959:. Dominant inheritance occurs when an abnormal gene from one parent causes disease even though the matching gene from the other parent is normal. The abnormal allele dominates. Recessive inheritance is when both matching genes must be abnormal to cause disease. If only one gene in the pair is abnormal, the disease does not occur, or is mild. Someone who has one abnormal gene (but no symptoms) is called a carrier. A carrier can pass this abnormal gene to his or her children. X chromosome carry about 1500 genes, more than any other chromosome in the human body. Most of them code for something other than female anatomical traits. Many of the non-sex determining X-linked genes are responsible for abnormal conditions. The Y chromosome carries about 78 genes. Most of the Y chromosome genes are involved with essential cell house-keeping activities and sperm production. Only one of the Y chromosome genes, the SRY gene, is responsible for male anatomical traits. When any of the 9 genes involved in sperm production are missing or defective the result is usually very low sperm counts and infertility. Examples of mutations on the X chromosome include more common diseases such as the following:
996:, also called XX male syndrome, is a condition in which individuals with two X chromosomes in each cell, the pattern normally found in females, have a male appearance. People with this disorder have male external genitalia. In most people with 46,XX testicular disorder of sex development, the condition results from an exchange of genetic material between chromosomes (translocation). This exchange occurs as a random event during the formation of sperm cells in the affected person's father. The SRY gene (normally on the Y chromosome) is misplaced in this disorder, onto an X chromosome. Any person with an X chromosome that carries the SRY gene will develop male characteristics despite not having a Y chromosome.
568:
2678:
53:
967:
a fault in the development of one or more sets of retinal cones that perceive color in light and transmit that information to the optic nerve. This type of color blindness is usually a sex-linked condition. The genes that produce photopigments are carried on the X chromosome; if some of these genes are missing or damaged, color blindness will be expressed in males with a higher probability than in females because males only have one X chromosome.
936:), three sex chromosomes are present, denoted as X, Y and Y. This corresponds with three sexes: females with XX chromosomes, males with XY, and hermaphrodites with XY. The hermaphrodite sex is estimated to have arisen only 4000 years ago, post-domestication of the plant. The genetic architecture suggests that either the Y chromosome has an X-inactivating gene, or that the Y chromosome has an X-activating gene.
863:, so there is no evidence for sex chromosomes. In the bryophytes, including liverworts, hornworts and mosses, sex chromosomes are common. The sex chromosomes in bryophytes affect what type of gamete is produced by the gametophyte, and there is wide diversity in gametophyte type. Unlike seed plants, where gametophytes are always unisexual, in bryophytes they may produce male, female, or both types of gamete.
1006:
change in the identity of the sex-determining genes (such as by mutation) or by a change in their location. In other cases, sex chromosomes may grow substantially with respect to their ancestral forms as a result of fusion events with autosomes, and autosome-sex chromosome fusions result in what are called neo-sex chromosomes. Five examples of this are now known in the songbird superfamily
974:
when they inherit one mutant allele. In contrast, a female must inherit two mutant alleles, a less frequent event since the mutant allele is rare in the population. X-linked traits are maternally inherited from carrier mothers or from an affected father. Each son born to a carrier mother has a 50% probability of inheriting the X chromosome carrying the mutant allele.
642:(i.e. humans who possess biological male-traits but actually have XX allosomes) were studied. After examination, it was discovered that the difference between a typical XX individual (traditional female) and a sex-reversed XX man was that the typical individuals lacked the SRY gene. It is theorized that in sex-reversed XX men, the SRY mistakenly gets
866:
Bryophytes most commonly employ a UV sex-determination system, where U produces female gametophytes and V produces male gametophytes. The U and V chromosomes are heteromorphic with U larger than V and are frequently both larger than the autosomes. There is variation even within this system, including
1005:
Sex chromosomes evolve from standard pairs of autosomal chromosomes. In a large number of organisms, the sex-determination systems presently observed are products of sex chromosome turnover. Sex chromosome turnover is a process defined as when the type of the sex chromosome changes as a product of a
966:
or color vision deficiency is the inability or decreased ability to see color, or perceive color differences, under normal lighting conditions. Color blindness affects many individuals in the population. There is no actual blindness, but there is a deficiency of color vision. The most usual cause is
551:: In some cells, the X chromosome inherited from the mother deactivates; in other cells, it is the X chromosome inherited from the father. This ensures that both sexes always have exactly one functional copy of an X chromosome in each body cell. The deactivated X chromosome is silenced by repressive
973:
refers to a group of bleeding disorders in which it takes a long time for the blood to clot. This is referred to as X-Linked recessive. Hemophilia is much more common in males than females because males are hemizygous. They only have one copy of the gene in question and therefore express the trait
658:
Diverse mechanisms are involved in the determination of sex in animals. For mammals, sex determination is carried by the genetic contribution of the spermatozoon. Many lower chordates, such as fish, amphibians and reptiles, have systems that are influenced by the environment. Fish and amphibians,
980:
is a genetic condition involving changes in part of the X chromosome. It is the most common form of inherited intellectual disability (mental retardation) in males. It is caused by a change in a gene called FMR1. A small part of the gene code is repeated on a fragile area of the X chromosome. The
614:
organisms with allosome-determined sex get half of their allosomes from each of their parents. In most mammals, females are XX, and can pass along either of their Xs; since males are XY they can pass along either an X or a Y. Females in such species receive an X chromosome from each parent while
730:
in plants also impacts the structure of their sex chromosomes. Polyploidization can occur before and after the development of sex chromosomes. If it occurs after sex chromosomes are established, dosage should stay consistent between the sex chromosomes and autosomes, with minimal impact on sex
710:
normally remain once sex chromosomes are fully differentiated. When chromosomes do not recombine, neutral sequence divergences begin to accumulate, which has been used to estimate the age of sex chromosomes in various plant lineages. Even the oldest estimated divergence, in the liverwort
810:
species. This would conclude that microsatellites do not participate in Y-chromosome evolution. The portion of Y-chromosome that never recombine with X-chromosome faces selection reduction. This reduced selection leads to insertion of transposable elements and accumulation of
915:
data from about 100 angiosperm species showed heteromorphic sex chromosomes in approximately half, mostly taking the form of XY sex-determination systems. Their Y is typically larger, unlike in humans; however there is diversity among angiosperms. In the Poplar genus
948:. Sex linked diseases are passed down through families through one of the X or Y chromosomes. Since usually men inherit Y chromosomes, they are the only ones to inherit Y-linked traits. Men and women can get the X-linked ones since both inherit X chromosomes.
