321:, a purification method that results in high purity and low endotoxin levels is desirable. Similarly, if the plasmid is to be used for sequencing or PCR, a purification method that results in high yield and minimal contaminants is desirable. However, multiple methods of nucleic acid purification exist. All work on the principle of generating conditions where either only the nucleic acid precipitates, or only other
114:, for example a gene encoding ampicillin or kanamycin resistance, which allows bacteria that have been successfully transformed to multiply uninhibited. Bacteria that have not taken up the plasmid vector are assumed to lack the resistance gene, and thus only colonies representing successful transformations are expected to grow. Bacteria are grown under favourable conditions.
225:
Kits are available from varying manufacturers to purify plasmid DNA, which are named by size of bacterial culture and corresponding plasmid yield. In increasing order they are: miniprep, midiprep, maxiprep, megaprep, and gigaprep. The plasmid DNA yield will vary depending on the plasmid copy number,
221:
Plasmid preparation can be divided into five main categories based on the scale of the preparation: minipreparation, midipreparation, maxipreparation, megapreparation, and gigapreparation. The choice of which method to use will depend on the amount of plasmid DNA required, as well as the specific
20:
408:
ions binds to plasmid DNA, separating them from unwanted compounds by a magnetic rod or stand. The plasmid-bound beads are then released by removal of the magnetic field and extracted in an elution solution for down-stream experiments such as
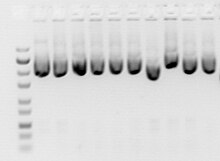
269:. A typical plasmid DNA yield of a miniprep is 5 to 50 μg depending on the cell strain. Miniprep of a large number of plasmids can also be done conveniently on filter paper by lysing the cell and eluting the plasmid on to filter paper.
363:
is a method of purifying DNA, RNA or plasmid from a sample using a spin column filter. The method is based on the principle of selectively binding nucleic acids to a solid matrix in the spin column, while other contaminants, such as
340:, including plasmid DNA. The basic principle of this method is that nucleic acids are insoluble in ethanol or isopropanol but soluble in water. Therefore, it works by using
380:
is that DNA and RNA are relatively insoluble in phenol and chloroform, while other cellular components are relatively soluble in these solvents. The addition of a
313:
It is important to consider the downstream applications of the plasmid DNA when choosing a purification method. For example, if the plasmid is to be used for
142:
are denatured; the plasmid DNA however, remains stable. Some scientists reduce the concentration of NaOH used to 0.1M in order to reduce the occurrence of
1545:
261:
method. The extracted plasmid DNA resulting from performing a miniprep is itself often called a "miniprep". Minipreps are used in the process of
368:
and salts, are washed away. The conditions are then changed to elute the purified nucleic acid off the column using a suitable elution buffer.
173:, to break down bacterial cells and release the plasmid DNA. There are several different mechanical lysis methods that can be used, including
360:
254:
388:
mixture will dissolve protein and lipid contaminants, leaving the nucleic acids in the aqueous phase. It also denatures proteins, like
201:
to digest the cell wall and release the plasmid DNA. The most commonly used enzyme for this purpose is lysozyme, which breaks down the
1676:
439:"Protocol: a rapid and economical procedure for purification of plasmid or plant DNA with diverse applications in plant biology"
213:
is usually added to the bacterial culture, followed by heating and/or shaking the culture to release the plasmid DNA.
130:
The most common method is alkaline lysis, which involves the use of a high concentration of a basic solution, such as
62:. During the purification procedure, the plasmid DNA is often separated from contaminating proteins and genomic DNA.
377:
615:
417:. This form of miniprep can also be automated, which increases the conveniency while reducing mechanical error.
161:
DNA and proteins form large complexes and precipitate; but the small bacterial DNA plasmids stay in solution.
