key being hashed and
1043:Message Authentication Codes
918:We can allow the table size
263:cryptographic hash functions
7:
3517:10.1007/978-3-031-33386-6_5
3303:10.1109/ICACEA.2015.7164747
3092:
3001:
2121:nonzero coefficients, then
930:be significantly less than
268:
10:
4464:
3930:10.1016/j.diin.2006.06.015
3884:10.1109/TrustCom.2016.0274
3727:10.1142/9789812819536_0023
3391:Stokes, Jon (2002-07-08).
3063:
2946:
2914:
2760:
2754:
2702:that takes the components
2633:
2505:
2162:Unique permutation hashing
1455:
1428:like 13083 to city names (
1380:and 64-bit floating-point
1372:and 32-bit floating-point
1338:Hashing integer data types
1261:with probability close to
980:
878:strict avalanche criterion
327:
287:parity-preserving operator
209:scatter-storage addressing
43:
36:
29:
4412:
4296:
4215:
3611:10.1016/j.tcs.2012.12.047
2560:—such as personal names,
1821:gives an example: taking
1142:, and use the division's
1067:A hash procedure must be
309:probability distributions
3915:Kornblum, Jesse (2006).
3767:A Handbook of Algorithms
3131:
3120:Low-discrepancy sequence
2973:, which is analogous if
2959:fingerprinting algorithm
2805:is a fixed integer, and
2645:Radix conversion hashing
2543:Customized hash function
1572:bits. In this approach,
1487:and the hash table size
1422:two-letter country codes
1298:to compute the value of
1136:), divide the result by
1125:of allowed hash values.
173:that can be used to map
4417:List of data structures
3962:. IEEE. pp. 7–13.
3835:10.1145/3176258.3176306
3798:10.6028/NIST.SP.800-168
3105:Nearest neighbor search
2971:locality-sensitive hash
1780:is constructed to have
1318:distributed hash tables
851:is the number of keys,
690:Testing and measurement
684:universal hash function
454:three-dimensional space
243:randomization functions
4100:University of Waterloo
3878:. pp. 1782–1787.
3247:
3110:Distributed hash table
3100:List of hash functions
2987:copyright infringement
2981:, which relies on the
2170:Multiplicative hashing
1980:
1579:, and we postulate an
1347:Identity hash function
1156:, this can be done by
839:
736:
442:computational geometry
257:. Hash tables may use
247:error-correcting codes
162:
3921:Digital Investigation
3270:Unisys large systems.
3248:
2979:cryptographic hashing
2607:based on the work of
2132:is not a multiple of
1981:
1583:th-degree polynomial
1439:Trivial hash function
1152:is itself a power of
840:
710:
626:records is hashed to
607:uniformly distributed
156:
46:Hash (disambiguation)
4314:Breadth-first search
3171:
3050:is the load factor,
2965:of various forms of
2935:data loss prevention
2896:="AAAAAAAAAAA", and
2537:3-tuple independence
2247:are powers of 2 and
1988:α ∈ GF(2)
1920:
1393:upper and lower case
1313:have been invented.
993:randomized algorithm
704:
658:is much larger than
511:improve this article
380:, a space-efficient
345:open address hashing
75:improve this article
4404:Topological sorting
4334:Dynamic programming
4094:Gonnet, G. (1978).
3368:1973acp..book.....K
3125:Transposition table
2630:Word length folding
2609:Peter J. Weinberger
2154:will get large, or
1175:, for any value of
4422:List of algorithms
4329:Divide and conquer
4324:Depth-first search
4319:Brute-force search
4233:Binary search tree
3968:10.1109/ctc.2013.9
3640:Zobrist, Albert L.
3569:Algorithms in Java
3243:
3077:notes that, while
2955:Perceptual hashing
2949:Perceptual hashing
2562:web page addresses
2508:Tabulation hashing
1976:
1953:
1606:+ ⋯ + ζ
1324:Data normalization
1284:Extendible hashing
1247: + 1) =
1082:garbage collection
1031:Integrity checking
835:
473:associative arrays
456:, such as finding
446:proximity problems
163:
4448:Search algorithms
4430:
4429:
4228:Associative array
4130:978-0-201-89685-5
4017:978-3-642-41487-9
3977:978-1-4799-3076-0
3893:978-1-5090-3205-1
3790:NIST Publications
3527:978-3-031-33386-6
3377:978-0-201-03803-3
2991:digital forensics
2904:Rabin fingerprint
2700: > 1
2595:Character folding
2558:character strings
2315:Fibonacci hashing
1938:
1794:is a function of
1389:character strings
1119:, and the number
989:universal hashing
983:Universal hashing
910:hardware multiply
830:
587:
586:
579:
561:
438:computer graphics
400:geometric hashing
391:is a member of a
353:quadratic probing
239:lossy compression
151:
150:
143:
125:
16:(Redirected from
4455:
4399:String-searching
4198:
4191:
4184:
4175:
4174:
4160:) by Mayur Patel
4135:
4134:
4117:Knuth, Donald E.
4113:
4104:
4103:
4091:
4085:
4084:
4073:Knuth, Donald E.
