170:
222:
176:
In the
Hofmann elimination, the least substituted alkene is typically favored due to intramolecular steric interactions. The quaternary ammonium group is large, and interactions with alkyl groups on the rest of the molecule are undesirable. As a result, the conformation necessary for the formation of
177:
the
Zaitsev product is less energetically favorable than the conformation required for the formation of the Hofmann product. As a result, the Hofmann product is formed preferentially. The
181:
is very similar to the
Hofmann elimination in principle, but occurs under milder conditions. It also favors the formation of the Hofmann product, and for the same reasons.
280:
169:
402:
89:
156:
to form a quaternary ammonium hydroxide. When this salt is decomposed by heat, the
Hofmann product is preferentially formed due to the
713:
184:
An example of a
Hofmann elimination (not involving a contrast between a Zaitsev product and a Hofmann product) is the synthesis of
17:
698:
459:
221:
329:
743:
895:
890:
117:. The least stable alkene (the one with the fewest substituents on the carbons of the double bond), called the
275:
74:
673:
678:
324:
130:
82:
48:
869:
240:
to the quaternary ammonium salt which when heated degrades to methyl iodide and the secondary amine.
236:, a tertiary amine with at least one methyl group and lacking a beta-proton is allowed to react with
849:
900:
809:
804:
683:
728:
452:
31:
738:
718:
655:
289:
197:
106:
58:
8:
688:
659:
646:
137:
293:
799:
773:
703:
305:
839:
763:
753:
723:
664:
374:
309:
213:
185:
129:
predicts the formation of the most stable alkene. It is named after its discoverer,
126:
819:
748:
733:
445:
411:
338:
297:
254:
249:
178:
859:
829:
758:
237:
369:
854:
844:
432:
201:
884:
814:
789:
693:
415:
342:
229:
193:
161:
141:
864:
794:
768:
398:"Ueber den Nachweis und die Bestimmung des am Stickstoff gebundenen Alkyls"
301:
149:
824:
157:
834:
650:
164:
causing the hydroxide to abstract the more easily accessible hydrogen.
397:
482:
567:
533:
499:
276:"Researches into the molecular constitution of the organic bases"
327:[Contribution to knowledge of volatile organic bases].
668:
618:
601:
584:
550:
516:
468:
114:
153:
110:
367:
437:
325:"Beiträge zur Kenntniss der flüchtigen organischen Basen"
281:
433:
An animation of the mechanism of the
Hofmann elimination
125:, is in contrast to usual elimination reactions, where
322:
140:iodide salt by treatment of the amine with excess
395:
882:
403:Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft
453:
136:The reaction starts with the formation of a
460:
446:
234:Herzig–Meyer alkimide group determination
121:, is formed. This tendency, known as the
368:Arthur C. Cope; Robert D. Bach (1973).
273:
14:
883:
27:Chemical reaction in organic chemistry
441:
24:
25:
912:
426:
714:Horner–Wadsworth–Emmons reaction
330:Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie
220:
168:
323:Aug. Wilh. von Hofmann (1851).
389:
361:
349:
316:
267:
148:), followed by treatment with
13:
1:
699:Corey–Winter olefin synthesis
260:
123:Hofmann alkene synthesis rule
396:J. Herzig; H. Meyer (1894).
216:article for better images):
7:
467:
243:
10:
917:
384:, vol. 5, p. 315
131:August Wilhelm von Hofmann
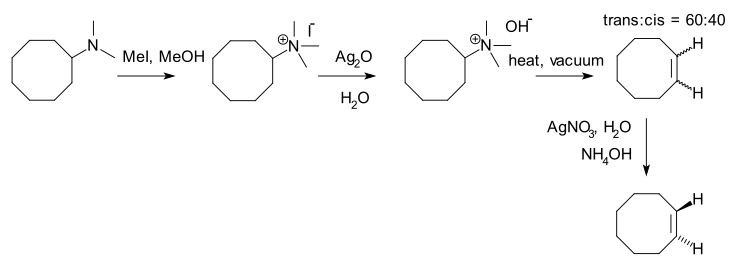
49:August Wilhelm von Hofmann
29:
870:Friedel-Crafts Alkylation
782:
744:Ramberg–Bäcklund reaction
639:
475:
355:
96:
70:Organic Chemistry Portal
64:
39:
674:Bamford–Stevens reaction
416:10.1002/cber.18940270163
343:10.1002/jlac.18510780302
30:Not to be confused with
810:Oxymercuration reaction
679:Barton–Kellogg reaction
274:Hofmann, A. W. (1851).
