827:), is a generally accepted indication for screening. It is more likely to be cost-effective in people with a strong personal or family history of thrombosis. In contrast, the combination of thrombophilia with other risk factors may provide an indication for preventive treatment, which is why thrombophilia testing may be performed even in those who would not meet the strict criteria for these tests. Searching for a coagulation abnormality is not normally undertaken in patients in whom thrombosis has an obvious trigger. For example, if the thrombosis is due to immobilization after recent
115:
58:
962:
744:
653:
1052:
856:, testing is discouraged altogether because thrombophilia is not regarded as a major risk factor. In other rare conditions generally linked with hypercoagulability, such as cerebral venous thrombosis and portal vein thrombosis, there is insufficient data to state for certain whether thrombophilia screening is helpful, and decisions on thrombophilia screening in these conditions are therefore not regarded as
34:
1022:
third of those with protein S deficiency. People with activated protein C resistance (usually resulting from factor V Leiden), in contrast, have a slightly raised absolute risk of thrombosis, with 15% having had at least one thrombotic event by the age of sixty. In general, men are more likely than women to experience repeated episodes of venous thrombosis.
1034:
The major ("type 1") thrombophilias are rare. Antithrombin deficiency is present in 0.2% of the general population and 0.5–7.5% of people with venous thrombosis. Protein C deficiency, too, is present in 0.2% of the population, and can be found in 2.5–6% of people with thrombosis. The exact prevalence
969:
There is no specific treatment for thrombophilia, unless it is caused by an underlying medical illness (such as nephrotic syndrome), where the treatment of the underlying disease is needed. In those with unprovoked and/or recurrent thrombosis, or those with a high-risk form of thrombophilia, the most
719:
In thrombophilia, the balance between "procoagulant" and "anticoagulant" activity is disturbed. The severity of the imbalance determines the likelihood that someone develops thrombosis. Even small perturbances of proteins, such as the reduction of antithrombin to only 70–80% of the normal level, can
668:
may include any combination of abnormalities in the blood vessel wall, abnormalities in the blood flow (as in immobilization), and abnormalities in the consistency of the blood. Thrombophilia is caused by abnormalities in blood consistency, which is determined by the levels of coagulation factors and
1038:
The minor ("type 2") thrombophilias are much more common. Factor V Leiden is present in 5% of the population of
Northern European descent, but much rarer in those of Asian or African extraction. In people with thrombosis, 10% have factor V Leiden. In those who are referred for thrombophilia testing,
977:
Apart from the abovementioned forms of thrombophilia, the risk of recurrence after an episode of thrombosis is determined by factors such as the extent and severity of the original thrombosis, whether it was provoked (such as by immobilization or pregnancy), the number of previous thrombotic events,
1021:
In people without a detectable thrombophilia, the cumulative risk of developing thrombosis by the age of 60 is about 12%. About 60% of people who are deficient in antithrombin will have experienced thrombosis at least once by age 60, as will about 50% of people with protein C deficiency and about a
818:
There are divergent views as to whether everyone with an unprovoked episode of thrombosis should be investigated for thrombophilia. Even those with a form of thrombophilia may not necessarily be at risk of further thrombosis, while recurrent thrombosis is more likely in those who have had previous
347:
determines thrombosis risk to a significant extent. Those with blood groups other than type O are at a 2- to 4-fold relative risk. O blood group is associated with reduced levels of von
Willebrand factor — because of increased clearance — and factor VIII, which is related to thrombotic risk .
282:
The most common types of congenital thrombophilia are those that arise as a result of overactivity of coagulation factors; hence they are considered "gain-of-function" alterations. They are relatively mild in the usual heterozygous state, and are therefore classified as "type II" defects. The most
901:
is an indication for thrombophilia screening, particularly antiphospholipid antibodies (anti-cardiolipin IgG and IgM, as well as lupus anticoagulant), factor V Leiden and prothrombin mutation, activated protein C resistance and a general assessment of coagulation through an investigation known as
847:
results of testing would lead to people inappropriately being labeled as having thrombophilia, and being treated with anticoagulants without clinical need. A 2016 study estimated that more than $ 1 million was wasted on inappropriate thrombophilia testing in a year at one academic medical center.
909:
Women who are planning to use oral contraceptives do not benefit from routine screening for thrombophilias, as the absolute risk of thrombotic events is low. If either the woman or a first-degree relative has had thrombosis, the risk of developing thrombosis is increased. Screening this selected
851:
In the United
Kingdom, professional guidelines give specific indications for thrombophilia testing. It is recommended that testing be done only after appropriate counseling, and hence the investigations are usually not performed at the time when thrombosis is diagnosed but at a later time. In
712:, TAFI) that enhance the fibrin clot. The process is inhibited by TFPI (which inactivates the first step catalyzed by factor VIIa/tissue factor), antithrombin (which inactivates thrombin, factor IXa, Xa and XIa), protein C (which inhibits factors Va and VIIIa in the presence of protein S), and
2997:
Stevens SM, Woller SC, Kreuziger LB, Bounameaux H, Doerschug K, Geersing GJ, Huisman MV, Kearon C, King CS, Knighton AJ, Lake E, Murin S, Vintch JR, Wells PS, Moores LK (December 2021). "Antithrombotic
Therapy for VTE Disease: Second Update of the CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report".
457:(spread to other places in the body), is a recognised risk factor for thrombosis. A number of mechanisms have been proposed, such as activation of the coagulation system by cancer cells or secretion of procoagulant substances. Furthermore, particular cancer treatments (such as the use of
1012:
When women experience recurrent pregnancy loss secondary to thrombophilia, some studies have suggested that low molecular weight heparin reduces the risk of miscarriage. When the results of all studies are analysed together, no statistically significant benefit could be demonstrated.
834:
When venous thromboembolism occurs when a patient is experiencing transient major risk factors such as prolonged immobility, surgery, or trauma, testing for thrombophilia is not appropriate because the outcome of the test would not change a patient's indicated treatment. In 2013, the
974:, on a long-term basis to reduce the risk of further episodes. This risk needs to weighed against the risk that the treatment will cause significant bleeding, as the reported risk of major bleeding is over 3% per year, and 11% of those with major bleeding may die as a result.
1039:
30–50% have the defect. The prothrombin mutation occurs at rates of 1–4% in the general population, 5–10% of people with thrombosis, and 15% of people referred for thrombophilia testing. Like factor V Leiden, this abnormality is uncommon in
Africans and Asians.
1107:, as genetic abnormalities are typically named after the place where they are discovered. Two years later, the same group described a common mutation in the prothrombin gene that caused elevation of prothrombin levels and a mild increase in thrombosis risk.
1025:
People with factor V Leiden are at a relatively low risk of thrombosis, but may develop thrombosis in the presence of an additional risk factor, such as immobilization. Most people with the prothrombin mutation (G20210A) never develop thrombosis.
531:), have been associated with a 2- to 6-fold increased risk of venous thrombosis. The risk depends on the types of hormones used, the dose of estrogen, and the presence of other thrombophilic risk factors. Various mechanisms, such as deficiency of
1087:
Antiphospholipid syndrome was described in full in the 1980s, after various previous reports of specific antibodies in people with systemic lupus erythematosus and thrombosis. The syndrome is often attributed to the
British rheumatologist
1042:
The exact prevalence of antiphospholipid syndrome is not well known, as different studies employ different definitions of the condition. Antiphospholipid antibodies are detected in 24% of those referred to thrombophilia testing.
3040:
Middeldorp S, Nieuwlaat R, Baumann
Kreuziger L, Coppens M, Houghton D, James AH, Lang E, Moll S, Myers T, Bhatt M, Chai-Adisaksopha C, Colunga-Lozano LE, Karam SG, Zhang Y, Wiercioch W, Schünemann HJ, Iorio A (November 2023).
90:
in the leg) that was not provoked by other causes. A significant proportion of the population has a detectable thrombophilic abnormality, but most of these develop thrombosis only in the presence of an additional risk factor.
1000:
Women with a thrombophilia who are contemplating pregnancy or are pregnant usually require alternatives to warfarin during pregnancy, especially in the first 13 weeks, when it may produce abnormalities in the unborn child.
308:
The rare forms of congenital thrombophilia are typically caused by a deficiency of natural anticoagulants. They are classified as "type I" and are more severe in their propensity to cause thrombosis. The main ones are
886:
issued new guidelines for thrombophilia testing. One departure from their previous guidelines relates to patients with nonsurgical major transient risk factors; testing may be appropriate. Thrombophilia testing after
3599:
3580:
1063:
categorized abnormalities in the consistency of the blood as a factor in the development of thrombosis in 1856. The exact nature of these abnormalities remained elusive until the first form of thrombophilia,
910:
group may be beneficial, but even when negative may still indicate residual risk. Professional guidelines therefore suggest that alternative forms of contraception be used rather than relying on screening.
471:, in which protein from the bloodstream is released into the urine due to kidney diseases, can predispose to thrombosis; this is particularly the case in more severe cases (as indicated by blood levels of
913:
Thrombophilia screening in people with arterial thrombosis is generally regarded as unrewarding and is generally discouraged, except possibly for unusually young patients (especially when precipitated by
545:
has long been regarded as a risk factor for venous thrombosis. It more than doubles the risk in numerous studies, particularly in combination with the use of oral contraceptives or in the period after
1099:
The more common genetic thrombophilias were described in the 1990s. Many studies had previously indicated that many people with thrombosis showed resistance activated protein C. In 1994 a group in
388:. In some cases, antiphospholipid syndrome can cause arterial as well as venous thrombosis. It is also more strongly associated with miscarriage, and can cause a number of other symptoms (such as
864:
in return for expenditure) is taken as a guide, it is generally unclear whether thrombophilia investigations justify the often high cost, unless the testing is restricted to selected situations.
