988:
69:
286:
28:
145:
1939:
245:(E) of a polymer is influenced by the load and the response time. Time–temperature superposition implies that the response time function of the elastic modulus at a certain temperature resembles the shape of the same functions of adjacent temperatures. Curves of E vs. log(response time) at one temperature can be shifted to overlap with adjacent curves, as long as the data sets did not suffer from ageing effects during the test time (see
2299:
2073:
2022:
226:
transition from a hard “glassy” state to a soft “rubbery” state in which the modulus can be several orders of magnitude lower than it was in the glassy state. The transition from glassy to rubbery behavior is continuous and the transition zone is often referred to as the leathery zone. The onset temperature of the transition zone, moving from glassy to rubbery, is known as the
628:
832:
237:
In the 1940s
Andrews and Tobolsky showed that there was a simple relationship between temperature and time for the mechanical response of a polymer. Modulus measurements are made by stretching or compressing a sample at a prescribed rate of deformation. For polymers, changing the rate of deformation
1954:
The principle of time-temperature superposition requires the assumption of thermorheologically simple behavior (all curves have the same characteristic time variation law with temperature). From an initial spectral window and a series of isotherms in this window, we can calculate the master curves
276:
or viscosity can often be a strong indicator of the molecular structure and molecular mobility. Time–temperature superposition avoids the inefficiency of measuring a polymer's behavior over long periods of time at a specified temperature by utilizing the fact that at higher temperatures and shorter
225:
polymer against the temperature at which you measured it, you will get a curve which can be divided up into distinct regions of physical behavior. At very low temperatures, the polymer will behave like a glass and exhibit a high modulus. As you increase the temperature, the polymer will undergo a
264:
Consider a viscoelastic body that is subjected to dynamic loading. If the excitation frequency is low enough the viscous behavior is paramount and all polymer chains have the time to respond to the applied load within a time period. In contrast, at higher frequencies, the chains do not have the
205:
The translation factor is often computed using an empirical relation first established by
Malcolm L. Williams, Robert F. Landel and John D. Ferry (also called the Williams-Landel-Ferry or WLF model). An alternative model suggested by Arrhenius is also used. The WLF model is related to macroscopic
2359:
For the superposition principle to apply, the sample must be homogeneous, isotropic and amorphous. The material must be linear viscoelastic under the deformations of interest, i.e., the deformation must be expressed as a linear function of the stress by applying very small strains, e.g. 0.01%.
136:
as a function of time do not change shape as the temperature is changed but appear only to shift left or right. This implies that a master curve at a given temperature can be used as the reference to predict curves at various temperatures by applying a shift operation. The time-temperature
1897:
1679:
1441:
470:
265:
time to fully respond and the resulting artificial viscosity results in an increase in the macroscopic modulus. Moreover, at constant frequency, an increase in temperature results in a reduction of the modulus due to an increase in free volume and chain movement.
238:
will cause the curve described above to be shifted along the temperature axis. Increasing the rate of deformation will shift the curve to higher temperatures so that the transition from a glassy to a rubbery state will happen at higher temperatures.
2254:
651:
1930:≈ 50 K. Experimentally observed values deviate from the values in the table. These orders of magnitude are useful and are a good indicator of the quality of a relationship that has been computed from experimental data.
1169:
909:
1697:
1270:
623:{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}&T>T_{0}\quad \implies \quad a_{\rm {T}}<1\\&T<T_{0}\quad \implies \quad a_{\rm {T}}>1\\&T=T_{0}\quad \implies \quad a_{\rm {T}}=1\,.\end{aligned}}}
452:
656:
475:
1497:
1212:
are positive constants that depend on the material and the reference temperature. This relationship holds only in the approximate temperature range . To determine the constants, the factor
2490:
Experiments that determine the mechanical properties of polymers often use periodic loading. For such situations, the loading rate is related to the frequency of the applied load.
2150:
827:{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}G'(\omega ,T)&=G'\left(a_{\rm {T}}\,\omega ,T_{0}\right)\\G''(\omega ,T)&=G''\left(a_{\rm {T}}\,\omega ,T_{0}\right).\end{aligned}}}
339:. At constant strain, the stress relaxes faster at the higher temperature. The principle of time-temperature superposition states that the change in temperature from
192:
experimental determination of frequency-dependent curves of isothermal viscoelastic mechanical properties at several temperatures and for a small range of frequencies
1192:
2018:
The viscoelastic behavior is well modeled and allows extrapolation beyond the field of experimental frequencies which typically ranges from 0.01 to 100 Hz .
2525:
Andrews, R. D.; Tobolsky, A. V. (August 1951). "Elastoviscous properties of polyisobutylene. IV. Relaxation time spectrum and calculation of bulk viscosity".