981:
more repeats, the more likely there is to be a problem. Males and females can both be affected, but because males have only one X chromosome, a single fragile X is likely to affect them more. Most fragile-X males have large testes, big ears, narrow faces, and
1386:
922:) some species have male heterogamety while others have female heterogamety. Sex chromosomes have arisen independently multiple times in angiosperms, from the monoecious ancestral condition. The move from a monoecious to dioecious system requires both
626:
that might contain two different sets of DNA one XX and the other XY. It could also result from exposure, often in utero, to chemicals that disrupt the normal conversion of the allosomes into sex hormones and further into the development of either
718:
is more recent than mammal or bird divergence. Due to this recency, most plant sex chromosomes also have relatively small sex-linked regions. Current evidence does not support the existence of plant sex chromosomes more ancient than those of
496:
926:
to be present in the population. Male sterility likely arises first as an adaptation to prevent selfing. Once male sterility has reached a certain prevalence, then female sterility may have a chance to arise and spread.
767:
size evolution. Retrotransposones contribute in size determination of sex chromosomes and its proliferation varies even in closely related species. LTR and tandom repeats play dominant role in the evolution of
1360:
638:. This gene produces a testis-determining factor ("TDF"), which initiates testis development in humans and other mammals. The SRY sequence's prominence in sex determination was discovered when the genetics of
1018:), in which hybridization experiments resulted in a translocation of the sex-determiner region of a sex chromosome into an autosome. This resulted in the autosome becoming a novel W sex chromosome.
911:
with either monoecious or hermaphroditic flowers do not have sex chromosomes. Angiosperms with separate sexes (dioecious) may use sex chromosomes or environmental flowers for sex determination.
944:
Allosomes not only carry the genes that determine male and female traits, but also those for some other characteristics as well. Genes that are carried by either sex chromosome are said to be
1713:
Kralova T, Cegan R, Kubat Z, Vrana J, Vyskot B, Vogel I, et al. (2014). "Identification of a novel retrotransposon with sex chromosome-specific distribution in Silene latifolia".
883:, found in an estimated 36% of species. However, heteromorphic sex chromosomes are relatively rare, with only five species known as of 2014. Five of these use an XY system, and one (
843:
is the rare case in plants in which Y is smaller than X, while its ancestor plant has the same size of both X and Y chromosomes. This size difference should be caused by deletion of
2505:
1804:"The sex chromosomes of bryophytes: Recent insights, open questions, and reinvestigations of Frullania dilatata and Plagiochila asplenioides: The sex chromosomes of bryophytes"
659:
for example, have genetic sex determination but their sex can also be influenced by externally available steroids and incubation temperature of eggs. In some reptiles, e.g.
615:
males receive an X chromosome from their mother and a Y chromosome from their father. It is thus the male's sperm that determines the sex of each offspring in such species.
679:
have a variety of mating systems, their sex determination primarily regulated by MADS-box genes. These genes code for proteins that form the sex organs in flowers.
1935:
1338:
1442:
Devlin RH, Nagahama Y (2002-06-21). "Sex determination and sex differentiation in fish: an overview of genetic, physiological, and environmental influences".
2015:
2498:
2127:"A novel neo-sex chromosome in Sylvietta brachyura (Macrosphenidae) adds to the extraordinary avian sex chromosome diversity among Sylvioidea songbirds"
739:
532:
in males. Females therefore have 23 homologous chromosome pairs, while males have 22. The X and Y chromosomes have small regions of homology called
1985:
763:
are responsible for plant sex chromosome evolution. The insertion of retrotransposons is probably the major cause of y-chromosome expansion and
702:
systems as well as many variants. Sex chromosomes have evolved independently across many plant groups. Recombination of chromosomes may lead to
2491:
524:(regions of DNA) in the same order along their chromosomal arms. The 23rd pair of chromosomes are called allosomes. These consist of two
1187:
547:. Early in female embryonic development, in cells other than egg cells, one of the X chromosomes is randomly and permanently partially
1010:. There is one experimentally documented case of sex chromosome turnover occurring during a 30-year evolutionary experiment involving
815:. The Y become larger and smaller than X due to insertion of retroelement and deletion of genetic material respectively. The genus
1964:
2597:
664:
114:
1078:
2544:
1756:
Divashuk MG, Alexandrov OS, Kroupin PY, Karlov GI (2011). "Molecular cytogenetic mapping of
Humulus lupulus sex chromosomes".
622:. This can result from allosomes that are neither XX nor XY. It can also occur when two fertilized embryo fuse, producing a
487:
both independently discovered sex chromosomes in 1905. However, Stevens is credited for discovering them earlier than Wilson.
