66:
43:
53:
526:, the younger brother of the dead king of Thanesar, vowed to avenge the death of his brother and rescue his sister. He repelled the invasion by the king of Gauda and rescued his widowed sister. He was then crowned the Emperor of Kannauj by the nobles of Kannauj in a grand ceremony at Kannauj attended by representatives of multiple principalities and kingdoms of North India. He carried out campaigns in Northern India to bring under his suzerainty the various kingdoms of northern India. He reigned until 647.
2041:
Dharmapāla after defeating Indrāyudha and capturing Kanuaj made it over to Cakrāyudha, who was a vassal king of Kanuaj subordinate to
Dharmapāla ... Dharmapāla was thus acknowledged paramount ruler of almost whole of North India as the Bhojas of Berar, Kīra (Kangra district), Gandhāra (West Punjab),
904:
Ultimately, Rajyapala, after fleeing to Bari, decided to surrender to Mahmud, acknowledging the nominal suzerainty of the
Ghaznavids. The seven forts of Kannauj fell in one day to the Ghaznavids. Following this development, Mahmud engaged in other campaigns within India after successfully asserting
1789:
But as
Budhagupta sat down to find out more about this ferocious looking man, he realized that behind this fierce exterior was a calm and composed man who believed in tact as much as in strength. He was a man who had a strong sense of morality. And behind that outer layer of toughness, he was also
770:
invaded
Kannauj and defeated the Gurjara armies, and Nagabhatta retreated back to his empire. Dharmapala and Chakrayudha acknowledged Govinda III as their overlords to earn his friendship after which Govinda went back and Kannauj came back under Bengal rule in 800. Kannauj remained a vassal of the
452:
who had conquered and held suzerainty over a large region including modern day western
Maharashtra and Karnataka. The Emperor of Magadha, Kumargupta III defeated Ishanavarman in 554 AD, but shortly died thereafter in Prayag. Harivarman's reign was followed by that of Adityavarman and Ishvavarman.
1834:
The
Disaffected elites and closet enemies to the imperial throne Harivarman tooth and nail. However, the latter showed both diplomatic tact and martial prowess to subdue the trouble makers. Using a combination of his sharp political acumen, amiable personality and fierce martial reputation, Hari
819:
The territories of Bhoja extended up till
Kashmir in the north after Bhoja conquered Punjab by defeating ruling Thakkiyaka dynasty. After Devapala's death, Bhoja defeated the Bengal emperor Narayanapala and expanded his boundaries eastward into Bengal-held territories near Gorakhpur.
981:, the Kingdom of Kannauj transformed once again into a vast realm, even larger than that of Harshavardhana. The empire including its vassals extended from Gujarat to Magadha during its initial rule. Later, it was reduced to a small dominion around the capital city.
815:
around 840 but failed to conquer it. He led campaigns in other neighbouring regions and was successful in conquering included
Travani, Valla, Mada, Arya, Gujarat, and Bundelkhand who acknowledged his suzerainty. He also managed to conquer Lata by the 870s.
667:
under a
Rashtrakuta branch. The Kingdom of Kannauj constituted a vast prosperous region to the centre of northern India and seeing the instability of the kingdom due to the recent coup, the three powers were hoping to succeed to the throne of Kannauj.
444:, (550–560) was the first prominent king of Kannauj. He pursued a policy of agression against the emperors of Magadha and thus declared his independence, proclaiming himself Maharajadhiraja of Kannauj. He invaded the Andhra country and defeated the
794:
Following the deposition of the
Ayudhas, and proclamation of Nagabhata II as king of Kannauj, the Pratiharas became the rulers of the Kingdom of Kannauj to which they added their dominions of Gurjaradesa as well. Nagabhata II was succeeded by
1813:
Budhagupta impressed by Harivarman, conferred on him the honorific title of "Maharaja" and assigned him the important regions of Ayodhya, Kanyakubja to the east of the river Ganga (in modern Uttar Pradesh) and Antarvedi or the Ganga-Yamuna
939:, the Kingdom of Thanesar, i.e., eastern Punjab and the Trans-Gangetic Plain was merged into the Kingdom of Kannauj. Harshavardhan's campaigns expanded the empire of Kannauj to include the entirety of the Gangetic plain and eastern
766:, seeking revenge and taking advantage of the succession crisis in the Rashtrakuta Empire, invaded Kannauj and defeated Dharmapala and made Chakrayudha his vassal. Before he could invade Bengal however, the new Rashtrakuta Emperor
427:
The nobles and elites of the doab opposed his rule, but he eventually subdued them with military prowess and diplomacy. His rule emphasised moral rightness and benevolence and he allied with other prominent families such as the
2042:
Pañcāla (Ramnagar area of U.P.), Kuru (eastern Punjab), Madra (Central Punjab), Avanti (Malwa), Yadus (Mathura or Dwarka or Siṁhapura in the Punjab), Matsya (a part of northeast Rajputana) were his vassals.
1748:
They explain that Budhagupta had selected this youth for public service as early as 168 GS (487 CE) if not earlier. This view is largely based on an interpretation of an inscription called the "Shankarpur
408:, had a well-built physique, excellent archery skill, and a fierce face but a great calmness inside, a strict moral code and sensitivity to public sufferings. Impressed by him, the emperor crowned
919:
After Rajyapala's demise, his successors persisted in maintaining control over certain territories by relocating their capital to Bari, near Kannauj, until the demise of the last ruler
2166:
759:
defeated the Gurjara Empire and Vatsaraja fled his empire, while Dhruva returned to his empire. Bengal re-installed Chakrayudha as the King of Kannauj and its vassal.
