430:
334:. This process is also known as neurulation. The neural tube is where the central nervous system forms, which later on in development will be subdivided and differentiated into distinct sections of the brain and spinal cord. These subdivisions occur by signaling molecules that direct differentiated cells to their correct location of the organism. The bilateral sides of this structure then give rise to the two hemispheres of the Homo sapiens cortex but do not merge at any point besides the corpus callosum. As a result, the longitudinal fissure is formed. The longitudinal fissure can appear as early as the eighth week of development, and distinctly separates the two hemispheres by around the tenth gestational week.
588:
540:
516:
464:
shapes making it difficult to find a brain surgical procedure that will work effectively for them. One goal of the study was to distinguish the longitudinal cerebral fissure anatomy and their possible variations in brachy‐(B), dolicho‐(D) and mesaticephalic‐(M) dogs. Even though the lateral cerebral fissure morphology was uniform in the dog breeds. Mesaticephalic‐(M) dogs were found to have the greatest surgical passage resulting in access to more brain structures, while the dolicho‐(D) dogs had the smallest surgical passage.
600:
40:
576:
552:
528:
393:. These two components combined give the ability to have a larger perceived visual field, which coincides with the hypothesis that this is an adaptive function given by the fissures placement and structure. Damage to the nerve past the optic chiasm, will cause loss or impairment to the corresponding eye. If the right side of the brain is damaged and the nerve is damaged or destroyed, then the left eye will also follow the severity of damage.
338:
564:
473:
418:
partial callosotomy, or the entirety in the case of complete callosotomy. Without the presence of longitudinal fissure, the corpus callosotomy procedure would be significantly more challenging and dangerous, as it would require the surgeon to navigate through densely connected cortical areas. Following the procedure, the two hemispheres are no longer able to communicate with each other as before.
505:
484:), fiber bundles passing through are densely packed together, and precision tracking is essential to distinguish between the individual bundles that originate from and lead to the same cortical centers. Understanding such connections allows us to understand the contralateral concurrences and what diseases can result from lesions to them.
463:
The longitudinal fissure can serve as an effective surgical passage in the frontal bone during central and pterional craniotomies, which is opening into the skull by surgery. While there are variations in the head shapes of many species, dogs have been found to have a high variation in terms of head
385:, which takes the nerve from the right eye to the left hemisphere and the left eye to the right hemisphere. The longitudinal fissure allows for this misdirection and crossover of nerves. The crossover seems to be counterintuitive, however it does serve an adaptive purpose. This purpose is to give us
454:
tasks. Studies have analyzed the effects of the low-frequency rTMS on tests of time perception when the rTMS has been applied to the "parietal medial longitudinal fissure". Findings have shown evidence to support the hypothesis that participants in this study would underestimate their perception of
417:
cases, and it consists of the division of the nerve fibers running between the two hemispheres through the corpus callosum. A neurosurgeon separates the two hemispheres physically by pulling them apart with special tools, and cuts through either approximately two thirds of the fibers in the case of
283:
connects the two halves of the brain below the fissure and conveys visual, auditory, and somatosensory messages between each half. The corpus callosum is responsible for eye movement and visual perception, maintaining a balance between arousal and attention, and the ability to identify locations of
246:
is the name given to the dura mater in-between the two hemispheres, whose significance arises from the fact that it is the outermost layer of the meninges. These layers prevent any direct connectivity between the bilateral lobes of the cortex, thus requiring any tracts to pass through the corpus
421:
While patients’ brains usually adapt and allow for uninterrupted daily life, cognitive tests can easily determine whether a patient has split-brain. In an experiment involving a chimeric figure, with a woman’s face on the left half and a man’s face on the right half, a patient with split-brain
1265:
Manaia, Fernanda; Rocha, Kaline; Marinho, Victor; Magalhães, Francisco; Oliveira, Thomaz; Carvalho, Valécia; Araújo, Thalys; Ayres, Carla; Gupta, Daya; Velasques, Bruna; Ribeiro, Pedro (June 2019). "The role of low-frequency rTMS in the superior parietal cortex during time estimation".
1328:
Carreira, L., & Ferreira, A. (2015).Longitudinal cerebral fissure anatomy variations in brachy-, dolicho- and mesaticephalic dogs and their importance to brain surgery. The
Anatomical Record : Advances in Integrative Anatomy and Evolutionary Biology., 298(9), 1612–1621.
309:
animal is one that has symmetrical left and right body halves. While it is still debated whether this species had a complex brain or not, development of similar species support the hypothesis that it had at least a simple anterior collection of nerve cells, called a
492:(fMRI) is used to image these bundles. For instance, occipital-callosal fiber tracts were localized with 1–2 mm precision using DTI-TF techniques - which are very important for the cooperation of visual cortices, and any lesion to them can lead to
1362:
Rokem, A., Takemura, H., Bock, A. S., Scherf, K. S., Behrmann, M., Wandell, B. A., . . . Pestilli, F. (2017). The visual white matter: The application of diffusion MRI and fiber tractography to vision science. Journal of Vision, 17(2), 4.
370:. Through "split-brain experiments", the left hemisphere is shown to specialize in mathematics, language and general logistics. The right hemisphere is further specialized, generally, in music, art, facial recognition and in most
1345:
Dougherty, R. F., Ben-Shachar, M., Bammer, R., Brewer, A. A., & Wandell, B. A. (2005). Functional organization of human occipital-callosal fiber tracts. Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences, 102(20), 7350-7355.
