398:
time is long and the protease concentration high enough. Upon removal of the calcium ions, the stability of the enzyme is reduced, but the proteolytic activity remains. Proteinase K has two binding sites for Ca, which are located close to the active center, but are not directly involved in the catalytic mechanism. The residual activity is sufficient to digest proteins, which usually contaminate nucleic acid preparations. Therefore, the digestion with
Proteinase K for the purification of nucleic acids is usually performed in the presence of
1856:
31:
650:
inhibitors. Proteinase K is used for the destruction of proteins in cell lysates (tissue, cell culture cells) and for the release of nucleic acids, since it very effectively inactivates DNases and RNases. Some examples for applications: Proteinase K is very useful in the isolation of highly native,
397:
Activated by calcium, the enzyme digests proteins preferentially after hydrophobic amino acids (aliphatic, aromatic and other hydrophobic amino acids). Although calcium ions do not affect the enzyme activity, they do contribute to its stability. Proteins will be completely digested if the incubation
674:), suggesting that the presumed reduction of its own disulfide bonds does not lead to its irreversible inactivation. Proteinase K is inhibited by serine protease inhibitors such as phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (
409:
range (4–12), with a pH optimum of pH 8.0. An elevation of the reaction temperature from 37 °C to 50–60 °C may increase the activity several times, like the addition of 0.5–1%
698:), although presumably if these reagents were included alongside disulfide reducing reagents which exposed the typically-unavailable Proteinase K thiols, it may then become inhibited.
180:
618:
that might otherwise degrade the DNA or RNA during purification. It is highly suited to this application since the enzyme is active in the presence of chemicals that
1055:
651:
undamaged DNAs or RNAs, since most microbial or mammalian DNases and RNases are rapidly inactivated by the enzyme, particularly in the presence of 0.5–1% SDS.
1510:
425:(4 M) . The above-mentioned conditions enhance proteinase K activity by making its substrate cleavage sites more accessible. Temperatures above 65 °C,
1370:
662:
the enzyme. The reason for this result is that the denaturing agents unfold the protein substrates and make them more accessible to the protease.
1110:
972:"Stimulation of Proteinase K action by denaturing agents: application to the isolation of nucleic acids and the degradation of 'masked' proteins"
353:
199:
948:
192:
1130:
908:
Müller A, Hinrichs W, Wolf WM, Saenger W (September 1994). "Crystal structure of calcium-free proteinase K at 1.5-A resolution".
481:
or by other serine protease inhibitors like Nα-Tosyl-Lys
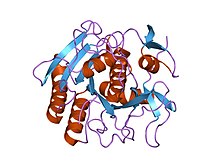
Chloromethyl Ketone (TLCK) and Nα-Tosyl-Phe Chloromethyl Ketone (TPCK).
670:
Proteinase K has two disulfide bonds, but it exhibits higher proteolytic activity in the presence of reducing agents (e.g. 5 mM
691:
159:
233:
1103:
654:
The enzyme's activity towards native proteins is stimulated by denaturants such as SDS. In contrast, when measured using
1044:
1575:
1088:
1019:
792:
Kraus E, Kiltz HH, Femfert UF (February 1976). "The specificity of proteinase K against oxidized insulin B chain".
153:
1096:
135:
716:"Structure of the complex of proteinase K with a substrate analogue hexapeptide inhibitor at 2.2-A resolution"
140:
1876:
1731:
686:). Proteinase K activity is unaffected by the sulfhydryl modifying reagents: para-chloromercuribenzoic acid (
1330:
204:
687:
679:
619:
438:
128:
1846:
555:
454:
63:
1832:
1819:
1806:
1793:
1780:
1767:
1754:
1716:
1245:
1230:
156:
1726:
1680:
1623:
1127:
304:
80:
46:
1628:
1520:
1485:
1480:
446:
418:
623:
466:
410:
1649:
1568:
1475:
1325:
385:. It is commonly used for its broad specificity. This enzyme belongs to Peptidase family S8 (
343:
116:
1721:
1465:
944:
536:
517:
442:
426:
414:
273:
92:
8:
1685:
1365:
1355:
1172:
1167:
58:
51:
1881:
1618:
1082:
988:
971:
885:
868:
846:
1118:
732:
715:
714:
Betzel C, Singh TP, Visanji M, Peters K, Fittkau S, Saenger W, Wilson KS (July 1993).
