439:
427:
512:, test sensitivity is the ability of a test to correctly identify those with the disease (true positive rate), whereas test specificity is the ability of the test to correctly identify those without the disease (true negative rate). If 100 patients known to have a disease were tested, and 43 test positive, then the test has 43% sensitivity. If 100 with no disease are tested and 96 return a completely negative result, then the test has 96% specificity. Sensitivity and specificity are prevalence-independent test characteristics, as their values are intrinsic to the test and do not depend on the disease
99:
409:
33:
420:
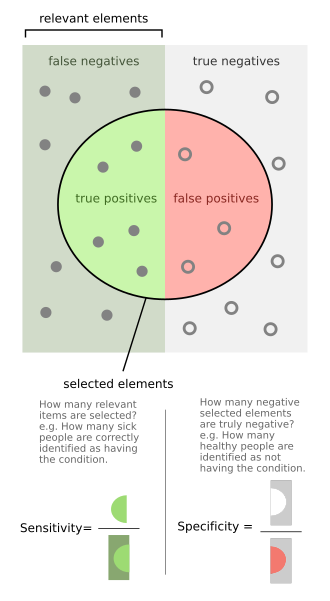
maximum value of 100% at line A, and the specificity decreases. The sensitivity at line A is 100% because at that point there are zero false negatives, meaning that all the negative test results are true negatives. When moving to the right, the opposite applies, the specificity increases until it reaches the B line and becomes 100% and the sensitivity decreases. The specificity at line B is 100% because the number of false positives is zero at that line, meaning all the positive test results are true positives.
253:
379:
477:
465:
2563:
164:
2577:
492:). This situation is also illustrated in the previous figure where the dotted line is at position A (the left-hand side is predicted as negative by the model, the right-hand side is predicted as positive by the model). When the dotted line, test cut-off line, is at position A, the test correctly predicts all the population of the true positive class, but it will fail to correctly identify the data point from the true negative class.
290:
2591:
248:{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\text{sensitivity}}&={\frac {\text{number of true positives}}{{\text{number of true positives}}+{\text{number of false negatives}}}}\\&={\frac {\text{number of true positives}}{\text{total number of sick individuals in population}}}\\&={\text{probability of a positive test given that the patient has the disease}}\end{aligned}}}
374:{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\text{specificity}}&={\frac {\text{number of true negatives}}{{\text{number of true negatives}}+{\text{number of false positives}}}}\\&={\frac {\text{number of true negatives}}{\text{total number of well individuals in population}}}\\&={\text{probability of a negative test given that the patient is well}}\end{aligned}}}
450:
tests below the cut off point and are considered negative (the blue dots indicate the False
Negatives (FN), the white dots True Negatives (TN)). The right-hand side of the line shows the data points that tests above the cut off point and are considered positive (red dots indicate False Positives (FP)). Each side contains 40 data points.
2434:. Unlike the Specificity vs Sensitivity tradeoff, these measures are both independent of the number of true negatives, which is generally unknown and much larger than the actual numbers of relevant and retrieved documents. This assumption of very large numbers of true negatives versus positives is rare in other applications.
263:
the presence of the disease in a patient. However, a positive result in a test with high sensitivity is not necessarily useful for "ruling in" disease. Suppose a 'bogus' test kit is designed to always give a positive reading. When used on diseased patients, all patients test positive, giving the test
267:
The calculation of sensitivity does not take into account indeterminate test results. If a test cannot be repeated, indeterminate samples either should be excluded from the analysis (the number of exclusions should be stated when quoting sensitivity) or can be treated as false negatives (which gives
258:
A negative result in a test with high sensitivity can be useful for "ruling out" disease, since it rarely misdiagnoses those who do have the disease. A test with 100% sensitivity will recognize all patients with the disease by testing positive. In this case, a negative test result would definitively
53:
mathematically describe the accuracy of a test that reports the presence or absence of a medical condition. If individuals who have the condition are considered "positive" and those who do not are considered "negative", then sensitivity is a measure of how well a test can identify true positives and
2382:
This hypothetical screening test (fecal occult blood test) correctly identified two-thirds (66.7%) of patients with colorectal cancer. Unfortunately, factoring in prevalence rates reveals that this hypothetical test has a high false positive rate, and it does not reliably identify colorectal cancer
419:
The above graphical illustration is meant to show the relationship between sensitivity and specificity. The black, dotted line in the center of the graph is where the sensitivity and specificity are the same. As one moves to the left of the black dotted line, the sensitivity increases, reaching its
94:
A test which reliably excludes individuals who do not have the condition, resulting in a high number of true negatives and low number of false positives, will have a high specificity. This is especially important when people who are identified as having a condition may be subjected to more testing,
2550:
as defined in biostatistics. The pair of thus defined specificity (as positive predictive value) and sensitivity (true positive rate) represent major parameters characterizing the accuracy of gene prediction algorithms. Conversely, the term specificity in a sense of true negative rate would have
495:
Similar to the previously explained figure, the red dot indicates the patient with the medical condition. However, in this case, the green background indicates that the test predicts that all patients are free of the medical condition. The number of data point that is true negative is then 26, and
487:
The red dot indicates the patient with the medical condition. The red background indicates the area where the test predicts the data point to be positive. The true positive in this figure is 6, and false negatives of 0 (because all positive condition is correctly predicted as positive). Therefore,
389:
the presence of the disease. However, a negative result from a test with high specificity is not necessarily useful for "ruling out" disease. For example, a test that always returns a negative test result will have a specificity of 100% because specificity does not consider false negatives. A test
143:
After getting the numbers of true positives, false positives, true negatives, and false negatives, the sensitivity and specificity for the test can be calculated. If it turns out that the sensitivity is high then any person who has the disease is likely to be classified as positive by the test. On
125:
Imagine a study evaluating a test that screens people for a disease. Each person taking the test either has or does not have the disease. The test outcome can be positive (classifying the person as having the disease) or negative (classifying the person as not having the disease). The test results
449:
The middle solid line in both figures above that show the level of sensitivity and specificity is the test cutoff point. As previously described, moving this line results in a trade-off between the level of sensitivity and specificity. The left-hand side of this line contains the data points that
384:
A positive result in a test with high specificity can be useful for "ruling in" disease, since the test rarely gives positive results in healthy patients. A test with 100% specificity will recognize all patients without the disease by testing negative, so a positive test result would definitively
2386:
On the other hand, this hypothetical test demonstrates very accurate detection of cancer-free individuals (NPV ≈ 99.5%). Therefore, when used for routine colorectal cancer screening with asymptomatic adults, a negative result supplies important data for the patient and doctor, such as
457:
For the figure that shows low sensitivity and high specificity, there are 8 FN and 3 FP. Using the same method as the previous figure, we get TP = 40 - 3 = 37. The number of sick people is 37 + 8 = 45, which gives a sensitivity of 37 / 45 = 82.2 %. There are 40 - 8 = 32 TN. The specificity
453:
For the figure that shows high sensitivity and low specificity, there are 3 FN and 8 FP. Using the fact that positive results = true positives (TP) + FP, we get TP = positive results - FP, or TP = 40 - 8 = 32. The number of sick people in the data set is equal to TP + FN, or 32 + 3 = 35. The
90:
A test which reliably detects the presence of a condition, resulting in a high number of true positives and low number of false negatives, will have a high sensitivity. This is especially important when the consequence of failing to treat the condition is serious and/or the treatment is very
2546:, the number of true negatives (non-genes) in genomic sequences is generally unknown and much larger than the actual number of genes (true positives). The convenient and intuitively understood term specificity in this research area has been frequently used with the mathematical formula for
157:
Consider the example of a medical test for diagnosing a condition. Sensitivity (sometimes also named the detection rate in a clinical setting) refers to the test's ability to correctly detect ill patients out of those who do have the condition. Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
585:= specificity + sensitivity − 1 = TPR − FPR, the magnitude of which gives the probability of an informed decision between the two classes (> 0 represents appropriate use of information, 0 represents chance-level performance, < 0 represents perverse use of information).
36:
Sensitivity and specificity - The left half of the image with the solid dots represents individuals who have the condition, while the right half of the image with the hollow dots represents individuals who do not have the condition. The circle represents all individuals who tested
2395:
Sensitivity and specificity values alone may be highly misleading. The 'worst-case' sensitivity or specificity must be calculated in order to avoid reliance on experiments with few results. For example, a particular test may easily show 100% sensitivity if tested against the
536:
It is often claimed that a highly specific test is effective at ruling in a disease when positive, while a highly sensitive test is deemed effective at ruling out a disease when negative. This has led to the widely used mnemonics SPPIN and SNNOUT, according to which a highly
840:
2509:
264:
100% sensitivity. However, sensitivity does not take into account false positives. The bogus test also returns positive on all healthy patients, giving it a false positive rate of 100%, rendering it useless for detecting or "ruling in" the disease.
117:), and "analytical specificity" is defined as the ability of an assay to measure one particular organism or substance, rather than others. However, this article deals with diagnostic sensitivity and specificity as defined at top.
2376:
295:
169:
144:
the other hand, if the specificity is high, any person who does not have the disease is likely to be classified as negative by the test. An NIH web site has a discussion of how these ratios are calculated.
283:
Consider the example of a medical test for diagnosing a disease. Specificity refers to the test's ability to correctly reject healthy patients without a condition. Mathematically, this can be written as:
565:
disease (SN-N-OUT). Both rules of thumb are, however, inferentially misleading, as the diagnostic power of any test is determined by the prevalence of the condition being tested, the test's sensitivity
731:
454:
sensitivity is therefore 32 / 35 = 91.4%. Using the same method, we get TN = 40 - 3 = 37, and the number of healthy people 37 + 8 = 45, which results in a specificity of 37 / 45 = 82.2 %.