233:
208:
834:(r. 913–944), the Manyakheta Rashtrakutas sacked Kannauj in 916, causing a weakening of the imperial power. This was also the period during which they used the title
1055:
604:. Though Kannauj records claim that he was victorious over Kashmir, Kashimri records claim that Yashovarman was defeated by the Kashmir king. He was succeeded by
2643:
893:
In January 1019, Mahmud of Ghazni reached Kannauj. Surprisingly, Rajyapala, the then king of Kannauj, offered no resistance and fled his capital by crossing the
2648:
683:, the Gurjara Emperor invaded Kannauj, made Indrayudha his vassal. Indrayudha continued rule over Kannauj under the suzerainty of the Gurjara emperor.
331:
declared himself the king of Kannauj. For nearly half a century, between 890 and 944, the kings of Kannauj also bore the imperial title of 'Emperor of
647:. This destabilised the political climate of eighth century northern India. Much of India at that time was under the rule of three great powers — the
335:'. However, after this period, the empire began to fragment as its vassals gradually declared their independence, eventually reducing the kingdom to
2658:
1946:
Cathay and the Way Thither: Preliminary essay on the intercourse between China and the western nations previous to the discovery of the Cape route
2638:
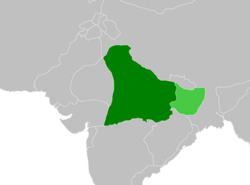
1074:
481:
who fled to Malwa (the remaining western portion of the empire) and established a rump state. His reign was followed by that of Avantivarman.
2653:
308:
during this period, and hence was contested by the three great powers of the subcontinent of the period — the Gurjara kingdom under the
1677:
762:
After the death of Dhruva in 793, the Rashtrakuta Empire fell into a war of succession. In the Gurjara Empire, the son of Vatsaraja,
2173:
885:
declared their independence during the tenth century as well. This reduced the Kingdom of Kannauj to the Ganga Yamuna Doab region.
823:
Bhoja also defeated the Arab invasions from Sindh into Kutch in 838 in the Battle of Sindhan, and conquered a portion of Sindh.
2139:
2109:
2082:
2034:
2007:
1713:
1446:
510:. Rajyavardhan the then king of Kannauj and brother of Rajyashri, defeated Devagupta but was himself killed by the king of
1942:
775:
invaded the Kingdom of Kannauj and conquered it and proclaimed himself as the king of Kannauj after deposing the Ayudhas.
857:
Mahipala was followed his son, Devapala I (r. 944–954), during whose decade-long reign the empire began to crumble away.
449:
1954:
1943:
Odorico (da Pordenone); Rashīd al-Dīn Ṭabīb; Francesco Balducci Pegolotti; Joannes de Marignolis; Ibn Batuta (1998).
1879:
1655:
1769:
A section of modern historians conclude that Harivarman was originally from Baghelkhand (in modern Madhya Pradesh)
2329:
812:
404:
met the young Harivarman in 487 AD, when he was choosing men for his public service. Harivarman, a warrior from
695:, the Emperor of Bengal invaded Kannauj and deposed Indrayudha and replaced him with Indrayudha's brother,
343:
in the early eleventh century, the kingdom came to an end and the prestige of Kannauj slowly dwindled, and
2633:
2628:
2223:
913:
1853:
2602:
909:
862:
1355:
Nagabhata conquers Kannauj and deposes the Ayudhas, and declares himself as the emperor of Kannauj.
830:(r. 890–910) who further expanded into the territories of the empire of Bengal. During the reign of
2663:
2607:
2250:
2238:
1285:
1268:
1251:
1234:
1204:
955:
581:
571:
699:
whom he made his vassal at an imperial court at Kannauj attended by the rulers of Bhoja (possibly
2493:
2159:
551:). Since Harsha had no heir, Arunasva usurped the throne. Arunavasa repelled an invasion by the
65:
2524:
2397:
2292:
901:. In his absence, Ghaznavid forces ransacked Kannauj, seizing a substantial amount of plunder.
870:
728:
398:
2024:
1703:
908:
Rajyapala's surrender to the Ghaznavids had consequences, leading to some turn of events. The
2566:
2456:
1997:
1869:
1645:
640:
1835:
managed to quickly outsmart his opponents and assume full control of his assigned provinces.
1671:
751:). This obviously led to war and the Gurjara Empire defeated Bengal and the Gurjara Emperor
558:. He had attacked the envoy of the Chinese emperor who had came earlier during the reign of
2556:
2446:
2341:
2190:
1944:
164:
8:
2551:
2505:
2466:
2314:
2208:
1728:
629:
466:
935:
and parts of middle Gangetic basin during its early stages. Following the coronation of
2581:
2576:
2561:
2519:
2476:
2471:
2402:
2387:
2265:
2260:
2218:
2213:
1925:
756:
555:
2461:
2412:
2382:
2360:
2355:
2309:
2297:
2135:
2105:
2078:
2030:
2003:
1971:
1950:
1875:
1709:
1651:
882:
784:
732:
664:
652:
499:
421:
309:
125:
1986:
Shyam Manohar Mishra (1977). Yaśovarman of Kanauj. Abhinav. pp. 120–121 OCLC 5782454
2586:
2451:
2434:
2429:
2407:
2392:
2324:
2287:
2228:
1614:
1280:
878:
613:
544:
511:
388:
340:
226:
966:, and significant power and territory was lost as the kingdom transitioned into a
298:, flourishing in the seventh century, and again in the ninth and tenth centuries.
2534:
2481:
2417:
2270:
2243:
2129:
2099:
2072:
2055:
1896:
1848:
1827:
1806:
1782:
1762:
1741:
1486:
916:, along with his allies, took matters into their own hands and killed Rajyapala.
