145:(WCET), which is theoretically less useful. The author of this change is unknown, but it was not Siple or Passel as is generally believed. At first, it was defined as the temperature at which the windchill index would be the same in the complete absence of wind. This led to equivalent temperatures that exaggerated the severity of the weather. Charles Eagan realized that people are rarely still and that even when it is calm, there is some air movement. He redefined the absence of wind to be an air speed of 1.8 metres per second (6.5 km/h; 4.0 mph), which was about as low a wind speed as a cup anemometer could measure. This led to more realistic (warmer-sounding) values of equivalent temperature.
609:
597:
38:
621:
910:
and is somewhat more involved than the simpler North
American model. The North American formula was designed to be applied at low temperatures (as low as −46 °C or −50 °F) when humidity levels are also low. The hot-weather version of the AT (1984) is used by the National Weather Service in
589:
As the air temperature falls, the chilling effect of any wind that is present increases. For example, a 16 km/h (10 mph) wind will lower the apparent temperature by a wider margin at an air temperature of −20 °C (−4 °F) than a wind of the same speed would if the air temperature
640:
The apparent temperature (AT), invented in the late 1970s, was designed to measure thermal sensation in indoor conditions. It was extended in the early 1980s to include the effect of sun and wind. The AT index used here is based on a mathematical model of an adult, walking outdoors, in the shade
133:
working in the
Antarctic before the Second World War, and were made available by the National Weather Service by the 1970s. They were based on the cooling rate of a small plastic bottle as its contents turned to ice while suspended in the wind on the expedition hut roof, at the same level as the
298:
under various wind speeds and temperatures using standard engineering correlations of wind speed and heat transfer rate. Heat transfer was calculated for a bare face in wind, facing the wind, while walking into it at 1.4 m/s (5.0 km/h; 3.1 mph). The model corrects the officially
92:
of warm air forms against the surface. Moving air disrupts this boundary layer, or epiclimate, carrying the warm air away, thereby allowing cooler air to replace the warm air against the surface and increasing the temperature difference in the boundary layer. The faster the wind speed, the more
871:
444:
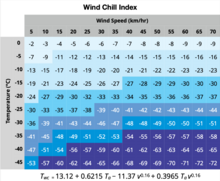
When the temperature is −20 °C (−4 °F) and the wind speed is 5 km/h (3 mph), the wind chill index is −24. If the temperature remains at −20 °C and the wind speed increases to 30 km/h (19 mph), the wind chill index falls to −33.
88:. The rate of convection depends on both the difference in temperature between the surface and the fluid surrounding it and the velocity of that fluid with respect to the surface. As convection from a warm surface heats the air around it, an insulating
561:
415:
293:
In
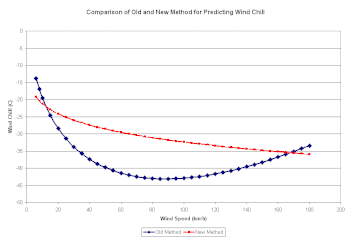
November 2001, Canada, the United States, and the United Kingdom implemented a new wind chill index developed by scientists and medical experts on the Joint Action Group for Temperature Indices (JAG/TI). It is determined by iterating a model of
158:/hour per square metre. Each individual calibrated the scale of numbers personally, through experience. The chart also provided general guidance to comfort and hazard through threshold values of the index, such as 1400, which was the threshold for
631:
The 2001 WCET is a steady-state calculation (except for the time-to-frostbite estimates). There are significant time-dependent aspects to wind chill because cooling is most rapid at the start of any exposure, when the skin is still warm.
113:
Many formulas exist for wind chill because, unlike temperature, wind chill has no universally agreed-upon standard definition or measurement. All the formulas attempt to qualitatively predict the effect of wind on the temperature humans
260:
766:
153:
Equivalent temperature was not universally used in North
America until the 21st century. Until the 1970s, the coldest parts of Canada reported the original Wind Chill Index, a three- or four-digit number with units of
711:
641:(Steadman 1994). The AT is defined as the temperature, at the reference humidity level, producing the same amount of discomfort as that experienced under the current ambient temperature and humidity.
