381:
motor neurons carrying the signal from the precentral gyrus down through the internal capsule, through the cerebral peduncle, and into the medulla. In the medullary pyramid, the corticospinal tract decussates and becomes the lateral corticospinal tract. The nerve signal will continue down the lateral corticospinal tract until it reaches spinal nerve L4. At this point, the nerve signal will synapse from the upper motor neurons to the lower motor neurons. The signal will travel through the anterior root of L4 and into the anterior rami of the L4 nerve, leaving the spinal cord through the lumbar plexus. The posterior division of the L4 root is the femoral nerve. The femoral nerve innervates the quadriceps femoris, a fourth of which is the rectus femoris. When the rectus femoris receives the signal that has traveled all the way from the medial side of the precentral gyrus, it contracts, extending the knee and flexing the thigh at the hip.
1498:
495:
464:
Rectus femoris strain, referred to as hip flexor strain, is an injury commonly at the tendon that attaches to the patella or in the muscle itself. The injury is usually a partial tear, but could be a full tear. The injury is caused by a forceful movement related to sprinting, jumping, or kicking and
380:
The neurons for voluntary thigh contraction originate near the summit of the medial side of the precentral gyrus (the primary motor area of the brain). These neurons send a nerve signal that is carried by the corticospinal tract down the brainstem and spinal cord. The signal starts with the upper
465:
is common in sports like football or soccer. The rectus femoris is prone to injury, since it crosses both the knee and the hip. Symptoms include a sudden sharp pain at the front of the hip or in the groin, swelling and bruising, and an inability to contract the rectus femoris with a full tear.
29:
420:
Similarly, the rectus femoris is not dominant in knee extension when the hip is flexed since it is already shortened and thus suffers from active insufficiency. In essence: the action of extending the knee from a seated position is primarily driven by the
1518:
368:
The muscle ends in a broad and thick aponeurosis that occupies the lower two-thirds of its posterior surface, and, gradually becoming narrowed into a flattened tendon, is inserted into the base of the
365:
The two unite at an acute angle and spread into an aponeurosis that is prolonged downward on the anterior surface of the muscle, and from this the muscular fibers arise.
397:
are the flexors of the thigh at the hip. The rectus femoris is a weaker hip flexor when the knee is extended because it is already shortened and thus suffers from
481:. This is due to forceful contraction of the muscle that generates a force greater than that which holds the bone together. This is a well recognized, but unusual
436:
In the other extreme, the muscle's ability to flex the hip and extend the knee can be compromised in a position of full hip extension and knee flexion, due to
243:
675:
648:
219:
1409:
668:
1538:
1464:
1459:
1370:
1296:
1048:
335:
327:
178:
171:
121:
105:
1291:
1053:
414:
575:
1543:
1533:
661:
311:
144:
1339:
1110:
1334:
1105:
1365:
1201:
890:
444:
1421:
1399:
1196:
840:
831:
474:
355:
238:
110:
1125:
1092:
1083:
948:
925:
764:
410:
504:
1488:
1469:
1426:
1227:
437:
398:
250:
163:
1206:
938:
868:
853:
807:
802:
430:
284:
272:
131:
1404:
1382:
1360:
1100:
880:
797:
787:
576:
A Rare Form of Soccer Injury – Rectus
Femoris Tendon Rupture – Orthopaedic Information | Singapore
1528:
1159:
968:
863:
422:
288:
527:
1387:
1301:
963:
958:
953:
913:
226:
214:
563:
113:
and the exterior surface of the bony ridge which forms the groove on the iliac portion of the
908:
903:
776:
1523:
1149:
1144:
564:
Rectus
Femoris Strain (“Hip Flexor Strain”) | Dr. David Geier – Sports Medicine Simplified
8:
1454:
1269:
185:
1497:
33:
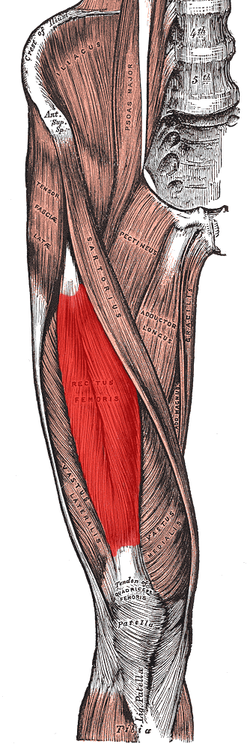
Muscles of the iliac and anterior femoral regions. (Rectus femoris visible near center.)
