40:
243:. The skin of the anterior chest is connected directly to the face, bypassing the formation of a neck, while the scalp is directly connected to the skin of the back. Because of this, those born with this anomaly either have a highly shortened neck or no neck at all. This causes extreme retroflexion, or backward bending, of the head in a "star-gazing" fashion. The spine is severely distorted as well along with significant shortening due to marked
572:
Even though KFS does experience malformed cervical vertebra due to failure of segmentation during early fetal development, there is not retroflexion of the head as seen in iniencephaly. While iniencephaly clausus is fatal, KFS is not and can be surgically corrected. Therefore, it is crucial to
473:
of iniencephaly is still unknown though there are proposed theories, most of which view the neural tube malformation from the primary neural anomaly standpoint. Marin-Padilla and MarinPadilla have proposed that the cause for the abnormalities has to do with a deficiency in the primary
569:, iniencephaly does not. In anencephaly, the retroflexed head is not covered with skin while in iniencephaly, the retroflexed head is covered with skin entirely. Cervical vertebrae are malformed and reduced in iniencephaly while they are almost normal in anencephaly.
542:
of the head in respect to the spine, can be precisely diagnosed as well as the severity and location established. Once established, further decisions can be made with regard to terminating the pregnancy or providing a plan of adequate postnatal care.
633:
Iniencephaly is thought to make up around 1% of all fetal abnormalities, with an incidence rate estimated at 0.1 to 10 in 10,000 deliveries. For unknown reasons, this disease seems to occur most often in newborn females (about 90%).
1120:
1053:
1038:
1023:
385:
Though the iniencephaly is not genetic with its cause unknown, studies have shown that there are certain factors that can increase the risk of mothers giving birth to children with these anomalies.
1113:
1106:
712:
502:
The most accurate method of diagnosis is prenatal screening through real-time fetal images. However, since maternal body habitus leads to diagnostic difficulties using this method,
453:
Studies have shown that obesity of the mother increases the risk of neural tube disorders such as iniencephaly by 1.7 fold while severe obesity increases the risk by over 3 fold.
247:. The vertebrae, especially cervical, are fused together in abnormal shapes and their numbers are reduced. The spinal cord is almost always defective while the
518:(CNS) and anatomic structures of the fetus can be clearly visualized and the characteristic malformations of iniencephaly, such as a shortened trunk, marked
223:
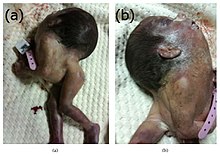
The affected infant tends to be short, with a disproportionately large head. The fetal head of infants born with iniencephaly are hyperextended while the
625:. Most infants die within hours of childbirth. There are only seven reported cases of relatively long-term survival of those born with iniencephaly.
1394:
724:
211:
There are two types of iniencephaly. The more severe group is iniencephaly apertus (open iniencephaly), involving the development of an
1305:
445:, a drug commonly used for ovulation stimulation in fertility treatments, has also been seen to be associated with iniencephaly.
188:
is the most common outcome, with a few rare examples of live birth, after which death invariably occurs within a short time.
558:
of the spine and fusion of the cervical vertebrae, are shared with other disorders, key differences are important to note.
413:
Mothers with poor socioeconomic conditions, poor nutrition, low parity, and lack of folic acid supplementation, and/or
192:
883:
1257:
748:
Erdinçler Pamir; Kaynar Mehmet Y.; et al. (1998). "Iniencephaly: Neuroradiological and
Surgical Features".
1098:
478:. P. Erdinçler, et al. suggests from their findings that the cause of the anomaly is actually a defect in the
1086:
1280:
609:
Since newborns with iniencephaly so rarely survive past childbirth, a standard treatment does not exist.
886:
National
Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). NINDS, 13 Feb. 2007. Web. 30 Nov. 2012.
585:
supplements to reduce risk of iniencephaly by up to 70%. Pregnant mothers are also advised not to take
441:, and antitumor agents to pregnant mothers have resulted in offspring born with iniencephaly. The drug
1214:
969:
Rasmussen S; et al. (2008). "Maternal
Obesity and Risk of Neural Tube Defects: A Metaanalysis".
228:
109:
461:
Once a mother has given birth to a child with iniencephaly, risk of reoccurrence increases to 1-5%.
