20:
153:, to a quantum of light, as a function of wavelength. In other contexts, the spectral sensitivity is expressed as the relative response per light energy, rather than per quantum, normalized to a peak value of 1, and a quantum efficiency is used to calibrate the sensitivity at that peak wavelength. In some linear applications, the spectral sensitivity may be expressed as a spectral
126:
can be extended to be wavelength dependent, incorporating the spectral sensitivity. When the sensor system is linear, its spectral sensitivity and spectral responsivity can both be decomposed with similar basis functions. When a system's responsivity is a fixed monotonic nonlinear function, that
134:, however, have a very context-dependent (coupled) nonlinear response, which complicates the analysis of their spectral sensitivities from experimental data. In spite of these complexities, however, the conversion of light energy spectra to the effective stimulus, the excitation of the
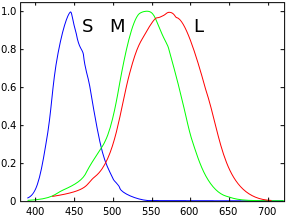
92:, and that they differ in their sensitivity to different wavelengths of light. It has been established that the maximum spectral sensitivity of the human eye under daylight conditions is at a wavelength of 555
32:
440:
521:
494:
467:
409:
127:
nonlinearity can be estimated and corrected for, to determine the spectral sensitivity from spectral input–output data via standard linear methods.
382:
297:
115:
films, the spectral sensitivity is chosen to be appropriate to the phosphors that respond to X-rays, rather than being related to human vision.
243:
602:
575:
548:
138:, is quite linear, and linear characterizations such as spectral sensitivity are therefore quite useful in describing many properties of
270:
355:
338:
280:
35:
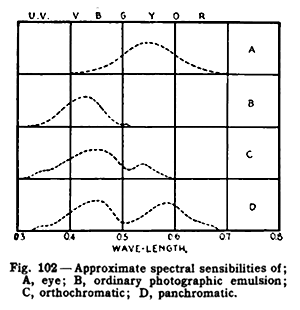
1916 plot of "spectral sensibilities." The author also uses the more modern term "spectral sensitivity" in the same book.
616:
585:
558:
531:
504:
477:
450:
423:
392:
365:
311:
253:
496:
Digital Image
Analysis of Microbes: Imaging, Morphometry, Fluorometry and Motility Techniques and Applications
103:, film and sensors are often described in terms of their spectral sensitivity, to supplement their
206:
228:
638:
8:
643:
16:
Relative efficiency of detection of a signal as a function of its frequency or wavelength
200:
174:
146:
612:
581:
554:
527:
500:
473:
446:
419:
388:
361:
334:
307:
276:
269:
Gross, Herbert; Blechinger, Fritz; Achtner, Bertram (2008). Gross, Herbert H. (ed.).
249:
604:
Analysis and
Application of Analog Electronic Circuits to Biomedical Instrumentation
111:. A database of camera spectral sensitivity is created and its space analyzed. For
89:
85:
380:
64:, spectral sensitivity is used to describe the different characteristics of the
179:
330:
What is the space of spectral sensitivity functions for digital color cameras?
632:
326:
149:, that is, as probability of getting a quantum reaction, such as a captured
328:
154:
139:
135:
123:
108:
104:
65:
61:
58:
24:
303:
100:
31:
51:
523:
Contrast
Sensitivity of the Human Eye and Its Effects on Image Quality
608:
93:
81:
73:
47:
415:
150:
69:
381:
Glenn E. Healey; Steven A. Shafer & Lawrence B. Wolff (1992).
327:
Jun Jiang; Dengyu Liu; Jinwei Gu & Sabine Süsstrunk (2013).
158:
131:
119:
77:
19:
112:
43:
162:
550:
Optics and lasers: including fibers and optical waveguides
492:
275:. Vol. 4. Weinheim, Germany: WILEY-VCH. p. 40.
268:
122:
systems, where the output is easily quantified, the
84:. It is known that the rod cells are more suited to
353:
600:
519:
241:
407:
145:Spectral sensitivity is sometimes expressed as a
96:, while at night the peak shifts to 507 nm.
630:
295:
198:
573:
130:The responses of the rod and cone cells of the
27:spectra) of human cone cells, S, M, and L types
222:
465:
442:Adaptive mechanisms in the ecology of vision
438:
42:is the relative efficiency of detection, of
546:
493:M. H. F. Wilkinson & F. Schut (1998).
577:Survey of Instrumentation and Measurement
245:Visual Perception: A Clinical Orientation
225:Fundamentals of Sensation and Perception
30:
18:
631:
202:Light and shade and their applications
46:or other signal, as a function of the
354:John Ball & Tony Price (1995).
205:. D. Van Nostrand Company. p.
23:Spectral sensitivities (normalized
13:
14:
655:
594:
567:
540:
513:
486:
459:
432:
401:
374:
357:Chesneys' Radiographic Imaging
347:
320:
289:
262:
235:
216:
211:spectral sensitivity luckiesh.
192:
1:
185:
248:. McGraw-Hill Professional.
7:
601:Robert B. Northrop (2004).
520:Peter G. J. Barten (1999).
