297:
194:
memory T cell maintenance is not fully understood. Activation through the T cell receptor may play a role. It is found that memory T cells can sometimes react to novel antigens, potentially caused by intrinsic the diversity and breadth of the T cell receptor binding targets. These T cells could cross-react to environmental or resident antigens in our bodies (like bacteria in our gut) and proliferate. These events would help maintain the memory T cell population. The cross-reactivity mechanism may be important for memory T cells in the mucosal tissues since these sites have higher antigen density. For those resident in blood, bone marrow, lymphoid tissues, and spleen, homeostatic cytokines (including
616:) expression on memory CD8+ T cells, leading to innate-like cytotoxicity, i.e. recognition of NKG2D ligands as indicators of infection, cell stress and cell transformation as well as destruction of altered cells in an NK-like manner. TCR activation was shown to abrogate IL-15 mediated NKG2D expression on T cells. Additionally, IL-15 induces expression of cytolytic molecules, cell expansion and enhances the cell response to IL-18. IL-18 is another cytokine involved in this process, typically acting in synergy with IL-12, enhancing the differentiation of memory T cells into effector cells, i.e. it induces
215:
stage, which lasts from birth to about 20–25 years old when our immune system encounters the greatest number of new antigens. During the memory homeostasis stage that comes next, the number of memory T cells plateaus and is stabilized by homeostatic maintenance. At this stage, the immune response shifts more towards maintaining homeostasis since few new antigens are encountered. Tumor surveillance also becomes important at this stage. At later stages of life, at about 65–70 years of age,
293:
antigen exposure. This model predicts that effector T cells can transit into memory T cells and survive, retaining the ability to proliferate. It also predicts that certain gene expression profiles would follow the on-off-on pattern during naive, effector, and memory stages. Evidence supporting this model includes the finding of genes related to survival and homing that follow the on-off-on expression pattern, including interleukin-7 receptor alpha (IL-7Rα), Bcl-2, CD26L, and others.
539:) differ from the other memory subsets in that they do not originate following a strong clonal expansion event. Thus, although this population as a whole is abundant within the peripheral circulation, individual virtual memory T cell clones reside at relatively low frequencies. One theory is that homeostatic proliferation gives rise to this T cell population. Although CD8 virtual memory T cells were the first to be described, it is now known that CD4 virtual memory cells also exist.
311:
Studies looking at cell division history found that the length of telomere and activity of telomerase were reduced in effector T cells compared to memory T cells, which suggests that memory T cells did not undergo as much cell division as effector T cells, which is inconsistent with the On-Off-On model. Repeated or chronic antigenic stimulation of T cells, like
354:, would not be expressed but they are transcriptionally poised for fast expression upon activation. Additionally, the enhancement of expression for certain genes also depends on the strength of the initial TCR signaling for the progeny of memory T cells, which is correlated to the regulatory element activation that directly changes gene expression level.
383:. The single unifying theme for all memory T cell subtypes is that they are long-lived and can quickly expand to large numbers of effector T cells upon re-exposure to their cognate antigen. By this mechanism, they provide the immune system with "memory" against previously encountered pathogens. Memory T cells may be either
90:-positive) and the cytotoxic T cells. Primary function of memory cells is augmented immune response after reactivation of those cells by reintroduction of relevant pathogen into the body. It is important to note that this field is intensively studied and some information may not be available as of yet.
579:
This phenomenon was observed predominantly in memory CD8+ T cells, which have lower sensitivity to cytokine stimulation, compared to their naive counterparts and get activated in this manner more easily. Virtual memory CD8+ T cells also display heightened sensitivity to cytokine-induced activation in
571:
T cells possess the ability to be activated independently of their cognate antigen stimulation, i.e. without TCR stimulation. At early stages of infection, T cells specific for unrelated antigen are activated only by the presence of inflammation. This happens in the inflammatory milieu resulting from
214:
Memory T cells undergo different changes and play different roles in different life stages for humans. At birth and early childhood, T cells in the peripheral blood are mainly naïve T cells. Through frequent antigen exposure, the population of memory T cells accumulates. This is the memory generation
583:
Apart from infections, bystander activation also plays an important role in antitumor immunity. In human cancerous tissues, a high number of virus-specific, not tumor-specific, CD8+ T cells was detected. This type of activation is considered to be beneficial for the host in terms of cancer clearance
193:
Clones of memory T cells expressing a specific T cell receptor can persist for decades in our body. Since memory T cells have shorter half-lives than naïve T cells do, continuous replication and replacement of old cells are likely involved in the maintenance process. Currently, the mechanism behind
656:
induce cytokine expression in effector and memory CD4+ T cells and IL-2 is considered to be a strong activation inducer of CD4+ T cells that can replace TCR stimulation even in naive cells. TLR2 was also reported to be present on memory CD4+ T cells, which respond to their agonist by IFNγ
310:
after antigen clearance. Memory T cells are instead produced by naive T cells that are activated but never entered with full strength into the effector stage. The progeny of memory T cells are not fully activated because they are not as specific to the antigen as the expanding effector T cells.
292:
clearance, some of these effector cells form memory T cells, either in a randomly determined manner or are selected based on their superior specificity. These cells would reverse from the active effector role to a state more similar to naive T cells and would be "turned on" again upon the next
143:
lymphocytes are present over long periods of time in tissues, or more importantly, barrier tissues (epithelium for example), they are crucial for quick response to barrier breach and response to any relevant pathogen present. One mechanism used by
315:, would induce elevated effector functions but reduce memory. It was also found that massively proliferated T cells are more likely to generate short-lived effector cells, while minimally proliferated T cells would form more long-lived cells.
665:
Bystander activation plays role in the elimination of the spread of infection in its early stages and helps in tumor clearance. However, this type of activation can also have deleterious outcome, especially in chronic infections and
674:
infection is a result of non-HBV-specific CD8+ T cell infiltration into the tissue. A similar situation occurs during the acute
Hepatitis A virus infection and activated virus unrelated CD4+ T cells contribute to ocular lesions in
450:
cells) subtype was identified based on intermediate CX3CR1 expression. These cells can migrate to the tissues from blood and traffic to the lymph nodes in a CD62L-independent manner, in order to survey the tissues.