457:
311:
299:
measured wind speed to the wind speed at face height, assuming the person is in an open field. The results of this model may be approximated, to within one degree, from the following formulas.
170:
118:. Weather services in different countries use standards unique to their country or region; for example, the U.S. and Canadian weather services use a model accepted by the
1174:
1389:
608:
649:
56:
from the body to the surrounding atmosphere. Its values are always lower than the air temperature in the range where the formula is valid. When the
1111:
1027:
Eagan, C. (1964). Review of research on military problems in cold regions. C. Kolb and F. Holstrom eds. TDR-64-28. Arctic
Aeromed. Lab. p 147–156.
1283:
964:
866:{\displaystyle e={\frac {\mathrm {RH} }{100}}\cdot 6.105\cdot \exp {\left({\frac {17.27\cdot T_{\mathrm {a} }}{237.7+T_{\mathrm {a} }}}\right)},}
586:
Windchill temperature is defined only for temperatures at or below 10 °C (50 °F) and wind speeds above 4.8 km/h (3.0 mph).
52:) is the sensation of cold produced by the wind for a given ambient air temperature on exposed skin as the air motion accelerates the rate of
959:
1843:
41:
Wind chill index values for a range of temperatures and wind speeds, from the standard wind chill formula for
Environment Canada.
1382:
1531:
1202:
1828:
1356:
1838:
97:, wind chill does not refer to how cold things get, and they will only get as cold as the air temperature. This means
1551:
1375:
1045:
943:
1699:
1056:
1833:
1746:
1178:
556:{\displaystyle T_{\mathrm {wc} }=35.74+0.6215T_{\mathrm {a} }-35.75v^{+0.16}+0.4275T_{\mathrm {a} }v^{+0.16},}
410:{\displaystyle T_{\mathrm {wc} }=13.12+0.6215T_{\mathrm {a} }-11.37v^{+0.16}+0.3965T_{\mathrm {a} }v^{+0.16},}
1578:
1546:
1493:
94:
1068:
1807:
31:
1119:
1741:
1498:
596:
1721:
1655:
1483:
620:
17:
1588:
1440:
119:
138:. The so-called Windchill Index provided a pretty good indication of the severity of the weather.
1789:
1711:
1003:
1643:
1603:
1556:
1541:
1523:
969:
1690:
1583:
1573:
1536:
1322:
1277:
255:{\displaystyle WCI=\left(10{\sqrt {v}}-v+10.5\right)\cdot \left(33-T_{\mathrm {a} }\right),}
1769:
1736:
1638:
1633:
1598:
1257:
1146:
900:
728:
438:
105:
cannot freeze when wind chill is below freezing and the air temperature is above freezing.
57:
1248:
Tikuisis, Peter; Osczevski, Randall J. (2003). "Facial
Cooling During Cold Air Exposure".
8:
1731:
1716:
1261:
1150:
1503:
911:
the United States. In the United States, this simple version of the AT is known as the
449:
303:
73:
1350:
1297:
1784:
1680:
1568:
1410:
1041:
939:
760:
130:
126:
30:
This article is about the meteorological effect of "wind chill". For other uses, see
1367:
1265:
1227:
1206:
1154:
295:
37:
1435:
933:
1726:
1361:
89:
1822:
1508:
53:
27:
Lowering of body temperature due to the passing flow of lower-temperature air
1159:
1134:
1089:
1685:
1660:
1593:
1470:
931:
740:
1269:
1069:"Environment Canada - Weather and Meteorology - Canada's Wind Chill Index"
1774:
1613:
1513:
155:
77:
1779:
1665:
1460:
1445:
1425:
912:
135:
81:
61:
614:
Comparison of old and new wind chill values at −15 °C (5 °F)
1621:
1450:
1430:
1415:
288:
159:
85:
1799:
1761:
1675:
1420:
907:
102:
98:
1670:
426:
is the wind chill index, based on the
Celsius temperature scale;
1090:"Meteorological Tables, Wind Chill. August, 2001 Press Release"
759:
The vapour pressure can be calculated from the temperature and
706:{\displaystyle \mathrm {AT} =T_{\mathrm {a} }+0.33e-0.7v-4.00,}
1478:
1175:"Calculation of the 1971 to 2000 Climate Normals for Canada"
1455:
125:
The first wind chill formulas and tables were developed by
1353:
Table of wind chill temperatures in
Celsius and Fahrenheit
1488:
1177:. Climate.weatheroffice.gc.ca. 2013-07-10. Archived from
932:
Vincent J. Schaefer; John A. Day; Jay
Pasachoff (1998).
