45:
78:
27:
449:
85:
52:
252:
The extension of the top layer required for this excursion of the arc and the trench comes from thinning of the back-arc ("in back of the arc"), weakening the crust there. There was already a mountain chain north of the arc, a legacy from the Alpine
Orogeny, called the "inner arc." Its tops are the
248:
The direction of subduction is northward. Locations on the arc or near it on the north side are therefore called "outer" as they are at the outer margin of the plate. Locations further north are "inner." Generally the motion of subduction is from outer to inner. It so happens that, due to back-arc
31:
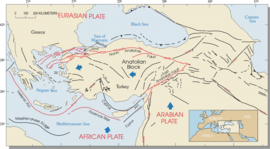
A combined diagram of the Aegean and
Anatolian Plates. The southern margin of the Hellenic arc is shown, which is the trend line of the faults separating the arc and the Hellenic Trench. The body of the arc is the chain called the outer Hellenides, which includes west Peloponnesus, Crete, Rhodes,
261:. The two arcs are considered distinct, being from different orogenies. The term "Hellenic Arc" most often refers to the marginal, or "non-volcanic" arc, also called the Aegean forearc in the direction from outer to inner, which is consonant with the Hellenic Trench being the foredeep.
249:
extension, the
Hellenic Arc and Trench are moving in the reverse direction, from inner to outer, accounting for the severe arcuate form. There are in essence two layers at the subduction zone, a bottom one moving from outer to inner, and a top one moving from inner to outer.
289:
The current geometry of the
Hellenic arc is a result of the southwards migration of the subduction zone. This has led to extension both along the line of the arc as it bulged out and extension perpendicular to the arc, which is the current tectonic state.
245:
group. It encroaches on mainland terrain in the
Peloponnesus, on Crete, on Rhodes, and on the southern coast of Anatolia, thus being encompassed by both Greece and Turkey.
241:
from which it is in the process of diverging. The arc itself is mainly marine, the mountaintops appearing as islands in the Ionian Sea, Crete and its environs, or in the
302:
earthquakes in the last hundred years of instrumental recording and the location for at least two historical events that were probably of about magnitude 8 or more, the
396:
Papadopoulos, G. A.; Ganas, A.; Karastathis, C. (2004). "Seismicity
Properties as a Marker of the Active Plate Convergence in the western Hellenic Arc".
257:. In addition, a chain of volcanos has appeared across it, due to magma breaking through the weakened crust; hence, this "inner arc" is termed the
468:
344:"Incipient continental collision and plate-boundary curvature: Late Pliocene–Holocene transtensional Hellenic forearc, Crete, Greece"
44:
136:
77:
298:
The
Hellenic arc is one of the most active seismic zones in western Eurasia. It has regularly been the source for
453:
424:
237:
trends parallel to its southern side. The Aegean Sea Plate, a microplate, is often considered part of the
473:
258:
230:
343:
307:
405:
355:
303:
8:
319:
409:
359:
371:
375:
363:
218:
234:
270:
238:
462:
299:
226:
151:
138:
367:
210:
26:
278:
242:
222:
214:
16:
Mountain chain located on the southern margin of the Aegean Sea Plate
254:
448:
274:
395:
416:
398:American Geophysical Union, Fall Meeting Abstracts
341:
126:The center of Crete is at about center of the arc
32:southwestern Turkey, and all the islands between.
460:
264:
389:
273:in the west to just east of the island of
342:ten Veen, J.H.; Kleinspehn, K.L. (2003).
181:Aegean Sea, Ionian Sea, Mediterranean Sea
335:
461:
217:located on the southern margin of the
422:
277:in the east, where it links to the
221:. Geologically it results from the
13:
269:The Hellenic arc extends from the
84:
51:
14:
485:
442:
348:Journal of the Geological Society
469:Megathrust earthquakes in Greece
447:
83:
76:
50:
43:
25:
213:mountain chain of the southern
284:
1:
328:
293:
425:"Tectonic Summary of Greece"
265:Geometry of the Hellenic arc
7:
313:
10:
490:
113:Hellenic Republic (Greece)
259:South Aegean Volcanic Arc
190:
185:
175:
171:southern outer Hellenides
167:
130:
122:
117:
109:
67:Show map of Mediterranean
64:Hellas and the Aegean Sea
37:
24:
231:Hellenic subduction zone
368:10.1144/0016-764902-067
423:USGS (29 March 2010).