572:
microbial infection, cancer or autoimmunity in both mice and humans and occurs locally as well as systematically . Moreover, bystander activated T cells can migrate to the site of infection, due to increased
500:
cells secrete higher levels of protective-immunity-related cytokines and express lower levels of the proliferation marker Ki67. It was proposed that these characteristics may help with the long-term maintenance of
370:
cells) subtypes, each with its own distinguishing set of cell surface markers (see below). Subsequently, numerous additional populations of memory T cells were discovered including tissue-resident memory T
907:
Gebhardt T, Wakim LM, Eidsmo L, Reading PC, Heath WR, Carbone FR (May 2009). "Memory T cells in nonlymphoid tissue that provide enhanced local immunity during infection with herpes simplex virus".
1705:
Gerlach, Carmen; Moseman, E. Ashley; Loughhead, Scott M.; Alvarez, David; Zwijnenburg, Anthonie J.; Waanders, Lisette; Garg, Rohit; de la Torre, Juan C.; von
Andrian, Ulrich H. (December 2016).
102:
lymphocytes have several attributes in common with stem cells, the most important being the ability of self-renewal, mainly because of high level of phosphorylation on key transcription factor
280:
As of April 2020, the lineage relationship between effector and memory T cells is unclear. Two competing models exist. One is called the On-Off-On model. When naive T cells are activated by
184:
cells is production of various cytokines, but there are speculations about their influence in subduing unwanted immunological states and their usage in treating autoimmune disorders.
273:
Some of the cells will form memory T cells (M) that will survive in an inactive state in the host for a long period of time until they re-encounter the same antigen and reactivate.
228:
644:(also known as IL2RB or IL15RB) expression. Similarly to their CD8+ counterparts, memory and effector CD4+ T cells exhibit increased sensitivity to TCR-independent activation.
346:. Some of these modifications persisted after antigen clearance, establishing an epigenetic memory that allows a faster activation upon re-encounter with the antigen. For
563:), CD27+, CD28+, and IL-7Rα+, but they also express large amounts of CD95, IL-2Rβ, CXCR3, and LFA-1, and show numerous functional attributes distinctive of memory cells.
1921:"+ virtual memory: Antigen-inexperienced T cells reside in the naïve, regulatory, and memory T cell compartments at similar frequencies, implications for autoimmunity"
2590:
1503:
Sallusto F, Lenig D, Förster R, Lipp M, Lanzavecchia A (October 1999). "Two subsets of memory T lymphocytes with distinct homing potentials and effector functions".
306:
The other model is the developmental differentiation model. This model argues that effector cells produced by the highly activated naive T cells would all undergo
284:(TCR) binding to antigen and its downstream signaling pathway, they actively proliferate and form a large clone of effector cells. Effector cells undergo active
203:
580:
mouse models, but this was not directly demonstrated in humans. Conversely, TCR-independent activation of naive CD8+ T cells remains controversial.
1707:"The Chemokine Receptor CX3CR1 Defines Three Antigen-Experienced CD8 T Cell Subsets with Distinct Roles in Immune Surveillance and Homeostasis"
461:) occupy tissues (skin, lung, gastrointestinal tract, etc.) without recirculating. Some cell surface markers that have been associated with T
636:
Despite TCR-independent activation being studied more extensively in CD8+ T cells, there's a clear evidence of this phenomenon occurring in
2319:"Single cell dynamics of tumor specificity vs bystander activity in CD8+ T cells define the diverse immune landscapes in colorectal cancer"
608:
or type I IFNs, often working synergistically. IL-15 is responsible for cytotoxic activity of bystander-activated T cells. It induces the
505:
cells, as well as keeping a balance between quick response to antigen invasion and avoidance of unnecessary tissue damage. Dysfunctional T
2123:
Pacheco, Yovana; Acosta-Ampudia, Yeny; Monsalve, Diana M.; Chang, Christopher; Gershwin, M. Eric; Anaya, Juan-Manuel (September 2019).
682:
Increased IL-15 expression and subsequent excessive NKG2D expression was linked to exacerbation of some autoimmune disorders, such as,
219:
stage comes, in which stage immune dysregulation, decline in T cell function and increased susceptibility to pathogens are observed.
439:. Because these memory T cells lack the CCR7 lymph node-homing receptors they are found in the peripheral circulation and tissues. T
443:
stands for terminally differentiated effector memory cells re-expressing CD45RA, which is a marker usually found on naive T cells.
296:
488:
cells are thought to play a major role in protective immunity against pathogens. Studies have also suggested a dual role for T
2504:
129:
lymphocytes are primarily active as the CD8 variants, thus being mainly responsible for cytotoxic action against pathogens.
784:"Central memory self/tumor-reactive CD8+ T cells confer superior antitumor immunity compared with effector memory T cells"
2723:
484:
cells localized in salivary glands, pancreas, and female reproductive tracts in mice express neither CD69 nor CD103. T
2759:
1856:
454:
1759:
Mueller SN, Mackay LK (February 2016). "Tissue-resident memory T cells: local specialists in immune defence".
782:
Klebanoff CA, Gattinoni L, Torabi-Parizi P, Kerstann K, Cardones AR, Finkelstein SE, et al. (July 2005).
2682:
1631:
409:
132:
2804:
2774:
2754:
20:
2792:
2787:
2627:
691:
518:
543:
There have been numerous other subpopulations of memory T cells suggested. Investigators have studied
2497:
2183:"The Ugly Duckling Turned to Swan: A Change in Perception of Bystander-Activated Memory CD8 T Cells"
628:, have been linked to TCR-independent activation of CD8+ T cells upon bacterial infection as well.
2831:
2124:
199:
110:
proved to confer more powerful immunity against viruses, bacteria and cancer cells, compared to T
2882:
2674:
1802:
Steinert EM, Schenkel JM, Fraser KA, Beura LK, Manlove LS, Igyártó BZ, et al. (May 2015).
1656:"Multiparameter flow cytometric analysis of CD4 and CD8 T cell subsets in young and old people"
1605:"Molecular signatures distinguish human central memory from effector memory CD8 T cell subsets"
476:
cells found in different tissues express different sets of cell surface markers. While CD103+ T
733:
Wherry EJ, Teichgräber V, Becker TC, Masopust D, Kaech SM, Antia R, et al. (March 2003).
2713:
2690:
2666:
1985:
Whiteside, Sarah K.; Snook, Jeremy P.; Williams, Matthew A.; Weis, Janis J. (December 2018).
