1607:
Polish, German, and
Pomeranian crusaders, as well as some Prussian militiamen auxiliaries. The Polish and Pomerellian dukes proved essential through their providing of troops and bases. Most of the secular crusaders would return to their homes after the end of the campaigns, leaving the monastic Teutonic Knights the task of consolidating the gains and garrisoning the newly built forts, most of which were small and made of timber. Some secular Polish knights were granted vacant territories, especially in Culmerland, although most of the conquered territory was retained by the Teutonic Order. Colonists from the Holy Roman Empire began to immigrate eastward, allowing the foundation of a new town each year, many of which were granted
1578:. Peter estimated that while most tribes could muster about 2,000 cavalry, Samland could raise 4,000 cavalry and 40,000 infantry, while Sudovia had 6,000 cavalry and "an almost innumerable multitude of other warriors". In contrast, the Prussians of ravaged Culmerland could raise fewer troops than the other tribes. Galindia, a forested wilderness of lakes and rivers, also had a small population to raise troops from. Modern estimates indicate a total Prussian population of 170,000, smaller than that suggested by Peter von Dusburg.
37:
531:
1234:
1818:
2238:, capturing large amounts of cattle, horses, and prisoners. They then successfully ambushed the 3,000-strong force of pursuing Sudovians, losing only six Christians in the process. In 1280 the Sudovians and Lithuanian invaded Samland, but the alerted Order had fortified their castles and deprived the raiders of provisions. While the pagans were in Samland, Komtur Ulrich Bayer of Tapiau led a devastating counter-raid into Sudovia. The Polish prince
1437:
2168:
siege ladders were placed, most of the warriors were slaughtered by the crusaders, with only a few natives surviving to be resettled. Conrad then led the
Knights past the destroyed border forts to assault the Nadrovians main redoubt of Kaminiswike, defended by 200 warriors. Most of the natives were killed after the Knights stormed the fortress, and the Nadrovian clans surrendered soon afterward to become auxiliaries of the crusaders.
1511:
Order's territorial claims. However, recent studies by Polish historians have established the treaty's legitimacy. From the viewpoint of Duke Conrad, Chełmno was only to be used as a temporary base against the
Prussians and future conquests were to be under the authority of the Duke of Masovia. However, Hermann von Salza saw the document as granting the Order autonomy in all territorial acquisitions, aside from allegiance to the
1700:, which the Knights were reluctant to do; Duke Conrad subsequently refused to aid the crusaders any further. With the approval of the pope and the bishop of Płock, the Teutonic Knights assimilated the Order of Dobrzyń in a bull on 19 April 1235; the displeased Conrad of Masovia had the castle of Dobrzyń returned to him. In 1237 the Teutonic Knights assimilated the
2215:, and Christburg. Theodoric of Samland was able to convince the Sambians not to rebel, and the Natangians and Warmians followed suit. Conrad von Thierberg the Elder led 1,500 men into Kimenau in summer 1277, and crushed a Sudovian army of 3,000 near the Winse forest. Many Pogesanians fled to the Lithuanians and were resettled at
1510:
with the Poles on 16 June 1230, by which the Order was to receive
Culmerland and any future conquests, similar to the terms of the Golden Bull of Rimini. The agreement has been disputed by historians; the document has been lost and many Polish historians have doubted its authenticity and the Teutonic
1388:
with estates and castles in Chełmno Land during the meantime. The lords agreed that the primary focus was to rebuild the colonizing fortresses of Chełmno Land, especially Chełmno itself, whose fortress was almost completely rebuilt. By 1223, however, most of the crusaders had left the region, and the
2143:
in Bartia, which was to be the focal point of their borders. Defenseless against the
Sudovians, the Natangians and Bartians allied with the Teutonic Knights for protection, although little assistance could be provided initially. The Christian Natangians clans gathered in 1274 and killed 2,000 of the
2167:
Theodoric of
Samland and his militia sacked two river forts and plundered a large amount of treasure and goods. Theodoric led another crusading force, including Teutonic Knights, 150 sergeants, and Prussian infantry, against another Nadrovian fort. Although the natives attempted to surrender after
2260:
protected the rights of converts. The
Prussian uprisings led to the crusaders only applying these rights to the most powerful converts, however, and the pace of conversion slowed. After the Prussians were militarily defeated in the second half of the 13th century, they were gradually subjected to
1841:
The crusaders' cavalry and crossbow artillery proved overwhelming in level terrain, but the
Prussians were more experienced and maneuverable in smaller skirmishes in wooded terrain. While the Prussian and Pomerellian troops captured the majority of the Order's castles and defeated the Knights at
1606:
While the earlier Polish expeditions had usually marched eastward into the
Prussian wilderness, the Order focused in the west to establish fortresses along the Vistula River. They campaigned annually whenever crusading knights from the west arrived. The early campaigns were primarily composed of
2203:
documented the crusaders as killing and capturing numerous pagans. When the
Scalovian warriors went in pursuit of the captured pagans, Conrad shattered the would-be rescuers in an ambush which killed the pagan leader, Steinegele. Most Scalovian nobles quickly surrendered to the Knights in the
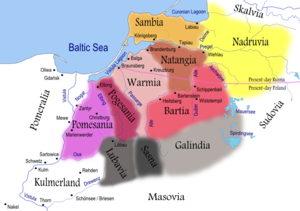
1936:
to prevent the Samogitians from assisting the Sambians. As the chronicles attest, the "founding" was accomplished by burning an existing native city to the ground and exterminating the entire population that seems to have lived there, according to contiguous archeological finds, for several
2249:, who had once been a captive of the Sudovians, negotiated the surrender of 1,600 Sudovians and their leader Katingerde, who were subsequently resettled in Samland. Most of the remaining Sudovians were redistributed to Pogesania and Samland; Skalmantas was pardoned and allowed to settle at
2253:. Sudovia was left unpopulated, becoming a border wilderness that protected Prussia, Masovia, and Volhynia from the Lithuanians. The Prussians rebelled in short-lived uprisings in 1286 and 1295, but the crusaders firmly controlled the Prussian tribes by the end of the 13th century.
1766:, leading Marshal Dietrich von Berheim to return with a larger army. When the Warmian commander Kodrune advised that the pagans should surrender and convert, Honeida's own garrison killed him, leading Dietrich to order a successful capture of the fort. The fort on the
2118:, while others were forcibly resettled by the crusaders. The tribal chiefs who remained in Prussia became vassals of the Teutonic Knights, who began rebuilding their castles in stone or brick to provide greater protection against the restive colonized population.
1846:
in 1244, they lacked the siege capabilities to finish the Knights off. The Germans used their politics and diplomacy to divide Swantopelk from the Prussians. The Poles sought the Pomerellian prince's territory along the Vistula, while the papal legate, the future
1586:
After receiving or forging the claim to Culmerland in 1230, Hermann von Salza dispatched Conrad von Landsberg as his envoy with a small force of seven Teutonic Knights and 70–100 squires and sergeants to Masovia as a vanguard. They took possession of Vogelsang
1253:
over the following two centuries. While the Poles sought control over the Prussians under the aegis of facilitating the conversion of the Prussians to Christianity, the Prussians engaged in reciprocal raids, capturing slaves in the bordering territories of
1837:
allied with the conquered Prussians and supported an armed rebellion against the crusaders. The Teutonic Order's capacity to resist was weakened, as there were fewer German crusaders arriving and the Polish princes were feuding amongst themselves.