906:
The Australian formula includes the important factor of
572:
is the wind chill index, based on the Fahrenheit scale;
1397:
769:
652:
460:
314:
173:
751:
is wind speed (m/s) at an elevation of 10 m (33
141:In the 1960s, wind chill began to be reported as a
1132:
865:
705:
635:
579:is the air temperature in degrees Fahrenheit; and
555:
409:
289:North American and United Kingdom wind chill index
254:
1247:
1135:"The new wind chill equivalent temperature chart"
1820:
1250:Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society
1139:Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society
1133:Osczevski, Randall; Bluestein, Maurice (2005).
965:National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
433:is the air temperature in degrees Celsius; and
1383:
1228:"A chart of windchills based on this formula"
1532:Convective available potential energy (CAPE)
1298:"The Apparent Temperature (AT) - Heat Index"
437:is the wind speed at 10 m (33 ft)
1282:: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of May 2024 (
1390:
1376:
1323:"The formula for the apparent temperature"
1205:. Weather.gov. 2009-12-17. Archived from
1158:
1001:
108:
1351:National Center for Atmospheric Research
997:
995:
993:
991:
989:
987:
165:The original formula for the index was:
60:is higher than the air temperature, the
36:
1357:Current map of global wind chill values
1197:
1195:
1104:
1082:
93:readily the surface cools. Contrary to
14:
1821:
1004:"How to Calculate a Wind Chill Factor"
1371:
984:
583:is the wind speed in miles per hour.
122:. That model has evolved over time.
1192:
302:The standard wind chill formula for
1494:Convective condensation level (CCL)
1002:Kozlowski, Rosann (30 March 2020).
24:
1700:Equivalent potential temperature (
1364:at the US National Weather Service
1116:BBC Weather, Understanding weather
846:
826:
782:
779:
670:
657:
654:
531:
494:
470:
467:
385:
348:
324:
321:
238:
25:
1855:
1552:Conditional symmetric instability
1398:Meteorological data and variables
1344:
960:"Windchill Terms and Definitions"
148:
143:wind chill equivalent temperature
1844:Units of meteorology measurement
1499:Lifting condensation level (LCL)
1327:Bureau Of Meteorology, Australia
1302:Bureau Of Meteorology, Australia
619:
607:
595:
1484:Cloud condensation nuclei (CCN)
1315:
1290:
1241:
1220:
1167:
1126:
935:A Field Guide to the Atmosphere
636:Australian apparent temperature
590:were −10 °C (14 °F).
1747:Wet-bulb potential temperature
1589:Level of free convection (LFC)
1061:
1050:
1030:
1021:
952:
925:
269:= wind chill index, kg⋅cal/m/h
67:
13:
1:
1790:Pressure-gradient force (PGF)
1712:Sea surface temperature (SST)
1547:Convective momentum transport
1038:Human Factors Design Handbook
938:. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt.
918:
72:A surface loses heat through
1604:Bulk Richardson number (BRN)
1036:*Woodson, Wesley E. (1981).
887:is dry-bulb temperature (°C)
7:
1808:Maximum potential intensity
1574:Free convective layer (FCL)
1537:Convective inhibition (CIN)
32:Wind chill (disambiguation)
10:
1860:
1829:Atmospheric thermodynamics
1742:Wet-bulb globe temperature
1599:Maximum parcel level (MPL)
1092:. National Weather Service
448:The equivalent formula in
441:, in kilometres per hour.