2259:
2101:
1107:
847:
in Y but that is not the case. This is because of complex dynamics like the larger size of X than Y-chromosome may be due to
429:
782:
region only. Athila retroelements overrepresented in X but absent in Y while tandem repeats enriched in Y-chromosome. Some
1884:
1328:
1927:
1278:
634:
There is a gene in the Y chromosome that has regulatory sequences that control genes that code for maleness, called the
2681:
1494:
1380:
1302:
706:
before the development of sex chromosomes, or recombination may be reduced after sex chromosomes develop. Only a few
731:
differentiation. If it occurs before sex chromosomes become heteromorphic, as is likely in the octoploid red sorrel
2537:
605:
584:
368:
203:
1259:"Human male sex determination and sexual differentiation: pathways, molecular interactions and genetic disorders"
675:
Many scientists argue that sex determination in plants is more complex than that in humans. This is because even
17:
2007:
473:
in form, size, and behavior. Whereas autosomes occur in homologous pairs whose members have the same form in a
296:
495:
465:
that carry the genes that determine the sex of an individual. The human sex chromosomes are a typical pair of
348:
2658:
2441:
825:
topology distribution there are three regions on sex chromosomes. One region that stops recombining in the
363:
173:
2592:
2587:
2582:
2186:"Long-term experimental hybridisation results in the evolution of a new sex chromosome in swordtail fish"
1047:
1042:
1037:
982:
109:
104:
99:
94:
923:
306:
168:
1993:
806:
data shows that there is no significant difference between X and Y-chromosome microsatellites in both
2627:
2549:
2252:
1670:
Kumar S, Kumari R, Sharma V (April 2014). "Genetics of dioecy and causal sex chromosomes in plants".
848:
643:
422:
158:
1574:"Large-scale suppression of recombination predates genomic rearrangements in Neurospora tetrasperma"
2577:
2514:
2472:
599:
151:
89:
575:
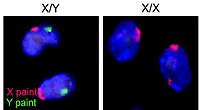
of a human, showing the sex chromosomes in green box at bottom right. The X chromosome is part of
1128:
Brush SG (June 1978). "Nettie M. Stevens and the discovery of sex determination by chromosomes".
353:
737:, sex is determined in a single XY system. In a more complicated system, the sandalwood species
698:. The diversity of plants is reflected in their sex-determination systems, which include XY and
2532:
2518:
707:
533:
517:
274:
269:
77:
72:
2184:
Franchini P, Jones JC, Xiong P, Kneitz S, Gompert Z, Warren WC, et al. (December 2018).
1027:
713:
555:
that compacts the DNA and prevents expression of most genes. This compaction is regulated by
484:
373:
1179:
2702:
2561:
2460:
2245:
2197:
1585:
1536:
1451:
952:
812:
774:
699:
567:
512:
contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, a total of 46 chromosomes. The first 22 pairs are called
415:
313:
1645:
8:
2467:
756:
583:
are annotated to the right of each chromosome (or chromosome pair), and the gene for the
576:
194:
2483:
2201:
2153:
1956:
1909:
1589:
1540:
1455:
1214:
Philosophical
Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences
2218:
2185:
2166:
2107:
2067:
1861:
1836:
1781:
1738:
1695:
1606:
1573:
1234:
1209:
1161:
1145:
977:
623:
318:
301:
286:
180:
1463:
871:
have been found to co-occur with sex chromosomes and likely impact sex determination.
2435:
2223:
2170:
2158:
2111:
2097:
2059:
1866:
1773:
1730:
1687:
1649:
1611:
1554:
1500:
1490:
1467:
1424:
1376:
1270:
1239:
1153:
1032:
703:
323:
131:
126:
67:
2071:
1785:
1742:
1699:
1070:
618:
However, a small percentage of humans have a divergent sexual development, known as
2556:
2213:
2205:
2148:
2138:
2093:
2089:
2049:
1856:
1848:
1815:
1765:
1722:
1679:
1641:
1601:
1593:
1544:
1459:
1416:
1368:
1229:
1221:
1165:
1137:
993:
844:
788:
733:
639:
580:
281:
1099:
1420:
1372:
1306:
963:
868:
831:
794:
779:
760:
676:
552:
358:
339:
291:
235:
2209:
1888:
1597:
891:
821:
is also used as model for the study of sex chromosomes evolution. Based on the
803:
727:
687:
548:
480:
1835:
VanBuren R, Zeng F, Chen C, Zhang J, Wai CM, Han J, et al. (April 2015).
1683:
1549:
1524:
895:), have homomorphic sex chromosomes that are almost indistinguishable through
2696:
2648:
2602:
2398:
2393:
2388:
2383:
2378:
2373:
2368:
2363:
2358:
2353:
2348:
2343:
2338:
1471:
1258:
932:
885:
822:
764:
752:
403:
384:
328:
264:
230:
163:
119:
27:
Chromosome that differs from an ordinary autosome in form, size, and behavior
1504:
2663:
2619:
2614:
2455:
2421:
2416:
2333:
2328:
2323:
2318:
2313:
2308:
2303:
2298:
2293:
2268:
2227:
2162:
2063:
2054:
2037:
1986:"Fragile X Syndrome - Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment of Fragile X Syndrome"
1870:
1777:
1734:
1691:
1653:
1615:
1558:
1428:
1274:
1243:
1225:
912:
529:
525:
509:
474:
252:
146:
141:
82:
34:
2126:
1852:
1365:
Sex
Determination, Differentiation and Intersexuality in Placental Mammals
1299:
2276:
1572:
Sun Y, Svedberg J, Hiltunen M, Corcoran P, Johannesson H (October 2017).
1157:
1015:
945:
896:
860:
783:
398:
185:
1007:
970:
908:
880:
660:
611:
462:
52:
2143:
1820:
1803:
1769:
1726:
1149:
772:
sex chromosomes. Athila is new family of retroelements, discovered in
956:
743:
has X1X1X2X2 chromosomes in females, and X1X2Y chromosomes in males.
695:
683:
591:
572:
513:
501:
470:
240:
220:
208:
543:, while either an X or Y chromosome may be present in an individual
2653:
2408:
2285:
1333:
1141:
826:
635:
628:
619:
257:
1314:
1011:
918:
817:
647:
225:
213:
539:
An X chromosome is always present as the 23rd chromosome in the
2237:
1755:
1411:. Environmental Regulation of Sex Dtermination in Vertebrates.
466:
393:
247:
2035:
2631:
889:) uses a WZ system. Some gymnosperms, such as Johann's Pine (
544:
521:
2125:
Sigeman H, Zhang H, Ali Abed S, Hansson B (December 2022).