1463:
from 1209 to 1239. With the permission of Duke Conrad of Masovia and the Masovian nobility, Christian requested aid from the Teutonic Order against the Prussians in 1226. Stability with the Prussians would then allow Conrad to pursue becoming
2187:, and the crusaders and pagans each engaged in border raids to distract enemy forces. Because the pagans were strongly defended in the wilderness, the Teutonic Knights focused on travelling up the Memel River toward the strong pagan fort
1595:. Other sources indicate that two knights constructed Vogelsang in 1229, but were killed by Prussians soon after. Soon after arriving at Vogelsang, Conrad von Landsberg began ordering small raids against pagans on the south side of the
2024:. Thirsko, a Christian Sambian chief, and his son Maidelo were entrusted with Wehlau. With the assistance of Sambian levies, the Teutonic Order advanced further into Natangia, capturing the fortresses of Capostete and Ocktolite near
1420:(or Dobrin). The Knights of Dobrzyń initially had success driving the Prussians from Chełmno Land, but a Prussian counterattack against them and Conrad killed most of the Order. The survivors were granted asylum in Pomerania by Duke
1855:
in February 1249. The treaty granted civil liberties and considerable autonomy to native converts to Christianity. While the majority of tribes followed the terms of the treaty, intermittent fighting continued until 1253, with the
2230:, which the Sudovians were particularly adept at. However, they lacked the sheer numbers to deal with their German, Polish, and Volhynian adversaries, and the Sudovian nobility began gradually surrendering one by one. Marshal
2126:
Although the Teutonic Knights' offensive capability was greatly weakened during the Great Pagan Uprising, they did engage in some campaigns against the pagan on their eastern flank. The Bartians, Natangians, and Warmians had
2102:
also campaigned with the Order in 1272. The crusaders gradually killed or forced the surrender of each Prussian tribes' war leader while exterminating the native population en masse if it refused to convert to Christianity.
2191:. Theodoric of Samland led 1,000 men in the assault. Artillery fire forced the defenders from the ramparts, allowing the crusaders to storm the walls with ladders and slaughter most of the pagans. Theodoric also captured
2582:, the arrival of the Teutonic Knights has sometimes been given as 1226; see Töppen, pp. 276–79. Töppen states von Landsberg arrived in Masovia in 1230, while Fahne states von Landsberg arrived ca. 1228; see Fahne, p. 50
2067:. The German princes of the Holy Roman Empire were distracted by the imperial succession, and few seasonal (summer) crusaders came to the assistance of the Prussian Brothers; the first reinforcements were defeated at
1988:; the Sambians who accepted baptism were left alive, but those who resisted were exterminated en masse. Samland was conquered in January 1255 in a campaign lasting less than a month. Near the native settlement of
1907:
but spared too much further violence; the Order was concerned that the Prussians would seek to join Poland if they were pressed too greatly. With the resisting tribes decimated, Pope Innocent IV directed
2364:
2091:
1309:, with the support of the King of Denmark and Polish dukes, found colonization of the natives in a better state than expected upon his arrival in the war-torn Chełmno Land. Inspired, he travelled to
2183:. Scalovia would then serve as a base against pagan Samogitia, which separated Teutonic Prussia from Teutonic Livonia. Because of this threat, the Lithuanians provided assistance to the pagan
2211:
engineered by Skalmantas of the Sudovians delayed the campaign. In 1276–77 the Sudovians and Lithuanians raided Culmerland and burned settlements near the castles of Rehden, Marienwerder,
1638:. The defecting captain then tricked Pipin into being captured by the Knights, ending Prussian resistance in the Culmerland. By 1232, the Knights had established or rebuilt fortresses at
2231:
2095:
1851:, wanted the Christians to direct their energies against pagans instead of each other. Swantopelk ceased aiding the Prussians in 1248, while most of the latter agreed to peace in the
2044:
entered a two-year truce with the Order in 1259. In 1259 the Samogitians decided to retain the independence of their pre-Christian religion. They defeated the Livonian Order at the
2223:. This new brick castle, built to replace Zantir, guarded against further rebellions with Elbing and Christburg. The central Prussian tribes surrendered to the crusaders by 1277.
2156:
1973:
476:
1503:
of 1226, granting them Chełmno Land, or Culmerland, and any future conquests. The mission to convert the Prussians remained under the command of Bishop Christian of Oliva.
1692:
mediated between the two sides, granting the Knights two-thirds but reserving extra rights for the bishop. The Teutonic Knights also sought the incorporation of the small
1348:
against the resisting Prussians. The following year the Prussians counter-attacked Chełmno Land and Masovia again, plundering 300 cathedrals and churches in revenge. Duke
844:
2000:, possibly named in honor of Bruno of Olmütz or Bruno of Querfurt, was also founded nearby, likely in place of an existing native town. The Knights built the castle
1226:
for his aim of conquering the Prussians in 997, but the missionary was killed by the natives. After some initial success among the Prussians, Adalbert's successor,
1599:, a region that was relatively safe with a mixed Christian and pagan population. Reinforcements began arriving at Vogelsang after the castle's completion. Led by
2245:
In summer 1283, Conrad von Thierberg the Younger was named Provincial Master of Prussia and led a large army into Sudovia, finding little resistance. The Knight
481:
1230:, was also killed in 1009. Bolesław I continued his conquests of surrounding lands and in 1015 he devastated the native populations of large parts of Prussia.
1148:
486:
2361:
1731:, the margrave supplied the Order with two large river-boats which defeated the smaller craft used by the Prussian tribes. Near the Prussian settlement of
577:
2106:
As a result of the uprising, many native Prussians lost some of the rights they had received in the Treaty of Christburg and were subsequently reduced to
1843:
1872:
After the western Prussians were forcibly colonized by the early 1250s, the Teutonic Knights continued their advance north and east, next facing the
2071:
in 1261. The Order had most of its Prussian castles destroyed during the early 1260s. Besides Prussia, the natives also raided Livonia, Poland, and
1372:. German and Polish crusaders began gathering in Masovia in 1219, but serious planning only began in 1222 upon the arrival of nobles such as Duke
1688:
The bishop of Prussia, Christian of Oliva, claimed two-thirds of conquered territory, granting one-third to the Teutonic Order. The papal legate
406:
2094:
was founded in their honor. King Ottokar II of Bohemia briefly returned to Prussia in 1267–68, but was deterred by poor weather, while Margrave
1681:
River by the arrival of the ducal cavalry, and the battlefield was subsequently known as the "Field of the Dead". The building of a fortress at
700:
3086:
2025:
3076:
1989:
1778:. A Prussian counterattack to reclaim the fort failed, and the local Prussian leader Piopso was killed. Seasonal reinforcements led by
1141:
1763:
159:
2235:
2192:
2082:, and Henry III, Landgrave of Thuringia, in 1265. In the following year German crusading reinforcements were provided by Margraves
1635:
1631:
667:, culture and pre-Christian religion by a combination of physical and ideological force. Some Prussians took refuge in neighboring
2079:
1495:'s borders easier to defend against invaders, presumably referring to Lithuanian counterattacks against Christian crusades. The
451:
2262:
2056:
the same year. In the minds of the indigenous peoples, their victories reinforced the validity of their pre-Christian beliefs.
1826:
1187:
1177:
660:
1134:
1779:
1627:
446:
2242:
achieved two significant victories over the pagans, securing the Polish border, and Skalmantas fled Sudovia to Lithuania.
