960:
948:
986:
79:
55:. This angle varies at different points on Earth's surface. Positive values of inclination indicate that the magnetic field of Earth is pointing downward, into Earth, at the point of measurement, and negative values indicate that it is pointing upward. The dip angle is in principle the angle made by the needle of a vertically held compass, though in practice ordinary compass needles may be weighted against dip or may be unable to move freely in the correct plane. The value can be measured more reliably with a special instrument typically known as a
907:
913:
30:
22:
976:
To compensate for turning errors, pilots in the
Northern Hemisphere will have to "undershoot" the turn when turning north, stopping the turn prior to the compass rotating to the correct heading; and "overshoot" the turn when turning south by stopping later than the compass. The effect is the opposite
924:
is significantly lower than the pivot point. As a result, the vertical component of the magnetic force is too weak to tilt the compass card significantly out of the horizontal plane, thus minimizing the dip angle shown in the compass. However, this also causes the airplane's compass to give erroneous
972:
Magnetic dip shifts the center of gravity of the compass card, causing temporary inaccurate readings when turning north or south. As the aircraft turns, the force that results from the magnetic dip causes the float assembly to swing in the same direction that the float turns. This compass error is
993:
The acceleration errors occur because the compass card tilts on its mount when under acceleration. In the
Northern Hemisphere, when accelerating on either an easterly or westerly heading, the error appears as a turn indication toward the north. When decelerating on either of these headings, the
707:
531:
86:
Magnetic dip results from the tendency of a magnet to align itself with lines of magnetic field. As Earth's magnetic field lines are not parallel to the surface, the north end of a compass needle will point upward in the
989:
Acceleration error in the
Northern Hemisphere, during an airplane's acceleration, cruising, and deceleration stages. A mnemonic for remembering the direction is the word “ANDS” (Acceleration-North/Deceleration-South).
211:
312:
409:
254:
143:
is defined locally for the magnetic field due to Earth's core, and has a positive value if the field points below the horizontal (i.e. into Earth). Here we show how to determine the value of
831:
455:
874:
1084:
The newe attractive: shewing the nature, propertie, and manifold vertues of the loadstone: with the declination of the needle, touched therewith under the plaine of the horizon
1002:
Compass needles are often weighted during manufacture to compensate for magnetic dip, so that they will balance roughly horizontally. This balancing is latitude-dependent; see
757:
733:
359:
896:
540:
777:
332:
161:
141:
1213:
465:
910:
Magnetic dip causes the compass' pivoting point (marked by the green circle) to no longer overlap with its center of gravity (marked by
1164:
169:
259:
1045:
1257:
364:
216:
1182:
1065:
1286:
1219:
1115:
782:
1143:
417:
1223:
838:
920:
The phenomenon is especially important in aviation. Magnetic compasses on airplanes are made so that the
1147:
1139:
334:
denotes the core as the origin of these fields. The first means we can introduce the scalar potential
52:
738:
714:
1003:
994:
compass indicates a turn toward the south. The effect is the opposite in the
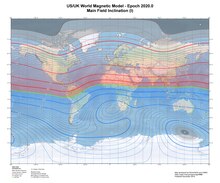
Southern Hemisphere.
1107:
1025:
1015:
337:
1240:. Federal Aviation Administration, US Department of Transportation. 2014. pp. 5–13, 5–14.
1057:
881:
1281:
412:
103:). Contour lines along which the dip measured at Earth's surface is equal are referred to as
1099:
702:{\displaystyle {\textbf {B}}_{c}=-\mu _{o}\nabla \phi _{c}={\frac {\mu _{o}}{4\pi }}{\big }}
1020:
985:
8:
100:
96:
92:
88:
1082:
762:
317:
146:
126:
1178:
1121:
1111:
1100:
1061:
1050:
921:
25:
Magnetic dip causes the compass to dip upward or downward depending on the latitude.
1170:
906:
78:
1261:
965:
In the
Southern Hemisphere, turning north causes the compass to "lead" the turn.
526:{\displaystyle \phi _{c}={\frac {{\textbf {m}}\cdot {\textbf {r}}}{4\pi r^{3}}}}
1266:
953:
In the
Northern Hemisphere, turning north causes the compass to "lag" the turn.