1164:"Strong homeostatic TCR signals induce formation of self-tolerant virtual memory CD8 T cells"
532:
380:
173:
1300:. Special section: Systems biology and bioinformatics / Immunogenetics and transplantation.
1162:
Drobek A, Moudra A, Mueller D, Huranova M, Horkova V, Pribikova M, et al. (July 2018).
2872:
2867:
2737:
2554:
2490:
1512:
1116:
795:
703:
676:
514:
1919:
Marusina AI, Ono Y, Merleev AA, Shimoda M, Ogawa H, Wang EA, et al. (February 2017).
8:
2877:
2746:
2585:
1406:"T-cell memory differentiation: insights from transcriptional signatures and epigenetics"
613:
529:, being highly active, roughly 20- to 30-fold more active than in other types of T-cells.
2345:
2318:
1516:
1120:
1005:
Gattinoni L, Lugli E, Ji Y, Pos Z, Paulos CM, Quigley MF, et al. (September 2011).
799:
2718:
2705:
2464:
2431:
2399:
2291:
2258:
2215:
2182:
2152:
2102:
2011:
1986:
1945:
1920:
1896:
1871:
1828:
1803:
1784:
1731:
1706:
1682:
1655:
1585:
1536:
1430:
1405:
1374:
1349:
1318:
1293:
1254:
1229:
1188:
1163:
1139:
1104:
1080:
1055:
1031:
1006:
979:
954:
932:
884:
859:
818:
783:
764:
702:. Furthermore, enhanced TLR2 expression was observed in joints, cartilage and bones of
695:
687:
667:
645:
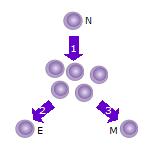
621:
170:
subpopulations. Presence of this population in humans is currently under investigation.
151:
2769:
2650:
2569:
2549:
2469:
2451:
2391:
2350:
2296:
2278:
2220:
2202:
2156:
2144:
2106:
2094:
2086:
2066:
2016:
1950:
1901:
1833:
1776:
1736:
1687:
1636:
1577:
1528:
1485:
1435:
1379:
1323:
1259:
1193:
1144:
1085:
1036:
984:
924:
889:
823:
756:
671:
244:
75:
1589:
2862:
2642:
2618:
2459:
2443:
2403:
2381:
2340:
2330:
2286:
2270:
2210:
2194:
2136:
2078:
2006:
1998:
1940:
1932:
1891:
1883:
1823:
1815:
1788:
1768:
1726:
1718:
1677:
1667:
1626:
1616:
1567:
1540:
1520:
1475:
1425:
1417:
1369:
1361:
1313:
1305:
1249:
1241:
1183:
1175:
1134:
1124:
1075:
1067:
1026:
1018:
974:
966:
916:
879:
871:
813:
803:
768:
746:
649:
617:
526:
351:
335:
267:
216:
648:, synergistically with IL-12 and IL-23, stimulates memory CD4+ T cells and drives
480:
cells are found to be restrictedly localized to epithelial and neuronal tissues, T
302:
In this model, memory T cells generate effector T cells, not the other way around.
2634:
1722:
1245:
936:
699:
683:
281:
1654:
Koch S, Larbi A, Derhovanessian E, Ozcelik D, Naumova E, Pawelec G (July 2008).
1621:
1604:
1572:
1555:
2447:
2335:
2254:
2140:
2082:
2062:
1936:
1819:
1480:
1463:
1109:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
788:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
711:
653:
605:
601:
597:
83:
34:
2274:
1804:"Quantifying Memory CD8 T Cells Reveals Regionalization of Immunosurveillance"
1309:
2856:
2841:
2823:
2623:
2544:
2455:
2282:
2259:"The activation of bystander CD8+ T cells and their roles in viral infection"
2206:
2198:
2090:
2002:
1887:
1603:
Willinger T, Freeman T, Hasegawa H, McMichael AJ, Callan MF (November 2005).
707:
637:
416:(CD62L). Central memory T cells also have intermediate to high expression of
362:
Historically, memory T cells were thought to belong to either the effector (T
339:
326:
modifications are involved in the change from naive T-cells. For example, in
263:
255:
248:
74:
subsets. Although most information is currently based on observations in the
1179:
1129:
808:
334:
genes that are up-regulated during the secondary immune response, including
2656:
2564:
2559:
2473:
2395:
2354:
2300:
2224:
2148:
2098:
2020:
1954:
1905:
1837:
1780:
1740:
1691:
1640:
1556:"Loss of CD45R and gain of UCHL1 reactivity is a feature of primed T cells"
1532:
1489:
1439:
1383:
1327:
1263:
1197:
1148:
1089:
1040:
988:
928:
893:
827:
760:
735:"Lineage relationship and protective immunity of memory CD8 T cell subsets"
236:
195:
30:
2386:
2369:
1672:
1581:
2836:
2539:
2534:
2432:"Bystander CD4+ T cells: crossroads between innate and adaptive immunity"
1365:
640:. However, it's considered to be less efficient, presumably due to lower
323:
1071:
860:"Human memory T cells: generation, compartmentalization and homeostasis"
2513:
1772:
781:
560:
432:
421:
413:
2317:
Borras, DM, Verbandt, S, Ausserhofer, M, et al. (November 2023).
1421:
1230:"Human T Cell Development, Localization, and Function throughout Life"
970:
2809:
2764:
2612:
1857:"Study highlights possible Achilles' heel in key immune memory cells"
1103:
Lee JY, Hamilton SE, Akue AD, Hogquist KA, Jameson SC (August 2013).
510:
469:
307:
49:
2181:
Maurice, Nicholas J.; Taber, Alexis K.; Prlic, Martin (2021-02-01).
2067:"Significance of bystander T cell activation in microbial infection"
1022:
920:
875:
82:-positive) subset, similar populations appear to exist for both the
2578:
2529:
593:
466:
331:
312:
285:
259:
2122:
1524:
751:
734:
2797:
1602:
1554:
Akbar AN, Terry L, Timms A, Beverley PC, Janossy G (April 1988).
1105:"Virtual memory CD8 T cells display unique functional properties"
289:
240:
45:
948:
946:
227:
2600:
2521:
732:
2482:
1704:
1653:
258:(E) that will perform the function of that cell (e.g. produce
1007:"A human memory T cell subset with stem cell-like properties"
943:
641:
609:
343:
103:
1462:
Schmidl C, Delacher M, Huehn J, Feuerer M (September 2018).
