103:
226:
22:
122:
214:
mildew growth by lowering indoor temperatures. For them to be effective, air conditioners must recirculate the existing indoor air and not be exposed to warm, humid outside air. Some energy efficient air conditioners may cool a room so quickly that they do not have an opportunity to also effectively collect and drain significant ambient water vapour.
118:, usually with a flat growth habit. Molds can thrive on many organic materials, including clothing, leather, paper, and the ceilings, walls and floors of homes or offices with poor moisture control. Mildew can be cleaned using specialized mildew remover, or substances such as bleach (though they may discolour the surface).
213:
Air conditioners are one effective tool for removing moisture and heat from otherwise humid warm air. The coils of an air conditioner cause moisture in the air to condense on them, eventually losing this excess moisture through a drain and placing it back into the environment. They can also inhibit
192:
of 62–93%), and reasonable warmth (77–88 °F or 25–31 °C) is optimal. Still, some growth can occur anywhere between freezing and 95 °F (35 °C). Slightly acidic conditions are also preferred. At warmer temperatures, air can hold a greater volume of water; as air temperatures drop,
209:
With warmer temperatures, the water holding capacity of the air increases. This means that if the amount of water vapour in the warming air remains the same, the air will become drier (i.e. it has a lower relative humidity). This again inhibits fungal growth. However, warm, growth-favoring
135:. Colour alone is not always a reliable indicator of the species of mold. Proper identification requires a microbiologist or mycologist. Mold growth found on cellulose-based substrates or materials where moisture levels are high (90 per cent or greater) is often
166:
that adheres to these surfaces. Glass, plastic, and concrete provide no food for organic growth and as such cannot support mold or mildew growth alone without biofilm present. In places with stagnant air, such as basements, molds can produce a strong
56:
filaments) produced especially on living plants or organic matter such as wood, paper or leather. Both mold and mildew produce distinct offensive odours, and both have been identified as the cause of certain human ailments.
193:
so does the ability of air to hold moisture, which then tends to condense on cool surfaces. This can work to bring moisture onto surfaces where mildew is then likely to grow (such as an exterior wall).
188:
Mildew requires certain factors to develop. Without any one of these, it cannot reproduce and grow. The requirements are a food source (any organic material), sufficient ambient moisture (a
48:, largely by its colour: molds appear in shades of black, blue, red, and green, whereas mildew is white. It appears as a thin, superficial growth consisting of minute
196:
Preventing the growth of mildew therefore requires a balance between moisture and temperature. This can be achieved by minimizing the moisture available in the air.
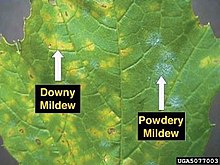
146:. This species is commonly found indoors on wet materials containing cellulose, such as wallboard (drywall), jute, wicker, straw baskets, and other paper materials.
321:
274:
129:
There are many species of mold. The black mold which grows in attics, on window sills, and other places where moisture levels are moderate often is
202:
at or below 70 °F (21 °C) will inhibit growth, but only if the relative humidity is low enough to prevent water condensation (i.e., the
411:
386:
150:
does not, however, grow on plastic, vinyl, concrete, glass, ceramic tile, or metals. A variety of other mold species, such as
448:
244:
421:
168:
282:
443:
334:
137:
106:
Unidentified species of mildew growing on a plastic shower curtain (scale gradations = 1p
174:
The pink "mildew" often found on plastic shower curtains and bathroom tile is a red yeast,
83:
102:
8:
21:
417:
254:
189:
393:
304:
199:
70:
356:
162:, may appear to grow on non-cellulosic surfaces but are actually growing on the
249:
30:
437:
210:
temperatures coupled with high relative humidity will support mildew growth.
239:
231:
131:
26:
176:
158:
152:
115:
79:
75:
65:
203:
142:"Black mold," also known as "toxic black mold", properly refers to
163:
121:
61:
53:
49:
41:
413:
Heritage Eaters – Insects & Fungi in
Heritage Collections
87:
107:
44:. It is distinguished from its closely related counterpart,
45:
91:
90:
on leaves, formerly thought to distill from the air like
322:
The
American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language
392:. University of Florida IFAS Extension. Archived from
114:
The term mildew is often used generically to refer to
221:
435:
183:
335:"Cleaning Mildew from Retractable Awnings"
94:), and later came to mean mold or fungus.