1001:"Programming pluripotent precursor cells derived from Xenopus embryos to generate specific tissues and organs"
943:"Combined enzymatic and mechanical cell disruption and lipid extraction of green alga Neochloris oleoabundans"
718:"Plasmid encoded antibiotic resistance: acquisition and transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in bacteria"
1681:
297:
The starting E. coli culture volume is 500 mL – 2.5 L of LB and the expected DNA yield is 1.5-2.5 mg.
122:
There are several methods for cell lysis, including alkaline lysis, mechanical lysis, and enzymatic lysis.
1656:
1577:
1686:
289:
The starting E. coli culture volume is 100-200 mL of LB and the expected DNA yield is 500-850 μg.
174:
823:"Recovering Microalgal Bioresources: A Review of Cell Disruption Methods and Extraction Technologies"
410:
103:
697:
614:
Suza W, Lee D (15 October 2021). "11. Recombinant DNA Technology; Ligase enzyme and gene cloning".
305:
The starting E. coli culture volume is 2.5-5 L of LB and the expected DNA yield is 7.5–10 mg.
93:
206:
65:
These methods invariably involve three steps: growth of the bacterial culture, harvesting and
1495:"Current Nucleic Acid Extraction Methods and Their Implications to Point-of-Care Diagnostics"
633:"Scaling-up recombinant plasmid DNA for clinical trial: current concern, solution and status"
333:
107:
69:
of the bacteria, and purification of the plasmid DNA. Purification of plasmids is central to
404:
In beads-based extraction, addition of a mixture containing magnetic beads commonly made of
890:
550:
1662:
A miniprep procedure using diatomaceous earth to bind DNA during purification and washing.
8:
782:
511:
494:
1237:"Simple methods for preparation of plasmid DNA yielding long and accurate sequence data"
894:
554:
1521:
1494:
1436:
1409:
1382:
1361:
1081:
1054:
1027:
1000:
969:
942:
913:
878:
849:
822:
791:
766:
742:
717:
573:
538:
465:
438:
414:
1632:
1607:
1336:
1310:
1285:
1261:
1236:
1212:
1187:
1163:
1138:
1637:
1526:
1462:
1441:
1387:
1315:
1266:
1217:
1168:
1086:
1032:
974:
918:
854:
796:
747:
654:
578:
516:
470:
262:
111:
70:
47:
1627:
1619:
1516:
1506:
1431:
1421:
1377:
1369:
1305:
1297:
1256:
1248:
1207:
1199:
1158:
1150:
1076:
1066:
1022:
1012:
964:
954:
908:
898:
844:
834:
786:
778:
737:
729:
672:
644:
568:
558:
506:
460:
450:
396:
digestion. Otherwise, smearing may occur in enzyme restricted form of plasmid DNA.
227:
131:
98:
27:
649:
632:
348:
of DNA, causing it to precipitate out of solution and then it can be collected by
903:
563:
539:"A one-step miniprep for the isolation of plasmid DNA and lambda phage particles"
318:
151:
50:
experiments and is essential for the successful use of plasmids in research and
1108:
349:
278:
258:
250:
74:
39:
839:
1670:
1608:"A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA"
1362:"Purifying plasmid DNA from bacterial colonies using the QIAGEN Miniprep Kit"
1301:
1252:
1139:"A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA"
202:
106:
and isolated. Virtually all plasmid vectors in common use encode one or more
51:
1203:
1071:
1623:
1530:
1511:
1445:
1391:
1154:
1090:
1036:
978:
922:
858:
800:
751:
733:
658:
582:
520:
474:
337:
314:
178:
78:
1426:
1319:
1270:
1221:
455:
1641:
1172:
959:
493:
Prazeres DM, Monteiro GA (December 2014). Tolmasky ME, Alonso JC (eds.).
345:
322:
169:
Mechanical lysis involves the use of physical force, such as grinding or
158:
155:
73:. A purified plasmid can be used for many standard applications, such as
24:
1055:"Vector Design for Improved DNA Vaccine Efficacy, Safety and Production"
1657:
http://www.protocol-online.org/prot/Molecular_Biology/Plasmid/Miniprep/
385:
182:
170:
1661:
1017:
143:
238:
Minipreparation of plasmid DNA is a rapid, small-scale isolation of
392:, which is especially important if the plasmids are to be used for
246:
210:
194:
139:
135:
89:
59:
19:
352:. The soluble fraction is discarded to remove other biomolecules.
