360:
411:. The duration of physical therapy a patient receives varies upon the severity of spondylolysis, however typically ranges from three to six months. The goal of physical therapy is to minimize movement at the unstable defect of the pars interarticularis. Once a patient completes physical therapy, and displays no symptoms or inflammation in the lower back, they are cleared to continue with daily or athletic activities. However, a patient may need to maintain a variety of rehabilitation techniques after physical therapy to prevent the recurrence of spondylolysis.
485:: This procedure is recommended when a set of vertebrae becomes loose or unstable. The surgeon joins two or more bones (vertebrae) together through the use of metal rods, screws, and bone grafts. The bone grafts complete their fusion in 4–8 months following the surgery, securing the spine in the correct position. The procedure is also used to treat spinal instability, fractures in the lumbar spine and, severe degenerative disc disease. The process is relatively non-invasive, performed through small incisions and has a high success rate.
462:) to control and limit spinal movement, and reduce stress on the injured spinal segment. Bracing immobilizes the spine in a flexed position for a short period to allow healing of the bony defect in the pars interarticularis. An antilordotic brace commonly utilizes a plastic component that is contoured to closely fit the body. Antilordotic bracing subsequently reduces the athlete's symptoms by decreasing the amount of stress on the low back, and allows a prompt return to sport for athletes. Typically, bracing is utilized for 6–12 weeks.
377:
351:
grey ranging from white to black. A vertebra with a fracture or defect of the pars interarticularis will have a dark mark through this region of bone. Since this is difficult to see on the AP (anterior posterior) x-ray view an oblique x-ray of the lumbar spine can usually identify the spondylolysis. If inconclusive a further CT scan can produce a 3-dimensional images to more clearly show the defect although the exam increases the patients radiation dose by at least an order of magnitude than plain x-rays.
314:
178:, leaving points of weakness in the spine. This leaves young athletes at increased risk, particularly when involved in repetitive hyperextension and rotation across the lumbar spine. Spondylolysis is a common cause of low back pain in preadolescents and adolescent athletes, as it accounts for about 50% of all low back pain. It is believed that both repetitive trauma and an inherent genetic weakness can make an individual more susceptible to spondylolysis.
442:
program. There should be restriction of heavy lifting, excessive bending, twisting and avoidance of any work, recreational activities or participation in sport that causes stress to the lumbar spine. Activity restriction can help eliminate and control a patient's symptoms so they are able to resume their normal activities. Activity restriction is most commonly used in conjunction with other rehabilitation techniques including bracing.
451:
47:
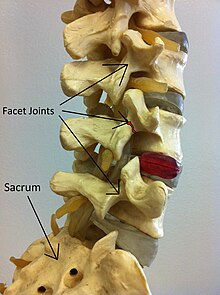
290:, which form joints that link the vertebrae together. When examining the vertebra, the pars interarticularis is the bony segment between the superior and inferior articular facet joints located anterior to the lamina and posterior to the pedicle. Separation of the pars interarticularis occurs when spondylolysis is present in the spinal column.