3631:"Diagnostic test online calculator calculates sensitivity, specificity, likelihood ratios and predictive values from a 2x2 table – calculator of confidence intervals for predictive parameters"
524:, but not sensitivity or specificity, are values influenced by the prevalence of disease in the population that is being tested. These concepts are illustrated graphically in this applet
2451:
4533:
2400:
four times, but a single additional test against the gold standard that gave a poor result would imply a sensitivity of only 80%. A common way to do this is to state the
719:
665:
692:
638:
3454:"The Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC) is more reliable than balanced accuracy, bookmaker informedness, and markedness in two-class confusion matrix evaluation"
4863:
609:. It provides the separation between the means of the signal and the noise distributions, compared against the standard deviation of the noise distribution. For
2903:
2410:
for sensitivity and specificity can be calculated, giving the range of values within which the correct value lies at a given confidence level (e.g., 95%).
113:, wherein "analytical sensitivity" is defined as the smallest amount of substance in a sample that can accurately be measured by an assay (synonymously to
4002:
4526:
408:
1178:
1747:
A diagnostic test with sensitivity 67% and specificity 91% is applied to 2030 people to look for a disorder with a population prevalence of 1.48%
87:, there is usually a trade-off between sensitivity and specificity, such that higher sensitivities will mean lower specificities and vice versa.
570:
its specificity. The SNNOUT mnemonic has some validity when the prevalence of the condition in question is extremely low in the tested sample.
4519:
2259:
4662:
3011:
Boyko EJ (Apr–Jun 1994). "Ruling out or ruling in disease with the most sensitive or specific diagnostic test: short cut or wrong turn?".
920:
The relationship between sensitivity, specificity, and similar terms can be understood using the following table. Consider a group with
438:
426:
3656:
3536:
Lin JS, Piper MA, Perdue LA, Rutter CM, Webber EM, O'Connor E, Smith N, Whitlock EP (21 June 2016). "Screening for
Colorectal Cancer".
1626:
3581:"Systematic review of colorectal cancer screening guidelines for average-risk adults: Summarizing the current global recommendations"
4569:
4294:
4290:
1733:
2695:
Yerushalmy J (1947). "Statistical problems in assessing methods of medical diagnosis with special reference to x-ray techniques".
2625:
4677:
4340:
4298:
4286:
2929:
2401:
2244:
3995:
2430:
2424:
2387:
ruling out cancer as the cause of gastrointestinal symptoms or reassuring patients worried about developing colorectal cancer.
3403:"The advantages of the Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC) over F1 score and accuracy in binary classification evaluation"
3359:
3242:
4461:
4377:
835:{\displaystyle d^{\prime }={\frac {\mu _{S}-\mu _{N}}{\sqrt {{\frac {1}{2}}\left(\sigma _{S}^{2}+\sigma _{N}^{2}\right)}}}}
2526:
in that context has a more general usage that is not applicable in the present context. A sensitive test will have fewer
889:
4953:
4242:
17:
4212:
71:(true negative rate) is the probability of a negative test result, conditioned on the individual truly being negative.
4667:
3988:
2635:
2052:
1284:
574:
528:
which show the positive and negative predictive values as a function of the prevalence, sensitivity and specificity.
476:
464:
4499:
2907:
2231:
1600:
2224:
4923:
4889:
4750:
1392:
4306:
3184:"A basal ganglia pathway drives selective auditory responses in songbird dopaminergic neurons via disinhibition"
2748:"[Sensitivity and specificity revisited: significance of the terms in analytic and diagnostic language]"
2504:{\displaystyle F=2\times {\frac {{\text{precision}}\times {\text{recall}}}{{\text{precision}}+{\text{recall}}}}}
106:
The terms "sensitivity" and "specificity" were introduced by
American biostatistician Jacob Yerushalmy in 1947.
4574:
4344:
4066:
2515:
1897:
1064:
390:
like that would return negative for patients with the disease, making it useless for "ruling out" the disease.
75:
If the true status of the condition cannot be known, sensitivity and specificity can be defined relative to a "
4584:
4492:
4177:
4840:
4599:
4471:
2615:
1726:
2250:
Negative likelihood ratio = (1 − sensitivity) / specificity ≈ (1 − 0.67) / 0.91 ≈ 0.37
4948:
4943:
4806:
4735:
4435:
4407:
4336:
4090:
2610:
4619:
4594:
4579:
4485:
4161:
1706:
Type I error: A test result which wrongly indicates that a particular condition or attribute is present
1679:
Type II error: A test result which wrongly indicates that a particular condition or attribute is absent
110:
2441:
can be used as a single measure of performance of the test for the positive class. The F-score is the
500:). Therefore, sensitivity or specificity alone cannot be used to measure the performance of the test.
4609:
4604:
4280:
3321:"Evaluation: From Precision, Recall and F-Measure to ROC, Informedness, Markedness & Correlation"
3161:"Evaluation: From Precision, Recall and F-Measure to ROC, Informedness, Markedness & Correlation"
2527:
2169:
2116:
2083:
2048:
1584:
1445:
1365:
1340:
1278:
521:
517:
3676:
3125:
4938:
4705:
4218:
4166:
4046:
2640:
4928:
4796:
4700:
4695:
4264:
4134:
4112:
4081:
4056:
4039:
2954:
2880:
2651:
2645:
1719:
978:
697:
643:
62:
4933:
4637:
4415:
4252:
4173:
3671:
3375:
Brooks H, Brown B, Ebert B, Ferro C, Jolliffe I, Koh TY, Roebber P, Stephenson D (2015-01-26).
3302:"Data Science for Business: What You Need to Know about Data Mining and Data-Analytic Thinking"
3120:
2620:
1789:
1770:
959:
670:
616:
4256:
4143:
4051:
4015:
2539:
2419:
2185:
1988:
1486:
3980:
3697:
4858:
4758:
4647:
4642:
4222:
3112:
2630:
2547:
2407:
2397:
2253:
2153:
1417:
991:
84:
76:
3714:
8:
4564:
4551:
4129:
4061:
2067:
1984:
1916:
1312:
1220:
1171:
1102:
1068:
610:
578:
3116:
98:
4884:
4850:
4730:
4559:
4382:
4332:
4147:
4076:
4034:
3893:
3868:
3845:
3746:
3721:
3607:
3580:
3480:
3453:
3429:
3402:
3282:
3208:
3183:
3138:
3036:
2993:
2857:
2832:
2805:
2778:
2728:
2712:
2672:
2013:
1893:
1757:
1214:
1060:
4511:
3936:
3911:
3820:
Yandell M, Ence D (April 2012). "A beginner's guide to eukaryotic genome annotation".
3797:
3770:
3080:
3055:
2933:
4879:
4768:
4715:
4456:
4420:
4387:
4312:
4234:
4011:
3941:
3898:
3837:
3802:
3751:
3689:
3648:
3612:
3561:
3553:
3485:
3434:
3355:
3320:
3301:
3238:
3213:
3160:
3085:
3028:
2985:
2862:
2810:
2759:
2720:
2519:
2237:
1074:
930:
594:
509:
80:
3040:
2997:
2732:
1670:
A test result that correctly indicates the presence of a condition or characteristic
126:
for each subject may or may not match the subject's actual status. In that setting:
4902:
4687:
4652:
4589:
4542:
4230:
4151:
4105:
4100:
3970:
3931:
3923:
3888:
3880:
3849:
3829:
3792:
3782:
3741:
3733:
3681:
3602:
3592:
3545:
3516:
3475:
3465:
3424:
3414:
3347:
3286:
3274:
3203:
3199:
3195:
3142:
3130:
3075:
3067:
3020:
2977:
2852:
2844:
2800:
2790:
2704:
2675:, such as those for colorectal cancer screening, describe these risks and benefits.
1697:
A test result that correctly indicates the absence of a condition or characteristic
936:
928:
negative instances of some condition. The four outcomes can be formulated in a 2×2
915:
606:
32:
3975:
3630:
3376:
525:
4835:
4778:
4657:
4425:
4248:
4203:
3278:
3259:
3232:
3134:
2596:
2543:
940:, as well as derivations of several metrics using the four outcomes, as follows:
114:
4451:
4372:
4324:
4117:
4029:
3960:
3470:
3024:
2981:
2582:
2568:
2247:= sensitivity / (1 − specificity) ≈ 0.67 / (1 − 0.91) ≈ 7.4
1148:
1049:
3884:
3521:
3504:
3419:
3351:
2848:
4917:
4720:
4430:
4397:
4392:
3927:
3652:
3557:
3071:
2442:
1160:
1112:
1037:
899:
272:
3912:"Understanding sensitivity and specificity with the right side of the brain"
2795:
2390:
4272:
4156:
3945:
3841:
3806:
3787:
3755:
3685:
3616:
3597:
3565:
3549:
3489:
3438:
3217:
3089:
3056:"Ruling a diagnosis in or out with "SpPIn" and "SnNOut": a note of caution"
2814:
2724:
1842:
1186:
582:
394:
3902:
3693:
3054:
Pewsner D, Battaglia M, Minder C, Marx A, Bucher HC, Egger M (July 2004).
3032:
2989:
2866:
2763:
2747:
496:
the number of false positives is 0. This result in 100% specificity (from
268:
the worst-case value for sensitivity and may therefore underestimate it).