4069:
4063:
4062:
4056:
4055:
4040:
4034:
4033:
3995:
3989:
3988:
3986:
3984:
3957:
3948:
3942:
3941:
3939:
3937:
3932:
3912:
3906:
3905:
3877:
3862:
3856:
3855:
3853:
3851:
3824:
3815:
3809:
3808:
3806:
3804:
3787:
3778:
3772:
3771:
3761:
3755:
3754:
3752:
3751:
3720:
3700:
3694:
3693:
3660:
3654:
3652:
3650:
3636:
3630:
3629:
3622:
3616:
3615:
3613:
3589:
3583:
3582:
3564:
3555:
3554:
3552:
3551:
3537:
3531:
3530:
3519:
3503:
3497:
3496:
3484:
3475:
3474:
3442:
3436:
3435:
3423:
3413:
3407:
3406:
3404:
3403:
3388:
3382:
3381:
3352:Knuth, Donald E.
3348:
3335:
3334:
3332:
3330:
3320:
3314:
3313:
3311:
3309:
3288:
3271:
3268:
3262:
3259:
3253:
3252:
3250:
3249:
3244:
3165:
3159:
3151:
3145:
3142:
3059:
3049:
3043:
3032:
3026:
3013:
2983:avalanche effect
2957:is the use of a
2901:
2895:
2889:
2874:
2852:
2846:
2836:
2830:
2820:
2814:
2804:
2798:
2792:
2782:
2776:
2769:substring search
2746:
2741:
2735:
2729:
2701:
2691:
2589:
2566:natural language
2497:
2487:
2486:
2483:
2480:
2477:
2474:
2471:
2465:
2461:
2460:
2457:
2454:
2438:
2437:
2434:
2431:
2428:
2422:
2418:
2417:
2414:
2398:
2397:
2394:
2391:
2385:
2381:
2380:
2364:
2363:
2357:
2333:
2329:
2325:
2303:
2299:
2285:
2281:
2280:
2272:
2250:
2246:
2239:
2232:
2227:relatively prime
2224:
2220:
2212:
2211:
2191:
2157:
2153:
2146:
2142:
2131:
2120:
2116:
2076:
2068:
2067:
2053:
2042:
2036:
2032:
2021:
2017:
2015:
2000:
1989:
1985:
1983:
1982:
1977:
1972:
1971:
1952:
1912:
1889:
1878:
1871:
1836:
1816:
1809:
1805:
1801:
1797:
1793:
1787:
1783:
1779:
1768:
1731:
1683:
1643:
1610:
1582:
1578:
1571:
1567:
1560:Algebraic coding
1551:
1543:
1524:
1517:Division hashing
1512:
1511:
1508:
1505:
1502:
1499:
1493:
1492:
1486:
1485:
1482:
1467:
1463:
1451:
1447:
1434:
1433:
1416:
1415:
1412:
1383:
1379:
1375:
1371:
1312:
1297:
1291:
1271:
1260:
1233:
1227:
1221:
1186:
1180:
1174:
1167:
1155:
1151:
1141:
1135:
1131:
1124:
1118:
1013:
1007:
1000:
968:
954:
944:
933:
929:
923:
913:functional units
869:
865:
854:
850:
844:
842:
841:
836:
831:
829:
795:
783:
779:
765:
764:
749:
748:
735:
724:
708:
696:chi-squared test
666:birthday problem
663:
657:
651:
641:
631:
625:
582:
575:
571:
568:
562:
560:
519:
495:
487:
364:Specialized uses
289:like ADD or XOR,
146:
139:
135:
132:
126:
124:
83:
59:
51:
21:
4463:
4462:
4458:
4457:
4456:
4454:
4453:
4452:
4433:
4432:
4431:
4426:
4408:
4339:Graph traversal
4292:
4216:Data structures
4211:
4205:Data structures
4202:
4144:
4139:
4138:
4131:
4114:
4107:
4092:
4088:
4079:. Reading, MA:
4070:
4066:
4053:
4051:
4041:
4037:
4018:
3996:
3992:
3982:
3980:
3978:
3955:
3949:
3945:
3935:
3933:
3913:
3909:
3894:
3875:
3863:
3859:
3849:
3847:
3845:
3822:
3816:
3812:
3802:
3800:
3785:
3779:
3775:
3762:
3758:
3749:
3747:
3737:
3701:
3697:
3690:
3682:. p. 435.