456:at Wikimedia Commons
308:1303 Crete earthquake
152:35.21389°N 24.96694°E
304:365 Crete earthquake
410:2004AGUFM.T53B0483P
360:2003JGSoc.160..161T
320:Mediterranean Ridge
229:under it along the
148: /
97:middle arc (Greece)
21:
157:35.21389; 24.96694
100:Show map of Greece
19:
474:Geology of Greece
452:Media related to
199:
198:
481:
451:
436:
435:
433:
431:
420:
414:
413:
393:
387:
386:
384:
382:
339:
219:Aegean Sea Plate
178:
163:
162:
160:
159:
158:
153:
149:
146:
145:
144:
141:
101:
87:
86:
80:
68:
54:
53:
47:
29:
22:
18:
489:
488:
484:
483:
482:
480:
479:
478:
459:
458:
445:
440:
439:
429:
427:
421:
417:
394:
390:
380:
378:
340:
336:
331:
325:
316:
296:
287:
267:
235:Hellenic Trench
195:
176:
156:
154:
150:
147:
142:
139:
137:
135:
134:
105:
104:
103:
102:
99:
98:
95:
94:
93:
92:
88:
71:
70:
69:
66:
65:
62:
61:
60:
59:
55:
33:
17:
12:
11:
5:
487:
477:
476:
471:
444:
443:External links
441:
438:
437:
415:
388:
354:(2): 161–181.
333:
332:
330:
327:
323:
322:
315:
312:
295:
292:
286:
283:
271:Ionian islands
266:
263:
239:Eurasian Plate
197:
196:
191:
188:
187:
186:Administration
183:
182:
179:
173:
172:
169:
165:
164:
132:
128:
127:
124:
120:
119:
115:
114:
111:
107:
106:
96:
90:
89:
82:
81:
75:
74:
73:
72:
63:
57:
56:
49:
48:
42:
41:
40:
39:
38:
35:
34:
30:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
486:
475:
472:
470:
467:
466:
464:
457:
455:
450:
426:
419:
411:
407:
403:
399:
392:
377:
373:
369:
365:
361:
357:
353:
349:
345:
338:
334:
326:
321:
318:
317:
311:
309:
305:
301:
291:
282:
280:
276:
272:
262:
260:
256:
250:
246:
244:
240:
236:
232:
228:
227:African Plate
224:
220:
216:
212:
208:
204:
194:
189:
184:
180:
174:
170:
166:
161:
133:
129:
125:
121:
116:
112:
108:
79:
46:
36:
28:
23:
454:Hellenic arc
446:
428:. Retrieved
418:
401:
397:
391:
379:. Retrieved
351:
347:
337:
324:
297:
288:
268:
251:
247:
206:
203:Hellenic arc
202:
200:
192:
20:Hellenic arc
300:magnitude 7
285:Development
177:Adjacent to
168:Archipelago
155: /
131:Coordinates
463:Categories
329:References
294:Seismicity
279:Cyprus arc
243:Dodecanese
223:subduction
215:Aegean Sea
207:Aegean arc
143:24°58′01″E
140:35°12′50″N
91:middle arc
58:middle arc
376:219542417
118:Geography
110:Etymology
404:: 0483.
314:See also
306:and the
255:Cyclades
123:Location
430:26 July
406:Bibcode
381:26 July
356:Bibcode
225:of the
211:arcuate
374:
275:Rhodes
233:. The
209:is an
193:Greece
372:S2CID
432:2010
383:2010
201:The
364:doi
352:160
205:or
465::
402:53
400:.
370:.
362:.
350:.
346:.
310:.
281:.
434:.
412:.
408::
385:.
366::
358::
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.