419:
The aim of deep abdominal co-contraction exercises is to train muscles surrounding the lumbar spine which provide stability of the spine. Spondylolysis results in a spinal instability and disrupts patterns of co-recruitment between muscle synergies. Specifically, local muscles that attach directly to
393:
MRI is a newer technique used to diagnose spondylolysis and is favorable for a few reasons. The MRI is much more accurate than the x-ray and also does not use radiation. The MRI uses powerful magnets and radio frequencies to produce very detailed images of many different densities of tissue including
384:
Commonly known as a CT Scan or CAT scan, this form of imaging is very similar to x-ray technology but produces many more images than an x-ray does. The multiple images produce cross-sectional views not possible with an x-ray. This allows a physician or radiologist to examine the images from many more
173:
The cause of spondylolysis remains unknown, however many factors are thought to contribute to its development. The condition is present in up to 6% of the population, the majority of which usually present asymptomatically. Research supports that there are hereditary and acquired risk factors that can
441:
Activity restriction of spondylolysis is advised for a short period of time once the patient becomes symptomatic, followed by a guided physical therapy program. Once spondylolysis has been diagnosed, treatment often consists of a short rest period of two to three days, followed by a physical therapy
520:
It is also critical to educate the athletes on the rehabilitation process so they know what to expect. For instance, explaining what activities to avoid and will cause pain as well as the duration of the treatment process. In addition, it is important to select the correct treatment option for each
428:
play a direct role in stabilizing the lumbar spine. Instead the local muscles in individuals with spondylolysis are vulnerable to dysfunction, which results in abnormal spinal stability causing chronic low back pain. To compensate, the large torque producing global muscles are used to stabilize the
297:
of the bone, and is especially common in adolescents who over-train in activities. The pars interarticularis is vulnerable to fracture during spinal hyperextension, especially when combined with rotation, or when experiencing a force during a landing. This stress fracture most commonly occurs where
256:
Although this condition can be caused by repetitive trauma to the lumbar spine in strenuous sports, other risk factors can also predispose individuals to spondylolysis. Males are more commonly affected by spondylolysis than females. In one study looking at youth athletes, it was found that the mean
465:
In order for a brace to be effective, it must be worn every day for the required amount of time. Patients are given a brace schedule determined by their physical therapist that explains the amount of time the brace must be worn daily. A brace's effectiveness increases with adherence to the bracing
432:
In one study, patients are taught to train the co-contraction of deep abdominal muscles and lumbar multifidus in static postures, functional tasks and aerobic activities. This technique was shown to reduce pain and functional disability when compared to other conservative treatments. These results
512:
Frustration, anger, confusion, fear and depression are some of the psychological factors that injured athletes experience, therefore a debilitating injury can have a large impact on an athlete's mental well-being. These psychological factors can also affect recovery and return to sport as fear of
350:
X-rays (electromagnetic radiation) are projected through the body to produce an image of its internal structures. The radiation is more attenuated (absorbed) by the denser tissues of the body (i.e. bone) than the softer tissues (i.e. muscles, organs, etc.) creating a picture composed of shades of
367:
Also known as a bone scan, bone scintigraphy involves the injection of a small amount of radioactive tracer into the bloodstream. This tracer decays and emits radioactive energy which can be detected by a special camera. The camera produces a black and white image where areas shown as dark black
516:
Social factors can also impact the cognitive, behavioural and physical responses to injury. More specifically, social isolation from the team can have a profound psychological effect. This makes it essential to provide social support through supportive listening, emotional support, personal
174:
make one more susceptible to the defect. The disorder is generally more prevalent in males than in females and tends to occur earlier in males due to their involvement in more strenuous activities at a younger age. In a young athlete, the spine is still growing; there are many
265:
Spondylolysis is a bony defect or fracture within the pars interarticularis of the vertebral arch in the spinal column. The vast majority of spondylolysis occur in the lumbar vertebrae, however it can also be seen in cervical vertebrae. The lumbar vertebra consist of a body,
186:
Sports involving repetitive or forceful hyperextension of the spine, especially when combined with rotation are the main mechanism of injury for spondylolysis. The stress fracture of the pars interarticularis occurs on the side opposite to activity. For instance, for a
703:
Debnath, U. K., Freeman, B. J. C., Gregory, P., de la Harpe, D., Kerslake, R. W. and Webb, J.K. Clinical outcome and return to sport after the surgical treatment of spondylolysis in young athletes. Journal of Bone and Joint
Surgery, British Volume. 2003, 85(2):
466:
schedule. Patients that do not follow their bracing schedule are more likely to have their symptoms progress. Research has demonstrated that when braces are used as prescribed with full compliance, they are successful at preventing spondylolysis progression.
385:
angles than an x-ray allows. For this reason the CT scan is much more accurate in detecting spondylolysis than an x-ray. Bone scintigraphy combined with CT scan is considered the gold standard which means that it is best at detecting spondylolysis.
433:
also had a long- term effect in reducing levels of pain and functional disability. This is because motor programming eventually became automatic, and conscious control was no longer needed to contract the deep abdominal muscles during activities.