104:
63:
1254:
1275:
1174:
67:
1125:
912:
112:
29:
926:
56:
1102:
Looking into the earth : an introduction to geological geophysics
66:
in 1544. A method of measuring it with a dip circle was described by
759:
on Earth's surface. From here it can be shown that the inclination
166:
Outside Earth's core we consider
Maxwell's equations in a vacuum,
1169:. Higher Education from Cambridge University Press. p. 49.
21:
163:
at a given latitude, following the treatment given by Fowler.
16:
Angle made with the horizontal by Earth's magnetic field lines
460:
Solving to leading order gives the magnetic dipole potential
206:{\displaystyle \nabla \times {\textbf {H}}_{c}={\textbf {0}}}
95:(positive dip). The range of dip is from -90 degrees (at the
929:(turning error) and airspeed changes (acceleration error).
307:{\displaystyle {\textbf {B}}_{c}=\mu _{0}{\textbf {H}}_{c}}
107:. The locus of the points having zero dip is called the
973:
amplified with the proximity to either magnetic pole.
1166:
884:
841:
785:
765:
741:
717:
543:
468:
420:
411:, while the second means the potential satisfies the
367:
340:
320:
262:
219:
172:
149:
129:
404:{\displaystyle {\textbf {H}}_{c}=-\nabla \phi _{c}}
118:
1106:. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp.
1049:
940:Northerly turning error caused by the magnetic dip
890:
868:
825:
771:
751:
727:
701:
525:
449:
403:
353:
326:
306:
248:
205:
155:
135:
898:is the latitude of the point on Earth's surface.
33:Illustration of magnetic dip from Norman's book,
1273:
249:{\displaystyle \nabla \cdot {\textbf {B}}_{c}=0}
62:Dip angle was discovered by the German engineer
694:
614:
1222:. 24 August 2016. p. 26. Archived from
1097:
1238:Instrument Flying Handbook: FAA-H-8083-15B
1215:Pilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge
1098:Mussett, Alan E.; Khan, M. Aftab (2000).
1056:(First ed.). HarperCollins. p.
51:is the angle made with the horizontal by
984:
905:
826:{\displaystyle \tan I=B_{r}/B_{\theta }}
77:
28:
20:
901:
1274:
1207:
1205:
1203:
1201:
1162:
1080:
1044:
450:{\displaystyle \nabla ^{2}\phi _{c}=0}
1163:Fowler, C. M. R. (20 December 2004).
980:
869:{\displaystyle \tan I=2\tan \lambda }
1138:
1198:
744:
720:
674:
661:
646:
629:
547:
497:
487:
371:
293:
266:
229:
198:
182:
13:
574:
422:
388:
220:
173:
91:(negative dip) or downward in the
82:Isoclinic lines for the year 2020.
14:
1298:
1248:
1212:"Chapter 8: Flight Instruments".
779:as defined above satisfies (from
1004:Compass balancing (magnetic dip)
958:
946:
932:
911:
119:Calculation for a given latitude
1220:Federal Aviation Administration
1230:
1156:
1132:
1091:
1074:
1038:
666:
650:
639:
633:
73:
1:
1031:
752:{\displaystyle {\textbf {r}}}
728:{\displaystyle {\textbf {m}}}
997:
977:in the Southern Hemisphere.
53:Earth's magnetic field lines
7:
1267:Look up magnetic dip values
1218:(FAA-H-8083-25B ed.).
1009:
10:
1303:
354:{\displaystyle \phi _{c}}
99:) to +90 degrees (at the
1260:1 September 2006 at the
1175:10.1017/cbo9780511819643
1149:The Nuttall Encyclopædia
891:{\displaystyle \lambda }
1081:Norman, Robert (1581).
1287:Orientation (geometry)
1026:South Atlantic Anomaly
1016:Aircraft compass turns
990:
917:
892:
870:
827:
773:
753:
729:
703:
527:
451:
405:
355:
328:
308:
250:
207:
157:
137:
83:
37:
26:
988:
909:
893:
871:
828:
774:
754:
730:
704:
528:
452:
406:
356:
329:
309:
251:
208:
158:
138:
81:
32:
24:
1052:Human Accomplishment
1021:Magnetic declination
902:Practical importance
882:
839:
783:
763:
739:
735:and position vector
715:
711:for magnetic moment
541:
535:and hence the field
466:
418:
365:
338:
318:
260:
217:
170:
147:
127:
70:in England in 1581.