823:
Mayer, G., Whitington, P. M., Sunnucks, P., & Pflüger, H. (2010). A revision of brain composition in
Onychophora (velvet worms) suggests that the tritocerebrum evolved in arthropods. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 10, 255.
455:
time for short amounts of time and overestimate for longer periods of time. Specifically, the 20 participants underestimated 1 second time intervals and overestimated 4 second/9 second intervals after applying 1-Hz rTMS.
807:
Hejnol, A., & Martindale, M. Q. (2008). Acoel development supports a simple planula-like urbilaterian. Philosophical
Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences,363(1496), 1493-1501.
52:
422:
focusing on the middle point will point to the woman’s face when prompted to point to the face in the picture, and will answer “a man” if asked what the picture is depicting. This is because the
362:
patients have been found to unilateral impairment following damage to either the left or right hemisphere, this effecting the opposite side of the body. Separating each hemisphere allows for
358:
to either side of each hemisphere, there is evidence that the left side of the brain controls the right side of the body, and the right side controlling the left side of the body.
892:"Junctional Neurulation: A Unique Developmental Program Shaping a Discrete Region of the Spinal Cord Highly Susceptible to Neural Tube Defectsdoi= 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1850-14.2014"
1038:
Gillen, Robert; Tennen, Howard; McKee, Tara (2005-04-01). "Unilateral spatial neglect: Relation to rehabilitation outcomes in patients with right hemisphere stroke".
981:
Purves, D., Augustine, G. J., Fitzpatrick, D., Hall, W. C., LaMantia, A., White, L. E., . . . Platt, M. L. (2018). Neuroscience. New York; Oxford: Sinauer
Associates.
2227:
255:
Though this fissure divides the brain, the two hemispheres of the human cortex are not perfectly symmetrical, both in structure and in function. For example, the
1389:
138:
330:
as soon as the 20th day of development. It is during embryonic development that a neural tube appears and is folded into a hollow structure, as shown in
599:
1248:
Levy, J., Trevarthen, C., & Sperry, R. W. (1972). Perception Of
Bilateral Chimeric Figures Following Hemispheric Deconnexion. Brain, 95(1), 61-78.
708:
Watkins, K. (2001). Structural
Asymmetries in the Human Brain: A Voxel-based Statistical Analysis of 142 MRI Scans. Cerebral Cortex, 11(9), 868-877.
587:
314:. Furthermore, studies have shown that this cephalon was bilateral, consisting of two or more connected sub-collections that are separated by the
2667:
575:
114:
551:
757:
Buklina, S. B. (2005-06-01). "The corpus callosum, interhemisphere interactions, and the function of the right hemisphere of the brain".
17:
429:
1544:
1416:
247:
callosum. The vasculature of falx cerebri supplies blood to the innermost surfaces of the cortex, neighboring the midsagittal plane.
1535:
1521:
1225:
527:
696:
489:
515:
1026:
539:
284:
sensory stimulation. In a clinical setting, those with epilepsy may benefit from the division of the corpus callosum.
1008:
447:
616:
145:
1317:
409:, as it provides unobstructed access to the corpus callosum. Corpus callosotomy is one of the procedures used for
2420:
481:
2008:
1700:
563:
2662:
2623:
1409:
371:
133:
1996:
1226:"Corpus Callosotomy - Treatments - For Patients - UR Neurosurgery - University of Rochester Medical Center"
939:
Patthey, Cédric; Gunhaga, Lena (2014-02-01). "Signaling pathways regulating ectodermal cell fate choices".
2088:
44:
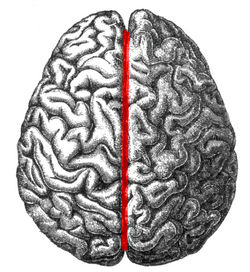
The human brain as viewed from above. Median longitudinal fissure visible in red, running top to bottom.
2500:
2056:
1383:
242:) fold and descend deep down into the longitudinal fissure, physically separating the two hemispheres.
636:
480:
As the corpus callosum is substantially smaller in surface area relative to the longitudinal fissure (
2459:
2157:
2020:
2001:
991:
Dooling, E.C.; Chi, J.G.; Gilles, F.H. (1983), "Telencephalic
Development: Changing Gyral Patterns",
311:
1394:
2331:
2278:
2199:
2166:
2066:
1882:
1865:
1805:
1402:
434:
301:, have evolved from a common wormlike ancestor that lived around 600 million years ago, called the
89:
426:(FFA) is in the right hemisphere, while language centers are predominantly in the left hemisphere.