601:
1203:
usurps the throne after Harsha's death. After Arunasva, Yashovarman establishes
2539:
2529:
2439:
2280:
2275:
2182:
1426:
1345:
1328:
1311:
1296:
1007:
932:
842:
827:
740:
712:
704:
648:
644:
625:
523:
295:
271:
264:
179:
42:
2622:
2571:
2319:
1793:
Like Krishnagupta, Hari had a strong physique and was a master archer himself
1699:
1185:
1172:
1113:
1011:
936:
835:
748:
478:
445:
213:
52:
2544:
2422:
2375:
2198:
1914:"Identification of Cha-Po-Ho-Lo and ITS Master A-Lo-Na-Shun (A. D. 647-48)"
1405:
1365:
1093:
967:
963:
772:
763:
660:
656:
589:
462:
441:
429:
328:
317:
313:
279:
275:
71:
2370:
2302:
2233:
1340:
1229:
1190:
1168:
1153:
971:
944:
898:
767:
696:
577:
507:
495:
474:
405:
376:
352:
305:
1929:
1913:
2365:
1466:
1385:
1323:
1306:
1035:
1015:
978:
831:
796:
692:
676:
409:
401:
372:
321:
291:
151:
105:
2060:
Centre for Rajasthan Studies, University of Rajasthan. pp. 91–92.
1999:
Land of Two Rivers: A History of Bengal from the Mahabharata to Mujib
1619:
1599:
1581:
1563:
1545:
1527:
1509:
1491:
1471:
1451:
1431:
1411:
1390:
1370:
920:
877:
declared its independence in 950. Other kingdoms such as that of the
866:
858:
846:
838:
752:
680:
503:
502:, the King of Thanesar as a part of an alliance. Mahasenagupta's son
348:
332:
283:
2057:
History and Culture of Rajasthan: From Earliest Times Upto 1956 A.D.
811:(r. 836–885), one of the greatest rulers of Kannauj. He invaded the
2255:
1214:
1200:
1158:
1138:
1118:
1098:
1079:
1060:
1040:
1019:
744:
700:
540:
413:
336:
267:
115:
95:
2488:
2151:
1263:
1023:
808:
720:
609:
597:
470:
417:
301:
294:, the Kingdom of Kannauj stood among the most powerful states in
85:
959:
940:
894:
874:
736:
724:
593:
585:
559:
287:
58:
1246:
605:
948:
708:
548:
344:
339:
region by the late tenth century. Following invasions of the
251:
958:, the Kingdom of Kannauj lost control over Malwa and later
716:
552:
416:
of Kannauj and granting him rule over the regions around
2022:
1949:. Munshiram Manoharlal Publishers Pvt. Ltd. p. 69.
327:
Following his victory in 816, the king of the Gurjaras,
865:, also declared his independence in 944 (in modern-day
465:(560–575) invaded and conquered eastern portion of the
1729:
https://journals.du.ac.in/humsoc/pdf/ZHANG%20Harsa.pdf
484:
2054:
Ratnawat, Shyam Singh; Sharma, Krishna Gopal (1999).
1894:
498:(r. 600–605) who married Rajyashri, the daughter of
679:succeeded to the throne of Kannauj in 770. In 785,
600:. Conflicting records exist regarding his war with
1995:
70:The Kingdom of Kannauj in 850 during the reign of
57:The Kingdom of Kannauj in 634 during the reign of
771:Bengal Empire until 816 when the Gurjara Emperor
2620:
132:
1898:Dynastic History of Magadha, Cir. 450-1200 A.D.
382:
2644:States and territories established in the 510s
2053:
2649:States and territories disestablished in 1036
2167:
1698:
1692:
778:
1825:
1804:
1780:
1760:
1739:
2134:. New Age International. pp. 345–355.
1171:is killed in war and the King of Thanesar,
931:The Kingdom of Kannauj dominated the upper
2174:
2160:
2074:History of Medieval India (1000-1740 A.D.)
1989:
1918:Proceedings of the Indian History Congress
826:His reign was followed by that of his son
64:
51:
41:
2016:
1871:History of Kanauj: To the Moslem Conquest
1708:. Motilal Banarsidass. pp. 282–285.
1647:History of Kanauj: To the Moslem Conquest
962:. Other territories were lost during the
2104:. Rupa & Company. pp. 192–193.
1874:. Motilal Banarsidass Publ. p. 40.
1867:
1650:. Motilal Banarsidass Publ. p. 36.
1643:
1299:rule over Kannauj after deposing Bhoja.
584:. Yashovarman led military campaigns in
543:who had previously been the governor of
432:. His reign was followed by that of his
69:
2659:11th-century disestablishments in India
2131:Ancient Indian History and Civilization
2002:. Penguin Books India. pp. 41–42.
539:Harsha's rule was succeeded by that of
274:from 510, when it was established as a
2639:Medieval empires and kingdoms of India
2621:
2070:
1911:
1664:
755:occupied Kannauj. Rashtrakuta Emperor
619:
282:, until 1036, when it collapsed after
2155:
2123:
2121:
2097:
2029:. Abhinav Publications. p. 177.
1969:
1790:sensitive to the suffering of others.
926:
494:Avantivarman's reign was followed by
363:The kingdom was also referred to as
2077:. Konark Publishers. pp. 8–10.
2654:6th-century establishments in India
2127:
807:Rambhadra was followed by his son,
715:(Haryana-Delhi-Western UP region),
707:(Jaipur and north-east Rajasthan),
485:Kannauj–Malwa War and Harshavardhan
13:
2181:
2118:
347:became the most important city of
304:became the most important city in
14:
2675:
2023:Bindeshwari Prasad Sinha (1977).