1994:. Conversely, lowering the temperature corresponds to the exploration of the part of the curve corresponding to high frequencies. For a reference temperature
268:
Time–temperature superposition is a procedure that has become important in the field of polymers to observe the dependence upon temperature on the change of
2320:
2094:
1916:
for a given polymer system be collected in a table. These constants are approximately the same for a large number of polymers and can be written
1058:
2388:
requires extensive dynamic testing at a number of scanning frequencies and temperature, which represents at least a hundred measurement points.
17:
1892:{\displaystyle C_{1}^{0}={\frac {C_{1}^{g}\,C_{2}^{g}}{C_{2}^{g}+(T_{0}-T_{g})}}\qquad {\rm {and}}\qquad C_{2}^{0}=C_{2}^{g}+(T_{0}-T_{g})\,.}
1436:{\displaystyle \log a_{\rm {T}}=-{\frac {C_{1}^{g}(T-T_{g})}{C_{2}^{g}+(T-T_{g})}}=\log \left({\frac {\eta _{\rm {T}}}{\eta _{T_{g}}}}\right)}
851:
201:
application of the translation factor to determine temperature-dependent moduli over the whole range of frequencies in the master curve.
2632:
374:
2589:
Curve has been generated with data from a dynamic test with a double scanning frequency / temperature on a viscoelastic polymer.
1684:
In particular, to transform the constants from those obtained at the glass transition temperature to a reference temperature
987:
2430:
Li, Rongzhi (February 2000). "Time-temperature superposition method for glass transition temperature of plastic materials".
1674:{\displaystyle C'_{1}={\frac {C_{1}\,C_{2}}{C_{2}+(T'_{0}-T_{0})}}\qquad {\rm {and}}\qquad C'_{2}=C_{2}+(T'_{0}-T_{0})\,.}
2414:
1017:, combined with the principle of time-temperature superposition, can account for variations in the intrinsic viscosity
2561:
2346:
2120:
2328:
2281:. This Arrhenius law, under this glass transition temperature, applies to secondary transitions (relaxation) called
2102:
845:
For a polymer in solution or "molten" state the following relationship can be used to determine the shift factor:
2576:
For the superposition principle to apply, the excitation frequency should be well above the characteristic time
2637:
2608:
2509:
2324:
2098:
2021:
246:
148:
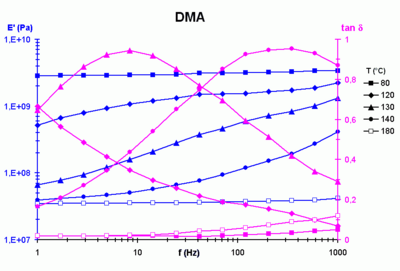
Moduli measured using a dynamic viscoelastic modulus analyzer. The plots show the variation of elastic modulus
1962:
is taken as a reference for setting the frequency scale (the curve at that temperature undergoes no shift).
198:
experimental determination of a master curve showing the effect of frequency for a wide range of frequencies
2363:
To apply the WLF relationship, such a sample should be sought in the approximate temperature range , where
1024:
of amorphous polymers as a function of temperature, for temperatures near the glass transition temperature
227:
1460:
are the coefficients of the WLF model when the reference temperature is the glass transition temperature.
1980:) decreases. This amounts to explore a part of the master curve corresponding to frequencies lower than
195:
computation of a translation factor to correlate these properties for the temperature and frequency range
2249:{\displaystyle \log(a_{\rm {T}})=-{\frac {E_{a}}{2.303R}}\left({\frac {1}{T}}-{\frac {1}{T_{0}}}\right)}
124:
This superposition principle is used to determine temperature-dependent mechanical properties of linear
2662:
2458:
837:
A decrease in temperature increases the time characteristics while frequency characteristics decrease.
128:
materials from known properties at a reference temperature. The elastic moduli of typical amorphous
285:
2652:
2309:
2083:
68:
2313:
2087:
206:
motion of the bulk material, while the
Arrhenius model considers local motion of polymer chains.
2657:
27:
1177:
144:
118:
1233:*. A good correlation between the two shift factors gives the values of the coefficients
960:
versus the reciprocal of temperature (in K), the slope of the curve can be interpreted as
132:
increase with loading rate but decrease when the temperature is increased. Curves of the
8:
464:
is called the horizontal translation factor or the shift factor and has the properties:
976:
2443:
2604:
2557:
2505:
2410:
1955:
of a material which extends over a broader frequency range. An arbitrary temperature
1195:
943:
1031:. The WLF model also expresses the change with the temperature of the shift factor.
2580:(also called relaxation time) which depends on the molecular weight of the polymer.
2534:
2439:
1477:
depend on the reference temperature. If the reference temperature is changed from
2627:
2044:
is the frequency. The shift factor is computed from data in the frequency range
242:
218:
138:
133:
114:
73:
1950:
as a function of frequency. The data have been fit to a polynomial of degree 7.
