126:
25:
433:
417:(ARDS) can be caused by ventilation with very large tidal volumes in normal lungs, as well as ventilation with moderate or small volumes in previously injured lungs, and research shows that the incidence of ALI increases with higher tidal volume settings in nonneurologically impaired patients. . Similarly A 2018 systematic review by
385:) is the volume of air inspired and expired with each passive breath. It is typically assumed that the volume of air inhaled is equal to the volume of air exhaled such as in the figure on the right. In a healthy, young human adult, tidal volume is approximately 500 ml per inspiration at rest or 7 ml/kg of body mass.
517:
6 to 8 ml/kg or as low as 5 ml/kg in severe cases. Permissive hypercapnia can be employed in an attempt to minimize aggressive ventilation leading to lung injury. Higher PEEPs are often required however not all ARDS patients require the same PEEP levels. Patient should be started on
397:
to ensure adequate ventilation without causing trauma to the lungs. Tidal volume is measured in milliliters and ventilation volumes are estimated based on a patient's ideal body mass. Measurement of tidal volume can be affected (usually overestimated) by leaks in the
584:
Gajic, Ognjen; Saqib Dara; Jose Mendez; Abedola
Adensanya; Emir Festic; Sean Caples; Rimki Rana; Jennifer StSauver; James Lymp; Bekele Afessa (2004). "Ventilator-associated lung injury in patients without acute lung injury at the onset of mechanical ventilation".
208:
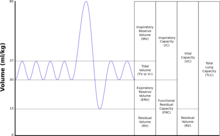
Tidal volume: that volume of air moved into or out of the lungs during quiet breathing (VT indicates a subdivision of the lung; when tidal volume is precisely measured, as in gas exchange calculation, the symbol TV or
144:
Tidal volume: that volume of air moved into or out of the lungs in 1 breath (TV indicates a subdivision of the lung; when tidal volume is precisely measured, as in gas exchange calculation, the symbol TV or
315:
Forced inspiratory flow: (Specific measurement of the forced inspiratory curve is denoted by nomenclature analogous to that for the forced expiratory curve. For example, maximum inspiratory flow is denoted
505:
Protective lung volumes apply 6ml/kg to 8ml/kg with a rate high enough for proper alveolar ventilation but does not create or aggravate intrinsic
Positive End-Expiry Pressure (PEEP).
630:"Intraoperative use of low volume ventilation to decrease postoperative mortality, mechanical ventilation, lengths of stay and lung injury in adults without acute lung injury"
421:
provided evidence that low tidal volume ventilation reduced post operative pneumonia and reduced the requirement for both invasive and non invasive ventilation after surgery
739:
358:
1105:
732:
89:
270:
Forced expiratory volume (time): a generic term indicating the volume of air exhaled under forced conditions in the first
414:
61:
1176:
1031:
475:
108:
68:
351:
320:. Unless otherwise specified, volume qualifiers indicate the volume inspired from RV at the point of measurement.)
1219:
725:
296:
Forced expiratory flow related to some portion of the FVC curve; modifiers refer to amount of FVC already exhaled
1095:
46:
75:
822:
457:
42:
1214:
944:
336:
Maximal voluntary ventilation: volume of air expired in a specified period during repetitive maximal effort
1114:
1063:
914:
344:
165:
Expiratory reserve volume: the maximal volume of air that can be exhaled from the end-expiratory position
57:
259:
Forced vital capacity: the determination of the vital capacity from a maximally forced expiratory effort
1068:
418:
976:
907:
888:
448:
1052:
919:
883:
777:
497:
6ml/kg to 8ml/kg with RR = 12 to 20 and an average starting target minute ventilation of 7 L/min.
189:
Inspiratory vital capacity: the maximum volume of air inhaled from the point of maximum expiration
1085:
954:
173:
Inspiratory reserve volume: the maximal volume that can be inhaled from the end-inspiratory level
35:
453:
unencyclopedic tone reads like instructions, but does not explain why the actions are justified.
902:
849:
839:
748:
394:
1090:
1026:
1224:
1145:
1000:
964:
799:
794:
82:
8:
827:
328:
Peak expiratory flow: The highest forced expiratory flow measured with a peak flow meter
136:
Total lung capacity: the volume in the lungs at maximal inflation, the sum of VC and RV.