4466:
4320:
4193:
4183:
3737:
2605:
2383:
in the overall population of asymptomatic people (PPV = 10%).
854:
54:
specificity is a measure of how well a test can identify true negatives:
2779:"Understanding and using sensitivity, specificity and predictive values"
2671:
There are advantages and disadvantages for all medical screening tests.
4814:
4725:
4710:
4268:
4260:
4226:
4188:
4095:
2716:
2033:
1473:
1253:
513:
46:
2562:
4632:
4328:
4316:
2371:{\displaystyle PT={\frac {{\sqrt {TPR(-TNR+1)}}+TNR-1}{(TPR+TNR-1)}}}
1849:
602:
238:
probability of a positive test given that the patient has the disease
3965:
3833:
2708:
4362:
2576:
1805:
1538:
850:
61:(true positive rate) is the probability of a positive test result,
42:
2551:
little, if any, application in the genome analysis research area.
4740:
4627:
4367:
3377:"WWRP/WGNE Joint Working Group on Forecast Verification Research"
2957:. Emory University Medical School Evidence Based Medicine course.
2777:
Parikh R, Mathai A, Parikh S, Chandra Sekhar G, Thomas R (2008).
2438:
2776:
573:
The tradeoff between specificity and sensitivity is explored in
4010:
3657:"Prediction of complete gene structures in human genomic DNA"
364:
probability of a negative test given that the patient is well
139:
False negative: Sick people incorrectly identified as healthy
136:
True negative: Healthy people correctly identified as healthy
133:
False positive: Healthy people incorrectly identified as sick
3579:
Bénard F, Barkun AN, Martel M, Renteln Dv (7 January 2018).
2227:= 1 − specificity = FP / (FP + TN) = 180 / (180 + 1820) = 9%
4819:
4791:
4786:
4763:
3722:"Gene finding in novel genomes by self-training algorithm"
3053:
3578:
3381:
Collaboration for
Australian Weather and Climate Research
2391:
Estimation of errors in quoted sensitivity or specificity
2234:= 1 − sensitivity = FN / (TP + FN) = 10 / (20 + 10) ≈ 33%
906:
indicates that the signal can be more readily detected.
577:
as a trade off between TPR and FPR (that is, recall and
4541:
2413:
414:
A graphical illustration of sensitivity and specificity
130:
True positive: Sick people correctly identified as sick
3374:
3224:
3103:
2454:
2262:
734:
700:
673:
646:
619:
293:
167:
3535:
2558:
3966:
Vassar
College's Sensitivity/Specificity Calculator
3451:
1073:probability of detection, hit rate,
613:signal and noise with mean and standard deviations
3869:"Diagnostic tests. 1: Sensitivity and specificity"
3299:
2968:Baron JA (Apr–Jun 1994). "Too bad it isn't true".
2833:"Diagnostic tests. 1: Sensitivity and specificity"
2745:
2503:
2404:, often calculated using a Wilson score interval.
2370:
834:
713:
686:
659:
632:
373:
247:
79:" which is assumed correct. For all testing, both
3230:
2533:
1625:Threat score (TS), critical success index (CSI),
120:
4915:
3452:Chicco D, Toetsch N, Jurman G (February 2021).
3231:Macmillan NA, Creelman CD (15 September 2004).
348:total number of well individuals in population
222:total number of sick individuals in population
27:Statistical measure of a binary classification
4527:
3996:
3154:
3152:
1727:
1688:the number of real negative cases in the data
1661:the number of real positive cases in the data
393:A test with a higher specificity has a lower
271:A test with a higher sensitivity has a lower
3400:
3175:
3047:
3866:
3819:
3813:
3647:
3096:
3004:
2932:. Michigan State University. Archived from
2883:. Centre for Evidence Based Medicine (CEBM)
2830:
1177:probability of false alarm,
849:can be also found from measurements of the
4534:
4520:
4003:
3989:
3502:
3342:Ting KM (2011). Sammut C, Webb GI (eds.).
3181:
3149:
2961:
2694:
2518:, the sensitivity of a test is called the
2422:, the positive predictive value is called
1734:
1720:
482:A test result with 100 percent specificity
470:A test result with 100 percent sensitivity
3976:Bayesian clinical diagnostic model applet
3935:
3892:
3796:
3786:
3745:
3675:
3606:
3596:
3520:
3479:
3469:
3428:
3418:
3207:
3124:
3079:
2856:
2804:
2794:
400:
4295:Preventable fraction among the unexposed
4291:Attributable fraction for the population
3719:
3325:Journal of Machine Learning Technologies
3165:Journal of Machine Learning Technologies
458:therefore comes out to 32 / 35 = 91.4%.
97:
91:effective and has minimal side effects.
31:
4299:Preventable fraction for the population
4287:Attributable fraction among the exposed
3257:
3102:
2739:
2402:binomial proportion confidence interval
109:There are different definitions within
65:on the individual truly being positive.
14:
4916:
3318:
3158:
2901:
581:). Giving them equal weight optimizes
4515:
3984:
3909:
3300:Provost F, Tom Fawcett (2013-08-01).
3010:
2967:
2826:
2824:
4462:Correlation does not imply causation
4378:Animal testing on non-human primates
3768:
3341:
2414:Terminology in information retrieval
588:
444:Low sensitivity and high specificity
432:High sensitivity and low specificity
3505:"Classification assessment methods"
3401:Chicco D, Jurman G (January 2020).
3383:. World Meteorological Organisation
3182:Gale SD, Perkel DJ (January 2010).
2873:
909:
24:
3859:
3641:
2821:
740:
526:Bayesian clinical diagnostic model
25:
4965:
3954:
3867:Altman DG, Bland JM (June 1994).
3585:World Journal of Gastroenterology
3509:Applied Computing and Informatics
3260:"An Introduction to ROC Analysis"
2831:Altman DG, Bland JM (June 1994).
2636:Receiver operating characteristic
531:
3344:Encyclopedia of machine learning
3234:Detection Theory: A User's Guide
2589:
2575:
2561:
1601:Matthews correlation coefficient
890:cumulative Gaussian distribution
549:disease (SP-P-IN), and a highly
503:
475:
463:
437:
425:
407:
4890:Pearson correlation coefficient
3771:"Gene finding in novel genomes"
3762:
3707:
3623:
3572:
3529:
3496:
3445:
3394:
3368:
3335:
3312:
3293:
3251:
3237:. Psychology Press. p. 7.
2904:"Diagnostic Reasoning I and II"
2783:Indian Journal of Ophthalmology
2665:
2522:of the test, although the word
2514:In the traditional language of
1874:(2030 × 1.48% × 67%)
1700:
1691:
1682:
1673:
1664:
1655:
942:
516:in the population of interest.
95:expense, stigma, anxiety, etc.
4345:Pre- and post-test probability
4067:Patient and public involvement
3971:MedCalc Free Online Calculator
3200:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3585-09.2010
2947:
2922:
2895:
2770:
2688:
2534:Terminology in genome analysis
2516:statistical hypothesis testing
2362:
2332:
2307:
2286:
601:(pronounced "dee-prime") is a
488:the sensitivity is 100% (from
278:
152:
121:Application to screening study
13:
1:
4829:Deep Learning Related Metrics
2955:"Sensitivity and Specificity"
2682:
2626:Hypothesis tests for accuracy
147:
4472:Sex as a biological variable
3664:Journal of Molecular Biology
3279:10.1016/j.patrec.2005.10.010
3135:10.1016/j.patrec.2005.10.010
2673:Clinical practice guidelines
2616:Discrimination (information)
2428:, and sensitivity is called
7:
4673:Sensitivity and specificity
4436:Intention-to-treat analysis
4408:Analysis of clinical trials
4337:Specificity and sensitivity
4091:Randomized controlled trial
3910:Loong TW (September 2003).
3267:Pattern Recognition Letters
3188:The Journal of Neuroscience
3105:Pattern Recognition Letters
2746:Saah AJ, Hoover DR (1998).
2611:Cumulative accuracy profile
2554:
2538:Similarly to the domain of
2140:= (10 / 30) / (1820 / 2000)
1155:false alarm, overestimation
983:bookmaker informedness (BM)
857:rate. It is calculated as:
714:{\displaystyle \sigma _{N}}
660:{\displaystyle \sigma _{S}}
102:Sensitivity and specificity
51:sensitivity and specificity
10:
4970:
4954:Statistical classification
3503:Tharwat A. (August 2018).
