26:
38:
98:
This section calculates the force required to cut a piece of material with a shearing action. The relevant information is the area of the material being sheared, i.e. the area across which the shearing action takes place, and the shear strength of the material. A round bar of steel is used as an
41:
A crack or tear may develop in a body from parallel shearing forces acting in opposite directions at different points of the body. If the forces were aligned with each other, they would elongate or shorten the body, depending on their direction, rather than tear or crack
99:
example. The shear strength is calculated from the tensile strength using a factor which relates the two strengths. In this case 0.6 applies to the example steel, known as EN8 bright, although it can vary from 0.58 to 0.62 depending on application.
163:, the strength comes from friction between the materials bolted together. Bolts are correctly torqued to maintain the friction. The shear force only becomes relevant when the bolts are not torqued.
230:
261:
29:
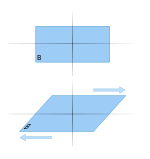
Shearing forces act in one direction at the top, and the opposite direction at the bottom, causing shearing
295:
62:
in a specific direction, and another part of the body in the opposite direction. When the forces are
30:
251:
8:
74:
257:
220:
82:: "If a plane is passed through a body, a force acting along this plane is called a
79:
47:
225:
290:
113:
To calculate the force to shear a 25 mm diameter bar of EN8 bright steel;
201:
N/mm) or 0.4 kN/mm and yield strength is 0.60 times tensile strength, 240
284:
68:
160:
63:
20:
214:
59:
25:
182:
kN/mm and the yield strength is 0.90 times tensile strength, 1080
106:
MPa and mild steel, for comparison, has a tensile strength of 400
253:
Schaum's
Outline of Theory and Problems of Strength of Materials
217:, mechanical properties of different grades of steel fasteners
166:
A bolt with property class 12.9 has a tensile strength of 1200
147:
tonne-force × 0.6 (to change force from tensile to shear) = 24
37:
16:
Coplanar forces acting on the same body in opposite directions
156:
55:
189:
A bolt with property class 4.6 has a tensile strength of 400
282:
93:
249:
78:. Shear force can also be defined in terms of
231:Newton's laws of motion § Newton's third law
66:(aligned with each other), they are called
117:area of the bar in mm = (12.5)(π) ≈ 490.8
256:. McGraw-Hill Professional. p. 82.
102:EN8 bright has a tensile strength of 800
36:
24:
243:
283:
13:
14:
307:
250:William A. Nash (1 July 1998).
1:
236:
94:Force required to shear steel
7:
208:
10:
312:
18:
58:acting on one part of a
43:
34:
40:
28:
19:Further information:
155:When working with a
205:MPa in this case.
186:MPa in this case.
75:compression forces
44:
35:
296:Civil engineering
263:978-0-07-046617-3
221:Cantilever method
303:
275:
274:
272:
270:
247:
204:
200:
196:
192:
185:
181:
177:
173:
169:
150:
146:
139:
135:
131:
127:
120:
109:
105:
311:
310:
306:
305:
304:
302:
301:
300:
281:
280:
279:
278:
268:
266:
264:
248:
244:
239:
211:
202:
198:
194:
190:
183:
179:
175:
171:
167:
148:
144:
137:
133:
129:
125:
118:
107:
103:
96:
52:shearing forces
48:solid mechanics
23:
17:
12:
11:
5:
309:
299:
298:
293:
277:
276:
262:
241:
240:
238:
235:
234:
233:
228:
223:
218:
210:
207:
153:
152:
141:
122:
95:
92:
88:shearing force
69:tension forces
54:are unaligned
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
308:
297:
294:
292:
289:
288:
286:
265:
259:
255:
254:
246:
242:
232:
229:
227:
224:
222:
219:
216:
213:
212:
206:
187:
164:
162:
159:or tensioned
158:
142:
128:kN/mm × 490.8
123:
116:
115:
114:
111:
100:
91:
89:
85:
81:
77:
76:
71:
70:
65:
61:
57:
53:
49:
39:
32:
27:
22:
267:. Retrieved
252:
245:
226:Résal effect
188:
178:N/mm) or 1.2
165:
161:bolted joint
154:
112:
101:
97:
87:
83:
73:
67:
51:
45:
21:Shear stress
151:tonne-force
140:tonne-force
132:mm = 392.64
84:shear force
31:deformation
285:Categories
237:References
215:ASTM F568M
64:collinear
209:See also
197:MPa = 1
174:MPa = 1
157:riveted
136:kN ≈ 40
269:20 May
260:
203:
199:
195:
193:MPa (1
191:
184:
180:
176:
172:
170:MPa (1
168:
149:
145:
138:
134:
130:
126:
119:
108:
104:
80:planes
56:forces
291:Force
110:MPa.
271:2012
258:ISBN
60:body
124:0.8
90:."
86:or
72:or
46:In
42:it.
287::
143:40
121:mm
50:,
273:.
33:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.