1456:
2273:
and the securing of Prussia, the Order then turned its focus against Christian Pomerellia, which separated Prussia from
2208:
922:
852:
730:
693:
3043:
3015:
2972:
2942:
2911:
2083:
1965:
1630:. A local Prussian captain defected and handed that castle to the crusaders, who then destroyed the Prussian fort of
1019:
456:
134:
254:
1469:
822:
2135:
and Lithuanians to their east remained pagan and continued their border warfare with the Teutonic Knights. Led by
2087:
1899:, the new Grand Master, began preaching a crusade against the Sambians. In 1253 Poppo and the Provincial Master,
264:
1696:
into the larger Teutonic Order. Conrad of Masovia was furious with this proposal and demanded the return of the
1642:
and Thorn. Pope Gregory IX called for reinforcements, which included 5,000 veterans under the leadership of the
1352:
succeeded in making the Prussians leave by paying a huge tribute, which only encouraged the Prussians, however.
3081:
1925:
1720:
1701:
1318:
466:
461:
471:
154:
1389:
Prussians devastated Chełmno Land and Masovia yet again, forcing Duke Conrad to seek refuge in the castle of
686:
2207:
The Teutonic Knights planned to advance against Samogitia after conquering Scalovia, but the outbreak of a
2001:
1109:
1099:
1829:
in 1242. Alarmed by the crusaders' rapid expansion into territory bordering his lands, the Christian Duke
1723:, in 1236, the crusaders advanced north along both banks of the Vistula and forced the submission of most
659:, the Knights had established control over Prussia and administered the conquered Prussians through their
1976:, and the fort's garrison surrendered quickly and underwent baptism. The crusaders then advanced against
1031:
1024:
927:
504:
1527:
in 1234 reaffirmed the Order's control of conquered lands, placing them only under the authority of the
2199:
near Königsberg. Conrad von Thierberg escalated the conflict by sending a large raid against Scalovia.
2059:
Despite their territorial gains in Prussia, the primary emphasis of the Teutonic Knights was still the
1830:
1662:
1421:
1295:
599:
496:
164:
3071:
2128:
179:
2964:
2957:
2063:, and few reinforcements could be spared to complete the Christianization of what was then known as
1900:
1682:
1413:
2111:
2045:
1953:
1405:
832:
356:
214:
2998:
1271:
2152:
2053:
1802:
1059:
398:
1219:
2200:
2159:, to attack eastward from Königsberg along the Pregel River to separate the Sudovians from the
2145:
1798:
1666:
1283:
1064:
992:
509:
199:
189:
2903:
2896:
2256:
The Prussian populace retained many of their traditions and way of life, especially after the
2246:
1949:
1887:
of Christburg led an army across the Vistula Lagoon in 1252, with the intention of attacking
1506:
Before beginning the campaign against the Prussians, the Teutonic Order allegedly signed the
1500:
1317:
in 1215, however, Christian found the Prussians hostile out of outrage at the actions of the
1094:
997:
987:
615:
436:
431:
224:
169:
2930:
2929:
2257:
2136:
1969:
1852:
1806:
1520:
1385:
1275:
536:
388:
219:
1861:
1360:
Honorius III called for a crusade under the leadership of Christian of Oliva and chose as
1206:, recorded the seafaring and cattle-herding Prussians as a strong and independent nation.
1182:
8:
2261:
Christianization and cultural assimilation during the following centuries as part of the
1653:
In summer 1233, the Knights led a crusading army of 10,000 and established a fortress at
1507:
1465:
1267:
1207:
1104:
1089:
1039:
897:
867:
491:
421:
411:
393:
2992:
2219:, while the ones who remained in Prussia were resettled by the crusaders, probably near
1693:
1417:
2281:
2277:
2068:
1516:
1496:
1481:
1468:. While Hermann was interested in the Polish offer, his focus was on assisting Emperor
1448:
1425:
1373:
1306:
1223:
1199:
1014:
957:
952:
947:
942:
937:
932:
917:
912:
885:
862:
807:
735:
725:
656:
633:
416:
361:
269:
259:
244:
236:
144:
63:
1369:
441:
249:
209:
3039:
3011:
2984:
Cyclopædia of Biblical, Theological, and Ecclesiastical Literature: Vol. VIII: PET-RE
2968:
2938:
2907:
2579:
2274:
1921:
1896:
1825:
The Teutonic Knights' further advance into Prussia was slowed by the outbreak of the
1794:
1689:
1535:
1492:
1452:
1440:
1349:
1337:
1227:
1049:
966:
857:
762:
664:
629:
514:
426:
378:
275:
229:
139:
111:
28:
2933:; Stefan Kieniewicz; Emanuel Rostworowski; Janusz Tazbir; Henryk Wereszycki (1979).
2148:
recruited Thuringians and Meisseners to complete the Teutonic recovery of Natangia.
1762:. A small force of crusading knights were slaughtered besieging the Warmian fort of
639:. Invited after earlier unsuccessful expeditions against the Prussians by Christian
3027:
Geschichte der Preussischen Historiographie von P. v. Dusburg bis aus auf K. Schütz
2293:
2239:
2227:
2064:
2028:. The Natangian leader Godecko and his two sons were killed resisting the advance.
1957:
1790:
1401:
1333:, and enabled Christian converts to return to their native, pre-Christian beliefs.
1279:
1211:
1203:
1172:
1081:
1044:
1004:
902:
872:
837:
767:
740:
626:
622:
284:
184:
174:
149:
129:
93:
1214:
tried to extend his realm from land he had just conquered around the mouth of the
2368:
2298:
2049:
1933:
1909:
1892:
1888:
1884:
1713:
1588:
1524:
1266:
under duress only to revert to native religious beliefs after hostilities ended.
1054:
979:
880:
817:
812:
787:
772:
757:
194:
124:
2052:
in 1260. The native victory inspired the Prussians to rebel again, starting the
1697:
1539:
1255:
2220:
2012:
Rivers to guard against and be able to continue the colonization of the native
1767:
1460:
1325:
or fear of Christian Polish expansion. The Prussians invaded Chełmno Land, and
1074:
974:
827:
792:
777:
204:
119:
36:
3065:
2952:
1848:
1473:
1436:
1278:
each led large armies into Prussia; while Bolesław's forces were defeated in
1242:
802:
797:
782:
752:
644:
636:
530:
292:
2005:
1993:
1484:, Hermann also desired greater autonomy for his forces in future endeavors.
2266:
1912:
friars to preach the crusade, and the Order sent embassies to the Kings of
1600:
1361:
1069:
890:
525:
383:
1940:
The 60,000-strong crusading army which gathered for the campaign included
1744:
2544:
Dariusz Sikorski, 'Neue Erkenntnisse ueber das Kruschwitzer Privileg' in
2115:
2041:
1728:
1724:
1709:
1674:
1615:
1571:
1302:
1115:
907:
652:
648:
339:
322:
317:
1929:
1622:
with the aid of Conrad of Masovia, Balk took control of ruins at modern
2184:
2160:
2140:
2021:
2017:
1904:
1857:
1834:
1755:
1477:
1341:
1326:
1233:
312:
307:
302:
2048:
in 1259, and then inflicted a crushing defeat on the crusaders in the
1817:
1727:. Although Henry did not participate in the 1237 campaign against the
1639:
1603:, a force numbering twenty knights and 200 sergeants arrived in 1230.