74:. It is also used more generally to mean
68:, or fungus-like organisms in the family
120:
101:
60:In horticulture, mildews are species of
20:
409:
436:
380:
378:
355:
97:
384:
245:Phase I environmental site assessment
324:, 1969, entry "mecnlit-" in Appendix
375:
309:Merriam-Webster's Online Dictionary
13:
387:"How to prevent and remove mildew"
14:
460:
311:(11th ed.). 14 January 2024.
279:Compact Oxford English Dictionary
385:Peart, Virginia (October 2001).
224:
403:
349:
327:
315:
297:
267:
1:
416:. London: James & James.
260:
449:Plant pathogens and diseases
357:"What does mold smell like?"
7:
217:
10:
465:
410:Florian, Mary-Lou (1997).
86:(a substance secreted by
184:Environmental conditions
125:A mildew-infected plant
33:(right) on a grape leaf
138:Stachybotrys chartarum
126:
111:
34:
337:. Shade & Privacy
124:
105:
24:
98:Household varieties
363:. 19 February 2019
127:
112:
35:
29:(left) along with
399:on 19 March 2015.
255:Obligate parasite
206:is not reached).
190:relative humidity
456:
444:Building defects
428:
427:
407:
401:
400:
398:
391:
382:
373:
372:
370:
368:
353:
347:
346:
344:
342:
331:
325:
319:
313:
312:
301:
295:
294:
292:
290:
281:. Archived from
271:
234:
229:
228:
227:
200:Air temperatures
464:
463:
459:
458:
457:
455:
454:
453:
434:
433:
432:
431:
424:
408:
404:
396:
389:
383:
376:
366:
364:
354:
350:
340:
338:
333:
332:
328:
320:
316:
303:
302:
298:
288:
286:
285:on 8 March 2016
273:
272:
268:
263:
230:
225:
223:
220:
186:
100:
82:, mildew meant
71:Peronosporaceae
17:
12:
11:
5:
462:
452:
451:
446:
430:
429:
422:
402:
374:
348:
326:
314:
296:
265:
264:
262:
259:
258:
257:
252:
250:Powdery mildew
247:
242:
236:
235:
219:
216:
185:
182:
99:
96:
31:powdery mildew
16:Form of fungus
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
461:
450:
447:
445:
442:
441:
439:
425:
423:1-873936-49-4
419:
415:
414:
406:
395:
388:
381:
379:
362:
358:
352:
336:
330:
323:
318:
310:
306:
300:
284:
280:
276:
270:
266:
256:
253:
251:
248:
246:
243:
241:
238:
237:
233:
222:
215:
211:
207:
205:
201:
197:
194:
191:
181:
179:
178:
172:
170:
165:
161:
160:
155:
154:
149:
145:
141:
139:
134:
133:
123:
119:
117:
109:
104:
95:
93:
89:
85:
81:
77:
73:
72:
67:
64:in the order
63:
58:
55:
51:
47:
43:
40:is a form of
39:
32:
28:
23:
19:
412:
405:
394:the original
365:. Retrieved
360:
351:
341:15 September
339:. Retrieved
329:
317:
308:
299:
287:. Retrieved
283:the original
278:
269:
240:Downy mildew
232:Fungi portal
212:
208:
198:
195:
187:
175:
173:
157:
151:
148:S. chartarum
147:
144:S. chartarum
143:
136:
132:Cladosporium
130:
128:
113:
69:
59:
37:
36:
27:downy mildew
18:
177:Rhodotorula
169:musty odour
159:Aspergillus
153:Penicillium
116:mold growth
80:Old English
76:mold growth
66:Erysiphales
25:Example of
438:Categories
261:References
204:dew point
305:"Mildew"
289:2 August
275:"Mildew"
218:See also
84:honeydew
164:biofilm
420:
367:11 May
361:US EPA
88:aphids
62:fungus
54:fungal
50:hyphae
42:fungus
38:Mildew
397:(PDF)
390:(PDF)
78:. In
418:ISBN
369:2023
343:2014
291:2013
46:mold
156:or
92:dew
440::
377:^
359:.
307:.
277:.
180:.
171:.
108:μm
426:.
371:.
345:.
293:.
140:.
110:)
52:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.