424:(e.g. crunches) or more advanced abdominal exercises tend to "flatten" the belly, this is owed to the tangential training of the TVA inherent in such exercises. Recently, the transverse abdominal has become the subject of debate between biokineticists, kinesiologists, strength trainers, and physical therapists. The two positions on the muscle are (1) that the muscle is effective and capable of bracing the human core during extremely heavy lifts and (2) that it is not. Specifically, one recent systematic review has found that the baseline dysfunction of TVA cannot predict the clinical outcomes of low back pain. Similarly, another systematic review has revealed that the changes in TVA function or morphology after different nonsurgical treatments are unrelated to the improvement of pain intensity or low back pain related-disability. These findings have challenged the traditional emphasis of using TVA-targeted intervention to treat low back pain.
1324:
436:. The TVA also (involuntarily) contracts during many lifts; it is the body's natural weight-lifting belt, stabilizing the spine and pelvis during lifting movements. It has been estimated that the contraction of the TVA and other muscles reduces the vertical pressure on the intervertebral discs by as much as 40%. Failure to engage the TVA during higher intensity lifts is dangerous and encourages injury to the spine. The TVA acts as a girdle or corset by creating hoop tension around the midsection.
448:
496:
460:
90:
472:
102:
520:
508:
484:
36:
537:
396:
Without a stable spine, one aided by proper contraction of the TVA, the nervous system fails to recruit the muscles in the extremities efficiently, and functional movements cannot be properly performed. The transverse abdominal and the segmental stabilizers (e.g. the
1344:
703:"Do Changes in Transversus Abdominis and Lumbar Multifidus During Conservative Treatment Explain Changes in Clinical Outcomes Related to Nonspecific Low Back Pain? A Systematic Review"
447:
357:; its upper three-fourths lie behind the rectus muscle and blend with the posterior lamella of the aponeurosis of the internal oblique; its lower fourth is in front of the
495:
303:
The transverse abdominal, so called for the direction of its fibers, is the innermost of the flat muscles of the abdomen. It is positioned immediately deep to the
656:"Do various baseline characteristics of transversus abdominis and lumbar multifidus predict clinical outcomes in nonspecific low back pain? A systematic review"
592:
Aruin, Alexanders; Latash, Markl (1995). "Directional specificity of postural muscles in feed-forward postural reactions during fast voluntary arm movements".
231:
420:
muscles alone will not and can not give one a "flat" belly; this effect is achieved only through training the TVA. Thus, to the extent that traditional
459:
849:
1049:
797:
785:
207:
389:
The transverse abdominal helps to compress the ribs and viscera, providing thoracic and pelvic stability. This is explained further
52:
If the information is appropriate for the lead of the article, this information should also be included in the body of the article.
45:
334:
fascia), the lower fibers of which curve inferomedially (medially and downward), and are inserted, together with those of the
576:
788:
at Human
Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Incision and reflection of the internal abdominal oblique muscle."
135:
125:
1248:
842:
1290:
1275:
1054:
655:
947:
898:
67:
453:
Diagram of a transverse section of the posterior abdominal wall, to show the disposition of the lumbodorsal fascia.
353:
Throughout the rest of its extent the aponeurosis passes horizontally to the middle line, and is inserted into the
471:
1258:
835:
567:
Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell; illustrations by
Richard; Richardson, Paul (2005).
350:
also called the aponeurotic falx. In layman's terms, the muscle ends in the middle line of a person's abdomen.
800:
at Human
Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Muscles and nerves of the posterior abdominal wall."
1349:
930:
226:
821:
815:
809:
803:
635:
Dart, R.A. (March 1947). "The Double-Spiral
Arrangement Of The Voluntary Musculature In The Human Body".
17:
546:
519:
1314:
238:
175:
1109:
1044:
390:
566:
791:
501:
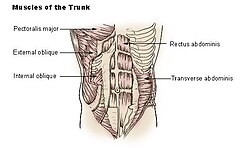
Diagram of a transverse section through the anterior abdomina wall, below the linea semicircularis.