158:: Those lymphocytes are capable of self-renewal as are the T
1801:
1461:
1161:
625:
573:
556:
509:
cells have been implicated in autoimmune diseases, such as
436:
417:
392:
1984:
1347:
906:
2430:
Lee, Hong-Gyun; Cho, Min-Zi; Choi, Je-Min (August 2020).
1918:
566:
388:
384:
347:
327:
162:
lymphocytes and are also capable of generating both the T
87:
79:
1987:"Bystander T Cells: A Balancing Act of Friends and Foes"
1502:
330:
memory T cells, positive histone modifications mark key
1553:
1102:
631:
1056:"+ T cells: where they come from and why we need them"
431:
cells) express CD45RO but lack expression of CCR7 and
48:-specific memory T cells specific to viruses or other
1294:"Lineage relationship of effector and memory T cells"
420:. This memory subpopulation is commonly found in the
148:
to restrict pathogens is the secretion of granzyme B.
857:
435:. They also have intermediate to high expression of
2370:"Bystander activation of CD4 + T cells: HIGHLIGHTS"
1464:"Epigenetic mechanisms regulating T-cell responses"
1403:
1348:Henning AN, Roychoudhuri R, Restifo NP (May 2018).
1004:
1869:
1227:
858:Farber DL, Yudanin NA, Restifo NP (January 2014).
587:
254:Some of the T cell clones will differentiate into
2316:
2180:
1870:Lee YJ, Jameson SC, Hogquist KA (February 2011).
1632:20.500.11820/f28e936e-a6a7-4f06-bdc9-79a1355c5f02
1228:Kumar BV, Connors TJ, Farber DL (February 2018).
492:cells in protection and regulation. Compared to T
2854:
1291:
350:memory T cells, certain effector genes, such as
288:secretion and other effector activities. After
1872:"Alternative memory in the CD8 T cell lineage"
1468:The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology
1053:
592:The major drivers of bystander activation are
33:that might have some of the same functions as
2498:
2312:
2310:
1758:
1223:
1221:
1219:
1217:
1215:
1213:
1211:
1209:
1207:
853:
851:
849:
847:
845:
843:
841:
839:
837:
472:(CD103). However, it is worth noticing that T
180:): As of now, the only function apparent in T
2060:
1851:
1849:
1847:
1404:Youngblood B, Hale JS, Ahmed R (July 2013).
1547:
952:
318:
114:lymphocytes in several experimental models.
2505:
2491:
2429:
2307:
1204:
834:
657:production, even without TCR stimulation.
188:
2463:
2385:
2344:
2334:
2290:
2214:
2010:
1944:
1895:
1844:
1827:
1730:
1681:
1671:
1630:
1620:
1571:
1479:
1429:
1373:
1317:
1253:
1187:
1138:
1128:
1079:
1054:White JT, Cross EW, Kedl RM (June 2017).
1030:
978:
883:
817:
807:
750:
706:patients and the presence of its ligand,
398:
206:(MHCII) signaling may be more important.
1292:Restifo NP, Gattinoni L (October 2013).
660:
295:
226:
2745:
2252:
2125:"Bystander activation and autoimmunity"
2855:
2367:
2056:
2054:
2052:
2050:
1754:
1752:
1750:
1457:
1455:
1453:
1451:
1449:
1399:
1397:
1395:
1393:
1343:
1341:
1339:
1337:
1287:
1285:
1283:
1281:
1279:
1277:
1275:
1273:
567:TCR-independent (bystander) activation
266:or invoke cell killing in the case of
2486:
2436:Experimental & Molecular Medicine
2425:
2423:
2421:
2419:
2417:
2415:
2413:
2263:Experimental & Molecular Medicine
2248:
2246:
2244:
2242:
2240:
2238:
2236:
2234:
2176:
2174:
2172:
2170:
2168:
2166:
2118:
2116:
2048:
2046:
2044:
2042:
2040:
2038:
2036:
2034:
2032:
2030:
1980:
1978:
1976:
1974:
1972:
1970:
1968:
1966:
1964:
652:response. Moreover, IL-18, IL-12 and
251:) into many clones or daughter cells.
1000:
998:
953:Shin H, Iwasaki A (September 2013).
728:
726:
632:Bystander activation of CD4+ T cells
300:Developmental differentiation model:
209:
2724:Mucosal associated invariant T cell
1747:
1446:
1390:
1334:
1270:
620:production and cell proliferation.
612:(a receptor typically expressed on
204:major histocompatibility complex II
13:
2410:
2231:
2163:
2113:
2027:
1961:
525:lymphocytes are genes involved in
424:and in the peripheral circulation.
395:and at the same time lack CD45RA.
357:
14:
2894:
995:
723:
222:
2760:Lymphokine-activated killer cell
955:"Tissue-resident memory T cells"
152:Stem cell-like memory T cells (T
2512:
2361:
1912:
1863:
1795:
1698:
1647:
1596:
1496:
588:Drivers of bystander activation
52:molecules can be found in both
2374:European Journal of Immunology
2061:Lee, Hoyoung; Jeong, Seongju;
1155:
1096:
1047:
900:
775:
670:. Liver injury during chronic
455:Tissue-resident memory T cells
1:
1298:Current Opinion in Immunology
717:
410:C-C chemokine receptor type 7
133:Tissue-resident memory T cell
2805:Type 3 innate lymphoid cells
2793:Type 2 innate lymphoid cells
2788:Type 1 innate lymphoid cells
2775:Uterine natural killer cells
2755:Cytokine-induced killer cell
1723:10.1016/j.immuni.2016.10.018
1246:10.1016/j.immuni.2018.01.007
551:cells. Like naive T cells, T
446:Peripheral memory T cells (T
37:. Their lineage is unclear.
21:Memory cell (disambiguation)
7:
2368:Boyman, Onur (April 2010).