993:
Those with antiphospholipid syndrome may be offered long-term anticoagulation after a first unprovoked episode of thrombosis. The risk is determined by the subtype of antibody detected, by the
2741:
Chong LY, Fenu E, Stansby G, Hodgkinson S, Guideline
Development G (2012). "Management of venous thromboembolic diseases and the role of thrombophilia testing: Summary of NICE guidance".
747:
A mutation of coagulation factor V (schematic representation drawn here) is much more common in people with thrombosis than in those without, but is only regarded as a weak risk factor.
242:, a severe clotting disorder in the newborn that leads to both tissue death and bleeding into the skin and other organs. The condition has also been described in adults. Protein C and
2778:
Baglin T, Gray E, Greaves M, Hunt BJ, Keeling D, Machin S, MacKie I, Makris M, Nokes T, Perry D, Tait RC, Walker I, Watson H, British
Committee for Standards in Haematology (2010).
891:(VTE) provoked by surgery, on the other hand, is not recommended, because the risk of recurrence is low. Some experts argue that unprovoked VTE requires indefinite (lifelong)
3173:"Venous thromboembolism, thrombophilia, antithrombotic therapy, and pregnancy: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition)"
3519:"A common genetic variation in the 3'-untranslated region of the prothrombin gene is associated with elevated plasma prothrombin levels and an increase in venous thrombosis"
2434:
Gomes MP, Deitcher SR (October 2004). "Risk of venous thromboembolic disease associated with hormonal contraceptives and hormone replacement therapy: a clinical review".
1103:, The Netherlands, identified the most common underlying defect—a mutation in factor V that made it resistant to the action of activated protein C. The defect was called
965:
People considered to be at a high risk of repeated thrombosis due to thrombophilia are often advised to take warfarin for prolonged periods of time or even indefinitely.
3090:
Exner T, Rigano J, Favaloro EJ (June 2020). "The effect of DOACs on laboratory tests and their removal by activated carbon to limit interference in functional assays".
3724:
895:
and therefore performing thrombophilia testing will not affect management. Nearly all recommendations in the guidelines were based on "very low certainty" evidence.
1789:
Crowther MA, Kelton JG (2003). "Congenital thrombophilic states associated with venous thrombosis: a qualitative overview and proposed classification system".
577:
A number of conditions that have been linked with venous thrombosis are possibly genetic and possibly acquired. These include: elevated levels of factor VIII,
1055:
Rudolf
Virchow, the German pathologist who distinguished the various causes of thrombosis, and whose work led to the development of thrombophilia as a concept
938:. Therefore, most thrombophilia testing should be done after the patient has completed the initial treatment course of anticoagulation. Efforts to remove
3127:"Antithrombotic therapy for venous thromboembolic disease: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition)"
831:, it is regarded as "provoked" by the immobilization and the surgery and it is less likely that investigations will yield clinically important results.
3466:
Bertina RM, Koeleman BP, Koster T, et al. (May 1994). "Mutation in blood coagulation factor V associated with resistance to activated protein C".
406:(or its derivatives). Though it is named for associated low platelet counts, HIT is strongly associated with risk of venous and arterial thrombosis.
205:) is less well established. However, more recent data suggest some forms of inherited thrombophilia are associated with increased risk for arterial
1068:, was recognized in 1965 by the Norwegian hematologist Olav Egeberg. Protein C deficiency followed in 1981, when described by researchers from the
819:
thrombosis even in those who have no detectable thrombophilic abnormalities. Recurrent thromboembolism, or thrombosis in unusual sites (e.g. the
3717:
94:
There is no specific treatment for most thrombophilias, but recurrent episodes of thrombosis may be an indication for long-term preventive
2086:
Brodsky RA (April 2008). "Narrative review: paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: the physiology of complement-related hemolytic anemia".
341:, for instance, mainly causes eye symptoms and sometimes problems in other organs, but the link with thrombosis has been more uncertain.
608:
and thrombosis, although this has not been reported consistently in all studies. Homocysteine levels are determined by mutations in the
3172:
3126:
1073:
997:(amount of antibodies), whether multiple antibodies are detected, and whether it is detected repeatedly or only on a single occasion.
2864:"Analysis of Thrombophilia Test Ordering Practices at an Academic Center: A Proposal for Appropriate Testing to Reduce Harm and Cost"
3710:
2303:"Defining venous thromboembolism and measuring its incidence using Swedish health registries: a nationwide pregnancy cohort study"
118:
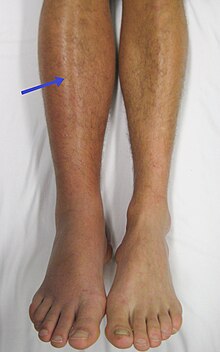
A right-sided acute deep vein thrombosis (to the left in the image). The leg is swollen and red due to venous outflow obstruction.
86:(blood clots in blood vessels). Such abnormalities can be identified in 50% of people who have an episode of thrombosis (such as
807:
levels. Testing may be more or less extensive depending on clinical judgement and abnormalities detected on initial evaluation.
3841:
2410:
1157:
664:
Thrombosis is a multifactorial problem because there are often multiple reasons why a person might develop thrombosis. These
601:
that is not attributable to factor V mutations is probably caused by other factors and remains a risk factor for thrombosis.
561:
aggregation may be increased, and there are higher levels of coagulation proteins such as von Willebrand factor, fibrinogen,
553:, an inhibitor of fibrinolysis, is present in higher levels in people with obesity. Obese people also have larger numbers of
871:
offered one testing-related recommendation in its venous thromboembolism guidelines. They recommended to consider positive
868:
3347:
Comp PC, Esmon CT (December 1984). "Recurrent venous thromboembolism in patients with a partial deficiency of protein S".
4016:
3999:
3614:
610:
407:
2139:
Papadakis E, Hoffman R, Brenner B (November 2010). "Thrombohemorrhagic complications of myeloproliferative disorders".
990:. These factors tend to be more important in the decision than the presence or absence of a detectable thrombophilia.
788:
134:(VTE). DVT usually occurs in the legs, and is characterized by pain, swelling and redness of the limb. It may lead to
2712:
1555:
Chiasakul T, De Jesus E, Tong J, Chen Y, Crowther M, Garcia D, Chai-Adisaksopha C, Messé SR, Cuker A (October 2019).
1110:
It is suspected that other genetic abnormalities underlying familial thrombosis will in future be discovered through
550:
4078:
4030:
3431:
Sanna G, D'Cruz D, Cuadrado MJ (August 2006). "Cerebral manifestations in the antiphospholipid (Hughes) syndrome".
399:
182:
170:
3216:"A meta-analysis of low-molecular-weight heparin to prevent pregnancy loss in women with inherited thrombophilia"
2708:
2350:
Bourjeily G, Paidas M, Khalil H, Rosene-Montella K, Rodger M (February 2010). "Pulmonary embolism in pregnancy".
2258:
Quera R, Shanahan F (October 2004). "Thromboembolism--an important manifestation of inflammatory bowel disease".
594:
536:
520:
498:
302:
217:
3043:"American Society of Hematology 2023 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: thrombophilia testing"
2915:"Thrombophilia testing in people with venous thromboembolism: systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis"
2301:
Abdul Sultan A, West J, Stephansson O, Grainge MJ, Tata LJ, Fleming KM, Humes D, Ludvigsson JF (November 2015).
3797:
2726:
1115:
1089:
923:
883:
836:
598:
497:
is associated with an increased risk of thrombosis of 2- to 7-fold. This probably results from a physiological
377:
142:) to arteries in the lungs. Depending on the size and the location of the clot, this may lead to sudden-onset
4084:
4070:
1111:
476:
491:) predispose to thrombosis, particularly when the disease is active. Various mechanisms have been proposed.
4058:
4021:
3891:
1520:
de Moerloose P, Boehlen F (April 2007). "Inherited thrombophilia in arterial disease: a selective review".
1002:
369:
1832:
427:
Hematologic conditions associated with sluggish blood flow can increase risk for thrombosis. For example,
4211:
3787:
1557:"Inherited Thrombophilia and the Risk of Arterial Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis"
764:
616:
436:
373:
305:
of the gene). Compound heterozygotes and homozygotes, while rare, are at significant risk of thrombosis.
1244:
Kyrle PA, Rosendaal FR, Eichinger S (December 2010). "Risk assessment for recurrent venous thrombosis".
4166:
4011:
2583:
Borissoff JI, Spronk HM, ten Cate H (2011). "The hemostatic system as a modulator of atherosclerosis".
1069:
939:
861:
524:
480:
424:(anemia resulting from destruction of red blood cells). Both HIT and PNH require particular treatment.
326:
2666:"Screening for thrombophilia in high-risk situations: a meta-analysis and cost-effectiveness analysis"
1719:
Stevens SM, Woller SC, Bauer KA, Kasthuri R, Cushman M, Streiff M, Lim W, Douketis JD (January 2016).
4282:
3853:
3834:
979:
784:
357:
337:(the system that destroys clots) are major contributors to thrombosis risk. Congenital deficiency of
2100:
1035:
of protein S deficiency in the population is unknown; it is found 1.3–5% of people with thrombosis.
439:, in which the bone marrow produces too many blood cells, predispose to thrombosis, particularly in
57:
4252:
3995:
3824:
3625:
3538:
3518:
983:
727:
In addition to its effects on thrombosis, hypercoagulable states may accelerate the development of
554:
528:
444:
190:
135:
3214:
Skeith L, Carrier M, Kaaja R, Martinelli I, Petroff D, Schleußner E, Laskin CA, Rodger MA (2016).