816:
O'Sullivan, P. B., Phyty, D. M., Twomey, L. T., & Allison, G. T.Evaluation of
Specific Stabilizing Exercise in the Treatment of Chronic Low Back Pain with Radiologic Diagnosis of Spondylolysis or Spondylolisthesis. Spine. 1997,
508:
Spondylolysis can have a huge impact on a young athlete's career, and may impede their future ability to perform. It is important to understand how social and psychological factors may affect rehabilitation of an injured athlete.
368:
indicate bone damage of some kind. If there is a black spot in the lumbar vertebrae (e.g. L5) this indicates damage and potentially spondylolysis. If this test is positive, a CT scan is usually ordered to confirm spondylolysis.
115:
In majority of cases, spondylolysis presents asymptomatically, which can make diagnosis both difficult and incidental. When a patient does present with symptoms, there are general signs and symptoms a clinician will look for:
590:
Iwamoto, J., Takeda, T., Wakano, K. Returning athletes with severe low back pain and spondylolysis to original sporting activities with conservative treatment. Sports
Scandinavian Journal of Medicine and Science in Sports.
959:
944:
915:
Klenk, CA. Psychological
Response to Injury, Recovery and Social Support: A Survey of Athletes at an NCAA Division I University Digital Commons at University of Rhode Island. Senior Honors Project. 2006.
619:
Syrmou, E., Tsitsopoulos, P. P., Marinopoulos, D., Tsonidis, C., Anagnostopoulos, I., & Tsitsopoulos, P. D.Spondylolysis: A Review and
Reappraisal. H Quarterly Medical Journal. 2010;14(1): 17–21
685:
Canzonieri, C., & Pilloud, M. A. The
Occurrence and Possible and Aetiology of spondylolysis in a Pre-Contact California Population. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology. 2012, 24:602-613
892:
Deguchi M, Rapoff AJ, Zdeblick TA. Posterolateral fusion for isthmic spondylolisthesis in adults: Analysis of fusion rate and clinical results. Journal of Spinal
Disorders. 1998;11:459-464.
842:
Bergmann TF, Hyde TE, Yochum TR. Active or
Inactive Spondylolysis and/or Spondylolisthesis: What's the Real Cause of Back Pain? Journal of the Neuromusculoskeletal System. 2002:10:70-78.
521:
individual. For conservative methods, adherence to the exercise requires motivated patients as it can be tedious and time-consuming. For instance, one study looking at deep abdominal
740:
Masci L, Pike J, Malara F, Phillips B, Bennell K, Brukner P. Use of the one-legged hyperextension test and magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of active spondylolysis.
257:
age of individuals with spondylolysis was 20 years of age. Spondylolysis also runs in families suggesting a hereditary component such as a predisposition to weaker vertebrae.
407:
Treatment for spondylolysis ranges from bracing, activity restriction, extension exercises, flexion exercises and deep abdominal strengthening, that is administered through
474:
Most patients with spondylolysis do not require surgery but, if the symptoms are not relieved with non-surgical treatments, or when the condition progresses to high grade
694:
McCleary, M. D. and
Congeni, J. A. Current concepts in the diagnosis and treatment of spondylolysis in young athletes. Current sports medicine reports. 2007;6(1):62-66.
499:
from the bony ring of the vertebra to reduce the pressure on the spinal cord. The laminectomy is commonly performed on the vertebrae in the lower back and in the neck.
874:
Parkview Spine
Institute. Treatment Options for Pediatric/Adolescent Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis - Parkview Orthopedics. Parkview Orthopedics. Available at:
804:
Pizzutillo, PD, Hummer, CD. Nonoperative Treatment for Painful Adolescent Spondylolysis or Spondylolisthesis. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics. 1989;9(5):538–540.
875:
676:
McTimoney, M. & Micheli, L. J. Current Evaluation and Management of Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis. Current Sports Medicine Reports. 2003, 2:41–46
603:
Dubousset, J. Treatment of Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis in Children and Adolescents. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 1997;337:77–85.
1059:
833:
Iwamoto, J. Return to sports activity by athletes after treatment of spondylolysis. World Journal of Orthopedics. 2010;1(1):26.