794:
at the SUNY Downstate
Medical Center - "Anterior Abdominal Wall: The Transversus Abdominis Muscle"
654:
Wong, Arnold Y.L; Parent, Eric C; Funabashi, Martha; Stanton, Tasha R; Kawchuk, Gregory N (2013).
920:
335:
331:
304:
284:
1285:
1001:
937:
507:
483:
343:
214:
202:
827:
1241:
1212:
374:
163:
318:, from the inner surfaces of the cartilages of the lower six ribs, interdigitating with the
1280:
1195:
1190:
1008:
354:
323:
288:
412:
health, the muscle also has the effect of pulling in what would otherwise be a protruding
8:
1236:
1200:
972:
421:
319:
1323:
1152:
1124:
1119:
1076:
1066:
1039:
925:
683:
617:
378:
370:
167:
150:
111:
1297:
1263:
1061:
1029:
1013:
996:
765:
724:
675:
609:
572:
551:
311:
276:
1345:
Knowledge articles incorporating text from the 20th edition of Gray's
Anatomy (1918)
687:
621:
1253:
1207:
1071:
989:
984:
977:
967:
942:
755:
714:
667:
601:
417:
358:
180:
Compresses abdominal contents (bilateral), rotates trunk ipsilaterally (unilateral)
107:
908:
744:"Contraction of the Abdominal Muscles Associated with Movement of the Lower Limb"
465:
Posterior surface of sternum and costal cartilages, showing
Transversus thoracis.
433:
347:
719:
702:
701:
Wong, Arnold Y.L; Parent, Eric C; Funabashi, Martha; Kawchuk, Gregory N (2014).
310:
The transverse abdominal arises as fleshy fibers, from the lateral third of the
130:
Iliac crest, inguinal ligament, thoracolumbar fascia, and costal cartilages 7-12
1328:
1129:
1034:
874:
671:
409:
292:
280:
1338:
1228:
915:
542:
393:. The transverse abdominal also helps a pregnant woman to deliver her child.
219:
140:
Xiphoid process, linea alba, pubic crest and pecten pubis via conjoint tendon
1270:
1170:
1147:
760:
743:
728:
679:
339:
769:
613:
1185:
327:
315:
244:
101:
605:
1114:
398:
89:
272:
48:
contains information that is not included elsewhere in the article
862:
413:
866:
858:
857:
571:(Pbk. ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone.
145:
190:
157:
432:
The most well known method of strengthening the TVA is the
405:
700:
653:
314:, from the anterior three-fourths of the inner lip of the
416:(hence its nickname, the “corset muscle”). Training the
373:(thoracoabdominal, nerve roots T7-T11), as well as the
1312:
369:
The transverse abdominal is innervated by the lower
162:Thoracoabdominal nn. (T6-T11), Subcostal n. (T12),
1336:
741:
477:The interfoveolar ligament, seen from in front.
401:) of the spine have evolved to work in tandem.
742:Hodges, Paul W; Richardson, Carolyn A (1997).
843:
591:
850:
836:
100:
88:
759:
718:
68:Learn how and when to remove this message
560:
14:
1337:
541:This article incorporates text in the
831:
735:
525:The abdominal aorta and its branches.
291:to be a significant component of the
824:at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
818:at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
812:at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
806:at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
694:
634:
585:
439:
404:It is true that the TVA is vital to
29:
647:
628:
24:
1055:Crura of superficial inguinal ring
25:
1361:
779:
1322:
535:
518:
506:
494:
482:
470:
458:
446:
326:. It ends anteriorly in a broad
34:
754:(2): 132–42, discussion 142–4.
364:
283:, deep to (layered below) the
196:musculus transversus abdominis
13:
1:
530:
513:The abdominal inguinal ring.
489:Diagram of sheath of Rectus.