2124:
1571:
867:
UU/V and U/VV chromosome arrangements. In some bryophytes,
798:
has more retroelements in their sex chromosomes compare to
786:
sequences have also been identified in the Y-chromosome of
691:
556:
540:
477:, members of an allosome pair may differ from one another.
1407:
Nakamura M (May 2009). "Sex determination in amphibians".
2513:
2183:
2038:"Steps in the evolution of heteromorphic sex chromosomes"
43:
2036:
Charlesworth D, Charlesworth B, Marais G (August 2005).
2088:(1 ed.). John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. 2001-05-30.
1712:
1632:
1834:
746:
1801:
1627:
1625:
1446:. Sex determination and sex differentation in fish.
839:
and the third region called pseudoautosomal region.
1837:"Origin and domestication of papaya Yh chromosome"
851:or retrotransposition and size of Y remains same.
663:, only the incubation temperature determines sex (
1669:
1622:
1210:"Polycomb complexes in X chromosome inactivation"
2694:
1885:"Biological Basis of Heredity: Sex Linked Genes"
1326:
755:especially accumulation of long tandom repeats (
1518:
1516:
1514:
2008:"46,XX testicular disorder of sex development"
1877:
1797:
1795:
1441:
1367:. Cambridge University Press. pp. 22–68.
2499:
2253:
1802:Renner SS, Heinrichs J, Sousa A (July 2017).
1665:
1663:
1300:Twenty-five years of the sex-determining gene
1256:
1172:
423:
1631:
1511:
1409:Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology
1250:
994:46,XX testicular disorder of sex development
629:ambiguous outer genitalia or internal organs
579:C, and the Y chromosome is part of group G.
1792:
1201:
2506:
2492:
2260:
2246:
1660:
1489:. Oxford, UK: BIOS Scientific Publishers.
1207:
1065:
1063:
835:, second that stops recombining in modern
430:
416:
2217:
2152:
2142:
2053:
1860:
1819:
1605:
1548:
1484:
1352:
1329:"Genetic Mechanisms of Sex Determination"
1233:
682:Plant sex chromosomes are most common in
646:to an X chromosome in the XX pair during
1406:
1320:
751:Amplification of transposable elements,
566:
520:i.e. chromosomes which contain the same
494:
1522:
1060:
939:
665:temperature-dependent sex determination
14:
2695:
2545:Development of the reproductive system
1358:
1180:"How many chromosomes do people have?"
1071:"Allosome - Biology-Online Dictionary"
854:
528:in females, and an X chromosome and a
2487:
2241:
1963:. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
1646:10.1146/annurev-arplant-043015-111911
1186:. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
1127:
985:that result in learning disabilities.
1916:. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
1808:Journal of Systematics and Evolution
1298:Graves, Jennifer A. Marshall (2015)
653:
562:
2014:. U.S. National Library of Medice.
924:male and female sterility mutations
859:Ferns and lycophytes have bisexual
451:heterotypical chromosome, gonosomes
24:
747:Sequence composition and evolution
490:
25:
2714:
1361:"Mechanisms of sex determination"
559:(Polycomb Repressive Complex 2).
2677:
2676:
2267:
606:Sexual differentiation in humans
585:sex-determining region Y protein
499:Human male XY chromosomes after
204:Evolution of sexual reproduction
51:
2177:
2131:Journal of Evolutionary Biology
2118:
2078:
2029:
2018:from the original on 2013-03-30
2000:
1978:
1967:from the original on 2013-12-22
1949:
1938:from the original on 2013-04-08
1920:
1902:
1828:
1758:Cytogenetic and Genome Research
1749:
1715:Cytogenetic and Genome Research
1706:
1565:
1478:
1435:
1400:
1389:from the original on 2018-06-10
1341:from the original on 2019-04-13
1315:https://doi.org/10.1038/528343a
1281:from the original on 2022-08-11
1190:from the original on 2013-04-02
1110:from the original on 2016-02-04
1081:from the original on 2018-02-11
951:An allele is either said to be
2094:10.1002/9780470015902.a0028747
1634:Annual Review of Plant Biology
1292:
1208:Brockdorff N (November 2017).
1121:
1092:
902:
874:
297:Sexual reproduction in animals
13:
1:
1464:10.1016/S0044-8486(02)00057-1
1053:
989:Other complications include:
2659:Disorders of sex development
1421:10.1016/j.semcdb.2008.10.003
1373:10.1017/CBO9780511565274.003
1257:Kucinskas L, Just W (2005).
1100:"the definition of allosome"
1000:
983:sensory processing disorders
930:In the domesticated papaya (
469:allosomes. They differ from
174:Simultaneous hermaphroditism
7:
1990:NY Times Health Information
1487:Sex determination in plants
1327:Hake L, O'Connor C (2008).
1048:X0 sex-determination system
1043:ZW sex-determination system
1038:XY sex-determination system
1021:
10:
2719:
2210:10.1038/s41467-018-07648-2
1598:10.1038/s41467-017-01317-6
603:
597:
589:
307:Penile-vaginal intercourse
169:Sequential hermaphroditism
2672:
2641:
2570:
2525:
2448:
2434:
2407:
2284:
2275:
1684:10.1007/s12041-014-0326-7
1550:10.1016/j.cub.2017.01.052
1525:"Plant Sex Determination"
1523:Pannell JR (March 2017).
670:
159:Testis-determining factor
2578:Sex-determination system
1359:Hunter RH (March 1995).
600:Sex-determination system
152:Sex chromosome anomalies
90:Sex-determination system
2442:Human mitochondrial DNA
2012:Genetics Home Reference
1184:Genetics Home Reference
1014:fish (specifically the
879:Dioecy is common among
726:The high prevalence of
708:pseudoautosomal regions
686:, relatively common in
534:pseudoautosomal regions
2626:Sex determining gene:
2533:Sexual differentiation
2055:10.1038/sj.hdy.6800697
1910:"Sex-linked recessive"
1317:Retrieved 24 Jan 2022.