1314:
2195:
on the other bank of the Memel. The Scalovians retaliated by sacking
2132:
2060:
2037:
2013:
1985:
1945:
1924:. While the Order waited for the crusaders to arrive in Prussia, the
1670:
1658:
1647:
1591:
for "bird song"), a castle being built by Conrad opposite the future
1559:
1555:
1246:
668:
594:
589:
572:
344:
1740:
1736:
1394:
2270:
2176:
2172:
2072:
2009:
1997:
1977:
1873:
1783:
1759:
1751:
1643:
1619:
1608:
1567:
1551:
1547:
1543:
1528:
1512:
1491:
and suggested that the subjugation of the Prussians would make the
1345:
1126:
710:
618:
332:
327:
297:
2078:
The crusaders began to stem the resistance with the assistance of
1891:. The Sambians defeated the crusaders in battle, however, killing
1623:
1592:
1390:
2180:
2107:
2099:
1941:
1917:
1913:
1809:, although the territory of the last had not yet been conquered.
1705:
1678:
1654:
1596:
1476:. Because the Teutonic Order had recently been expelled from the
1409:
1377:
1365:
1322:
1287:
1263:
1259:
1222:, son of Mieszko I, greatly expanded his land conquests and used
568:
541:
2036:
The Livonian Order had been invading and attempting to colonize
2925:(in German). Düsseldorf: Schaub'sche Buchhandlung. p. 240.
2216:
2212:
2196:
2188:
1981:
1961:
1881:
1877:
1775:
1750:
From 1238 to 1240, the Teutonic Knights campaigned against the
1575:
1563:
1488:
1330:
1291:
640:
563:
559:
554:
550:
545:
71:
67:
1673:
during the winter of 1233–34. After a close battle, the pagan
2250:
1895:
in the process. To replace the fallen soldiers, the pope and
1771:
1732:
1381:
1344:
to Christian in March 1217 allowing him to begin preaching a
1250:
2994:
Preussisch-Polnische Studien zur Geschichte des Mittelalters
1903:, as well as the Margrave of Meissen, reduced the resisting
643:
princes, the Teutonic Knights began campaigning against the
16:
Series of 13th-century campaigns of Roman Catholic crusaders
3029:(in German). Berlin: Verlag von Wilhelm Hertz. p. 290.
2164:
1793:
and William of Modena divided Prussia into the Dioceses of
1310:
1215:
678:
655:
in 1230. By the end of the century, having quelled several
1996:("King's Mountain"), named in honor of the Bohemian king.
1404:
knights were recruited by Conrad and Christian to form a
1774:
and rebuilt in 1239 to protect the Order's territory in
1614:
The crusaders began campaigning against the neighboring
1393:. The Sarmatians (as they were then known) even reached
1336:
Because of the growing intensity of reciprocal attacks,
2923:
Livland: Ein Beitrag zur Kirchen- und Sitten-Geschichte
2805:
2803:
2981:
2362:
Recent Issues in Polish Historiography of the Crusades
2031:
1282:, Casimir imposed peace until his death in 1194. King
2775:
2773:
1313:
to prepare for a larger mission. When he returned to
2800:
1428:, granted a base near Gdańsk, was also ineffective.
1384:. Numerous Polish nobles began endowing Christian's
2040:, which was northeast of the Prussians. The native
1431:
2956:
2895:
2770:
3063:
2986:. New York: Harper & Brothers. p. 1086.
2139:during the Great Uprising, the Sudovians sacked
3008:The Monks of War: The Military Religious Orders
1538:mentioned eleven districts in Prussia: Bartia,
674:
3057:. London: Longmans, Green and Co. p. 506.
1704:or Livonian Order, a military order active in
41:Map of the Prussian clans in the 13th century.
2155:, directed the Provincial Master of Prussia,
1581:
1142:
694:
2893:
1669:supported a smaller army for an invasion of
1685:stabilized the eastern Culmerland in 1234.
1499:gave his approval of the enterprise in the
1270:was killed fighting the Prussians in 1166.
274:other guest crusaders, especially from the
2997:(in German). Halle: Max Niemeyer. p.
1812:
1245:waged war with the neighboring Prussians,
1149:
1135:
701:
687:
614:was a series of 13th-century campaigns of
2546:Zeitschrift für Ostmitteleuropa-Forschung
1747:protected the land east of Marienwerder.
1408:. First granted the estate of Cedlitz in
3038:. London: Greenhill Books. p. 290.
3036:The Teutonic Knights: A Military History
2990:
1816:
1435:
1237:Baltic tribes and Prussian clans c. 1200
1232:
2982:McClintock, John; James Strong (1883).
2951:
2727:
2725:
2631:
2629:
2486:
2484:
2226:The crusaders and Sudovians engaged in
1626:and advanced toward the pagan-occupied
1618:and their leader Pepin. Advancing from
3064:
3024:
3010:. London: Penguin Books. p. 416.
3005:
2670:
2668:
2610:
2608:
2606:
2565:
2563:
2456:
2454:
2452:
2424:
2422:
2263:monastic state of the Teutonic Knights
1708:, after they were nearly wiped out by
160:Principality of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel
3052:
3033:
2920:
1443:, Grand Master of the Teutonic Order.
1355:
1290:supported Danish expeditions against
1130:
682:
3087:Wars involving the Holy Roman Empire
2963:. New York: Roy Publishers. p.
2722:
2626:
2617:
2481:
2080:Albert I, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg
1412:until the completion of a castle at
1262:. Many Prussians nominally accepted
1156:
2782:
2665:
2603:
2560:
2449:
2419:
2371:Darius von Güttner Sporzyński. 2005
2032:Great Prussian Uprising (1260–1274)
1972:. The Sambians were crushed at the
1782:consolidated Teutonic control over
13:
2151:Anno's successor as Grand Master,
2121:
2090:of Brandenburg, and the castle of
1780:Otto I, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg
747:In the Holy Land (1095–1291)
731:Military order (religious society)
14:
3098:
3077:Wars involving the Teutonic Order
2902:. London: Penguin Books. p.
2110:. Numerous Prussians fled to the
1542:(formerly under Polish control),
1487:Hermann met with Frederick II at
92:Teutonic Knights gain control of
3055:The History of Prussia, Volume 1
2232:Conrad von Thierberg the Younger
1739:was founded with colonists from
1432:Invitation of the Teutonic Order
1416:, the group became known as the
529:
35:
2875:
2866:
2857:
2848:
2839:
2830:
2821:
2812:
2791:
2761:
2752:
2743:
2734:
2713:
2704:
2695:
2686:
2677:
2656:
2647:
2638:
2594:
2585:
2572:
2551:
2538:
2529:
2520:
2511:
2502:
2493:
2472:
2463:
2440:
2431:
2410:
2401:
2171:The Teutonic Knights then used
2144:Sudovian raiders; Grand Master
1992:, the Teutonic Knights founded
2392:
2383:
2374:
2355:
2346:
2337:
2328:
2319:
2310:
2157:Conrad von Thierberg the Elder
1968:, and a contingent brought by
1721:Henry III, Margrave of Meissen
853:Crusades after Acre, 1291–1399
255:Duchy of Świecie and Lubiszewo
1:
2887:
2578:Due to a clerical mistake by
1789:In a bull of 1 October 1243,
1451:had made the acquaintance of
3053:Wyatt, Walter James (1876).
2937:. Warsaw: PWN. p. 668.
2304:
1860:even defeating the Order at
1534:The 14th century chronicler
708:
675:Early missions and conflicts
7:
2894:Christiansen, Erik (1997).