277:
time the polymer will behave the same, provided there are no phase transitions.
2538:
253:
840:
2646:
1014:
1938:
1164:{\displaystyle \log a_{\rm {T}}=-{\frac {C_{1}(T-T_{0})}{C_{2}+(T-T_{0})}}}
982:
217:
properties on the temperature at which they are measured. If you plot the
214:
125:
32:
222:
188:
The application of the principle typically involves the following steps:
942:
The time–temperature shift factor can also be described in terms of the
921:
is the viscosity (non-Newtonian) during continuous flow at temperature
904:{\displaystyle a_{\rm {T}}={\frac {\eta _{\rm {T}}}{\eta _{\rm {T0}}}}}
76:
of a viscoelastic material under periodic excitation. The frequency is
979:= 8.64x10 eV/K and the activation energy is expressed in terms of eV.
269:
256:
is closely related to the concept of time-temperature superposition.
2298:
2072:
1034:
Williams, Landel and Ferry proposed the following relationship for
273:
129:
2133:
The shift factor (which depends on the nature of the transition)
350:
is equivalent to multiplying the time scale by a constant factor
210:
2367:-transitions are observed (relaxation). The study to determine
2278:
633:
The superposition principle for complex dynamic moduli (G* = G
2015:
is described by an homographic function of the temperature.
1965:
In the frequency range , if the temperature increases from
1902:
These same authors have proposed the "universal constants"
841:
Relationship between shift factor and intrinsic viscosities
447:{\displaystyle E(t,T)=E({\frac {t}{a_{\rm {T}}}},T_{0})\,.}
31:
Temperature dependence of elastic relaxation modulus of a
2554:
Physical aging in amorphous polymers and other materials
2409:(2nd ed.). Taylor & Francis. pp. 486–491.
983:
Shift factor using the
Williams-Landel-Ferry (WLF) model
289:
Schematic of the evolution of the instantaneous modulus
2001:, shifts of the modulus curves have the amplitude log(
2459:"Time-temperature superposition for polymeric blends"
2153:
1700:
1500:
1273:
1180:
1061:
854:
654:
473:
377:
2062:
2248:
1891:
1673:
1435:
1186:
1163:
903:
826:
622:
446:
357:which is only a function of the two temperatures
280:
2644:
2025:Principle of construction of a master curve for
1933:
2524:
2456:
1013:The empirical relationship of Williams-Landel-
176:is the phase angle as a function of frequency
2457:van Gurp, Marnix; Palmen, Jo (January 1998).
2405:Hiemenz, Paul C.; Lodge, Timothy P. (2007).
2404:
1942:Master curves for the instantaneous modulus
2499:
2327:. Unsourced material may be challenged and
2101:. Unsourced material may be challenged and
213:in particular, show a strong dependence of
2633:Temperature dependence of liquid viscosity
2556:. Amsterdam: Elsevier Scientific Pub. Co.
2502:Theory of viscoelasticity: an introduction
592:
588:
546:
542:
500:
496:
241:It has been shown experimentally that the
2347:Learn how and when to remove this message
2121:Learn how and when to remove this message
1885:
1737:
1667:
1530:
795:
714:
612:
440:
2504:. New York: Academic Press. p. 92.
2020:
1937:
986:
284:
143:
111:time–temperature superposition principle
67:
26:
14:
2645:
2551:
2598:
2008:). In the area of glass transition,
1987:while maintaining the temperature at
259:
2570:
2484:
2432:Materials Science and Engineering: A
2325:adding citations to reliable sources
2292:
2099:adding citations to reliable sources
2066:
1491:, the new coefficients are given by
2601:Viscoelastic properties of polymers
2270:is the universal gas constant, and
141:is based on the above observation.
24:
2429:
2169:
1814:
1811:
1808:
1600:
1597:
1594:
1404:
1286:
1074:
890:
878:
861:
789:
708:
600:
554:
508:
416:
137:superposition principle of linear
25:
2674:
1219:is calculated for each component
2603:(3d ed.). New York: Wiley.
2500:Christensen, Richard M. (1971).
2297:
2071:
2063:Shift factor using Arrhenius law
1247:that characterize the material.
1229:of the complex measured modulus
953:). By plotting the shift factor
935:is the viscosity at temperature
313:Consider the relaxation modulus
2592:
1819:
1805:
1605:
1591:
593:
587:
547:
541:
501:
495:
301:) in a static relaxation test.