1281:
713:
709:
684:
622:
589:
406:
1235:
1115:
1058:
812:
627:
609:
509:
478:
296:
127:
1519:
Knowledge articles incorporating text from the 20th edition of Gray's
Anatomy (1918)
590:"Proximal Rectus Femoris Avulsion: Ultrasonic Diagnosis and Nonoperative Management"
1245:
1240:
1213:
1171:
1043:
933:
848:
653:
617:
601:
390:
49:
1164:
1019:
1014:
943:
873:
792:
757:
747:
742:
426:
280:
1502:
1446:
1009:
992:
752:
718:
402:
315:
605:
1512:
1191:
1154:
997:
613:
500:
482:
231:
156:
358:; the other, the posterior or reflected, from a groove above the rim of the
307:
1004:
696:
631:
588:
Esser, Stephan; Jantz, David; Hurdle, Mark F.; Taylor, Walter (July 2015).
1031:
323:
256:
359:
276:
114:
1078:
898:
704:
688:
448:
394:
190:
730:
354:
It arises by two tendons: one, the anterior or straight, from the
369:
302:
The rectus femoris is situated in the middle of the front of the
292:
28:
1438:
1257:
980:
138:
87:
826:
303:
202:
151:
1319:
343:
168:
81:
67:
58:
339:
331:
175:
90:
291:. All four parts of the quadriceps muscle attach to the
310:
in shape, and its superficial fibers are arranged in a
587:
551:
Anatomy and
Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function
1486:
93:
78:
70:
61:
683:
64:
55:
477:of the hip (AIIS) to avulse in what is known as an
84:
75:
52:
473:The Rectus femoris tendon can cause a fragment of
1510:
578:. Orthopaedic.com.sg. Retrieved on 2015-09-30.
669:
525:
676:
662:
314:manner, the deep fibers running straight (
27:
621:
454:
528:"Function of the Rectus Femoris Muscle"
1511:
499:This article incorporates text in the
287:(deep to the rectus femoris), and the
1049:Lateral intermuscular septum of thigh
657:
1054:Medial intermuscular septum of thigh
468:
13:
433:, and less by the rectus femoris.
14:
1555:
642:
417:than it will the rectus femoris.
145:lateral femoral circumflex artery
1496:
493:
485:that can affect young athletes.
48:
443:The rectus femoris is a direct
401:; the action will recruit more
375:
581:
569:
556:
544:
519:
451:, at the hip and at the knee.
1:
1539:Anterior compartment of thigh
488:
475:anterior inferior iliac spine
356:anterior inferior iliac spine
111:Anterior inferior iliac spine
1236:Fibularis (peroneus) muscles
1116:Fibularis (peroneus) tertius
594:Journal of Athletic Training
349:
7:
1410:Flexor digiti minimi brevis
507:of the 20th edition of
384:
10:
1560:
562:Geier, David (2011-01-18)
251:Anatomical terms of muscle
1544:Muscles of the lower limb
1534:Muscles of the quadriceps
1437:
1348:
1340:Extensor digitorum brevis
1327:
1318:
1278:
1265:
1256:
1226:
1180:
1133:
1124:
1111:Extensor digitorum longus
1091:
1077:
1028:
988:
979:
924:
889:
839:
825:
773:
738:
729:
695:
606:10.4085/1052-6050-50.2.13
459:
249:
237:
225:
213:
201:
196:
184:
162:
150:
143:Descending branch of the
137:
120:
104:
43:
38:
26:
21:
1335:Extensor hallucis brevis
1106:Extensor hallucis longus
1366:Flexor digitorum brevis
1202:Flexor digitorum longus
326:. Its functions are to
208:musculus rectus femoris
1400:Flexor hallucis brevis
1371:Abductor digiti minimi
1197:Flexor hallucis longus
319:
777:Lateral rotator group
455:Clinical significance
438:passive insufficiency
279:. The others are the
269:rectus femoris muscle
22:Rectus femoris muscle
765:Tensor fasciae latae
413:, and the remaining
411:tensor fasciae latae
399:active insufficiency
389:The rectus femoris,
1282:Intermuscular septa
566:. drdavidgeier.com.