1226:10.1098/rstb.2017.0021
1075:www.biology-online.org
595:
518:homologous chromosomes
505:
275:Internal fertilization
270:External fertilization
73:Sexual differentiation
2598:Temperature-dependent
2190:Nature Communications
1932:Heredity and genetics
1853:10.1101/gr.183905.114
1578:Nature Communications
1485:Ainsworth CC (1999).
714:Marchantia polymorpha
590:Further information:
587:is located at Yp11.2.
570:
498:
485:Edmund Beecher Wilson
445:(also referred to as
115:Temperature-dependent
2562:Paramesonephric duct
2461:Human Genome Project
2436:Mitochondrial genome
940:Medical applications
813:deleterious mutation
775:Arabidopsis thaliana
2468:List of human genes
2202:2018NatCo...9.5136F
1928:"Sex-Linked Traits"
1672:Journal of Genetics
1590:2017NatCo...8.1140S
1541:2017CBio...27.R191P
1456:2002Aquac.208..191D
855:Non-vascular plants
640:sex-reversed XX men
581:Bands and sub-bands
292:Fungal reproduction
195:Sexual reproduction
1305:2022-01-11 at the
1220:(1733): 20170021.
1028:Fisher's principle
978:Fragile X syndrome
596:
506:
319:Human reproduction
302:Sexual intercourse
287:Plant reproduction
181:Intersex (biology)
2690:
2689:
2515:Sex determination
2481:
2480:
2473:Human archaeology
2430:
2429:
2144:10.1111/jeb.14096
2137:(12): 1797–1805.
2103:978-0-470-01617-6
1821:10.1111/jse.12266
1770:10.1159/000328831
1727:10.1159/000362142
761:retrotransposones
654:Other vertebrates
563:Sex determination
455:heterochromosomes
440:
439:
324:Lordosis behavior
127:Heterogametic sex
68:Sexual dimorphism
16:(Redirected from
2710:
2680:
2679:
2557:Mesonephric duct
2508:
2501:
2494:
2485:
2484:
2282:
2281:
2262:
2255:
2248:
2239:
2238:
2232:
2231:
2221:
2181:
2175:
2174:
2156:
2146:
2122:
2116:
2115:
2082:
2076:
2075:
2057:
2033:
2027:
2026:
2024:
2023:
2004:
1998:
1997:
1992:. Archived from
1982:
1976:
1975:
1973:
1972:
1953:
1947:
1946:
1944:
1943:
1934:. Khan Academy.
1924:
1918:
1917:
1906:
1900:
1899:
1897:
1896:
1887:. Archived from
1881:
1875:
1874:
1864:
1832:
1826:
1825:
1823:
1799:
1790:
1789:
1753:
1747:
1746:
1710:
1704:
1703:
1667:
1658:
1657:
1629:
1620:
1619:
1609:
1569:
1563:
1562:
1552:
1535:(5): R191–R197.
1520:
1509:
1508:
1482:
1476:
1475:
1439:
1433:
1432:
1404:
1398:
1397:
1395:
1394:
1356:
1350:
1349:
1347:
1346:
1324:
1318:
1296:
1290:
1289:
1287:
1286:
1254:
1248:
1247:
1237:
1205:
1199:
1198:
1196:
1195:
1176:
1170:
1169:
1136:(247): 163–172.
1125:
1119:
1118:
1116:
1115:
1096:
1090:
1089:
1087:
1086:
1067:
869:microchromosomes
845:genetic material
734:Rumex acetosella
677:flowering plants
577:chromosome group
516:. Autosomes are
508:In humans, each
504:
432:
425:
418:
354:Animal sexuality
282:Sexual selection
60:Biological terms
55:
30:
29:
21:
2718:
2717:
2713:
2712:
2711:
2709:
2708:
2707:
2693:
2692:
2691:
2686:
2668:
2637:
2566:
2521:
2519:differentiation
2512:
2482:
2477:
2444:
2426:
2403:
2271:
2266:
2236:
2235:
2182:
2178:
2123:
2119:
2104:
2084:
2083:
2079:
2034:
2030:
2021:
2019:
2006:
2005:
2001:
1996:on 6 July 2013.
1984:
1983:
1979:
1970:
1968:
1955:
1954:
1950:
1941:
1939:
1926:
1925:
1921:
1908:
1907:
1903:
1894:
1892:
1883:
1882:
1878:
1841:Genome Research
1833:
1829:
1800:
1793:
1754:
1750:
1711:
1707:
1668:
1661:
1630:
1623:
1570:
1566:
1529:Current Biology
1521:
1512:
1497:
1483:
1479:
1440:
1436:
1405:
1401:
1392:
1390:
1383:
1357:
1353:
1344:
1342:
1325:
1321:
1307:Wayback Machine
1297:
1293:
1284:
1282:
1255:
1251:
1206:
1202:
1193:
1191:
1178:
1177:
1173:
1126:
1122:
1113:
1111:
1098:
1097:
1093:
1084:
1082:
1069:
1068:
1061:
1056:
1024:
1003:
964:Color blindness
942:
905:
877:
857:
780:heterochromatin
749:
740:Viscum fischeri
690:and unknown in
688:vascular plants
673:
656:
608:
602:
594:
588:
565:
553:heterochromatin
500:
493:
491:Differentiation
459:idiochromosomes
443:Sex chromosomes
436:
369:Differentiation
359:Human sexuality
349:Plant sexuality
236:Spermatogenesis
132:Homogametic sex
28:
23:
22:
18:Sex chromosomes
15:
12:
11:
5:
2716:
2706:
2705:
2688:
2687:
2685:
2684:
2673:
2670:
2669:
2667:
2666:
2661:
2656:
2651:
2645:
2643:
2639:
2638:
2636:
2635:
2624:
2623:
2622:
2617:
2610:Sex chromosome
2607:
2606:
2605:
2600:
2595:
2590:
2585:
2574:
2572:
2568:
2567:
2565:
2564:
2559:
2554:
2553:
2552:
2542:
2541:
2540:
2529:
2527:
2523:
2522:
2511:
2510:
2503:
2496:
2488:
2479:
2478:
2476:
2475:
2470:
2465:
2464:
2463:
2452:
2450:
2449:Related topics
2446:
2445:
2440:
2438:
2432:
2431:
2428:
2427:
2425:
2424:
2419:
2413:
2411:
2409:Sex chromosome
2405:
2404:
2402:
2401:
2396:
2391:
2386:
2381:
2376:
2371:
2366:
2361:
2356:
2351:
2346:
2341:
2336:
2331:
2326:
2321:
2316:
2311:
2306:
2301:
2296:
2290:
2288:
2279:
2277:Nuclear genome
2273:
2272:
2265:
2264:
2257:
2250:
2242:
2234:
2233:
2176:
2117:
2102:
2077:
2048:(2): 118–128.
