641:
95:(literally "five-step" in a mixture of Latin and German) transposed a triad by a perfect fifth, transforming C major into G major (up) or F major (down). A Wechsel inverted a triad according to the Riemann's theory of dualism, mapping a major triad to a minor triad. For example, Seitenwechsel ("die Seiten wechseln" translates as "to exchange sides") mapped a triad on to its parallel minor or major, transforming C major to C minor and conversely. Riemann's theory of transformations formed the basis for
27:
604:
94:
In the 1880s, Riemann proposed a system of transformations that related triads directly to each other. Riemann's system had two classes of transformations: "Schritt" and "Wechsel". A Schritt transposed one triad into another, moving it a certain number of scale steps. For example, the "Quintschritt"
30:
Illustration of
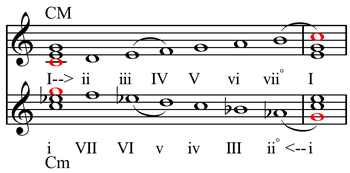
Riemann's "dualist" system: minor as upside down major. Half-steps are indicated by slur marks, other notes are separated by whole steps. The descending melodic minor scale shown has the same order of half steps and whole steps as the ascending major
46:(1849–1919). His theoretical writings cover many topics, including musical logic, notation, harmony, melody, phraseology, the history of music theory, etc. More particularly, the term
564:
682:
532:
82:; this "harmonic dualism" (harmonic polarity) is what produces the change-in-direction described above. See also the related term
278:
265:
99:, which expanded the idea of transformations beyond the basic tonal triads that Riemann was mostly concerned with.
675:
525:
557:
427:
401:
397:
393:
358:
354:
350:
337:
711:
706:
51:
701:
668:
518:
133:
Musikalische Logik. Hauptzüge der physiologischen und psychologischen Begründung unseres Musik-systems
414:
50:
often refers to his theory of harmony, characterized mainly by its dualism and by a concept of
243:
70:
theorists. The term "dualism" refers to the emphasis on the inversional relationship between
640:
579:
258:
96:
656:
108:
8:
20:
552:
380:
251:
113:
71:
652:
282:
274:
695:
574:
324:
63:
26:
648:
569:
410:
43:
39:
585:
371:
362:
79:
75:
389:
333:
83:
510:
423:
592:
346:
67:
603:
273:
217:
235:Some Remarks on the Use of Riemann Transformations
693:
229:
227:
225:
676:
526:
259:
222:
165:Skizze einer neuen Methode der Harmonielehre
78:being considered "upside down" versions of
683:
669:
533:
519:
266:
252:
62:Riemann's "dualist" system for relating
25:
145:Studien zur Geschichte der Notenschrift
694:
66:was adapted from earlier 19th-century
540:
514:
247:
149:Die Entwickelung unserer Notenschrift
19:For the mathematical conjecture, see
635:
13:
89:
14:
723:
237:, Music Theory Online 0.9 (1994).
639:
602:
16:Musical theories of Hugo Riemann
210:
190:
178:
158:
138:
126:
1:
655:. You can help Knowledge by
558:Parallel and contrast chords
199:, Leipzig, 1890, 2d edition
38:, in general, refers to the
7:
197:Katechismus der Phrasierung
153:Notenschrift und Notendruck
102:
10:
728:
634:
616:Handbuch der Harmonielehre
173:Vereinfachte Harmonielehre
169:Handbuch der Harmonielehre
119:
57:
18:
621:Lehrbuch des Contrapunkts
611:
600:
548:
483:
316:
289:
201:Vademecum der Phrasierung
205:Handbuch der Phrasierung
175:, London/New York, 1893.
203:, 1900, 8th edition as
185:Neue Schule der Melodik
233:Klumpenhouwer, Henry,
32:
580:Neo-Riemannian theory
97:Neo-Riemannian theory
29:
109:Schenkerian analysis
42:of German theorist
712:Music theory stubs
707:Diatonic functions
553:Functional harmony
52:harmonic functions
33:
21:Riemann hypothesis
702:Riemannian theory
664:
663:
629:
628:
542:Riemannian theory
508:
507:
503:
502:
499:
481:
457:
299:
171:, Leipzig, 1887;
167:, Leipzig, 1880;
151:, Leipzig, 1881;
147:, Leipzig, 1878;
48:Riemannian theory
36:Riemannian theory
719:
685:
678:
671:
643:
636:
606:
565:Harmonic dualism
535:
528:
521:
512:
511:
497:
495:
494:
489:
488:
479:
477:
476:
471:
470:
455:
453:
452:
447:
446:
297:
292:
291:
268:
261:
254:
245:
244:
238:
231:
220:
214:
208:
194:
188:
187:, Hamburg, 1883.