3200:
3154:
1986:
Ruiz-Irastorza G, Crowther M, Branch W, Khamashta MA (October 2010). "Antiphospholipid syndrome".
4339:
4242:
4035:
1065:
919:
857:
853:
696:
into thrombin. Thrombin is a central enzyme in the coagulation process: it generates fibrin from
458:
99:
2543:
447:(excess platelets). Again, these conditions usually warrant specific treatment when identified.
4156:
4131:
4089:
2472:
Tchaikovski SN, Rosing J (July 2010). "Mechanisms of estrogen-induced venous thromboembolism".
2095:
1081:
888:
344:
174:
131:
1009:) is generally used as an alternative. Warfarin and LMWH may safely be used in breastfeeding.
4151:
4141:
3959:
898:
810:
For hereditary cases, the patient must have at least two abnormal tests plus family history.
732:
516:
502:
213:
198:
186:
2109:
1848:
1802:
3907:
3802:
3792:
3475:
1077:
824:
768:
752:
318:
314:
270:" may be used) that increase the tendency to develop thrombosis, while, on the other hand,
243:
235:
178:
123:
87:
8:
4146:
4136:
3932:
3812:
3665:
3603:
950:
903:
780:
657:
590:
428:
365:
294:
194:
159:
3479:
3067:
3042:
2823:"The ASH Choosing Wisely(R) campaign: five hematologic tests and treatments to question"
569:. Obesity also increases the risk of recurrence after an initial episode of thrombosis.
114:
4272:
3954:
3912:
3886:
3759:
3499:
3408:
3383:
3280:
2979:
2890:
2863:
2766:
2416:
2375:
2327:
2302:
2283:
2235:
2210:
2121:
2021:
1860:
1814:
1745:
1720:
1640:
1589:
1556:
1533:
1415:
1390:
1269:
828:
660:, consists of a group of proteins that interact in the formation of a fibrin-rich clot.
488:
484:
468:
389:
385:
356:
A number of acquired conditions augment the risk of thrombosis. A prominent example is
229:
155:
127:
3608:
3324:
3299:
2363:
2187:
1999:
1628:
1257:
4161:
3937:
3846:
3702:
3636:
3543:
3491:
3448:
3413:
3364:
3329:
3272:
3237:
3192:
3146:
3107:
3072:
3058:
3015:
2971:
2936:
2895:
2844:
2801:
2796:
2779:
2758:
2687:
2682:
2665:
2646:
2600:
2565:
2524:
2489:
2451:
2420:
2406:
2367:
2332:
2275:
2271:
2240:
2191:
2156:
2113:
2065:
2060:
2043:
2013:
1961:
1956:
1939:
1920:
1852:
1806:
1750:
1698:
1693:
1676:
1632:
1594:
1576:
1537:
1499:
1494:
1477:
1455:
1420:
1371:
1366:
1349:
1317:
1261:
1219:
1153:
440:
417:
247:
239:
79:
46:
3284:
2983:
2770:
2287:
2174:
Prandoni P, Falanga A, Piccioli A (June 2005). "Cancer and venous thromboembolism".
2125:
2025:
1864:
1818:
1721:"Guidance for the evaluation and treatment of hereditary and acquired thrombophilia"
1644:
1273:
1214:
1197:
3987:
3927:
3922:
3782:
3691:
3533:
3503:
3483:
3440:
3403:
3395:
3356:
3319:
3311:
3264:
3227:
3184:
3138:
3099:
3062:
3054:
3007:
2963:
2954:
Wu O, Greer IA (September 2007). "Is screening for thrombophilia cost-effective?".
2926:
2885:
2875:
2834:
2791:
2750:
2677:
2636:
2592:
2555:
2516:
2485:
2481:
2443:
2398:
2393:
Daughety MM, Samuelson Bannow BT (2019). "Hemostasis and Thrombosis in Pregnancy".
2379:
2359:
2322:
2314:
2267:
2230:
2222:
2183:
2148:
2105:
2055:
2003:
1995:
1951:
1910:
1844:
1798:
1740:
1732:
1688:
1624:
1584:
1568:
1529:
1489:
1447:
1410:
1402:
1361:
1307:
1253:
1209:
760:
421:
16:
Abnormality of blood coagulation increasing the risk of blood clotting (thrombosis)
3255:
Egeberg O (June 1965). "Inherited antithrombin deficiency causing thrombophilia".
2862:
Shen YM, Tsai J, Taiwo E, Gavva C, Yates SG, Patel V, Frenkel E, Sarode R (2016).
1915:
1898:
435:) is regarded as a mild prothrombotic state induced by impaired flow. Similarly,
4267:
4101:
3942:
3807:
3630:
3232:
3215:
2967:
2880:
2839:
2822:
2721:
2717:
2641:
2624:
2447:
2402:
1312:
1295:
946:
915:
892:
840:
796:
728:
284:
206:
103:
3676:
3360:
3011:
2318:
2226:
669:
other circulating blood proteins that participate in the "coagulation cascade".
4292:
4004:
3947:
3829:
3641:
3125:
Kearon C, Kahn SR, Agnelli G, Goldhaber S, Raskob GE, Comerota AJ (June 2008).
2152:
1060:
994:
844:
776:
163:
138:
due to damage to valves in the veins. The clot may also break off and migrate (
41:
An ultrasound image demonstrating a blood clot in the left common femoral vein.
3593:
3589:
3444:
3399:
2520:
1736:
4333:
4302:
4124:
4119:
4114:
1580:
935:
772:
724:, which only arises if levels of coagulation factors are markedly decreased.
673:
225:
98:. The first major form of thrombophilia to be identified by medical science,
95:
4045:
2625:"Should patients with venous thromboembolism be screened for thrombophilia?"
2507:
Stein PD, Goldman J (September 2009). "Obesity and thromboembolic disease".
1572:
1296:"Advances in understanding pathogenic mechanisms of thrombophilic disorders"
4312:
3754:
3452:
3276:
3268:
3241:
3196:
3150:
3111:
3076:
3039:
3019:
2975:
2940:
2899:
2848:
2805:
2762:
2691:
2650:
2604:
2569:
2528:
2493:
2455:
2371:
2336:
2279:
2244:
2195:
2160:
2117:
2069:
2017:
1965:
1924:
1856:
1810:
1754:
1702:
1636:
1598:
1541:
1503:
1459:
1424:
1375:
1321:
1265:
1223:
820:
804:
605:
510:
462:
334:
310:
151:
3547:
3495:
3417:
3368:
3333:
3188:
3142:
2596:
1451:
970:
important decision is whether to use anticoagulation medications, such as
505:. This hypercoagulability in turn is likely related to the high levels of
420:. PNH increases the risk of venous thrombosis but is also associated with
4109:
3917:
3749:
3738:
3298:
Griffin JH, Evatt B, Zimmerman TS, Kleiss AJ, Wideman C (November 1981).
2560:
1478:"Does thrombophilia testing help in the clinical management of patients?"
1198:"Thrombophilia: common questions on laboratory assessment and management"
879:
may suggest that the ongoing thrombotic tendency has not fully resolved.
800:
709:
701:
693:
665:
647:
632:
566:
402:(HIT) is due to an immune system reaction against the anticoagulant drug
338:
322:
298:
102:, was identified in 1965, while the most common abnormalities (including
3572:
2008:
1406:
4297:
4262:
4237:
3881:
3863:
3671:
3103:
1006:
961:
792:
756:
721:
697:
677:
625:
621:
586:
562:
454:
432:
361:
330:
221:
147:
83:
51:
3315:
2754:
1825:
875:
in the decision to continue or discontinue anticoagulation. Positive
743:
549:. Various coagulation abnormalities have been described in the obese.
4287:
4232:
3819:
3660:
3487:
3384:"Thrombosis, abortion, cerebral disease, and the lupus anticoagulant"
2931:
2914:
1985:
713:
705:
685:
582:
578:
532:
506:
494:
410:(PNH) is a rare condition resulting from acquired alterations in the
2349:
266:
refers to inborn conditions (and usually hereditary, in which case "
4201:
4196:
4186:
3876:
3734:
2544:"Is thrombin a key player in the 'coagulation-atherogenesis' maze?"
971:
689:
681:
652:
558:
416:
gene, which plays a role in the protection of blood cells from the
393:
289:
251:
139:
2913:
Simpson EL, Stevenson MD, Rawdin A, Papaioannou D (January 2009).
2300:
475:
below 25 g/L) and if the syndrome is caused by the condition
4247:
4206:
2912:
1899:"Venous thrombosis: the role of genes, environment, and behavior"
1051:
987:
876:
872:
546:
542:
472:
403:
143:
3619:
3517:
Poort SR, Rosendaal FR, Reitsma PH, Bertina RM (November 1996).
2996:
1833:"Congenital Causes of Venous Thrombosis—A Classification System"
1438:
Agnelli G, Becattini C (July 2010). "Acute pulmonary embolism".
934:
Several thrombophilia assays can be impacted by the presence of
843:
campaign, cautioned against overuse of thrombophilia screening;
169:
Venous thrombosis may also occur in more unusual places: in the
4191:
3584:
3171:
Bates SM, Greer IA, Pabinger I, Sofaer S, Hirsh J (June 2008).
2541:
1100:
450:
202:
2707:
1148:
Mitchell RS, Kumar V, Abbas AK, Fausto N (2007). "Chapter 4".
2780:"Clinical guidelines for testing for heritable thrombophilia"
1677:"Clinical guidelines for testing for heritable thrombophilia"
122:
The most common conditions associated with thrombophilia are
3516:
3213:
2386:
1843:(2). American College of Physicians: I39. January 21, 2003.