2028:
1999:
1977:
1948:
1919:
1901:
1876:
1847:(4): 524–533.
1827:
1814:(4): 333–339.
1791:
1764:(3): 213–219.
1748:
1721:(1–3): 87–95.
1705:
1678:(1): 241–277.
1659:
1640:(1): 397–420.
1621:
1564:
1510:
1495:
1477:
1450:(3): 191–364.
1434:
1415:(3): 271–282.
1399:
1381:
1351:
1319:
1291:
1269:(8): 633–640.
1249:
1200:
1171:
1142:10.1086/352001
1120:
1104:Dictionary.com
1091:
1058:
1057:
1055:
1052:
1051:
1050:
1045:
1040:
1035:
1033:Haldane's rule
1030:
1023:
1020:
1002:
999:
998:
997:
987:
986:
975:
968:
941:
938:
904:
901:
892:Pinus johannis
876:
873:
856:
853:
804:Microsatellite
753:tandom repeats
748:
745:
728:autopolyploidy
672:
669:
655:
652:
598:Main article:
564:
561:
492:
489:
481:Nettie Stevens
438:
437:
435:
434:
427:
420:
412:
409:
408:
407:
406:
401:
396:
388:
387:
381:
380:
379:
378:
377:
376:
371:
366:
356:
351:
343:
342:
336:
335:
334:
333:
332:
331:
326:
321:
316:
311:
310:
309:
294:
289:
284:
279:
278:
277:
272:
262:
261:
260:
255:
245:
244:
243:
238:
228:
223:
218:
217:
216:
211:
198:
197:
191:
190:
189:
188:
183:
178:
177:
176:
171:
161:
156:
155:
154:
149:
144:
137:Sex chromosome
134:
129:
124:
123:
122:
117:
112:
107:
102:
97:
87:
86:
85:
80:
70:
62:
61:
57:
56:
48:
47:
39:
38:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2715:
2704:
2701:
2700:
2698:
2683:
2675:
2674:
2671:
2665:
2662:
2660:
2657:
2655:
2652:
2650:
2649:Hermaphrodite
2647:
2646:
2644:
2640:
2633:
2629:
2625:
2621:
2618:
2616:
2613:
2612:
2611:
2608:
2604:
2603:Haplodiploidy
2601:
2599:
2596:
2594:
2591:
2589:
2586:
2584:
2581:
2580:
2579:
2576:
2575:
2573:
2571:Genetic basis
2569:
2563:
2560:
2558:
2555:
2551:
2548:
2547:
2546:
2543:
2539:
2536:
2535:
2534:
2531:
2530:
2528:
2524:
2520:
2516:
2509:
2504:
2502:
2497:
2495:
2490:
2489:
2486:
2474:
2471:
2469:
2466:
2462:
2459:
2458:
2457:
2454:
2453:
2451:
2447:
2443:
2439:
2437:
2433:
2423:
2420:
2418:
2415:
2414:
2412:
2410:
2406:
2400:
2397:
2395:
2392:
2390:
2387:
2385:
2382:
2380:
2377:
2375:
2372:
2370:
2367:
2365:
2362:
2360:
2357:
2355:
2352:
2350:
2347:
2345:
2342:
2340:
2337:
2335:
2332:
2330:
2327:
2325:
2322:
2320:
2317:
2315:
2312:
2310:
2307:
2305:
2302:
2300:
2297:
2295:
2292:
2291:
2289:
2287:
2283:
2280:
2278:
2274:
2270:
2263:
2258:
2256:
2251:
2249:
2244:
2243:
2240:
2229:
2225:
2220:
2215:
2211:
2207:
2203:
2199:
2195:
2191:
2187:
2180:
2172:
2168:
2164:
2160:
2155:
2150:
2145:
2140:
2136:
2132:
2128:
2121:
2113:
2109:
2105:
2099:
2095:
2091:
2087:
2081:
2073:
2069:
2065:
2061:
2056:
2051:
2047:
2043:
2039:
2032:
2017:
2013:
2009:
2003:
1995:
1991:
1987:
1981:
1966:
1962:
1961:PubMed Health
1958:
1952:
1937:
1933:
1929:
1923:
1915:
1911:
1905:
1891:on 2013-04-11
1890:
1886:
1880:
1872:
1868:
1863:
1858:
1854:
1850:
1846:
1842:
1838:
1831:
1822:
1817:
1813:
1809:
1805:
1798:
1796:
1787:
1783:
1779:
1775:
1771:
1767:
1763:
1759:
1752:
1744:
1740:
1736:
1732:
1728:
1724:
1720:
1716:
1709:
1701:
1697:
1693:
1689:
1685:
1681:
1677:
1673:
1666:
1664:
1655:
1651:
1647:
1643:
1639:
1635:
1628:
1626:
1617:
1613:
1608:
1603:
1599:
1595:
1591:
1587:
1583:
1579:
1575:
1568:
1560:
1556:
1551:
1546:
1542:
1538:
1534:
1530:
1526:
1519:
1517:
1515:
1506:
1502:
1498:
1496:0-585-40066-0
1492:
1488:
1481:
1473:
1469:
1465:
1461:
1457:
1453:
1449:
1445:
1438:
1430:
1426:
1422:
1418:
1414:
1410:
1403:
1388:
1384:
1382:9780521462181
1378:
1374:
1370:
1366:
1362:
1355:
1340:
1336:
1335:
1330:
1323:
1316:
1312:
1308:
1304:
1301:
1295:
1280:
1276:
1272:
1268:
1264:
1260:
1253:
1245:
1241:
1236:
1231:
1227:
1223:
1219:
1215:
1211:
1204:
1189:
1185:
1181:
1175:
1167:
1163:
1159:
1155:
1151:
1147:
1143:
1139:
1135:
1131:
1124:
1109:
1105:
1101:
1095:
1080:
1076:
1072:
1066:
1064:
1059:
1049:
1046:
1044:
1041:
1039:
1036:
1034:
1031:
1029:
1026:
1025:
1019:
1017:
1013:
1009:
995:
992:
991:
990:
984:
979:
976:
972:
969:
965:
962:
961:
960:
958:
954:
949:
947:
937:
935:
934:
933:Carica papaya
928:
925:
921:
920:
914:
910:
900:
898:
894:
893:
888:
887:
886:Ginkgo biloba
882:
872:
870:
864:
862:
852:
850:
846:
842:
838:
834:
833:
828:
824:
820:
819:
814:
809:
805:
801:
797:
796:
791:
790:
785:
781:
778:, present in
777:
776:
771:
766:
762:
758:
754:
744:
742:
741:
736:
735:
729:
724:
722:
721:M. polymorpha
717:
715:
709:
705:
701:
697:
693:
689:
685:
680:
678:
668:
666:
662:
651:
649:
645:
641:
637:
632:
630:
625:
621:
616:
613:
607:
601:
593:
586:
582:
578:
574:
569:
560:
558:
554:
550:
546:
542:
537:
535:
531:
527:
526:X chromosomes
523:
519:
515:
511:
503:
497:
488:
486:
482:
478:
476:
472:
468:
464:
460:
456:
452:
448:
444:
433:
428:
426:
421:
419:
414:
413:
411:
410:
405:
404:Hermaphrodite
402:
400:
397:
395:
392:
391:
390:
389:
386:
385:Sexual system
383:
382:
375:
372:
370:
367:
365:
362:
361:
360:
357:
355:
352:
350:
347:
346:
345:
344:
341:
338:
337:
330:
329:Pelvic thrust
327:
325:
322:
320:
317:
315:
312:
308:
305:
304:
303:
300:
299:
298:
295:
293:
290:
288:
285:
283:
280:
276:
273:
271:
268:
267:
266:
265:Fertilization
263:
259:
256:
254:
251:
250:
249:
246:
242:
239:
237:
234:
233:
232:
231:Gametogenesis
229:
227:
224:
222:
219:
215:
212:
210:
207:
206:
205:
202:
201:
200:
199:
196:
193:
192:
187:
184:
182:
179:
175:
172:
170:
167:
166:
165:
164:Hermaphrodite
162:
160:
157:
153:
150:
148:
145:
143:
140:
139:
138:
135:
133:
130:
128:
125:
121:
120:Haplodiploidy
118:
116:
113:
111:
108:
106:
103:
101:
98:
96:
93:
92:
91:
88:
84:
81:
79:
76:
75:
74:
71:
69:
66:
65:
64:
63:
59:
58:
54:
50:
49:
46:
45:
41:
40:
36:
32:
31:
19:
2664:Sex reversal
2620:Y chromosome
2615:X chromosome
2609:
2456:Human genome
2269:Human genome
2193:
2189:
2179:
2134:
2130:
2120:
2085:
2080:
2045:
2041:
2031:
2020:. Retrieved
2011:
2002:
1994:the original
1989:
1980:
1969:. Retrieved
1960:
1957:"Hemophilia"
1951:
1940:. Retrieved
1931:
1922:
1913:
1904:
1893:. Retrieved
1889:the original
1879:
1844:
1840:
1830:
1811:
1807:
1761:
1757:
1751:
1718:
1714:
1708:
1675:
1671:
1637:
1633:
1581:
1577:
1567:
1532:
1528:
1486:
1480:
1447:
1443:
1437:
1412:
1408:
1402:
1391:. Retrieved
1364:
1354:
1343:. Retrieved
1332:
1322:
1310:
1294:
1283:. Retrieved
1266:
1262:
1252:
1217:
1213:
1203:
1192:. Retrieved
1183:
1174:
1133:
1129:
1123:
1112:. Retrieved
1103:
1094:
1083:. Retrieved
1074:
1004:
988:
950:
943:
931:
929:
917:
906:
890:
884:
878:
865:
861:gametophytes
858:
840:
836:
830:
823:phylogenetic
816:
807:
800:S. latifolia
799:
793:
789:S. latifolia
787:
773:
770:S. latifolia
769:
765:plant genome
750:
738:
732:
725:
720:
712:
704:heterogamety
681:
674:
657:
644:translocated
633:
617:
609:
538:
530:Y chromosome
510:cell nucleus
507:
479:
475:diploid cell
458:
454:
450:
446:
442:
441:
253:spermatozoon
147:Y chromosome
142:X chromosome
136:
83:Virilization
78:Feminization
42:
2703:Chromosomes
2196:(1): 5136.
1584:(1): 1140.
1444:Aquaculture
1313:, 343–344.
