73:
38:
349:) can identify characteristic physical abnormalities. After birth, diagnosis may be delayed for several months because the infant's early behavior appears to be relatively normal. The most accurate diagnostic techniques are thorough clinical evaluation (considering physical findings and a detailed patient history); advanced imaging techniques, such as
442:
The prognosis for children with hydranencephaly is generally quite poor. Death often occurs within the first year of life, though many children live several years, or even into adulthood; in one reported case, a woman with hydranencephaly was assessed at age 32.
587:
Ulmer S, Moeller F, Brockmann MA, Kuhtz-Buschbeck JP, Stephani U, Jansen O (2005). "Living a normal life with the nondominant hemisphere: magnetic resonance imaging findings and clinical outcome for a patient with left-hemispheric hydranencephaly".
982:
225:
problems. Still other infants display no obvious symptoms at birth, going many months without a confirmed diagnosis of hydranencephaly. In some cases severe hydrocephalus, or another cephalic condition, is misdiagnosed.
245:
Although the exact cause of hydranencephaly remains undetermined in most cases, the most likely general cause is by vascular insult, such as stroke, injury, intrauterine infections, or traumatic disorders after the
882:
867:
852:
975:
968:
372:
Preliminary diagnosis may be made in utero via standard ultrasound, and can be confirmed with a standard anatomy ultrasound. Hydranencephaly is sometimes misdiagnosed as
829:
376:(a less destructive developmental process on the brain), severe hydrocephalus (cerebrospinal fluid excess within the skull), or alobar holoprosencephaly (a
174:
may all seem normal, depending on the severity of the condition. However, after a few weeks the infant sometimes becomes irritable and has increased
558:
1256:
806:
294:
circulation through twin-to-twin transfusion, causing hydranencephaly in the surviving fetus. One medical journal reports hydranencephaly as an
784:
109:
290:
pregnancies, involving the death of one twin in the second trimester, which in turn causes vascular exchange to the living twin through
1167:
116:. These conditions do not have any definitive identifiable cause factor. Instead, they are generally attributed to a variety of
659:
686:"Everything Guide to Children with Hydranencephaly" by Brayden Alexander Global Foundation for Hydranencephaly, Incorporated.
539:
495:
740:
317:
Though hydranencephaly is typically a congenital disorder, it can occur as a postnatal diagnosis in the aftermath of
1119:
960:
341:
An accurate, confirmed diagnosis is generally impossible until after birth, though prenatal diagnosis using
436:
250:. In a number of cases where intrauterine infection was determined to be the causing factor, most involved
738:
S. A. Counter (Dec 15, 2007). "Preservation of brainstem neurophysiological function in hydranencephaly".
1142:
948:
824:
566:
283:
162:
and upper facial features due to fluid pressure inside the skull. The infant's head size and spontaneous
415:, which results from inadequate reabsorption of the cerebrospinal fluid produced in the choroid plexus.
358:
218:
511:
1076:
342:
45:
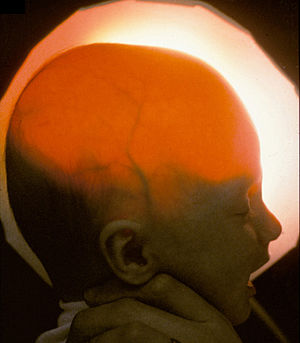
Light passing through the skull of a hydranencephalic baby, underscoring the absence of the forebrain
72:
897:
322:
222:
792:
1261:
330:
279:
861:
1124:
424:
412:
158:
An infant with hydranencephaly may appear normal at birth or may have some distortion of the
125:
466:
263:
113:
86:
8:
1050:
991:
886:
637:
427:. An accompanying diagnosis of hydrocephalus may be treated with surgical insertion of a
147:
94:
697:
1221:
1192:
1134:
1100:
1012:
765:
698:"Prolonged survival with hydranencephaly: report of two patients and literature review"
613:
550:
287:
140:
891:
716:
1090:
908:
800:
757:
720:
605:
491:
362:
199:
191:
101:
61:
937:
769:
670:
617:
556:
1226:
749:
712:
597:
298:
121:
66:
902:
408:
306:
271:
453:
This condition affects under 1 in 10,000 births worldwide. Hydranencephaly is a
1162:
1153:
1129:
995:
990:
913:
428:
404:
400:
373:
302:
275:
267:
90:
876:
753:
365:. However, diagnostic literature fails to provide a clear distinction between
1250:
1231:
1095:
1071:
1045:
457:
in the United States, which is defined as affecting fewer than 1 in 250,000.