2638:Williams-Landel-Ferry equation
2583:
2545:
2518:
2493:
2450:
2423:
2398:
2288:
2277:is a reference temperature in
2175:
2160:
1882:
1856:
1799:
1773:
1664:
1635:
1585:
1556:
1377:
1358:
1335:
1316:
1155:
1136:
1118:
1099:
760:
748:
679:
667:
589:
543:
497:
437:
402:
393:
381:
281:Time-temperature superposition
247:Williams-Landel-Ferry equation
18:Time-temperature superposition
13:
1:
2444:10.1016/S0921-5093(99)00602-4
2391:
1934:Construction of master curves
2029:for a reference temperature
1002:for a reference temperature
228:glass transition temperature
84:is the elastic modulus, and
7:
2621:
160:) and the loss factor, tan
10:
2679:
2539:10.1002/pol.1951.120070210
2527:Journal of Polymer Science
2266:is the activation energy,
991:Curve of the variation of
72:Temperature dependence of
2552:Struik, L. C. E. (1978).
2144:using an Arrhenius law:
2599:Ferry, John D. (1980).
1946:and the loss factor tan
645:is obtained similarly:
641:) at a fixed frequency
2250:
2135:can be defined, below
2059:
1972:, the complex modulus
1951:
1893:
1675:
1437:
1188:
1165:
1010:
905:
828:
624:
448:
310:
272:of a polymeric fluid.
221:of a noncrystallizing
185:
117:and in the physics of
106:
65:
2374:and the coefficients
2251:
2024:
1941:
1894:
1676:
1438:
1189:
1187:{\displaystyle \log }
1166:
990:
906:
829:
625:
449:
288:
147:
134:instantaneous modulus
119:glass-forming liquids
71:
30:
2321:improve this section
2151:
2095:improve this section
1698:
1498:
1271:
1178:
1059:
852:
652:
471:
375:
317:at two temperatures
43:is the modulus, and
1852:
1834:
1769:
1752:
1736:
1715:
1650:
1618:
1571:
1513:
1354:
1315:
368:. In other words,
309:is the temperature.
2246:
2060:
1952:
1889:
1838:
1820:
1755:
1738:
1722:
1701:
1671:
1638:
1606:
1559:
1501:
1433:
1340:
1301:
1184:
1161:
1011:
977:Boltzmann constant
901:
824:
822:
620:
618:
444:
311:
260:Physical principle
186:
107:
66:
2663:Rubber properties
2466:Rheology Bulletin
2407:Polymer chemistry
2357:
2356:
2349:
2239:
2219:
2204:
2131:
2130:
2123:
1803:
1589:
1463:The coefficients
1427:
1381:
1196:decadic logarithm
1159:
998:as a function of
944:activation energy
899:
422:
16:(Redirected from
2670:
2615:
2614:
2596:
2590:
2587:
2581:
2574:
2568:
2567:
2549:
2543:
2542:
2522:
2516:
2515:
2497:
2491:
2488:
2482:
2481:
2479:
2477:
2463:
2454:
2448:
2447:
2427:
2421:
2420:
2402:
2352:
2345:
2341:
2338:
2332:
2301:
2293:
2255:
2253:
2252:
2247:
2245:
2241:
2240:
2238:
2237:
2225:
2220:
2212:
2205:
2203:
2195:
2194:
2185:
2174:
2173:
2172:
2143:
2126:
2119:
2115:
2112:
2106:
2075:
2067:
1898:
1896:
1895:
1890:
1881:
1880:
1868:
1867:
1851:
1846:
1833:
1828:
1818:
1817:
1804:
1802:
1798:
1797:
1785:
1784:
1768:
1763:
1753:
1751:
1746:
1735:
1730:
1720:
1714:
1709:
1680:
1678:
1677:
1672:
1663:
1662:
1646:
1631:
1630:
1614:
1604:
1603:
1590:
1588:
1584:
1583:
1567:
1552:
1551:
1541:
1540:
1539:
1529:
1528:
1518:
1509:
1442:
1440:
1439:
1434:
1432:
1428:
1426:
1425:
1424:
1423:
1409:
1408:
1407:
1397:
1382:
1380:
1376:
1375:
1353:
1348:
1338:
1334:
1333:
1314:
1309:
1299:
1291:
1290:
1289:
1193:
1191:
1190:
1185:
1170:
1168:
1167:
1162:
1160:
1158:
1154:
1153:
1132:
1131:
1121:
1117:
1116:
1098:
1097:
1087:
1079:
1078:
1077:
910:
908:
907:
902:
900:
898:
897:
896:
883:
882:
881:
871:
866:
865:
864:
833:
831:
830:
825:
823:
816:
812:
811:
810:
794:
793:
792:
777:
747:
735:
731:
730:
729:
713:
712:
711:
696:
666:
629:
627:
626:
621:
619:
605:
604:
603:
586:
585:
569:
559:
558:
557:
540:
539:
523:
513:
512:
511:
494:
493:
477:
453:
451:
450:
445:
436:
435:
423:
421:
420:
419:
406:
305:is the time and
209:Some materials,
180:and temperature
113:is a concept in
35:material. Here
21:
2678:
2677:
2673:
2672:
2671:
2669:
2668:
2667:
2653:Polymer physics
2643:
2642:
2628:Viscoelasticity
2624:
2619:
2618:
2611:
2597:
2593:
2588:
2584:
2575:
2571:
2564:
2550:
2546:
2533:(23): 221–242.