365:
341:
266:
239:
147:
43:
1373:
1188:"A rapid and efficient 'miniprep' for isolation of plasmid DNA"
393:
381:
198:
879:"Insights into cell wall disintegration of Chlorella vulgaris"
1286:"One step 'miniprep' method for the isolation of plasmid DNA"
389:
134:, to lyse the bacterial cells. When bacteria are lysed under
66:
1410:"DNA, RNA, and protein extraction: the past and the present"
405:
1185:
537:
Lezin G, Kosaka Y, Yost HJ, Kuehn MR, Brunelli L (2011).
242:
55:
336:
is a widely used method for purifying and concentrating
325:
precipitate, allowing the nucleic acid to be separated.
1492:
696:
Batree L, Shriner W, Creech C (2017). "Biotechnology".
117:
1463:"Phenol-Chloroform Extraction | Herman Lab | Nebraska"
876:
54:. Many methods have been developed to purify plasmid
1337:"Plasmid Mini-Prep | College of Biological Sciences"
1234:
536:
281:(LB) and the expected DNA yield is 100-350 μg.
16:
Biological method of DNA extraction and purification
1578:"Barrick Lab :: ProtocolsEthanolPrecipitation"
695:
277:The starting E. coli culture volume is 15-25 mL of
138:conditions (pH 12.0–12.5) both chromosomal DNA and
820:
767:"Plasmid Detection, Characterization, and Ecology"
630:
84:
1493:Ali N, Rampazzo RC, Costa AD, Krieger MA (2017).
1235:Kovalenko SA, Tanaka M, Ozawa T (December 1994).
1186:Serghini MA, Ritzenthaler C, Pinck L (May 1989).
764:
631:Ismail R, Allaudin ZN, Lila MA (September 2012).
1668:
941:Wang D, Li Y, Hu X, Su W, Zhong M (April 2015).
492:
154:to lower the pH to around 7, the large and less
371:
998:
877:Weber S, Grande PM, Blank LM, Klose H (2022).
765:Smalla K, Jechalke S, Top EM (February 2015).
308:
1543:
1605:
1359:
1136:
821:Rahman MM, Hosano N, Hosano H (April 2022).
947:International Journal of Molecular Sciences
361:Spin column-based nucleic acid purification
1414:Journal of Biomedicine & Biotechnology
940:
1631:
1520:
1510:
1435:
1425:
1381:
1309:
1283:
1260:
1211:
1162:
1080:
1070:
1026:
1016:
968:
958:
912:
902:
848:
838:
790:
741:
648:
600:. Universal Scientific. pp. 119–126.
572:
562:
510:
464:
454:
436:
399:
249:. Commonly used miniprep methods include
1052:
617:Genetics, Agriculture, and Biotechnology
595:
328:
18:
1407:
1106:
715:
613:
222:application for which it will be used.
216:
92:are almost always purified from liquid
1669:
1331:
1329:
1132:
1130:
1128:
1102:
1100:
999:Borchers A, Pieler T (November 2010).
936:
934:
932:
872:
870:
868:
816:
814:
812:
810:
230:, the growth conditions, and the kit.
1606:Birnboim HC, Doly J (November 1979).
1488:
1486:
1484:
1482:
1457:
1455:
1403:
1401:
1137:Birnboim HC, Doly J (November 1979).
1048:
1046:
994:
992:
990:
988:
488:
486:
484:
437:Li JF, Li L, Sheen J (January 2010).
783:10.1128/microbiolspec.PLAS-0038-2014
711:
709:
702:. Open Oregon Educational Resources.