3678:. Reading, MA:
3661:
3657:
3648:
3637:
3633:
3624:
3623:
3619:
3590:
3586:
3579:
3565:
3558:
3549:
3547:
3545:docs.python.org
3539:
3538:
3534:
3528:
3504:
3500:
3485:
3478:
3443:
3439:
3432:
3414:
3410:
3401:
3399:
3389:
3385:
3378:
3349:
3338:
3328:
3326:
3322:
3321:
3317:
3307:
3305:
3289:
3285:
3280:
3275:
3274:
3269:
3265:
3260:
3256:
3172:
3169:
3168:
3166:
3162:
3152:
3148:
3143:
3139:
3134:
3129:
3095:
3079:Hans Peter Luhn
3066:
3051:
3045:
3034:
3028:
3022:
3008:
3004:
2999:
2998:
2952:
2944:
2942:Perceptual hash
2939:
2938:
2920:
2912:
2897:
2891:
2876:
2875:and worst case
2861:
2848:
2838:
2832:
2822:
2816:
2806:
2800:
2794:
2788:
2778:
2772:
2765:
2759:
2753:
2744:
2737:
2731:
2727:
2717:
2710:
2703:
2696:
2690:
2680:
2673:
2663:
2654:
2647:
2638:
2632:
2597:
2585:
2582:
2580:Middle and ends
2574:character pairs
2554:
2545:
2518:Zobrist hashing
2514:
2512:Zobrist hashing
2506:Main articles:
2504:
2502:Zobrist hashing
2495:
2490:
2484:
2481:
2478:
2475:
2472:
2469:
2467:
2464:
2458:
2455:
2452:
2450:
2449:
2441:
2435:
2432:
2429:
2426:
2424:
2421:
2415:
2412:
2410:
2409:
2401:
2395:
2392:
2389:
2387:
2384:
2378:
2376:
2375:
2367:
2361:
2359:
2356:
2352:
2331:
2327:
2323:
2317:
2312:
2301:
2297:
2294:
2283:
2278:
2270:
2264:
2256:
2251:is the machine
2248:
2241:
2234:
2230:
2222:
2214:
2209:
2189:
2183:
2175:
2172:
2164:
2155:
2151:
2144:
2133:
2122:
2118:
2115:
2105:
2095:
2078:
2075:
2066:
2061:
2060:
2059:
2055:
2044:
2038:
2034:
2023:
2019:
2011:
2002:
1991:
1987:
1967:
1963:
1942:
1921:
1918:
1917:
1891:
1880:
1876:
1838:
1822:
1814:
1807:
1803:
1799:
1795:
1791:
1785:
1781:
1770:
1767:
1763:
1757:
1750:
1733:
1730:
1720:
1710:
1685:
1682:
1672:
1662:
1645:
1642:
1638:
1632:
1625:
1612:
1609:
1602:
1584:
1580:
1573:
1569:
1565:
1562:
1545:
1526:
1522:
1519:
1509:
1506:
1503:
1500:
1497:
1495:
1490:
1488:
1483:
1480:
1478:
1475:
1465:
1461:
1458:
1449:
1445:
1441:
1431:
1429:
1413:
1410:
1408:
1381:
1377:
1373:
1369:
1349:
1340:
1326:
1299:
1293:
1287:
1270: + 1)
1262:
1235:
1229:
1223:
1208:
1201:
1182:
1176:
1169:
1165:
1153:
1147:
1137:
1134:2 − 1
1133:
1129:
1120:
1114:
1110:
1101:
1065:
1021:
1009:
1002:
996:
985:
979:
964:(key) >>
960:
946:
939:
931:
925:
919:
902:microprogrammed
886:
867:
864:
856:
852:
848:
791:
784:
775:
760:
756:
744:
740:
725:
714:
709:
707:
705:
702:
701:
692:
659:
653:
643:
633:
627:
621:
592:
583:
572:
566:
563:
526:"Hash function"
520:
518:
508:
496:
485:
366:
341:chained hashing
332:
326:
271:
147:
136:
130:
127:
90:"Hash function"
84:
82:
72:
60:
49:
42:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
4461:
4451:
4450:
4445:
4443:Hash functions
4428:
4427:
4425:
4424:
4419:
4413:
4410:
4409:
4407:
4406:
4401:
4396:
4391:
4386:
4381:
4376:
4371:
4366:
4361:
4356:
4351:
4346:
4341:
4336:
4331:
4326:
4321:
4316:
4311:
4306:
4300:
4298:
4294:
4293:
4291:
4290:
4285:
4280:
4275:
4270:
4265:
4260:
4255:
4250:
4245:
4240:
4235:
4230:
4225:
4219:
4217:
4213:
4212:
4201:
4200:
4193:
4186:
4178:
4172:
4171:
4161:
4151:
4143:
4142:External links
4140:
4137:
4136:
4129:
4105:
4102:. CS-RR-78-46.
4086:
4083:. p. 540.
4081:Addison-Wesley
4064:
4035:
4016:
3990:
3976:
3943:
3907:
3892:
3857:
3843:
3810:
3773:
3756:
3735:
3718:10.1.1.18.7520
3695:
3688:
3680:Addison-Wesley
3655:
3642:(April 1970),
3631:
3617:
3584:
3578:978-0201361209
3577:
3556:
3532:
3526:
3498:
3493:Probably Dance
3476:
3437:
3431:978-0849385230
3430:
3408:
3383:
3376:
3360:Addison-Wesley
3336:
3315:
3282:
3281:
3279:
3276:
3273:
3272:
3263:
3254:
3242:
3239:
3236:
3233:
3230:
3227:
3224:
3221:
3218:
3215:
3212:
3209:
3206:
3203:
3200:
3197:
3194:
3191:
3188:
3185:
3182:
3179:
3176:
3160:
3146:
3136:
3135:
3133:
3130:
3128:
3127:
3122:
3117:
3112:
3107:
3102:
3096:
3094:
3091:
3065:
3062:
3003:
3000:
2989:as well as in
2953:
2945:
2943:
2940:
2921:
2913:
2911:
2908:
2755:Main article:
2752:
2749:
2722:
2715:
2708:
2688:
2678:
2674:a + ⋯ +
2668:
2658:
2646:
2643:
2631:
2628:
2596:
2593:
2581:
2578:
2553:
2550:
2544:
2541:
2522:Albert Zobrist
2503:
2500:
2492:
2491:
2488:
2462:
2442:
2439:
2419:
2402:
2399:
2382:
2368:
2365:
2354:
2316:
2313:
2310:
2296:and for fixed
2292:
2260:
2179:
2171:
2168:
2163:
2160:
2113:
2103:
2090:
2073:
2062:
1975:
1970:
1966:
1962:
1959:
1956:
1951:
1948:
1945:
1941:
1937:
1934:
1931:
1928:
1925:
1765:
1761:
1755:
1745:
1728:
1718:
1705:
1680:
1670:
1657:
1640:
1636:
1630:
1620:
1607:
1597:
1561:
1558:
1518:
1515:
1474:
1471:
1457:
1454:
1440:
1437:
1397:extended ASCII
1348:
1345:
1339:
1336:
1325:
1322:
1280:spiral hashing
1276:Linear hashing
1200:
1197:
1173: − 1
1109:
1108:Variable range
1106:
1100:
1097:
1064:
1061:
1060:
1059:
1053:
1050:
1040:
1037:Key derivation
1034:
1020:
1017:
981:Main article:
978:
975:
885:
882:
860:
834:
828:
825:
822:
819:
816:
813:
810:
807:
804:
801:
798:
794:
790:
787:
782:
778:
774:
771:
768:
763:
759:
755:
752:
747:
743:
739:
734:
731:
728:
723:
720:
717:
713:
691:
688:
591:
588:
585:
584:
499:
497:
490:
484:
481:
466:image database
385:data structure
365:
362:
357:double hashing
349:linear probing
328:Main article:
325:
322:
301:
300:
297:
290:
270:
267:
255:data integrity
149:
148:
63:
61:
54:
26:
18:Hash algorithm
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
4460:
4449:
4446:
4444:
4441:
4440:
4438:
4423:
4420:
4418:
4415:
4414:
4411:
4405:
4402:
4400:
4397:
4395:
4392:
4390:
4387:
4385:
4382:
4380:
4377:
4375:
4372:
4370:
4367:
4365:
4362:
4360:
4357:
4355:
4354:Hash function
4352:
4350:
4347:
4345:
4342:
4340:
4337:
4335:
4332:
4330:
4327:
4325:
4322:
4320:
4317:
4315:
4312:
4310:
4309:Binary search
4307:
4305:
4302:
4301:
4299:
4295:
4289:
4286:
4284:
4281:
4279:
4276:
4274:
4271:
4269:
4266:
4264:
4261:
4259:
4256:
4254:
4251:
4249:
4246:
4244:
4241:
4239:
4236:
4234:
4231:
4229:
4226:
4224:
4221:
4220:
4218:
4214:
4210:
4206:
4199:
4194:
4192:
4187:
4185:
4180:
4179:
4176:
4169:
4165:
4162:
4159:
4155:
4152:
4149:
4146:
4145:
4132:
4126:
4122:
4118:
4112:
4110:
4101:
4097:
4090:
4082:
4078:
4074:
4068:
4061:
4050:
4046:
4039:
4032:
4027:
4023:
4019:
4013:
4009:
4005:
4001:
3994:
3979:
3973:
3969:
3965:
3961:
3954:
3947:
3931:
3926:
3922:
3918:
3911:
3903:
3899:
3895:
3889:
3885:
3881:
3874:
3873:
3868:
3861:
3846:
3844:9781450356329
3840:
3836:
3832:
3828:
3821:
3814:
3799:
3795:
3791:
3784:
3777:
3770:. N.B. Singh.
3769:
3768:
3764:Singh, N. B.
3760:
3746:
3742:
3738:
3736:981-02-3107-5
3732:
3728:
3724:
3719:
3714:
3710:
3706:
3699:
3691:
3689:0-201-10088-6
3685:
3681:
3677:
3673:
3672:Ullman, J. D.
3669:
3665:
3659:
3647:
3646:
3641:
3635:
3627:
3621:
3612:
3607:
3603:
3599:
3595:
3588:
3580:
3574:
3570:
3563:
3561:
3546:
3542:
3536:
3529:
3523:
3518:
3513:
3509:
3502:
3494:
3490:
3483:
3481:
3472:
3468:
3464:
3460:
3456:
3452:
3448:
3441:
3433:
3427:
3424:. CRC Press.