1622:10.4049/jimmunol.175.9.5895
1573:10.4049/jimmunol.140.7.2171
692:inflammatory bowel diseases
366:cells) or central memory (T
247:and begins to proliferate (
40:
10:
2899:
2448:10.1038/s12276-020-00486-7
2336:10.1038/s41421-023-00605-4
2141:10.1016/j.jaut.2019.06.012
2083:10.1038/s41590-021-00985-3
1937:10.1016/j.jaut.2016.11.001
1820:10.1016/j.cell.2015.03.031
1761:Nature Reviews. Immunology
1481:10.1016/j.jaci.2018.07.014
1354:Nature Reviews. Immunology
1350:"+ T cell differentiation"
1060:Nature Reviews. Immunology
864:Nature Reviews. Immunology
519:inflammatory bowel disease
427:Effector memory T cells (T
117:Effector memory T cells (T
18:
2822:
2783:
2736:
2704:
2608:
2599:
2520:
2275:10.1038/s12276-019-0316-1
2187:The Journal of Immunology
1310:10.1016/j.coi.2013.09.003
404:Central memory T cells (T
94:Central memory T cells (T
2199:10.4049/jimmunol.2000937
2003:10.1016/j.it.2018.10.003
1888:10.1016/j.it.2010.12.004
710:, was detected in their
319:Epigenetic modifications
2832:Hematopoietic stem cell
2591:Lymphoplasmacytoid cell
2129:Journal of Autoimmunity
1925:Journal of Autoimmunity
1180:10.15252/embj.201798518
1130:10.1073/pnas.1307572110
809:10.1073/pnas.0503726102
408:cells) express CD45RO,
189:Homeostatic maintenance
65:effector memory T cells
16:Subset of T lymphocytes
533:Virtual memory T cells
399:Memory T cell subtypes
381:virtual memory T cells
375:) cells, stem memory T
303:
277:
54:central memory T cells
2738:Innate lymphoid cells
2714:Natural killer T cell
2387:10.1002/eji.201040466
1673:10.1186/1742-4933-5-6
1660:Immunity & Ageing
1609:Journal of Immunology
1560:Journal of Immunology
959:Immunological Reviews
661:Role in pathogenicity
299:
230:
174:Virtual memory T cell
1991:Trends in Immunology
1876:Trends in Immunology
1366:10.1038/nri.2017.146
704:rheumatoid arthritis
677:Herpes Simplex Virus
559:+, CD45RA+, CD62L+ (
515:rheumatoid arthritis
391:and usually express
19:For other uses, see
2706:Innate-like T cells
2586:Transitional B cell
1517:1999Natur.401..708S
1121:2013PNAS..11013498L
1072:10.1038/nri.2017.34
800:2005PNAS..102.9571K
668:autoimmune diseases
624:(TLRs), especially
622:Toll-like receptors
555:cells are CD45RO−,
1773:10.1038/nri.2015.3
688:multiple sclerosis
304:
278:
239:(N) encounters an
2850:
2849:
2818:
2817:
2732:
2731:
2257:(December 2019).
2071:Nature Immunology
1997:(12): 1021–1035.
1422:10.1111/imm.12074
1115:(33): 13498–503.
971:10.1111/imr.12087
909:Nature Immunology
739:Nature Immunology
672:Hepatitis B virus
268:cytotoxic T cells
231:On-Off-On model:
210:Lifetime overview
76:cytotoxic T cells
2890:
2770:Adaptive NK cell
2743:
2742:
2606:
2605:
2507:
2500:
2493:
2484:
2483:
2478:
2477:
2467:
2442:(8): 1255–1263.
2427:
2408:
2407:
2389:
2365:
2359:
2358:
2348:
2338:
2314:
2305:
2304:
2294:
2250:
2229:
2228:
2218:
2178:
2161:
2160:
2120:
2111:
2110:
2065:(January 2022).
2058:
2025:
2024:
2014:
1982:
1959:
1958:
1948:
1916:
1910:
1909:
1899:
1867:
1861:
1860:
1853:
1842:
1841:
1831:
1799:
1793:
1792:
1756:
1745:
1744:
1734:
1717:(6): 1270–1284.
1702:
1696:
1695:
1685:
1675:
1651:
1645:
1644:
1634:
1624:
1600:
1594:
1593:
1575:
1551:
1545:
1544:
1511:(6754): 708–12.
1500:
1494:
1493:
1483:
1459:
1444:
1443:
1433:
1401:
1388:
1387:
1377:
1345:
1332:
1331:
1321:
1289:
1268:
1267:
1257:
1225:
1202:
1201:
1191:
1168:The EMBO Journal
1159:
1153:
1152:
1142:
1132:
1100:
1094:
1093:
1083:
1051:
1045:
1044:
1034:
1002:
993:
992:
982:
950:
941:
940:
904:
898:
897:
887:
855:
832:
831:
821:
811:
779:
773:
772:
754:
730:
527:lipid metabolism
256:effector T cells
217:immunosenescence
29:are a subset of
2898:
2897:
2893:
2892:
2891:
2889:
2888:
2887:
2853:
2852:
2851:
2846:
2814:
2779:
2728:
2700:
2694:
2686:
2678:
2670:
2646:
2638:
2631:
2595:
2573:
2516:
2511:
2481:
2428:
2411:
2366:
2362:
2315:
2308:
2255:Shin, Eui-Cheol
2253:Kim, Tae-Shin;
2251:
2232:
2179:
2164:
2121:
2114:
2063:Shin, Eui-Cheol
2059:
2028:
1983:
1962:
1917:
1913:
1868:
1864:
1855:
1854:
1845:
1800:
1796:
1757:
1748:
1703:
1699:
1652:
1648:
1615:(9): 5895–903.
1601:
1597:
1552:
1548:
1501:
1497:
1460:
1447:
1402:
1391:
1346:
1335:
1290:
1271:
1226:
1205:
1160:
1156:
1101:
1097:
1052:
1048:
1023:10.1038/nm.2446
1011:Nature Medicine
1003:
996:
951:
944:
921:10.1038/ni.1718
905:
901:
876:10.1038/nri3567
856:
835:
780:
776:
731:
724:
720:
696:Crohn's disease
694:, for instance
684:type I diabetes
663:
634:
590:
569:
554:
550:
538:
524:
521:. Specific to T
508:
504:
499:
495:
491:
487:
483:
479:
475:
464:
460:
449:
442:
430:
407:
401:
378:
374:
369:
365:
360:
358:Sub-populations
321:
301:
282:T cell receptor
276:
262:in the case of
225:
212:
191:
183:
179:
169:
165:
161:
155:
147:
142:
138:
128:
124:
120:
113:
109:
101:
97:
71:
60:
43:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2896:
2886:
2885:
2880:
2875:
2870:
2865:
2848:
2847:
2845:
2844:
2839:
2834:
2828:
2826:
2820:
2819:
2816:
2815:
2813:
2812:
2807:
2802:
2801:
2800:
2790:
2784:
2781:
2780:
2778:
2777:
2772:
2767:
2762:
2757:
2751:
2749:
2740:
2734:
2733:
2730:
2729:
2727:
2726:
2721:
2716:
2710:
2708:
2702:
2701:
2699:
2698:
2697:
2696:
2692:
2688:
2684:
2680:
2676:
2672:
2668:
2659:
2654:
2644:
2636:
2629:
2621:
2615:
2609:
2603:
2597:
2596:
2594:
2593:
2588:
2583:
2582:
2581:
2571:
2567:
2562:
2557:
2552:
2547:
2542:
2537:
2532:
2526:
2524:
2518:
2517:
2510:
2509:
2502:
2495:
2487:
2480:
2479:
2409:
2380:(4): 936–939.