609:
607:
532:
530:
512:10.1128/microbiolspec.PLAS-0022-2014
432:
430:
118:Harvesting and lysis of the bacteria
1326:
1125:
1097:
929:
865:
807:
164:
13:
1598:
1537:
1479:
1452:
1398:
1360:Zhang S, Cahalan MD (2007-07-29).
1043:
985:
758:
598:Laboratory Methods in Microbiology
481:
300:
292:
284:
272:
233:
188:
46:. It is an important step in many
14:
1698:
1650:
1366:Journal of Visualized Experiments
706:
604:
527:
427:
125:
596:Bouchard R, et al. (2010).
1677:Biological techniques and tools
1570:
1353:
1277:
1228:
1179:
722:British Journal of Pharmacology
257:based kits. It is based on the
85:Growth of the bacterial culture
1546:"Ethanol Precipitation of DNA"
1544:Zeugin JA, Hartley JL (1985).
689:
665:
624:
589:
355:
1:
1499:BioMed Research International
650:10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.02.061
420:
193:Enzymatic lysis, also called
904:10.1371/journal.pone.0262500
564:10.1371/journal.pone.0023457
495:"Plasmid Biopharmaceuticals"
378:phenol-chloroform extraction
372:Phenol–chloroform extraction
7:
376:The basic principle of the
309:Purification of plasmid DNA
197:lysis, involves the use of
150:-containing neutralization
10:
1703:
1053:Williams JA (June 2013).
840:10.3390/molecules27092786
716:Bennett PM (March 2008).
1408:Tan SC, Yiap BC (2009).
1284:Chowdhury K (May 1991).
1107:Zazilek G (2010-04-12).
620:. Iowa State University.
146:. After the addition of
1072:10.3390/vaccines1030225
23:Plasmid miniprep. 0.8%
1612:Nucleic Acids Research
1302:10.1093/nar/19.10.2792
1290:Nucleic Acids Research
1253:10.1093/nar/22.25.5771
1241:Nucleic Acids Research
1192:Nucleic Acids Research
1143:Nucleic Acids Research
734:10.1038/sj.bjp.0707607
728:(Suppl 1): S347–S357.
400:Beads-based extraction
207:Gram-positive bacteria
31:
1204:10.1093/nar/17.9.3604
1113:askabiologist.asu.edu
777:(1): PLAS–0038–2014.
771:Microbiology Spectrum
699:Principles of biology
499:Microbiology Spectrum
456:10.1186/1746-4811-6-1
415:restriction digestion
334:Ethanol precipitation
329:Ethanol precipitation
265:to analyze bacterial
108:antibiotic resistance
42:and purification for
22:
1624:10.1093/nar/7.6.1513
1512:10.1155/2017/9306564
1155:10.1093/nar/7.6.1513
960:10.3390/ijms16047707
217:Preparations by size
205:in the cell wall of
1682:Genetics techniques
1427:10.1155/2009/574398
895:2022PLoSO..1762500W
555:2011PLoSO...623457L
226:type and size, the
36:plasmid preparation
102:, which have been
32:
1687:Molecular biology
1467:hermanlab.unl.edu
1247:(25): 5771–5772.
1018:10.3390/mi8030083
643:(41): 5914–5920.
263:molecular cloning
112:selectable marker
94:bacteria cultures
71:molecular cloning
48:molecular biology
1694:
1645:
1635:
1618:(6): 1513–1523.
1592:
1591:
1589:
1588:
1574:
1568:
1567:
1565:
1564:
1550:
1541:
1535:
1534:
1524:
1514:
1490:
1477:
1476:
1474:
1473:
1459:
1450:
1449:
1439:
1429:
1405:
1396:
1395:
1385:
1357:
1351:
1350:
1348:
1347:
1333:
1324:
1323:
1313:
1281:
1275:
1274:
1264:
1232:
1226:
1225:
1215:
1183:
1177:
1176:
1166:
1149:(6): 1513–1523.