298:
269:transversus abdominis muscle
27:Muscle of the abdominal area
7:
720:10.1016/j.jpain.2013.10.008
594:Experimental Brain Research
569:Gray's anatomy for students
549:of the 20th edition of
427:
384:
271:, is a muscle layer of the
257:transverse abdominal muscle
106:The transversus abdominis,
83:Transverse abdominal muscle
10:
1366:
948:Abdominal internal oblique
899:Abdominal external oblique
672:10.1016/j.pain.2013.07.010
239:Anatomical terms of muscle
1221:
1178:
1169:
1140:
1102:
1095:
1045:Superficial inguinal ring
1022:
963:
956:
891:
882:
873:
259:(TVA), also known as the
237:
225:
213:
201:
189:
184:
174:
156:
144:
134:
124:
119:
99:
87:
82:
798:Anatomy figure: 40:07-06
792:Anatomy photo:35:17-0100
786:Anatomy figure: 35:07-04
338:, into the crest of the
287:. It is thought by most
346:, forming the inguinal
336:internal oblique muscle
305:internal oblique muscle
285:internal oblique muscle
1286:Puboprostatic ligament
1002:Interfoveolar ligament
938:Tendinous intersection
637:Surgeons' Hall Journal
1242:Rectoprostatic fascia
375:iliohypogastric nerve
164:iliohypogastric nerve
94:Muscles of the trunk.
1350:Muscles of the torso
1281:Pubovesical ligament
904:Transverse abdominal
761:10.1093/ptj/77.2.132
324:thoracolumbar fascia
265:transversalis muscle
261:transverse abdominis
1237:Rectovaginal fascia
973:Panniculus adiposus
707:The Journal of Pain
422:abdominal exercises
289:fitness instructors
1153:Iliopectineal arch
1110:Quadratus lumborum
1077:Reflected ligament
1067:Pectineal ligament
1050:Intercrural fibers
1040:Deep inguinal ring
822:Anatomy image:7311
816:Anatomy image:7209
810:Anatomy image:7194
804:Anatomy image:7183
606:10.1007/BF00231718
379:ilioinguinal nerve
371:intercostal nerves
168:ilioinguinal nerve
151:Subcostal arteries
1310:
1309:
1306:
1305:
1298:Anococcygeal body
1264:Piriformis fascia
1165:
1164:
1161:
1160:
1091:
1090:
1087:
1086:
1062:Inguinal ligament
1030:Inguinal triangle
1014:Linea semilunaris
997:Transverse fascia
861:and ligaments of
578:978-0-443-06612-2
440:Additional images
312:inguinal ligament
279:(front and side)
253:
252:
248:
78:
77:
70:
16:(Redirected from
1357:
1327:
1326:
1318:
1254:Obturator fascia
1176:
1175:
1100:
1099:
1072:Lacunar ligament
990:Fascia of Scarpa
985:Membranous layer
978:Fascia of Camper
968:Abdominal fascia
961:
960:
921:Rectus abdominis
889:
888:
880:
879:
852:
845:
838:
829:
828:
774:
773:
763:
748:Physical Therapy
739:
733:
732:
722:
713:(4): 377.e1–35.
698:
692:
691:
666:(12): 2589–602.