1680:from the original on 8 March 2024
371:during diplomatic exchanges with
1970:Virji, krishnakumari J. (1952).
984:
517:
231:
206:
2091:
2064:
2047:
1980:
1963:
1936:
1905:
1888:
1861:
1846:
1840:
1175:is crowned Emperor of Kannauj.
897:, ultimately seeking refuge in
789:
529:
506:invaded the Kannauj and killed
456:
435:
312:, the Bengal kingdom under the
1819:
1798:
1774:
1754:
1733:
1722:
1676:. Upkar Prakashan. p. 9.
1637:
686:
565:
489:
1:
1973:Ancient History Of Saurashtra
1630:
852:
671:
639:In 770, Bhoja was deposed by
634:
393:
47:The Kingdom of Kannauj in 575
2128:Sen, Sailendra Nath (1999).
888:
383:Establishment and early rule
7:
2026:Dynastic History of Magadha
1996:Nitish K. Sengupta (2011).
534:
10:
2680:
1895:Bindeshwari Prasad Sinha.
1868:Tripathi, Rama S. (1989).
1854:World History Encyclopedia
1644:Tripathi, Rama S. (1989).
802:
782:
779:Pratihara rule and decline
623:
576:Arunasva was succeeded by
569:
386:
379:in Sanskrit within India.
2603:Template:History of India
2595:
2504:
2340:
2189:
1912:Mishra, Yogendra (1977).
1354:
1294:
1199:
1167:
1005:
420:, Kannauj and Antarvedi (
247:
185:
175:
171:
158:
145:
141:
131:
121:
111:
101:
91:
81:
38:
33:
23:
2608:Template:Medieval Deccan
572:Varman dynasty (Kannauj)
522:Following these events,
358:
1295:Vajrayudha establishes
729:Siṁhapura in the Punjab
92:Official languages
2398:Kingdom of Bundelkhand
2293:Kingdom of Anahilavada
2101:A History of Rajasthan
2071:Sharma, L. P. (1989).
905:control over Kannauj.
871:Kingdom of Bundelkhand
616:who were weak rulers.
290:, and later under the
286:. During the reign of
16:Kingdom in North India
2567:Sultanate of Khandesh
2403:Kingdom of Trikalinga
2346:(Post Tripartite Era)
2251:Kingdom of Mahishmati
691:In response to this,
102:Common languages
2557:Sultanate of Gujarat
2447:Kingdom of Jaisalmer
2098:Hooja, Rima (2006).
580:who established the
440:His great-grandson,
2552:Sultanate of Bengal
2467:Sultanate of Multan
2356:Kingdom of Junagadh
2342:Middle Medieval Era
2315:Tripartite Struggle
2256:Kingdom of Samatata
2209:Kingdom of Thanesar
1829:Age of Pi and Prose
1808:Age of Pi and Prose
1784:Age of Pi and Prose
1764:Age of Pi and Prose
1743:Age of Pi and Prose
1207:rule over Kannauj.
630:Tripartite struggle
620:Tripartite Struggle
461:Ishvavarman's son,
284:Ghaznavid invasions
180:Early Mediaeval Era
2634:History of Kannauj
2629:Kingdom of Kannauj
2577:Kingdom of Bikaner
2562:Sultanate of Malwa
2520:Sultanate of Delhi
2472:Kingdom of Mithila
2457:Kingdom of Kalyani
2388:Kingdom of Sambhar
2383:Kingdom of Amarkot
2266:Kingdom of Kashmir
2219:Kingdom of Gurjara
2214:Kingdom of Valabhi
2204:Kingdom of Kannauj
2191:Early Medieval Era
1849:"Maukhari Dynasty"
1826:Venkatesh Rangan.
1805:Venkatesh Rangan.
1781:Venkatesh Rangan.
1761:Venkatesh Rangan.
1740:Venkatesh Rangan.
1673:Pratiyogita Darpan
927:Territorial extent
841:(ancient name for
556:Rashidun Caliphate
547:(modern-day north
261:Kingdom of Kannauj
25:Kingdom of Kannauj
2616:
2615:
2587:Kingdom of Orissa
2506:Late Medieval Era
2462:Kingdom of Marwar
2413:Kingdom of Bengal
2361:Emirate of Multan
2310:Kingdom of Dahala
2298:Kingdom of Bengal
2141:978-81-224-1198-0
2111:978-81-291-0890-6
2084:978-81-220-0042-9
2036:978-81-7017-059-4
2009:978-0-14-341678-4
1715:978-81-208-0436-4
1628:
1627:
943:, as well as the
883:Kingdom of Dahala
785:Pratihara dynasty
733:Katas Raj Temples
665:Manyakheta empire
653:Pratihara dynasty
651:under the Rajput
500:Prabhakarvardhana
422:Ganga-Yamuna Doab
310:Pratihara dynasty
257:
256:
243:
242:
239:
238:
219:
218:
160:• 1024–1036
126:Absolute monarchy
2671:
2582:Kingdom of Mewat
2572:Kingdom of Sindh
2512:
2511:
2489:Lords of Magadha
2452:Kingdom of Kutch
2435:Kingdom of Sindh
2430:Kingdom of Amber
2408:Kingdom of Malwa
2393:Kingdom of Mewar
2348:
2347:
2288:Kingdom of Gauda
2261:Kingdom of Nepal
2229:Kingdom of Sindh
2224:Kingdom of Malwa
2176:
2169:
2162:
2153:
2152:
2146:
2145:
2125:
2116:
2115:
2095:
2089:
2088:
2068:
2062:
2061:
2051:
2045:
2044:
2020:
2014:
2013:
1993:
1987:
1984:
1978:
1977:
1967:
1961:
1960:
1940:
1934:
1933:
1909:
1903:
1902:
1892:
1886:
1885:
1865:
1859:
1858:
1844:
1838:
1837:
1823:
1817:
1816:
1802:
1796:
1795:
1778:
1772:
1771:
1758:
1752:
1751:
1737:
1731:
1726:
1720:
1719:
1696:
1690:
1689:
1687:
1685:
1668:
1662:
1661:
1641:
1125:
989:
988:
879:Tomaras of Delhi
836:King of Kings of
450:Madhava Varma IV
399:Magadhan emperor
389:Maukhari dynasty
341:Ghaznavid Empire
235:
234:
227:Ghaznavid Empire
223:
222:
210:
209:
203:
202:
187:
186:
75:
68:
61:
55:
48:
45:
28:Kānyakubja Rājya
21:
20:
2679:
2678:
2674:
2673:
2672:
2670:
2669:
2668:
2664:Former kingdoms
2619:
2618:
2617:
2612:
2591:
2510:(Sultanate Era)
2509:
2508:
2507:
2500:
2345:
2344:
2343:
2336:
2320:Kingdom of Lata
2199:Magadhan Empire
2185:
2180:
2150:
2149:
2142:
2126:
2119:
2112:
2096:
2092:
2085:
2069:
2065:
2052:
2048:
2037:
2021:
2017:
2010:
1994:
1990:
1985:
1981:
1968:
1964:
1957:
1941:
1937:
1910:
1906:
1893:
1889:
1882:
1866:
1862:
1847:Lal, Avantika.