3471:10.1186/s13040-021-00244-z
3025:10.1177/0272989X9401400210
2982:10.1177/0272989X9401400202
2930:"Evidence-Based Diagnosis"
2542:, in the research area of
2230:False negative rate (β) =
2223:False positive rate (α) =
2107:= (20 / 30) / (180 / 2000)
1995:probability of false alarm
1886:(2030 × 1.48% ×
913:
888:∈ , is the inverse of the
522:negative predictive values
111:laboratory quality control
4898:
4872:
4849:
4828:
4805:
4777:
4749:
4686:
4618:
4550:
4480:
4445:Interpretation of results
4444:
4406:
4355:
4305:
4279:
4241:
4211:
4202:
4178:Nested case–control study
4128:
4075:
4022:
3885:10.1136/bmj.308.6943.1552
3522:10.1016/j.aci.2018.08.003
3420:10.1186/s12864-019-6413-7
3352:10.1007/978-0-387-30164-8
2849:10.1136/bmj.308.6943.1552
2648:, also called proficiency
2445:of precision and recall:
2184:
2170:Negative predictive value
2117:Negative likelihood ratio
2084:Positive likelihood ratio
2049:Positive predictive value
2030:
1838:
1763:
1755:
1753:
1624:
1446:Negative predictive value
1366:Negative likelihood ratio
1341:Positive likelihood ratio
1279:Positive predictive value
1250:
1023:
954:
949:
945:
326:number of false positives
200:number of false negatives
4047:Academic clinical trials
3928:10.1136/bmj.327.7417.716
3822:Nature Reviews. Genetics
3072:10.1136/bmj.329.7459.209
2658:
2641:Statistical significance
687:{\displaystyle \mu _{N}}
633:{\displaystyle \mu _{S}}
345:number of true negatives
318:number of true negatives
313:number of true negatives
219:number of true positives
192:number of true positives
187:number of true positives
4701:Calinski-Harabasz index
4265:Relative risk reduction
4113:Adaptive clinical trial
4057:Evidence-based medicine
4040:Adaptive clinical trial
3013:Medical Decision Making
2970:Medical Decision Making
2796:10.4103/0301-4738.37595
2646:Uncertainty coefficient
1818:precision × recall
1516:Balanced accuracy (BA)
1113:type II error
974:Predicted negative (PN)
969:Predicted positive (PP)
924:positive instances and
4924:Accuracy and precision
4253:Number needed to treat
3788:10.1186/1471-2105-5-59
3726:Nucleic Acids Research
3686:10.1006/jmbi.1997.0951
3598:10.3748/wjg.v24.i1.124
3550:10.1001/jama.2016.3332
2621:False positive paradox
2505:
2372:
1187:type I error
836:
715:
688:
661:
634:
401:Graphical illustration
375:
249:
103:
38:
4864:Intra-list Similarity
4257:Number needed to harm
4144:Cross-sectional study
4096:Scientific experiment
4052:Clinical study design
2752:Ann Dermatol Venereol
2697:Public Health Reports
2540:information retrieval
2506:
2420:information retrieval
2373:
2240:= sensitivity = 1 − β
2186:Diagnostic odds ratio
1919:(FNR), miss rate
1619:FNR × FPR × FOR × FDR
1610:TPR × TNR × PPV × NPV
1585:Fowlkes–Mallows index
1056:miss, underestimation
837:
716:
689:
662:
635:
376:
250:
101:
35:
4223:Cumulative incidence
2652:Youden's J statistic
2631:Precision and recall
2548:precision and recall
2452:
2408:Confidence intervals
2260:
2254:Prevalence threshold
2218:Related calculations
2176:= 1820 / (10 + 1820)
2154:False discovery rate
1979:(100% − 1.48%)
1959:(100% − 1.48%)
1943:(100% − 1.48%)
1862:(2030 × 1.48%)
1796:= (20 + 1820) / 2030
1418:False discovery rate
992:Prevalence threshold
902:statistic. A higher
732:
698:
671:
644:
617:
611:normally distributed
291:
165:
4130:Observational study
4062:Real world evidence
4016:experimental design
3720:Lomsadze A (2005).
3306:O'Reilly Media, Inc
3117:2006PaReL..27..861F
2068:False omission rate
1985:False positive rate
1917:False negative rate
1760:screen test outcome
1313:False omission rate
1172:False positive rate
1103:False negative rate
951:Predicted condition
872:(false alarm rate),
823:
805:
18:Sensitivity (tests)
4949:Statistical ratios
4944:Medical statistics
4885:Euclidean distance
4851:Recommender system
4731:Similarity measure
4545:evaluation metrics
4416:Risk–benefit ratio
4383:First-in-man study
4333:Case fatality rate
4174:Case–control study
4148:Longitudinal study
3775:BMC Bioinformatics
3738:10.1093/nar/gki937
3319:Powers DM (2011).
3258:Fawcett T (2006).
3159:Powers DM (2011).
2881:"SpPin and SnNout"
2501:
2368:
2160:= 180 / (20 + 180)
2074:= 10 / (10 + 1820)
2014:true negative rate
1963:(100% − 91%)
1894:True positive rate
1888:(100% − 67%)
1824:precision + recall
1794:= (TP + TN) / pop.
1758:Fecal occult blood
1223:(SPC), selectivity
1215:True negative rate
1061:True positive rate
832:
809:
791:
711:
684:
657:
630:
557:sitive test, when
541:ecific test, when
371:
369:
245:
243:
104:
77:gold standard test
39:
4911:
4910:
4880:Cosine similarity
4716:Hopkins statistic
4509:
4508:
4457:Survivorship bias
4421:Systematic review
4388:Multicenter trial
4351:
4350:
4341:Likelihood-ratios
4313:Clinical endpoint
4281:Population impact
4235:Period prevalence
4012:Clinical research
3732:(20): 6494–6906.
3544:(23): 2576–2594.
3361:978-0-387-30164-8
3244:978-1-4106-1114-7
2520:statistical power
2499:
2496:
2488:
2481:
2473:
2366:
2310:
2215:
2214:
2058:= 20 / (20 + 180)
1651:
1650:
1167:correct rejection
931:contingency table
830:
829:
784:
595:sensitivity index
589:Sensitivity index
510:medical diagnosis
365:
350:
349:
346:
330:
327:
319:
314:
301:
239:
224:
223:
220:
204:
201:
193:
188:
175:
16:(Redirected from
4961:
4903:Confusion matrix
4678:Logarithmic Loss
4543:Machine learning
4536:
4529:
4522:
4513:
4512:
4356:Trial/test types
4231:Point prevalence
4209:
4208:
4152:Ecological study
4135:EBM II-2 to II-3
4106:Open-label trial
4101:Blind experiment
4077:Controlled study
4005:
3998:
3991:
3982:
3981:
3949:
3939:
3906:
3896:
3854:
3853:
3817:
3811:
3810:
3800:
3790:
3766:
3760:
3759:
3749:
3718:
3711:
3705:
3704:
3702:
3696:. Archived from
3679:
3661:
3645:
3639:
3638:
3627:
3621:
3620:
3610:
3600:
3576:
3570:
3569:
3533:
3527:
3526:
3524:
3500:
3494:
3493:
3483:
3473:
3449:
3443:
3442:
3432:
3422:
3398:
3392:
3391:
3389:
3388:
3372:
3366:
3365:
3339:
3333:
3332:
3316:
3310:
3309:
3297:
3291:
3290:
3264:
3255:
3249:
3248:
3228:
3222:
3221:
3211:
3179:
3173:
3172:
3156:
3147:
3146:
3128:
3100:
3094:
3093:
3083:
3066:(7459): 209–13.
3051:
3045:
3044:
3008:
3002:
3001:
2965:
2959:
2958:
2951:
2945:
2944:
2942:
2941:
2926:
2920:
2919:
2917:
2915:
2910:on 1 August 2011
2906:. Archived from
2899:
2893:
2892:
2890:
2888:
2877:
2871:
2870:
2860:
2828:
2819:
2818:
2808:
2798:
2774:
2768:
2767:
2743:
2737:
2736:
2692:
2676:
2669:
2599:
2594:
2593:
2592:
2585:
2580:
2579:
2571:
2566:
2565:
2510:
2508:
2507:
2502:
2500:
2498:
2497:
2494:
2489:
2486:
2483:
2482:
2479:
2474:
2471:
2468:
2378:≈ 0.2686 ≈ 26.9%
2377:
2375:
2374:
2369:
2367:
2365:
2330:
2311:
2276:
2273:
2245:likelihood ratio
2205:
2203:
2202:
2199:
2196:
2174:= TN / (FN + TN)
2158:= FP / (TP + FP)
2138:
2136:
2135:
2132:
2129:
2121:
2105:
2103:
2102:
2099:
2096:
2088:
2072:= FN / (FN + TN)
2056:= TP / (TP + FP)
1996:
1991:
1980:
1973:
1964:
1960:
1953:
1944:
1935:Actual condition
1889:
1882:
1870:
1856:Actual condition
1828:
1826:
1825:
1822:
1819:
1771:Total population
1751:
1750:
1744:A worked example
1736:
1729:
1722:
1707:
1704:
1698:
1695:
1689:
1686:
1680:
1677:
1671:
1668:
1662:
1659:
1647:
1646:
1644:
1643:
1640:
1637:
1622:
1621:
1620:
1613:
1612:
1611:
1597:
1596:
1595:
1581:
1580:
1578:
1577:
1574:
1571:
1563:
1562:
1560:
1559:
1556:
1553:
1535:
1534:
1532:
1531:
1528:
1525:
1511:
1510:
1508:
1507:
1504:
1501:
1490:
1483:
1479:
1478:deltaP (Δp)
1470:
1467:
1466:
1464:
1463:
1460:
1457:
1442:
1439:
1438:
1436:
1435:
1432:
1429:
1414:
1413:
1411:
1410:
1407:
1404:
1387:
1386:
1384:
1383:
1380:
1377:
1362:
1361:
1359:
1358:
1355:
1352:
1337:
1334:
1333:
1331:
1330:
1327:
1324:
1309:
1306:
1305:
1303:
1302:
1299:
1296:
1287:
1282:
1274:
1273:
1271:
1270:
1267:
1264:
1246:
1243:
1242:
1240:
1239:
1236:
1233:
1224:
1211:
1208:
1207:
1205:
1204:
1201:
1198:
1189:
1183:
1181:
1168:
1156:
1137:
1134:
1133:
1131:
1130:
1127:
1124:
1115:
1109:
1099:
1096:
1095:
1093:
1092:
1089:
1086:
1077:
1057:
1045:
1026:Actual condition
1019:
1018:
1016:
1015:
1012:
1009:
1007:
1006:
988:
984:
965:
960:Total population
943:
937:confusion matrix
916:Confusion matrix
910:Confusion matrix
841:
839:
838:
833:
831:
828:
824:
822:
817:
804:
799:
785:
777:
775:
774:
773:
772:
760:
759:
749:
744:
743:
721:, respectively,
720:
718:
717:
712:
710:
709:
693:
691:
690:
685:
683:
682:
666:
664:
663:
658:
656:
655:
639:
637:
636:
631:
629:
628:
607:detection theory
499:
491:
479:
467:
441:
429:
411:
380:
378:
377:
372:
370:
366:
363:
355:
351:
347:
344:
343:
335:
331:
329:
328:
325:
320:
317:
312:
311:
302:
299:
254:
252:
251:
246:
244:
240:
237:
229:
225:
221:
218:
217:
209:
205:
203:
202:
199:
194:
191:
186:
185:
176:
173:
21:
4969:
4968:
4964:
4963:
4962:
4960:
4959:
4958:
4939:Cheminformatics
4914:
4913:
4912:
4907:
4894:
4868:
4845:
4836:Inception score
4824:
4801:
4779:Computer Vision
4773:
4745:
4682:
4614:
4546:
4540:
4510:
4505:
4476:
4440:
4402:
4347:
4301:
4275:
4249:Risk difference
4237:
4198:
4132:
4124:
4079:
4071:
4035:Trial protocols
4018:
4009:
3957:
3952:
3922:(7417): 716–9.