2360:
2323:Cell Discovery
2306:
2230:
2193:(3): 455–462.
2162:
2112:
2026:
1960:
1911:
1862:
1843:
1794:
1746:
1697:
1646:
1595:
1546:
1495:
1474:(3): 728–743.
1445:
1389:
1360:(5): 340–356.
1333:
1269:
1240:(2): 202–213.
1203:
1154:
1095:
1066:(6): 391–400.
1046:
1017:(10): 1290–7.
994:
942:
899:
833:
794:(27): 9571–6.
774:
721:
719:
716:
712:synovial fluid
700:celiac disease
662:
659:
633:
630:
589:
586:
568:
565:
552:
548:
541:
540:
536:
530:
522:
506:
502:
497:
493:
489:
485:
481:
477:
473:
462:
458:
452:
447:
444:
440:
428:
425:
405:
400:
397:
376:
372:
367:
363:
359:
356:
320:
317:
275:
274:
271:
264:helper T cells
252:
232:
224:
223:Lineage debate
221:
211:
208:
190:
187:
186:
185:
181:
177:
171:
167:
163:
159:
153:
149:
145:
140:
136:
130:
126:
122:
118:
115:
111:
107:
99:
95:
84:helper T cells
69:
58:
42:
39:
35:memory B cells
27:Memory T cells
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2895:
2884:
2883:Immune system
2881:
2879:
2876:
2874:
2871:
2869:
2866:
2864:
2861:
2860:
2858:
2843:
2842:Prolymphocyte
2840:
2838:
2835:
2833:
2830:
2829:
2827:
2825:
2824:Lymphopoiesis
2821:
2811:
2808:
2806:
2803:
2799:
2796:
2795:
2794:
2791:
2789:
2786:
2785:
2782:
2776:
2773:
2771:
2768:
2766:
2763:
2761:
2758:
2756:
2753:
2752:
2750:
2748:
2744:
2741:
2739:
2735:
2725:
2722:
2720:
2717:
2715:
2712:
2711:
2709:
2707:
2703:
2695:
2689:
2687:
2681:
2679:
2673:
2671:
2665:
2664:
2663:
2662:Memory T cell
2660:
2658:
2655:
2652:
2648:
2640:
2632:
2625:
2622:
2620:
2619:Cytotoxic CD8
2616:
2614:
2611:
2610:
2607:
2604:
2602:
2598:
2592:
2589:
2587:
2584:
2580:
2577:
2576:
2575:
2568:
2566:
2563:
2561:
2558:
2556:
2555:Marginal zone
2553:
2551:
2548:
2546:
2543:
2541:
2538:
2536:
2533:
2531:
2528:
2527:
2525:
2523:
2519:
2515:
2508:
2503:
2501:
2496:
2494:
2489:
2488:
2485:
2475:
2471:
2466:
2461:
2457:
2453:
2449:
2445:
2441:
2437:
2433:
2426:
2424:
2422:
2420:
2418:
2416:
2414:
2405:
2401:
2397:
2393:
2388:
2383:
2379:
2375:
2371:
2364:
2356:
2352:
2347:
2342:
2337:
2332:
2328:
2324:
2320:
2313:
2311:
2302:
2298:
2293:
2288:
2284:
2280:
2276:
2272:
2268:
2264:
2260:
2256:
2249:
2247:
2245:
2243:
2241:
2239:
2237:
2235:
2226:
2222:
2217:
2212:
2208:
2204:
2200:
2196:
2192:
2188:
2184:
2177:
2175:
2173:
2171:
2169:
2167:
2158:
2154:
2150:
2146:
2142:
2138:
2134:
2130:
2126:
2119:
2117:
2108:
2104:
2100:
2096:
2092:
2088:
2084:
2080:
2076:
2072:
2068:
2064:
2057:
2055:
2053:
2051:
2049:
2047:
2045:
2043:
2041:
2039:
2037:
2035:
2033:
2031:
2022:
2018:
2013:
2008:
2004:
2000:
1996:
1992:
1988:
1981:
1979:
1977:
1975:
1973:
1971:
1969:
1967:
1965:
1956:
1952:
1947:
1942:
1938:
1934:
1930:
1926:
1922:
1915:
1907:
1903:
1898:
1893:
1889:
1885:
1881:
1877:
1873:
1866:
1858:
1852:
1850:
1848:
1839:
1835:
1830:
1825:
1821:
1817:
1814:(4): 737–49.
1813:
1809:
1805:
1798:
1790:
1786:
1782:
1778:
1774:
1770:
1766:
1762:
1755:
1753:
1751:
1742:
1738:
1733:
1728:
1724:
1720:
1716:
1712:
1708:
1701:
1693:
1689:
1684:
1679:
1674:
1669:
1665:
1661:
1657:
1650:
1642:
1638:
1633:
1628:
1623:
1618:
1614:
1610:
1606:
1599:
1591:
1587:
1583:
1579:
1574:
1569:
1566:(7): 2171–8.
1565:
1561:
1557:
1550:
1542:
1538:
1534:
1530:
1526:
1525:10.1038/44385
1522:
1518:
1514:
1510:
1506:
1499:
1491:
1487:
1482:
1477:
1473:
1469:
1465:
1458:
1456:
1454:
1452:
1450:
1441:
1437:
1432:
1427:
1423:
1419:
1416:(3): 277–84.
1415:
1411:
1407:
1400:
1398:
1396:
1394:
1385:
1381:
1376:
1371:
1367:
1363:
1359:
1355:
1351:
1344:
1342:
1340:
1338:
1329:
1325:
1320:
1315:
1311:
1307:
1304:(5): 556–63.