1845:
1841:
1824:
1820:
1803:
1799:
1792:
1791:
1779:
1775:
1759:
1755:
1738:
1734:
1727:
1723:
1716:
1697:
1693:
1683:
1681:
1670:
1669:
1665:
1658:
1642:
1638:
1633:
1610:Maharajadhiraja
1596:Trilochanapala
1592:Maharajadhiraja
1574:Maharajadhiraja
1556:Maharajadhiraja
1538:Maharajadhiraja
1520:Maharajadhiraja
1502:Maharajadhiraja
1487:Mahendrapala II
1482:Maharajadhiraja
1462:Maharajadhiraja
1442:Maharajadhiraja
1422:Maharajadhiraja
1401:Maharajadhiraja
1381:Maharajadhiraja
1361:Maharajadhiraja
1123:
987:
929:
891:
863:King of Sambhar
855:
813:Kingdom of Lata
805:
792:
787:
781:
711:(East Punjab),
689:
674:
637:
632:
624:Main articles:
622:
574:
568:
537:
532:
520:
492:
487:
467:Magadhan Empire
459:
438:
396:
391:
385:
361:
280:Magadhan Empire
232:
207:
161:
148:
147:• 510–520
77:
76:
62:
56:
49:
46:
29:
26:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2677:
2667:
2666:
2661:
2656:
2651:
2646:
2641:
2636:
2631:
2614:
2613:
2611:
2610:
2605:
2599:
2597:
2593:
2592:
2590:
2589:
2584:
2579:
2574:
2569:
2564:
2559:
2554:
2549:
2548:
2547:
2542:
2537:
2532:
2527:
2516:
2514:
2502:
2501:
2499:
2498:
2497:
2496:
2486:
2485:
2484:
2479:
2469:
2464:
2459:
2454:
2449:
2444:
2443:
2442:
2432:
2427:
2426:
2425:
2420:
2410:
2405:
2400:
2395:
2390:
2385:
2380:
2379:
2378:
2373:
2363:
2358:
2352:
2350:
2338:
2337:
2335:
2334:
2333:
2332:
2327:
2317:
2312:
2307:
2306:
2305:
2295:
2290:
2285:
2284:
2283:
2278:
2273:
2263:
2258:
2253:
2248:
2247:
2246:
2241:
2236:
2226:
2221:
2216:
2211:
2206:
2201:
2195:
2193:
2187:
2186:
2183:Medieval India
2179:
2178:
2171:
2164:
2156:
2148:
2147:
2140:
2117:
2110:
2090:
2083:
2063:
2046:
2035:
2015:
2008:
1988:
1979:
1962:
1955:
1935:
1904:
1887:
1880:
1860:
1839:
1818:
1797:
1773:
1753:
1732:
1721:
1714:
1691:
1663:
1656:
1635:
1634:
1632:
1629:
1626:
1625:
1622:
1617:
1612:
1606:
1605:
1602:
1597:
1594:
1588:
1587:
1584:
1579:
1576:
1570:
1569:
1566:
1561:
1560:Vijayapala II
1558:
1552:
1551:
1548:
1543:
1540:
1534:
1533:
1530:
1525:
1522:
1516:
1515:
1512:
1507:
1504:
1498:
1497:
1494:
1489:
1484:
1478:
1477:
1474:
1469:
1464:
1458:
1457:
1454:
1449:
1444:
1438:
1437:
1434:
1429:
1427:Mahendrapala I
1424:
1418:
1417:
1414:
1409:
1403:
1397:
1396:
1393:
1388:
1383:
1377:
1376:
1373:
1368:
1363:
1357:
1356:
1352:
1351:
1348:
1343:
1338:
1335:
1334:
1331:
1326:
1321:
1318:
1317:
1314:
1309:
1304:
1301:
1300:
1292:
1291:
1288:
1283:
1278:
1275:
1274:
1271:
1266:
1261:
1258:
1257:
1254:
1249:
1244:
1241:
1240:
1237:
1232:
1227:
1224:
1223:
1220:
1217:
1212:
1209:
1208:
1197:
1196:
1193:
1188:
1183:
1177:
1176:
1165:
1164:
1161:
1156:
1151:
1145:
1144:
1141:
1136:
1133:
1127:
1126:
1121:
1116:
1111:
1105:
1104:
1101:
1096:
1091:
1085:
1084:
1082:
1077:
1072:
1066:
1065:
1063:
1058:
1053:
1047:
1046:
1043:
1038:
1033:
1027:
1026:
1008:Narasimhagupta
1003:
1002:
999:
996:
993:
986:
983:
933:Gangetic basin
928:
925:
890:
887:
854:
851:
843:northern India
828:Mahendrapala I
804:
801:
799:(r. 833–836).