2523:
2519:
2512:
2498:
2494:
2489:
2485:
2475:
2473:
2461:
2455:
2451:
2428:
2424:
2417:
2403:
2399:
2394:
2387:
2380:
2373:
2353:
2342:
2336:
2333:
2318:
2302:
2291:
2276:
2265:
2233:
2229:
2224:
2211:
2210:
2206:
2196:
2190:
2186:
2184:
2168:
2167:
2163:
2152:
2149:
2148:
2141:
2134:
2127:
2116:
2110:
2107:
2092:
2076:
2065:
2057:
2050:
2035:
2014:
2007:
2000:
1993:
1986:
1971:
1961:
1936:
1929:
1922:
1915:
1908:
1876:
1872:
1863:
1859:
1847:
1842:
1829:
1824:
1807:
1806:
1793:
1789:
1780:
1776:
1764:
1759:
1754:
1747:
1742:
1731:
1726:
1721:
1719:
1710:
1705:
1699:
1696:
1695:
1690:
1658:
1654:
1642:
1626:
1622:
1610:
1593:
1592:
1579:
1575:
1563:
1547:
1543:
1542:
1535:
1531:
1524:
1520:
1519:
1517:
1505:
1499:
1496:
1495:
1490:
1487:
1483:
1476:
1469:
1459:
1452:
1419:
1415:
1414:
1410:
1403:
1402:
1398:
1396:
1392:
1371:
1367:
1349:
1344:
1339:
1329:
1325:
1310:
1305:
1300:
1298:
1285:
1284:
1280:
1272:
1269:
1268:
1263:
1256:
1246:
1239:
1228:
1218:
1211:
1204:
1179:
1176:
1175:
1149:
1145:
1127:
1123:
1122:
1112:
1108:
1093:
1089:
1088:
1086:
1073:
1072:
1068:
1060:
1057:
1056:
1051:
1040:
1030:
1023:
1008:
997:
985:
966:
959:
952:
934:
927:
920:
889:
888:
884:
877:
876:
872:
870:
860:
859:
855:
853:
850:
849:
843:
821:
820:
806:
802:
788:
787:
783:
782:
778:
770:
763:
740:
737:
736:
725:
721:
707:
706:
702:
701:
697:
689:
682:
659:
655:
653:
650:
649:
617:
616:
599:
598:
594:
581:
577:
567:
566:
553:
552:
548:
535:
531:
521:
520:
507:
506:
502:
489:
485:
474:
472:
469:
468:
463:
431:
427:
415:
414:
410:
405:
376:
373:
372:
367:
356:
349:
338:
327:
283:
262:
243:elastic modulus
233:
219:elastic modulus
139:viscoelasticity
115:polymer physics
104:
97:
90:
74:elastic modulus
63:
56:
49:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2676:
2666:
2665:
2660:
2655:
2641:
2640:
2635:
2630:
2623:
2620:
2617:
2616:
2609:
2591:
2582:
2569:
2562:
2544:
2517:
2510:
2492:
2483:
2449:
2438:(1–2): 36–45.
2422:
2416:978-1574447798
2415:
2396:
2395:
2393:
2390:
2385:
2378:
2371:
2355:
2354:
2305:
2303:
2296:
2290:
2287:
2285:-transitions.