2283:
2173:
1817:
1558:
1553:
331:
327:
2544:
1610:
1508:
1462:
121:
109:
476:
Figure 3: Area of the corpus callosum in comparison with the longitudinal fissure surface area
2531:
2390:
2304:
2204:
504:
210:
2504:
2244:
1921:
1781:
1678:
1627:
1484:
183:
263:, was found to be 10 times larger in the left than the right hemisphere. In contrast, the
8:
2481:
1891:
351:
2539:
2362:
2336:
2187:
1937:
1907:
1829:
1761:
1749:
1650:
1646:
1299:
1000:
916:
891:
867:
842:
790:
423:
402:
363:
260:
725:
Goldstein, Andrea; Covington, Benjamin P.; Mahabadi, Navid; Mesfin, Fassil B. (2019),
2657:
2618:
2447:
2413:
2408:
2403:
1992:
1602:
1581:
1454:
1291:
1283:
1202:
1170:
1138:
1063:
1055:
1004:
964:
956:
921:
872:
858:
782:
774:
734:
692:
669:
1303:
1105:
1081:
1027:
http://www.wou.edu/~lemastm/Teaching/BI335/Laboratory%2001%20-%20Brain%20Anatomy.pdf
794:
2570:
2519:
2514:
2509:
2491:
2486:
2474:
2469:
2464:
2452:
2435:
2425:
2357:
2288:
2269:
2264:
2259:
2254:
2249:
2237:
2209:
2191:
2183:
2178:
2128:
2109:
2076:
2071:
1912:
1896:
1887:
1741:
1726:
1717:
1712:
1705:
1693:
1688:
1683:
1667:
1655:
1576:
1568:
1540:
1531:
1517:
1512:
1499:
1494:
1364:
1347:
1330:
1275:
1249:
1047:
996:
948:
911:
907:
903:
862:
854:
825:
808:
766:
709:
390:
256:
51:
39:
450:(rTMS) applications have been tested with various cognitive processes during time
2439:
2367:
2161:
2025:
2013:
1976:
1969:
1957:
1952:
1947:
1942:
1875:
1870:
1834:
1822:
1810:
1798:
1793:
1786:
1754:
1637:
1632:
1620:
1615:
1526:
1489:
1477:
1472:
1467:
1426:
280:
264:
235:
102:
952:
2602:
2594:
2326:
2321:
2232:
2061:
2041:
1731:
1662:
1318:
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/craniotomy
1279:
1194:
1162:
1130:
1051:
726:
661:
770:
713:
2651:
2636:
2554:
2549:
2142:
2121:
2104:
2083:
1900:
1850:
1287:
1059:
960:
829:
778:
485:
341:
Figure 1: Early embryonic neural tube, depicting the separation of two sides
268:
126:
1351:
1253:
1674:
1438:
1295:
1206:
1174:
1142:
1067:
968:
925:
876:
812:
786:
738:
673:
605:
An anatomical illustration from the 1908 edition of
Sobotta's Anatomy Atlas
410:
382:
315:
302:
298:
243:
202:
27:
Deep groove separating the two cerebral hemispheres of the vertebrate brain
2381:
1430:
691:
Jill B. Becker (2002). Behavioral
Endocrinology 2e. MIT Press. pp. 103–.
472:
406:
378:
581:
Meninges and superficial cerebral veins. Deep dissection. Superior view.
151:
451:
386:
231:
194:
187:
84:
1964:
1424:
1386:
at Human Anatomy Lecture (Biology 129), Pennsylvania State University
1334:
557:
Cerebrum. Optic and olfactory nerves. Inferior view. Deep dissection.
367:
350:
Essentially, the fissure's purpose is to separate the brain into two
306:
239:
890:
Dady, A.; Havis, E.; Escriou, V.; Catala, M.; Duband, J. L. (2014).
389:, (depth and three-dimensional vision), as well as a development of
2580:
1368:
493:
414:
227:
198:
96:
1316:
Johns Hopkins Medicine. (n.d). Craniotomy. Health. Retrieved from
337:
724:
2116:
637:"longitudinal fissure - Ontology Browser - Rat Genome Database"
441:
359:
355:
205:. The inner surfaces of the two hemispheres are convoluted by
78:
fissura longitudinalis cerebri, fissura cerebri longitudinalis
2575:
297:
It is thought that a majority of existing animals, including
190:
72:
488:(DTI or dMRI) along with fiber-tracking (FT) algorithms and
1264:
206:
354:, left and right. Through case studies of brain damage or
533:
Cerebrum. Medial face. Dissection of corpus callosum etc.
889:
840:
318:, suggesting the first example of such a division.
2635:Some categorizations are approximations, and some
843:"The development of the neural crest in the human"
271:, was found to be larger in the right hemisphere.
1037:
377:The longitudinal fissure also pays a role in the
2649:
1040:Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
990:
1193:Ireland, Ashley C.; Carter, Iverson B. (2019),
1161:Ireland, Ashley C.; Carter, Iverson B. (2019),
1129:Ireland, Ashley C.; Carter, Iverson B. (2019),
938:
1410:
1192:
1160:
1128:
401:The longitudinal fissure plays a key role in
381:tract. This is shown in (figure 4.) with the
56:Longitudinal fissure shown in red (animation)
841:O'Rahilly, R.; Müller, F. (September 2007).
659:
448:repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation
442:Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation
182:) is the deep groove that separates the two
213:just as is the outer surface of the brain.
193:. Lying within it is a continuation of the
1417:
1403:
660:Bair, Michael M.; Munakomi, Sunil (2019),
50:
38:
915:
866:
569:Cerebrum. Inferior view. Deep dissection.