791:
788:
783:Main article:
780:
777:
688:
685:
673:
670:
649:Gurjara Empire
645:Ayudha dynasty
636:
633:
626:Ayudha dynasty
621:
618:
582:Varman dynasty
570:Main article:
567:
564:
536:
533:
531:
528:
524:Harshavardhana
519:
516:
491:
488:
486:
483:
458:
455:
446:king of Andhra
437:
434:
395:
392:
387:Main article:
384:
381:
365:Middle Country
360:
357:
272:northern India
255:
254:
249:
245:
244:
241:
240:
237:
236:
229:
220:
217:
216:
214:Magadha Empire
211:
199:
198:
193:
183:
182:
177:
176:Historical era
173:
172:
169:
168:
162:
159:
156:
155:
149:
146:
143:
142:
139:
138:
135:
129:
128:
123:
119:
118:
113:
109:
108:
103:
99:
98:
93:
89:
88:
83:
79:
78:
63:
50:
40:
39:
36:
35:
31:
30:
27:
24:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2676:
2665:
2662:
2660:
2657:
2655:
2652:
2650:
2647:
2645:
2642:
2640:
2637:
2635:
2632:
2630:
2627:
2626:
2624:
2609:
2606:
2604:
2601:
2600:
2598:
2594:
2588:
2585:
2583:
2580:
2578:
2575:
2573:
2570:
2568:
2565:
2563:
2560:
2558:
2555:
2553:
2550:
2546:
2543:
2541:
2538:
2536:
2533:
2531:
2528:
2526:
2523:
2522:
2521:
2518:
2517:
2515:
2513:
2503:
2495:
2492:
2491:
2490:
2487:
2483:
2480:
2478:
2475:
2474:
2473:
2470:
2468:
2465:
2463:
2460:
2458:
2455:
2453:
2450:
2448:
2445:
2441:
2438:
2437:
2436:
2433:
2431:
2428:
2424:
2421:
2419:
2416:
2415:
2414:
2411:
2409:
2406:
2404:
2401:
2399:
2396:
2394:
2391:
2389:
2386:
2384:
2381:
2377:
2374:
2372:
2369:
2368:
2367:
2364:
2362:
2359:
2357:
2354:
2353:
2351:
2349:
2339:
2331:
2328:
2326:
2323:
2322:
2321:
2318:
2316:
2313:
2311:
2308:
2304:
2301:
2300:
2299:
2296:
2294:
2291:
2289:
2286:
2282:
2279:
2277:
2274:
2272:
2269:
2268:
2267:
2264:
2262:
2259:
2257:
2254:
2252:
2249:
2245:
2242:
2240:
2237:
2235:
2232:
2231:
2230:
2227:
2225:
2222:
2220:
2217:
2215:
2212:
2210:
2207:
2205:
2202:
2200:
2197:
2196:
2194:
2192:
2188:
2184:
2177:
2172:
2170:
2165:
2163:
2158:
2157:
2154:
2143:
2137:
2133:
2132:
2124:
2122:
2113:
2107:
2103:
2102:
2094:
2086:
2080:
2076:
2075:
2067:
2059:
2058:
2050:
2043:
2038:
2032:
2028:
2027:
2019:
2011:
2005:
2001:
2000:
1992:
1983:
1975:
1974:
1966:
1958:
1956:9788121508391
1952:
1948:
1947:
1939:
1931:
1927:
1923:
1919:
1915:
1908:
1900:
1899:
1891:
1883:
1881:9788120804043
1877:
1873:
1872:
1864:
1856:
1855:
1850:
1843:
1836:
1831:
1830:
1822:
1815:
1810:
1809:
1801:
1794:
1786:
1785:
1777:
1770:
1766:
1765:
1757:
1750:
1745:
1744:
1736:
1730:
1725:
1717:
1711:
1707:
1706:
1705:Ancient India
1701:
1700:R.C. Majumdar
1695:
1679:
1675:
1674:
1667:
1659:
1657:9788120804043
1653:
1649:
1648:
1640:
1636:
1623:
1621:
1618:
1616:
1613:
1611:
1608:
1607:
1603:
1601:
1598:
1595:
1593:
1590:
1589:
1585:
1583:
1580:
1577:
1575:
1572:
1571:
1567:
1565:
1562:
1559:
1557:
1554:
1553:
1549:
1547:
1544:
1541:
1539:
1536:
1535:
1531:
1529:
1526:
1524:Vinayakapala
1523:
1521:
1518:
1517:
1513:
1511:
1508:
1505:
1503:
1500:
1499:
1495:
1493:
1490:
1488:
1485:
1483:
1480:
1479:
1475:
1473:
1470:
1468:
1465:
1463:
1460:
1459:
1455:
1453:
1450:
1448:
1445:
1443:
1440:
1439:
1435:
1433:
1430:
1428:
1425:
1423:
1420:
1419:
1415:
1413:
1410:
1407:
1404:
1402:
1399:
1398:
1394:
1392:
1389:
1387:
1384:
1382:
1379:
1378:
1374:
1372:
1369:
1367:
1364:
1362:
1359:
1358:
1353:
1349:
1347:
1344:
1342:
1339:
1337:
1336:
1332:
1330:
1327:
1325:
1322:
1320:
1319:
1315:
1313:
1310:
1308:
1305:
1303:
1302:
1298:
1293:
1289:
1287:
1284:
1282:
1279:
1277:
1276:
1272:
1270:
1267:
1265:
1262:
1260:
1259:
1255:
1253:
1250:
1248:
1245:
1243:
1242:
1238:
1236:
1233:
1231:
1228:
1226:
1225:
1221:
1218:
1216:
1213:
1211:
1210:
1206:
1202:
1198:
1194:
1192:
1189:
1187:
1186:Harshavardhan
1184:
1182:
1181:Maharadhiraja
1179:
1178:
1174:
1173:Harshavardhan
1170:
1166:
1162:
1160:
1157:
1155:
1152:
1150:
1149:Maharadhiraja
1147:
1146:
1142:
1140:
1137:
1135:Avantivarman
1134:
1132:
1131:Maharadhiraja
1129:
1128:
1122:
1120:
1117:
1115:
1112:
1110:
1109:Maharadhiraja
1107:
1106:
1102:
1100:
1097:
1095:
1092:
1090:
1089:Maharadhiraja
1087:
1086:
1083:
1081:
1078:
1076:
1075:Ishvaravarman
1073:
1071:
1068:
1067:
1064:
1062:
1059:
1057:
1054:
1052:
1049:
1048:
1044:
1042:
1039:
1037:
1034:
1032:
1029:
1028:
1025:
1021:
1017:
1013:
1009:
1004:
1000:
997:
994:
991:
990:
985:List of kings
982:
980:
975:
973:
969:
965:
961:
957:
952:
950:
946:
942:
938:
937:Harshavardhan
934:
924:
922:
917:
915:
911:
906:
902:
900:
896:
886:
884:
880:
876:
872:
868:
864:
860:
850:
848:
844:
840:
837:
833:
829:
824:
821:
817:
814:
810:
800:
798:
786:
776:
774:
769:
765:
760:
758:
754:
750:
749:Kangra Valley
746:
742:
738:
734:
730:
726:
722:
718:
714:
710:
706:
702:
698:
694:
684:
682:
678:
669:
666:
662:
661:House of Pala
658:
657:Bengal Empire
654:
650:
646:
643:founding the
642:
631:
627:
617:
615:
611:
607:
603:
599:
595:
591:
587:
583:
579:
573:
563:
561:
557:
554:
550:
546:
542:
527:
525:
518:Harshavardhan
515:
513:
509:
505:
501:
497:
482:
480:
479:Mahasenagupta
476:
472:
468:
464:
454:
451:
447:
443:
433:
431:
425:
423:
419:
415:
411:
407:
403:
400:
390:
380:
378:
375:, as well as
374:
370:
366:
356:
354:
350:
346:
342:
338:
334:
330:
325:
323:
319:
315:
311:
307:
303:
299:
297:
293:
289:
285:
281:
277:
273:
269:
266:
262:
253:
250:
248:Today part of
246:
230:
228:
225:
224:
221:
215:
212:
205:
204:
201:
200:
197:
194:
192:
189:
188:
184:
181:
178:
174:
170:
166:
163:
157:
153:
150:
144:
140:
136:
134:
130:
127:
124:
120:
117:
114:
110:
107:
104:
100:
97:
94:
90:
87:
84:
80:
73:
67:
60:
54:
44:
37:
32:
22:
19:
2203:
2130:
2100:
2093:
2073:
2066:
2056:
2049:
2040:
2025:
2018:
1998:
1991:
1982:
1972:
1965:
1945:
1938:
1921:
1917:
1907:
1901:p. 120.
1897:
1890:
1870:
1863:
1852:
1842:
1833:
1828:
1821:
1812:
1807:
1800:
1788:
1783:
1776:
1768:
1763:
1756:
1747:
1742:
1735:
1724:
1704:
1694:
1682:. Retrieved
1672:
1666:
1646:
1639:
1609:
1591:
1573:
1555:
1542:Mahipala II
1537:
1519:
1501:
1481:
1461:
1441:
1421:
1406:Mihira Bhoja
1400:
1380:
1366:Nagabhata II
1360:
1180:
1148:
1130:
1114:Sharvavarman
1108:
1094:Ishanavarman
1088:
1069:
1056:Adityavarman
1050:
1030:
992:Royal title
976:
968:vassal state
964:Kannauj Wars
953:
930:
918:
907:
903:
892:
856:
825:
822:
818:
806:
793:
790:Nagabhata II
773:Nagabhata II
764:Nagabhata II
761:
690:
675:
638:
590:Indus Valley
575:
538:
530:Interwar era
521:
493:
463:Sharvavarman
460:
457:Sharvavarman
442:Ishanavarman
439:
436:Ishanavarman
430:later Guptas
426:
397:
369:Middle India
368:
364:
362:
329:Nagabhata II
326:
318:Rashtrakutas
314:Pala dynasty
300:
276:vassal state
260:
258:
196:Succeeded by
195:
190:
74:with vassals
18:
2366:Kabul Shahi
2330:Rashtrakuta
1924:: 117–121.