439:standard anemometer height
29:
1839:Meteorological quantities
1798:
1760:
1722:Thermodynamic temperature
1656:Forest fire weather index
1612:
1522:
1469:
1403:
1230:. Weather.gov. 2009-12-17
1040:, page 815. McGraw-Hill.
1644:Equivalent temperature (
1557:Convective temperature (
1441:Surface weather analysis
1329:. Bom.gov.au. 2010-02-05
1304:. Bom.gov.au. 2010-02-05
893:is relative humidity (%)
602:Celsius wind chill index
120:National Weather Service
1691:Potential temperature (
1436:Surface solar radiation
1160:10.1175/BAMS-86-10-1453
1057:Aquation 55, page 6-113
1834:Meteorological indices
1681:Relative humidity (RH)
1569:Equilibrium level (EL)
1542:Convective instability
1272:(inactive 2024-05-02).
1203:"NWS Wind Chill Index"
867:
707:
557:
411:
256:
109:Alternative approaches
42:
1362:Wind chill calculator
1270:10.1175/BAMS-84-7-927
1118:. BBC. Archived from
972:on September 17, 2008
868:
708:
626:Wind chill calculator
558:
412:
284:= air temperature, °C
257:
40:
1770:Atmospheric pressure
1737:Wet-bulb temperature
1639:Dry-bulb temperature
1634:Dew point depression
901:exponential function
767:
763:using the equation:
729:dry-bulb temperature
650:
458:
312:
275:= wind velocity, m/s
171:
58:apparent temperature
1732:Virtual temperature
1717:Temperature anomaly
1411:Adiabatic processes
1262:2003BAMS...84..927T
1151:2005BAMS...86.1453O
1122:on 11 October 2010.
1504:Precipitable water
863:
703:
553:
450:US customary units
407:
304:Environment Canada
252:
43:
1816:
1815:
1785:Pressure gradient
1594:Lifted index (LI)
1145:(10): 1453–1458.
853:
789:
761:relative humidity
199:
131:Charles F. Passel
127:Paul Allman Siple
64:is used instead.
50:wind chill factor
16:(Redirected from
1851:
1392:
1385:
1378:
1369:
1368:
1338:
1337:
1335:
1334:
1319:
1313:
1312:
1310:
1309:
1294:
1288:
1287:
1281:
1273:
1245:
1239:
1238:
1236:
1235:
1224:
1218:
1217:
1215:
1214:
1199:
1190:
1189:
1187:
1186:
1171:
1165:
1164:
1162:
1130:
1124:
1123:
1108:
1102:
1101:
1099:
1097:
1086:
1080:
1079:
1077:
1076:
1065:
1059:
1054:
1048:
1034:
1028:
1025:
1019:
1018:
1016:
1014:
999:
982:
981:
979:
977:
968:. Archived from
956:
950:
949:
929:
898:
892:
886:
872:
870:
869:
864:
859:
858:
854:
852:
851:
850:
849:
832:
831:
830:
829:
812:
790:
785:
777:
754:
750:
738:
726:
712:
710:
709:
704:
675:
674:
673:
660:
644:The formula is:
623:
611:
599:
562:
560:
559:
554:
549:
548:
536:
535:
534:
518:
517:
499:
498:
497:
475:
474:
473:
416:
414:
413:
408:
403:
402:
390:
389:
388:
372:
371:
353:
352:
351:
329:
328:
327:
296:skin temperature
261:
259:
258:
253:
248:
244:
243:
242:
241:
217:
213:
200:
195:
21:
1859:
1858:
1854:
1853:
1852:
1850:
1849:
1848:
1819:
1818:
1817:
1812:
1794:
1756:
1706:
1650:
1628:
1608:
1563:
1518:
1465:
1399:
1396:
1347:
1342:
1341:
1332:
1330:
1321:
1320:
1316:
1307:
1305:
1296:
1295:
1291:
1275:
1274:
1246:
1242:
1233:
1231:
1226:
1225:
1221:
1212:
1210:
1201:
1200:
1193:
1184:
1182:
1173:
1172:
1168:
1131:
1127:
1110:
1109:
1105:
1095:
1093:
1088:
1087:
1083:
1074:
1072:
1067:
1066:
1062:
1055:
1051:
1035:
1031:
1026:
1022:
1012:
1010:
1000:
985:
975:
973:
958:
957:
953:
946:
930:
926:
921:
899:represents the
896:
890:
885:
879:
845:
844:
840:
833:
825:
824:
820:
813:
811:
807:
806:
778:
776:
768:
765:
764:
752:
746:
734:
725:
719:
669:
668:
664:
653:
651:
648:
647:
638:
627:
624:
615:
612:
603:
600:
578:
571:
541:
537:
530:
529:
525:
510:
506:
493:
492:
488:
466:
465:
461:
459:
456:
455:
432:
425:
395:
391:
384:
383:
379:
364:
360:
347:
346:
342:
320:
319:
315:
313:
310:
309:
291:
283:
237:
236:
232:
225:
221:
194:
190:
186:
172:
169:
168:
151:
111:
70:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1857:
1847:
1846:
1841:
1836:
1831:
1814:
1813:
1811:
1810:
1804:
1802:
1796:
1795:
1793:
1792:
1787:
1782:
1777:
1772:
1766:
1764:
1758:
1757:
1755:
1754:
1749:
1744:
1739:
1734:
1729:
1727:Vapor pressure
1724:
1719:
1714:
1709:
1704:
1697:
1688:
1683:
1678:
1673:
1668:
1663:
1658:
1653:
1648:
1641:
1636:
1631:
1626:
1618:
1616:
1610:
1609:
1607:
1606:
1601:
1596:
1591:
1586:
1581:
1576:
1571:
1566:
1561:
1554:
1549:
1544:
1539:
1534:
1528:
1526:
1520:
1519:
1517:
1516:
1511:
1506:
1501:
1496:
1491:
1486:
1481:
1475:
1473:
1467:
1466:
1464:
1463:
1458:
1453:
1448:
1443:
1438:
1433:
1428:
1423:
1418:
1413:
1407:
1405:
1401:
1400:
1395:
1394:
1387:
1380:
1372:
1366:
1365:
1359:
1354:
1346:
1345:External links
1343:
1340:
1339:
1314:
1289:
1256:(7): 927–933.
1240:
1219:
1191:
1166:
1125:
1103:
1081:
1060:
1049:
1029:
1020:
983:
951:
944:
923:
922:
920:
917:
904:
903:
894:
888:
883:
862:
857:
848:
843:
839:
836:
828:
823:
819:
816:
810:
805:
802:
799:
796:
793:
788:
784:
781:
775:
772:
757:
756:
744:
743:pressure (hPa)
732:
723:
702:
699:
696:
693:
690:
687:
684:
681:
678:
672:
667:
663:
659:
656:
637:
634:
629:
628:
625:
618:
616:
613:
606:
604:
601:
594:
576:
569:
552:
547:
544:
540:
533:
528:
524:
521:
516:
513:
509:
505:
502:
496:
491:
487:
484:
481:
478:
472:
469:
464:
430:
423:
406:
401:
398:
394:
387:
382:
378:
375:
370:
367:
363:
359:
356:
350:
345:
341:
338:
335:
332:
326:
323:
318:
290:
287:
286:
285:
281:
276:
270:
251:
247:
240:
235:
231:
228:
224:
220:
216:
212:
209:
206:
203:
198:
193:
189:
185:
182:
179:
176:
150:
149:Original model
147:
110:
107:
95:popular belief
90:boundary layer
69:
66:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1856:
1845:
1842:
1840:
1837:
1835:
1832:
1830:
1827:
1826:
1824:
1809:
1806:
1805:
1803:
1801:
1797:
1791:
1788:
1786:
1783:
1781:
1780:Barotropicity
1778:
1776:
1773:
1771:
1768:
1767:
1765:
1763:
1759:
1753:
1750:
1748:
1745:
1743:
1740:
1738:
1735:
1733:
1730:
1728:
1725:
1723:
1720:
1718:
1715:
1713:
1710:
1708:
1703:
1698:
1696:
1694:
1689:
1687:
1684:
1682:
1679:
1677:
1674:
1672:
1669:
1667:
1664:
1662:
1659:
1657:
1654:
1652:
1647:
1642:
1640:
1637:
1635:
1632:
1630:
1625:
1620:
1619:
1617:
1615:
1611:
1605:
1602:
1600:
1597:
1595:
1592:
1590:
1587:
1585:
1582:
1580:
1577:
1575:
1572:
1570:
1567:
1565:
1560:
1555:
1553:
1550:
1548:
1545:
1543:
1540:
1538:
1535:
1533:
1530:
1529:
1527:
1525:
1521:
1515:
1512:
1510:
1509:Precipitation
1507:
1505:
1502:
1500:
1497:
1495:
1492:
1490:
1487:
1485:
1482:
1480:
1477:
1476:
1474:
1472:
1468:
1462:
1459:
1457:
1454:
1452:
1449:
1447:
1444:
1442:
1439:
1437:
1434:
1432:
1429:
1427:
1424:
1422:
1419:
1417:
1414:
1412:
1409:
1408:
1406:
1402:
1393:
1388:
1386:
1381:
1379:
1374:
1373:
1370:
1363:
1360:
1358:
1355:
1352:
1349:
1348:
1328:
1324:
1318:
1303:
1299:
1293:
1285:
1279:
1271:
1267:
1263:
1259:
1255:
1251:
1244:
1229:
1223:
1209:on 2011-09-18
1208:
1204:
1198:
1196:
1181:on 2013-06-27
1180:
1176:
1170:
1161:
1156:
1152:
1148:
1144:
1140:
1136:
1129:
1121:
1117:
1113:
1107:
1091:
1085:
1070:
1064:
1058:
1053:
1047:
1046:0-07-071765-6
1043:
1039:
1033:
1024:
1009:
1008:sciencing.com
1005:
998:
996:
994:
992:
990:
988:
971:
967:
966:
961:
955:
947:
945:0-395-97631-6
941:
937:
936:
928:
924:
916:
914:
909:
902:
895:
889:
882:
878:
877:
876:
873:
860:
855:
841:
837:
834:
821:
817:
814:
808:
803:
800:
797:
794:
791:
786:
773:
770:
762:
749:
745:
742:
737:
733:
730:
722:
718:
717:
716:
713:
700:
697:
694:
691:
688:
685:
682:
679:
676:
665:
661:
645:
642:
633:
622:
617:
610:
605:
598:
593:
592:
591:
587:
584:
582:
575:
568:
563:
550:
545:
542:
538:
526:
522:
519:
514:
511:
507:
503:
500:
489:
485:
482:
479:
476:
462:
453:
451:
446:
442:
440:
436:
429:
422:
417:
404:
399:
396:
392:
380:
376:
373:
368:
365:
361:
357:
354:
343:
339:
336:
333:
330:
316:
307:
305:
300:
297:
280:
277:
274:
271:
268:
265:
264:
263:
249:
245:
233:
229:
226:
222:
218:
214:
210:
207:
204:
201:
196:
191:
187:
183:
180:
177:
174:
166:
163:
161:
157:
146:
144:
139:
137:
132:
128:
123:
121:
117:
106:
104:
100:
96:
91:
87:
83:
79:
75:
65:
63:
59:
55:
54:heat transfer
51:
47:
39:
33:
19:
1751:
1701:
1692:
1686:Mixing ratio
1661:Haines Index
1645:
1623:
1558:
1471:Condensation
1331:. Retrieved
1326:
1317:
1306:. Retrieved
1301:
1292:
1278:cite journal
1253:
1249:
1243:
1232:. Retrieved
1222:
1211:. Retrieved
1207:the original
1183:. Retrieved
1179:the original