3862:
3860:Further reading
3857:
3834:10.1038/nrg3174
3818:
3814:
3769:Korf I (2004).
3767:
3763:
3713:
3712:
3708:
3700:
3677:10.1.1.115.3107
3659:
3646:
3642:
3629:
3628:
3624:
3577:
3573:
3534:
3530:
3501:
3497:
3450:
3446:
3413:(1): 6-1–6-13.
3399:
3395:
3386:
3384:
3373:
3369:
3362:
3340:
3336:
3317:
3313:
3298:
3294:
3262:
3256:
3252:
3245:
3229:
3225:
3180:
3176:
3157:
3150:
3126:10.1.1.646.2144
3101:
3097:
3052:
3048:
3009:
3005:
2966:
2962:
2953:
2952:
2948:
2939:
2937:
2928:
2927:
2923:
2913:
2911:
2900:
2896:
2886:
2884:
2879:
2878:
2874:
2829:
2822:
2775:
2771:
2744:
2740:
2709:10.2307/4586294
2693:
2689:
2685:
2680:
2679:
2670:
2666:
2661:
2656:
2597:Medicine portal
2595:
2590:
2588:
2581:
2574:
2567:
2560:
2557:
2544:gene prediction
2536:
2493:
2485:
2484:
2478:
2470:
2469:
2467:
2453:
2450:
2449:
2416:
2393:
2331:
2275:
2274:
2272:
2261:
2258:
2257:
2211:
2206:
2200:
2197:
2194:
2193:
2191:
2182:
2177:
2175:
2166:
2161:
2159:
2146:
2141:
2139:
2133:
2130:
2127:
2126:
2124:
2119:
2113:
2108:
2106:
2100:
2097:
2094:
2093:
2091:
2086:
2080:
2075:
2073:
2064:
2059:
2057:
2045:
2040:
2038:
2026:
2021:
2019:
2012:, selectivity,
2006:
2001:
1999:
1994:
1989:
1978:
1976:
1974:
1968:
1962:
1958:
1956:
1954:
1948:
1942:
1940:
1938:
1936:
1930:
1925:
1923:
1920:
1913:
1908:
1906:
1887:
1885:
1883:
1877:
1873:
1871:
1865:
1861:
1859:
1857:
1847:
1845:
1841:
1834:
1829:
1823:
1820:
1817:
1816:
1814:
1809:
1802:
1797:
1795:
1773:
1741:
1740:
1713:
1711:
1710:
1705:
1701:
1696:
1692:
1687:
1683:
1678:
1674:
1669:
1665:
1660:
1656:
1641:
1638:
1635:
1634:
1632:
1630:
1629:
1618:
1616:
1614:
1609:
1607:
1605:
1604:
1593:
1591:
1589:
1588:
1575:
1572:
1569:
1568:
1566:
1564:
1557:
1554:
1551:
1550:
1548:
1546:
1545:
1542:
1529:
1526:
1523:
1522:
1520:
1518:
1517:
1505:
1502:
1499:
1498:
1496:
1494:
1493:
1488:
1482:= PPV + NPV − 1
1481:
1480:
1477:
1468:
1461:
1458:
1455:
1454:
1452:
1450:
1449:
1440:
1433:
1430:
1427:
1426:
1424:
1422:
1421:
1408:
1405:
1402:
1401:
1399:
1397:
1396:
1381:
1378:
1375:
1374:
1372:
1370:
1369:
1356:
1353:
1350:
1349:
1347:
1345:
1344:
1335:
1328:
1325:
1322:
1321:
1319:
1317:
1316:
1307:
1300:
1297:
1294:
1293:
1291:
1289:
1288:
1283:
1277:
1268:
1265:
1262:
1261:
1259:
1257:
1256:
1244:
1237:
1234:
1231:
1230:
1228:
1226:
1225:
1219:
1218:
1209:
1202:
1199:
1196:
1195:
1193:
1191:
1190:
1185:
1184:
1179:
1176:
1175:
1166:
1165:
1154:
1153:
1135:
1128:
1125:
1122:
1121:
1119:
1117:
1116:
1111:
1110:
1107:
1106:
1097:
1090:
1087:
1084:
1083:
1081:
1079:
1078:
1072:
1055:
1054:
1043:
1042:
1028:
1013:
1010:
1004:
1002:
1001:
1000:
998:
996:
995:
987:= TPR + TNR − 1
986:
985:
982:
963:
962:
918:
912:
876:where function
845:An estimate of
818:
813:
800:
795:
790:
786:
776:
768:
764:
755:
751:
750:
748:
739:
735:
733:
730:
729:
725:is defined as:
705:
701:
699:
696:
695:
678:
674:
672:
669:
668:
651:
647:
645:
642:
641:
624:
620:
618:
615:
614:
605:used in signal
591:
561:egative, rules
545:ositive, rules
534:
506:
497:
489:
483:
480:
471:
468:
445:
442:
433:
430:
415:
412:
403:
368:
367:
362:
353:
352:
342:
333:
332:
324:
316:
315:
310:
303:
298:
294:
292:
289:
288:
281:
242:
241:
236:
227:
226:
216:
207:
206:
198:
190:
189:
184:
177:
172:
168:
166:
163:
162:
155:
150:
123:
115:detection limit
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
4967:
4957:
4956:
4951:
4946:
4941:
4936:
4931:
4929:Bioinformatics
4926:
4909:
4908:
4906:
4905:
4899:
4896:
4895:
4893:
4892:
4887:
4882:
4876:
4874:
4870:
4869:
4867:
4866:
4861:
4855:
4853:
4847:
4846:
4844:
4843:
4838:
4832:
4830:
4826:
4825:
4823:
4822:
4817:
4811:
4809:
4803:
4802:
4800:
4799:
4794:
4789:
4783:
4781:
4775:
4774:
4772:
4771:
4766:
4761:
4755:
4753:
4747:
4746:
4744:
4743:
4738:
4733:
4728:
4723:
4718:
4713:
4708:
4706:Davies-Bouldin
4703:
4698:
4692:
4690:
4684:
4683:
4681:
4680:
4675:
4670:
4665:
4660:
4655:
4650:
4645:
4640:
4635:
4630:
4624:
4622:
4620:Classification
4616:
4615:
4613:
4612:
4607:
4602:
4597:
4592:
4587:
4582:
4577:
4572:
4567:
4562:
4556:
4554:
4548:
4547:
4539:
4538:
4531:
4524:
4516:
4507:
4506:
4504:
4503:
4500:List of topics
4496:
4489:
4481:
4478:
4477:
4475:
4474:
4469:
4464:
4459:
4454:
4452:Selection bias
4448:
4446:
4442:
4441:
4439:
4438:
4433:
4428:
4423:
4418:
4412:
4410:
4404:
4403:
4401:
4400:
4395:
4390:
4385:
4380:
4375:
4373:Animal testing
4370:
4365:
4359:
4357:
4353:
4352:
4349:
4348:
4325:Mortality rate
4311:
4309:
4303:
4302:
4285:
4283:
4277:
4276:
4247:
4245:
4239:
4238:
4217:
4215:
4206:
4200:
4199:
4197:
4196:
4191:
4186:
4181:
4171:
4170:
4169:
4164:
4154:
4140:
4138:
4126:
4125:
4123:
4122:
4121:
4120:
4118:Platform trial
4110:
4109:
4108:
4103:
4098:
4087:
4085:
4073:
4072:
4070:
4069:
4064:
4059:
4054:
4049:
4044:
4043:
4042:
4037:
4030:Clinical trial
4026:
4024:
4020:
4019:
4008:
4007:
4000:
3993:
3985:
3979:
3978:
3973:
3968:
3963:
3961:UIC Calculator
3956:
3955:External links
3953:
3951:
3950:
3907:
3879:(6943): 1552.
3863:
3861:
3858:
3856:
3855:
3812:
3761:
3706:
3703:on 2015-06-20.
3640:
3622:
3591:(1): 124–138.
3571:
3528:
3495:
3458:BioData Mining
3444:
3393:
3367:
3360:
3334:
3311:
3292:
3273:(8): 861–874.