3422:
3421:
3412:
3398:
3394:
3387:
3379:
3373:
3369:
3365:
3361:
3357:
3353:
3347:
3345:
3343:
3341:
3325:
3319:
3304:
3300:
3296:
3295:
3287:
3283:
3267:
3258:
3237:
3234:
3231:
3228:
3225:
3222:
3219:
3216:
3213:
3210:
3207:
3204:
3201:
3198:
3195:
3192:
3189:
3186:
3183:
3177:
3174:
3164:
3156:
3150:
3141:
3137:
3126:
3123:
3121:
3118:
3116:
3113:
3111:
3108:
3106:
3103:
3101:
3098:
3097:
3090:
3088:
3084:
3080:
3076:
3071:
3061:
3058:
3054:
3048:
3041:
3038:
3031:
3025:
3020:
3015:
3012:
2996:
2992:
2988:
2984:
2980:
2976:
2972:
2968:
2964:
2960:
2956:
2950:
2936:
2932:
2928:
2924:
2923:Fuzzy hashing
2918:
2917:Fuzzy hashing
2907:
2905:
2900:
2894:
2887:
2883:
2879:
2872:
2868:
2864:
2859:
2854:
2851:
2845:
2842: +
2841:
2835:
2829:
2825:
2819:
2813:
2809:
2803:
2797:
2791:
2786:
2781:
2775:
2770:
2764:
2758:
2748:
2740:
2734:
2725:
2721:
2714:
2707:
2699:
2695:
2687:
2683:
2677:
2671:
2667:
2661:
2657:
2652:
2642:
2637:
2627:
2624:
2622:
2618:
2617:"Dragon Book"
2614:
2610:
2606:
2601:
2592:
2588:
2577:
2575:
2571:
2567:
2563:
2559:
2549:
2540:
2538:
2533:
2529:
2525:
2523:
2519:
2513:
2509:
2499:
2447:
2443:
2407:
2403:
2373:
2369:
2350:
2346:
2345:
2344:
2341:
2337:
2334:(phi) is the
2321:
2309:
2305:
2291:
2289:
2276:
2268:
2263:
2259:
2254:
2244:
2237:
2228:
2221:. The value
2218:
2215:{0, …,
2207:
2203:
2199:
2195:
2187:
2182:
2178:
2167:
2159:
2148:
2140:
2136:
2129:
2125:
2112:
2108:
2102:
2098:
2093:
2089:
2085:
2081:
2072:
2065:
2058:
2051:
2047:
2041:
2030:
2026:
2022:is a root of
2014:
2009:
2005:
1998:
1994:
1968:
1964:
1960:
1957:
1949:
1946:
1943:
1939:
1935:
1929:
1923:
1914:
1911:
1907:
1903:
1899:
1895:
1888:
1884:
1881:{1,2,…,
1873:
1869:
1865:
1861:
1857:
1853:
1849:
1845:
1841:
1835:) = (15,10,7)
1834:
1830:
1826:
1820:
1813:
1789:
1777:
1773:
1760:
1754:
1748:
1744:
1740:
1736:
1727:
1723:
1717:
1713:
1708:
1704:
1700:
1696:
1692:
1688:
1679:
1675:
1669:
1665:
1660:
1656:
1652:
1648:
1635:
1629:
1623:
1619:
1615:
1605:
1600:
1595:
1591:
1587:
1576:
1557:
1555:
1549:
1541:
1537:
1533:
1529:
1514:
1470:
1453:
1436:
1427:
1423:
1418:
1406:
1402:
1398:
1394:
1390:
1385:
1367:
1362:
1360:
1356:
1355:
1344:
1335:
1332:
1321:
1319:
1314:
1310:
1306:
1302:
1296:
1290:
1285:
1281:
1277:
1273:
1269:
1265:
1258:
1254:
1250:
1246:
1242:
1238:
1232:
1226:
1219:
1215:
1211:
1205:
1196:
1194:
1193:prime numbers
1190:
1185:
1179:
1172:
1163:
1159:
1150:
1145:
1140:
1126:
1123:
1117:
1105:
1099:Defined range
1096:
1094:
1090:
1085:
1083:
1078:
1074:
1070:
1069:deterministic
1063:Deterministic
1057:
1054:
1051:
1048:
1044:
1041:
1038:
1035:
1032:
1029:
1028:
1027:
1024:
1019:Applicability
1016:
1012:
1006:
999:
994:
990:
984:
974:
970:
967:
963:
958:
952:
949:
942:
937:
934:. Consider a
928:
922:
916:
914:
911:
907:
903:
898:
894:
890:
881:
879:
874:
871:
863:
859:
845:
832:
823:
820:
817:
814:
811:
808:
799:
796:
792:
788:
780:
776:
769:
766:
761:
757:
745:
741:
732:
729:
726:
721:
718:
715:
711:
699:
697:
687:
685:
680:
676:
675:
669:
667:
662:
656:
650:
646:
640:
636:
630:
624:
618:
614:
612:
608:
603:
601:
597:
581:
578:
570:
559:
556:
552:
549:
545:
542:
538:
535:
531:
528: –
527:
523:
522:Find sources:
516:
512:
506:
505:
500:This section
498:
494:
489:
488:
480:
478:
474:
469:
468:, and so on.
467:
463:
459:
458:closest pairs
455:
451:
447:
443:
439:
435:
431:
427:
423:
422:
417:
413:
409:
405:
401:
396:
394:
390:
386:
383:
382:probabilistic
379:
374:
371:
361:
358:
354:
350:
346:
342:
337:
331:
321:
319:
314:
310:
306:
298:
295:
291:
288:
284:
280:
279:
278:
275:
266:
264:
260:
256:
252:
248:
244:
240:
236:
232:
228:
223:
221:
216:
212:
210:
206:
202:
201:
196:
192:
188:
184:
180:
176:
172:
168:
167:hash function
160:
155:
145:
142:
134:
123:
120:
116:
113:
109:
106:
102:
99:
95:
92: –
91:
87:
86:Find sources:
80:
76:
70:
69:
64:This article
62:
58:
53:
52:
47:
40:
33:
19:
4379:Root-finding
4353:
4304:Backtracking
4268:Segment tree
4238:Fenwick tree
4150:by Timo Denk
4120:
4095:
4089:
4076:
4067:
4058:
4052:. Retrieved
4048:
4038:
4029:
3999:
3993:
3983:December 12,
3981:. Retrieved
3959:
3946:
3934:. Retrieved
3920:
3910:
3871:
3860:
3850:December 12,
3848:. Retrieved
3826:
3813:
3801:. Retrieved
3789:
3776:
3766:
3759:
3748:. Retrieved
3708:
3698:
3675:
3658:
3644:
3634:
3620:
3601:
3597:
3587:
3568:
3548:. Retrieved
3544:
3535:
3507:
3501:
3492:
3450:
3446:
3440:
3419:
3411:
3400:. Retrieved
3397:Ars Technica
3396:
3386:
3355:
3327:. Retrieved
3318:
3306:. Retrieved
3293:
3286:
3266:
3257:
3163:
3149:
3140:
3086:
3075:Donald Knuth
3069:
3067:
3056:
3052:
3046:
3039:
3036:
3029:
3023:
3016:
3010:
3005:
2898:
2892:
2885:
2881:
2877:
2870:
2866:
2862:
2855:
2849:
2843:
2839:
2833:
2827:
2823:
2817:
2811:
2807:
2801:
2795:
2789:
2779:
2773:
2766:
2757:Rolling hash
2751:Rolling hash
2738:
2732:
2723:
2719:
2712:
2705:
2697:
2685:
2681:
2675:
2669:
2665:
2659:
2655:
2648:
2639:
2625:
2602:
2598:
2586:
2583:
2555:
2546:
2536:
2534:
2530:
2526:
2517:
2515:
2493:
2445:
2405:
2371:
2348:
2336:golden ratio
2318:
2306:
2295:
2274:
2266:
2261:
2257:
2242:
2235:
2216:
2205:
2201:
2197:
2193:
2185:
2180:
2176:
2173:
2165:
2149:
2138:
2134:
2127:
2123:
2110:
2106:
2100:
2099:+ ⋯ +
2096:
2091:
2087:
2083:
2079:
2070:
2063:
2056:
2049:
2045:
2039:
2028:
2024:
2012:
2007:
2003:
1996:
1992:
1915:
1909:
1905:
1901:
1897:
1893:
1886:
1882:
1874:
1867:
1863:
1859:
1855:
1851:
1847:
1843:
1839:
1832:
1828:
1824:
1812:finite field
1790:
1775:
1771:
1758:
1752:
1746:
1742:
1738:
1734:
1725:
1721:
1715:
1711:
1706:
1702:
1698:
1694:
1690:
1686:
1677:
1673:
1667:
1666:+ ⋯ +
1663:
1658:
1654:
1650:
1646:
1633:
1627:
1621:
1617:
1613:
1603:
1598:
1593:
1589:
1585:
1574:
1563:
1547:
1539:
1535:
1531:
1527:
1520:
1476:
1464:bits, where
1459:
1442:
1419:
1386:
1363:
1352:
1350:
1341:
1327:
1315:
1308:
1304:
1300:
1294:
1288:
1274:
1267:
1263:
1256:
1252:
1248:
1244:
1240:
1236:
1230:
1224:
1217:
1213:
1209:
1206:
1202:
1183:
1177:
1170:
1162:bit shifting
1148:
1138:
1127:
1121:
1115:
1111:
1102:
1086:
1066:
1025:
1022:
1010:
1004:
997:
991:scheme is a
988:
986:
977:Universality
971:
965:
961:
950:
947:
940:
926:
920:
917:
899:
895:
891:
887:
875:
872:
861:
857:
846:
700:
693:
672:
670:
660:
654:
648:
644:
638:
634:
628:
622:
619:
615:
610:
606:
604:
599:
593:
573:
567:October 2017
564:
554:
547:
540:
533:
521:
509:Please help
504:verification
501:
477:dynamic sets
470:
429:
425:
419:
415:
408:metric space
403:
397:
378:Bloom filter
375:
367:
344:
340:
333:
318:linked lists
313:pathological
302:
283:machine-word
276:
272:
235:fingerprints
231:check digits
224:
217:
213:
208:
204:
198:
194:
193:, or simply
190:
187:hash digests
186:
182:
178:
166:
164:
137:
128:
118:
111:
104:
97:
85:
73:Please help
68:verification
65:
4258:Linked list
3803:January 11,
3308:January 24,
2963:fingerprint
2787:of a given
2783:-character
1808:2 − 1
1473:Mid-squares
1401:ISO Latin 1
1331:equivalence
1158:bit masking
596:probability
430:bucket grid
404:grid method
336:hash tables
324:Hash tables
179:hash values
4437:Categories
4394:Sweep line
4369:Randomized
4297:Algorithms
4248:Hash table
4209:algorithms
4054:2018-07-05
3750:2021-12-06
3550:2017-03-24
3402:2022-02-06
3329:January 1,
3278:References
3035:α / (
2967:multimedia
2910:Fuzzy hash
2858:Rabin-Karp
2777:for every
2761:See also:
2634:See also:
2570:characters
2324:2 / ϕ
2277:mod 2) / 2
2219:− 1}
2010:) = |
1900:) ∈
1885:} ⊆
1714:+ ⋯
1550:− 1}
1534:) ≡
1056:Signatures
884:Efficiency
600:collisions
590:Uniformity
537:newspapers
483:Properties
426:grid index
330:Hash table
305:collisions
200:hash table
183:hash codes
101:newspapers
4389:Streaming
4374:Recursion
4049:pHash.org
4026:0302-9743
3713:CiteSeerX
3668:Sethi, R.
3604:: 59–65.
3115:Identicon
3068:The term
2995:watermark
2785:substring
2613:Bell Labs
2320:Fibonacci
2253:word size
2033:whenever
1965:α
1961:−
1947:∈
1940:∏
1611:. A key
1426:ZIP codes
1417:entries.
1329:the data
1144:remainder
957:bit shift
953:(key) / 2
938:function
821:−
730:−
712:∑
679:factorial
664:—see the
421:grid file
412:partition
227:checksums
220:collision
159:collision
131:July 2010
4119:(2000).