2287:
2175:and Memel as bases against
1376:, Archbishop Laurentius of
265:Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia
155:Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg
10:
3103:
1948:under the command of King
1867:
1683:Rehden (Radzyń Chełmiński)
1677:were routed on the frozen
1582:Initial Teutonic campaigns
1400:In 1225 or 1228, fourteen
1296:Henry I, Count of Schwerin
497:Swietopelk II of Pomerania
165:Margraviate of Brandenburg
2129:converted to Christianity
1920:, and the princes of the
1168:
721:Ideology and institutions
718:
663:, eventually erasing the
369:
180:Landgraviate of Thuringia
103:
45:
34:
26:
21:
3006:Seward, Desmond (1995).
2141:Bartenstein (Bartoszyce)
2112:Grand Duchy of Lithuania
1661:. The Pomerellian dukes
1397:(Danzig) in Pomerellia.
357:Grand Duchy of Lithuania
215:Burgraviate of Magdeburg
3034:Urban, William (2003).
2548:, 51 (2002), p. 317-350
2153:Hartmann von Heldrungen
2054:Great Prussian uprising
2004:at the junction of the
1966:Otto III of Brandenburg
1827:First Prussian Uprising
1821:Teutonic state ca. 1260
1813:First Prussian Uprising
1329:, besieged Chełmno and
1188:Great Prussian Uprising
621:, primarily led by the
457:Otto III of Brandenburg
399:Hartmann von Heldrungen
340:Yotvingians (Sudovians)
2991:Perlbach, Max (1886).
2201:Nicholas von Jeroschin
2146:Anno von Sangershausen
2092:Brandenburg (Ushakovo)
1901:Dietrich von Grüningen
1822:
1745:Christburg (Dzierzgoń)
1655:Marienwerder (Kwidzyn)
1444:
1238:
510:Sambor II of Pomerania
403:Marshal Heinrich Botel
370:Commanders and leaders
200:Principality of Anhalt
190:Margraviate of Moravia
175:Margraviate of Lusatia
170:Margraviate of Meissen
3082:Wars involving Poland
2931:Gieysztor, Aleksander
2921:Fahne, Anton (1875).
2898:The Northern Crusades
2247:Ludwig von Liebenzell
1998:Braunsberg (Braniewo)
1950:Ottokar II of Bohemia
1876:of thickly-populated
1820:
1501:Golden Bull of Rimini
1439:
1294:until his capture by
1236:
1178:1st Prussian Uprising
482:Burchard of Magdeburg
467:Engelbert of the Mark
437:Ottokar II of Bohemia
225:County of Schwarzburg
3025:Töppen, Max (1853).
2809:Christiansen, p. 108
2692:Christiansen, p. 105
2635:Christiansen, p. 106
2258:Treaty of Christburg
2221:Marienburg (Malbork)
2204:battle's aftermath.
1853:Treaty of Christburg
1719:With the support of
1521:Golden Bull of Rieti
1386:Bishopric of Prussia
1380:, and Laurentius of
1220:Bolesław I of Poland
584:Allies of Prussians:
537:Skomantas of Sudovia
505:Warcisław of Świecie
487:Henry of Schwarzburg
472:William IV of Jülich
462:Henry III of Meissen
389:Konrad von Thuringen
351:Allies of Prussians:
220:County of Regenstein
2959:A History of Poland
2535:Christiansen, p. 83
2517:Christiansen, p. 82
2316:Christiansen, p. 38
2265:. With the fall of
1970:Rudolph of Habsburg
1508:Treaty of Kruszwica
1466:High Duke of Poland
1268:Henry of Sandomierz
1218:as far as Prussia.
1105:Crusade of the Poor
477:Friedrich of Anhalt
422:Leszek II the Black
394:Gerhard von Malberg
2779:Wyatt, pp. 216–217
2767:Wyatt, pp. 214–216
2758:Wyatt, pp. 212–213
2749:Wyatt, pp. 209–210
2740:Wyatt, pp. 203–204
2490:McClintock, p. 720
2367:2007-11-28 at the
1986:Tapiau (Gvardeysk)
1864:in November 1249.
1823:
1517:Holy Roman Emperor
1497:Holy Roman Emperor
1482:Kingdom of Hungary
1449:Christian of Oliva
1445:
1426:Order of Calatrava
1364:the Archbishop of
1356:Crusade of 1222/23
1307:Christian of Oliva
1239:
1224:Adalbert of Prague
1200:Wulfstan of Hedeby
1032:Against Christians
736:Crusade indulgence
726:Crusading movement
657:Prussian uprisings
578:Pepin of Pomesania
492:Rudolf of Habsburg
417:Henry II the Pious
362:Duchy of Pomerania
270:Order of Calatrava
260:Duchy of Lubiszewo
245:Duchy of Pomerelia
237:Duchy of Pomerania
230:County of Habsburg
145:Kingdom of Bohemia
64:Kaliningrad Oblast
2935:History of Poland
2580:Peter von Dusburg
2046:Battle of Skuodas
2002:Wehlau (Znamensk)
1922:Holy Roman Empire
1897:Poppo von Osterna
1690:William of Modena
1620:Nessau (Nieszawa)
1536:Peter von Dusburg
1493:Holy Roman Empire
1453:Hermann von Salza
1441:Hermann von Salza
1378:Breslau (Wroclaw)
1370:Wincenty I Niałek
1350:Conrad of Masovia
1338:Pope Honorius III
1228:Bruno of Querfurt
1196:
1195:
1124:
1123:
1110:Shepherds' (1320)
1100:Shepherds' (1251)
1084:(1096–1320)
1034:(1209–1588)
969:(1147–1410)
847:(1291–1717)
665:Prussian language
608:
607:
515:Daniel of Galicia
427:Henry the Bearded
412:Konrad of Masovia
379:Hermann von Salza
241:
140:Holy Roman Empire
135:Kingdom of Poland
99:
98:
70:and northeastern
29:Northern Crusades
3094:
3072:Prussian Crusade
3058:
3049:
3030:
3021:
3002:
2987:
2978:
2962:
2948:
2926:
2917:
2901:
2882:
2879:
2873:
2870:
2864:
2861:
2855:
2852:
2846:
2843:
2837:
2834:
2828:
2827:Urban, pp. 64–65
2825:
2819:
2816:
2810:
2807:
2798:
2795:
2789:
2786:
2780:
2777:
2768:
2765:
2759:
2756:
2750:
2747:
2741:
2738:
2732:
2729:
2720:
2717:
2711:
2708:
2702:
2699:
2693:
2690:
2684:
2681:
2675:
2672:
2663:
2660:
2654:
2653:Wyatt, pp. 92–93
2651:
2645:
2642:
2636:
2633:
2624:
2621:
2615:
2612:
2601:
2598:
2592:
2589:
2583:
2576:
2570:
2567:
2558:
2555:
2549:
2542:
2536:
2533:
2527:
2524:
2518:
2515:
2509:
2506:
2500:
2497:
2491:
2488:
2479:
2476:
2470:
2467:
2461:
2458:
2447:
2446:Gieysztor, p. 93
2444:
2438:
2435:
2429:
2428:Gieysztor, p. 94
2426:
2417:
2414:
2408:
2405:
2399:
2396:
2390:
2389:Gieysztor, p. 69
2387:
2381:
2378:
2372:
2359:
2353:
2352:Gieysztor, p. 77
2350:
2344:
2341:
2335:
2334:Wyatt, pp. 22–23
2332:
2326:
2325:Gieysztor, p. 50
2323:
2317:
2314:
2294:Livonian Crusade
2240:Leszek the Black
2228:guerilla warfare
2065:Sarmatia Europea
1930:Memel (Klaipėda)
1791:Pope Innocent IV
1694:Order of Dobrzyń
1418:Order of Dobrzyń
1374:Henry of Silesia
1280:guerilla warfare
1204:Alfred of Wessex
1163:
1161:
1160:Prussian Crusade
1151:
1144:
1137:
1128:
1127:
838:Fall of Outremer
741:Papal income tax
713:
703:
696:
689:
680:
679:
623:Teutonic Knights
612:Prussian Crusade
533:
501:
432:Ladislaus Odonic
239:
210:County of Jülich
185:Duchy of Austria
150:Duchy of Silesia
130:Duchy of Masovia
82:Crusader victory
47:
46:
39:
22:Prussian Crusade
19:
18:
3102:
3101:
3097:
3096:
3095:
3093:
3092:
3091:
3062:
3061:
3046:
3018:
2975:
2945:
2914:
2890:
2885:
2880:
2876:
2871:
2867:
2862:
2858:
2853:
2849:
2844:
2840:
2835:
2831:
2826:
2822:
2817:
2813:
2808:
2801:
2796:
2792:
2787:
2783:
2778:
2771:
2766:
2762:
2757:
2753:
2748:
2744:
2739:
2735:
2730:
2723:
2718:
2714:
2709:
2705:
2700:
2696:
2691:
2687:
2682:
2678:
2673:
2666:
2661:
2657:
2652:
2648:
2643:
2639:
2634:
2627:
2622:
2618:
2613:
2604:
2599:
2595:
2590:
2586:
2577:
2573:
2568:
2561:
2556:
2552:
2543:
2539:
2534:
2530:
2525:
2521:
2516:
2512:
2507:
2503:
2499:Perlbach, p. 61
2498:
2494:
2489:
2482:
2477:
2473:
2468:
2464:
2459:
2450:
2445:
2441:
2436:
2432:
2427:
2420:
2415:
2411:
2406:
2402:
2397:
2393:
2388:
2384:
2379:
2375:
2369:Wayback Machine
2360:
2356:
2351:
2347:
2342:
2338:
2333:
2329:
2324:
2320:
2315:
2311:
2307:
2299:Wendish Crusade
2290:
2282:pagan Lithuania
2124:
2122:Later campaigns
2050:Battle of Durbe
2034:
1974:Battle of Rudau
1964:under Margrave
1958:Bruno of Olmütz
1934:Curonian Lagoon
1926:Livonian branch
1885:Heinrich Stango
1870:
1815:
1737:Elbing (Elbląg)
1714:Battle of Saule
1584:
1525:Pope Gregory IX
1447:While in Rome,
1434:
1358:
1197:
1192:
1164:
1159:
1157:
1155:
1125:
1120:
1090:People's (1096)
714:
709:
707:
677:
604:
519:
499:
452:Albert the Tall
442:Bruno of Olmütz
250:Duchy of Gdańsk
195:Duchy of Saxony
125:Order of Dobrin
88:
74:
40:
17:
12:
11:
5:
3100:
3090:
3089:
3084:
3079:
3074:
3060:
3059:
3050:
3044:
3031:
3022:
3016:
3003:
2988:
2979:
2973:
2953:Halecki, Oskar
2949:
2943:
2927:
2918:
2912:
2889:
2886:
2884:
2883:
2874:
2865:
2856:
2847:
2838:
2829:
2820:
2811:
2799:
2790:
2781:
2769:
2760:
2751:
2742:
2733:
2721:
2712:
2703:
2694:
2685:
2676:
2664:
2655:
2646:
2637:
2625:
2623:Seward, p. 101
2616:
2602:
2600:Töppen, p. 276
2593:
2584:
2571:
2559:
2557:Halecki, p. 35
2550:
2537:
2528:
2519:
2510:
2501:
2492:
2480:
2471:
2462:
2448:
2439:
2430:
2418:
2409:
2400:
2391:
2382:
2373:
2354:
2345:
2336:
2327:
2318:
2308:
2306:
2303:
2302:
2301:
2296:
2289:
2286:
2280:, and against
2123:
2120:
2033:
2030:
1869:
1866:
1814:
1811:
1768:Vistula Lagoon
1702:Sword-Brothers
1640:Culm (Chełmno)
1583:
1580:
1461:Teutonic Order
1433:
1430:
1406:military order
1357:
1354:
1319:Sword-Brothers
1202:, an agent of
1194:
1193:
1191:
1190:
1185:
1180:
1175:
1169:
1166:
1165:
1154:
1153:
1146:
1139:
1131:
1122:
1121:
1113:
1112:
1107:
1102:
1097:
1092:
1078:
1077:
1075:Spanish Armada
1072:
1067:
1062:
1057:
1052:
1047:
1042:
1028:
1027:
1022:
1017:
1012:
1007:
1002:
1001:
1000:
995:
990:
982:
977:
963:
962:
961:
960:
955:
950:
945:
940:
935:
930:
925:
920:
915:
905:
900:
895:
894:
893:
888:
883:
875:
870:
865:
860:
855:
845:Later Crusades
841:
840:
835:
830:
825:
820:
815:
810:
805:
800:
795:
790:
785:
780:
775:
770:
765:
760:
755:
744:
743:
738:
733:
728:
719:
716:
715:
706:
705:
698:
691:
683:
676:
673:
661:monastic state
616:Roman Catholic
606:
605:
603:
602:
597:
592:
581:
580:
575:
566:
557:
548:
539:
534:
522:
520:
518:
517:
512:
507:
502:
494:
489:
484:
479:
474:
469:
464:
459:
454:
449:
447:Otto the Child
444:
439:
434:
429:
424:
419:
414:
409:
404:
401:
396:
391:
386:
381:
375:
372:
371:
367:
366:
365:
364:
359:
348:
347:
342:
337:
336:
335:
330:
325:
320:
315:
310:
305:
300:
280:
279:
278:
272:
267:
262:
257:
252:
247:
242:
234:
233:
232:
227:
222:
217:
212:
207:
205:County of Mark
202:
197:
192:
187:
182:
177:
172:
167:
162:
157:
152:
147:
137:
132:
127:
122:
120:Teutonic Order
106:
105:
101:
100:
97:
96:
90:
84:
83:
80:
76:
75:
61:
59:
55:
54:
51:
43:
42:
32:
31:
24:
23:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3099:
3088:
3085:
3083:
3080:
3078:
3075:
3073:
3070:
3069:
3067:
3056:
3051:
3047:
3045:1-85367-535-0
3041:
3037:
3032:
3028:
3023:
3019:
3017:0-14-019501-7
3013:
3009:
3004:
3000:
2996:
2995:
2989:
2985:
2980:
2976:
2974:0-679-51087-7
2970:
2966:
2961:
2960:
2954:
2950:
2946:
2944:83-01-00392-8
2940:
2936:
2932:
2928:
2924:
2919:
2915:
2913:0-14-026653-4
2909:
2905:
2900:
2899:
2892:
2891:
2878:
2872:Wyatt, p. 262
2869:
2860:
2854:Wyatt, p. 259
2851:
2842:
2833:
2824:
2815:
2806:
2804:
2794:
2785:
2776:
2774:
2764:
2755:
2746:
2737:
2731:Wyatt, p. 152
2728:
2726:
2719:Wyatt, p. 151
2716:
2710:Wyatt, p. 143
2707:
2701:Wyatt, p. 101
2698:
2689:
2680:
2671:
2669:
2659:
2650:
2641:
2632:
2630:
2620:
2611:
2609:
2607:
2597:
2588:
2581:
2575:
2566:
2564:
2554:
2547:
2541:
2532:
2523:
2514:
2505:
2496:
2487:
2485:
2475:
2466:
2457:
2455:
2453:
2443:
2434:
2425:
2423:
2413:
2404:
2395:
2386:
2377:
2370:
2366:
2363:
2358:
2349:
2340:
2331:
2322:
2313:
2309:
2300:
2297:
2295:
2292:
2291:
2285:
2283:
2279:
2276:
2272:
2268:
2264:
2259:
2254:
2252:
2248:
2243:
2241:
2237:
2233:
2229:
2224:
2222:
2218:
2214:
2210:
2209:new rebellion
2205:
2202:
2198:
2194:
2190:
2186:
2182:
2179:on the lower
2178:
2174:
2169:
2166:
2162:
2158:
2154:
2149:
2147:
2142:
2138:
2134:
2130:
2119:
2117:
2113:
2109:
2104:
2101:
2097:
2093:
2089:
2085:
2081:
2076:
2074:
2070:
2066:
2062:
2057:
2055:
2051:
2047:
2043:
2039:
2029:
2027:
2023:
2019:
2015:
2011:
2007:
2003:
1999:
1995:
1991:
1987:
1983:
1979:
1975:
1971:
1967:
1963:
1959:
1956:under Bishop
1955:
1951:
1947:
1943:
1938:
1935:
1931:
1927:
1923:
1919:
1915:
1911:
1906:
1902:
1898:
1894:
1890:
1886:
1883:
1879:
1875:
1865:
1863:
1859:
1854:
1850:
1849:Pope Urban IV
1845:
1839:
1836:
1832:
1828:
1819:
1810:
1808:
1804:
1800:
1796:
1792:
1787:
1785:
1781:
1777:
1773:
1769:
1765:
1761:
1757:
1753:
1748:
1746:
1742:
1738:
1734:
1730:
1726:
1722:
1717:
1715:
1711:
1707:
1703:
1699:
1695:
1691:
1686:
1684:
1680:
1676:
1672:
1668:
1664:
1660:
1656:
1651:
1649:
1645:
1641:
1637:
1633:
1629:
1625:
1621:
1617:
1612:
1610:
1604:
1602:
1598:
1594:
1593:Thorn (Toruń)
1590:
1579:
1577:
1573:
1569:
1565:
1561:
1557:
1553:
1549:
1545:
1541:
1537:
1532:
1530:
1526:
1522:
1518:
1514:
1509:
1504:
1502:
1498:
1494:
1490:
1485:
1483:
1479:
1475:
1474:Fifth Crusade
1471:
1467:
1462:
1458:
1454:
1450:
1442:
1438:
1429:
1427:
1423:
1422:Swantopelk II
1419:
1415:
1411:
1407:
1403:
1398:
1396:
1392:
1387:
1383:
1379:
1375:
1371:
1367:
1363:
1353:
1351:
1347:
1343:
1339:
1334:
1332:
1328:
1324:
1320:
1316:
1312:
1308:
1304:
1301:In 1206, the
1299:
1297:
1293:
1289:
1285:
1281:
1277:
1273:
1269:
1265:
1261:
1257:
1252:
1248:
1244:
1235:
1231:
1229:
1225:
1221:
1217:
1213:
1209:
1205:
1201:
1189:
1186:
1184:
1181:
1179:
1176:
1174:
1173:Sirgune River
1171:
1170:
1167:
1162:
1152:
1147:
1145:
1140:
1138:
1133:
1132:
1129:
1119:
1117:
1111:
1108:
1106:
1103:
1101:
1098:
1096:
1093:
1091:
1088:
1087:
1086:
1085:
1083:
1076:
1073:
1071:
1068:
1066:
1063:
1061:
1058:
1056:
1053:
1051:
1048:
1046:
1043:
1041:
1038:
1037:
1036:
1035:
1033:
1026:
1023:
1021:
1018:
1016:
1013:
1011:
1008:
1006:
1003:
999:
996:
994:
991:
989:
986:
985:
983:
981:
978:
976:
973:
972:
971:
970:
968:
959:
956:
954:
951:
949:
946:
944:
941:
939:
936:
934:
931:
929:
926:
924:
921:
919:
916:
914:
911:
910:
909:
906:
904:
901:
899:
896:
892:
889:
887:
884:
882:
879:
878:
876:
874:
871:
869:
866:
864:
861:
859:
856:
854:
851:
850:
849:
848:
846:
839:
836:
834:
833:Lord Edward's
831:
829:
826:
824:
821:
819:
816:
814:
811:
809:
806:
804:
801:
799:
796:
794:
791:
789:
786:
784:
781:
779:
776:
774:
771:
769:
766:
764:
761:
759:
756:
754:
751:
750:
749:
748:
742:
739:
737:
734:
732:
729:
727:
724:
723:
722:
717:
712:
704:
699:
697:
692:
690:
685:
684:
681:
672:
670:
666:
662:
658:
654:
650:
646:
642:
638:
637:Old Prussians
635:
631:
628:
624:
620:
617:
613:
601:
600:Swietopelk II
598:
596:
593:
591:
588:
587:
586:
585:
579:
576:
574:
570:
567:
565:
561:
558:
556:
552:
549:
547:
543:
540:
538:
535:
532:
527:
524:
523:
521:
516:
513:
511:
508:
506:
503:
498:
495:
493:
490:
488:
485:
483:
480:
478:
475:
473:
470:
468:
465:
463:
460:
458:
455:
453:
450:
448:
445:
443:
440:
438:
435:
433:
430:
428:
425:
423:
420:
418:
415:
413:
410:
408:
407:Master Brunon
405:
402:
400:
397:
395:
392:
390:
387:
385:
382:
380:
377:
376:
374:
373:
368:
363:
360:
358:
355:
354:
353:
352:
346:
343:
341:
338:
334:
331:
329:
326:
324:
321:
319:
316:
314:
311:
309:
306:
304:
301:
299:
296:
295:
294:
291:
290:
289:
288:
286:
285:Baltic pagans
281:
277:
273:
271:
268:
266:
263:
261:
258:
256:
253:
251:
248:
246:
243:
238:
235:
231:
228:
226:
223:
221:
218:
216:
213:
211:
208:
206:
203:
201:
198:
196:
193:
191:
188:
186:
183:
181:
178:
176:
173:
171:
168:
166:
163:
161:
158:
156:
153:
151:
148:
146:
143:
142:
141:
138:
136:
133:
131:
128:
126:
123:
121:
118:
117:
116:
115:
113:
108:
107:
102:
95:
91:
86:
85:
81:
78:
77:
73:
69:
65:
60:
57:
56:
52:
49:
48:
44:
38:
33:
30:
25:
20:
3054:
3035:
3026:
3007:
2993:
2983:
2958:
2934:
2922:
2897:
2881:Urban, p. 78
2877:
2868:
2863:Urban, p. 71
2859:
2850:
2845:Urban, p. 70
2841:
2836:Urban, p. 67
2832:
2823:
2818:Urban, p. 63
2814:
2793:
2788:Urban, p. 59
2784:
2763:
2754:
2745:
2736:
2715:
2706:
2697:
2688:
2683:Wyatt, p. 99
2679:
2674:Urban, p. 56
2662:Wyatt, p. 95
2658:
2649:
2644:Urban, p. 57
2640:
2619:
2614:Urban, p. 52
2596:
2591:Fahne, p. 50
2587:
2574:
2569:Urban, p. 43
2553:
2545:
2540:
2531:
2526:Wyatt, p. 81
2522:
2513:
2508:Wyatt, p. 36
2504:
2495:
2478:Wyatt, p. 39
2474:
2469:Wyatt, p. 34
2465:
2460:Wyatt, p. 33
2442:
2437:Wyatt, p. 32
2433:
2416:Urban, p. 51
2412:
2407:Wyatt, p. 47
2403:
2398:Wyatt, p. 29
2394:
2385:
2380:Urban, p. 50
2376:
2357:
2348:
2343:Wyatt, p. 24
2339:
2330:
2321:
2312:
2255:
2244:
2225:
2206:
2170:
2150:
2125:
2105:
2077:
2058:
2035:
1939:
1871:
1840:
1824:
1788:
1786:and Bartia.