322:) down to the deep
271:is one of the four
130:as one of the four
1427:Plantar interossei
1207:Tibialis posterior
939:External obturator
869:Vastus intermedius
808:External obturator
803:Internal obturator
685:Muscles of the hip
553:, Saladin, 5th ed.
431:vastus intermedius
295:(knee cap) by the
285:vastus intermedius
273:quadriceps muscles
132:quadriceps muscles
16:Muscle in the quad
1484:
1483:
1480:
1479:
1465:Superior extensor
1460:Inferior extensor
1422:Dorsal interossei
1405:Adductor hallucis
1383:Quadratus plantae
1361:Abductor hallucis
1314:
1313:
1310:
1309:
1222:
1221:
1101:Tibialis anterior
1073:
1072:
1069:
1068:
1059:Cribriform fascia
881:Articularis genus
821:
820:
798:Superior gemellus
793:Inferior gemellus
788:Quadratus femoris
526:Elizabeth Quinn.
479:Avulsion fracture
469:Avulsion fracture
330:the thigh at the
297:quadriceps tendon
265:
264:
260:
126:Inserts into the
1551:
1501:
1500:
1492:
1388:Lumbrical muscle
1325:
1324:
1285:
1263:
1262:
1185:
1160:Accessory soleus
1138:
1131:
1130:
1089:
1088:
1044:Iliotibial tract
1035:
986:
985:
864:Vastus lateralis
837:
836:
781:
736:
735:
678:
671:
664:
655:
654:
636:
635:
625:
585:
579:
573:
567:
560:
554:
548:
542:
541:
539:
538:
523:
497:
496:
423:vastus lateralis
289:vastus lateralis
257:edit on Wikidata
254:
100:
99:
96:
95:
92:
89:
86:
83:
80:
77:
73:
72:
69:
66:
63:
60:
57:
54:
31:
19:
18:
1559:
1558:
1554:
1553:
1552:
1550:
1549:
1548:
1509:
1508:
1507:
1495:
1487:
1485:
1476:
1433:
1344:
1306:
1279:
1274:
1252:
1218:
1181:
1176:
1165:Achilles tendon
1134:
1120:
1082:
1065:
1029:
1024:
1020:Muscular lacuna
1015:Adductor hiatus
975:
920:
914:Semimembranosus
885:
874:Vastus medialis
830:
817:
774:
769:
743:Gluteal muscles
725:
691:
682:
645:
640:
639:
586:
582:
574:
570:
561:
557:
549:
545:
536:
534:
524:
520:
494:
491:
471:
462:
457:
427:vastus medialis
387:
378:
352:
281:vastus medialis
261:
128:patellar tendon
74:
51:
47:
34:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1557:
1547:
1546:
1541:
1536:
1531:
1529:Knee extensors
1526:
1521:
1506:
1505:
1482:
1481:
1478:
1477:
1475:
1474:
1473:
1472:
1467:
1462:
1457:
1449:
1447:Plantar fascia
1443:
1441:
1435:
1434:
1432:
1431:
1430:
1429:
1424:
1414:
1413:
1412:
1407:
1402:
1392:
1391:
1390:
1385:
1375:
1374:
1373:
1368:
1363:
1352:
1350:
1346:
1345:
1343:
1342:
1337:
1331:
1329:
1322:
1316:
1315:
1312:
1311:
1308:
1307:
1305:
1304:
1299:
1294:
1288:
1286:
1276:
1275:
1273:
1272:
1266:
1260:
1254:
1253:
1251:
1250:
1249:
1248:
1243:
1232:
1230:
1224:
1223:
1220:
1219:
1217:
1216:
1211:
1210:
1209:
1204:
1199:
1188:
1186:
1178:
1177:
1175:
1174:
1169:
1168:
1167:
1162:
1157:
1152:
1141:
1139:
1128:
1122:
1121:
1119:
1118:
1113:
1108:
1103:
1097:
1095:
1086:
1075:
1074:
1071:
1070:
1067:
1066:
1064:
1063:
1062:
1061:
1056:
1051:
1046:
1038:
1036:
1026:
1025:
1023:
1022:
1017:
1012:
1010:Adductor canal
1007:
1002:
1001:
1000:
993:Femoral sheath
989:
983:
977:
976:
974:
973:
972:
971:
966:
961:
956:
946:
941:
936:
930:
928:
922:
921:
919:
918:
917:
916:
911:
909:Semitendinosus
906:
904:Biceps femoris
895:
893:
887:
886:
884:
883:
878:
877:
876:
871:
866:
861:
859:Rectus femoris
851:
845:
843:
834:
823:
822:
819:
818:
816:
815:
810:
805:
800:
795:
790:
784:
782:
771:
770:
768:
767:
762:
761:
760:
755:
750:
739:
733:
727:
726:
724:
723:
722:
721:
716:
701:
699:
693:
692:
681:
680:
673:
666:
658:
652:
651:
644:
643:External links
641:
638:
637:
600:(7): 778–780.