396:
366:
255:
251:
187:
136:
17:
1205:
1200:
1148:
1066:
1038:
761:
724:
609:
601:
454:
235:
105:
533:
531:
529:
411:
is absent; however, in most cases, the fetal head remains enlarged due to
1183:
1020:
1003:
350:
259:
175:
844:
369:
and hydranencephaly, leaving some children with an unsettled diagnosis.
190:
may develop, if they did not exist at birth. Other symptoms may include
1105:
526:
384:
346:
318:
305:
where it enters the cranium; this causes obstruction and damage to the
179:
97:. "Cephalic" is the scientific term for "head" or "head end of body".
1033:
932:
512:"Hydranencephaly: Definition, Information, Diagnosis & Prognosis"
432:
377:
247:
214:
203:
171:
129:
586:
537:
943:
392:
388:
326:
295:
291:
195:
117:
209:
Some infants may have additional abnormalities at birth including
37:
1028:
557:
National
Institute of Neurological Conditions and Stroke, NINDS.
423:
There is no standard treatment for hydranencephaly. Treatment is
354:
210:
183:
53:
301:
with an unknown mode of transmission, causing a blockage of the
871:
856:
163:
490:(5. ed.). Appleton and Lange: McGraw Hill. p. 1020.
159:
139:, which is an accumulation of excess cerebrospinal fluid in
128:, pharmaceutical intake, or even exposure to high levels of
108:
that derive from damage to, or abnormal development of, the
239:
782:
167:
631:
629:
627:
834:
166:
such as sucking, swallowing, crying, and moving the
407:typically remain preserved to varying degrees. The
624:
1248:
635:
383:Once destruction of the brain is complete, the
150:, only half of the cranial cavity is affected.
89:are absent to a great degree and the remaining
695:
976:
737:
135:Hydranencephaly should not be confused with
124:, but also by environmental factors such as
805:: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (
689:
580:
217:(involuntary sudden, rapid jerks), limited
983:
969:
636:Kurtz & Johnson, Alfred & Pamela.
538:National Organization for Rare Disorders.
312:
71:
1168:Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria
653:
651:
242:or cavity in the cerebral hemispheres.
1257:Congenital disorders of nervous system
1249:
485:
234:Hydranencephaly is an extreme form of
964:
479:
153:
741:Journal of the Neurological Sciences
648:
374:bilaterally symmetric schizencephaly
85:is a condition in which the brain's
696:McAbee GN, Chan A, Erde EL (2000).
13:
994:malformations and deformations of
660:"Is it Hydranencephaly-A Variant?"
559:"Hydranencephaly Information Page"
14:
1273:
817:
657:
182:). After several months of life,
638:"Case Number 7: Hydranencephaly"
367:severe obstructive hydrocephalus
36:
1120:Agenesis of the corpus callosum
783:Rare Disease Day: February 28.
776:
731:
413:increased intracranial pressure
680:
504:
238:, which is characterized by a
206:), and intellectual deficits.
1:
717:10.1016/S0887-8994(00)00154-5
472:
448:
100:Hydranencephaly is a type of
488:Principles of neural science
418:
336:
248:first trimester of pregnancy
7:
1086:other reduction deformities
460:
141:the ventricles of the brain
10:
1278:
425:symptomatic and supportive
359:magnetic resonance imaging
286:. Another cause factor is
112:in the earliest stages of
15:
1214:
1191:
1182:
1059:
1011:
1002:
923:
838:
785:"What is a Rare Disease?"
754:10.1016/j.jns.2007.06.043
544:Rare Diseases Information
361:(MRI); and (more rarely)
229:
202:, spastic quadriparesis (
60:
44:
35:
28:
1072:Congenital hydrocephalus
486:Kandel, Eric R. (2013).
380:developmental anomaly).
323:intracerebral infarction
16:Not to be confused with
642:Radiology, 210, 419-422
355:computerized tomography
313:Post-natal brain injury
667:MJAFI 2002; 58:338-339
602:10.1542/peds.2004-0425
431:; this often improves
403:, and portions of the
331:traumatic brain injury
104:. These disorders are
1125:Septo-optic dysplasia
1077:Dandy–Walker syndrome
343:fetal ultrasonography
106:congenital conditions
467:Microhydranencephaly
114:development in utero
110:fetal nervous system
87:cerebral hemispheres
1051:Chiari malformation
514:. 29 September 2012
148:hemihydranencephaly
95:cerebrospinal fluid
1222:Currarino syndrome
1193:Neural tube defect
1135:Hemimegalencephaly
1101:Microlissencephaly
1013:Neural tube defect
924:External resources
658:Dubey, AK Lt Col.