4075:(1975).
3936:June 30,
3902:32568938
3674:(1986).
3471:18086276
3455:Elsevier
3354:(1973).
3158:entries.
3093:See also
3044:, where
3002:Analysis
2975:features
2672:−2
2662:−1
2605:PJW hash
2326:, where
2094:−1
2054:satisfy
2018:. Since
1908:∈
1749:−1
1709:−1
1661:−1
1624:−1
1601:−1
1596:+ ζ
1568:bits to
1391:between
1384:cannot.
1354:identity
1073:function
1008:, where
294:keyspace
269:Overview
261:, while
171:function
32:HashLink
4384:Sorting
4359:Minimax
3745:8250194
3664:Aho, A.
3457:: 1–7.
3364:Bibcode
3064:History
1916:Define
1904:∀
1837:yields
1751:…
1732:. Then
1626:…
1456:Folding
1405:Unicode
1370:Integer
1359:perfect
1222:(where
1187:, e.g.
1093:SipHash
674:perfect
551:scholar
448:in the
402:or the
389:element
251:ciphers
205:hashing
191:digests
169:is any
115:scholar
4364:Online
4349:Greedy
4278:String
4127:
4024:
4014:
3974:
3900:
3890:
3841:
3743:
3733:
3715:
3686:
3575:
3524:
3469:
3428:
3374:
3153:Plain
3047:α
3017:While
2847:where
2651:EBCDIC
2572:, and
2520:after
2340:blocks
2332:ϕ
2035:α
2020:α
2016:|
1986:where
1802:, and
1693:) mod
1382:Double
1089:Python
906:modulo
847:where
611:random
609:, not
553:
546:
539:
532:
524:
464:in an
462:images
452:or in
370:caches
249:, and
195:hashes
117:
110:
103:
96:
88:
4273:Stack
4263:Queue
4243:Graph
4223:Array
3956:(PDF)
3898:S2CID
3876:(PDF)
3823:(PDF)
3786:(PDF)
3741:S2CID
3649:(PDF)
3467:S2CID
3453:(1).
3155:ASCII
3132:Notes
3019:Knuth
2810:>
2718:,...,
2694:radix
2621:xored
2444:64:
2404:48:
2370:32:
2347:16:
2200:) / (
1819:Knuth
1815:GF(2)
1769:. If
1741:) = (
1538:(mod
1374:Float
1146:. If
1047:HMACs
943:(key)
647:<
558:JSTOR
544:books
450:plane
434:tuple
416:cells
355:, or
296:, and
122:JSTOR
108:books
4344:Fold
4288:Trie
4283:Tree
4253:Heap
4207:and
4125:ISBN
4060:C++.
4022:ISSN
4012:ISBN
3985:2022
3972:ISBN
3938:2022
3888:ISBN
3852:2022
3839:ISBN
3805:2023
3731:ISBN
3684:ISBN
3573:ISBN
3522:ISBN
3426:ISBN
3372:ISBN
3331:2024
3310:2023
3070:hash
2664:a +
2510:and
2459:7C15
2456:7F4A
2453:79B9
2451:9E37
2416:7F4B
2413:79B9
2411:9E37
2379:79B9
2377:9E37
2353:9E37
2300:and
2269:) =
2240:and
2196:mod
2188:) =
2086:) =
1896:mod
1890:and
1875:Let
1846:) =
1701:) =
1653:) =
1592:) =
1546:{0,
1378:Long
1366:Java
1278:and
1168:and
1160:and
530:news
475:and
175:data
94:news
4168:PDF
4158:PDF
4004:doi
3964:doi
3925:doi
3880:doi
3831:doi
3794:doi
3723:doi
3606:doi
3602:475
3512:doi
3459:doi
3299:doi
3083:IBM
3081:of
3027:of
2611:at
2485:485
2482:198
2479:323
2476:819
2473:714
2470:400
2436:771
2433:589
2430:102
2427:961
2425:173
2396:769
2393:435
2390:654
2362:503
2245:= 2
2238:= 2
2229:to
2043:of
1870:+ 1
1817:.
1616:= (
1577:= 2
1554:x86
1510:521
1507:190
1504:750
1501:578
1498:241
1491:000
1484:789
1481:456
1479:123
1432:000
1430:100
1414:112
1411:114
1399:or
1191:or
1189:odd
1132:to
962:n P
513:by
393:set
222:).
207:or
77:by
4439::
4108:^
4057:.
4047:.
4028:.
4020:.
4010:.
3970:.
3958:.
3919:.
3896:.
3886:.
3869:.
3837:.
3825:.
3792:.
3788:.
3739:.
3729:.
3721:.
3707:.
3670:;
3666:;
3600:.
3596:.
3559:^
3543:.
3520:,
3491:.
3479:^
3465:.
3451:68
3449:.
3395:.
3370:.
3362:.
3339:^
3232:12
3226:10
3060:.
3042:!)
3009:1/
2997:).
2871:mk
2840:mk
2745:10
2726:−1
2684:+
2489:10
2468:11
2466:=
2463:16
2448:=
2440:10
2423:=
2420:16
2408:=
2400:10
2386:=
2383:16
2374:=
2366:10
2360:40
2358:=
2355:16
2351:=
2275:aK
2194:aK
2109:+
2069:=
1913:.
1892:(2
1866:+
1862:+
1858:+
1854:+
1850:+
1798:,
1724:+
1676:+
1496:15
1489:10
1452:.