1347:
993:
925:
890:
841:
820:
801:
737:
607:
296:
147:
850:
1664:
1659:
1633:
1561:
1139:
983:
917:
880:
836:
772:
727:
659:
1711:
1695:
1608:
1380:
1375:
1147:
1123:
474:
331:
283:
1860:
1749:
1690:
671:
570:
528:
509:
462:
175:
1870:
1654:
1613:
1525:
1398:
1387:
1119:
777:
756:
614:. Addition of Proteinase K to nucleic acid preparations rapidly inactivates
492:
Buffer (pH = 8.0, 50 °C, 1.25 μg/mL protease K, 15 min incubation)
1603:
1421:
1315:
1157:
647:
611:
574:
532:
513:
458:
367:
366:), hence, the name "Proteinase K". The predominant site of cleavage is the
349:
997:
929:
921:
894:
741:
1827:
1762:
1598:
1540:
1535:
1184:
1011:
867:
Ebeling W, Hennrich N, Klockow M, Metz H, Orth HD, Lang H (August 1974).
805:
382:
378:
307:
254:
104:
1502:
1444:
1225:
1220:
1200:
639:
386:
249:
389:). The molecular weight of Proteinase K is 28,900 daltons (28.9 kDa).
1801:
1775:
1530:
1516:
1335:
1215:
1205:
631:
371:
1855:
1416:
1411:
1360:
1210:
1195:
1162:
615:
375:
1470:
1460:
1406:
1320:
1152:
655:
643:
470:
363:
123:
610:
to digest protein and remove contamination from preparations of
1814:
1584:
1497:
1439:
402:(inhibition of metal-ion dependent enzymes such as nucleases).
339:
335:
187:
99:
87:
75:
30:
1788:
1506:
1492:
1431:
1305:
1300:
1295:
1290:
1285:
1280:
683:
441:
inhibit the activity. Proteinase K will not be inhibited by
430:
1275:
1270:
1265:
1260:
1255:
1250:
1240:
1235:
695:
675:
635:
627:
478:
450:
434:
422:
399:
359:
111:
1553:
866:
907:
694:), or N-alpha-Tosyl-l-phenylalanine Chloromethyl Ketone (
713:
1012:"PROK - Proteinase K precursor - Parengyodontium album"
406:
1844:
969:
821:"Amino acid sequence of proteinase K from the mold
791:
1868:
818:
682:), or 4-(2-aminoethyl)benzenesulfonyl fluoride (
546:10 mM Tris·Cl; 25 mM EDTA; 100 mM NaCl; 0.5% SDS
945:"Frequently asked questions about Proteinase K"
754:
690:), N-alpha-tosyl-L-lysyl-chloromethyl-ketone (
1569:
1104:
869:"Proteinase K from Tritirachium album Limber"
1039:
1037:
485:Protease K activity in commonly used buffers
554:10 mM Tris·Cl; 100 mM EDTA; 20 mM NaCl; 1%
1576:
1562:
1111:
1097:
707:
338:was discovered in 1974 in extracts of the
29:
1034:
987:
942:
884:
862:
860:
840:
785:
776:
731:
429:(TCA) or the serine protease-inhibitors
405:Proteinase K is also stable over a wide
1869:
1124:serine proteases/serine endopeptidases
1004:
970:Hilz H, Wiegers U, Adamietz P (1975).
857:
1557:
1092:
1022:from the original on 19 November 2020
901:
565:10 mM Tris·Cl; 50 mM KCl; 1.5 mM MgCl
951:from the original on 17 October 2020
819:Jany KD, Lederer G, Mayer B (1986).
584:10 mM Tris·Cl; 100 mM EDTA; 0.5% SDS
324:Tritirachium album serine proteinase
13:
989:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02211.x
886:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03671.x
757:"Specificity of proteinase K from
392:
370:adjacent to the carboxyl group of
358:). Proteinase K is able to digest
14:
1893:
1076:
606:Proteinase K is commonly used in
592:30 mM Tris·Cl; 10 mM EDTA; 1% SDS
1854:
1061:from the original on 6 June 2024
976:European Journal of Biochemistry
320:Tritirachium alkaline proteinase
1045:"Novagen Proteinase K protocol"
794:Hoppe-Seyler's Z. Physiol. Chem
678:), diisopropylfluorophosphate (
601:
328:Tritirachium album proteinase K
963:
936:
812:
761:Limber for synthetic peptides"
755:Morihara K, Tsuzuki H (1975).