503:
471:
428:
396:
336:
756:
14:
2650:
759:Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology
2668:Medial surface of cerebral hemisphere
1398:
1106:"Neuroscience For Kids - Hemispheres"
1082:"Neuroscience For Kids - Hemispheres"
490:functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
250:
499:
2327:Lateral (frontal+parietal+temporal)
292:
24:
1001:10.1016/b978-0-7236-7017-9.50015-6
593:Sheep Brain Dissection with labels
508:Figure 4: Optical nerve cross over
321:
274:
25:
2679:
1377:
859:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2007.00773.x
617:Lateralization of brain function
598:
586:
574:
562:
550:
538:
526:
514:
146:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
2421:Posterior parahippocampal gyrus
2363:Collateral (temporal+occipital)
1356:
1339:
1322:
1310:
1258:
1242:
1218:
1186:
1154:
1122:
1098:
1074:
1031:
1016:
984:
975:
932:
883:
727:"Neuroanatomy, Corpus Callosum"
458:
259:, roughly corresponding to the
221:
2009:Secondary somatosensory cortex
1701:Ventromedial prefrontal cortex
908:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1850-14.2014
834:
817:
801:
750:
718:
702:
685:
653:
629:
326:A neural crest appears in the
287:
13:
1:
2624:Poles of cerebral hemispheres
2358:Cingulate (frontal+cingulate)
1384:Anatomy image: nerv/brainsup2
995:, Elsevier, pp. 94–104,
622:
1997:Primary somatosensory cortex
1195:"Neuroanatomy, Optic Chiasm"
1163:"Neuroanatomy, Optic Chiasm"
1131:"Neuroanatomy, Optic Chiasm"
662:"Neuroanatomy, Falx Cerebri"
521:facies dorsalis cerebri gyri
405:, neurosurgery resulting in
216:
7:
2089:Transverse occipital sulcus
953:10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.08.002
896:The Journal of Neuroscience
699:. Retrieved 4 January 2013.
610:
545:Basal view of a human brain
467:
366:of storage, procedural and
345:
176:median longitudinal fissure
18:Median longitudinal fissure
10:
2684:
2501:Isthmus of cingulate gyrus
2322:Central (frontal+parietal)
2057:Occipital pole of cerebrum
1280:10.1007/s10072-019-03820-8
1052:10.1016/j.apmr.2004.10.029
993:The Developing Human Brain
941:Experimental Cell Research
446:In studies, low-frequency
172:great longitudinal fissure
2632:
2611:
2593:
2563:
2530:
2434:
2389:
2380:
2345:
2314:
2303:
2220:
2158:Transverse temporal gyrus
2150:
2141:
2097:
2049:
2040:
2021:Posterior parietal cortex
1985:
1930:
1858:
1849:
1774:
1740:
1601:
1594:
1567:
1453:
1446:
1437:
1201:, StatPearls Publishing,
1169:, StatPearls Publishing,
1137:, StatPearls Publishing,
943:. Developmental Biology.
771:10.1007/s11055-005-0082-5
733:, StatPearls Publishing,
668:, StatPearls Publishing,
496:, the inability to read.
144:
132:
120:
108:
95:
83:
71:
66:
61:
49:
37:
32:
2279:Inferior temporal sulcus
2200:Superior temporal sulcus
1883:Inferior parietal lobule
1866:Superior parietal lobule
1806:Supplementary motor area
830:10.1186/1471-2148-10-255
486:Diffusion tensor imaging
435:Diffusion tensor imaging
180:interhemispheric fissure
2284:Inferior temporal gyrus
2228:Occipitotemporal sulcus
2174:Superior temporal gyrus
2067:Lateral occipital gyrus
1818:Supplementary eye field
1559:Inferior frontal sulcus
1554:Superior frontal sulcus
1352:10.1073/pnas.0500003102
714:10.1093/cercor/11.9.868
2545:Fimbria of hippocampus
1611:Superior frontal gyrus
1509:Inferior frontal gyrus
1463:Superior frontal gyrus
1230:www.urmc.rochester.edu
1110:faculty.washington.edu
1086:faculty.washington.edu
813:10.1098/rstb.2007.2239
509:
477:
438:
342:
2532:Hippocampal formation
2391:Parahippocampal gyrus
2205:Middle temporal gyrus
1268:Neurological Sciences
1254:10.1093/brain/95.1.61
507:
475:
432:
413:treating intractable
397:Clinical significance
340:
2663:Sulci (neuroanatomy)
2505:Retrosplenial cortex
2353:Longitudinal fissure
2245:Medial temporal lobe
1922:Intraparietal sulcus
1782:Primary motor cortex
1679:Orbitofrontal cortex
1628:Medial frontal gyrus
1485:Middle frontal gyrus
184:cerebral hemispheres
164:longitudinal fissure
33:Longitudinal fissure
2482:Posterior cingulate
1892:Supramarginal gyrus
902:(39): 13208–13221.