713:
Standaert, C.J., Herring, S.A., Cole, A.J., Stratton, S.A. The Lumbar Spine and Sports. Low Back Pain Handbook. 2003:385–404.
1329:
876:
http://parkviewspine.com/patient-education/treatment-options-for-pediatricadolescent-spondylolysis-and-spondylolisthesis/
634:
556:
513:
re-injury often prevents athletes from adhering to rehabilitation and returning to their sport at full intensity.
1324:
723:
Cianfoni A, Cerase A, Magarelli N, Bonomo L. Lumbar spondylolysis: a review. Skeletal Radiology. 2011;40:683-700.
856:
Boston Brace: The Orthotics and Prosthetics Leaders. Boston Overlap Brace. Boston Overlap Brace. Available at:
653:
Humphreys, D. "Lecture on Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis". . Western University Kinesiology Program; 2015.
633:
Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis of the Lumbar Spine. Children's Orthopaedics, Mass General. Available at:
906:
Tenenbaum, G. & Eklund, RC. Handbook of Sport Psychology. Psychology. John Wiley & Sons Inc. 2007, 3
1052:
496:
271:
425:
331:
326:
There are several imaging techniques used to diagnose spondylolysis. Common imaging techniques include
1293:
267:
1117:
974:
1280:
1045:
542:
1298:
1156:
857:
758:
495:
occurs in conjunction with spondylolysis. The procedure surgically removes part or all of the
359:
1303:
565:
478:, then patients may require surgery. There are two main types of surgery for this condition:
275:
92:
570:
8:
963:
722:
525:
reported that it can take as long a 4–5 weeks to achieve this pattern of co-contraction.
522:
287:
175:
54:
Spondylolysis (wrong descriptions: the upper 3 arrows should be partes interarticulares)
1288:
458:
Acute spondylolysis is most commonly treated through the use of an antilordotic brace (
279:
104:
968:
1204:
1178:
985:
792:
775:
475:
421:
335:
307:
71:
59:
28:
1025:
376:
306:
sacrum (L5-S1). A significant number of individuals with spondylolysis will develop
1173:
1083:
635:
http://www.massgeneral.org/ortho-childrens/conditions-treatments/spondylolysis.aspx
408:
100:
662:
1248:
1216:
979:
538:
492:
294:
283:
1221:
1209:
1068:
990:
96:
953:
1318:
1270:
1253:
1136:
482:
363:
Bone scintigraphy showing black marks where pelvic bone damage has occurred.
1163:
459:
313:
188:
299:
1194:
1151:
1122:
488:
124:
64:
24:
20:
936:
787:
Body MRI - magnetic resonance imaging of the chest, abdomen and pelvis.
303:
1258:
551:
534:
789:
Body MRI - magnetic resonance imaging of the chest, abdomen and pelvis
1243:
1235:
1101:
1020:
996:
16:
Defect or fracture in the pars interarticularis of the vertebral arch
1263:
1168:
1096:
1091:
194:
Spondylolysis has a higher occurrence in the following activities:
1001:
450:
1037:
560:
339:
46:
948:
191:
player, the fracture occurs on the left side of the vertebrae.
327:
76:
858:
http://www.bostonbrace.com/content/boston_overlap_brace.asp
759:
https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003337.htm
246:
Ultimate Frisbee (especially during impact from laying out)
414:
380:
Cross-sectional image of a vertebra showing spondylolysis.
546:
80:
926:
573:, but his spondylolysis forced him out of the sport.
528:
136:
Visible on diagnostic imaging (Scottie dog fracture)
793:http://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=bodymr
776:http://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=bodyct
503:
1316:
99:. The vast majority of cases occur in the lower
310:, which is true for 50-81% of this population.
103:(L5), but spondylolysis may also occur in the
1053:
454:Antilordotic lumbosacral brace (Boston brace)
569:. He initially aspired to be a professional
147:Pain that radiates into the buttocks or legs
317:Pars interarticularis marked with red lines
1060:
1046:
402:
159:Pain aggravated with lumbar hyperextension
156:Pain that worsens after strenuous activity
45:
753:X-ray: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia.