2274:
2263:
2257:
2256:
2244:
2236:
2232:
2228:
2223:
2218:
2215:
2209:
2202:
2199:
2193:
2189:
2183:
2180:
2177:
2171:
2166:
2162:
2159:
2156:
2139:
2129:
2128:
2079:
2077:
2070:
2064:
2061:
2055:
2048:
2033:
2012:
2005:
1998:
1991:
1984:
1969:
1959:
1935:
1932:
1927:
1920:
1913:
1906:
1900:
1899:
1888:
1884:
1879:
1875:
1871:
1866:
1862:
1858:
1855:
1850:
1845:
1841:
1837:
1832:
1827:
1823:
1816:
1813:
1810:
1801:
1796:
1792:
1788:
1783:
1779:
1775:
1772:
1767:
1762:
1758:
1750:
1745:
1741:
1734:
1729:
1725:
1718:
1713:
1708:
1704:
1688:
1682:
1681:
1670:
1666:
1661:
1657:
1653:
1649:
1645:
1641:
1637:
1634:
1629:
1625:
1621:
1617:
1613:
1609:
1602:
1599:
1596:
1587:
1582:
1578:
1574:
1570:
1566:
1562:
1558:
1555:
1550:
1546:
1538:
1534:
1527:
1523:
1516:
1512:
1508:
1504:
1488:
1485:
1481:
1474:
1467:
1457:
1450:
1444:
1443:
1431:
1422:
1418:
1413:
1406:
1401:
1395:
1391:
1388:
1385:
1379:
1374:
1370:
1366:
1363:
1360:
1357:
1352:
1347:
1343:
1337:
1332:
1328:
1324:
1321:
1318:
1313:
1308:
1304:
1297:
1294:
1288:
1283:
1279:
1276:
1261:
1254:
1244:
1237:
1224:
1216:
1209:
1202:
1183:
1172:
1171:
1157:
1152:
1148:
1144:
1141:
1138:
1135:
1130:
1126:
1120:
1115:
1111:
1107:
1104:
1101:
1096:
1092:
1085:
1082:
1076:
1071:
1067:
1064:
1049:
1038:
1028:
1021:
1006:
995:
984:
981:
964:
957:
950:
932:
925:
918:
912:
911:
895:
892:
887:
880:
875:
869:
863:
858:
842:
839:
835:
834:
819:
815:
809:
805:
801:
798:
791:
786:
781:
776:
773:
769:
766:
764:
762:
759:
756:
753:
750:
746:
743:
739:
738:
734:
728:
724:
720:
717:
710:
705:
700:
695:
692:
688:
685:
683:
681:
678:
675:
672:
669:
665:
662:
658:
657:
631:
630:
615:
611:
608:
602:
597:
591:
584:
580:
576:
573:
570:
568:
565:
562:
556:
551:
545:
538:
534:
530:
527:
524:
522:
519:
516:
510:
505:
499:
492:
488:
484:
481:
478:
476:
461:
455:
454:
443:
439:
434:
430:
426:
418:
413:
409:
404:
401:
398:
395:
392:
389:
386:
383:
380:
365:
354:
347:
336:
325:
282:
279:
261:
258:
254:Deborah number
231:
203:
202:
199:
196:
193:
102:
95:
88:
61:
54:
47:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2675:
2664:
2661:
2659:
2658:Glass physics
2656:
2654:
2651:
2650:
2648:
2639:
2636:
2634:
2631:
2629:
2626:
2625:
2612:
2606:
2602:
2595:
2586:
2579:
2573:
2565:
2563:9780444416551
2559:
2555:
2548:
2540:
2536:
2532:
2528:
2521:
2513:
2507:
2503:
2496:
2487:
2471:
2467:
2460:
2453:
2445:
2441:
2437:
2433:
2426:
2418:
2412:
2408:
2401:
2397:
2389:
2384:
2377:
2370:
2366:
2361:
2351:
2348:
2340:
2337:December 2021
2330:
2326:
2322:
2316:
2315:
2311:
2306:This section
2304:
2300:
2295:
2294:
2286:
2284:
2280:
2273:
2269:
2262:
2242:
2234:
2230:
2226:
2221:
2216:
2213:
2207:
2200:
2197:
2191:
2187:
2181:
2178:
2164:
2157:
2154:
2147:
2146:
2145:
2138:
2125:
2122:
2114:
2111:December 2021
2104:
2100:
2096:
2090:
2089:
2085:
2080:This section
2078:
2074:
2069:
2068:
2054:
2047:
2043:
2039:
2032:
2028:
2023:
2019:
2016:
2011:
2004:
1997:
1990:
1983:
1979:
1975:
1968:
1963:
1958:
1949:
1945:
1940:
1931:
1926:
1919:
1912:
1905:
1886:
1877:
1873:
1869:
1864:
1860:
1853:
1848:
1843:
1839:
1835:
1830:
1825:
1821:
1794:
1790:
1786:
1781:
1777:
1770:
1765:
1760:
1756:
1748:
1743:
1739:
1732:
1727:
1723:
1716:
1711:
1706:
1702:
1694:
1693:
1692:
1687:
1668:
1659:
1655:
1651:
1647:
1643:
1639:
1632:
1627:
1623:
1619:
1615:
1611:
1607:
1580:
1576:
1572:
1568:
1564:
1560:
1553:
1548:
1544:
1536:
1532:
1525:
1521:
1514:
1510:
1506:
1502:
1494:
1493:
1492:
1480:
1473:
1466:
1461:
1456:
1449:
1429:
1420:
1416:
1411:
1399:
1393:
1389:
1386:
1383:
1372:
1368:
1364:
1361:
1355:
1350:
1345:
1341:
1330:
1326:
1322:
1319:
1311:
1306:
1302:
1295:
1292:
1281:
1277:
1274:
1267:
1266:
1265:
1260:
1253:
1248:
1243:
1236:
1232:
1227:
1222:
1215:
1208:
1201:
1197:
1181:
1150:
1146:
1142:
1139:
1133:
1128:
1124:
1113:
1109:
1105:
1102:
1094:
1090:
1083:
1080:
1069:
1065:
1062:
1055:
1054:
1053:
1048:
1044:
1041:in terms of (
1037:
1032:
1027:
1020:
1016:
1005:
1001:
994:
989:
980:
978:
974:
970:
963:
956:
949:
945:
940:
938:
931:
924:
917:
893:
885:
873:
867:
856:
848:
847:
846:
838:
817:
813:
807:
803:
799:
796:
784:
779:
774:
771:
767:
765:
757:
754:
751:
744:
741:
732:
726:
722:
718:
715:
703:
698:
693:
690:
686:
684:
676:
673:
670:
663:
660:
648:
647:
646:
644:
640:
636:
613:
609:
606:
595:
582:
578:
574:
571:
563:
560:
549:
536:
532:
528:
525:
517:
514:
503:
490:
486:
482:
479:
467:
466:
465:
460:
457:The quantity
441:
432:
428:
424:
411:
407:
399:
396:
390:
387:
384:
378:
371:
370:
369:
364:
360:
353:
346:
342:
335:
331:
324:
320:
316:
308:
304:
300:
296:
292:
287:
278:
275:
271:
266:
257:
255:
250:
248:
244:
239:
235:
229:
224:
220:
216:
212:
207:
200:
197:
194:
191:
190:
189:
183:
179:
175:
171:
167:
163:
159:
155:
151:
146:
142:
140:
135:
131:
127:
122:
120:
116:
112:
101:
94:
87:
83:
79:
75:
70:
60:
53:
46:
42:
39:is the time,
38:
34:
29:
19:
2600:
2594:
2585:
2577:
2572:
2553:
2547:
2530:
2526:
2520:
2501:
2495:
2486:
2474:. Retrieved
2469:
2465:
2452:
2435:
2431:
2425:
2406:
2400:
2382:
2375:
2368:
2364:
2362:
2358:
2343:
2334:
2319:Please help
2307:
2282:
2271:
2267:
2260:
2258:
2136:
2132:
2117:
2108:
2093:Please help
2081:
2052:
2045:
2041:
2037:
2030:
2026:
2017:
2009:
2002:
1995:
1988:
1981:
1977:
1973:
1966:
1964:
1956:
1953:
1947:
1943:
1924:
1917:
1910:
1903:
1901:
1685:
1683:
1478:
1471:
1464:
1462:
1454:
1447:
1445:
1258:
1251:
1249:
1241:
1234:
1230:
1225:
1220:
1213:
1206:
1199:
1173:
1046:
1042:
1035:
1033:
1025:
1018:
1012:
1003:
999:
992:
972:
968:
961:
954:
947:
941:
936:
929:
922:
915:
913:
844:
836:
642:
638:
634:
632:
458:
456:
362:
358:
351:
344:
340:
333:
329:
322:
318:
314:
312:
306:
302:
298:
294:
290:
267:
263:
251:
240:
236:
215:viscoelastic
208:
204:
187:
181:
177:
173:
169:
165:
161:
157:
153:
149:
126:viscoelastic
123:
110:
108:
99:
92:
85:
81:
77:
58:
51:
44:
40:
36:
33:viscoelastic
2289:Limitations
2051:= 1 Hz and
223:crosslinked
2647:Categories
2610:0471048941
2511:0121742504
2476:7 December
2392:References
2058:= 1000 Hz.
328:such that
2308:does not
2222:−
2182:−
2158:
2082:does not
1923:≈ 15 and
1870:−
1787:−
1652:−
1573:−
1412:η
1400:η
1390:
1365:−
1323:−
1296:−
1278:
1143:−
1106:−
1084:−
1066:
1052:) :
886:η
874:η
797:ω
752:ω
716:ω
671:ω
590:⟹
544:⟹
498:⟹
270:viscosity
172:), where
2622:See also
2472:(1): 5–8
1648:′
1616:′
1569:′
1511:′
971:, where
775:″
745:″
694:′
664:′
274:Rheology
211:polymers
130:polymers
2329:removed
2314:sources
2279:kelvins
2103:removed
2088:sources
1194:is the
975:is the
2607:
2560:
2508:
2413:
2259:where
1446:where
1174:where
914:where
230:, or T
2462:(PDF)
2198:2.303
1015:Ferry
637:+ i G
332:>
98:<
91:<
57:<
50:<
2605:ISBN
2558:ISBN
2506:ISBN
2478:2021
2411:ISBN
2381:and
2312:any
2310:cite
2086:any
2084:cite
1909:and
1470:and
1453:and
1240:and
1223:and
1205:and
1198:and
928:and
561:>
529:<
515:<
483:>
361:and
321:and
252:The
109:The
2535:doi
2440:doi
2436:278
2323:by
2155:log
2097:by
2036:.
1691:,
1484:to
1387:log
1275:log
1250:If
1182:log
1063:log
639:''
343:to
249:).
82:G'
2649::
2529:.