1320:.
1272:.
1266:/(
1195:.
1003:1/
987:A
969:.
959::
870:.
686:.
668:.
479:.
440:,
428:,
424:,
395:.
351:,
245:,
241:,
237:,
233:,
229:,
211:.
189:,
185:,
181:,
165:A
4197:e
4190:t
4183:v
4166:(
4156:(
4133:.
4006::
3987:.
3966::
3940:.
3927::
3882::
3854:.
3833::
3807:.
3796::
3753:.
3725::
3692:.
3653:.
3614:.
3608::
3581:.
3553:.
3514::
3495:.
3473:.
3461::
3434:.
3405:.
3380:.
3366::
3333:.
3312:.
3301::
3241:}
3238:9
3235:,
3229:,
3223:,
3220:8
3217:,
3214:6
3211:,
3208:5
3205:,
3202:4
3199:,
3196:3
3193:,
3190:2
3187:,
3184:1
3181:{
3178:=
3175:S
3057:m
3055:/
3053:n
3040:k
3037:e
3030:n
3024:k
3011:m
2951:.
2919:.
2899:s
2893:t
2888:)
2886:k
2884:·
2882:n
2880:(
2878:O
2873:)
2869:+
2867:n
2865:(
2863:O
2850:m
2844:n
2834:h
2828:n
2826:·
2824:k
2818:h
2812:k
2808:n
2802:k
2796:k
2790:n
2780:k
2774:h
2739:a
2733:k
2728:)
2724:k
2720:x
2716:1
2713:x
2711:,
2709:0
2706:x
2704:(
2698:a
2689:0
2686:x
2682:a
2679:1
2676:x
2670:k
2666:x
2660:k
2656:x
2587:n
2496:2
2446:a
2406:a
2388:2
2372:a
2349:a
2328:w
2302:w
2298:m
2288:C
2284:2
2279:⌋
2273:(
2271:⌊
2267:K
2265:(
2262:a
2258:h
2249:w
2243:M
2236:W
2231:W
2223:a
2217:M
2210:⌋
2208:)
2206:M
2204:/
2202:W
2198:W
2192:(
2190:⌊
2186:K
2184:(
2181:a
2177:h
2156:t
2152:n
2145:t
2141:)
2139:x
2137:(
2135:P
2130:)
2128:x
2126:(
2124:R
2119:t
2114:0
2111:r
2107:x
2104:1
2101:r
2097:x
2092:n
2088:r
2084:x
2082:(
2080:R
2074:i
2071:p
2064:i
2057:p
2052:)
2050:x
2048:(
2046:P
2040:p
2031:)
2029:x
2027:(
2025:P
2013:S
2008:x
2006:(
2004:P
1999:)
1997:x
1995:(
1993:P
1974:)
1969:j
1958:x
1955:(
1950:S
1944:j
1936:=
1933:)
1930:x
1927:(
1924:P
1910:S
1906:j
1902:S
1898:n
1894:j
1887:S
1883:t
1877:S
1868:x
1864:x
1860:x
1856:x
1852:x
1848:x
1844:x
1842:(
1840:Z
1833:t
1831:,
1829:m
1827:,
1825:n
1823:(
1804:n
1800:t
1796:k
1792:Z
1786:t
1782:t
1778:)
1776:x
1774:(
1772:Z
1766:2
1764:)
1762:0
1759:h
1756:1
1753:h
1747:m
1743:h
1739:K
1737:(
1735:h
1729:0
1726:h
1722:x
1719:1
1716:h
1712:x
1707:m
1703:h
1699:x
1697:(
1695:Z
1691:x
1689:(
1687:K
1681:0
1678:k
1674:x
1671:1
1668:k
1664:x
1659:n
1655:k
1651:x
1649:(
1647:K
1641:2
1639:)
1637:0
1634:k
1631:1
1628:k
1622:n
1618:k
1614:K
1608:0
1604:x
1599:m
1594:x
1590:x
1588:(
1586:Z
1581:m
1575:M
1570:m
1566:n
1548:M
1542:)
1540:M
1536:K
1532:K
1530:(
1528:h
1523:M
1466:2
1462:m
1450:2
1446:m
1409:1
1311:)
1309:n
1307:,
1305:z
1303:(
1301:H
1295:n
1289:n
1268:n
1264:n
1259:)
1257:n
1255:,
1253:z
1251:(
1249:H
1245:n
1243:,
1241:z
1239:(
1237:H
1231:n
1225:z
1220:)
1218:n
1216:,
1214:z
1212:(
1210:H
1184:n
1178:n
1171:n
1166:0
1154:2
1149:n
1139:n
1130:0
1122:n
1116:z
1049:.
1011:m
1005:m
998:h
966:b
951:P
948:n
941:P
932:2
927:n
921:n
868:j
862:j
858:b
853:m
849:n
833:,
827:)
824:1
818:m
815:2
812:+
809:n
806:(
803:)
800:m
797:2
793:/
789:n
786:(
781:2
777:/
773:)
770:1
767:+
762:j
758:b
754:(
751:)
746:j
742:b
738:(
733:1
727:m
722:0
719:=
716:j
661:m
655:n
649:n
645:m
639:n
637:/
635:m
629:n
623:m
580:)
574:(
569:)
565:(
555:·
548:·
541:·
534:·
507:.
144:)
138:(
133:)
129:(
119:·
112:·
105:·
98:·
71:.
48:.
41:.
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.