299:inherited disorder
288:monochorionic twin
194:, lack of growth,
154:Signs and symptoms
126:maternal infection
122:genetic conditions
52:Image courtesy of
1244:
1243:
1240:
1239:
1178:
1177:
1091:Holoprosencephaly
958:
957:
540:"Hydranencephaly"
497:978-0-07-139011-8
363:transillumination
284:syncytial viruses
192:visual impairment
102:cephalic disorder
80:
79:
23:Medical condition
1269:
1227:Diastomatomyelia
1189:
1188:
1009:
1008:
985:
978:
971:
962:
961:
836:
835:
811:
810:
804:
796:
791:. Archived from
780:
774:
773:
748:(1–2): 198–207.
735:
729:
728:
702:
693:
687:
684:
678:
677:
675:
669:. Archived from
664:
655:
646:
645:
633:
622:
621:
584:
578:
577:
575:
574:
565:. Archived from
554:
548:
547:
535:
524:
523:
521:
519:
508:
502:
501:
483:
256:viral infections
219:thermoregulation
76:
75:
67:Medical genetics
54:D. P. Agamanolis
51:
40:
29:Hydranencephaly
26:
25:
1277:
1276:
1272:
1271:
1270:
1268:
1267:
1266:
1247:
1246:
1245:
1236:
1210:
1174:
1111:Hydranencephaly
1055:
998:
989:
959:
954:
953:
919:
918:
847:
825:Hydranencephaly
820:
815:
814:
798:
797:
781:
777:
736:
732:
705:Pediatr. Neurol
700:
694:
690:
685:
681:
673:
662:
656:
649:
634:
625:
585:
581:
572:
570:
555:
551:
536:
527:
517:
515:
510:
509:
505:
498:
484:
480:
475:
463:
451:
445:
444:
437:quality of life
421:
409:cerebral cortex
405:occipital lobes
357:(CT scan), and
339:
315:
307:cerebral cortex
272:cytomegalovirus
232:
221:abilities, and
156:
93:is filled with
83:Hydranencephaly
70:
49:
46:
30:
24:
21:
12:
11:
5:
1275:
1265:
1264:
1259:
1242:
1241:
1238:
1237:
1235:
1234:
1229:
1224:
1218:
1216:
1212:
1211:
1209:
1208:
1203:
1197:
1195:
1186:
1180:
1179:
1176:
1175:
1173:
1172:
1171:
1170:
1163:Polymicrogyria
1159:
1158:
1157:
1156:
1154:Schizencephaly
1151:
1138:
1137:
1132:
1130:Megalencephaly
1127:
1122:
1116:
1115:
1114:
1113:
1108:
1103:
1098:
1093:
1082:
1081:
1080:
1079:
1069:
1063:
1061:
1057:
1056:
1054:
1053:
1048:
1043:
1042:
1041:
1036:
1031:
1026:
1017:
1015:
1006:
1000:
999:
996:nervous system
988:
987:
980:
973:
965:
956:
955:
952:
951:
940:
928:
927:
925:
921:
920:
917:
916:
905:
894:
879:
864:
848:
843:
842:
840:
839:Classification
833:
832:
819:
818:External links
816:
813:
812:
795:on 2018-10-24.
775:
730:
688:
679:
676:on 2014-04-02.
647:
623:
579:
549:
525:
503:
496:
477:
476:
474:
471:
470:
469:
462:
459:
450:
447:
420:
417:
401:choroid plexus
338:
335:
314:
311:
303:carotid artery
276:herpes simplex
231:
228:
155:
152:
91:cranial cavity
78:
77:
64:
58:
57:
42:
41:
33:
32:
22:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1274:
1263:
1262:Rare diseases
1260:
1258:
1255:
1254:
1252:
1233:
1232:Syringomyelia
1230:
1228:
1225:
1223:
1220:
1219:
1217:
1213:
1207:
1204:
1202:
1199:
1198:
1196:
1194:
1190:
1187:
1185:
1181:
1169:
1166:
1165:
1164:
1161:
1160:
1155:
1152:
1150:
1147:
1146:
1145:
1144:
1140:
1139:
1136:
1133:
1131:
1128:
1126:
1123:
1121:
1118:
1117:
1112:
1109:
1107:
1104:
1102:
1099:
1097:
1096:Lissencephaly
1094:
1092:
1089:
1088:
1087:
1084:
1083:
1078:
1075:
1074:
1073:
1070:
1068:
1065:
1064:
1062:
1058:
1052:
1049:
1047:
1046:Encephalocele
1044:
1040:
1037:
1035:
1032:
1030:
1027:
1024:
1023:
1022:
1019:
1018:
1016:
1014:
1010:
1007:
1005:
1001:
997:
993:
986:
981:
979:
974:
972:
967:
966:
963:
950:
946:
945:
941:
939:
935:
934:
930:
929:
926:
922:
915:
911:
910:
906:
904:
900:
899:
895:
893:
889:
888:
884:
880:
878:
874:
873:
869:
865:
863:
859:
858:
854:
850:
849:
846:
841:
837:
831:
827:
826:
822:
821:
808:
802:
794:
790:
786:
779:
771:
767:
763:
759:
755:
751:
747:
743:
742:
734:
726:
722:
718:
714:
710:
706:
699:
692:
683:
672:
668:
661:
654:
652:
643:
639:
632:
630:
628:
619:
615:
611:
607:
603:
599:
595:
591:
583:
569:on 2016-12-02
568:
564:
560:
553:
545:
541:
534:
532:
530:
513:
507:
499:
493:
489:
482:
478:
468:
465:
464:
458:
456:
455:rare disorder
446:
440:
438:
434:
430:
426:
416:
414:
410:
406:
402:
398:
397:basal ganglia
394:
390:
386:
381:
379:
375:
370:
368:
364:
360:
356:
352:
348:
344:
334:
332:
328:
324:
320:
310:
308:
304:
300:
297:
293:
289:
285:
281:
277:
273:
269:
265:
261:
257:
253:
252:toxoplasmosis
249:
243:
241:
237:
227:
224:
220:
216:
212:
207:
205:
201:
197:
193:
189:
188:hydrocephalus
185:
181:
177:
173:
169:
165:
161:
151:
149:
144:
142:
138:
137:hydrocephalus
133:
131:
127:
123:
119:
115:
111:
107:
103:
98:
96:
92:
88:
84:
74:
68:
65:
63:
59:
56:
55:
43:
39:
34:
31:Hydrancephaly
27:
19:
18:Hydrocephalus
1206:Rachischisis
1201:Spina bifida
1149:Porencephaly
1141:
1110:
1085:
1067:Microcephaly
1039:Iniencephaly
942:
931:
907:
896:
881:
866:
851:
823:
793:the original
789:Rare Disease
788:
778:
745:
739:
733:
708:
704:
691:
682:
671:the original
666:
641:
596:(1): 242–5.
593:
589:
582:
571:. Retrieved
567:the original
562:
552:
543:
516:. Retrieved
506:
487:
481:
452:
441:
422:
382:
378:neurological
371:
340:
316:
280:Epstein-Barr
244:
236:porencephaly
233:
208:
157:
145:
134:
99:
82:
81:
47:
1184:Spinal cord
1021:Anencephaly
711:(1): 80–4.
518:24 February
351:angiography
260:enterovirus
223:respiratory
176:muscle tone
1251:Categories
1106:Pachygyria
992:Congenital
909:DiseasesDB
590:Pediatrics
573:2011-06-19
473:References
449:Occurrence
385:cerebellum
347:ultrasound
319:meningitis
268:parvovirus
264:adenovirus
180:hypertonia
118:hereditary
1034:Acalvaria
938:radio/351
933:eMedicine
563:Disorders
433:prognosis
419:Prognosis
337:Diagnosis
296:autosomal
292:placental
215:myoclonus
204:paralysis
200:blindness
130:radiation
62:Specialty
1143:CNS cyst
1025:Acephaly
944:Orphanet
801:cite web
770:26948761
762:17719607
725:10963978
618:45671819
610:15995064
461:See also
389:midbrain
327:ischemia
258:such as
211:seizures
196:deafness
184:seizures
164:reflexes
1029:Acrania
903:D006832
862:LA05.62
393:thalami
329:, or a
50:
768:
760:
723:
616:
608:
494:
282:, and
230:Causes
69:
1215:Other
1060:Other
1004:Brain
914:31516
892:742.3
877:Q04.3
830:NINDS
766:S2CID
701:(PDF)
674:(PDF)
663:(PDF)
614:S2CID
429:shunt
160:skull
949:2177
898:MeSH
887:9-CM
807:link
758:PMID
721:PMID
606:PMID
520:2018
492:ISBN
435:and
254:and
240:cyst
186:and
172:legs
170:and
168:arms
883:ICD
868:ICD
853:ICD
828:at
750:doi
746:263
713:doi
598:doi
594:116
146:In
120:or
1253::
947::
936::
912::
901::
890::
875::
872:10
860::
857:11
803:}}
799:{{
787:.
764:.
756:.
744:.
719:.
709:23
707:.
703:.
665:.
650:^
640:.
626:^
612:.
604:.
592:.
561:.
542:.
528:^
439:.
399:,
395:,
391:,
387:,
353:,
333:.
325:,
321:,
309:.
278:,
274:,
270:,
266:,
262:,
213:,
198:,
143:.
132:.
984:e
977:t
970:v
885:-
870:-
855:-
845:D
809:)
772:.
752::
727:.
715::
644:.
620:.
600::
576:.
546:.
522:.
500:.
345:(
178:(
48:—
20:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.