40:
378:. This suggests that the disease is more frequent in insular areas where there is more likelihood that both parents are carriers, a higher birth rate, and a greater frequency of consanguineous marriages. As all types of 3-Methylglutaconic aciduria are known to be genetic diseases and show a recessive inheritance pattern, consanguineous marriages (in which both partners may have inherited the mutation from the same ancestor) increase the chances of having a baby with the condition.
129:, one of the two sex chromosomes. In males (who have only one X chromosome), one altered copy of the gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the condition. In females (who have two X chromosomes), a mutation must be present in both copies of the gene to cause the disorder. Males are affected by X-linked recessive disorders much more frequently than females. A striking characteristic of X-linked inheritance is that fathers cannot pass X-linked traits to their sons.
332:, delayed development of both mental and motor skills (psychomotor delay), elevated levels of acid in the blood and tissues (metabolic acidosis), abnormal muscle tone (dystonia), and spasms and weakness affecting the arms and legs (spastic quadriparesis). Fewer than 20 cases of 3-methylglutaconic aciduria type I have been reported.
343:
muscle tone, the development of certain involuntary movements (extrapyramidal dysfunction), and a general decrease in brain function (cognitive deficit). The incidence of 3-methylglutaconic aciduria type III is about 1 in 10,000 newborns in the Iraqi Jewish population. This disorder is extremely rare in all other populations.
246:. This protein plays a critical role in maintaining the levels of a particular lipid, called cardiolipin, located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. A lack of tafazzin results in abnormalities in the structure and function of mitochondria, leading to the heart defects and other problems seen in this disorder.
342:
Costeff syndrome is another name for 3-methylglutaconic aciduria type III. This disorder is characterized mainly by the degeneration of the optic nerves, which carry information from the eyes to the brain. Sometimes other nervous system problems occur, such as an inability to maintain posture, poor
277:
gene cause 3-methylglutaconic aciduria type III. This gene carries instructions for making a protein that is also found in mitochondria, but whose function is unknown. Researchers have suggested that cells with a defective OPA3 protein are more susceptible to a process that eliminates damaged or
210:
leucine. This amino acid is broken down in the mitochondria during the process of energy production. A deficiency of this enzyme leads to a buildup of 3-methylglutaconic acid, which is eliminated in the urine. Researchers believe that other genes or environmental factors also contribute to the
338:
is a common name for 3-methylglutaconic aciduria type II. The main features of Barth syndrome include a weakened and enlarged heart (dilated cardiomyopathy), recurrent infections due to low numbers of white blood cells (neutropenia), skeletal problems, and delayed growth. The incidence of
117:
pattern, which means two copies of the gene in each cell are altered. Most often, the parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder are carriers of one copy of the altered gene but do not show signs and symptoms of the
1472:
1465:
1458:
101:
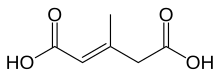
of this acid. 3-methylglutaconic acid can be detected by the presence of the acid function and the double connection that involves reactivity with some specific substances.
346:
The signs and symptoms of 3-methylglutaconic aciduria type IV are variable and overlap with types I-III. The incidence of 3-methylglutaconic aciduria type IV is unknown.
1374:
572:
1439:
1539:
1367:
653:
1039:
900:
858:
761:
923:
565:
1521:
1221:
658:
17:
1749:
1360:
1262:
558:
585:
1236:
1231:
242:
gene cause 3-methylglutaconic aciduria type II (Barth syndrome). This gene provides instructions for making a protein called
1153:
1680:
1434:
989:
472:
1690:
1633:
1352:
741:
448:
1387:
1240:
203:
1644:
1486:
1044:
1450:
195:
3-Methylglutaconic aciduria type I, 3-Methylglutaconic acidemia or 3-Methylglutaconyl-CoA Hydratase
Deficiency
1714:
1649:
1585:
1289:
1257:
1125:
125:
pattern. A condition is considered X-linked if the mutated gene that causes the disorder is located on the X
928:
538:
1629:
1504:
1331:
1724:
1670:
1383:
1321:
1300:
972:
581:
1526:
1326:
1216:
933:
905:
673:
410:
620:
615:
498:
1666:
1580:
1121:
786:
371:
83:
47:
1575:
1482:
1418:
1115:
984:
766:
109:
The inheritance patterns of 3-methylglutaconic aciduria differ depending on the gene involved.