1770:was renamed
1749:
1718:
1698:Dobrzyń Land
1687:
1652:
1613:
1605:
1601:Hermann Balk
1585:
1533:
1505:
1486:
1470:Frederick II
1457:Grand Master
1446:
1402:north German
1399:
1362:papal legate
1359:
1335:
1300:
1256:Chełmno Land
1240:
1198:
1158:
1114:
1080:
1079:
1030:
1029:
1009:
965:
964:
908:Holy Leagues
843:
842:
746:
745:
720:
630:under duress
627:Christianize
611:
609:
583:
582:
526:Herkus Monte
384:Hermann Balk
350:
349:
283:
282:
110:
109:
104:Belligerents
27:Part of the
2181:Memel River
2096:Dietrich II
2042:Samogitians
1937:millennia.
1729:Pogesanians
1725:Pomesanians
1710:Lithuanians
1675:Pogesanians
1616:Pomesanians
1298:, in 1223.
1284:Valdemar II
1272:Bolesław IV
1116:Reconquista
1065:Despenser's
1040:Albigensian
868:Alexandrian
653:Samogitians
649:Lithuanians
323:Pogesanians
318:Pomesanians
87:Territorial
62:Modern-day
3066:Categories
2888:References
2797:Urban p.59
2185:Scalovians
2161:Nadrovians
2137:Skalmantas
2131:, but the
1994:Königsberg
1980:, Waldau,
1932:along the
1928:"founded"
1905:Galindians
1858:Natangians
1835:Pomerellia
1831:Swantopelk
1756:Natangians
1663:Swantopelk
1540:Culmerland
1523:issued by
1478:Burzenland
1342:papal bull
1327:Pomerellia
1303:Cistercian
1276:Casimir II
1118:(722–1492)
1095:Children's
1015:Lithuanian
313:Nadruvians
308:Natangians
303:Galindians
2305:Footnotes
2278:Pomerania
2133:Sudovians
2061:Holy Land
2038:Samogitia
2026:Wohnsdorf
2022:Scalovian
2018:Nadrovian
1954:Moravians
1946:Austrians
1942:Bohemians
1910:Dominican
1799:Pomesania
1671:Pogesania
1659:Pomesania
1648:Magdeburg
1560:Pomesania
1556:Pogesania
1472:with the
1247:Sudovians
1208:Mieszko I
1050:Stedinger
898:Nicopolis
863:Smyrniote
858:Aragonese
763:Norwegian
669:Lithuania
645:Prussians
619:crusaders
595:Traidenis
590:Mindaugas
573:Pogesania
345:Skalvians
293:Prussians
112:Crusaders
53:1217–1274
2955:(1970).
2365:Archived
2288:See also
2275:imperial
2271:Outremer
2217:Gardinas
2177:Scalovia
2173:Nadrovia
2084:Otto III
2073:Volhynia
2069:Pokarwis
2014:Sudovian
1990:Tvangste
1978:Quedenau
1874:Sambians
1803:Ermeland
1784:Natangia
1776:Ermeland
1760:Warmians
1752:Bartians
1743:, while
1644:Burgrave
1609:Kulm law
1568:Scalovia
1552:Natangia
1548:Nadrovia
1544:Galindia
1529:Holy See
1515:and the
1513:Holy See
1060:Bohemian
1045:Drenther
1010:Prussian
1005:Livonian
984:Swedish
967:Northern
877:Barbary
873:Savoyard
768:Venetian
711:Crusades
500:(turned)
333:Warmians
328:Sambians
298:Bartians
240:(turned)
58:Location
2234:raided
2116:Sudovia
2108:serfdom
2100:Meissen
1918:Bohemia
1914:Hungary
1878:Samland
1868:Samland
1862:Krücken
1807:Samland
1764:Honeida
1712:in the
1706:Livonia
1679:Sirgune
1597:Vistula
1576:Ermland
1572:Sudovia
1564:Samland
1480:in the
1459:of the
1414:Dobrzyń
1410:Kuyavia
1366:Gniezno
1346:crusade
1340:sent a
1323:Livonia
1315:Chełmno
1305:bishop
1292:Samland
1288:Denmark
1264:baptism
1260:Masovia
1210:of the
1183:Krücken
1082:Popular
1070:Hussite
1055:Bosnian
1020:Russian
980:Wendish
823:Catalan
813:Seventh
808:Barons'
569:Auctume
542:Diwanus
94:Prussia
89:changes
3042:
3014:
2971:
2941:
2910:
2236:Pokima
2213:Zantir
2197:Labiau
2193:Romige
2189:Ragnit
2114:or to
2088:John I
2020:, and
2010:Pregel
1984:, and
1982:Caimen
1962:Saxons
1893:Stango
1889:Romuve
1882:Komtur
1844:Rensen
1805:, and
1758:, and
1741:Lübeck
1667:Sambor
1636:Gurske
1632:Quercz
1589:German
1574:, and
1519:. The
1489:Rimini
1455:, the
1424:. The
1395:Gdańsk
1331:Lubawa
1249:, and
1212:Polans
975:Kalmar
828:Eighth
793:Fourth
778:Second
641:Polish
564:Warmia
560:Glappo
555:Sambia
551:Glande
546:Bartia
528:
79:Result
72:Poland
68:Russia
2251:Balga
1772:Balga
1733:Truso
1628:Rogów
1624:Toruń
1391:Płock
1382:Lebus
1251:Wends
1243:Poles
1025:Tatar
903:Varna
803:Sixth
798:Fifth
783:Third
753:First
634:pagan
625:, to
3040:ISBN
3012:ISBN
2969:ISBN
2939:ISBN
2908:ISBN
2269:and
2267:Acre
2165:Vogt
2086:and
2008:and
2006:Alle
1944:and
1795:Culm
1665:and
1311:Rome
1274:and
1258:and
1241:The
1216:Oder
998:1293
993:1249
988:1150
958:1717
953:1684
948:1594
943:1571
938:1538
933:1535
928:1526
923:1511
918:1495
913:1332
891:1399
886:1398
881:1390
818:1267
788:1197
773:1129
758:1101
651:and
632:the
610:The
50:Date
2999:128
2965:366
2904:287
2098:of
1833:of
1657:in
1646:of
1634:or
1321:in
1286:of
571:of
562:of
553:of
544:of
276:HRE
3068::
2967:.
2906:.
2802:^
2772:^
2724:^
2667:^
2628:^
2605:^
2562:^
2483:^
2451:^
2421:^
2284:.
2163:.
2075:.
2016:,
1960:,
1952:,
1916:,
1880:.
1801:,
1797:,
1754:,
1735:,
1716:.
1650:.
1611:.
1570:,
1566:,
1562:,
1558:,
1554:,
1550:,
1546:,
1531:.
1368:,
671:.
647:,
66:,
3048:.
3020:.
3001:.
2977:.
2947:.
2916:.
1587:(
1150:e
1143:t
1136:v
702:e
695:t
688:v
287::
114::
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.