1475:
3297:
412:
3300:"Deficiency of protein C in congenital thrombotic disease"
3124:
2740:
2664:
Wu O, Robertson L, Twaddle S, et al. (October 2005).
1718:
216:, and possibly various complications of pregnancy such as
1554:
942:
using activated carbon may prove helpful in this regard.
700:, and activates a number of other enzymes and cofactors (
3170:
2542:
Borissoff JI, Spronk HM, Heeneman S, ten Cate H (2009).
2392:
1147:
953:
are unaffected by the physiologic state of the patient.
676:
from damaged tissue. Tissue factor binds to circulating
364:
against constituents of the cell membrane, particularly
33:
3430:
2582:
2173:
2138:
1675:
Baglin T, Gray E, Greaves M, et al. (April 2010).
1615:
Rai R, Regan L (August 2006). "Recurrent miscarriage".
1243:
720:
increase the thrombosis risk; this is in contrast with
3732:
557:(fragments of damaged cells) that bear tissue factor.
3465:
2777:
2713:"Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question"
2041:
3562:
2044:"The management of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia"
604:
There is an association between the blood levels of
246:
have also been associated with an increased risk of
3089:
2821:Hicks LK, Bering H, Carson KR, et al. (2013).
1981:
1979:
1977:
1975:
1519:
372:but often detected in people without the disease),
193:. Whether thrombophilia also increases the risk of
2861:
2663:
1476:Middeldorp S, van Hylckama Vlieg A (August 2008).
1343:
1341:
1339:
1337:
1335:
1333:
1331:
1080:followed in 1984, described by researchers at the
672:Normal coagulation is initiated by the release of
2820:
2471:
1674:
1391:"Diagnosis and treatment of deep-vein thrombosis"
926:, fails because of rapid occlusion of the graft.
333:). It is unclear whether congenital disorders of
4331:
1972:
1892:
1890:
1888:
1886:
1884:
1882:
1880:
1878:
1876:
1874:
1437:
1347:
1328:
922:) and those in whom revascularization, such as
465:) may increase the risk of thrombosis further.
274:refers to conditions that arise later in life.
3539:10.1182/blood.V88.10.3698.bloodjournal88103698
1788:
1388:
3718:
2433:
2257:
2208:
1871:
1515:
1513:
688:to factor IXa. Factor Xa (in the presence of
656:The coagulation system, often described as a
262:Thrombophilia can be congenital or acquired.
2506:
2467:
2465:
2294:
2042:Keeling D, Davidson S, Watson H (May 2006).
1937:
1896:
1784:
1471:
1469:
321:. Milder rare congenital thrombophilias are
130:(PE), which are referred to collectively as
3035:
3033:
3031:
3029:
1782:
1780:
1778:
1776:
1774:
1772:
1770:
1768:
1766:
1764:
1670:
1668:
1666:
1664:
1662:
1660:
1658:
1656:
1654:
1610:
1608:
735:and other forms of cardiovascular disease.
591:thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor
250:on commencing anticoagulant treatment with
3725:
3711:
2703:
2701:
2085:
2081:
2079:
2037:
2035:
1903:Hematology Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program
1714:
1712:
1510:
1293:
1289:
1287:
1285:
1283:
1202:Hematology Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program
56:
32:
3537:
3407:
3381:
3346:
3323:
3254:
3231:
3066:
2930:
2889:
2879:
2838:
2795:
2681:
2640:
2559:
2462:
2326:
2234:
2099:
2059:
2007:
1955:
1914:
1744:
1692:
1588:
1561:Journal of the American Heart Association
1493:
1466:
1414:
1382:
1365:
1311:
1239:
1237:
1235:
1233:
1213:
3166:
3164:
3026:
2622:
2618:
2616:
2614:
2167:
1761:
1651:
1614:
1605:
1152:(8th ed.). Philadelphia: Saunders.
1143:
1141:
1139:
1137:
1135:
1133:
1131:
1050:
960:
742:
651:
368:(first found in people with the disease
113:
3979:
2953:
2698:
2110:10.7326/0003-4819-148-8-200804150-00003
2076:
2032:
1849:10.7326/0003-4819-138-2-200301210-00005
1803:10.7326/0003-4819-138-2-200301210-00014
1709:
1280:
1195:
1191:
1189:
4332:
3375:
3118:
1431:
1389:Scarvelis D, Wells PS (October 2006).
1348:Rosendaal FR, Reitsma PH (July 2009).
1230:
1187:
1185:
1183:
1181:
1179:
1177:
1175:
1173:
1171:
1169:
982:, the presence of cancer, symptoms of
731:, the arterial disease that underlies
3706:
3161:
2611:
1938:Mehta R, Shapiro AD (November 2008).
1128:
109:
929:
869:American College of Chest Physicians
839:, as part of recommendations in the
2132:
1166:
408:Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
13:
2209:Hull RP, Goldsmith DJ (May 2008).
1534:10.1053/j.seminhematol.2007.01.008
1112:studies of the entire genetic code
791:, activated protein C resistance,
197:(which is the underlying cause of
14:
4351:
3558:
551:Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1
384:; it is therefore regarded as an
212:Thrombophilia has been linked to
4079:platelet storage pool deficiency
4031:Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
3059:10.1182/bloodadvances.2023010177
2797:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2009.08022.x
2683:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2005.05715.x
2272:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.40923.x
2061:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2006.06018.x
1957:10.1111/j.1365-2516.2008.01825.x
1694:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2009.08022.x
1495:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2008.07339.x
1367:10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03394.x
751:Tests for thrombophilia include
400:Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
136:long-term swelling and heaviness
3510:
3459:
3424:
3340:
3291:
3248:
3207:
3083:
2990:
2947:
2906:
2855:
2814:
2657:
2576:
2535:
2500:
2427:
2343:
2251:
2202:
1931:
1548:
1350:"Genetics of venous thrombosis"
1215:10.1182/asheducation-2007.1.127
1029:
852:particular situations, such as
789:anti-β2 glycoprotein 1 antibody
595:tissue factor pathway inhibitor
537:tissue factor pathway inhibitor
521:combined hormonal birth control
499:hypercoagulability in pregnancy
218:intrauterine growth restriction
106:) were described in the 1990s.
3798:Activated protein C resistance
2784:British Journal of Haematology
2727:American Society of Hematology
2709:American Society of Hematology
2486:10.1016/j.thromres.2010.01.045
2211:"Nephrotic syndrome in adults"
1092:, and is often referred to as
918:or use of estrogen-containing
884:American Society of Hematology
837:American Society of Hematology
599:Activated protein C resistance
539:, are said to be responsible.
1:
2364:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60996-X
2188:10.1016/S1470-2045(05)70207-2
2000:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60709-X
1916:10.1182/asheducation-2005.1.1
1629:10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69204-0
1258:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60962-2
1121:
978:male sex, the presence of an
620:genes, but also by levels of
513:that occur during pregnancy.
443:(excess red blood cells) and
277:
3892:Trousseau sign of malignancy
3388:Br. Med. J. (Clin. Res. Ed.)
3233:10.1182/blood-2015-12-626739
2968:10.1097/MOH.0b013e32825f5318
2881:10.1371/journal.pone.0155326
2840:10.1182/blood-2013-07-518423
2642:10.1016/j.amjmed.2007.10.042
2448:10.1001/archinte.164.18.1965
2403:10.1007/978-3-030-19330-0_30
1313:10.1182/blood-2008-01-077909
1016:
1003:Low molecular weight heparin
956:
813:
738:
716:(which inhibits factor Xa).
680:. The combination activates
641:
437:myeloproliferative disorders
370:systemic lupus erythematosus
7:
4212:Nonthrombocytopenic purpura
3788:Antithrombin III deficiency
3361:10.1056/NEJM198412133112401
3012:10.1016/j.chest.2021.07.055
2319:10.1136/bmjopen-2015-008864
2227:10.1136/bmj.39576.709711.80
1837:Annals of Internal Medicine
1116:small alternations in genes
862:quality-adjusted life years
765:partial thromboplastin time
374:anti-cardiolipin antibodies
351:
293:gene at position 1691) and
82:that increases the risk of
10:
4356:
4167:Congenital afibrinogenemia
4071:Glanzmann's thrombasthenia
3433:Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am
3382:Hughes GR (October 1983).
2153:10.1016/j.blre.2010.08.002
1074:Centers of Disease Control
1070:Scripps Research Institute
1046:
940:direct oral anticoagulants
645:
593:, and decreased levels of
572:
525:menopausal hormone therapy
481:Inflammatory bowel disease
382:-glycoprotein 1 antibodies
327:familial dysfibrinogenemia
301:(at position 20210 in the
154:and may be complicated by
4283:Gastrointestinal bleeding
4222:
4179:
4100:
4085:Hermansky–Pudlak syndrome
4044:
3986:
3972:
3900:
3862:
3854:Antiphospholipid syndrome
3835:Essential thrombocythemia
3775:
3768:
3745:
3651:
3566:
3445:10.1016/j.rdc.2006.05.010
3400:10.1136/bmj.287.6399.1088
2521:10.1016/j.ccm.2009.05.006
2395:Hemostasis and Thrombosis
1737:10.1007/s11239-015-1316-1
980:inferior vena cava filter
860:. If cost-effectiveness (
785:anti-cardiolipin antibody
755:(with examination of the
555:circulating microvesicles
358:antiphospholipid syndrome
257:
45:
40:
31:
26:
4253:Subconjunctival bleeding
4059:Bernard–Soulier syndrome
4022:Upshaw–Schulman syndrome
3996:Thrombocytopenic purpura
3825:Sticky platelet syndrome
1940:"Plasminogen deficiency"
1294:Dahlbäck B (July 2008).
984:post-thrombotic syndrome
945:Molecular tests such as
924:coronary arterial bypass
638:, which depend on diet.