805:Electrophilic addition
684:Boord olefin synthesis
302:10.1098/rstl.1851.0017
192:isomer is selectively
146:exhaustive methylation
896:Olefination reactions
891:Elimination reactions
729:Kauffmann olefination
204:(in this diagram the
32:Hofmann rearrangement
850:Diels–Alder reaction
739:Peterson olefination
719:Hydrazone iodination
656:Dehydration reaction
107:elimination reaction
59:Elimination reaction
40:Hofmann elimination
709:Hofmann elimination
689:Chugaev elimination
647:Dehydrohalogenation
370:"trans-Cyclooctene"
294:1851RSPT..141..357H
138:quaternary ammonium
103:Hofmann elimination
75:hofmann-elimination
18:Hofmann's Rule
774:Cope rearrangement
704:Grieco elimination
212:form, but see the
208:form looks like a
878:
877:
840:Hydrohalogenation
764:Olefin metathesis
754:Takai olefination
724:Julia olefination
665:Semihydrogenation
382:Collected Volumes
375:Organic Syntheses
214:trans-cyclooctene
186:trans-cyclooctene
100:
99:
16:(Redirected from
908:
820:Cyclopropanation
749:Shapiro reaction
734:McMurry reaction
631:
614:
597:
580:
563:
546:
529:
512:
495:
462:
455:
448:
439:
438:
420:
419:
393:
387:
385:
378:
365:
359:
353:
347:
346:
320:
314:
313:
271:
255:Emde degradation
250:Cope elimination
224:
179:Cope elimination
172:
92:
77:
37:
36:
21:
916:
915:
911:
910:
909:
907:
906:
905:
881:
880:
879:
874:
860:Dehydrogenation
830:Dihydroxylation
778:
759:Wittig reaction
635:
630:
626:
622:
613:
609:
605:
596:
592:
588:
579:
575:
571:
562:
558:
554:
545:
541:
537:
528:
524:
520:
511:
507:
503:
494:
490:
486:
471:
466:
429:
424:
423:
394:
390:
380:
366:
362:
354:
350:
321:
317:
272:
268:
263:
246:
238:hydrogen iodide
232:, known as the
119:Hofmann product
88:
73:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
914:
904:
903:
901:Name reactions
898:
893:
876:
875:
873:
872:
867:
862:
857:
855:Wacker process
852:
847:
845:Polymerization
842:
837:
832:
827:
822:
817:
812:
807:
802:
797:
792:
786:
784:
780:
779:
777:
776:
771:
766:
761:
756:
751:
746:
741:
736:
731:
726:
721:
716:
711:
706:
701:
696:
691:
686:
681:
676:
671:
662:
653:
643:
641:
637:
636:
634:
633:
628:
624:
616:
611:
607:
599:
594:
590:
582:
577:
573:
565:
560:
556:
548:
543:
539:
531:
526:
522:
514:
509:
505:
497:
492:
488:
479:
477:
473:
472:
465:
464:
457:
450:
442:
436:
435:
428:
427:External links
425:
422:
421:
410:(1): 319–320.
388:
360:
348:
337:(3): 253–286.