443:
1270:
705:
202:
gene cause 3-methylglutaconic aciduria type I. This gene provides instructions for producing
1698:
1675:
1550:
1131:
1081:
836:
593:
87:
8:
1719:
1336:
1187:
1076:
736:
691:
668:
114:
550:
1516:
1382:
1071:
994:
961:
630:
75:
1659:
1603:
1535:
1341:
813:
509:
431:
54:
1640:
1296:
1178:
1159:
976:
951:
268:
166:
59:
235:(BTHS), 3-Methylglutaconic aciduria type II or Cardiomyopathy-neutropenia syndrome
1567:
1284:
1279:
1111:
1031:
831:
635:
503:
339:
3-methylglutaconic aciduria type II is approximately 1 in 200,000 male infants.
1611:
1480:
1412:
1191:
1145:
956:
895:
625:
514:
394:
335:
232:
423:
1743:
1226:
1085:
1018:
873:
98:
1654:
1391:
1062:
878:
808:
803:
746:
435:
329:
94:
79:
328:
The characteristic features of 3-methylglutaconic aciduria type I include
132:
The inheritance pattern of 3-methylglutaconic aciduria type IV is unknown.
39:
1211:
1054:
464:
149:
There are five known subgroups of MGA; MGA type I, II, III, IV & V.
1305:
1274:
1066:
943:
915:
683:
597:
422:
Anikster Y (2020). Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, et al. (eds.).
207:
187:
126:
97:. The double carboxylic acid functions are the principal cause of the
1621:
1201:
850:
846:
795:
781:
279:
122:
362:
3-Methylglutaconic aciduria seems to be most prevalent amongst the
1500:
1400:
1196:
1141:
1107:
1095:
1022:
1009:
757:
715:
533:
243:
224:
1099:
823:
753:
728:
719:
645:
314:
492:
488:
484:
480:
477:
309:
290:
254:
219:
182:
887:
606:
375:
363:
1546:
370:. However, a high concentration of one type is found in the
1510:
367:
259:
158:
580:
78:
that impair the body's ability to make energy in the
454:
1440:Hyperphosphatasia with mental retardation syndrome
713:
1741:
1540:Leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter
654:3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase deficiency
206:, an enzyme that is involved in processing the
1040:6-Pyruvoyltetrahydropterin synthase deficiency
86:and 3-methylglutaric acid build up and can be
1466:
1368:
566:
924:2-Methylbutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency
1522:Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome
1222:Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I deficiency
659:3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase deficiency
1473:
1459:
1375:
1361:
573:
559:
38:
421:
267:3-Methylglutaconic aciduria type III or
901:Isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency
395:Costeff's syndrome (www.whonamedit.com)
14:
1742:
727:
1681:Multiple familial trichoepithelioma 1
1454:
1356:
1237:Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency
1232:N-Acetylglutamate synthase deficiency
554:
354:There is no known treatment or cure.
1154:Dopamine beta hydroxylase deficiency
301:3-Methylglutaconic aciduria type IV
141:Diagnosis is typically post-mortem.
121:Type II is inherited in an X-linked
113:Types I and III are inherited in an
1435:Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
990:Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase deficiency
322:3-Methylglutaconic aciduria type V
24:
1634:X-linked spinal muscular atrophy 2
82:. As a result of this impairment,
25:
1761:
1750:Phospholipid metabolism disorders
742:Glutathione synthetase deficiency
403:
144:
204:3-methylglutaconyl-CoA hydratase
357:
1560:Posttranslational modification
1487:posttranslational modification
1045:Tetrahydrobiopterin deficiency
388:
211:development of this disorder.