459:central venous catheters
445:essential thrombocytosis
431:(caused by mutations of
268:hereditary thrombophilia
264:Congenital thrombophilia
4243:Intracranial hemorrhage
3257:Thromb. Diath. Haemorrh
2720:: an initiative of the
1573:10.1161/JAHA.119.012877
1150:Robbins Basic Pathology
1066:antithrombin deficiency
920:hormonal contraceptives
854:retinal vein thrombosis
179:hepatic vein thrombosis
100:antithrombin deficiency
78:) is an abnormality of
4157:Factor XIII deficiency
4137:Hypoprothrombinemia/II
4132:von Willebrand disease
4090:Gray platelet syndrome
3269:10.1055/s-0038-1656297
3183:(6 Suppl): 844S–886S.
3137:(6 Suppl): 454S–545S.
2925:(2): iii, ix–x, 1–91.
2919:Health Technol. Assess
2623:Dalen JE (June 2008).
1082:University of Oklahoma
1056:
966:
889:venous thromboembolism
748:
661:
501:that protects against
477:membranous nephropathy
303:3' untranslated region
272:acquired thrombophilia
175:portal vein thrombosis
132:venous thromboembolism
119:
4152:Factor XII deficiency
4142:Factor VII deficiency
3960:Renal vein thrombosis
3189:10.1378/chest.08-0761
3143:10.1378/chest.08-0658
2597:10.1056/NEJMra1011670
1897:Rosendaal FR (2005).
1725:J Thromb Thrombolysis
1452:10.1056/NEJMra0907731
1054:
964:
899:Recurrent miscarriage
746:
733:myocardial infarction
655:
527:(in combination with
503:postpartum hemorrhage
360:, which is caused by
214:recurrent miscarriage
191:the veins of the arms
187:renal vein thrombosis
117:
3908:Deep vein thrombosis
3803:Protein S deficiency
3793:Protein C deficiency
2397:. pp. 197–206.
2260:Am. J. Gastroenterol
1078:Protein S deficiency
825:Budd-Chiari syndrome
803:mutation, and basal
769:thrombodynamics test
753:complete blood count
453:, particularly when
319:protein S deficiency
315:protein C deficiency
244:protein S deficiency
236:Protein C deficiency
124:deep vein thrombosis
88:deep vein thrombosis
4147:Factor X deficiency
4036:May–Hegglin anomaly
3813:Prothrombin G20210A
3480:1994Natur.369...64B
2956:Curr. Opin. Hematol
2515:(3): 489–93, viii.
1407:10.1503/cmaj.060366
951:Prothrombin G20210A
904:thromboelastography
781:lupus anticoagulant
429:sickle-cell disease
366:lupus anticoagulant
295:prothrombin G20210A
287:(a mutation in the
195:arterial thrombosis
144:shortness of breath
76:prothrombotic state
4273:Pulmonary hematoma
4180:Signs and symptoms
3955:Pulmonary embolism
3760:Bleeding diathesis
3652:External resources
3104:10.1111/ijlh.13196
3098:(Suppl 1): 41–48.
2711:(September 2013),
2561:10.1093/cvr/cvp066
1994:(9751): 1498–509.
1360:(Suppl 1): 301–4.
1354:J. Thromb. Haemost
1090:Graham R.V. Hughes
1057:
967:
829:orthopedic surgery
749:
662:
485:ulcerative colitis
469:Nephrotic syndrome
390:livedo reticularis
386:autoimmune disease
254:or related drugs.
230:abruptio placentae
171:veins of the brain
128:pulmonary embolism
120:
110:Signs and symptoms
72:hypercoagulability
70:(sometimes called
4327:
4326:
4323:
4322:
4175:
4174:
4162:Dysfibrinogenemia
4046:Platelet function
3968:
3967:
3847:Purpura fulminans
3686:
3685:
3394:(6399): 1088–89.
3316:10.1172/JCI110385
3092:Int J Lab Hematol
2755:10.1136/bmj.e3979
2436:Arch. Intern. Med
2412:978-3-030-19329-4
1159:978-1-4160-2973-1
1096:for that reason.
1059:German physician
930:Timing of Testing
684:to factor Xa and
441:polycythemia vera
418:complement system
240:purpura fulminans
80:blood coagulation
65:
64:
21:Medical condition
4347:
3988:Thrombocytopenia
3984:
3983:
3977:
3976:
3933:Lowenberg's sign
3783:Clotting factors
3773:
3772:
3727:
3720:
3713:
3704:
3703:
3699:
3564:
3563:
3552:
3551:
3541:
3532:(10): 3698–703.
3523:
3514:
3508:
3507:
3488:10.1038/369064a0
3463:
3457:
3456:
3428:
3422:
3421:
3411:
3379:
3373:
3372:
3344:
3338:
3337:
3327:
3295:
3289:
3288:
3252:
3246:
3245:
3235:
3211:
3205:
3204:
3199:. Archived from
3168:
3159:
3158:
3153:. Archived from
3122:
3116:
3115:
3087:
3081:
3080:
3070:
3037:
3024:
3023:
3006:(6): e545–e608.
2994:
2988:
2987:
2951:
2945:
2944:
2934:
2932:10.3310/hta13020
2910:
2904:
2903:
2893:
2883:
2859:
2853:
2852:
2842:
2818:
2812:
2809:
2799:
2774:
2736:
2735:
2733:
2705:
2696:
2695:
2685:
2661:
2655:
2654:
2644:
2620:
2609:
2608:
2580:
2574:
2573:
2563:
2539:
2533:
2532:
2504:
2498:
2497:
2469:
2460:
2459:
2431:
2425:
2424:
2390:
2384:
2383:
2358:(9713): 500–12.
2347:
2341:
2340:
2330:
2298:
2292:
2291:
2255:
2249:
2248:
2238:
2221:(7654): 1185–9.
2206:
2200:
2199:
2171:
2165:
2164:
2136:
2130:
2129:
2103:
2088:Ann. Intern. Med
2083:
2074:
2073:
2063:
2039:
2030:
2029:
2011:
1983:
1970:
1969:
1959:
1935:
1929:
1928:
1918:
1894:
1869:
1868:
1829:
1823:
1822:
1791:Ann. Intern. Med
1786:
1759:
1758:
1748:
1716:
1707:
1706:
1696:
1672:
1649:
1648:
1623:(9535): 601–11.
1612:
1603:
1602:
1592:
1552:
1546:
1545:
1517:
1508:
1507:
1497:
1473:
1464:
1463:
1435:
1429:
1428:
1418:
1386:
1380:
1379:
1369:
1345:
1326:
1325:
1315:
1291:
1278:
1277:
1252:(9757): 2032–9.
1241:
1228:
1227:
1217:
1196:Heit JA (2007).
1193:
1164:
1163:
1145:
761:prothrombin time
422:hemolytic anemia
392:of the skin and
311:antithrombin III
297:, a mutation in
283:common ones are
61:
60:
36:
24:
23:
4355:
4354:
4350:
4349:
4348:
4346:
4345:
4344:
4330:
4329:
4328:
4319:
4268:Hemopericardium
4218:
4171:
4102:Clotting factor
4096:
4040:
3964:
3913:Bancroft's sign
3896:
3887:Virchow's triad
3858:
3808:Factor V Leiden
3764:
3741:
3731:
3692:"Thrombophilia"
3690:
3687:
3682:
3681:
3647:
3646:
3575:
3561:
3556:
3555:
3521:
3515:
3511:
3464:
3460:
3429:
3425:
3380:
3376:
3349:N. Engl. J. Med
3345:
3341:
3304:J. Clin. Invest
3296:
3292:
3253:
3249:
3226:(13): 1650–55.
3212:
3208:
3169:
3162:
3123:
3119:
3088:
3084:
3053:(22): 7101–38.
3038:
3027:
2995:
2991:
2952:
2948:
2911:
2907:
2874:(5): e0155326.
2860:
2856:
2833:(24): 3879–83.
2819:
2815:
2731:
2729:
2722:ABIM Foundation
2718:Choosing Wisely
2706:
2699:
2670:Br. J. Haematol
2662:
2658:
2621:
2612:
2591:(18): 1746–60.
2585:N. Engl. J. Med
2581:
2577:
2548:Cardiovasc. Res
2540:
2536:
2509:Clin. Chest Med
2505:
2501:
2470:
2463:
2442:(18): 1965–76.
2432:
2428:
2413:
2391:
2387:
2348:
2344:
2313:(11): e008864.
2299:
2295:
2256:
2252:
2207:
2203:
2172:
2168:
2137:
2133:
2101:10.1.1.668.4942
2084:
2077:
2048:Br. J. Haematol
2040:
2033:
1984:
1973:
1936:
1932:
1895:
1872:
1831:
1830:
1826:
1787:
1762:
1717:
1710:
1681:Br. J. Haematol
1673:
1652:
1613:
1606:
1567:(19): e012877.