182:
176:
162:
156:
155:, Leipzig, 1896.
142:
136:
135:, Leipzig, 1873.
130:
114:Undertone series
40:musical theories
727:
726:
722:
721:
720:
718:
717:
716:
692:
691:
690:
689:
632:
630:
625:
607:
598:
544:
539:
509:
504:
496:
492:
491:
486:
485:
478:
474:
473:
468:
467:
454:
450:
449:
444:
443:
431:
426:
418:
413:
405:
392:
384:
375:
366:
349:
341:
336:
328:
296:
285:
272:
242:
241:
232:
223:
219:, Berlin, 1898.
215:
211:
195:
191:
183:
179:
163:
159:
143:
139:
131:
127:
122:
105:
92:
90:Transformations
72:major and minor
60:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
725:
715:
714:
709:
704:
688:
687:
680:
673:
665:
662:
661:
644:
627:
626:
624:
623:
618:
612:
609:
608:
601:
599:
597:
596:
589:
582:
577:
572:
567:
562:
561:
560:
549:
546:
545:
538:
537:
530:
523:
515:
506:
505:
501:
500:
482:
464:
461:
458:
440:
437:
433:
432:
421:
419:
408:
406:
387:
385:
378:
376:
369:
367:
344:
342:
331:
329:
322:
319:
318:
315:
312:
309:
306:
303:
300:
290:
287:
286:
283:diatonic scale
271:
270:
263:
256:
248:
240:
239:
221:
209:
189:
177:
157:
137:
124:
123:
121:
118:
117:
116:
111:
104:
101:
91:
88:
59:
56:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
724:
713:
710:
708:
705:
703:
700:
699:
697:
686:
681:
679:
674:
672:
667:
666:
660:
658:
654:
651:article is a
650:
645:
642:
638:
637:
633:
622:
619:
617:
614:
613:
610:
605:
595:
594:
590:
588:
587:
583:
581:
578:
576:
573:
571:
568:
566:
563:
559:
556:
555:
554:
551:
550:
547:
543:
536:
531:
529:
524:
522:
517:
516:
513:
498:(Major/Minor)
480:(Major/Minor)
465:
462:
459:
456:(Major/Minor)
441:
438:
435:
434:
430:
429:
425:
420:
417:
416:
412:
407:
404:
403:
399:
395:
391:
386:
383:
382:
377:
374:
373:
368:
365:
364:
360:
356:
352:
348:
343:
340:
339:
335:
330:
327:
326:
321:
320:
313:
310:
307:
304:
301:
298:(Major/Minor)
294:
293:
288:
284:
280:
276:
269:
264:
262:
257:
255:
250:
249:
246:
236:
230:
228:
226:
218:
213:
206:
202:
198:
193:
186:
181:
174:
170:
166:
161:
154:
150:
146:
141:
134:
129:
125:
115:
112:
110:
107:
106:
100:
98:
87:
85:
81:
77:
73:
69:
65:
55:
53:
49:
45:
41:
37:
28:
22:
657:expanding it
649:music theory
646:
631:
620:
615:
591:
584:
570:Hugo Riemann
541:
422:
411:Leading-tone
409:
388:
379:
370:
345:
332:
323:
234:
216:
212:
204:
200:
196:
192:
184:
180:
172:
168:
164:
160:
152:
148:
144:
140:
132:
128:
93:
80:major triads
76:minor triads
61:
47:
44:Hugo Riemann
35:
34:
586:Terzschritt
372:Subdominant
696:Categories
390:Submediant
334:Supertonic
317:vii / VII
305:iii / III
279:functions
84:utonality
493:♭
487:♮
475:♭
469:♮
451:♭
445:♮
424:Subtonic
381:Dominant
103:See also
68:harmonic
593:Tonnetz
347:Mediant
314:vi / VI
308:IV / iv
302:ii / ii
281:of the
275:Degrees
120:Sources
74:, with
58:Dualism
64:triads
31:scale.
647:This
575:Klang
325:Tonic
311:V / v
295:I / i
653:stub
363:(Sp)
277:and
490:/ B
472:/ A
448:/ E
402:tCp
355:Tkp
698::
428:dP
415:D̸
400:,
398:sP
396:,
394:Tp
361:,
359:tP
357:,
353:,
351:Dp
338:Sp
224:^
86:.
54:.
684:e
677:t
670:v
659:.
534:e
527:t
520:v
484:B
466:A
463:G
460:F
442:E
439:D
436:C
267:e
260:t
253:v
207:.
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.