340:
357:
1399:
515:
430:
215:. In the other group, iniencephaly clausus (closed iniencephaly), the encephalocele is absent.
104:
1032:
1262:
618:
414:
325:
8:
1188:
1129:
1057:
586:
1359:
1330:
1272:
1238:
1150:
919:
902:
820:
795:
688:
661:
511:
248:
177:
52:
1062:
942:
Bhambhani Vikas; George Sanila (2004). "Association of
Clomiphene with Iniencephaly".
1228:
986:
951:
924:
863:
825:
765:
693:
310:
165:
94:
796:"Antenatal Diagnosis of Iniencephaly: Sonographic and MR Correlation: A Case Report"
1364:
978:
914:
855:
815:
807:
757:
683:
673:
531:
527:
252:
1248:
601:, all of which have been associated with increased risk for neural tube defects.
523:
368:
1300:
1291:
1267:
1133:
1128:
982:
761:
594:
479:
438:
300:
224:
181:
169:
1047:
617:
Iniencephaly of both types carry a lethal prognosis, sometimes even ending in
1388:
1369:
1233:
1209:
1183:
811:
535:
335:
278:
259:(sac-like protrusions of the brain through an opening in the cranium) forms.
256:
212:
196:
16:
Rare neural tube defect characterised by fusion of the occiput with the spine
678:
231:. The defective neural arches directly into the upper cervical reach of the
1343:
1338:
1286:
1204:
990:
955:
928:
867:
829:
697:
566:
555:
539:
483:
470:
434:
320:
315:
295:
232:
173:
769:
1321:
1158:
1141:
598:
562:
426:
330:
272:
236:
1015:
1243:
622:
582:
552:
507:
487:
442:
402:
398:
394:
373:
185:
132:
39:
1171:
859:
590:
491:
305:
142:
573:
correctly diagnose KFS and not mistake it for iniencephaly clausus.
1081:
519:
510:
are the most commonly used technique since there is no exposure to
475:
290:
284:
244:
1166:
352:
903:"Iniencephaly with Mediastinal Bronchogenic Cyst: A Case Report"
1042:
1027:
747:
662:"Iniencephaly clausus: A case report with review of literature"
346:
255:
is thinned. Sometimes, in the case of iniencephaly apertus, an
235:, causing the formation of a common cavity between most of the
168:
characterised by three common characteristics: a defect to the
362:
240:
941:
47:
Iniencephaly showing a stargazing head and an enlarged skull
710:
551:
Since many of the characteristics of iniencephaly, such as
425:
Animal studies have shown that administration of the drugs
503:
660:
Kulkarni, PR; Rao, RV; Alur, MB; Joshi, SK (July 2011).
490:
of neural tissue through the opening in the bone during
180:
and retroflexion (backward bending) of the head on the
655:
653:
651:
649:
647:
789:
787:
785:
783:
781:
779:
1005:
659:
845:
711:Hemal U, Solanki RS, Varsheney A, Baliga S (2004).
644:
776:
713:"Prenatal diagnosis of iniencephaly on ultrasound"
793:
1386:
514:. At the beginning of the second trimester, the
275:(failure of major sections of the brain to form)
841:
839:
1114:
971:American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology
900:
896:
894:
892:
526:vertebrae, absence or partial absence of the
486:of the posterior vertebral arches leading to
405:have been shown to be tied to this disorder.
846:Cimmino Christian V (1962). "Iniencephaly".
388:
968:
836:
565:experiences a partial to total lack of the
281:(cranial contents protrudes from the skull)
203:, for the occipital bone/nape of the neck.
1121:
1107:
889:
456:
227:is enlarged and opens through the widened
81:Iniencephaly apertus, Iniencephaly clausus
38:
935:
918:
819:
743:
741:
687:
677:
546:
408:
1306:Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria
879:
877:
794:Pungavkar Sona A.; et al. (2007).
530:, abnormal fusion of vertebrae, closed
1395:Congenital disorders of nervous system
1387:
962:
884:"NINDS Iniencephaly Information Page."
738:
262:
195:in 1836. The name is derived from the
1102:
581:Pregnant mothers are advised to take
393:Abnormalities in chromosomes such as
218:
874:
287:(the two eye cavities fuse into one)
191:The disorder was first described by
901:Akdemir Yeşim; et al. (2010).