1553:
1549:
1518:
1511:
1482:Br. J. Haematol
1474:
1467:
1440:N. Engl. J. Med
1436:
1432:
1387:
1383:
1346:
1329:
1292:
1281:
1242:
1231:
1194:
1167:
1160:
1146:
1129:
1124:
1105:factor V Leiden
1094:Hughes syndrome
1049:
1032:
1019:
1005:(LMWH, such as
959:
947:Factor V Leiden
932:
893:anticoagulation
841:Choosing Wisely
816:
797:factor V Leiden
741:
729:atherosclerosis
708:, factor V and
650:
644:
636:
629:
575:
519:, when used in
489:Crohn's disease
381:
354:
285:factor V Leiden
280:
260:
207:ischemic stroke
183:mesenteric vein
112:
104:factor V Leiden
96:anticoagulation
55:
22:
17:
12:
11:
5:
4353:
4343:
4342:
4340:Coagulopathies
4325:
4324:
4321:
4320:
4318:
4317:
4316:
4315:
4307:
4306:
4305:
4300:
4295:
4293:Hemoperitoneum
4290:
4285:
4277:
4276:
4275:
4270:
4265:
4257:
4256:
4255:
4250:
4245:
4240:
4235:
4226:
4224:
4220:
4219:
4217:
4216:
4215:
4214:
4204:
4199:
4194:
4189:
4183:
4181:
4177:
4176:
4173:
4172:
4170:
4169:
4164:
4159:
4154:
4149:
4144:
4139:
4134:
4129:
4128:
4127:
4122:
4117:
4106:
4104:
4098:
4097:
4095:
4094:
4093:
4092:
4087:
4075:
4074:
4073:
4063:
4062:
4061:
4050:
4048:
4042:
4041:
4039:
4038:
4033:
4027:
4026:
4025:
4024:
4019:
4009:
4008:
4007:
4005:Evans syndrome
3992:
3990:
3981:
3974:
3970:
3969:
3966:
3965:
3963:
3962:
3957:
3952:
3951:
3950:
3945:
3940:
3938:Peabody's sign
3935:
3930:
3925:
3920:
3915:
3904:
3902:
3898:
3897:
3895:
3894:
3889:
3884:
3879:
3874:
3868:
3866:
3860:
3859:
3857:
3856:
3851:
3850:
3849:
3839:
3838:
3837:
3832:
3830:Thrombocytosis
3827:
3817:
3816:
3815:
3810:
3805:
3800:
3795:
3790:
3779:
3777:
3770:
3766:
3765:
3763:
3762:
3757:
3752:
3746:
3743:
3742:
3730:
3729:
3722:
3715:
3707:
3701:
3700:
3684:
3683:
3680:
3679:
3668:
3666:article/211039
3656:
3655:
3653:
3649:
3648:
3645:
3644:
3633:
3622:
3611:
3596:
3576:
3571:
3570:
3568:
3567:Classification
3560:
3559:External links
3557:
3554:
3553:
3509:
3474:(6475): 64–7.
3458:
3423:
3374:
3355:(24): 1525–8.
3339:
3290:
3247:
3206:
3203:on 2013-01-12.
3160:
3157:on 2013-01-12.
3117:
3082:
3025:
2989:
2946:
2905:
2854:
2813:
2811:
2810:
2790:(2): 209–220.
2775:
2737:, which cites
2697:
2656:
2610:
2575:
2554:(3): 392–403.
2534:
2499:
2461:
2426:
2411:
2385:
2342:
2293:
2266:(10): 1971–3.
2250:
2201:
2166:
2131:
2075:
2031:
1971:
1930:
1870:
1824:
1760:
1731:(1): 154–164.
1708:
1650:
1604:
1547:
1522:Semin. Hematol
1509:
1465:
1430:
1401:(9): 1087–92.
1381:
1327:
1279:
1229:
1165:
1158:
1126:
1125:
1123:
1120:
1114:, looking for
1061:Rudolf Virchow
1048:
1045:
1031:
1028:
1018:
1015:
995:antibody titer
958:
955:
936:anticoagulants
931:
928:
858:evidence-based
845:false positive
815:
812:
777:reptilase time
740:
737:
646:Main article:
643:
640:
634:
627:
574:
571:
379:
353:
350:
279:
276:
259:
256:
164:cardiac arrest
111:
108:
63:
62:
49:
43:
42:
38:
37:
29:
28:
20:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
4352:
4341:
4338:
4337:
4335:
4314:
4311:
4310:
4308:
4304:
4303:Hematosalpinx
4301:
4299:
4296:
4294:
4291:
4289:
4286:
4284:
4281:
4280:
4278:
4274:
4271:
4269:
4266:
4264:
4261:
4260:
4258:
4254:
4251:
4249:
4246:
4244:
4241:
4239:
4236:
4234:
4231:
4230:
4228:
4227:
4225:
4221:
4213:
4210:
4209:
4208:
4205:
4203:
4200:
4198:
4195:
4193:
4190:
4188:
4185:
4184:
4182:
4178:
4168:
4165:
4163:
4160:
4158:
4155:
4153:
4150:
4148:
4145:
4143:
4140:
4138:
4135:
4133:
4130:
4126:
4123:
4121:
4118:
4116:
4113:
4112:
4111:
4108:
4107:
4105:
4103:
4099:
4091:
4088:
4086:
4083:
4082:
4081:
4080:
4076:
4072:
4069:
4068:
4067:
4064:
4060:
4057:
4056:
4055:
4052:
4051:
4049:
4047:
4043:
4037:
4034:
4032:
4029:
4028:
4023:
4020:
4018:
4015:
4014:
4013:
4010:
4006:
4003:
4002:
4001:
3997:
3994:
3993:
3991:
3989:
3985:
3982:
3978:
3975:
3971:
3961:
3958:
3956:
3953:
3949:
3946:
3944:
3941:
3939:
3936:
3934:
3931:
3929:
3928:Louvel's sign
3926:
3924:
3923:Lisker's sign
3921:
3919:
3916:
3914:
3911:
3910:
3909:
3906:
3905:
3903:
3899:
3893:
3890:
3888:
3885:
3883:
3880:
3878:
3875:
3873:
3872:Thrombophilia
3870:
3869:
3867:
3865:
3861:
3855:
3852:
3848:
3845:
3844:
3843:
3840:
3836:
3833:
3831:
3828:
3826:
3823:
3822:
3821:
3818:
3814:
3811:
3809:
3806:
3804:
3801:
3799:
3796:
3794:
3791:
3789:
3786:
3785:
3784:
3781:
3780:
3778:
3774:
3771:
3767:
3761:
3758:
3756:
3753:
3751:
3748:
3747:
3744:
3740:
3736:
3733:Disorders of
3728:
3723:
3721:
3716:
3714:
3709:
3708:
3705:
3697:
3693:
3689:
3688:
3678:
3677:Thrombophilia
3674:
3673:
3669:
3667:
3663:
3662:
3658:
3657:
3654:
3650:
3643:
3639:
3638:
3634:
3632:
3628:
3627:
3623:
3621:
3617:
3616:
3612:
3610:
3606:
3605:
3601:
3597:
3595:
3591:
3587:
3586:
3582:
3578:
3577:
3574:
3569:
3565:
3549:
3545:
3540:
3535:
3531:
3527:
3520:
3513:
3505:
3501:
3497:
3493:
3489:
3485:
3481:
3477:
3473:
3469:
3462:
3454:
3450:
3446:
3442:
3439:(3): 465–90.
3438:
3434:
3427:
3419:
3415:
3410:
3405:
3401:
3397:
3393:
3389:
3385:
3378:
3370:
3366:
3362:
3358:
3354:
3350:
3343:
3335:
3331:
3326:
3321:
3317:
3313:
3310:(5): 1370–3.
3309:
3305:
3301:
3294:
3286:
3282:
3278:
3274:
3270:
3266:
3263:(2): 516–30.
3262:
3258:
3251:
3243:
3239:
3234:
3229:
3225:
3221:
3217:
3210:
3202:
3198:
3194:
3190:
3186:
3182:
3178:
3174:
3167:
3165:
3156:
3152:
3148:
3144:
3140:
3136:
3132:
3128:
3121:
3113:
3109:
3105:
3101:
3097:
3093:
3086:
3078:
3074:
3069:
3064:
3060:
3056:
3052:
3048:
3044:
3036:
3034:
3032:
3030:
3021:
3017:
3013:
3009:
3005:
3001:
2993:
2985:
2981:
2977:
2973:
2969:
2965:
2961:
2957:
2950:
2942:
2938:
2933:
2928:
2924:
2920:
2916:
2909:
2901:
2897:
2892:
2887:
2882:
2877:
2873:
2869:
2865:
2858:
2850:
2846:
2841:
2836:
2832:
2828:
2824:
2817:
2807:
2803:
2798:
2793:
2789:
2785:
2781:
2776:
2772:
2768:
2764:
2760:
2756:
2752:
2748:
2744:
2739:
2738:
2728:
2724:
2723:
2719:
2714:
2710:
2704:
2702:
2693:
2689:
2684:
2679:
2675:
2671:
2667:
2660:
2652:
2648:
2643:
2638:
2635:(6): 458–63.
2634:
2630:
2626:
2619:
2617:
2615:
2606:
2602:
2598:
2594:
2590:
2586:
2579:
2571:
2567:
2562:
2557:
2553:
2549:
2545:
2538:
2530:
2526:
2522:
2518:
2514:
2510:
2503:
2495:
2491:
2487:
2483:
2479:
2475:
2468:
2466:
2457:
2453:
2449:
2445:
2441:
2437:
2430:
2422:
2418:
2414:
2408:
2404:
2400:
2396:
2389:
2381:
2377:
2373:
2369:
2365:
2361:
2357:
2353:
2346:
2338:
2334:
2329:
2324:
2320:
2316:
2312:
2308:
2304:
2297:
2289:
2285:
2281:
2277:
2273:
2269:
2265:
2261:
2254:
2246:
2242:
2237:
2232:
2228:
2224:
2220:
2216:
2212:
2205:
2197:
2193:
2189:
2185:
2182:(6): 401–10.
2181:
2177:
2170:
2162:
2158:
2154:
2150:
2147:(6): 227–32.
2146:
2142:
2135:
2127:
2123:
2119:
2115:
2111:
2107:
2102:
2097:
2094:(8): 587–95.
2093:
2089:
2082:
2080:
2071:
2067:
2062:
2057:
2054:(3): 259–69.