748:
527:36 mM Tris·Cl; 36 mM EDTA; 5%
508:30 mM Tris·Cl; 30 mM EDTA; 5%
16:Broad-spectrum serine protease
1:
1336:Urinary plasminogen activator
733:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)82332-8
701:
665:
1331:Tissue plasminogen activator
842:10.1016/0014-5793(86)80467-7
594:
586:
578:
559:
548:
540:
521:
502:
7:
1583:
10:
1898:
495:Proteinase K activity (%)
35:Structure of Proteinase K.
1740:
1732:Michaelis–Menten kinetics
1704:
1673:
1642:
1591:
1453:
1430:
1422:Proteinase 3/Myeloblastin
1396:
1346:
1183:
1138:
1085:Worthington enzyme manual
279:
269:
264:
260:
248:
240:
228:
223:
218:
198:
186:
174:
169:
165:
146:
134:
122:
110:
98:
86:
74:
69:
57:
45:
40:
28:
23:
1624:Diffusion-limited enzyme
658:substrates, denaturants
778:10.1271/bbb1961.39.1489
447:Guanidinium thiocyanate
419:Guanidinium thiocyanate
330:) is a broad-spectrum
1476:Proprotein convertases
411:sodium dodecyl sulfate
1717:Eadie–Hofstee diagram
1650:Allosteric regulation
1326:Plasminogen activator
642:reagents, as well as
344:Parengyodontium album
1877:Biochemistry methods
1727:Lineweaver–Burk plot
1466:Prolyl endopeptidase
1054:. 11 December 2019.
1018:. 11 December 2019.
443:Guanidinium chloride
427:trichloroacetic acid
415:Guanidinium chloride
922:10.2210/pdb2pkc/pdb
381:with blocked alpha
1686:Enzyme superfamily
1619:Enzyme promiscuity
823:Tritirachium album
759:Tritirachium album
622:proteins, such as
234:Engyodontium album
1842:
1841:
1551:
1550:
1348:Complement system
1140:Digestive enzymes
765:Agric. Biol. Chem
608:molecular biology
599:
598:
297:molecular biology
293:
292:
289:
288:
214:
213:
210:
209:
129:metabolic pathway
1889:
1859:
1858:
1850:
1722:Hanes–Woolf plot
1665:Enzyme activator
1660:Enzyme inhibitor
1634:Enzyme catalysis
1578:
1571:
1564:
1555:
1554:
1113:
1106:
1099:
1090:
1089:
1071:
1070:
1068:
1066:
1060:
1049:
1041:
1032:
1031:
1029:
1027:
1008:
1002:
1001:
991:
967:
961:
960:
958:
956:
940:
934:
933:
916:(37): 23108–11.
905:
899:
898:
888:
864:
855:
854:
844:
816:
810:
809:
789:
783:
782:
780:
771:(7): 1489–1492.
752:
746:
745:
735:
711:
489:
488:
262:
261:
236:
216:
215:
167:
166:
33:
21:
20:
1897:
1896:
1892:
1891:
1890:
1888:
1887:
1886:
1867:
1866:
1865:
1853:
1845:
1843:
1838:
1750:Oxidoreductases
1736:
1712:Enzyme kinetics
1700:
1696:List of enzymes
1669:
1638:
1609:Catalytic triad
1587:
1582:
1552:
1547:
1449:
1426:
1392:
1342:
1179:
1148:Enteropeptidase
1134:
1117:
1079:
1074:
1064:
1062:
1058:
1047:
1043:
1042:
1035:
1025:
1023:
1010:
1009:
1005:
968:
964:
954:
952:
943:Ag-Scientific.
941:
937:
906:
902:
873:Eur. J. Biochem
865:
858:
817:
813:
790:
786:
753:
749:
726:(21): 15854–8.