449:
375:
358:
312:
436:
415:Deep abdominal co-contraction exercises
293:Spondylolysis is typically caused by a
153:Pain that can restrict daily activities
127:(placed in hyperextension and rotation)
1317:
902:
900:
898:
888:
886:
884:
517:assistance, and reality conformation.
371:
91:is a defect or stress fracture in the
1041:
870:
868:
866:
852:
850:
848:
829:
827:
825:
823:
812:
810:
736:
734:
732:
730:
649:
647:
645:
643:
162:Difficulty in movement in spinal cord
150:Onset of pain can be acute or gradual
110:
672:
670:
629:
627:
625:
615:
613:
611:
609:
599:
597:
354:
895:
881:
13:
1067:
863:
845:
820:
807:
742:British Journal of Sports Medicine
727:
707:
640:
260:
133:Unilateral tenderness on palpation
14:
1341:
922:
667:
622:
606:
594:
529:Notable people with spondylolysis
302:lumbar spine transitions to the
909:
836:
798:
781:
764:
755:US National Library of Medicine
747:
716:
697:
504:Implications for rehabilitation
181:
688:
679:
656:
584:
1:
577:
1281:Intervertebral disc disorder
420:the spine are affected. The
397:
321:
7:
10:
1346:
1330:Vertebral column disorders
878:. Accessed March 27, 2016.
860:. Accessed March 27, 2016.
795:. Accessed March 30, 2016.
778:. Accessed March 30, 2016.
761:. Accessed March 30, 2016.
469:
445:
286:and superior and inferior
130:Excessive lordotic posture
123:Pain on completion of the
18:
1294:Degenerative disc disease
1279:
1234:
1187:
1144:
1135:
1110:
1082:
1075:
1011:
930:
637:. Accessed March 28, 2016
70:
58:
53:
44:
39:
345:
168:
144:Unilateral low back pain
19:Not to be confused with
537:: Actor who played the
491:: Often performed when
403:Conservative management
394:bone and soft tissues.
1325:Deforming dorsopathies
1299:Spinal disc herniation
1157:Ankylosing spondylitis
791:. 2014. Available at:
774:. 2016. Available at:
757:. 2014. Available at:
455:
388:
381:
364:
318:
1304:Facet joint arthrosis
1118:Scheuermann's disease
453:
426:transversus abdominis
379:
362:
316:
276:pars interarticularis
93:pars interarticularis
770:Body CT (CAT Scan).
663:Scottie dog fracture
539:eleventh incarnation
437:Activity restriction
219:Association Football
176:ossification centers
591:2004;14(6):346–351.
372:Computed tomography
340:Computed Tomography
1012:External resources
772:Body CT (CAT Scan)
744:. 2006;40:940-946.
456:
382:
365:
319:
280:transverse process
111:Signs and symptoms
105:cervical vertebrae
1312:
1311:
1230:
1229:
1205:Spondylolisthesis
1131:
1130:
1035:
1034:
817:22(24):2959-2967.