315:
265:
264:
262:
259:
258:
257:
252:
245:
242:
226:
225:
202:silver nitrate
174:
173:
127:Zaitsev's rule
98:
97:
94:
93:
86:
79:
78:
71:
67:
66:
62:
61:
56:
55:Reaction type
52:
51:
46:
42:
41:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
913:
902:
899:
897:
894:
892:
889:
888:
886:
871:
868:
866:
863:
861:
858:
856:
853:
851:
848:
846:
843:
841:
838:
836:
833:
831:
828:
826:
823:
821:
818:
816:
815:Hydroboration
813:
811:
808:
806:
803:
801:
798:
796:
793:
791:
790:Hydrogenation
788:
787:
785:
781:
775:
772:
770:
767:
765:
762:
760:
757:
755:
752:
750:
747:
745:
742:
740:
737:
735:
732:
730:
727:
725:
722:
720:
717:
715:
712:
710:
707:
705:
702:
700:
697:
695:
694:Cope reaction
692:
690:
687:
685:
682:
680:
677:
675:
672:
670:
666:
663:
661:
657:
654:
652:
648:
645:
644:
642:
638:
620:
617:
603:
600:
586:
583:
569:
566:
552:
549:
535:
532:
518:
515:
501:
498:
484:
481:
480:
478:
474:
470:
463:
458:
456:
451:
449:
444:
443:
440:
434:
431:
430:
417:
413:
409:
405:
404:
399:
392:
383:
377:
376:
371:
364:
357:
352:
344:
340:
336:
333:(in German).
332:
331:
326:
319:
311:
307:
303:
299:
295:
291:
287:
283:
282:
277:
270:
266:
256:
253:
251:
248:
247:
241:
239:
235:
231:
230:chemical test
228:In a related
223:
219:
218:
217:
215:
211:
207:
203:
199:
195:
191:
187:
182:
180:
171:
167:
166:
165:
163:
162:leaving group
159:
155:
151:
147:
143:
142:methyl iodide
139:
134:
132:
128:
124:
120:
116:
112:
108:
104:
95:
91:
87:
84:
81:
80:
76:
72:
69:
68:
63:
60:
57:
54:
53:
50:
47:
44:
43:
38:
33:
19:
865:Ene reaction
795:Halogenation
769:Ene reaction
708:
640:Preparations
407:
401:
391:
381:
373:
363:
351:
334:
328:
318:
285:
279:
269:
233:
227:
209:
205:
189:
183:
175:
150:silver oxide
145:
135:
122:
118:
102:
101:
90:RXNO:0000166
85:ontology ID
65:Identifiers
45:Named after
825:Epoxidation
288:: 357–398.
158:steric bulk
885:Categories
835:Ozonolysis
651:haloalkane
261:References
800:Hydration
783:Reactions
358:, p. 903.
310:108453887
244:See also
113:to form
660:alcohol
568:Heptene
534:Pentene
500:Propene
476:Alkenes
469:Alkenes
290:Bibcode
198:complex
194:trapped
160:of the
115:alkenes
669:alkyne
619:Decene
602:Nonene
585:Octene
551:Hexene
517:Butene
483:Ethene
308:
188:. The
109:of an
105:is an
667:from
658:from
649:from
306:S2CID
206:trans
200:with
196:as a
190:trans
154:water
111:amine
356:Wade
152:and
412:doi
339:doi
298:doi
286:141
210:cis
83:RSC
887::
629:20
625:10
612:18
595:16
578:14
561:12
544:10
408:27
406:.
400:.
379:;
372:.
335:78
304:.
296:.
284:.
278:.
133:.
632:)
627:H
623:C
621:(
615:)
610:H
608:9
606:C
604:(
598:)
593:H
591:8
589:C
587:(
581:)
576:H
574:7
572:C
570:(
564:)
559:H
557:6
555:C
553:(
547:)
542:H
540:5
538:C
536:(
530:)
527:8
525:H
523:4
521:C
519:(
513:)
510:6
508:H
506:3
504:C
502:(
496:)
493:4
491:H
489:2
487:C
485:(
461:e
454:t
447:v
418:.
414::
386:.
345:.
341::
312:.
300::
292::
144:(
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.