1169:
1142:
1138:
1128:
1120:the original
1115:
1112:"Wind Chill"
1106:
1094:. Retrieved
1084:
1073:. Retrieved
1063:
1052:
1037:
1032:
1023:
1011:. Retrieved
1007:
974:. Retrieved
970:the original
963:
954:
934:
927:
905:
880:
874:
758:
747:
741:water vapour
735:
720:
714:
646:
643:
639:
630:
588:
585:
580:
573:
566:
564:
454:
447:
443:
434:
427:
420:
418:
308:
301:
292:
278:
272:
266:
167:
164:
156:kilocalories
152:
142:
140:
124:
115:
112:
71:
49:
45:
44:
1775:Baroclinity
1622:Dew point (
1614:Temperature
1514:Water vapor
78:evaporation
68:Explanation
48:(popularly
1823:Categories
1752:Wind chill
1666:Heat index
1524:Convection
1461:Wind shear
1446:Visibility
1426:Lapse rate
1333:2013-08-09
1308:2018-08-01
1234:2017-04-13
1213:2013-08-09
1185:2013-08-09
1096:14 January
1075:2013-08-09
1071:. Ec.gc.ca
919:References
913:heat index
136:anemometer
82:convection
74:conduction
62:heat index
46:Wind chill
1451:Vorticity
1431:Lightning
1416:Advection
1013:5 October
818:⋅
804:
798:⋅
792:⋅
695:−
686:−
501:−
355:−
230:−
219:⋅
202:−
160:frostbite
99:radiators
86:radiation
18:Windchill
1800:Velocity
1762:Pressure
1676:Humidity
1579:Helicity
1421:Buoyancy
908:humidity
116:perceive
1671:Humidex
1584:K Index
1404:General
1258:Bibcode
1147:Bibcode
976:July 3,
875:where:
715:where:
262:where:
1044:
942:
753:
565:where
523:0.4275
486:0.6215
419:where
377:0.3965
340:0.6215
84:, and
1479:Cloud
835:237.7
815:17.27
795:6.105
504:35.75
480:35.74
358:11.37
334:13.12
103:pipes
1456:Wind
1284:link
1098:2013
1042:ISBN
1015:2021
978:2024
940:ISBN
731:(°C)
698:4.00
680:0.33
546:0.16
515:0.16
452:is:
400:0.16
369:0.16
306:is:
211:10.5
129:and
101:and
1489:Fog
1266:doi
1155:doi
897:exp
801:exp
787:100
755:ft)
739:is
727:is
689:0.7
267:WCI
1825::
1325:.
1300:.
1280:}}
1276:{{
1264:.
1254:84
1252:.
1194:^
1153:.
1143:86
1141:.
1137:.
1114:.
1006:.
986:^
962:.
915:.
891:RH
570:wc
424:wc
227:33
192:10
162:.
80:,
76:,
1707:)
1705:e
1702:θ
1695:)
1693:θ
1651:)
1649:e
1646:T
1629:)
1627:d
1624:T
1564:)
1562:c
1559:T
1391:e
1384:t
1377:v
1336:.
1311:.
1286:)
1268::
1260::
1237:.
1216:.
1188:.
1163:.
1157::
1149::
1100:.
1078:.
1017:.
980:.
948:.
884:a
881:T
861:,
856:)
847:a
842:T
838:+
827:a
822:T
809:(
783:H
780:R
774:=
771:e
748:v
736:e
724:a
721:T
701:,
692:v
683:e
677:+
671:a
666:T
662:=
658:T
655:A
581:v
577:a
574:T
567:T
551:,
543:+
539:v
532:a
527:T
520:+
512:+
508:v
495:a
490:T
483:+
477:=
471:c
468:w
463:T
435:v
431:a
428:T
421:T
405:,
397:+
393:v
386:a
381:T
374:+
366:+
362:v
349:a
344:T
337:+
331:=
325:c
322:w
317:T
282:a
279:T
273:v
250:,
246:)
239:a
234:T
223:(
215:)
208:+
205:v
197:v
188:(
184:=
181:I
178:C
175:W
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.