3250:
3243:
3223:
3194:(3): 1027–37.
3174:
3148:
3111:(8): 861–874.
3095:
3046:
3003:
2960:
2946:
2921:
2902:Mangrulkar R.
2894:
2872:
2843:(6943): 1552.
2820:
2769:
2738:
2703:(2): 1432–39.
2686:
2684:
2681:
2678:
2677:
2663:
2662:
2660:
2657:
2655:
2654:
2649:
2643:
2638:
2633:
2628:
2623:
2618:
2613:
2608:
2602:
2601:
2600:
2586:
2583:Biology portal
2572:
2569:Science portal
2556:
2553:
2535:
2532:
2528:Type II errors
2512:
2511:
2492:
2477:
2466:
2463:
2460:
2457:
2415:
2412:
2392:
2389:
2380:
2379:
2364:
2361:
2358:
2355:
2352:
2349:
2346:
2343:
2340:
2337:
2334:
2329:
2326:
2323:
2320:
2317:
2314:
2309:
2306:
2303:
2300:
2297:
2294:
2291:
2288:
2285:
2282:
2279:
2271:
2268:
2265:
2251:
2248:
2241:
2235:
2228:
2213:
2212:
2189:
2183:
2173:
2167:
2157:
2151:
2148:
2147:
2122:
2114:
2089:
2081:
2071:
2065:
2055:
2046:
2036:
2031:
2028:
2027:
2017:
2007:
1997:
1982:
1966:
1950:False positive
1946:
1932:
1931:
1921:
1914:
1904:
1891:
1879:False negative
1875:
1863:
1854:
1836:
1835:
1812:
1807:
1803:
1793:
1787:
1781:
1775:
1774:(pop.) = 2030
1768:
1765:
1764:
1762:
1754:
1749:
1748:
1745:
1739:
1738:
1731:
1724:
1716:
1715:
1709:
1708:
1699:
1690:
1681:
1672:
1663:
1653:
1652:
1649:
1648:
1623:
1598:
1582:
1576:2 TP + FP + FN
1540:
1536:
1513:
1512:
1484:
1471:
1443:
1415:
1389:
1388:
1363:
1338:
1310:
1275:
1251:
1248:
1247:
1212:
1169:
1157:
1149:False positive
1145:
1139:
1138:
1108:miss rate
1100:
1058:
1050:False negative
1046:
1034:
1029:
1024:
1021:
1020:
989:
976:
971:
966:
956:
955:
953:
948:
946:
914:Main article:
911:
908:
874:
873:
843:
842:
827:
821:
816:
812:
808:
803:
798:
794:
789:
783:
780:
771:
767:
763:
758:
754:
747:
742:
738:
708:
704:
681:
677:
654:
650:
627:
623:
590:
587:
533:
532:Misconceptions
530:
505:
502:
485:
484:
481:
474:
472:
469:
462:
447:
446:
443:
436:
434:
431:
424:
417:
416:
413:
406:
402:
399:
382:
381:
361:
358:
356:
354:
341:
338:
336:
334:
323:
309:
306:
304:
297:
296:
280:
277:
256:
255:
235:
232:
230:
228:
215:
212:
210:
208:
197:
183:
180:
178:
171:
170:
154:
151:
149:
146:
141:
140:
137:
134:
131:
122:
119:
73:
72:
66:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
4966:
4955:
4952:
4950:
4947:
4945:
4942:
4940:
4937:
4935:
4934:Biostatistics
4932:
4930:
4927:
4925:
4922:
4921:
4919:
4904:
4901:
4900:
4897:
4891:
4888:
4886:
4883:
4881:
4878:
4877:
4875:
4871:
4865:
4862:
4860:
4857:
4856:
4854:
4852:
4848:
4842:
4839:
4837:
4834:
4833:
4831:
4827:
4821:
4818:
4816:
4813:
4812:
4810:
4808:
4804:
4798:
4795:
4793:
4790:
4788:
4785:
4784:
4782:
4780:
4776:
4770:
4767:
4765:
4762:
4760:
4757:
4756:
4754:
4752:
4748:
4742:
4739:
4737:
4734:
4732:
4729:
4727:
4724:
4722:
4721:Jaccard index
4719:
4717:
4714:
4712:
4709:
4707:
4704:
4702:
4699:
4697:
4694:
4693:
4691:
4689:
4685:
4679:
4676:
4674:
4671:
4669:
4666:
4664:
4661:
4659:
4656:
4654:
4651:
4649:
4646:
4644:
4641:
4639:
4636:
4634:
4631:
4629:
4626:
4625:
4623:
4621:
4617:
4611:
4608:
4606:
4603:
4601:
4598:
4596:
4593:
4591:
4588:
4586:
4583:
4581:
4578:
4576:
4573:
4571:
4568:
4566:
4563:
4561:
4558:
4557:
4555:
4553:
4549:
4544:
4537:
4532:
4530:
4525:
4523:
4518:
4517:
4514:
4502:
4501:
4497:
4495:
4494:
4490:
4488:
4487:
4483:
4482:
4479:
4473:
4470:
4468:
4465:
4463:
4460:
4458:
4455:
4453:
4450:
4449:
4447:
4443:
4437:
4434:
4432:
4431:Meta-analysis
4429:
4427:
4424:
4422:
4419:
4417:
4414:
4413:
4411:
4409:
4405:
4399:
4398:Vaccine trial
4396:
4394:
4393:Seeding trial
4391:
4389:
4386:
4384:
4381:
4379:
4376:
4374:
4371:
4369:
4366:
4364:
4361:
4360:
4358:
4354:
4346:
4342:
4338:
4334:
4330:
4326:
4322:
4318:
4314:
4310:
4308:
4304:
4300:
4296:
4292:
4288:
4284:
4282:
4278:
4274:
4270:
4266:
4262:
4258:
4254:
4250:
4246:
4244:
4240:
4236:
4232:
4228:
4224:
4220:
4216:
4214:
4210:
4207:
4205:
4201:
4195:
4192:
4190:
4187:
4185:
4182:
4179:
4175:
4172:
4168:
4165:
4163:
4162:Retrospective
4160:
4159:
4158:
4155:
4153:
4149:
4145:
4142:
4141:
4139:
4136:
4131:
4127:
4119:
4116:
4115:
4114:
4111:
4107:
4104:
4102:
4099:
4097:
4094:
4093:
4092:
4089:
4088:
4086:
4083:
4082:EBM I to II-1
4078:
4074:
4068:
4065:
4063:
4060:
4058:
4055:
4053:
4050:
4048:
4045:
4041:
4038:
4036:
4033:
4032:
4031:
4028:
4027:
4025:
4021:
4017:
4013:
4006:
4001:
3999:
3994:
3992:
3987:
3986:
3983:
3977:
3974:
3972:
3969:
3967:
3964:
3962:
3959:
3958:
3947:
3943:
3938:
3933:
3929:
3925:
3921:
3917:
3913:
3908:
3904:
3900:
3895:
3890:
3886:
3882:
3878:
3874:
3870:
3865:
3864:
3851:
3847:
3843:
3839:
3835:
3831:
3828:(5): 329–42.