1134:
1123:
1122:
1120:
1119:
1109:"Alkaline Lysis"
1104:
1095:
1094:
1084:
1074:
1050:
1041:
1040:
1030:
1020:
996:
983:
982:
972:
962:
953:(4): 7707–7722.
938:
927:
926:
916:
906:
874:
863:
862:
852:
842:
818:
805:
804:
794:
762:
756:
755:
745:
713:
704:
703:
693:
687:
686:
684:
683:
669:
663:
662:
652:
628:
622:
621:
611:
602:
601:
593:
587:
586:
576:
566:
534:
525:
524:
514:
490:
479:
478:
468:
458:
434:
228:bacterial strain
165:Mechanical lysis
132:sodium hydroxide
28:ethidium bromide
1702:
1701:
1697:
1696:
1695:
1693:
1692:
1691:
1667:
1666:
1653:
1648:
1601:
1599:Further reading
1596:
1595:
1586:
1584:
1576:
1575:
1571:
1562:
1560:
1548:
1542:
1538:
1491:
1480:
1471:
1469:
1461:
1460:
1453:
1406:
1399:
1358:
1354:
1345:
1343:
1335:
1334:
1327:
1282:
1278:
1233:
1229:
1184:
1180:
1135:
1126:
1117:
1115:
1105:
1098:
1051:
1044:
997:
986:
939:
930:
889:(1): e0262500.
875:
866:
819:
808:
763:
759:
714:
707:
694:
690:
681:
679:
671:
670:
666:
629:
625:
612:
605:
594:
590:
535:
528:
491:
482:
435:
428:
423:
402:
374:
358:
331:
319:electroporation
311:
303:
301:Gigapreparation
295:
293:Megapreparation
287:
285:Maxipreparation
275:
273:Midipreparation
236:
234:Minipreparation
219:
191:
189:Enzymatic lysis
183:ultrasonication
167:
128:
120:
87:
38:is a method of
17:
12:
11:
5:
1700:
1690:
1689:
1684:
1679:
1665:
1664:
1659:
1652:
1651:External links
1649:
1647:
1646:
1602:
1600:
1597:
1594:
1593:
1582:barricklab.org
1569:
1536:
1478:
1451:
1397:
1352:
1325:
1276:
1227:
1178:
1124:
1096:
1065:(3): 225–249.
1042:
1011:(3): 413–426.
984:
928:
864:
806:
757:
705:
688:
664:
623:
603:
588:
526:
480:
425:
424:
422:
419:
411:transformation
401:
398:
373:
370:
357:
354:
350:centrifugation
330:
327:
310:
307:
302:
299:
294:
291:
286:
283:
279:Lysogeny broth
274:
271:
259:alkaline lysis
251:alkaline lysis
235:
232:
218:
215:
190:
187:
166:
163:
127:
126:Alkaline lysis
124:
119:
116:
86:
83:
40:DNA extraction
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1699:
1688:
1685:
1683:
1680:
1678:
1675:
1674:
1672:
1663:
1660:
1658:
1655:
1654:
1643:
1639:
1634:
1629:
1625:
1621:
1617:
1613:
1609:
1604:
1603:
1583:
1579:
1573:
1558:
1554:
1547:
1540:
1532:
1528:
1523:
1518:
1513:
1508:
1504:
1500:
1496:
1489:
1487:
1485:
1483:
1468:
1464:
1458:
1456:
1447:
1443:
1438:
1433:
1428:
1423:
1419:
1415:
1411:
1404:
1402:
1393:
1389:
1384:
1379:
1375:
1371:
1367:
1363:
1356:
1342:
1338:
1332:
1330:
1321:
1317:
1312:
1307:
1303:
1299:
1295:
1291:
1287:
1280:
1272:
1268:
1263:
1258:
1254:
1250:
1246:
1242:
1238:
1231:
1223:
1219:
1214:
1209:
1205:
1201:
1197:
1193:
1189:
1182:
1174:
1170:
1165:
1160:
1156:
1152:
1148:
1144:
1140:
1133:
1131:
1129:
1114:
1110:
1103:
1101:
1092:
1088:
1083:
1078:
1073:
1068:
1064:
1060:
1056:
1049:
1047:
1038:
1034:
1029:
1024:
1019:
1014:
1010:
1006:
1002:
995:
993:
991:
989:
980:
976:
971:
966:
961:
956:
952:
948:
944:
937:
935:
933:
924:
920:
915:
910:
905:
900:
896:
892:
888:
884:
880:
873:
871:
869:
860:
856:
851:
846:
841:
836:
832:
828:
824:
817:
815:
813:
811:
802:
798:
793:
788:
784:
780:
776:
772:
768:
761:
753:
749:
744:
739:
735:
731:
727:
723:
719:
712:
710:
701:
700:
692:
678:
674:
668:
660:
656:
651:
646:
642:
638:
634:
627:
619:
618:
610:
608:
599:
592:
584:
580:
575:
570:
565:
560:
556:
552:
549:(8): e23457.