1303:
1299:
1295:
1288:
1286:
1284:
1282:
1280:
1278:
1276:
1274:
1265:
1261:
1256:
1251:
1247:
1243:
1239:
1235:
1231:
1224:
1222:
1220:
1218:
1216:
1214:
1212:
1210:
1208:
1199:
1195:
1190:
1185:
1181:
1177:
1173:
1169:
1165:
1158:
1150:
1146:
1141:
1136:
1131:
1126:
1122:
1118:
1114:
1110:
1106:
1099:
1091:
1087:
1082:
1077:
1073:
1069:
1065:
1061:
1057:
1050:
1042:
1038:
1033:
1028:
1024:
1020:
1016:
1012:
1008:
1001:
999:
990:
986:
981:
976:
972:
968:
965:(1): 165–81.
964:
960:
956:
949:
947:
938:
934:
930:
926:
922:
918:
915:(5): 524–30.
914:
910:
903:
895:
891:
886:
881:
877:
873:
869:
865:
861:
854:
852:
850:
848:
846:
844:
842:
840:
838:
829:
825:
820:
815:
810:
805:
801:
797:
793:
789:
785:
778:
770:
766:
762:
758:
753:
752:10.1038/ni889
748:
745:(3): 225–34.
744:
740:
736:
729:
727:
722:
715:
713:
709:
708:peptidoglycan
705:
701:
697:
693:
689:
685:
680:
678:
673:
669:
658:
655:
651:
647:
643:
639:
629:
627:
623:
619:
615:
611:
607:
603:
599:
595:
585:
581:
577:
575:
564:
562:
558:
546:
534:
531:
528:
520:
516:
512:
471:
468:
465:are CD69 and
456:
453:
445:
438:
434:
426:
423:
419:
415:
411:
403:
402:
396:
394:
390:
386:
382:
355:
353:
349:
345:
341:
337:
333:
329:
325:
316:
314:
313:HIV infection
309:
298:
294:
291:
287:
283:
272:
269:
265:
261:
257:
253:
250:
246:
242:
238:
234:
233:
229:
220:
218:
207:
205:
201:
197:
175:
172:
157:
150:
134:
131:
116:
105:
93:
92:
91:
89:
85:
81:
77:
73:
66:
62:
55:
51:
47:
38:
36:
32:
31:T lymphocytes
28:
22:
2661:
2439:
2435:
2377:
2373:
2363:
2329:(114): 114.
2326:
2322:
2266:
2262:
2190:
2186:
2132:
2128:
2077:(1): 13–22.
2074:
2070:
1994:
1990:
1928:
1924:
1914:
1879:
1875:
1865:
1811:
1807:
1797:
1767:(2): 79–89.
1764:
1760:
1714:
1710:
1700:
1663:
1659:
1649:
1612:
1608:
1598:
1563:
1559:
1549:
1508:
1504:
1498:
1471:
1467:
1413:
1409:
1357:
1353:
1301:
1297:
1237:
1233:
1171:
1167:
1157:
1112:
1108:
1098:
1063:
1059:
1049:
1014:
1010:
962:
958:
912:
908:
902:
870:(1): 24–35.
867:
863:
791:
787:
777:
742:
738:
681:
679:infections.
664:
638:CD4+ T cells
635:
591:
584:efficiency.
582:
578:
576:expression.
570:
544:
542:
412:(CCR7), and
361:
322:
305:
279:
237:naive T cell
213:
192:
139:): Because T
106:. In mice, T
67:
64:
56:
53:
44:
26:
25:
2873:Human cells
2868:Lymphocytes
2837:Lymphoblast
2535:Plasmablast
2514:Lymphocytes
2269:(12): 1–9.
1882:(2): 50–6.
545:Stem memory
422:lymph nodes
379:cells, and
243:it becomes
2878:Immunology
2857:Categories
2651:Regulatory
2624:Helper CD4
2550:Follicular
2135:: 102301.
1410:Immunology
718:References
596:, such as
561:L-selectin
433:L-selectin
414:L-selectin
324:Epigenetic
235:After the
2810:LTi cells
2765:Null cell
2613:Thymocyte
2456:1226-3613
2283:1226-3613
2207:0022-1767
2157:198133084
2107:236933989
2091:1529-2908
1931:: 76–88.
594:cytokines
511:psoriasis
308:apoptosis
260:cytokines
245:activated
50:microbial
2798:Nuocytes
2747:NK cells
2579:B10 cell
2474:32859954
2396:20309907
2355:37968259
2346:10652011
2301:31827070
2225:33468558
2149:31326230
2099:34354279
2021:30413351
1955:27894837
1906:21288770
1838:25957682
1781:26688350
1741:27939671
1711:Immunity
1692:18657274
1666:(6): 6.
1641:16237082
1590:22340282
1533:10537110
1490:30195378
1440:23347146
1384:29379213
1328:24148236
1264:29466753
1234:Immunity
1198:29752423
1149:23898211
1090:28480897
1041:21926977
989:23947354
929:19305395
894:24336101
828:15980149
761:12563257
614:NK cells
496:cells, T
467:integrin
332:cytokine
286:cytokine
41:Function
2863:T cells
2601:T cells
2530:B1 cell
2522:B cells
2465:8080565
2404:7918378
2292:6906361
2216:7839146
2012:6269193
1946:6066671
1897:3039080
1829:4426972
1789:3155731
1732:5177508
1683:2515281
1582:2965180
1541:4378970
1513:Bibcode
1431:3701173
1375:6327307
1319:3858177
1255:5826622
1189:6043851
1140:3746847
1117:Bibcode
1081:5569888
1032:3192229
980:3748618
885:4032067
819:1172264
796:Bibcode
769:7209417
290:antigen
241:antigen
46:Antigen
2545:Memory
2540:Plasma
2472:
2462:
2454:
2402:
2394:
2353:
2343:
2299:
2289:
2281:
2223:
2213:
2205:
2155:
2147:
2105:
2097:
2089:
2019:
2009:
1953:
1943:
1904:
1894:
1836:
1826:
1787:
1779:
1739:
1729:
1690:
1680:
1639:
1588:
1580:
1539:
1531:
1505:Nature
1488:
1438:
1428:
1382:
1372:
1326:
1316:
1262:
1252:
1196:
1186:
1174:(14).