712:
708:
704:
668:
634:agents such as
604:
568:
475:iodoacetic acid
395:
393:Enzyme activity
332:serine protease
316:endopeptidase K
232:
36:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1895:
1885:
1884:
1879:
1864:
1863:
1840:
1839:
1837:
1836:
1823:
1810:
1797:
1784:
1771:
1758:
1744:
1742:
1738:
1737:
1735:
1734:
1729:
1724:
1719:
1714:
1708:
1706:
1702:
1701:
1699:
1698:
1693:
1688:
1683:
1677:
1675:
1674:Classification
1671:
1670:
1668:
1667:
1662:
1657:
1652:
1646:
1644:
1640:
1639:
1637:
1636:
1631:
1626:
1621:
1616:
1611:
1606:
1601:
1595:
1593:
1589:
1588:
1581:
1580:
1573:
1566:
1558:
1549:
1548:
1546:
1545:
1544:
1543:
1538:
1528:
1523:
1514:
1500:
1495:
1490:
1489:
1488:
1483:
1473:
1468:
1463:
1457:
1455:
1451:
1450:
1448:
1447:
1442:
1436:
1434:
1428:
1427:
1425:
1424:
1419:
1414:
1409:
1403:
1401:
1394:
1393:
1391:
1390:
1385:
1384:
1383:
1378:
1368:
1363:
1358:
1352:
1350:
1344:
1343:
1341:
1340:
1339:
1338:
1333:
1323:
1311:
1310:
1309:
1308:
1303:
1298:
1293:
1288:
1283:
1278:
1273:
1268:
1263:
1258:
1253:
1248:
1243:
1238:
1233:
1223:
1218:
1213:
1208:
1203:
1198:
1189:
1187:
1181:
1180:
1178:
1177:
1176:
1175:
1170:
1160:
1155:
1150:
1144:
1142:
1136:
1135:
1120:Endopeptidases
1116:
1115:
1108:
1101:
1093:
1087:
1086:
1078:
1077:External links
1075:
1073:
1072:
1033:
1003:
982:(1): 103–108.
962:
935:
900:
856:
835:(2): 139–144.
811:
784:
747:
705:
703:
700:
667:
664:
603:
600:
597:
596:
593:
589:
588:
585:
581:
580:
577:
566:
562:
561:
558:
551:
550:
547:
543:
542:
539:
524:
523:
520:
505:
504:
501:
497:
496:
493:
394:
391:
291:
290:
287:
286:
281:
277:
276:
271:
267:
266:
258:
257:
252:
246:
245:
242:
238:
237:
230:
226:
225:
221:
220:
212:
211:
208:
207:
202:
196:
195:
190:
184:
183:
178:
172:
171:
163:
162:
151:
144:
143:
138:
132:
131:
126:
120:
119:
114:
108:
107:
102:
96:
95:
90:
84:
83:
78:
72:
71:
67:
66:
61:
55:
54:
49:
43:
42:
38:
37:
34:
26:
25:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1894:
1883:
1880:
1878:
1875:
1874:
1872:
1862:
1857:
1852:
1851:
1848:
1834:
1830:
1829:
1824:
1821:
1817:
1816:
1811:
1808:
1804:
1803:
1798:
1795:
1791:
1790:
1785:
1782:
1778:
1777:
1772:
1769:
1765:
1764:
1759:
1756:
1752:
1751:
1746:
1745:
1743:
1739:
1733:
1730:
1728:
1725:
1723:
1720:
1718:
1715:
1713:
1710:
1709:
1707:
1703:
1697:
1694:
1692:
1691:Enzyme family
1689:
1687:
1684:
1682:
1679:
1678:
1676:
1672:
1666:
1663:
1661:
1658:
1656:
1655:Cooperativity
1653:
1651:
1648:
1647:
1645:
1641:
1635:
1632:
1630:
1627:
1625:
1622:
1620:
1617:
1615:
1614:Oxyanion hole
1612:
1610:
1607:
1605:
1602:
1600:
1597:
1596:
1594:
1590:
1586:
1579:
1574:
1572:
1567:
1565:
1560:
1559:
1556:
1542:
1539:
1537:
1534:
1533:
1532:
1529:
1527:
1526:Streptokinase
1524:
1522:
1518:
1515:
1512:
1508:
1504:
1501:
1499:
1496:
1494:
1491:
1487:
1484:
1482:
1479:
1478:
1477:
1474:
1472:
1469:
1467:
1464:
1462:
1459:
1458:
1456:
1452:
1446:
1443:
1441:
1438:
1437:
1435:
1433:
1429:
1423:
1420:
1418:
1415:
1413:
1410:
1408:
1405:
1404:
1402:
1400:
1399:immune system
1395:
1389:
1388:C3-convertase
1386:
1382:
1379:
1377:
1374:
1373:
1372:
1369:
1367:
1364:
1362:
1359:
1357:
1354:
1353:
1351:
1349:
1345:
1337:
1334:
1332:
1329:
1328:
1327:
1324:
1322:
1319:
1317:
1313:
1312:
1307:
1304:
1302:
1299:
1297:
1294:
1292:
1289:
1287:
1284:
1282:
1279:
1277:
1274:
1272:
1269:
1267:
1264:
1262:
1259:
1257:
1254:
1252:
1249:
1247:
1244:
1242:
1239:
1237:
1234:
1232:
1229:
1228:
1227:
1224:
1222:
1219:
1217:
1214:
1212:
1209:
1207:
1204:
1202:
1199:
1197:
1194:
1191:
1190:
1188:
1186:
1182:
1174:
1171:
1169:
1166:
1165:
1164:
1161:
1159:
1156:
1154:
1151:
1149:
1146:
1145:
1143:
1141:
1137:
1132:
1129:
1125:
1121:
1114:
1109:
1107:
1102:
1100:
1095:
1094:
1091:
1084:
1081:
1080:
1057:
1053:
1052:Sigma Aldrich
1046:
1040:
1038:
1021:
1017:
1013:
1007:
999:
995:
990:
985:
981:
977:
973:
966:
950:
946:
939:
931:
927:
923:
919:
915:
911:
910:J. Biol. Chem
904:
896:
892:
887:
882:
878:
874:
870:
863:
861:
852:
848:
843:
838:
834:
830:
826:
824:
815:
807:
803:
799:
795:
788:
779:
774:
770:
766:
762:
760:
751:
743:
739:
734:
729:
725:
721:
720:J. Biol. Chem
717:
710:
706:
699:
697:
693:
689:
685:
681:
677:
673:
663:
661:
657:
652:
649:
645:
641:
637:
633:
629:
625:
621:
617:
613:
609:
591:
590:
583:
582:
576:
572:
564:
563:
557:
553:
552:
545:
544:
538:
534:
530:
526:
525:
519:
515:
511:
507:
506:
500:30 mM Tris·Cl
499:
498:
494:
491:
490:
487:
486:
482:
480:
476:
472:
468:
464:
460:
456:
452:
448:
444:
440:
436:
432:
428:
424:
420:
416:
412:
408:
403:
401:
390:
388:
384:
380:
377:
373:
369:
365:
361:
357:
355:
351:
346:
345:
341:
337:
333:
329:
325:
321:
317:
313:
309:
306:
302:
298:
285:
282:
278:
275:
272:
268:
263:
259:
256:
253:
251:
247:
243:
239:
235:
231:
227:
222:
217:
206:
203:
201:
197:
194:
191:
189:
185:
182:
179:
177:
173:
168:
164:
161:
158:
155:
152:
149:
145:
142:
139:
137:
133:
130:
127:
125:
121:
118:
115:
113:
109:
106:
105:NiceZyme view
103:
101:
97:
94:
91:
89:
85:
82:
79:
77:
73:
68:
65:
62:
60:
56:
53:
50:
48:
44:
39:
32:
27:
22:
19:
1828:Translocases
1825:
1812:
1799:
1786:
1773:
1763:Transferases
1760:
1747:
1604:Binding site
1316:fibrinolysis
1314:
1192:
1158:Chymotrypsin
1083:Proteinase K
1063:. Retrieved
1051:
1024:. Retrieved
1015:
1006:
979:
975:
965:
953:. Retrieved
938:
913:
909:
903:
876:
872:
832:
828:
822:
814:
800:(2): 233–7.
797:
793:
787:
768:
764:
758:
750:
723:
719:
709:
669:
653:
648:chymotrypsin
612:nucleic acid
605:
602:Applications
575:Triton X-100
533:Triton X-100
514:Triton X-100
484:
483:
459:Triton X-100
404:
396:
383:amino groups
368:peptide bond
354:Tritirachium
350:Engyodontium
348:
342:
327:
323:
319:
315:
311:
301:Proteinase K
300:
294:
219:Proteinase K
93:BRENDA entry
24:Proteinase K
18:
1599:Active site
1221:Factor XIIa
1201:Factor VIIa
1185:Coagulation
879:(1): 91–7.