913:Cytogenetic
909:angiosperms
903:Angiosperms
897:karyotyping
881:gymnosperms
875:Gymnosperms
849:duplication
795:S. vulgaris
784:chloroplast
661:sea turtles
549:deactivated
463:chromosomes
399:Gonochorism
186:Mating type
2022:2013-04-07
1971:2017-11-01
1942:2013-04-07
1895:2013-04-07
1393:2019-11-04
1345:2019-10-24
1311:Nature 528
1285:2022-03-29
1194:2013-04-03
1114:2018-02-22
1085:2018-02-22
1054:References
1016:swordtails
1008:Sylvioidea
971:Hemophilia
946:sex linked
841:H. lupulus
837:H. lupulus
832:H. lupulus
696:lycophytes
684:bryophytes
604:See also:
571:Schematic
314:Copulation
2630:(mammal)
2171:252543767
2112:208574438
1472:0044-8486
1001:Evolution
957:recessive
907:Cosexual
592:Karyogram
573:karyogram
514:autosomes
502:G-banding
471:autosomes
447:allosomes
364:Mechanics
340:Sexuality
241:Oogenesis
221:Germ cell
209:Anisogamy
2697:Category
2682:Category
2654:Intersex
2642:See also
2526:Overview
2286:Autosome
2228:30510159
2163:36156325
2154:10087220
2072:10026903
2064:15931241
2042:Heredity
2016:Archived
1965:Archived
1936:Archived
1871:25762551
1786:23042305
1778:21709414
1743:45809762
1735:24751661
1700:14956007
1692:24840848
1654:26653795
1616:29074958
1559:28267976
1505:50174640
1429:18996493
1387:Archived
1339:Archived
1334:Scitable
1303:Archived
1279:Archived
1275:16160410
1263:Medicina
1244:28947664
1188:Archived
1108:Archived
1079:Archived
1022:See also
953:dominant
827:ancestor
636:SRY gene
620:intersex
374:Activity
35:a series
33:Part of
2634:(birds)
2219:6277394
2198:Bibcode
1862:4381524
1607:5658415
1586:Bibcode
1537:Bibcode
1452:Bibcode
1235:5627167
1166:1919033
1012:teleost
919:Populus
818:Humulus
648:meiosis
624:chimera
612:diploid
226:Meiosis
214:Isogamy
2550:gonads
2538:humans
2226:
2216:
2169:
2161:
2151:
2110:
2100:
2070:
2062:
1914:PubMed
1869:
1859:
1784:
1776:
1741:
1733:
1698:
1690:
1652:
1614:
1604:
1557:
1503:
1493:
1470:
1427:
1379:
1273:
1242:
1232:
1164:
1158:389882
1156:
1150:230427
1148:
808:Silene
671:Plants
467:mammal
461:) are
394:Dioecy
248:Gamete
2632:DMRT1
2167:S2CID
2108:S2CID
2068:S2CID
1782:S2CID
1739:S2CID
1696:S2CID
1162:S2CID
1146:JSTOR
692:ferns
545:sperm
522:genes
457:, or
2517:and
2224:PMID
2159:PMID
2098:ISBN
2060:PMID
1867:PMID
1774:PMID
1731:PMID
1688:PMID
1650:PMID
1612:PMID
1555:PMID
1501:OCLC
1491:ISBN
1468:ISSN
1425:PMID
1377:ISBN
1271:PMID
1240:PMID
1154:PMID
1130:Isis
694:and
610:All
557:PRC2
541:ovum
483:and
258:ovum
2628:SRY
2214:PMC
2206:doi
2149:PMC
2139:doi
2090:doi
2086:eLS
2050:doi
1857:PMC
1849:doi
1816:doi
1766:doi
1762:134
1723:doi
1719:143
1680:doi
1642:doi
1602:PMC
1594:doi
1545:doi
1460:doi
1448:208
1417:doi
1369:doi
1230:PMC
1222:doi
1218:372
1138:doi
955:or
829:of
757:LTR
667:).
44:Sex
2699::
2593:ZW
2588:X0
2583:XY
2399:22
2394:21
2389:20
2384:19
2379:18
2374:17
2369:16
2364:15
2359:14
2354:13
2349:12
2344:11
2339:10
2222:.
2212:.
2204:.
2192:.
2188:.
2165:.
2157:.
2147:.
2135:35
2133:.
2129:.
2106:.
2096:.
2066:.
2058:.
2046:95
2044:.
2040:.
2010:.
1988:.
1959:.
1930:.
1912:.
1865:.
1855:.
1845:25
1843:.
1839:.
1812:55
1810:.
1806:.
1794:^
1780:.
1772:.
1760:.
1737:.
1729:.
1717:.
1694:.
1686:.
1676:93
1674:.
1662:^
1648:.
1638:67
1636:.
1624:^
1610:.
1600:.
1592:.
1580:.
1576:.
1553:.
1543:.
1533:27
1531:.
1527:.
1513:^
1499:.
1466:.
1458:.
1423:.
1413:20
1385:.
1375:.
1363:.
1337:.
1331:.
1309:,
1277:.
1267:41
1265:.
1261:.
1238:.
1228:.
1216:.
1212:.
1182:.
1160:.
1152:.
1144:.
1134:69
1132:.
1106:.
1102:.
1077:.
1073:.
1062:^
899:.
802:.
792:.
759:)
723:.
700:UV
650:.
631:.
536:.
453:,
449:,
110:ZO
105:ZW
100:XO
95:XY
37:on
2507:e
2500:t
2493:v
2422:Y
2417:X
2334:9
2329:8
2324:7
2319:6
2314:5
2309:4
2304:3
2299:2
2294:1
2261:e
2254:t
2247:v
2230:.
2208::
2200::
2194:9
2173:.
2141::
2114:.
2092::
2074:.
2052::
2025:.
1974:.
1945:.
1898:.
1873:.
1851::
1824:.
1818::
1788:.
1768::
1745:.
1725::
1702:.
1682::
1656:.
1644::
1618:.
1596::
1588::
1582:8
1561:.
1547::
1539::
1507:.
1474:.
1462::
1454::
1431:.
1419::
1396:.
1371::
1348:.
1288:.
1246:.
1224::
1197:.
1168:.
1140::
1117:.
1088:.
916:(
716:,
431:e
424:t
417:v
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.