651:
645:
644:
632:
626:
625:
589:
583:
582:
564:
539:
538:
522:
510:
498:
486:
474:
462:
450:
418:rectus abdominis
359:rectus abdominis
245:edit on Wikidata
242:
108:rectus abdominis
104:
92:
80:
79:
73:
66:
62:
59:
53:
38:
37:
30:
21:
1365:
1364:
1360:
1359:
1358:
1356:
1355:
1354:
1335:
1334:
1333:
1321:
1313:
1311:
1302:
1291:Inferior fascia
1276:Superior fascia
1217:
1157:
1136:
1083:
1018:
952:
909:Conjoint tendon
884:
869:
856:
782:
777:
740:
736:
699:
695:
652:
648:
633:
629:
590:
586:
579:
565:
561:
536:
533:
526:
523:
514:
511:
502:
499:
490:
487:
478:
475:
466:
463:
454:
451:
442:
434:vacuum exercise
430:
387:
367:
348:conjoint tendon
322:, and from the
301:
249:
115:
95:
74:
63:
57:
54:
51:
43:This article's
39:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1363:
1353:
1352:
1347:
1332:
1331:
1308:
1307:
1304:
1303:
1301:
1300:
1295:
1294:
1293:
1288:
1283:
1278:
1268:
1267:
1266:
1261:
1259:Tendinous arch
1256:
1246:
1245:
1244:
1239:
1231:
1225:
1223:
1219:
1218:
1216:
1215:
1213:Rectococcygeus
1210:
1205:
1204:
1203:
1198:
1193:
1182:
1180:
1173:
1167:
1166:
1163:
1162:
1159:
1158:
1156:
1155:
1150:
1144:
1142:
1138:
1137:
1135:
1134:
1133:
1132:
1127:
1122:
1112:
1106:
1104:
1097:
1093:
1092:
1089:
1088:
1085:
1084:
1082:
1081:
1080:
1079:
1074:
1069:
1059:
1058:
1057:
1052:
1047:
1042:
1035:Inguinal canal
1032:
1026:
1024:
1020:
1019:
1017:
1016:
1011:
1006:
1005:
1004:
994:
993:
992:
982:
981:
980:
975:
964:
958:
954:
953:
951:
950:
945:
940:
935:
934:
933:
928:
923:
913:
912:
911:
901:
895:
893:
886:
877:
875:Abdominal wall
871:
870:
855:
854:
847:
840:
832:
826:
825:
819:
813:
807:
801:
795:
789:
781:
780:External links
778:
776:
775:
734:
693:
646:
627:
584:
577:
558:
552:Gray's Anatomy
532:
529:
528:
527:
524:
517:
515:
512:
505:
503:
500:
493:
491:
488:
481:
479:
476:
469:
467:
464:
457:
455:
452:
445:
441:
438:
429:
426:
386:
383:
366:
363:
344:pectineal line
300:
297:
281:abdominal wall
251:
250:
241:
235:
234:
229:
223:
222:
217:
211:
210:
205:
199:
198:
193:
187:
186:
182:
181:
178:
172:
171:
160:
154:
153:
148:
142:
141:
138:
132:
131:
128:
122:
121:
117:
116:
105:
97:
96:
93:
85:
84:
76:
75:
42:
40:
33:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1362:
1351:
1348:
1346:
1343:
1342:
1340:
1330:
1325:
1320:
1319:
1316:
1299:
1296:
1292:
1289:
1287:
1284:
1282:
1279:
1277:
1274:
1273:
1272:
1269:
1265:
1262:
1260:
1257:
1255:
1252:
1251:
1250:
1247:
1243:
1240:
1238:
1235:
1234:
1232:
1230:
1229:Pelvic fascia
1227:
1226:
1224:
1220:
1214:
1211:
1209:
1206:
1202:
1199:
1197:
1196:Pubococcygeus
1194:
1192:
1191:Iliococcygeus
1189:
1188:
1187:
1184:
1183:
1181:
1177:
1174:
1172:
1168:
1154:
1151:
1149:
1146:
1145:
1143:
1139:
1131:
1128:
1126:
1123:
1121:
1118:
1117:
1116:
1113:
1111:
1108:
1107:
1105:
1101:
1098:
1094:
1078:
1075:
1073:
1070:
1068:
1065:
1064:
1063:
1060:
1056:
1053:
1051:
1048:
1046:
1043:
1041:
1038:
1037:
1036:
1033:
1031:
1028:
1027:
1025:
1021:
1015:
1012:
1010:
1007:
1003:
1000:
999:
998:
995:
991:
988:
987:
986:
983:
979:
976:
974:
971:
970:
969:
966:
965:
962:
959:
955:
949:
946:
944:
941:
939:
936:
932:
929:
927:
924:
922:
919:
918:
917:
916:Rectus sheath
914:
910:
907:
906:
905:
902:
900:
897:
896:
894:
890:
887:
881:
878:
876:
872:
868:
864:
860:
853:
848:
846:
841:
839:
834:
833:
830:
823:
820:
817:
814:
811:
808:
805:
802:
799:
796:
793:
790:
787:
784:
783:
771:
767:
762:
757:
753:
749:
745:
738:
730:
726:
721:
716:
712:
708:
704:
697:
689:
685:
681:
677:
673:
669:
665:
661:
657:
650:
642:
638:
631:
623:
619:
615:
611:
607:
603:
600:(2): 323–32.