49:magnetic inclination
101:North Magnetic Pole
97:South Magnetic Pole
93:Northern Hemisphere
89:Southern Hemisphere
35:The Newe Attractive
991:
981:Acceleration error
918:
888:
866:
823:
769:
749:
725:
699:
523:
447:
401:
351:
324:
314:and the subscript
304:
246:
203:
153:
133:
84:
38:
27:
922:center of gravity
772:{\displaystyle I}
746:
722:
690:
676:
663:
653:
648:
636:
631:
610:
549:
521:
499:
489:
373:
327:{\displaystyle c}
295:
268:
231:
200:
184:
156:{\displaystyle I}
136:{\displaystyle I}
1294:
1242:
1241:
1234:
1228:
1227:
1226:on 20 June 2023.
1209:
1196:
1195:
1193:
1191:
1160:
1154:
1153:
1136:
1130:
1129:
1105:
1095:
1089:
1088:
1078:
1072:
1071:
1055:
1042:
962:
961:
950:
949:
925:readings during
915:
897:
895:
894:
889:
875:
873:
872:
867:
832:
830:
829:
824:
822:
821:
812:
807:
806:
778:
776:
775:
770:
758:
756:
755:
750:
748:
747:
734:
732:
731:
726:
724:
723:
708:
706:
705:
700:
698:
697:
691:
689:
688:
679:
678:
677:
665:
664:
655:
654:
649:
644:
638:
637:
632:
627:
620:
618:
617:
611:
609:
601:
600:
591:
586:
585:
573:
572:
557:
556:
551:
550:
532:
530:
529:
524:
522:
520:
519:
518:
502:
501:
500:
491:
490:
483:
478:
477:
456:
454:
453:
448:
440:
439:
430:
429:
413:Laplace equation
410:
408:
407:
402:
400:
399:
381:
380:
375:
374:
360:
358:
357:
352:
350:
349:
333:
331:
330:
325:
313:
311:
310:
305:
303:
302:
297:
296:
289:
288:
276:
275:
270:
269:
255:
253:
252:
247:
239:
238:
233:
232:
212:
210:
209:
204:
202:
201:
192:
191:
186:
185:
162:
160:
159:
154:
142:
140:
139:
134:
123:The inclination
109:magnetic equator
1302:
1301:
1297:
1296:
1295:
1293:
1292:
1291:
1272:
1271:
1262:Wayback Machine
1251:
1246:
1245:
1236:
1235:
1231:
1211:
1210:
1199:
1189:
1187:
1185:
1161:
1157:
1142:, ed. (1907) .
1137:
1133:
1118:
1096:
1092:
1079:
1075:
1068:
1046:Murray, Charles
1043:
1039:
1034:
1012:
1000:
983:
970:
969:
968:
967:
966:
963:
959:
955:
954:
951:
947:
942:
941:
935:
904:
883:
880:
879:
840:
837:
836:
817:
813:
808:
802:
798:
784:
781:
780:
764:
761:
760:
743:
742:
740:
737:
736:
719:
718:
716:
713:
712:
693:
692:
684:
680:
673:
672:
660:
659:
645:
643:
642:
628:
626:
625:
621:
619:
613:
612:
602:
596:
592:
590:
581:
577:
568:
564:
552:
546:
545:
544:
542:
539:
538:
514:
510:
503:
496:
495:
486:
485:
484:
482:
473:
469:
467:
464:
463:
435:
431:
425:
421:
419:
416:
415:
395:
391:
376:
370:
369:
368:
366:
363:
362:
345:
341:
339:
336:
335:
319:
316:
315:
298:
292:
291:
290:
284:
280:
271:
265:
264:
263:
261:
258:
257:
234:
228:
227:
226:
218:
215:
214:
197:
196:
187:
181:
180:
179:
171:
168:
167:
148:
145:
144:
128:
125:
124:
121:
105:isoclinic lines
76:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1300:
1290:
1289:
1284:
1270:
1269:
1264:
1255:Compass errors
1250:
1249:External links
1247:
1244:
1243:
1229:
1197:
1183:
1155:
1144:"Aclinic Line"
1131:
1116:
1090:
1073:
1066:
1036:
1035:
1033:
1030:
1029:
1028:
1023:
1018:
1011:
1008:
999:
996:
982:
979:
964:
957:
956:
952:
945:
944:
943:
939:
938:
937:
936:
934:
931:
903:
900:
887:
865:
862:
859:
856:
853:
850:
847:
844:
820:
816:
811:
805:
801:
797:
794:
791:
788:
768:
696:
687:
683:
671:
668:
658:
652:
641:
635:
624:
616:
608:
605:
599:
595:
589:
584:
580:
576:
571:
567:
563:
560:
555:
517:
513:
509:
506:
494:
481:
476:
472:
446:
443:
438:
434:
428:
424:
398:
394:
390:
387:
384:
379:
348:
344:
323:
301:
287:
283:
279:
274:
245:
242:
237:
225:
222:
195:
190:
178:
175:
152:
132:
120:
117:
75:
72:
64:Georg Hartmann
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1299:
1288:
1285:
1283:
1280:
1279:
1277:
1268:
1265:
1263:
1259:
1256:
1253:
1252:
1239:
1233:
1225:
1221:
1217:
1216:
1208:
1206:
1204:
1202:
1186:
1184:9780521893077
1180:
1176:
1172:
1168:
1167:
1159:
1151:
1150:
1145:
1141:
1135:
1127:
1123:
1119:
1113:
1109:
1104:
1103:
1094:
1086:
1085:
1077:
1069:
1067:9780060192471
1063:
1059:
1054:
1053:
1047:
1041:
1037:
1027:
1024:
1022:
1019:
1017:
1014:
1013:
1007:
1005:
995:
987:
978:
974:
933:Turning error
930:
928:
923:
914:
908:
899:
885:
876:
863:
860:
857:
854:
851:
848:
845:
842:
834:
818:
814:
809:
803:
799:
795:
792:
789:
786:
766:
709:
685:
681:
669:
656:
622:
606:
603:
597:
593:
587:
582:
578:
569:
565:
561:
558:
553:
536:
533:
515:
511:
507:
504:
492:
479:
474:
470:
461:
458:
444:
441:
436:
432:
426:
414:
396:
392:
385:
382:
377:
346:
342:
321:
299:
285:
281:
277:
272:
243:
240:
235:
223:
193:
188:
176:
164:
150:
130:
116:
114:
110:
106:
102:
98:
94:
90:
80:
71:
69:
68:Robert Norman
65:
60:
58:
54:
50:
46:
42:
36:
31:
23:
19:
1282:Geomagnetism
1237:
1232:
1224:the original
1214:
1188:. Retrieved
1165:
1158:
1148:
1134:
1101:
1093:
1083:
1076:
1051:
1040:
1001:
992:
975:
971:
927:banked turns
919:
877:
835:
710:
537:
534:
462:
459:
165:
122:
113:aclinic line
108:
85:
61:
48:
44:
41:Magnetic dip
40:
39:
34:
18:
1140:Wood, James
74:Explanation
1276:Categories
1190:13 January
1117:0521780853
1032:References
361:such that
57:dip circle
45:dip angle,
998:Balancing
886:λ
864:λ
861:
846:
819:θ
790:
670:−
657:⋅
651:^
634:^
607:π
594:μ
579:ϕ
575:∇
566:μ
562:−
508:π
493:⋅
471:ϕ
433:ϕ
423:∇
393:ϕ
389:∇
386:−
343:ϕ
282:μ
224:⋅
221:∇
177:×
174:∇
1258:Archived
1126:43227335
1048:(2003).
1010:See also
1181:
1124:
1114:
1064:
878:where
256:where
1192:2022
1179:ISBN
1122:OCLC
1112:ISBN
1062:ISBN
213:and
1171:doi
1108:140
1058:176
858:tan
843:tan
787:tan
111:or
47:or
1278::
1200:^
1177:.
1146:.
1120:.
1110:.
1060:.
1006:.
916:).
833:)
457:.
115:.
59:.
43:,
1194:.
1173::
1152:.
1128:.
1087:.
1070:.
855:2
852:=
849:I
815:B
810:/
804:r
800:B
796:=
793:I
767:I
745:r
721:m
695:]
686:3
682:r
675:m
667:)
662:m
647:r
640:(
630:r
623:3
615:[
604:4
598:o
588:=
583:c
570:o
559:=
554:c
548:B
516:3
512:r
505:4
498:r
488:m
480:=
475:c
445:0
442:=
437:c
427:2
397:c
383:=
378:c
372:H
347:c
322:c
300:c
294:H
286:0
278:=
273:c
267:B
244:0
241:=
236:c
230:B
199:0
194:=
189:c
183:H
151:I
131:I
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.