1147:
1137:
1088:
1078:
1039:
1029:
987:
977:
935:
927:
892:
882:
826:
816:
767:
759:
517:, and
393:CD45RO
342:, and
249:divide
2657:Naïve
2565:Pre-B
2560:Naïve
2400:S2CID
2153:S2CID
2103:S2CID
1785:S2CID
1586:S2CID
1537:S2CID
937:24388
933:S2CID
765:S2CID
654:IL-27
646:IL-1β
642:CD122
618:IFN-γ
610:NKG2D
606:IL-12
602:IL-18
598:IL-15
344:IL17A
202:) or
200:IL-15
196:IL-17
166:and T
125:and T
104:STAT5
2617:αβ (
2574:cell
2470:PMID
2452:ISSN
2392:PMID
2351:PMID
2297:PMID
2279:ISSN
2221:PMID
2203:ISSN
2145:PMID
2095:PMID
2087:ISSN
2017:PMID
1951:PMID
1902:PMID
1834:PMID
1808:Cell
1777:PMID
1737:PMID
1688:PMID
1637:PMID
1578:PMID
1529:PMID
1486:PMID
1436:PMID
1380:PMID
1324:PMID
1260:PMID
1194:PMID
1145:PMID
1086:PMID
1037:PMID
985:PMID
925:PMID
890:PMID
824:PMID
757:PMID
698:and
690:and
650:Th17
626:TLR2
574:CCR5
557:CCR7
470:αeβ7
441:EMRA
437:CD44
418:CD44
352:IFNγ
336:IFNγ
198:and
127:EMRA
121:): T
98:): T
63:and
2572:reg
2460:PMC
2444:doi
2382:doi
2341:PMC
2331:doi
2287:PMC
2271:doi
2211:PMC
2195:doi
2191:206
2137:doi
2133:103
2079:doi
2007:PMC
1999:doi
1941:PMC
1933:doi
1892:PMC
1884:doi
1824:PMC
1816:doi
1812:161
1769:doi
1727:PMC
1719:doi
1678:PMC
1668:doi
1627:hdl
1617:doi
1613:175
1568:doi
1564:140
1521:doi
1509:401
1476:doi
1472:142
1426:PMC
1418:doi
1414:139
1370:PMC
1362:doi
1314:PMC
1306:doi
1250:PMC
1242:doi
1184:PMC
1176:doi
1135:PMC
1125:doi
1113:110
1076:PMC
1068:doi
1027:PMC
1019:doi
975:PMC
967:doi
963:255
917:doi
880:PMC
872:doi
814:PMC
804:doi
792:102
747:doi
553:SCM
549:SCM
389:CD8
387:or
385:CD4
377:SCM
348:CD8
340:IL4
328:CD4
154:SCM
88:CD4
80:CD8
2859::
2719:γδ
2693:VM
2685:RM
2677:EM
2669:CM
2649:/
2647:17
2641:/
2633:/
2630:FH
2626:/
2468:.
2458:.
2450:.
2440:52
2438:.
2434:.
2412:^
2398:.
2390:.
2378:40
2376:.
2372:.
2349:.
2339:.
2325:.
2321:.
2309:^
2295:.
2285:.
2277:.
2267:51
2265:.
2261:.
2233:^
2219:.
2209:.
2201:.
2189:.
2185:.
2165:^
2151:.
2143:.
2131:.
2127:.
2115:^
2101:.
2093:.
2085:.
2075:23
2073:.
2069:.
2029:^
2015:.
2005:.
1995:39
1993:.
1989:.
1963:^
1949:.
1939:.
1929:77
1927:.
1923:.
1900:.
1890:.
1880:32
1878:.
1874:.
1846:^
1832:.
1822:.
1810:.
1806:.
1783:.
1775:.
1765:16
1763:.
1749:^
1735:.
1725:.
1715:45
1713:.
1709:.
1686:.
1676:.
1662:.
1658:.
1635:.
1625:.
1611:.
1607:.
1584:.
1576:.
1562:.
1558:.
1535:.
1527:.
1519:.
1507:.
1484:.
1470:.
1466:.
1448:^
1434:.
1424:.
1412:.
1408:.
1392:^
1378:.
1368:.
1358:18
1356:.
1352:.
1336:^
1322:.
1312:.
1302:25
1296:.
1272:^
1258:.
1248:.
1238:48
1236:.
1232:.
1206:^
1192:.
1182:.
1172:37
1170:.
1166:.
1143:.
1133:.
1123:.
1111:.
1107:.
1084:.
1074:.
1064:17
1062:.
1058:.
1035:.
1025:.
1015:17
1013:.
1009:.
997:^
983:.
973:.
961:.
957:.
945:^
931:.
923:.
913:10
911:.
888:.
878:.
868:14
866:.
862:.
836:^
822:.
812:.
802:.
790:.
786:.
763:.
755:.
741:.
737:.
725:^
714:.
686:,
604:,
600:,
537:VM
535:(T
523:RM
513:,
507:RM
503:RM
498:RM
494:EM
490:RM
486:RM
482:RM
478:RM
474:RM
463:RM
459:RM
457:(T
448:PM
429:EM
406:CM
373:RM
371:(T
368:CM
364:EM
338:,
270:).
182:VM
178:VM
176:(T
168:EM
164:CM
160:CM
146:RM
141:RM
137:RM
135:(T
123:EM
119:EM
112:EM
108:CM
100:CM
96:CM
70:EM
68:(T
59:CM
57:(T
2691:T
2683:T
2675:T
2667:T
2653:)
2645:h
2643:T
2639:3
2637:h
2635:T
2628:T
2570:B
2506:e
2499:t
2492:v
2476:.
2446::
2406:.
2384::
2357:.
2333::
2327:9
2303:.
2273::
2227:.
2197::
2159:.
2139::
2109:.
2081::
2023:.
2001::
1957:.
1935::
1908:.
1886::
1859:.
1840:.
1818::
1791:.
1771::
1743:.
1721::
1694:.
1670::
1664:5
1643:.
1629::
1619::
1592:.
1570::
1543:.
1523::
1515::
1492:.
1478::
1442:.
1420::
1386:.
1364::
1330:.
1308::
1266:.
1244::
1200:.
1178::
1151:.
1127::
1119::
1092:.
1070::
1043:.
1021::
991:.
969::
939:.
919::
896:.
874::
830:.
806::
798::
771:.
749::
743:4
547:T
501:T
156:)
144:T
86:(
78:(
72:)
61:)
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.