2053:
2049:
2045:
2038:
2036:
2027:
2023:
2019:
2015:
2010:
2005:
2001:
1997:
1993:
1989:
1982:
1980:
1978:
1976:
1967:
1963:
1958:
1953:
1950:(6): 1261–8.
1949:
1945:
1941:
1934:
1926:
1922:
1917:
1912:
1908:
1904:
1900:
1893:
1891:
1889:
1887:
1885:
1883:
1881:
1879:
1877:
1875:
1866:
1862:
1858:
1854:
1850:
1846:
1842:
1838:
1834:
1828:
1820:
1816:
1812:
1808:
1804:
1800:
1797:(2): 128–34.
1796:
1792:
1785:
1783:
1781:
1779:
1777:
1775:
1773:
1771:
1769:
1767:
1765:
1756:
1752:
1747:
1742:
1738:
1734:
1730:
1726:
1722:
1715:
1713:
1704:
1700:
1695:
1690:
1687:(2): 209–20.
1686:
1682:
1678:
1671:
1669:
1667:
1665:
1663:
1661:
1659:
1657:
1655:
1646:
1642:
1638:
1634:
1630:
1626:
1622:
1618:
1611:
1609:
1600:
1596:
1591:
1586:
1582:
1578:
1574:
1570:
1566:
1562:
1558:
1551:
1543:
1539:
1535:
1531:
1528:(2): 106–13.
1527:
1523:
1516:
1514:
1505:
1501:
1496:
1491:
1488:(3): 321–35.
1487:
1483:
1479:
1472:
1470:
1461:
1457:
1453:
1449:
1446:(3): 266–74.
1445:
1441:
1434:
1426:
1422:
1417:
1412:
1408:
1404:
1400:
1396:
1392:
1385:
1377:
1373:
1368:
1363:
1359:
1355:
1351:
1344:
1342:
1340:
1338:
1336:
1334:
1332:
1323:
1319:
1314:
1309:
1305:
1301:
1297:
1290:
1288:
1286:
1284:
1275:
1271:
1267:
1263:
1259:
1255:
1251:
1247:
1240:
1238:
1236:
1234:
1225:
1221:
1216:
1211:
1208:(1): 127–35.
1207:
1203:
1199:
1192:
1190:
1188:
1186:
1184:
1182:
1180:
1178:
1176:
1174:
1172:
1170:
1161:
1155:
1151:
1144:
1142:
1140:
1138:
1136:
1134:
1132:
1127:
1119:
1117:
1113:
1108:
1106:
1102:
1097:
1095:
1091:
1085:
1083:
1079:
1075:
1072:and the U.S.
1071:
1067:
1062:
1053:
1044:
1040:
1036:
1027:
1023:
1014:
1010:
1008:
1004:
998:
996:
991:
989:
985:
981:
975:
973:
963:
954:
952:
948:
943:
941:
937:
927:
925:
921:
917:
911:
907:
905:
900:
896:
894:
890:
885:
882:In 2023, the
880:
878:
874:
870:
867:In 2021, the
865:
863:
859:
855:
849:
846:
842:
838:
832:
830:
826:
822:
811:
808:
806:
802:
798:
794:
790:
786:
782:
778:
774:
773:thrombin time
770:
766:
762:
758:
754:
745:
736:
734:
730:
725:
723:
717:
715:
711:
707:
703:
699:
695:
691:
687:
683:
679:
675:
674:tissue factor
670:
667:
659:
654:
649:
639:
637:
630:
623:
619:
618:
613:
612:
607:
602:
600:
596:
592:
588:
584:
580:
570:
568:
564:
560:
556:
552:
548:
544:
540:
538:
534:
530:
526:
522:
518:
514:
512:
508:
504:
500:
496:
492:
490:
486:
482:
478:
474:
470:
466:
464:
460:
456:
452:
448:
446:
442:
438:
434:
430:
425:
423:
419:
415:
414:
409:
405:
401:
397:
395:
391:
387:
383:
375:
371:
367:
363:
359:
349:
346:
342:
340:
336:
332:
329:(an abnormal
328:
325:mutation and
324:
320:
316:
312:
306:
304:
300:
296:
292:
291:
286:
275:
273:
269:
265:
255:
253:
249:
248:skin necrosis
245:
241:
237:
233:
231:
227:
226:pre-eclampsia
223:
219:
215:
210:
208:
204:
200:
199:heart attacks
196:
192:
188:
184:
180:
176:
172:
167:
165:
161:
157:
153:
149:
145:
141:
137:
133:
129:
125:
116:
107:
105:
101:
97:
92:
89:
85:
81:
77:
73:
69:
68:Thrombophilia
59:
53:
50:
48:
44:
39:
35:
30:
27:Thrombophilia
25:
19:
4313:Hemarthrosis
4077:
4065:
4053:
3943:Pratt's sign
3871:
3755:coagulopathy
3695:
3670:
3659:
3635:
3624:
3613:
3598:
3579:
3529:
3525:
3512:
3471:
3467:
3461:
3436:
3432:
3426:
3391:
3387:
3377:
3352:
3348:
3342:
3307:
3303:
3293:
3260:
3256:
3250:
3223:
3219:
3209:
3201:the original
3180:
3176:
3155:the original
3134:
3130:
3120:
3095:
3091:
3085:
3050:
3046:
3003:
2999:
2992:
2962:(5): 500–3.
2959:
2955:
2949:
2922:
2918:
2908:
2871:
2867:
2857:
2830:
2826:
2816:
2787:
2783:
2746:
2742:
2730:, retrieved
2716:
2676:(1): 80–90.
2673:
2669:
2659:
2632:
2628:
2588:
2584:
2578:
2551:
2547:
2537:
2512:
2508:
2502:
2477:
2473:
2439:
2435:
2429:
2394:
2388:
2355:
2351:
2345:
2310:
2306:
2296:
2263:
2259:
2253:
2218:
2214:
2204:
2179:
2176:Lancet Oncol
2175:
2169:
2144:
2140:
2134:
2091:
2087:
2051:
2047:
2009:2318/1609788
1991:
1987:
1947:
1943:
1933:
1906:
1902:
1840:
1836:
1827:
1794:
1790:
1728:
1724:
1684:
1680:
1620:
1616:
1564:
1560:
1550:
1525:
1521:
1485:
1481:
1443:
1439:
1433:
1398:
1394:
1384:
1357:
1353:
1306:(1): 19–27.
1303:
1299:
1249:
1245:
1205:
1201:
1149:
1109:
1104:
1098:
1093:
1086:
1058:
1041:
1037:
1033:
1030:Epidemiology
1024:
1020:
1011:
999:
992:
976:
968:
944:
933:
912:
908:
897:
881:
866:
850:
833:
821:hepatic vein
817:
809:
805:homocysteine
750:
726:
718:
692:) activates
671:
666:risk factors
663:
615:
609:
606:homocysteine
603:
576:
541:
529:progestogens
515:
511:progesterone
493:
467:
463:chemotherapy
449:
426:
411:
398:
355:
343:
335:fibrinolysis
313:deficiency,
307:
288:
281:
271:
267:
263:
261:
234:
211:
168:
152:palpitations
121:
93:
75:
71:
67:
66:
18:
4066:aggregation
3948:Rose's sign
3918:Homans sign
3750:Coagulation
2732:10 December
2480:(1): 5–11.
2474:Thromb. Res
1944:Haemophilia
1909:(1): 1–12.
801:prothrombin
710:factor VIII
702:factor XIII
694:prothrombin
678:factor VIIa
648:Coagulation
567:factor VIII
345:Blood group
339:plasminogen
323:factor XIII
299:prothrombin
4298:Hematocele
4263:Hemothorax
4238:Hemoptysis
4110:Hemophilia
3882:Thrombosis
3696:Patient UK
3672:Patient UK
3637:DiseasesDB
2629:Am. J. Med
1122:References
1007:enoxaparin
793:fibrinogen
757:blood film
722:hemophilia
698:fibrinogen
622:folic acid
587:fibrinogen
563:factor VII
455:metastatic
433:hemoglobin
362:antibodies
331:fibrinogen
278:Congenital
238:may cause
222:stillbirth
185:, kidney (
148:chest pain
126:(DVT) and
84:thrombosis
52:Hematology
4288:Hemobilia
4233:Epistaxis
3820:Platelets
3661:eMedicine
3047:Blood Adv
2749:: e3979.