2470:67
2468:.
2464:.
2434:.
2027:E′
1974:E′
1944:E′
1486:T′
1264::
1257:=
1221:M′
939:.
919:T0
635:'
234:.
168:,
156:,
150:E′
121:.
80:,
2613:.
2578:τ
2566:.
2541:.
2537::
2531:7
2514:.
2480:.
2446:.
2442::
2419:.
2386:2
2383:C
2379:1
2376:C
2372:T
2369:a
2365:α
2350:)
2344:(
2339:)
2335:(
2331:.
2317:.
2283:β
2275:0
2272:T
2268:R
2264:a
2261:E
2243:)
2235:0
2231:T
2227:1
2217:T
2214:1
2208:(
2201:R
2192:a
2188:E
2179:=
2176:)
2170:T
2165:a
2161:(
2142:,
2140:g
2137:T
2124:)
2118:(
2113:)
2109:(
2105:.
2091:.
2056:2
2053:ω
2049:1
2046:ω
2042:ω
2040:=
2038:f
2034:0
2031:T
2013:T
2010:a
2006:T
2003:a
1999:0
1996:T
1992:0
1989:T
1985:1
1982:ω
1978:ω
1976:(
1970:0
1967:T
1960:0
1957:T
1948:δ
1928:2
1925:C
1921:1
1918:C
1914:2
1911:C
1907:1
1904:C
1887:.
1883:)
1878:g
1874:T
1865:0
1861:T
1857:(
1854:+
1849:g
1844:2
1840:C
1836:=
1831:0
1826:2
1822:C
1815:d
1812:n
1809:a
1800:)
1795:g
1791:T
1782:0
1778:T
1774:(
1771:+
1766:g
1761:2
1757:C
1749:g
1744:2
1740:C
1733:g
1728:1
1724:C
1717:=
1712:0
1707:1
1703:C
1689:0
1686:T
1669:.
1665:)
1660:0
1656:T
1644:0
1640:T
1636:(
1633:+
1628:2
1624:C
1620:=
1612:2
1608:C
1601:d
1598:n
1595:a
1586:)
1581:0
1577:T
1565:0
1561:T
1557:(
1554:+
1549:2
1545:C
1537:2
1533:C
1526:1
1522:C
1515:=
1507:1
1503:C
1489:0
1482:0
1479:T
1475:2
1472:C
1468:1
1465:C
1458:2
1455:C
1451:1
1448:C
1430:)
1421:g
1417:T
1405:T
1394:(
1384:=
1378:)
1373:g
1369:T
1362:T
1359:(
1356:+
1351:g
1346:2
1342:C
1336:)
1331:g
1327:T
1320:T
1317:(
1312:g
1307:1
1303:C
1293:=
1287:T
1282:a
1262:g
1259:T
1255:0
1252:T
1245:2
1242:C
1238:1
1235:C
1231:M
1226:M
1217:T
1214:a
1210:2
1207:C
1203:1
1200:C
1156:)
1151:0
1147:T
1140:T
1137:(
1134:+
1129:2
1125:C
1119:)
1114:0
1110:T
1103:T
1100:(
1095:1
1091:C
1081:=
1075:T
1070:a
1050:0
1047:T
1045:-
1043:T
1039:T
1036:a
1029:g
1026:T
1022:0
1019:η
1009:.
1007:0
1004:T
1000:T
996:T
993:a
973:k
969:k
967:/
965:a
962:E
958:T
955:a
951:a
948:E
946:(
937:T
933:T
930:η
926:0
923:T
916:η
894:0
891:T
879:T
868:=
862:T
857:a
818:.
814:)
808:0
804:T
800:,
790:T
785:a
780:(
772:G
768:=
761:)
758:T
755:,
749:(
742:G
733:)
727:0
723:T
719:,
709:T
704:a
699:(
691:G
687:=
680:)
677:T
674:,
668:(
661:G
643:ω
614:.
610:1
607:=
601:T
596:a
583:0
579:T
575:=
572:T
564:1
555:T
550:a
537:0
533:T
526:T
518:1
509:T
504:a
491:0
487:T
480:T
462:T
459:a
442:.
438:)
433:0
429:T
425:,
417:T
412:a
408:t
403:(
400:E
397:=
394:)
391:T
388:,
385:t
382:(
379:E
366:0
363:T
359:T
355:T
352:a
348:0
345:T
341:T
337:0
334:T
330:T
326:0
323:T
319:T
315:E
307:T
303:t
299:T
297:,
295:t
293:(
291:E
232:g
184:.
182:T
178:f
174:δ
170:T
166:f
164:(
162:δ
158:T
154:f
152:(
105:.
103:2
100:T
96:1
93:T
89:0
86:T
78:ω
64:.
62:2
59:T
55:1
52:T
48:0
45:T
41:G
37:t
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.