476:spondylolisthesis
422:lumbar multifidus
355:Bone scintigraphy
338:(Bone Scan), and
336:Bone Scintigraphy
308:spondylolisthesis
216:Gridiron Football
86:
85:
72:Diagnostic method
34:Medical condition
29:Spondylolisthesis
1337:
1188:non inflammatory
1174:Spondylodiscitis
1142:
1141:
1084:Spinal curvature
1080:
1079:
1062:
1055:
1048:
1039:
1038:
928:
927:
916:
913:
907:
904:
893:
890:
879:
872:
861:
854:
843:
840:
834:
831:
818:
814:
805:
802:
796:
785:
779:
768:
762:
751:
745:
738:
725:
720:
714:
711:
705:
701:
695:
692:
686:
683:
677:
674:
665:
660:
654:
651:
638:
631:
620:
617:
604:
601:
592:
588:
409:physical therapy
288:articular facets
201:Military service
120:Clinical signs:
101:lumbar vertebrae
49:
37:
36:
1345:
1344:
1340:
1339:
1338:
1336:
1335:
1334:
1315:
1314:
1313:
1308:
1289:Schmorl's nodes
1275:
1249:Upper back pain
1226:
1217:Spinal stenosis
1183:
1127:
1106:
1071:
1066:
1036:
1031:
1030:
1007:
1006:
939:
925:
920:
919:
914:
910:
905:
896:
891:
882:
873:
864:
855:
846:
841:
837:
832:
821:
815:
808:
803:
799:
786:
782:
769:
765:
752:
748:
739:
728:
721:
717:
712:
708:
702:
698:
693:
689:
684:
680:
675:
668:
661:
657:
652:
641:
632:
623:
618:
607:
602:
595:
589:
585:
580:
531:
506:
493:spinal stenosis
472:
448:
439:
417:
405:
400:
391:
374:
357:
348:
324:
295:stress fracture
284:spinous process
263:
261:Pathophysiology
184:
171:
113:
35:
32:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1343:
1333:
1332:
1327:
1310:
1309:
1307:
1306:
1301:
1296:
1291:
1285:
1283:
1277:
1276:
1274:
1273:
1268:
1267:
1266:
1261:
1251:
1246:
1240:
1238:
1232:
1231:
1228:
1227:
1225:
1224:
1222:Facet syndrome
1219:
1214:
1213:
1212:
1210:Retrolisthesis
1202:
1197:
1191:
1189:
1185:
1184:
1182:
1181:
1179:Pott's disease
1176:
1171:
1166:
1161:
1160:
1159:
1148:
1146:
1139:
1133:
1132:
1129:
1128:
1126:
1125:
1120:
1114:
1112:
1108:
1107:
1105:
1104:
1099:
1094:
1088:
1086:
1077:
1073:
1072:
1069:Spinal disease
1065:
1064:
1057:
1050:
1042:
1033:
1032:
1029:
1028:
1016:
1015:
1013:
1009:
1008:
1005:
1004:
993:
982:
971:
956:
940:
935:
934:
932:
931:Classification
924:
923:External links
921:
918:
917:
908:
894:
880:
862:
844:
835:
819:
806:
797:
780:
763:
746:
726:
715:
706:
696:
687:
678:
666:
655:
639:
621:
605:
593:
582:
581:
579:
576:
575:
574:
530:
527:
523:co-contraction
505:
502:
501:
500:
486:
471:
468:
447:
444:
438:
435:
416:
413:
404:
401:
399:
396:
390:
387:
373:
370:
356:
353:
347:
344:
323:
320:
262:
259:
254:
253:
250:
247:
244:
241:
238:
235:
232:
229:
226:
223:
220:
217:
214:
211:
208:
205:
202:
199:
183:
180:
170:
167:
166:
165:
164:
163:
160:
157:
154:
151:
148:
145:
139:
138:
137:
134:
131:
128:
112:
109:
97:vertebral arch
84:
83:
74:
68:
67:
62:
56:
55:
51:
50:
42:
41:
33:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1342:
1331:
1328:
1326:
1323:
1322:
1320:
1305:
1302:
1300:
1297:
1295:
1292:
1290:
1287:
1286:
1284:
1282:
1278:
1272:
1271:Radiculopathy
1269:
1265:
1262:
1260:
1257:
1256:
1255:
1254:Low back pain
1252:
1250:
1247:
1245:
1242:
1241:
1239:
1237:
1233:
1223:
1220:
1218:
1215:
1211:
1208:
1207:
1206:
1203:
1201:
1200:Spondylolysis
1198:
1196:
1193:
1192:
1190:
1186:
1180:
1177:
1175:
1172:
1170:
1167:
1165:
1162:
1158:
1155:
1154:
1153:
1150:
1149:
1147:
1143:
1140:
1138:
1137:Spondylopathy
1134:
1124:
1121:
1119:
1116:
1115:
1113:
1109:
1103:
1100:
1098:
1095:
1093:
1090:
1089:
1087:
1085:
1081:
1078:
1074:
1070:
1063:
1058:
1056:
1051:
1049:
1044:
1043:
1040:
1027:
1023:
1022:
1018:
1017:
1014:
1010:
1003:
999:
998:
994:
992:
988:
987:
983:
981:
977:
976:
972:
970:
966:
965:
961:
957:
955:
951:
950:
946:
942:
941:
938:
933:
929:
912:
903:
901:
899:
889:
887:
885:
877:
871:
869:
867:
859:
853:
851:
849:
839:
830:
828:
826:
824:
813:
811:
801:
794:
790:
784:
777:
773:
767:
760:
756:
750:
743:
737:
735:
733:
731:
724:
719:
710:
700:
691:
682:
673:
671:
664:
659:
650:
648:
646:
644:
636:
630:
628:
626:
616:
614:
612:
610:
600:
598:
587:
583:
572:
568:
567:
562:
558:
557:Prince Philip
554:
553:
548:
544:
540:
536:
533:
532:
526:
524:
518:
514:
510:
498:
494:
490:
487:
484:
483:Spinal fusion
481:
480:
479:
477:
467:
463:
461:
452:
443:
434:
430:
427:
423:
412:
410:
395:
386:
378:
369:
361:
352:
343:
341:
337:
333:
329:
315:
311:
309:
305:
301:
296:
291:
289:
285:
281:
277:
273:
269:
258:
251:
248:
245:
242:
239:
236:
233:
230:
227:
225:Weightlifting
224:
221:
218:
215:
212:
209:
206:
203:
200:
197:
196:
195:
192:
190:
179:
177:
161:
158:
155:
152:
149:
146:
143:
142:
140:
135:
132:
129:
126:
122:
121:
119:
118:
117:
108:
106:
102:
98:
94:
90:
89:Spondylolysis
82:
78:
75:
73:
69:
66:
63:
61:
57:
52:
48:
43:
40:Spondylolysis
38:
30:
26:
22:
1199:
1164:Sacroiliitis
1145:inflammatory
1019:
995:
984:
973:
958:
943:
911:
838:
800:
788:
783:
771:
766:
754:
749:
741:
718:
709:
699:
690:
681:
658:
586:
564:
550:
519:
515:
511:
507:
473:
464:
460:Boston brace
457:
440:
431:
418:
406:
392:
383:
366:
349:
325:
292:
264:
255:
228:Roller Derby
210:Cheerleading
193:
189:right-handed
185:
182:Risk factors
172:
114:
88:
87:
1195:Spondylosis
1152:Spondylitis
1123:Torticollis
489:Laminectomy
342:(CT Scan).
65:Orthopedics
25:Spondylitis
21:Spondylosis
1319:Categories
1259:Coccydynia
986:DiseasesDB
578:References
571:footballer
552:Doctor Who
543:the Doctor
535:Matt Smith
240:Volleyball
234:Pole Vault
213:Gymnastics
141:Symptoms:
125:stork test
1244:Neck pain
1236:Back pain
1102:Scoliosis
1076:Deforming
1026:radio/650
1021:eMedicine
1002:240221008
997:SNOMED CT
566:The Crown
398:Treatment
322:Diagnosis
252:Muay Thai
222:Wrestling
60:Specialty
1264:Sciatica
1169:Discitis
1097:Lordosis
1092:Kyphosis
704:244-249.
198:Baseball
980:D013169
563:series
561:Netflix
559:in the
549:series
545:in the
470:Surgery
446:Bracing
429:spine.
300:concave
268:pedicle
231:Cricket
95:of the
497:lamina
304:convex
272:lamina
249:Ballet
207:Diving
204:Tennis
1111:Other
991:12322
969:738.4
954:M43.0
346:X-Ray
328:X-ray
237:Rugby
169:Cause
77:X-ray
27:, or
975:MeSH
964:9-CM
555:and
424:and
298:the
960:ICD
945:ICD
547:BBC
541:of
389:MRI
332:MRI
243:Gym
81:MRI
1321::
1024::
1000::
989::
978::
967::
952::
949:10
897:^
883:^
865:^
847:^
822:^
809:^
729:^
669:^
642:^
624:^
608:^
596:^
334:,
330:,
282:,
278:,
274:,
270:,
107:.
79:,
23:,
1061:e
1054:t
1047:v
962:-
947:-
937:D
31:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.