2421:201995636
2141:Blood Rev
2096:CiteSeerX
1581:2047-9980
1017:Prognosis
957:Treatment
814:Screening
739:Diagnosis
714:protein Z
706:factor XI
686:factor IX
658:"cascade"
642:Mechanism
633:vitamin B
626:vitamin B
583:factor XI
579:factor IX
533:protein S
517:Estrogens
507:estradiol
495:Pregnancy
224:, severe
173:, liver (
47:Specialty
4334:Category
4279:abdomen
4202:Petechia
4197:Hematoma
4187:Bleeding
4054:adhesion
3980:By cause
3973:Bleeding
3877:Thrombus
3776:By cause
3769:Clotting
3739:clotting
3735:bleeding
3453:16880079
3285:42594050
3277:14347873
3242:26837697
3197:18574280
3151:18574272
3112:32543072
3077:37195076
3068:10709681
3020:34352278
2984:22896788
2976:17934357
2941:19080721
2900:27176603
2868:PLoS One
2849:24307720
2806:20128794
2771:42342532
2763:22740565
2692:16173967
2651:18501222
2605:21542745
2570:19228706
2529:19700047
2494:20163835
2456:15477430
2372:19889451
2337:26560059
2307:BMJ Open
2288:11391129
2280:15447758
2245:18497417
2196:15925818
2161:20817333
2126:19715590
2118:18413620
2070:16643427
2026:25554663
2018:20822807
1966:19141167
1925:16304352
1865:53089216
1857:12529110
1819:43161448
1811:12529095
1755:26780744
1703:20128794
1645:42968924
1637:16905025
1599:31549567
1542:17433903
1504:18710381
1460:20592294
1425:17060659
1376:19630821
1322:18574041
1274:31610364
1266:21131039
1224:18024620
972:warfarin
690:factor V
682:factor X
559:Platelet
394:migraine
352:Acquired
252:warfarin
156:collapse
140:embolize
4248:Hyphema
4223:By site
4207:Purpura
3901:By site
3631:D019851
3548:8916933
3504:4314040
3496:8164741
3476:Bibcode
3418:6414579
3409:1549319
3369:6239102
3334:6895379
2891:4866738
2380:8633455
2328:4654387
2236:2394708
1746:4715840
1590:6806047
1416:1609160
1047:History
988:obesity
916:smoking
877:D-dimer
873:D-dimer
795:tests,
573:Unclear
547:surgery
543:Obesity
523:and in
473:albumin
404:heparin
203:strokes
4309:joint
4259:torso
4192:Bruise
4115:A/VIII
3620:188050
3546:
3502:
3494:
3468:Nature
3451:
3416:
3406:
3367:
3332:
3325:370934
3322:
3283:
3275:
3240:
3195:
3149:
3110:
3075:
3065:
3018:
2982:
2974:
2939:
2898:
2888:
2847:
2804:
2769:
2761:
2690:
2649:
2603:
2568:
2527:
2492:
2454:
2419:
2409:
2378:
2370:
2352:Lancet
2335:
2325:
2286:
2278:
2243:
2233:
2194:
2159:
2124:
2116:
2098:
2068:
2024:
2016:
1988:Lancet
1964:
1923:
1863:
1855:
1817:
1809:
1753:
1743:
1701:
1643:
1635:
1617:Lancet
1597:
1587:
1579:
1540:
1502:
1458:
1423:
1413:
1374:
1320:
1272:
1264:
1246:Lancet
1222:
1156:
1101:Leiden
986:, and
451:Cancer
378:anti-β
376:, and
258:Causes
189:) and
54:
4229:head
3864:Clots
3642:29080
3609:286.9
3594:D68.6
3590:D68.5
3526:Blood
3522:(PDF)
3500:S2CID
3281:S2CID
3220:Blood
3177:Chest
3131:Chest
3000:Chest
2980:S2CID
2827:Blood
2767:S2CID
2417:S2CID
2376:S2CID
2284:S2CID
2122:S2CID
2022:S2CID
1861:S2CID
1815:S2CID
1641:S2CID
1300:Blood
1270:S2CID
611:MTHFR
589:and
160:shock
74:or a
4125:C/XI
4120:B/IX
3737:and
3626:MeSH
3615:OMIM
3604:9-CM
3544:PMID
3492:PMID
3449:PMID
3414:PMID
3365:PMID
3330:PMID
3273:PMID
3238:PMID
3193:PMID
3147:PMID
3108:PMID
3073:PMID
3016:PMID
2972:PMID
2937:PMID
2896:PMID
2845:PMID
2802:PMID
2759:PMID
2734:2013
2688:PMID
2647:PMID
2601:PMID
2566:PMID
2525:PMID
2490:PMID
2452:PMID
2407:ISBN
2368:PMID
2333:PMID
2276:PMID
2241:PMID
2192:PMID
2157:PMID
2114:PMID
2066:PMID
2014:PMID
1962:PMID
1921:PMID
1907:2005
1853:PMID
1807:PMID
1751:PMID
1699:PMID
1633:PMID
1595:PMID
1577:ISSN
1538:PMID
1500:PMID
1456:PMID
1421:PMID
1395:CMAJ
1372:PMID
1318:PMID
1262:PMID
1220:PMID
1206:2007
1154:ISBN
949:and
799:and
775:and
631:and
614:and
565:and
535:and
509:and
487:and
461:for
413:PIGA
317:and
228:and
201:and
177:and
162:and
4017:TTP
4000:ITP
3842:DIC
3600:ICD
3581:ICD
3534:doi
3484:doi
3472:369
3441:doi
3404:PMC
3396:doi
3392:287
3357:doi
3353:311
3320:PMC
3312:doi
3265:doi
3228:doi
3224:127
3185:doi
3181:133
3139:doi
3135:133
3100:doi
3063:PMC
3055:doi
3008:doi
3004:160
2964:doi
2927:doi
2886:PMC
2876:doi
2835:doi
2831:122
2792:doi
2788:149
2751:doi
2747:344
2743:BMJ
2678:doi
2674:131
2637:doi
2633:121
2593:doi
2589:364
2556:doi
2517:doi
2482:doi
2478:126
2444:doi
2440:164
2399:doi
2360:doi
2356:375
2323:PMC
2315:doi
2268:doi
2231:PMC
2223:doi
2219:336
2215:BMJ
2184:doi
2149:doi
2106:doi
2092:148
2056:doi
2052:133
2004:hdl
1996:doi
1992:376
1952:doi
1911:doi
1845:doi
1841:138
1799:doi
1795:138
1741:PMC
1733:doi
1689:doi
1685:149
1625:doi
1621:368
1585:PMC
1569:doi
1530:doi
1490:doi
1486:143
1448:doi
1444:363
1411:PMC
1403:doi
1399:175
1362:doi
1308:doi
1304:112
1254:doi
1250:376
1210:doi
823:in
759:),
617:CBS
396:).
181:),
4336::
4012:TM
3998::
3694:.
3675::
3664::
3640::
3629::
3618::
3607::
3588::
3585:10
3542:.
3530:88
3528:.
3524:.
3498:.
3490:.
3482:.
3470:.
3447:.
3437:32
3435:.
3412:.
3402:.
3390:.
3386:.
3363:.
3351:.
3328:.
3318:.
3308:68
3306:.
3302:.
3279:.
3271:.
3261:13
3259:.
3236:.
3222:.
3218:.
3191:.
3179:.
3175:.
3163:^
3145:.
3133:.
3129:.
3106:.
3096:42
3094:.
3071:.
3061:.
3049:.
3045:.
3028:^
3014:.
3002:.
2978:.
2970:.
2960:14
2958:.
2935:.
2923:13
2921:.
2917:.
2894:.
2884:.
2872:11
2870:.
2866:.
2843:.
2829:.
2825:.
2800:.
2786:.
2782:.
2765:.
2757:.
2745:.
2725:,
2715:,
2700:^
2686:.
2672:.
2668:.
2645:.
2631:.
2627:.
2613:^
2599:.
2587:.
2564:.
2552:82
2550:.
2546:.
2523:.
2513:30
2511:.
2488:.
2476:.
2464:^
2450:.
2438:.
2415:.
2405:.
2374:.
2366:.
2354:.
2331:.
2321:.
2309:.
2305:.
2282:.
2274:.
2264:99
2262:.
2239:.
2229:.
2217:.
2213:.
2190:.
2178:.
2155:.
2145:24
2143:.
2120:.
2112:.
2104:.
2090:.
2078:^
2064:.
2050:.
2046:.
2034:^
2020:.
2012:.
2002:.
1990:.
1974:^
1960:.
1948:14
1946:.
1942:.
1919:.
1905:.
1901:.
1873:^
1859:.
1851:.
1839:.
1835:.
1813:.
1805:.
1793:.
1763:^
1749:.
1739:.
1729:41
1727:.
1723:.
1711:^
1697:.
1683:.
1679:.
1653:^
1639:.
1631:.
1619:.
1607:^
1593:.
1583:.
1575:.
1563:.
1559:.
1536:.
1526:44
1524:.
1512:^
1498:.
1484:.
1480:.
1468:^
1454:.
1442:.
1419:.
1409:.
1397:.
1393:.
1370:.
1356:.
1352:.
1330:^
1316:.
1302:.
1298:.
1282:^
1268:.
1260:.
1248:.
1232:^
1218:.
1204:.
1200:.
1168:^
1130:^
1118:.
1084:.
1076:.
906:.
787:,
783:,
779:,
771:,
767:,
763:,
704:,
635:12
624:,
597:.
585:,
581:,
479:.
290:F5
232:.
220:,
209:.
166:.
158:,
150:,
146:,
3726:e
3719:t
3712:v
3698:.
3602:-
3592:-
3583:-
3573:D
3550:.
3536::
3506:.
3486::
3478::
3455:.
3443::
3420:.
3398::
3371:.
3359::
3336:.
3314::
3287:.
3267::
3244:.
3230::
3187::
3141::
3114:.
3102::
3079:.
3057::
3051:7
3022:.
3010::
2986:.
2966::
2943:.
2929::
2902:.
2878::
2851:.
2837::
2808:.
2794::
2773:.
2753::
2694:.
2680::
2653:.
2639::
2607:.
2595::
2572:.
2558::
2531:.
2519::
2496:.
2484::
2458:.
2446::
2423:.
2401::
2382:.
2362::
2339:.
2317::
2311:5
2290:.
2270::
2247:.
2225::
2198:.
2186::
2180:6
2163:.
2151::
2128:.
2108::
2072:.
2058::
2028:.
2006::
1998::
1968:.
1954::
1927:.
1913::
1867:.
1847::
1821:.
1801::
1757:.
1735::
1705:.
1691::
1647:.
1627::
1601:.
1571::
1565:8
1544:.
1532::
1506:.
1492::
1462:.
1450::
1427:.
1405::
1378:.
1364::
1358:7
1324:.
1310::
1276:.
1256::
1226:.
1212::
1162:.
628:6
483:(
380:2
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.