272:Handbook of optical systems
242:Steven H. Schwartz (2004).
168:
10:
660:
408:Steven K. Shevell (2003).
296:Michael Langford (1998).
199:Matthew Luckiesh (1916).
574:Stephen A. Dyer (2001).
360:. Blackwell Publishing.
499:. John Wiley and Sons.
472:. John Wiley and Sons.
229:Oxford University Press
223:Michael Levine (2000).
36:
28:
466:Arne Valberg (1995).
439:S. N. Archer (1999).
157:, with units such as
105:characteristic curves
34:
22:
411:The Science of Color
387:. A. K. Peters Ltd.
384:Physics-Based Vision
299:Advanced Photography
107:that describe their
40:Spectral sensitivity
547:Matt Young (1993).
469:Light Vision Color
175:Frequency response
147:quantum efficiency
88:and cone cells to
37:
29:
340:978-1-4673-5053-2
282:978-3-527-40380-6
651:
623:
622:
598:
592:
591:
571:
565:
564:
544:
538:
537:
517:
511:
510:
490:
484:
483:
463:
457:
456:
436:
430:
429:
405:
399:
398:
378:
372:
371:
351:
345:
344:
324:
318:
317:
293:
287:
286:
266:
260:
259:
239:
233:
232:
227:(3rd ed.).
220:
214:
213:
196:
659:
658:
654:
653:
652:
650:
649:
648:
629:
628:
627:
626:
619:
599:
595:
588:
572:
568:
561:
545:
541:
534:
518:
514:
507:
491:
487:
480:
464:
460:
453:
437:
433:
426:
406:
402:
395:
379:
375:
368:
352:
348:
341:
325:
321:
314:
294:
290:
283:
267:
263:
256:
240:
236:
221:
217:
197:
193:
188:
171:
90:photopic vision
86:scotopic vision
54:of the signal.
17:
12:
11:
5:
657:
647:
646:
641:
625:
624:
617:
593:
586:
580:. Wiley-IEEE.
566:
559:
539:
532:
526:. SPIE Press.
512:
505:
485:
478:
458:
451:
431:
424:
400:
393:
373:
366:
346:
339:
319:
312:
288:
281:
261:
254:
234:
215:
190:
189:
187:
184:
183:
182:
180:Orthochromasia
177:
170:
167:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
656:
645:
642:
640:
637:
636:
634:
620:
618:0-8493-2143-3
614:
610:
606:
605:
597:
589:
587:0-471-39484-X
583:
579:
578:
570:
562:
560:3-540-65741-X
556:
552:
551:
543:
535:
533:0-8194-3496-5
529:
525:
524:
516:
508:
506:0-471-97440-4
502:
498:
497:
489:
481:
479:0-470-84902-9
475:
471:
470:
462:
454:
452:0-7923-5319-6
448:
444:
443:
435:
427:
425:0-444-51251-9
421:
417:
413:
412:
404:
396:
394:0-86720-295-5
390:
386:
385:
377:
369:
367:0-632-03901-9
363:
359:
358:
350:
342:
336:
332:
331:
323:
315:
313:0-240-51486-6
309:
305:
301:
300:
292:
284:
278:
274:
273:
265:
257:
255:0-07-141187-9
251:
247:
246:
238:
230:
226:
219:
212:
208:
204:
203:
195:
191:
181:
178:
176:
173:
172:
166:
164:
160:
156:
152:
148:
143:
141:
137:
133:
128:
125:
121:
116:
114:
110:
106:
102:
97:
95:
91:
87:
83:
79:
75:
71:
67:
66:photopigments
63:
60:
55:
53:
49:
45:
41:
33:
26:
21:
639:Color vision
603:
596:
576:
569:
553:. Springer.
549:
542:
522:
515:
495:
488:
468:
461:
445:. Springer.
441:
434:
410:
403:
383:
376:
356:
349:
329:
322:
298:
291:
271:
264:
244:
237:
224:
218:
210:
201:
194:
155:responsivity
144:
140:color vision
136:photopigment
129:
124:responsivity
117:
109:responsivity
98:
62:neuroscience
56:
39:
38:
25:responsivity
304:Focal Press
101:photography
644:Radiometry
633:Categories
186:References
74:cone cells
52:wavelength
609:CRC Press
70:rod cells
48:frequency
416:Elsevier
333:. IEEE.
169:See also
151:electron
159:amperes
80:of the
76:in the
68:in the
615:
584:
557:
530:
503:
476:
449:
422:
391:
364:
337:
310:
279:
252:
132:retina
120:sensor
78:retina
59:visual
113:X-ray
44:light
613:ISBN
582:ISBN
555:ISBN
528:ISBN
501:ISBN
474:ISBN
447:ISBN
420:ISBN
389:ISBN
362:ISBN
335:ISBN
308:ISBN
277:ISBN
250:ISBN
163:watt
161:per
72:and
118:In
99:In
82:eye
57:In
50:or
635::
611:.
607:.
418:.
414:.
306:.
302:.
209:.
207:95
165:.
142:.
94:nm
621:.
590:.
563:.
536:.
509:.
482:.
455:.
428:.
397:.
370:.
343:.
316:.
285:.
258:.
231:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.