3827:
3823:
3816:
3808:
3804:
3799:
3794:
3789:
3784:
3780:
3776:
3772:
3765:
3757:
3753:
3748:
3743:
3739:
3735:
3731:
3727:
3723:
3716:
3715:"GeneMark-ES"
3710:
3699:
3695:
3691:
3687:
3683:
3678:
3673:
3669:
3665:
3658:
3654:
3650:
3644:
3636:
3632:
3626:
3618:
3614:
3609:
3604:
3599:
3594:
3590:
3586:
3582:
3575:
3567:
3563:
3559:
3555:
3551:
3547:
3543:
3539:
3532:
3523:
3518:
3514:
3510:
3506:
3499:
3491:
3487:
3482:
3477:
3472:
3467:
3463:
3459:
3455:
3448:
3440:
3436:
3431:
3426:
3421:
3416:
3412:
3408:
3404:
3397:
3382:
3378:
3371:
3363:
3357:
3353:
3349:
3345:
3338:
3330:
3326:
3322:
3315:
3307:
3303:
3296:
3288:
3284:
3280:
3276:
3272:
3268:
3261:
3254:
3246:
3240:
3236:
3235:
3227:
3219:
3215:
3210:
3205:
3201:
3197:
3193:
3189:
3185:
3178:
3170:
3166:
3162:
3155:
3153:
3144:
3140:
3136:
3132:
3127:
3122:
3118:
3114:
3110:
3106:
3099:
3091:
3087:
3082:
3077:
3073:
3069:
3065:
3061:
3057:
3050:
3042:
3038:
3034:
3030:
3026:
3022:
3018:
3014:
3007:
2999:
2995:
2991:
2987:
2983:
2979:
2975:
2971:
2964:
2956:
2950:
2936:on 2013-07-06
2935:
2931:
2925:
2909:
2905:
2898:
2882:
2876:
2868:
2864:
2859:
2854:
2850:
2846:
2842:
2838:
2834:
2827:
2825:
2816:
2812:
2807:
2802:
2797:
2792:
2788:
2784:
2780:
2773:
2765:
2761:
2757:
2753:
2749:
2742:
2734:
2730:
2726:
2722:
2718:
2714:
2710:
2706:
2702:
2698:
2691:
2687:
2674:
2668:
2664:
2653:
2650:
2647:
2644:
2642:
2639:
2637:
2634:
2632:
2629:
2627:
2624:
2622:
2619:
2617:
2614:
2612:
2609:
2607:
2604:
2603:
2598:
2587:
2584:
2578:
2573:
2570:
2564:
2559:
2552:
2549:
2545:
2541:
2531:
2529:
2525:
2521:
2517:
2490:
2475:
2464:
2461:
2458:
2455:
2448:
2447:
2446:
2444:
2443:harmonic mean
2440:
2435:
2433:
2432:
2427:
2426:
2421:
2411:
2409:
2405:
2403:
2399:
2398:gold standard
2388:
2384:
2359:
2356:
2353:
2350:
2347:
2344:
2341:
2338:
2335:
2327:
2324:
2321:
2318:
2315:
2312:
2304:
2301:
2298:
2295:
2292:
2289:
2283:
2280:
2277:
2269:
2266:
2263:
2255:
2252:
2249:
2246:
2242:
2239:
2236:
2233:
2232:type II error
2229:
2226:
2222:
2221:
2220:
2219:
2210:
2187:
2181:
2171:
2168:
2165:
2155:
2152:
2150:
2149:
2145:
2118:
2115:
2112:
2085:
2082:
2079:
2069:
2066:
2063:
2054:
2050:
2047:
2044:
2035:
2032:
2029:
2025:
2020:= 1820 / 2000
2015:
2011:
2008:
2005:
1992:
1986:
1983:
1977:(2030 ×
1971:
1970:True negative
1967:
1957:(2030 ×
1951:
1947:
1941:(2030 ×
1937:negative (AN)
1934:
1933:
1929:
1918:
1915:
1912:
1903:
1899:
1895:
1892:
1880:
1876:
1868:
1867:True positive
1864:
1858:positive (AP)
1855:
1853:
1851:
1846:(as confirmed
1844:
1840:Patients with
1837:
1833:
1811:
1804:
1801:
1791:
1788:
1786:
1783:Test outcome
1782:
1780:
1777:Test outcome
1776:
1772:
1769:
1767:
1766:
1761:
1759:
1752:
1746:
1743:
1742:
1737:
1732:
1730:
1725:
1723:
1718:
1717:
1714:
1703:
1694:
1685:
1676:
1667:
1658:
1654:
1628:
1627:Jaccard index
1602:
1599:
1586:
1583:
1544:
1537:
1515:
1514:
1491:
1485:
1475:
1472:
1447:
1444:
1419:
1416:
1394:
1391:
1390:
1367:
1364:
1342:
1339:
1314:
1311:
1286:
1280:
1276:
1255:
1252:
1249:
1222:
1216:
1213:
1188:
1182:
1173:
1170:
1163:
1162:
1161:True negative
1158:
1151:
1150:
1146:
1144:
1141:
1140:
1114:
1104:
1101:
1076:
1070:
1066:
1062:
1059:
1052:
1051:
1047:
1040:
1039:
1038:True positive
1035:
1033:
1030:
1027:
1022:
993:
990:
980:
977:
975:
972:
970:
967:
961:
958:
957:
952:
947:
944:
941:
939:
938:
933:
932:
927:
923:
917:
907:
905:
901:
900:dimensionless
897:
893:
891:
887:
883:
879:
871:
868:(hit rate) −
867:
863:
860:
859:
858:
856:
852:
848:
825:
819:
814:
810:
806:
801:
796:
792:
787:
781:
778:
769:
765:
761:
756:
752:
745:
736:
728:
727:
726:
724:
706:
702:
679:
675:
652:
648:
625:
621:
612:
608:
604:
600:
596:
586:
584:
580:
576:
571:
569:
564:
560:
556:
552:
548:
544:
540:
529:
527:
523:
519:
515:
511:
504:Medical usage
501:
498:26 / (26 + 0)
493:
478:
473:
466:
461:
460:
459:
455:
451:
440:
435:
428:
423:
422:
421:
410:
405:
404:
398:
396:
391:
388:
359:
357:
339:
337:
321:
307:
305:
287:
286:
285:
276:
274:
273:type II error
269:
265:
262:
233:
231:
213:
211:
195:
181:
179:
161:
160:
159:
145:
138:
135:
132:
129:
128:
127:
118:
116:
112:
107:
100:
96:
92:
88:
86:
82:
78:
70:
67:
64:
60:
57:
56:
55:
52:
48:
44:
34:
30:
19:
4672:
4498:
4491:
4484:
4273:Hazard ratio
4157:Cohort study
3919:
3915:
3876:
3872:
3825:
3821:
3815:
3778:
3774:
3764:
3729:
3725:
3709:
3698:the original
3670:(1): 78–94.
3667:
3663:
3643:
3634:
3625:
3588:
3584:
3574:
3541:
3537:
3531:
3512:
3508:
3498:
3461:
3457:
3447:
3410:
3407:BMC Genomics
3406:
3396:
3385:. Retrieved
3380:
3370:
3346:. Springer.
3343:
3337:
3328:
3324:
3314:
3305:
3295:
3270:
3266:
3253:
3233:
3226:
3191:
3187:
3177:
3168:
3164:
3108:
3104:
3098:
3063:
3059:
3049:
3019:(2): 175–9.
3016:
3012:
3006:
2973:
2969:
2963:
2949:
2938:. Retrieved
2934:the original
2924:
2912:. Retrieved
2908:the original
2897:
2885:. Retrieved
2875:
2840:
2836:
2789:(1): 45–50.
2786:
2782:
2772:
2758:(4): 291–4.
2755:
2751:
2741:
2700:
2696:
2690:
2667:
2537:
2523:
2513:
2436:
2429:
2423:
2417:
2406:
2394:
2385:
2381:
2225:type I error
2217:
2216:
2208:
2179:
2163:
2143:
2110:
2077:
2061:
2042:
2023:
2009:
2003:
2000:= 180 / 2000
1981:× 91%)
1969:
1949:
1927:
1910:
1901:
1878:
1866:
1843:bowel cancer
1839:
1831:
1799:
1784:
1778:
1756:
1712:
1702:
1693:
1684:
1675:
1666:
1657:
1642:TP + FN + FP
1159:
1147:
1143:Negative (N)
1142:
1048:
1036:
1032:Positive (P)
1031:
1025:
979:Informedness
973:
968:
950:
935:
929:
925:
921:
919:
903:
895:
894:
885:
881:
877:
875:
869:
865:
861:
846:
844:
722:
598:
592:
583:informedness
575:ROC analysis
572:
567:
562:
558:
554:
550:
546:
542:
538:
535:
507:
494:
486:
456:
452:
448:
418:
395:type I error
392:
386:
383:
282:
270:
266:
260:
257:
156:
142:
124:
108:
105:
93:
89:
74:
68:
58:
50:
40:
29:
4467:Null result
4426:Replication
4321:Infectivity
4243:Association
4194:Case report
4184:Case series
4167:Prospective
3635:medcalc.org
3515:: 168–192.
3331:(1): 37–63.
3171:(1): 37–63.
2606:Brier score
2120:(LR−)
2039:= 30 / 2030
2037:= AP / pop.
2010:Specificity
1902:sensitivity
1813:= 2 ×
1552:2 PPV × TPR
1487:Diagnostic
1221:specificity
1069:sensitivity
855:false-alarm
490:6 / (6 + 0)
300:specificity
279:Specificity
174:sensitivity
153:Sensitivity
69:Specificity
63:conditioned
59:Sensitivity
4918:Categories
4873:Similarity
4815:Perplexity
4726:Rand index
4711:Dunn index
4696:Silhouette
4688:Clustering
4552:Regression
4269:Odds ratio
4261:Risk ratio
4227:Prevalence
4213:Occurrence
4189:Case study
3464:(13): 13.
3387:2019-07-17
2976:(2): 107.
2940:2013-08-23
2914:24 January
2887:18 January
2683:References
2034:Prevalence
1489:odds ratio
1474:Markedness
1254:Prevalence
514:prevalence
148:Definition
47:statistics
4643:Precision
4595:RMSE/RMSD
4329:Morbidity
4317:Virulence
4219:Incidence
3672:CiteSeerX
3558:0098-7484
3121:CiteSeerX
2487:precision
2476:×
2472:precision
2465:×
2425:precision
2357:−
2325:−
2290:−
2243:Positive
2201:LR−
2053:precision
2018:= TN / AN
1998:= FP / AN
1924:= 10 / 30
1922:= FN / AP
1907:= 20 / 30
1905:= TP / AP
1850:endoscopy
1594:PPV × TPR
1558:PPV + TPR
1524:TPR + TNR
1469:= 1 − FOR
1441:= 1 − PPV
1336:= 1 − NPV
1308:= 1 − FDR
1285:precision
1245:= 1 − FPR
1210:= 1 − TNR
1136:= 1 − TPR
1098:= 1 − FNR
1014:TPR - FPR
1005:TPR × FPR
811:σ
793:σ
766:μ
762:−
753:μ
741:′
703:σ
676:μ
649:σ
622:μ
603:statistic
85:screening
81:diagnoses
37:positive.
4859:Coverage
4638:Accuracy
4493:Glossary
4486:Category
4363:In vitro
4204:Measures
4023:Overview
3946:14512479
3842:22510764
3807:15144565
3756:16314312
3655:(1997).