599:
595:
588:
580:
574:
570:
563:
559:
557:
556:
553:
550:
548:
544:
543:public domain
521:
516:
509:
504:
497:
492:
485:
480:
473:
468:
461:
456:
449:
444:
443:
437:
435:
425:
423:
419:
415:
411:
407:
402:
400:
394:
392:
382:
380:
376:
372:
362:
360:
356:
351:
349:
345:
341:
337:
333:
329:
325:
321:
317:
313:
308:
306:
296:
294:
290:
286:
282:
278:
274:
270:
266:
262:
258:
246:
240:
236:
233:
230:
228:
224:
221:
218:
216:
212:
209:
206:
204:
200:
197:
194:
192:
188:
183:
179:
177:
173:
169:
165:
161:
159:
155:
152:
149:
147:
143:
139:
137:
133:
129:
127:
123:
118:
113:
109:
103:
98:
91:
86:
81:
72:
69:
61:
49:
47:
41:
32:
31:
19:
1201:Puborectalis
1148:Iliac fascia
931:Arcuate line
903:
751:
747:
737:
710:
706:
696:
663:
659:
649:
640:
636:
630:
597:
593:
587:
568:
562:
554:
540:
534:
431:
403:
395:
388:
368:
352:
309:
302:
268:
264:
260:
256:
254:
208:A04.5.01.019
195:
64:
55:
46:lead section
44:
1186:Levator ani
1125:Psoas minor
1120:Psoas major
926:Pyramidalis
365:Innervation
328:aponeurosis
316:iliac crest
185:Identifiers
112:pyramidalis
18:Transversus
1339:Categories
1009:Linea alba
531:References
355:linea alba
166:(L1), and
1233:Visceral
1208:Coccygeus
1115:Iliopsoas
1096:Posterior
943:Cremaster
883:Anterior/
399:multifidi
332:Spigelian
320:diaphragm
299:Structure
136:Insertion
58:July 2024
1249:Parietal
1023:Inguinal
729:24184573
688:26095069
680:23867731
622:24706658
547:page 414
428:Exercise
385:Function
377:and the
273:anterior
1329:Anatomy
1130:Iliacus
885:lateral
863:abdomen
859:Muscles
770:9037214
614:7789439
414:abdomen
277:lateral
176:Actions
120:Details
1315:Portal
1222:Fascia
1179:Muscle
1171:Pelvis
1141:Fascia
1103:Muscle
957:Fascia
892:Muscle
867:pelvis
768:
727:
686:
678:
620:
612:
575:
555:(1918)
146:Artery
126:Origin
110:, and
1271:Floor
684:S2CID
618:S2CID
545:from
340:pubis
330:(the
243:[
232:15570
191:Latin
158:Nerve
865:and
766:PMID
725:PMID
676:PMID
660:Pain
643:(2).
610:PMID
573:ISBN
410:core
408:and
406:back
391:here
342:and
293:core
275:and
267:and
255:The
220:2375
203:TA98
170:(L1)
756:doi
715:doi
668:doi
664:154
602:doi
598:103
227:FMA
215:TA2
1341::
764:.
752:77
750:.
746:.
723:.
711:15
709:.
705:.
682:.
674:.
662:.
658:.
641:10
639:.
616:.
608:.
596:.
381:.
361:.
307:.
295:.
263:,
1317::
851:e
844:t
837:v
772:.
758::
731:.
717::
690:.
670::
624:.
604::
581:.
247:]
114:.
71:)
65:(
60:)
56:(
50:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.