580:
568:
555:
543:
517:
516:
510:Gray's Anatomy
490:
487:
470:
467:
461:
458:
456:
453:
386:
383:
377:
374:
351:
348:
263:
262:
253:
247:
246:
241:
235:
234:
229:
223:
222:
217:
211:
210:
205:
199:
198:
194:
193:
188:
182:
181:
166:
160:
159:
154:
148:
147:
141:
135:
134:
124:
118:
117:
108:
102:
101:
45:
41:
40:
36:
35:
32:
24:
23:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1556:
1545:
1542:
1540:
1537:
1535:
1532:
1530:
1527:
1525:
1522:
1520:
1517:
1516:
1514:
1504:
1499:
1494:
1493:
1490:
1471:
1468:
1466:
1463:
1461:
1458:
1456:
1453:
1452:
1450:
1448:
1445:
1444:
1442:
1440:
1436:
1428:
1425:
1423:
1420:
1419:
1418:
1415:
1411:
1408:
1406:
1403:
1401:
1398:
1397:
1396:
1393:
1389:
1386:
1384:
1381:
1380:
1379:
1376:
1372:
1369:
1367:
1364:
1362:
1359:
1358:
1357:
1354:
1353:
1351:
1347:
1341:
1338:
1336:
1333:
1332:
1330:
1326:
1323:
1321:
1317:
1303:
1300:
1298:
1295:
1293:
1290:
1289:
1287:
1284:
1283:
1277:
1271:
1270:Pes anserinus
1268:
1267:
1264:
1261:
1259:
1255:
1247:
1244:
1242:
1239:
1238:
1237:
1234:
1233:
1231:
1229:
1225:
1215:
1212:
1208:
1205:
1203:
1200:
1198:
1195:
1194:
1193:
1192:tarsal tunnel
1190:
1189:
1187:
1184:
1179:
1173:
1170:
1166:
1163:
1161:
1158:
1156:
1153:
1151:
1150:Gastrocnemius
1148:
1147:
1146:
1145:Triceps surae
1143:
1142:
1140:
1137:
1132:
1129:
1127:
1123:
1117:
1114:
1112:
1109:
1107:
1104:
1102:
1099:
1098:
1096:
1094:
1090:
1087:
1085:
1080:
1076:
1060:
1057:
1055:
1052:
1050:
1047:
1045:
1042:
1041:
1040:
1039:
1037:
1034:
1033:
1027:
1021:
1018:
1016:
1013:
1011:
1008:
1006:
1003:
999:
998:Femoral canal
996:
995:
994:
991:
990:
987:
984:
982:
978:
970:
967:
965:
962:
960:
957:
955:
952:
951:
950:
947:
945:
942:
940:
937:
935:
932:
931:
929:
927:
923:
915:
912:
910:
907:
905:
902:
901:
900:
897:
896:
894:
892:
888:
882:
879:
875:
872:
870:
867:
865:
862:
860:
857:
856:
855:
852:
850:
847:
846:
844:
842:
838:
835:
833:
828:
824:
814:
811:
809:
806:
804:
801:
799:
796:
794:
791:
789:
786:
785:
783:
780:
778:
772:
766:
763:
759:
756:
754:
751:
749:
746:
745:
744:
741:
740:
737:
734:
732:
728:
720:
717:
715:
711:
708:
707:
706:
703:
702:
700:
698:
694:
690:
686:
679:
674:
672:
667:
665:
660:
659:
656:
650:
647:
646:
633:
629:
624:
619:
615:
611:
607:
603:
599:
595:
591:
584:
577:
572:
565:
559:
552:
547:
533:
529:
522:
518:
515:
514:
511:
508:
506:
502:
501:public domain
486:
484:
483:sports injury
480:
476:
466:
452:
450:
446:
441:
439:
434:
432:
428:
424:
418:
416:
412:
408:
404:
400:
396:
392:
382:
373:
371:
366:
363:
361:
357:
347:
345:
341:
337:
334:joint and to
333:
329:
325:
321:
317:
313:
309:
305:
300:
298:
294:
290:
286:
282:
278:
274:
270:
258:
252:
248:
245:
242:
240:
236:
233:
230:
228:
224:
221:
218:
216:
212:
209:
206:
204:
200:
195:
192:
189:
187:
183:
180:
177:
173:
170:
167:
165:
161:
158:
157:Femoral nerve
155:
153:
149:
146:
142:
140:
136:
133:
129:
125:
123:
119:
116:
112:
109:
107:
103:
98:
46:
44:Pronunciation
42:
37:
30:
25:
20:
1416:
1394:
1377:
1355:
1280:
1182:
1135:
1084:compartments
1030:
1005:Femoral ring
858:
832:compartments
775:
697:Iliac region
597:
593:
583:
571:
558:
550:
546:
535:. Retrieved
532:Verywell Fit
531:
521:
512:
498:
492:
472:
463:
442:
435:
419:
388:
379:
376:Nerve supply
367:
364:
353:
301:
268:
266:
220:A04.7.02.018
207:
1524:Hip flexors
1451:retinacula
1136:Superficial
1032:Fascia lata
714:Psoas minor
710:Psoas major
415:hip flexors
407:psoas major
324:aponeurosis
312:bipenniform
197:Identifiers
1513:Categories
1302:Transverse
854:Quadriceps
813:Piriformis
537:2022-07-23
489:References
449:hamstrings
445:antagonist
360:acetabulum
277:human body
186:Antagonist
115:acetabulum
1417:4th layer
1395:3rd layer
1378:2nd layer
1356:1st layer
1297:Posterior
1214:Popliteus
1172:Plantaris
1126:Posterior
934:Pectineus
899:Hamstring
891:Posterior
849:Sartorius
705:Iliopsoas
689:human leg
649:PTCentral
614:1062-6050
395:iliopsoas
391:sartorius
350:Structure
191:Hamstring
172:extension
122:Insertion
1455:Peroneal
1292:Anterior
1093:Anterior
949:Adductor
944:Gracilis
841:Anterior
731:Buttocks
632:25978099
505:page 470
385:Function
308:fusiform
306:; it is
1503:Anatomy
1349:Plantar
1228:Lateral
969:Minimus
758:Minimus
748:Maximus
719:Iliacus
623:4532190
447:to the
403:iliacus
370:patella
346:joint.
342:at the
293:patella
275:of the
179:flexion
164:Actions
39:Details
1489:Portal
1470:Flexor
1439:Fascia
1328:Dorsal
1258:Fascia
1246:Brevis
1241:Longus
1155:Soleus
981:Fascia
964:Magnus
959:Brevis
954:Longus
926:Medial
753:Medius
630:
620:
612:
513:(1918)
460:Strain
429:, and
393:, and
336:extend
320:rectus
283:, the
139:Artery
106:Origin
827:Thigh
503:from
316:Latin
304:thigh
255:[
244:22430
203:Latin
152:Nerve
1320:Foot
1183:Deep
687:and
628:PMID
610:ISSN
344:knee
338:the
328:flex
267:The
232:2614
215:TA98
169:Knee
1079:Leg
618:PMC
602:doi
340:leg
332:hip
239:FMA
227:TA2
176:hip
1515::
626:.
616:.
608:.
598:50
596:.
592:.
530:.
440:.
425:,
409:,
405:,
372:.
362:.
318::
299:.
174:;
88:ər
1491::
1081:/
829:/
779::
712:/
677:e
670:t
663:v
634:.
604::
540:.
259:]
97:/
94:s
91:ɪ
85:m
82:ɛ
79:f
76:ˈ
71:s
68:ə
65:t
62:k
59:ɛ
56:r
53:ˈ
50:/
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.