3653:Karlin S
3617:29358889
3566:27305422
3490:33541410
3439:31898477
3218:20089911
3090:15271832
3041:31400167
2998:44505648
2815:18158403
2733:19967899
2725:20340527
2555:See also
2207:≈
2178:≈
2142:≈
2109:≈
2076:≈
2041:≈
1990:fall-out
1926:≈
1909:≈
1798:≈
1790:Accuracy
1785:negative
1779:positive
1393:Accuracy
1180:fall-out
851:hit rate
518:Positive
261:rule out
43:medicine
4751:Ranking
4741:SimHash
4628:F-score
4368:In vivo
3903:8019315
3894:2540489
3850:3352427
3747:1298918
3694:9149143
3649:Burge C
3608:5757117
3481:7863449
3430:6941312
3287:2027090
3209:2824341
3143:2027090
3113:Bibcode
3033:8028470
2990:8028462
2867:8019315
2858:2540489
2806:2636062
2764:9747274
2717:4586294
2439:F-score
2204:
2192:
2137:
2125:
2104:
2092:
2051:(PPV),
1987:(FPR),
1961:×
1896:(TPR),
1827:
1815:
1645:
1633:
1617:√
1608:√
1592:√
1579:
1567:
1561:
1549:
1533:
1521:
1509:
1497:
1465:
1453:
1437:
1425:
1412:
1403:TP + TN
1400:
1385:
1373:
1360:
1348:
1332:
1320:
1304:
1292:
1272:
1260:
1241:
1229:
1217:(TNR),
1206:
1194:
1174:(FPR),
1132:
1120:
1105:(FNR),
1094:
1082:
1071:(SEN),
1063:(TPR),
1017:
1003:√
999:
964:= P + N
579:fallout
387:rule in
4648:Recall
3944:
3937:200804
3934:
3901:
3891:
3848:
3840:
3805:
3798:421630
3795:
3781:: 59.
3754:
3744:
3692:
3674:
3615:
3605:
3564:
3556:
3488:
3478:
3437:
3427:
3358:
3285:
3241:
3216:
3206:
3141:
3123:
3088:
3081:487735
3078:
3039:
3031:
2996:
2988:
2865:
2855:
2813:
2803:
2762:
2731:
2723:
2715:
2495:recall
2480:recall
2431:recall
2188:(DOR)
2180:99.45%
1975:= 1820
1939:= 2000
1898:recall
1800:90.64%
1792:(ACC)
1603:(MCC)
1492:(DOR)
1476:(MK),
1448:(NPV)
1420:(FDR)
1395:(ACC)
1368:(LR−)
1343:(LR+)
1315:(FOR)
1281:(PPV),
1164:(TN),
1152:(FP),
1065:recall
1053:(FN),
1041:(TP),
667:, and
397:rate.
275:rate.
4653:Kappa
4570:sMAPE
4307:Other
3846:S2CID
3701:(PDF)
3660:(PDF)
3283:S2CID
3263:(PDF)
3139:S2CID
3037:S2CID
2994:S2CID
2729:S2CID
2713:JSTOR
2659:Notes
2524:power
2238:Power
2172:(NPV)
2164:90.0%
2156:(FDR)
2144:0.366
2087:(LR+)
2078:0.55%
2070:(FOR)
2043:1.48%
2016:(TNR)
1955:= 180
1928:33.3%
1911:66.7%
1832:0.174
1810:score
1587:(FM)
1543:score
1409:P + N
1269:P + N
1075:power
1008:- FPR
994:(PT)
898:is a
4820:BLEU
4792:SSIM
4787:PSNR
4764:NDCG
4585:MSPE
4580:MASE
4575:MAPE
4146:vs.
4014:and
3942:PMID
3899:PMID
3838:PMID
3803:PMID
3752:PMID
3690:PMID
3613:PMID
3562:PMID
3554:ISSN
3538:JAMA
3486:PMID
3435:PMID
3356:ISBN
3239:ISBN
3214:PMID
3086:PMID
3029:PMID
2986:PMID
2916:2012
2889:2023
2863:PMID
2811:PMID
2760:PMID
2721:PMID
2437:The
2209:20.2
2111:7.41
2004:9.0%
1972:(TN)
1952:(FP)
1900:,
1884:= 10
1881:(FN)
1872:= 20
1869:(TP)
1860:= 30
1735:edit
1728:talk
1721:view
1570:2 TP
853:and
694:and
640:and
593:The
520:and
83:and
45:and
4841:FID
4807:NLP
4797:IoU
4759:MRR
4736:SMC
4668:ROC
4663:AUC
4658:MCC
4610:MAD
4605:MDA
4590:RMS
4565:MAE
4560:MSE
3932:PMC
3924:doi
3920:327
3916:BMJ
3889:PMC
3881:doi
3877:308
3873:BMJ
3830:doi
3793:PMC
3783:doi
3742:PMC
3734:doi
3682:doi
3668:268
3603:PMC
3593:doi
3546:doi
3542:315
3517:doi
3476:PMC
3466:doi
3425:PMC
3415:doi
3348:doi
3275:doi
3204:PMC
3196:doi
3131:doi
3076:PMC
3068:doi
3064:329
3060:BMJ
3021:doi
2978:doi
2853:PMC
2845:doi
2841:308
2837:BMJ
2801:PMC
2791:doi
2756:125
2705:doi
2418:In
2195:LR+
2134:TNR
2128:FNR
2101:FPR
2095:TPR
2062:10%
2024:91%
1848:on
1506:LR−
1500:LR+
1382:TNR
1376:FNR
1357:FPR
1351:TPR
1044:hit
934:or
884:),
597:or
568:and
563:out
508:In
41:In
4920::
4769:AP
4633:P4
4343:,
4339:,
4335:,
4331:,
4327:,
4323:,
4319:,
4315:,
4297:,
4293:,
4289:,
4271:,
4267:,
4263:,
4259:,
4255:,
4251:,
4233:,
4229:,
4225:,
4221:,
4150:,
3940:.
3930:.
3918:.
3914:.
3897:.
3887:.
3875:.
3871:.
3844:.
3836:.
3826:13
3824:.
3801:.
3791:.
3777:.
3773:.
3750:.
3740:.
3730:33
3728:.
3724:.
3688:.
3680:.
3666:.
3662:.
3651:,
3633:.
3611:.
3601:.
3589:24
3587:.
3583:.
3560:.
3552:.
3540:.
3513:17
3511:.
3507:.
3484:.
3474:.
3462:14
3460:.
3456:.
3433:.
3423:.
3411:21
3409:.
3405:.
3379:.
3354:.
3327:.
3323:.
3304:.
3281:.
3271:27
3269:.
3265:.
3212:.
3202:.
3192:30
3190:.
3186:.
3167:.
3163:.
3151:^
3137:.
3129:.
3119:.
3109:27
3107:.
3084:.
3074:.
3062:.
3058:.
3035:.
3027:.
3017:14
3015:.
2992:.
2984:.
2974:14
2972:.
2861:.
2851:.
2839:.
2835:.
2823:^
2809:.
2799:.
2787:56
2785:.
2781:.
2754:.
2750:.
2727:.
2719:.
2711:.
2701:62
2699:.
2530:.
2256:=
2190:=
2162:=
2123:=
2090:=
2060:=
2022:=
2002:=
1993:,
1965:)
1945:)
1890:)
1830:≈
1636:TP
1631:=
1615:-
1606:=
1590:=
1565:=
1547:=
1519:=
1495:=
1462:PN
1456:TN
1451:=
1434:PP
1428:FP
1423:=
1398:=
1371:=
1346:=
1329:PN
1323:FN
1318:=
1301:PP
1295:TP
1290:=
1258:=
1232:TN
1227:=
1197:FP
1192:=
1123:FN
1118:=
1085:TP
1080:=
1067:,
997:=
981:,
904:d′
896:d′
892:.
864:=
862:d′
847:d′
723:d′
599:d′
547:in
539:sp
49:,
4600:R
4535:e
4528:t
4521:v
4180:)
4176:(
4137:)
4133:(
4084:)
4080:(
4004:e
3997:t
3990:v
3948:.
3926::
3905:.
3883::
3852:.
3832::
3809:.
3785::
3779:5
3758:.
3736::
3717:.
3684::
3637:.
3619:.
3595::
3568:.
3548::
3525:.
3519::
3492:.
3468::
3441:.
3417::
3390:.
3364:.
3350::
3329:2
3308:.
3289:.
3277::
3247:.
3220:.
3198::
3169:2
3145:.
3133::
3115::
3092:.
3070::
3043:.
3023::
3000:.
2980::
2943:.
2918:.
2891:.
2869:.
2847::
2817:.
2793::
2766:.
2735:.
2707::
2491:+
2462:2
2459:=
2456:F
2363:)
2360:1
2354:R
2351:N
2348:T
2345:+
2342:R
2339:P
2336:T
2333:(
2328:1
2322:R
2319:N
2316:T
2313:+
2308:)
2305:1
2302:+
2299:R
2296:N
2293:T
2287:(
2284:R
2281:P
2278:T
2270:=
2267:T
2264:P
2198:/
2131:/
2098:/
1852:)
1821:/
1808:1
1806:F
1639:/
1573:/
1555:/
1541:1
1539:F
1530:2
1527:/
1503:/
1459:/
1431:/
1406:/
1379:/
1354:/
1326:/
1298:/
1266:/
1263:P
1238:N
1235:/
1203:N
1200:/
1129:P
1126:/
1091:P
1088:/
1011:/
926:N
922:P
886:p
882:p
880:(
878:Z
870:Z
866:Z
826:)
820:2
815:N
807:+
802:2
797:S
788:(
782:2
779:1
770:N
757:S
746:=
737:d
707:N
680:N
653:S
626:S
559:n
555:n
553:e
551:s
543:p
360:=
340:=
322:+
308:=
234:=
214:=
196:+
182:=
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.