379:amino acids
274:Swiss-model
224:Identifiers
81:IntEnz view
64:39450-01-6
41:Identifiers
1871:Categories
1802:Isomerases
1776:Hydrolases
1643:Regulation
1503:Subtilisin
1445:Batroxobin
1226:Kallikrein
1216:Factor XIa
1206:Factor IXa
1173:Pancreatic
1168:Neutrophil
1065:7 February
1026:7 February
955:15 October
702:References
666:Inhibitors
640:sulfhydryl
421:(1 M) and
387:subtilisin
347:(formerly
312:protease K
270:Structures
265:Search for
150:structures
117:KEGG entry
1882:EC 3.4.21
1681:EC number
1531:Cathepsin
1517:Sedolisin
1493:Prostasin
1211:Factor Xa
829:FEBS Lett
632:chelating
616:nucleases
535:; 735 mM
516:; 800 mM
413:(SDS) or
372:aliphatic
352:album or
308:3.4.21.64
70:Databases
52:3.4.21.64
1705:Kinetics
1629:Cofactor
1592:Activity
1432:Venombin
1417:Tryptase
1412:Granzyme
1366:Factor I
1361:Factor D
1356:Factor B
1196:Thrombin
1193:factors:
1163:Elastase
1056:Archived
1020:Archived
949:Archived
851:85577597
620:denature
571:Tween 20
569:; 0.45%
556:Sarkosyl
531:; 0.36%
529:Tween 20
510:Tween 20
463:Tween 20
455:Sarkosyl
376:aromatic
284:InterPro
229:Organism
205:proteins
193:articles
181:articles
154:RCSB PDB
1861:Biology
1815:Ligases
1585:Enzymes
1471:Pronase
1461:Acrosin
1407:Chymase
1321:Plasmin
1153:Trypsin
1016:Uniprot
998:1236799
930:8083213
895:4373242
825:Limber"
742:8340410
660:inhibit
656:peptide
644:trypsin
573:; 0.5%
512:; 0.5%
471:citrate
417:(3 M),
364:keratin
280:Domains
250:UniProt
141:profile
124:MetaCyc
59:CAS no.
1847:Portal
1789:Lyases
1498:Reelin
1440:Ancrod
1397:Other
1131:3.4.21
996:
928:
893:
849:
806:943367
804:
740:
340:fungus
336:enzyme
334:. The
255:P06873
241:Symbol
188:PubMed
170:Search
160:PDBsum
100:ExPASy
88:BRENDA
76:IntEnz
47:EC no.
1741:Types
1507:Furin
1454:Other
1381:MASP2
1376:MASP1
1306:KLK15
1301:KLK14
1296:KLK13
1291:KLK12
1286:KLK11
1281:KLK10
1059:(PDF)
1048:(PDF)
847:S2CID
684:AEBSF
537:GuHCl
518:GuHCl
431:AEBSF
356:album
136:PRIAM
1833:list
1826:EC7
1820:list
1813:EC6
1807:list
1800:EC5
1794:list
1787:EC4
1781:list
1774:EC3
1768:list
1761:EC2
1755:list
1748:EC1
1521:TPP1
1371:MASP
1276:KLK9
1271:KLK8
1266:KLK7
1261:KLK6
1256:KLK5
1251:KLK4
1246:KLK3
1241:KLK2
1236:KLK1
1067:2020
1028:2020
994:PMID
957:2020
926:PMID
891:PMID
802:PMID
738:PMID
696:TPCK
692:TLCK
688:PCMB
676:PMSF
636:EDTA
628:urea
626:and
595:203
587:120
579:106
549:128
541:301
522:313
503:100
479:EDTA
451:urea
435:PMSF
423:urea
400:EDTA
374:and
360:hair
244:PROK
200:NCBI
157:PDBe
112:KEGG
1511:S1P
1231:PSA
984:doi
918:doi
914:269
881:doi
837:doi
833:199
798:357
773:doi
728:doi
724:268
680:DFP
672:DTT
646:or
624:SDS
560:74
467:SDS
439:DFP
437:or
295:In
176:PMC
148:PDB
1873::
1128:EC
1122::
1050:.
1036:^
1014:.
992:.
980:56
978:.
974:.
947:.
924:.
912:.
889:.
877:47
875:.
871:.
859:^
845:.
831:.
827:.
796:.
769:39
767:.
763:.
736:.
722:.
718:.
638:,
630:,
477:,
473:,
469:,
465:,
461:,
457:,
453:,
449:,
445:,
433:,
407:pH
326:,
322:,
318:,
314:,
310:,
305:EC
299:,
1849::
1835:)
1831:(
1822:)
1818:(
1809:)
1805:(
1796:)
1792:(
1783:)
1779:(
1770:)
1766:(
1757:)
1753:(
1577:e
1570:t
1563:v
1541:G
1536:A
1519:/
1513:4
1509:/
1505:/
1486:2
1481:1
1318::
1133:)
1126:(
1112:e
1105:t
1098:v
1069:.
1030:.
1000:.
986::
959:.
932:.
920::
897:.
883::
853:.
839::
808:.
781:.
775::
744:.
730::
567:2
362:(
303:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.