548:
544:
540:
533:
531:
522:
518:
513:
508:
505:(6): 2.6.02.
504:
500:
496:
489:
487:
485:
476:
472:
467:
462:
457:
452:
448:
444:
443:Plant Methods
440:
433:
431:
426:
418:
416:
412:
407:
397:
395:
391:
387:
383:
379:
369:
367:
362:
353:
351:
347:
343:
339:
338:nucleic acids
335:
326:
324:
320:
316:
306:
298:
290:
282:
280:
270:
268:
264:
260:
256:
252:
248:
244:
241:
231:
229:
223:
214:
212:
208:
204:
203:peptidoglycan
200:
196:
186:
184:
180:
176:
172:
162:
160:
157:
153:
149:
145:
141:
137:
133:
123:
115:
113:
109:
105:
101:
100:
95:
91:
82:
80:
79:transfections
76:
72:
68:
63:
61:
57:
53:
52:biotechnology
49:
45:
41:
37:
29:
26:
21:
1615:
1611:
1585:. Retrieved
1581:
1572:
1561:. Retrieved
1556:
1552:
1539:
1502:
1498:
1470:. Retrieved
1466:
1417:
1413:
1365:
1355:
1344:. Retrieved
1340:
1296:(10): 2792.
1293:
1289:
1279:
1244:
1240:
1230:
1195:
1191:
1181:
1146:
1142:
1116:. Retrieved
1112:
1062:
1058:
1008:
1004:
950:
946:
886:
882:
830:
826:
774:
770:
760:
725:
721:
698:
691:
680:. Retrieved
676:
667:
640:
636:
626:
616:
597:
591:
546:
542:
502:
498:
446:
442:
403:
375:
359:
332:
323:biomolecules
315:transfection
312:
304:
296:
288:
276:
237:
224:
220:
192:
179:bead-beating
175:French press
168:
129:
121:
97:
88:
81:into cells.
64:
35:
33:
1505:: 9306564.
1374:10.3791/247
1341:cbs.umn.edu
1198:(9): 3604.
833:(9): 2786.
356:Spin column
346:antisolvent
255:spin-column
159:chromosomal
156:supercoiled
110:genes as a
104:transformed
44:plasmid DNA
25:agarose gel
1671:Categories
1587:2023-01-10
1563:2008-09-10
1472:2023-01-10
1420:: 574398.
1368:(6): 247.
1346:2023-01-10
1118:2023-01-02
682:2022-12-10
677:Genome.gov
421:References
386:chloroform
171:sonication
96:, usually
75:sequencing
827:Molecules
673:"Plasmid"
30:-stained.
1559:(4): 1–2
1531:28785592
1446:20011662
1392:18997895
1091:26344110
1059:Vaccines
1037:24710095
979:25853267
923:35030225
883:PLOS ONE
859:35566139
801:26104560
752:18193080
659:22406276
583:21858126
543:PLOS ONE
521:26104457
475:20180960
449:(1): 1.