2540:Hippocampal sulcus
2460:Anterior cingulate
2337:Preoccipital notch
1938:Paracentral lobule
1908:Parietal operculum
1830:Frontal eye fields
1762:Paracentral sulcus
1750:Paracentral lobule
1651:Paraolfactory area
1647:Paraterminal gyrus
1390:Diagram at nih.gov
847:Journal of Anatomy
510:
478:
439:
424:Fusiform Face Area
403:corpus callosotomy
368:cognitive function
343:
316:mid-sagittal plane
251:Cerebral asymmetry
2645:
2644:
2589:
2588:
2414:Postrhinal cortex
2409:Perirhinal cortex
2404:Entorhinal cortex
2376:
2375:
2332:Parieto-occipital
2299:
2298:
2137:
2136:
2036:
2035:
1993:Postcentral gyrus
1845:
1844:
1770:
1769:
1590:
1589:
1582:Precentral sulcus
1545:Pars triangularis
697:978-0-262-52321-9
500:Additional images
411:pharmacologically
160:
159:
155:
16:(Redirected from
2675:
2571:Indusium griseum
2436:Cingulate cortex
2426:Prepyriform area
2387:
2386:
2312:
2311:
2192:Planum temporale
2148:
2147:
2129:Calcarine sulcus
2047:
2046:
1856:
1855:
1727:Olfactory sulcus
1713:Subcallosal area
1599:
1598:
1577:Precentral gyrus
1536:Pars opercularis
1451:
1450:
1444:
1443:
1419:
1412:
1405:
1396:
1395:
1371:
1360:
1354:
1343:
1337:
1335:10.1002/ar.23183
1326:
1320:
1314:
1308:
1307:
1274:(6): 1183–1189.
1262:
1256:
1246:
1240:
1239:
1237:
1236:
1222:
1216:
1215:
1214:
1213:
1190:
1184:
1183:
1182:
1181:
1158:
1152:
1151:
1150:
1149:
1126:
1120:
1119:
1117:
1116:
1102:
1096:
1095:
1093:
1092:
1078:
1072:
1071:
1035:
1029:
1020:
1014:
1013:
988:
982:
979:
973:
972:
936:
930:
929:
919:
887:
881:
880:
870:
838:
832:
821:
815:
805:
799:
798:
754:
748:
747:
746:
745:
722:
716:
706:
700:
689:
683:
682:
681:
680:
657:
651:
650:
648:
647:
633:
602:
590:
578:
566:
554:
542:
530:
518:
391:binocular vision
328:mammalian embryo
293:Phylogenetically
257:planum temporale
168:cerebral fissure
152:edit on Wikidata
149:
54:
42:
30:
29:
21:
2683:
2682:
2678:
2677:
2676:
2674:
2673:
2672:
2648:
2647:
2646:
2641:
2628:
2607:
2585:
2559:
2526:
2430:
2372:
2368:Callosal sulcus
2346:Medial/inferior
2341:
2306:
2295:
2221:Medial/inferior
2216:
2188:Wernicke's area
2162:Auditory cortex
2133:
2098:Medial/inferior
2093:
2032:
1981:
1977:Marginal sulcus
1931:Medial/inferior
1926:
1841:
1794:Premotor cortex
1766:
1736:
1595:Medial/inferior
1586:
1563:
1433:
1427:cerebral cortex
1425:Anatomy of the
1423:
1380:
1375:
1374:
1361:
1357:
1344:
1340:
1327:
1323:
1315:
1311:
1263:
1259:
1247:
1243:
1234:
1232:
1224:
1223:
1219:
1211:
1209:
1191:
1187:
1179:
1177:
1159:
1155:
1147:
1145:
1127:
1123:
1114:
1112:
1104:
1103:
1099:
1090:
1088:
1080:
1079:
1075:
1036:
1032:
1022:Marieb, Hoehn.
1021:
1017:
1011:
989:
985:
980:
976:
937:
933:
888:
884:
839:
835:
822:
818:
806:
802:
755:
751:
743:
741:
723:
719:
707:
703:
690:
686:
678:
676:
658:
654:
645:
643:
635:
634:
630:
625:
613:
606:
603:
594:
591:
582:
579:
570:
567:
558:
555:
546:
543:
534:
531:
522:
519:
502:
470:
461:
444:
399:
348:
324:
322:Ontogenetically
295:
290:
281:corpus callosum
277:
275:Corpus callosum
265:caudate nucleus
261:Wernicke’s area
253:
236:arachnoid mater
230:of the cortex (
224:
219:
156:
57:
45:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2681:
2671:
2670:
2665:
2660:
2643:
2642:
2637:Brodmann areas
2633:
2630:
2629:
2627:
2626:
2621:
2615:
2613:
2609:
2608:
2606:
2605:
2603:Insular cortex
2599:
2597:
2595:Insular cortex
2591:
2590:
2587:
2586:
2584:
2583:
2578:
2573:
2567:
2565:
2561:
2560:
2558:
2557:
2552:
2547:
2542:
2536:
2534:
2528:
2527:
2525:
2524:
2523:
2522:
2517:
2512:
2497:
2496:
2495:
2494:
2489:
2479:
2478:
2477:
2472:
2467:
2457:
2456:
2455:
2448:Subgenual area
2444:
2442:
2432:
2431:
2429:
2428:
2423:
2418:
2417:
2416:
2411:
2406:
2395:
2393:
2384:
2378:
2377:
2374:
2373:
2371:
2370:
2365:
2360:
2355:
2349:
2347:
2343:
2342:
2340:
2339:
2334:
2329:
2324:
2318:
2316:
2309:
2307:sulci/fissures
2301:
2300:
2297:
2296:
2294:
2293:
2292:
2291:
2281:
2275:
2274:
2273:
2272:
2267:
2262:
2257:
2252:
2242:
2241:
2240:
2233:Fusiform gyrus
2230:
2224:
2222:
2218:
2217:
2215:
2214:
2213:
2212:
2202:
2197:
2196:
2195:
2181:
2171:
2170:
2169:
2154:
2152:
2145:
2139:
2138:
2135:
2134:
2132:
2131:
2125:
2124:
2119:
2114:
2113:
2112:
2101:
2099:
2095:
2094:
2092:
2091:
2086:
2081:
2080:
2079:
2074:
2064:
2062:Occipital gyri
2059:
2053:
2051:
2044:
2042:Occipital lobe
2038:
2037:
2034:
2033:
2031:
2030:
2029:
2028:
2018:
2017:
2016:
2006:
2005:
2004:
1989:
1987:
1983:
1982:
1980:
1979:
1974:
1973:
1972:
1962:
1961:
1960:
1955:
1950:
1945:
1934:
1932:
1928:
1927:
1925:
1924:
1918:
1917:
1916:
1915:
1905:
1904:
1903:
1894:
1880:
1879:
1878:
1873:
1862:
1860:
1853:
1847:
1846:
1843:
1842:
1840:
1839:
1838:
1837:
1827:
1826:
1825:
1815:
1814:
1813:
1803:
1802:
1801:
1791:
1790:
1789:
1778:
1776:
1772:
1771:
1768:
1767:
1765:
1764:
1759:
1758:
1757:
1746:
1744:
1738:
1737:
1735:
1734:
1732:Orbital sulcus
1729:
1723:
1722:
1721:
1720:
1710:
1709:
1708:
1698:
1697:
1696:
1691:
1686:
1672:
1671:
1670:
1663:Straight gyrus
1660:
1659:
1658:
1643:
1642:
1641:
1640:
1635:
1625:
1624:
1623:
1618:
1607:
1605:
1596:
1592:
1591:
1588:
1587:
1585:
1584:
1579:
1573:
1571:
1565:
1564:
1562:
1561:
1556:
1550:
1549:
1548:
1547:
1538:
1524:
1522:Pars orbitalis
1515:
1505:
1504:
1503:
1502:
1497:
1492:
1482:
1481:
1480:
1475:
1470:
1459:
1457:
1448:
1441:
1435:
1434:
1422:
1421:
1414:
1407:
1399:
1393:
1392:
1387:
1379:
1378:External links
1376:
1373:
1372:
1369:10.1167/17.2.4
1355:
1338:
1321:
1309:
1257:
1241:
1217:
1185:
1153:
1121:
1097:
1073:
1046:(4): 763–767.
1030:
1024:Brain Anatomy.
1015:
1009:
983:
974:
931:
882:
833:
816:
800:
765:(5): 473–480.
749:
717:
701:
684:
652:
627:
626:
624:
621:
620:
619:
612:
609:
608:
607:
604:
597:
595:
592:
585:
583:
580:
573:
571:
568:
561:
559:
556:
549:
547:
544:
537:
535:
532:
525:
523:
520:
513:
501:
498:
469:
466:
460:
457:
443:
440:
398:
395:
364:specialization
347:
344:
323:
320:
294:
291:
289:
286:
276:
273:
252:
249:
223:
220:
218:
215:
158:
157:
148:
142:
141:
136:
130:
129:
124:
118:
117:
112:
106:
105:
100:
93:
92:
87:
81:
80:
75:
69:
68:
64:
63:
59:
58:
55:
47:
46:
43:
35:
34:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2680:
2669:
2666:
2664:
2661:
2659:
2656:
2655:
2653:
2640:
2638:
2631:
2625:
2622:
2620:
2617:
2616:
2614:
2610:
2604:
2601:
2600:
2598:
2596:
2592:
2582:
2579:
2577:
2574:
2572:
2569:
2568:
2566:
2562:
2556:
2555:Rhinal sulcus
2553:
2551:
2550:Dentate gyrus
2548:
2546:
2543:
2541:
2538:
2537:
2535:
2533:
2529:
2521:
2518:
2516:
2513:
2511:
2508:
2507:
2506:
2502:
2499:
2498:
2493:
2490:
2488:
2485:
2484:
2483:
2480:
2476:
2473:
2471:
2468:
2466:
2463:
2462:
2461:
2458:
2454:
2451:
2450:
2449:
2446:
2445:
2443:
2441:
2437:
2433:
2427:
2424:
2422:
2419:
2415:
2412:
2410:
2407:
2405:
2402:
2401:
2400:
2397:
2396:
2394:
2392:
2388:
2385:
2383:
2379:
2369:
2366:
2364:
2361:
2359:
2356:
2354:
2351:
2350:
2348:
2344:
2338:
2335:
2333:
2330:
2328:
2325:
2323:
2320:
2319:
2317:
2315:Superolateral
2313:
2310:
2308:
2302:
2290:
2287:
2286:
2285:
2282:
2280:
2277:
2276:
2271:
2268:
2266:
2263:
2261:
2258:
2256:
2253:
2251:
2248:
2247:
2246:
2243:
2239:
2236:
2235:
2234:
2231:
2229:
2226:
2225:
2223:
2219:
2211:
2208:
2207:
2206:
2203:
2201:
2198:
2193:
2189:
2185:
2182:
2180:
2177:
2176:
2175:
2172:
2168:
2165:
2164:
2163:
2159:
2156:
2155:
2153:
2151:Superolateral
2149:
2146:
2144:
2143:Temporal lobe
2140:
2130:
2127:
2126:
2123:
2122:Lingual gyrus
2120:
2118:
2115:
2111:
2108:
2107:
2106:
2105:Visual cortex
2103:
2102:
2100:
2096:
2090:
2087:
2085:
2084:Lunate sulcus
2082:
2078:
2075:
2073:
2070:
2069:
2068:
2065:
2063:
2060:
2058:
2055:
2054:
2052:
2050:Superolateral
2048:
2045:
2043:
2039:
2027:
2024:
2023:
2022:
2019:
2015:
2012:
2011:
2010:
2007:
2003:
2000:
1999:
1998:
1994:
1991:
1990:
1988:
1984:
1978:
1975:
1971:
1968:
1967:
1966:
1963:
1959:
1956:
1954:
1951:
1949:
1946:
1944:
1941:
1940:
1939:
1936:
1935:
1933:
1929:
1923:
1920:
1919:
1914:
1911:
1910:
1909:
1906:
1902:
1901:Angular gyrus
1898:
1895:
1893:
1889:
1886:
1885:
1884:
1881:
1877:
1874:
1872:
1869:
1868:
1867:
1864:
1863:
1861:
1859:Superolateral
1857:
1854:
1852:
1851:Parietal lobe
1848:
1836:
1833:
1832:
1831:
1828:
1824:
1821:
1820:
1819:
1816:
1812:
1809:
1808:
1807:
1804:
1800:
1797:
1796:
1795:
1792:
1788:
1785:
1784:
1783:
1780:
1779:
1777:
1773:
1763:
1760:
1756:
1753:
1752:
1751:
1748:
1747:
1745:
1743:
1739:
1733:
1730:
1728:
1725:
1724:
1719:
1716:
1715:
1714:
1711:
1707:
1704:
1703:
1702:
1699:
1695:
1692:
1690:
1687:
1685:
1682:
1681:
1680:
1676:
1673:
1669:
1666:
1665:
1664:
1661:
1657:
1654:
1653:
1652:
1648:
1645:
1644:
1639:
1636:
1634:
1631:
1630:
1629:
1626:
1622:
1619:
1617:
1614:
1613:
1612:
1609:
1608:
1606:
1604:
1600:
1597:
1593:
1583:
1580:
1578:
1575:
1574:
1572:
1570:
1566:
1560:
1557:
1555:
1552:
1551:
1546:
1542:
1539:
1537:
1533:
1530:
1529:
1528:
1525:
1523:
1519:
1516:
1514:
1510:
1507:
1506:
1501:
1498:
1496:
1493:
1491:
1488:
1487:
1486:
1483:
1479:
1476:
1474:
1471:
1469:
1466:
1465:
1464:
1461:
1460:
1458:
1456:
1452:
1449:
1447:Superolateral
1445:
1442:
1440:
1436:
1432:
1428:
1420:
1415:
1413:
1408:
1406:
1401:
1400:
1397:
1391:
1388:
1385:
1382:
1381:
1370:
1366:
1359:
1353:
1349:
1342:
1336:
1332:
1325:
1319:
1313:
1305:
1301:
1297:
1293:
1289:
1285:
1281:
1277:
1273:
1269:
1261:
1255:
1251:
1245:
1231:
1227:
1221:
1208:
1204:
1200:
1196:
1189:
1176:
1172:
1168:
1164:
1157:
1144:
1140:
1136:
1132:
1125:
1111:
1107:
1101:
1087:
1083:
1077:
1069:
1065:
1061:
1057:
1053:
1049:
1045:
1041:
1034:
1028:
1025:
1019:
1012:
1010:9780723670179
1006:
1002:
998:
994:
987:
978:
970:
966:
962:
958:
954:
950:
946:
942:
935:
927:
923:
918:
913:
909:
905:
901:
897:
893:
886:
878:
874:
869:
864:
860:
856:
853:(3): 335–51.
852:
848:
844:
837:
831:
827:
820:
814:
810:
804:
796:
792:
788:
784:
780:
776:
772:
768:
764:
760:
753:
740:
736:
732:
728:
721:
715:
711:
705:
698:
694:
688:
675:
671:
667:
663:
656:
642:
638:
632:
628:
618:
615:
614:
601:
596:
589:
584:
577:
572:
565:
560:
553:
548:
541:
536:
529:
524:
517:
512:
511:
506:
497:
495:
491:
487:
483:
474:
465:
456:
453:
449:
436:
431:
427:
425:
419:
416:
412:
408:
404:
394:
392:
388:
384:
380:
375:
373:
369:
365:
361:
357:
353:
339:
335:
333:
329:
319:
317:
313:
308:
304:
300:
285:
282:
272:
270:
269:basal ganglia
267:, within the
266:
262:
258:
248:
245:
241:
237:
233:
229:
214:
212:
208:
204:
201:) called the
200:
196:
192:
189:
185:
181:
177:
173:
169:
165:
153:
147:
143:
140:
137:
135:
131:
128:
125:
123:
119:
116:
113:
111:
107:
104:
101:
98:
94:
91:
88:
86:
82:
79:
76:
74:
70:
65:
60:
53:
48:
41:
36:
31:
19:
2634:
2398:
2352:
1675:Orbital gyri
1527:Broca's area
1439:Frontal lobe
1358:
1341:
1324:
1312:
1271:
1267:
1260:
1244:
1233:. Retrieved
1229:
1220:
1210:, retrieved
1198:
1188:
1178:, retrieved
1166:
1156:
1146:, retrieved
1134:
1124:
1113:. Retrieved
1109:
1100:
1089:. Retrieved
1085:
1076:
1043:
1039:
1033:
1023:
1018:
992:
986:
977:
947:(1): 11–16.