13:
1132:malformations and deformations of
666:Journal of Pediatric Neurosciences
206:
14:
1411:
1001:
417:have shown to be at larger risk.
538:(for iniencephaly apertus), and
1258:Agenesis of the corpus callosum
628:
464:
704:
193:Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire
1:
637:
576:
267:Additional symptoms include:
907:Journal of Prenatal Medicine
612:
604:
497:
429:, streptonigrin, triparano,
7:
1224:other reduction deformities
800:Korean Journal of Radiology
10:
1416:
983:10.1016/j.ajog.2008.04.021
762:10.3171/jns.1998.89.2.0317
448:
1352:
1329:
1320:
1197:
1149:
1140:
1072:
1009:
389:Chromosomal abnormalities
380:
251:is often dilated and the
151:
141:
131:
123:
115:
103:
93:
85:
77:
69:
61:
51:
46:
37:
29:
24:
1210:Congenital hydrocephalus
812:10.3348/kjr.2007.8.4.351
420:
341:cardiovascular disorders
750:Journal of Neurosurgery
723:: 265–6. Archived from
717:Indian J Radiol Imaging
679:10.4103/1817-1745.92831
457:History of iniencephaly
358:single umbilical artery
547:Differential diagnosis
516:central nervous system
105:Differential diagnosis
1263:Septo-optic dysplasia
1215:Dandy–Walker syndrome
409:Environmental factors
110:Klippel–Feil syndrome
619:spontaneous abortion
415:hyperhomocysteinemia
326:pulmonary hypoplasia
57:Neural malformations
33:Iniencephaly clausus
1189:Chiari malformation
587:antiepileptic drugs
263:Additional symptoms
1360:Currarino syndrome
1331:Neural tube defect
1273:Hemimegalencephaly
1239:Microlissencephaly
1151:Neural tube defect
1073:External resources
534:, formation of an
512:ionizing radiation
249:ventricular system
219:Signs and symptoms
178:cervical vertebrae
164:is a rare type of
119:Prenatal screening
99:Prenatal screening
1382:
1381:
1378:
1377:
1316:
1315:
1229:Holoprosencephaly
1096:
1095:
944:Indian Pediatrics
351:gastrointestinal
311:holoprosencephaly
166:cephalic disorder
159:
158:
95:Diagnostic method
19:Medical condition
1407:
1365:Diastomatomyelia
1327:
1326:
1147:
1146:
1123:
1116:
1109:
1100:
1099:
1007:
1006:
995:
994:
966:
960:
959:
939:
933:
932:
922:
898:
887:
881:
872:
871:
860:10.1148/79.6.942
843:
834:
833:
823:
791:
774:
773:
745:
736:
735:
733:
732:
708:
702:
701:
691:
681:
657:
532:vertebral arches
528:occipital squama
147:Invariably fatal
42:
22:
21:
1415:
1414:
1410:
1409:
1408:
1406:
1405:
1404:
1385:
1384:
1383:
1374:
1348:
1312:
1249:Hydranencephaly
1193:
1136:
1127:
1097:
1092:
1091:
1068:
1067:
1018:
1004:
999:
998:
967:
963:
940:
936:
899:
890:
882:
875:
844:
837:
792:
777:
746:
739:
730:
728:
709:
705:
658:
645:
640:
631:
615:
607:
579:
549:
524:cervicothoracic
500:
467:
459:
451:
423:
411:
391:
383:
378:
369:genu recurvatum
265:
221:
209:
207:Classifications
20:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1413:
1403:
1402:
1397:
1380:
1379:
1376:
1375:
1373:
1372:
1367:
1362:
1356:
1354:
1350:
1349:
1347:
1346:
1341:
1335:
1333:
1324:
1318:
1317:
1314:
1313:
1311:
1310:
1309:
1308:
1301:Polymicrogyria
1297:
1296:
1295:
1294:
1292:Schizencephaly
1289:
1276:
1275:
1270:
1268:Megalencephaly
1265:
1260:
1254:
1253:
1252:
1251:
1246:
1241:
1236:
1231:
1220:
1219:
1218:
1217:
1207:
1201:
1199:
1195:
1194:
1192:
1191:
1186:
1181:
1180:
1179:
1174:
1169:
1164:
1155:
1153:
1144:
1138:
1137:
1134:nervous system
1126:
1125:
1118:
1111:
1103:
1094:
1093:
1090:
1089:
1077:
1076:
1074:
1070:
1069:
1066:
1065:
1050:
1035:
1019:
1014:
1013:
1011:
1010:Classification
1003:
1002:External links
1000:
997:
996:
961:
934:
888:
873:
835:
775:
737:
703:
642:
641:
639:
636:
630:
627:
614:
611:
606:
603:
595:antihistamines
578:
575:
548:
545:
499:
496:
480:occipital bone
466:
463:
458:
455:
450:
447:
439:antihistamines
422:
419:
410:
407:
390:
387:
382:
379:
377:
376:
371:
366:
360:
355:
349:
345:diaphragmatic
343:
338:
333:
328:
323:
318:
313:
308:
303:
301:arthrogryposis
298:
293:
288:
282:
276:
269:
264:
261:
225:foramen magnum
220:
217:
208:
205:
182:cervical spine
170:occipital bone
157:
156:
153:
149:
148:
145:
139:
138:
135:
129:
128:
125:
121:
120:
117:
113:
112:
107:
101:
100:
97:
91:
90:
87:
83:
82:
79:
75:
74:
71:
67:
66:
63:
59:
58:
55:
49:
48:
44:
43:
35:
34:
31:
27:
26:
18:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1412:
1401:
1400:Rare diseases
1398:
1396:
1393:
1392:
1390:
1371:
1370:Syringomyelia
1368:
1366:
1363:
1361:
1358:
1357:
1355:
1351:
1345:
1342:
1340:
1337:
1336:
1334:
1332:
1328:
1325:
1323:
1319:
1307:
1304:
1303:
1302:
1299:
1298:
1293:
1290:
1288:
1285:
1284:
1283:
1282:
1278:
1277:
1274:
1271:
1269:
1266:
1264:
1261:
1259:
1256:
1255:
1250:
1247:
1245:
1242:
1240:
1237:
1235:
1234:Lissencephaly
1232:
1230:
1227:
1226:
1225:
1222:
1221:
1216:
1213:
1212:
1211:
1208:
1206:
1203:
1202:
1200:
1196:
1190:
1187:
1185:
1184:Encephalocele
1182:
1178:
1175:
1173:
1170:
1168:
1165:
1162:
1161:
1160:
1157:
1156:
1154:
1152:
1148:
1145:
1143:
1139:
1135:
1131:
1124:
1119:
1117:
1112:
1110:
1105:
1104:
1101:
1088:
1084:
1083:
1079:
1078:
1075:
1071:
1064:
1060:
1059:
1055:
1051:
1049:
1045:
1044:
1040:
1036:
1034:
1030:
1029:
1025:
1021:
1020:
1017:
1012:
1008:
992:
988:
984:
980:
977:(6): 611–19.
976:
972:
965:
957:
953:
949:
945:
938:
930:
926:
921:
916:
912:
908:
904:
897:
895:
893:
885:
880:
878:
869:
865:
861:
857:
854:(6): 942–44.
853:
849:
842:
840:
831:
827:
822:
817:
813:
809:
805:
801:
797:
790:
788:
786:
784:
782:
780:
771:
767:
763:
759:
756:(2): 317–20.
755:
751:
744:
742:
727:on 2020-09-23
726:
722:
718:
714:
707:
699:
695:
690:
685:
680:
675:
671:
667:
663:
656:
654:
652:
650:
648:
643:
635:
626:
624:
620:
610:
602:
600:
596:
592:
588:
584:
574:
570:
568:
564:
559:
557:
554:
544:
541:
537:
536:encephalocele
533:
529:
525:
521:
517:
513:
509:
505:
495:
493:
489:
485:
481:
477:
472:
462:
454:
446:
444:
440:
436:
432:
428:
418:
416:
406:
404:
400:
396:
386:
375:
372:
370:
367:
365:abnormalities
364:
361:
359:
356:
354:
350:
348:
344:
342:
339:
337:
336:gastroschisis
334:
332:
329:
327:
324:
322:
319:
317:
314:
312:
309:
307:
304:
302:
299:
297:
294:
292:
289:
286:
283:
280:
279:encephalocele
277:
274:
271:
270:
268:
260:
258:
257:encephalocele
254:
250:
246:
242:
238:
234:
230:
226:
216:
214:
213:encephalocele
204:
202:
198:
197:Ancient Greek
194:
189:
187:
183:
179:
175:
171:
167:
163:
154:
150:
146:
144:
140:
136:
134:
130:
126:
122:
118:
114:
111:
108:
106:
102:
98:
96:
92:
88:
84:
80:
76:
72:
68:
64:
60:
56:
54:
50:
45:
41:
36:
32:
28:
23:
1344:Rachischisis
1339:Spina bifida
1287:Porencephaly
1279:
1223:
1205:Microcephaly
1177:Iniencephaly
1176:
1080:
1052:
1037:
1022:
974:
970:
964:
947:
943:
937:
913:(4): 74–76.