1684:15 November
1408:or Bhoja I
1341:Chakrayudha
1230:Yashovarman
1191:Pushyabhuti
1169:Grahavarman
1154:Grahavarman
945:Bundelkhand
910:Bundelkhand
895:Ganga River
768:Govinda III
697:Chakrayudha
687:Chakrayudha
578:Yashovarman
566:Yashovarman
508:Grahavarman
496:Grahavarman
490:Grahavarman
475:Bundelkhand
406:Baghelkhand
377:Madhyadesha
353:North India
306:North India
191:Preceded by
2623:Categories
2494:Pithipatis
1631:References
1624:1024–1036
1604:1018–1027
1467:Mahipala I
1386:Ramabhadra
1324:Indrayudha
1307:Vajrayudha
1036:Harivarman
1016:Harivarman
979:Pratiharas
977:Under the
954:Under the
914:Vidyadhara
853:Devapala I
832:Mahipala I
797:Ramabhadra
747:and Kira (
719:(possibly
693:Dharmapala
677:Indrayudha
672:Indrayudha
663:, and the
659:under the
641:Vajrayudha
635:Vajrayudha
545:Tirabhukti
410:Harivarman
402:Budhagupta
394:Harivarman
373:Tang China
322:Manyakheta
316:, and the
292:Pratiharas
152:Harivarman
122:Government
106:Shauraseni
1749:charter."
1620:Pratihara
1615:Yasahpala
1600:Pratihara
1586:960–1018
1582:Pratihara
1578:Rajapala
1564:Pratihara
1546:Pratihara
1528:Pratihara
1510:Pratihara
1506:Devapala
1492:Pratihara
1472:Pratihara
1452:Pratihara
1432:Pratihara
1412:Pratihara
1391:Pratihara
1371:Pratihara
1014:appoints
923:in 1036.
921:Yasahpala
889:Rajyapala
867:Rajasthan
859:Simharaja
847:Hindustan
839:Aryavarta
753:Vatsaraja
681:Vatsaraja
504:Devagupta
349:Hindustan
333:Aryavarta
165:Yasahpala
112:Religion
1930:44139059
1702:(1994).
1678:Archived
1568:956–960
1550:955–956
1532:954–955
1514:948–954
1496:944–948
1476:913–944
1456:910–913
1447:Bhoja II
1436:885–910
1416:836–885
1395:833–836
1375:800–833
1316:770–783
1239:725–752
1215:Arunasva
1201:Arunasva
1195:606–647
1163:600–605
1159:Maukhari
1143:586–600
1139:Maukhari
1119:Maukhari
1103:560–574
1099:Maukhari
1080:Maukhari
1070:Maharaja
1061:Maukhari
1051:Maharaja
1041:Maukhari
1031:Maharaja
1020:Maharaja
1006:Emperor
998:Dynasty
881:and the
745:Gandhara
701:Vidarbha
541:Arunasva
535:Arunasva
469:, i.e.,
414:Maharaja
337:the Doab
265:medieval
116:Hinduism
96:Sanskrit
34:510–1036
2596:Related
2535:Tughlaq
2482:Oiniwar
2418:Chandra
2325:Gurjara
2271:Karkota
2244:Habbari
2239:Brahman
1264:Dunduka
1124:574–586
1024:Kannauj
1018:as the
1012:Magadha
956:Varmans
869:). The
809:Bhoja I
803:Bhoja I
721:Mathura
610:Dunduka
602:Kashmir
598:Kashmir
471:Magadha
418:Ayodhya
412:as the
302:Kannauj
278:of the
268:kingdom
154:(first)
86:Kannauj
82:Capital
72:Bhoja I
2540:Sayyid
2530:Khalji
2525:Mamluk
2477:Karnat
2440:Soomra
2281:Lohara
2276:Utpala
2138:
2108:
2081:
2033:
2006:
1953:
1928:
1878:
1712:
1654:
1350:?–816
1346:Ayudha
1333:783–?
1329:Ayudha
1312:Ayudha
1297:Ayudha
1290:?–770
1286:Varman
1269:Varman
1256:752–?
1252:Varman
1235:Varman
1222:647–?
1205:Varman
1045:510–?
1001:Reign
972:Bengal
970:under
960:Bengal
941:Punjab
875:Dhanga
873:under
861:, the
757:Dhruva
741:Avanti
737:Yavana
725:Dwarka
705:Matsya
655:, the
594:Deccan
592:, the
586:Bengal
560:Harsha
288:Harsha
263:was a
167:(last)
137:
59:Harsha
2376:Hindu
1926:JSTOR
1814:Doab.
1281:Bhoja
995:Name
949:Malwa
912:king
709:Madra
614:Bhoja
549:Bihar
512:Gauda
477:from
359:Names
345:Delhi
296:India
252:India
2545:Lodi
2423:Sena
2371:Turk
2303:Pala
2136:ISBN
2106:ISBN
2079:ISBN
2031:ISBN
2004:ISBN
1951:ISBN
1876:ISBN
1710:ISBN
1686:2015
1652:ISBN
947:and
899:Bari
849:).
717:Yadu
713:Kuru
628:and
612:and
596:and
553:Arab
473:and
259:The
133:King
2234:Rai
1247:Āma
1022:of
1010:of
951:.
735:),
727:or
703:),
606:Ama
424:.
367:or
355:).
324:.
320:of
270:in
2625::
2120:^
2039:.
1922:38
1920:.
1916:.
1851:.
1832:.
1811:.
1787:.
1767:.
1746:.
1273:?
1219:?
974:.
743:,
739:,
723:,
608:,
588:,
562:.
514:.
448:,
2175:e
2168:t
2161:v
2144:.
2114:.
2087:.
2012:.
1976:.
1959:.
1932:.
1884:.
1857:.
1718:.
1688:.
1660:.
845:/
731:(
351:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.