1155:
1150:
1130:
988:
864:
662:
629:
610:
598:
1193:
1109:
1075:
877:
832:
814:
706:
667:
649:
602:
548:
443:
410:
399:
221:
Functional residual capacity: the volume in the lungs at the end-expiratory position
157:
Residual volume: the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a maximal exhalation
1010:
959:
869:
784:
698:
657:
645:
641:
614:
594:
1188:
1036:
1005:
285:
Volume that has been exhaled at the end of the first second of forced expiration
1134:
1124:
981:
939:
804:
540:
402:
or the introduction of additional gas, for example during the introduction of
1208:
1140:
896:
809:
653:
689:
Ricard JD (May 2003). "Are we really reducing tidal volume—and should we?".
197:
Vital capacity: the volume of air breathed out after the deepest inhalation.
1080:
931:
789:
710:
671:
606:
583:
552:
518:
6 ml/kg and PEEP increased until plateau pressure is 30 cm H
1119:
717:
702:
251:
Actual volume of the lung including the volume of the conducting airway.
1181:
1100:
995:
772:
767:
125:
1057:
403:
24:
500:
16:
Volume of air displaced between normal inhalation and exhalation
762:
493:
Protective lung ventilation strategies should be applied with V
488:
307:
The maximum instantaneous flow achieved during a FVC maneuver
628:
Guay, Joanne; Ochroch, Edward A; Kopp, Sandra (2018-07-09).
1159:
858:
691:
American
Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine
508:
49:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
1206:
574:, page 33, Royal Society of Medicine Press, 2009
627:
547:, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing,
513:Protective lung ventilation strategies apply. V
501:Patients with chronic obstructive lung disease
733:
393:Tidal volume plays a significant role during
352:
538:
424:Initial settings of mechanical ventilation:
229:Residual volume expressed as percent of TLC
181:Inspiratory capacity: the sum of IRV and TV
747:
740:
726:
489:Patients without pre-existing lung disease
359:
345:
124:
688:
661:
476:Learn how and when to remove this message
388:
109:Learn how and when to remove this message
634:Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
539:Haddad, Moshe; Sharma, Sandeep (2021),
409:Ventilator-induced lung injury such as
1207:
721:
1106:oxygen–hemoglobin dissociation curve
426:
47:adding citations to reliable sources
18:
509:Acute respiratory distress syndrome
415:Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
13:
1032:hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction
599:10.1097/01.CCM.0000133019.52531.30
14:
1236:
682:
431:
23:
34:needs additional citations for
646:10.1002/14651858.cd011151.pub3
621:
577:
564:
532:
1:
525:
7:
1064:Ventilation/perfusion ratio
915:pulmonary stretch receptors
451:. The specific problem is:
10:
1241:
1096:alveolar–arterial gradient
419:The Cochrane Collaboration
1169:
1045:
1019:
977:respiratory minute volume
930:
889:ventral respiratory group
848:
755:
340:
332:
324:
311:
300:
289:
278:
263:
255:
244:
233:
225:
217:
201:
193:
185:
177:
169:
161:
153:
140:
132:
123:
884:dorsal respiratory group
778:obligate nasal breathing
522:0 in most severe cases.
1086:pulmonary gas pressures
1220:Respiratory physiology
840:mechanical ventilation
749:Respiratory physiology
587:Critical Care Medicine
395:mechanical ventilation
389:Mechanical ventilation
1091:alveolar gas equation
1027:pulmonary circulation
1146:respiratory quotient
1001:body plethysmography
920:Hering–Breuer reflex
795:pulmonary surfactant
703:10.1164/rccm.2303003
570:Beardsell, I et al:
458:improve this section
447:to meet Knowledge's
43:improve this article
1215:Respiratory therapy
989:Lung function tests
823:hyperresponsiveness
240:Alveolar gas volume
1156:diffusion capacity
1151:arterial blood gas
1131:carbonic anhydrase
865:pneumotaxic center
541:"Physiology, Lung"
1202:
1201:
1110:Oxygen saturation
1076:zones of the lung
815:airway resistance
486:
485:
478:
449:quality standards
440:This section may
411:Acute lung injury
400:breathing circuit
369:
368:
119:
118:
111:
93:
1232:
1011:nitrogen washout
870:apneustic center
785:respiratory rate
742:
735:
728:
719:
718:
714:
676:
675:
665:
640:(10): CD011151.