910:
906:
851:
847:
806:(4): 351–5.
803:
799:
753:
749:
729:. Retrieved
725:the original
720:
716:
706:
672:(2): 121–3.
669:
665:
632:
629:Epidemiology
616:
608:
580:
571:
567:neurocranium
560:
556:retroflexion
550:
540:dorsiflexion
501:
484:rachischisis
471:pathogenesis
468:
465:Pathogenesis
460:
452:
435:tetracycline
424:
412:
392:
384:
321:low-set ears
316:spina bifida
296:cleft palate
266:
233:spinal canal
222:
210:
200:
190:
174:spina bifida
162:Iniencephaly
161:
160:
25:Iniencephaly
1322:Spinal cord
1159:Anencephaly
599:sulfa drugs
563:anencephaly
431:sulfonamide
427:vinblastine
331:omphalocele
273:anencephaly
237:spinal cord
199:word ἰνίον
62:Usual onset
30:Other names
1389:Categories
1244:Pachygyria
1130:Congenital
950:(5): 517.
731:2014-07-02
638:References
623:stillborns
583:folic acid
577:Prevention
553:congenital
508:sonography
488:herniation
469:The exact
443:clomiphene
403:monosomy X
399:trisomy 13
395:trisomy 18
374:hydramnios
186:Stillbirth
133:Medication
116:Prevention
65:Congenital
1172:Acalvaria
848:Radiology
613:Prognosis
605:Treatment
591:diuretics
498:Diagnosis
492:gestation
152:Frequency
143:Prognosis
124:Treatment
73:Long term
1281:CNS cyst
1163:Acephaly
1082:Orphanet
991:18538144
956:15181310
929:22439066
868:14021377
830:17673848
698:22408660
520:lordosis
476:mesoderm
306:clubfeet
291:agnathia
285:cyclopia
245:lordosis
239:and the
229:pedicles
70:Duration
53:Symptoms
1167:Acrania
920:3279188
821:2627161
770:9688130
689:3296405
522:in the
449:Obesity
353:atresia
347:hernias
176:of the
89:Unknown
1033:LA00.1
989:
954:
927:
917:
866:
828:
818:
768:
696:
686:
597:, and
561:While
401:, and
381:Causes
253:cortex
86:Causes
1353:Other
1198:Other
1142:Brain
1087:63259
1063:740.2
1048:Q00.2
421:Drugs
363:renal
241:brain
201:inion
78:Types
1058:9-CM
987:PMID
952:PMID
925:PMID
864:PMID
826:PMID
766:PMID
694:PMID
506:and
482:and
155:Rare
137:None
127:None
1054:ICD
1039:ICD
1024:ICD
979:doi
975:198
915:PMC
856:doi
816:PMC
808:doi
758:doi
684:PMC
674:doi
621:or
504:MRI
1391::
1085::
1061::
1046::
1043:10
1031::
1028:11
985:.
973:.
948:41
946:.
923:.
909:.
905:.
891:^
876:^
862:.
852:79
850:.
838:^
824:.
814:.
802:.
798:.
778:^
764:.
754:89
752:.
740:^
721:14
719:.
715:.
692:.
682:.
668:.
664:.
646:^
593:,
589:,
494:.
437:,
433:,
397:,
184:.
172:,
1122:e
1115:t
1108:v
1056:-
1041:-
1026:-
1016:D
993:.
981::
958:.
931:.
911:4
870:.
858::
832:.
810::
804:8
772:.
760::
734:.
700:.
676::
670:6
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.