366:proteins
247:bacteria
211:Lysozyme
195:Lysozyme
136:alkaline
90:Plasmids
60:bacteria
1522:5529626
1437:2789530
1383:2557117
1320:2041760
1271:7838738
1222:2726501
1082:4494225
1028:6190294
970:4425044
914:8759652
891:Bibcode
850:9104913
792:4480600
743:2268074
637:Vaccine
574:3156146
551:Bibcode
466:2829548
342:ethanol
240:plasmid
199:enzymes
148:acetate
140:protein
99:E. coli
1642:388356
1640:
1633:342324
1630:
1529:
1519:
1444:
1434:
1390:
1380:
1318:
1311:328215
1308:
1269:
1262:310149
1259:
1220:
1213:317816
1210:
1173:388356
1171:
1164:342324
1161:
1089:
1079:
1035:
1025:
977:
967:
921:
911:
857:
847:
799:
789:
750:
740:
657:
581:
571:
519:
473:
463:
394:enzyme
382:phenol
344:as an
267:clones
181:, and
152:buffer
1553:Focus
1549:(PDF)
1005:Genes
390:DNase
245:from
144:ssDNA
67:lysis
58:from
1638:PMID
1527:PMID
1503:2017
1442:PMID
1418:2009
1388:PMID
1316:PMID
1267:PMID
1218:PMID
1169:PMID
1087:PMID
1033:PMID
975:PMID
919:PMID
855:PMID
797:PMID
748:PMID
655:PMID
579:PMID
517:PMID
471:PMID
406:iron
253:and
77:and
1628:PMC
1620:doi
1517:PMC
1507:doi
1432:PMC
1422:doi
1378:PMC
1370:doi
1306:PMC
1298:doi
1257:PMC
1249:doi
1208:PMC
1200:doi
1159:PMC
1151:doi
1077:PMC
1067:doi
1023:PMC
1013:doi
965:PMC
955:doi
909:PMC
899:doi
845:PMC
835:doi
787:PMC
779:doi
738:PMC
730:doi
726:153
645:doi
569:PMC
559:doi
507:doi
461:PMC
451:doi
413:or
317:or
243:DNA
56:DNA
1673::
1636:.
1626:.
1614:.
1610:.
1580:.
1555:.
1551:.
1525:.
1515:.
1501:.
1497:.
1481:^
1465:.
1454:^
1440:.
1430:.
1416:.
1412:.
1400:^
1386:.
1376:.
1364:.
1339:.
1328:^
1314:.
1304:.
1294:19
1292:.
1288:.
1265:.
1255:.
1245:22
1243:.
1239:.
1216:.
1206:.
1196:17
1194:.
1190:.
1167:.
1157:.
1145:.
1141:.
1127:^
1111:.
1099:^
1085:.
1075:.
1061:.
1057:.
1045:^
1031:.
1021:.
1007:.
1003:.
987:^
973:.
963:.
951:16
949:.
945:.
931:^
917:.
907:.
897:.
887:17
885:.
881:.
867:^
853:.
843:.
831:27
829:.
825:.
809:^
795:.
785:.
773:.
769:.
746:.
736:.
724:.
720:.
708:^
675:.
653:.
641:30
639:.
635:.
606:^
577:.
567:.
557:.
545:.
541:.
529:^
515:.
501:.
497:.
483:^
469:.
459:.
445:.
441:.
429:^
209:.
185:.
177:,
34:A
1644:.
1622::
1616:7
1590:.
1566:.
1557:7
1533:.
1509::
1475:.
1448:.
1424::
1394:.
1372::
1349:.
1322:.
1300::
1273:.
1251::
1224:.
1202::
1175:.
1153::
1147:7
1121:.
1093:.
1069::
1063:1
1039:.
1015::
1009:1
981:.
957::
925:.
901::
893::
861:.
837::
803:.
781::
775:3
754:.
732::
685:.
661:.
647::
585:.
561::
553::
547:6
523:.
509::
503:2
477:.
453::
447:6
384:/
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.