944:
940:
934:
899:
895:
885:
850:
846:
836:
819:
803:
762:
758:
752:
742:, retrieved
730:
720:
704:
687:
677:, retrieved
665:
655:
644:. Retrieved
640:
631:
479:
462:
459:Neurosurgery
445:
420:
400:
383:optic chiasm
376:
349:
325:
303:urbilaterian
299:Homo sapiens
296:
278:
254:
244:Falx cerebri
225:
222:Falx cerebri
203:falx cerebri
197:(one of the
179:
175:
171:
167:
163:
161:
115:A14.1.09.007
103:birnlex_4041
77:
2382:Limbic lobe
1431:human brain
641:rgd.mcw.edu
407:split brain
379:optic nerve
352:hemispheres
288:Development
67:Identifiers
2652:Categories
2639:span gyri.
2305:Interlobar
2002:3, 1 and 2
1742:Precentral
1603:Prefrontal
1569:Precentral
1455:Prefrontal
1235:2019-09-20
1212:2019-11-02
1199:StatPearls
1180:2019-11-02
1167:StatPearls
1148:2019-11-02
1135:StatPearls
1115:2019-10-21
1091:2019-10-21
744:2019-11-02
731:StatPearls
679:2019-09-24
666:StatPearls
646:2019-09-24
623:References
452:perception
433:Figure 2:
387:stereopsis
307:bilaterian
232:dura mater
226:All three
195:dura mater
188:vertebrate
85:NeuroNames
2619:Operculum
2167:41 and 42
1965:Precuneus
1288:1590-3478
1060:0003-9993
961:0014-4827
779:1573-899X
240:pia mater
217:Structure
2658:Cerebrum
2581:Amygdala
2399:anterior
1304:71716091
1296:30850896
1207:31194427
1175:31194427
1143:31194427
1068:15827929
969:23939346
926:25253865
877:17848161
795:14145192
787:16033195
739:28846239
674:31424888
611:See also
482:Figure 3
468:Research
415:epilepsy
374:events.
346:Function
332:Figure 1
312:cephalon
228:meninges
199:meninges
97:NeuroLex
2612:General
1429:of the
917:6608335
868:2375817
437:example
372:spatial
186:of the
62:Details
2117:Cuneus
1302:
1294:
1286:
1205:
1173:
1141:
1066:
1058:
1007:
967:
959:
924:
914:
875:
865:
793:
785:
777:
737:
695:
672:
494:alexia
360:Stroke
356:stroke
2576:Uncus
2564:Other
2440:gyrus
1300:S2CID
791:S2CID
211:sulci
191:brain
150:[
139:83727
73:Latin
1986:Both
1775:Both
1292:PMID
1284:ISSN
1203:PMID
1171:PMID
1139:PMID
1064:PMID
1056:ISSN
1005:ISBN
965:PMID
957:ISSN
922:PMID
873:PMID
783:PMID
775:ISSN
735:PMID
693:ISBN
670:PMID
305:. A
279:The
209:and
207:gyri
166:(or
162:The
127:5417
110:TA98
1365:doi
1348:doi
1331:doi
1276:doi
1250:doi
1048:doi
997:doi
949:doi
945:321
912:PMC
904:doi
863:PMC
855:doi
851:211
826:doi
809:doi
767:doi
710:doi
134:FMA
122:TA2
2654::
2520:30
2515:29
2510:26
2503::
2492:31
2487:23
2475:33
2470:32
2465:24
2453:25
2289:20
2270:36
2265:35
2260:34
2255:28
2250:27
2238:37
2210:21
2184:22
2179:38
2110:17
2077:19
2072:18
1913:43
1897:39
1888:40
1718:25
1706:10
1694:12
1689:11
1684:10
1668:11
1656:12
1541:45
1532:44
1518:47
1513:11
1511::
1500:46
1495:10
1298:.
1290:.
1282:.
1272:40
1270:.
1228:.
1197:,
1165:,
1133:,
1108:.
1084:.
1062:.
1054:.
1044:86
1042:.
1003:,
963:.
955:.
920:.
910:.
900:34
898:.
894:.
871:.
861:.
849:.
845:.
789:.
781:.
773:.
763:35
761:.
729:,
664:,
639:.
238:,
234:,
178:,
174:,
170:,
99:ID
90:35
2438:/
2194:)
2190:(
2186:/
2160:/
2026:7
2014:5
1995:/
1970:7
1958:5
1953:3
1948:2
1943:1
1899:-
1890:-
1876:7
1871:5
1835:8
1823:6
1811:6
1799:6
1787:4
1755:4
1677:/
1649:/
1638:9
1633:8
1621:6
1616:4
1543:-
1534:-
1520:-
1490:9
1478:8
1473:6
1468:4
1418:e
1411:t
1404:v
1367::
1350::
1333::
1306:.
1278::
1252::
1238:.
1118:.
1094:.
1070:.
1050::
999::
971:.
951::
928:.
906::
879:.
857::
828::
811::
797:.
769::
712::
649:.
154:]
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.