625:
619:
618:
593:(9): 1817–1824.
581:
575:
572:MCEM Part A:MCQs
568:
562:
561:
560:
559:
536:
481:
474:
470:
467:
461:
435:
434:
427:
361:
354:
347:
128:
121:
120:
114:
107:
103:
100:
94:
92:
51:
27:
19:
1240:
1239:
1235:
1234:
1233:
1231:
1230:
1229:
1205:
1204:
1203:
1198:
1189:oxygen toxicity
1165:
1053:ventilation (V)
1041:
1037:pulmonary shunt
1015:
1006:peak flow meter
926:
844:
751:
746:
685:
680:
679:
626:
622:
582:
578:
569:
565:
557:
555:
537:
533:
528:
521:
516:
511:
503:
496:
491:
482:
471:
465:
462:
455:
436:
432:
391:
379:
365:
319:
304:
293:
282:
267:
248:
237:
212:
205:
148:
115:
104:
98:
95:
52:
50:
40:
28:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1238:
1228:
1227:
1222:
1217:
1200:
1199:
1197:
1196:
1191:
1186:
1185:
1184:
1173:
1171:
1167:
1166:
1164:
1163:
1153:
1148:
1143:
1138:
1135:chloride shift
1128:
1125:Haldane effect
1122:
1117:
1112:
1103:
1098:
1093:
1088:
1083:
1078:
1073:
1072:
1071:
1066:
1055:
1049:
1047:
1043:
1042:
1040:
1039:
1034:
1029:
1023:
1021:
1017:
1016:
1014:
1013:
1008:
1003:
998:
993:
991:
985:
984:
982:FEV1/FVC ratio
979:
974:
972:
968:
967:
962:
957:
952:
947:
942:
936:
934:
928:
927:
925:
924:
923:
922:
912:
911:
910:
905:
897:chemoreceptors
893:
892:
891:
886:
874:
873:
872:
867:
854:
852:
846:
845:
843:
842:
837:
836:
835:
830:
825:
817:
812:
807:
805:elastic recoil
802:
797:
792:
787:
782:
781:
780:
775:
770:
759:
757:
753:
752:
745:
744:
737:
730:
722:
716:
715:
697:(10): 1297–8.
684:
683:External links
681:
678:
677:
620:
576:
563:
530:
529:
527:
524:
519:
514:
510:
507:
502:
499:
494:
490:
487:
484:
483:
439:
437:
430:
390:
387:
377:
367:
366:
364:
363:
356:
349:
341:
338:
337:
334:
330:
329:
326:
322:
321:
317:
313:
309:
308:
305:
302:
298:
297:
294:
291:
287:
286:
283:
280:
276:
275:
268:
265:
261:
260:
257:
253:
252:
249:
246:
242:
241:
238:
235:
231:
230:
227:
223:
222:
219:
215:
214:
210:
206:
203:
199:
198:
195:
191:
190:
187:
183:
182:
179:
175:
174:
171:
167:
166:
163:
159:
158:
155:
151:
150:
146:
142:
138:
137:
134:
130:
129:
117:
116:
58:"Tidal volume"
31:
29:
22:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1237:
1226:
1223:
1221:
1218:
1216:
1213:
1212:
1210:
1195:
1192:
1190:
1187:
1183:
1180:
1179:
1178:
1177:high altitude
1175:
1174:
1172:
1170:Insufficiency
1168:
1161:
1157:
1154:
1152:
1149:
1147:
1144:
1142:
1141:oxyhemoglobin
1139:
1136:
1132:
1129:
1126:
1123:
1121:
1118:
1116:
1113:
1111:
1107:
1104:
1102:
1099:
1097:
1094:
1092:
1089:
1087:
1084:
1082:
1079:
1077:
1074:
1070:
1067:
1065:
1062:
1061:
1059:
1056:
1054:
1051:
1050:
1048:
1044:
1038:
1035:
1033:
1030:
1028:
1025:
1024:
1022:
1018:
1012:
1009:
1007:
1004:
1002:
999:
997:
994:
992:
990:
987:
986:
983:
980:
978:
975:
973:
970:
969:
966:
963:
961:
958:
956:
953:
951:
948:
946:
943:
941:
938:
937:
935:
933:
929:
921:
918:
917:
916:
913:
909:
906:
904:
901:
900:
899:
898:
894:
890:
887:
885:
882:
881:
880:
879:
875:
871:
868:
866:
863:
862:
861:
860:
856:
855:
853:
851:
847:
841:
838:
834:
831:
829:
826:
824:
821:
820:
818:
816:
813:
811:
810:hysteresivity
808:
806:
803:
801:
798:
796:
793:
791:
788:
786:
783:
779:
776:
774:
771:
769:
766:
765:
764:
761:
760:
758:
754:
750:
743:
738:
736:
731:
729:
724:
723:
720:
712:
708:
704:
700:
696:
692:
687:
686:
673:
669:
664:
659:
655:
651:
647:
643:
639:
635:
631:
624:
616:
612:
608:
604:
600:
596:
592:
588:
580:
573:
567:
554:
550:
546:
542:
535:
531:
523:
506:
498:
480:
477:
469:
459:
454:
450:
446:
445:
438:
429:
428:
425:
422:
420:
416:
412:
407:
405:
401:
396:
386:
384:
380:
373:
362:
357:
355:
350:
348:
343:
342:
339:
335:
331:
327:
323:
314:
310:
306:
299:
295:
288:
284:
277:
273:
269:
262:
258:
254:
250:
243:
239:
232:
228:
224:
220:
216:
207:
200:
196:
192:
188:
184:
180:
176:
172:
168:
164:
160:
156:
152:
143:
139:
135:
131:
127:
122:
113:
110:
102:
91:
88:
84:
81:
77:
74:
70:
67:
63:
60: –
59:
55:
54:Find sources:
48:
44:
38:
37:
32:This article
30:
26:
21:
20:
1081:gas exchange
1046:Interactions
971:calculations
949:
932:Lung volumes
895:
876:
857:
828:constriction
790:respirometer
694:
690:
637:
633:
623:
590:
586:
579:
571:
566:
556:, retrieved
544:
534:
512:
504:
492:
472:
466:January 2020
463:
456:Please help
452:
441:
423:
408:
392:
382:
375:
372:Tidal volume
371:
370:
271:
105:
99:October 2009
96:
86:
79:
72:
65:
53:
41:Please help
36:verification
33:
1225:Respiration
1120:Bohr effect
1020:Circulation
756:Respiration
460:if you can.
1209:Categories
1182:death zone
1101:hemoglobin
996:spirometry
955:dead space
908:peripheral
833:dilatation
819:bronchial
800:compliance
773:exhalation
768:inhalation
558:2021-03-17
545:StatPearls
526:References
69:newspapers
1058:Perfusion
654:1465-1858
404:nebulized
213:is used.)
149:is used.)
1069:V/Q scan
711:12738592
672:29985541
607:15343007
553:31424761
442:require
374:(symbol
1194:hypoxia
1115:2,3-BPG
903:central
878:medulla
850:Control
663:6513630
615:6386675
444:cleanup
413:(ALI) /
406:drugs.
274:seconds
226:RV/TLC%
83:scholar
763:breath
709:
670:
660:
652:
613:
605:
551:
85:
78:
71:
64:
56:
611:S2CID
90:JSTOR
76:books
1160:DLCO
1060:(Q)
859:pons
707:PMID
668:PMID
650:ISSN
603:PMID
549:PMID
62:news
965:PEF
945:FRC
699:doi
695:167
658:PMC
642:doi
595:doi
381:or
333:MVV
325:PEF
318:max
316:FIF
312:FIF
303:max
301:FEF
290:FEF
279:FEV
264:FEV
256:FVC
218:FRC
186:IVC
170:IRV
162:ERV
133:TLC
45:by
1211::
960:CC
950:Vt
940:VC
705:.
693:.
666:.
656:.
648:.
636:.
632:.
609:.
601:.
591:32
589:.
543:,
383:TV
194:VC
178:IC
154:RV
141:TV
1162:)
1158:(
1137:)
1133:(
1127:)
1108:(
741:e
734:t
727:v
713:.
701::
674:.
644::
638:7
617:.
597::
520:2
515:T
495:T
479:)
473:(
468:)
464:(
378:T
376:V
360:e
353:t
346:v
292:x
281:1
272:t
266:t
247:L
245:V
236:A
234:V
211:T
209:V
204:T
202:V
147:T
145:V
112:)
106:(
101:)
97:(
87:·
80:·
73:·
66:·
39:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.