93:3-Methylglutaconic acid is an
13:
1:
1715:Multiple sulfatase deficiency
1594:3-Methylglutaconic aciduria 5
1409:3-Methylglutaconic aciduria 2
1290:Lysinuric protein intolerance
664:3-Methylglutaconic aciduria 1
411:"3-METHYLGLUTACONIC ACIDURIA"
381:
929:Beta-ketothiolase deficiency
430:. University of Washington.
349:
136:
7:
1527:Premature ovarian failure 1
1332:Ethylmalonic encephalopathy
444:3-Methylglutaconic aciduria
104:
68:3-Methylglutaconic aciduria
33:3-Methylglutaconic aciduria
18:3-methylglutaconic aciduria
10:
1766:
1645:Johanson–Blizzard syndrome
1322:2-Hydroxyglutaric aciduria
1301:Oculocerebrorenal syndrome
278:unneeded cells (so-called
74:) is any of at least five
1707:
1689:
1650:Von Hippel–Lindau disease
1620:
1602:
1586:Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease
1566:
1559:
1493:
1427:
1399:
1327:Aminoacylase 1 deficiency
1314:
1256:
1217:Argininosuccinic aciduria
1186:
1176:
1140:
1126:Hermansky–Pudlak syndrome
1094:
1053:
1030:
1017:
1007:
970:
942:
934:Maple syrup urine disease
914:
906:Maple syrup urine disease
886:
871:
845:
822:
794:
779:
704:
682:
674:Maple syrup urine disease
644:
605:
592:
524:
458:
171:Also known as/Description
53:
46:
37:
32:
1725:Ehlers–Danlos syndrome 6
616:Glutaric acidemia type 1
1667:Deubiquitinating enzyme
1551:Retinitis pigmentosa 33
1505:Diamond–Blackfan anemia
1122:Oculocutaneous albinism
451:Genetics Home Reference
372:Saguenay-Lac-Saint-Jean
84:3-methylglutaconic acid
48:3-methylglutaconic acid
1671:Machado–Joseph disease
1241:translocase deficiency
985:Methylmalonic acidemia
767:Glycine encephalopathy
1271:Solute carrier family
586:amino acid metabolism
88:detected in the urine
1676:Aneurysmal bone cyst
1581:Huntington's disease
1394:metabolism disorders
1132:Waardenburg syndrome
1082:Tyrosinemia type III
837:Prolidase deficiency
1720:Hyperproinsulinemia
1576:Alzheimer's disease
1337:Fumarase deficiency
1077:Tyrosinemia type II
737:D-Glyceric acidemia
692:Hypertryptophanemia
669:Isovaleric acidemia
115:autosomal recessive
76:metabolic disorders
1517:Fragile X syndrome
1072:Tyrosinemia type I
995:Propionic acidemia
962:Hypermethioninemia
631:Pipecolic acidemia
525:External resources
424:"Costeff Syndrome"
1737:
1736:
1733:
1732:
1660:Angelman syndrome
1604:Protein targeting
1536:Initiation factor
1448:
1447:
1350:
1349:
1342:Trimethylaminuria
1252:
1251:
1248:
1247:
1172:
1171:
1168:
1167:
1003:
1002:
867:
866:
814:Urocanic aciduria
775:
774:
700:
699:
548:
547:
326:
325:
273:Mutations in the
238:Mutations in the
198:Mutations in the
65:
64:
27:Medical condition
16:(Redirected from
1757:
1564:
1563:
1475:
1468:
1461:
1452:
1451:
1388:lipid metabolism
1377:
1370:
1363:
1354:
1353:
1297:Fanconi syndrome
1184:
1183:
1160:Brunner syndrome
1028:
1027:
1015:
1014:
952:Cystathioninuria
884:
883:
792:
791:
725:
724:
711:
710:
603:
602:
575:
568:
561:
552:
551:
456:
455:
439:
418:
397:
392:
269:Costeff syndrome
152:
151:
60:Medical genetics
42:
30:
29:
21:
1765:
1764:
1760:
1759:
1758:
1756:
1755:
1754:
1740:
1739:
1738:
1729:
1703:
1685:
1616:
1598:
1568:Protein folding
1555:
1489:
1479:
1449:
1444:
1423:
1395:
1381:
1351:
1346:
1310:
1285:Iminoglycinuria
1280:Hartnup disease
1261:
1244:
1194:
1164:
1136:
1112:Ocular albinism
1090:
1049:
1032:Phenylketonuria
999:
966:
938:
910:
877:
863:
841:
832:Hyperprolinemia
818:
787:α-ketoglutarate
785:
771:
762:GAMT deficiency
696:
678:
640:
636:Saccharopinuria
609:/straight chain
588:
579:
549:
544:
543:
520:
519:
467:
409:
406:
401:
400:
393:
389:
384:
360:
352:
147:
139:
107:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1763:
1753:
1752:
1735:
1734:
1731:
1730:
1728:
1727:
1722:
1717:
1711:
1709:
1705:
1704:
1702:
1701:
1695:
1693:
1687:
1686:
1684:
1683:
1678:
1673:
1663:
1662:
1657:
1652:
1647:
1637:
1636:
1626:
1624:
1618:
1617:
1615:
1614:
1612:I-cell disease
1608:
1606:
1600:
1599:
1597:
1596:
1589:
1588:
1583:
1578:
1572:
1570:
1561:
1557:
1556:
1554:
1553:
1543:
1542:
1532:
1531:
1530:
1529:
1524:
1519:
1507:
1497:
1495:
1491:
1490:
1478:
1477:
1470:
1463:
1455:
1446:
1445:
1443:
1442:
1437:
1431:
1429:
1425:
1424:
1422:
1421:
1416:
1413:Barth syndrome
1405:
1403:
1397:
1396:
1380:
1379:
1372:
1365:
1357:
1348:
1347:
1345:
1344:
1339:
1334:
1329:
1324:
1318:
1316:
1312:
1311:
1309:
1308:
1303:
1293:
1292:
1287:
1282:
1277:
1267:
1265:
1254:
1253:
1250:
1249:
1246:
1245:
1243:
1234:
1229:
1224:
1219:
1214:
1209:
1207:
1206:
1205:
1192:Hyperammonemia
1181:
1174:
1173:
1170:
1169:
1166:
1165:
1163:
1162:
1156:
1150:
1148:
1146:Norepinephrine
1138:
1137:
1135:
1134:
1129:
1119:
1104:
1102:
1092:
1091:
1089:
1088:
1079:
1074:
1069:
1059:
1057:
1051:
1050:
1048:
1047:
1042:
1036:
1034:
1025:
1012:
1005:
1004:
1001:
1000:
998:
997:
992:
987:
981:
979:
968:
967:
965:
964:
959:
957:Homocystinuria
954:
948:
946:
940:
939:
937:
936:
931:
926:
920:
918:
912:
911:
909:
908:
903:
898:
896:Hypervalinemia
892:
890:
881:
869:
868:
865:
864:
862:
861:
855:
853:
843:
842:
840:
839:
834:
828:
826:
820:
819:
817:
816:
811:
806:
800:
798:
789:
777:
776:
773:
772:
770:
769:
764:
750:
749:
744:
739:
733:
731:
722:
708:
702:
701:
698:
697:
695:
694:
688:
686:
680:
679:
677:
676:
671:
666:
661:
656:
650:
648:
642:
641:
639:
638:
633:
628:
626:Hyperlysinemia
623:
618:
612:
610:
600:
590:
589:
578:
577:
570:
563:
555:
546:
545:
542:
541:
529:
528:
526:
522:
521:
518:
517:
506:
495:
468:
463:
462:
460:
459:Classification
453:
452:
440:
419:
405:
404:External links
402:
399:
398:
386:
385:
383:
380:
366:population of
359:
356:
351:
348:
336:Barth syndrome
324:
323:
320:
317:
312:
307:
303:
302:
299:
296:
293:
288:
284:
283:
271:
265:
262:
257:
252:
248:
247:
236:
233:Barth syndrome
230:
227:
222:
217:
213:
212:
196:
193:
190:
185:
180:
176:
175:
172:
169:
164:
161:
156:
146:
145:Classification
143:
138:
135:
134:
133:
130:
119:
106:
103:
63:
62:
57:
51:
50:
44:
43:
35:
34:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1762:
1751:
1748:
1747:
1745:
1726:
1723:
1721:
1718:
1716:
1713:
1712:
1710:
1706:
1700:
1697:
1696:
1694:
1692:
1688:
1682:
1679:
1677:
1674:
1672:
1668:
1665:
1664:
1661:
1658:
1656:
1653:
1651:
1648:
1646:
1642:
1639:
1638:
1635:
1631:
1628:
1627:
1625:
1623:
1619:
1613:
1610:
1609:
1607:
1605:
1601:
1595:
1592:chaperonins:
1591:
1590:
1587:
1584:
1582:
1579:
1577:
1574:
1573:
1571:
1569:
1565:
1562:
1558:
1552:
1548:
1545:
1544:
1541:
1537:
1534:
1533:
1528:
1525:
1523:
1520:
1518:
1515:
1514:
1513:
1512:
1508:
1506:
1502:
1499:
1498:
1496:
1492:
1488:
1484:
1481:Disorders of
1476:
1471:
1469:
1464:
1462:
1457:
1456:
1453:
1441:
1438:
1436:
1433:
1432:
1430:
1426:
1420:
1417:
1414:
1410:
1407:
1406:
1404:
1402:
1398:
1393:
1389:
1385:
1378:
1373:
1371:
1366:
1364:
1359:
1358:
1355:
1343:
1340:
1338:
1335:
1333:
1330:
1328:
1325:
1323:
1320:
1319:
1317:
1313:
1307:
1304:
1302:
1298:
1295:
1294:
1291:
1288:
1286:
1283:
1281:
1278:
1276:
1272:
1269:
1268:
1266:
1264:
1259:
1255:
1242:
1238:
1235:
1233:
1230:
1228:
1227:Citrullinemia
1225:
1223:
1220:
1218:
1215:
1213:
1210:
1208:
1203:
1200:
1199:
1198:
1193:
1189:
1185:
1182:
1180:
1175:
1161:
1157:
1155:
1152:
1151:
1149:
1147:
1143:
1139:
1133:
1130:
1127:
1123:
1120:
1117:
1113:
1109:
1106:
1105:
1103:
1101:
1097:
1093:
1087:
1086:Hawkinsinuria
1083:
1080:
1078:
1075:
1073:
1070:
1068:
1064:
1061:
1060:
1058:
1056:
1052:
1046:
1043:
1041:
1038:
1037:
1035:
1033:
1029:
1026:
1024:
1020:
1019:Phenylalanine
1016:
1013:
1011:
1006:
996:
993:
991:
988:
986:
983:
982:
980:
978:
974:
969:
963:
960:
958:
955:
953:
950:
949:
947:
945:
941:
935:
932:
930:
927:
925:
922:
921:
919:
917:
913:
907:
904:
902:
899:
897:
894:
893:
891:
889:
885:
882:
880:
875:
874:propionyl-CoA
870:
860:
857:
856:
854:
852:
848:
844:
838:
835:
833:
830:
829:
827:
825:
821:
815:
812:
810:
807:
805:
802:
801:
799:
797:
793:
790:
788:
783:
778:
768:
765:
763:
759:
755:
752:
751:
748:
745:
743:
740:
738:
735:
734:
732:
730:
726:
723:
721:
717:
712:
709:
707:
703:
693:
690:
689:
687:
685:
681:
675:
672:
670:
667:
665:
662:
660:
657:
655:
652:
651:
649:
647:
643:
637:
634:
632:
629:
627:
624:
622:
619:
617:
614:
613:
611:
608:
604:
601:
599:
595:
591:
587:
583:
576:
571:
569:
564:
562:
557:
556:
553:
540:
536:
535:
531:
530:
527:
523:
516:
512:
511:
507:
505:
501:
500:
496:
494:
490:
486:
482:
479:
475:
474:
470:
469:
466:
461:
457:
450:
446:
445:
441:
437:
433:
429:
428:GeneReviews®
425:
420:
416:
412:
408:
407:
396:
391:
387:
379:
377:
373:
369:
365:
355:
347:
344:
340:
337:
333:
331:
321:
318:
316:
313:
311:
308:
305:
304:
300:
297:
294:
292:
289:
286:
285:
281:
276:
272:
270:
266:
264:19q13.2-q13.3
263:
261:
258:
256:
253:
250:
249:
245:
241:
237:
234:
231:
228:
226:
223:
221:
218:
215:
214:
209:
205:
201:
197:
194:
191:
189:
186:
184:
181:
178:
177:
173:
170:
168:
165:
162:
160:
157:
154:
153:
150:
142:
131:
128:
124:
120:
116:
112:
111:
110:
102:
100:
96:
91:
89:
85:
81:
77:
73:
69:
61:
58:
56:
52:
49:
45:
41:
36:
31:
19:
1655:3-M syndrome
1593:
1509:
1408:
1392:Phospholipid
1384:Inborn error
1179:oxaloacetate
1063:Alkaptonuria
879:succinyl-CoA
809:Histidinemia
804:Carnosinemia
747:Sarcosinemia
663:
582:Inborn error
532:
508:
497:
471:
442:
427:
414:
390:
361:
358:Epidemiology
353:
345:
341:
334:
330:speech delay
327:
274:
239:
199:
148:
140:
108:
95:organic acid
92:
80:mitochondria
71:
67:
66:
1494:Translation
1483:translation
1212:Argininemia
1055:Tyrosinemia
1306:Cystinosis
1275:Cystinuria
1188:Urea cycle
1067:Ochronosis
944:Methionine
916:Isoleucine
684:Tryptophan
598:acetyl-CoA
510:DiseasesDB
438:. NBK1473.
382:References
374:region of
208:amino acid
127:chromosome
1622:Ubiquitin
1263:IE of RTT
1258:Transport
1202:aspartate
1158:reverse:
851:glutamine
847:Glutamate
796:Histidine
782:glutamate
415:Datagenno
350:Treatment
280:apoptosis
174:Genetics
137:Diagnosis
123:recessive
118:disorder.
55:Specialty
1744:Category
1501:Ribosome
1401:Tafazzin
1197:arginine
1142:Tyrosine
1108:Albinism
1096:Tyrosine
1023:tyrosine
1010:fumarate
971:General
758:Creatine
716:pyruvate
534:Orphanet
436:20301646
251:Type III
244:tafazzin
105:Genetics
99:strength
1100:Melanin
824:Proline
754:Glycine
729:Glycine
720:citrate
646:Leucine
504:C579867
315:DNAJC19
287:Type IV
216:Type II
183:250950
888:Valine
859:SSADHD
621:type 2
607:Lysine
539:289902
493:606580
489:258501
485:606580
481:258501
478:210000
434:
376:Canada
364:Jewish
319:3q26.3
310:610198
306:Type V
291:250951
255:258501
220:302060
179:Type I
1708:Other
1699:OFC10
1547:snRNP
1428:Other
1419:CMD3A
1315:Other
515:29831
192:Chr.9
167:Locus
1691:SUMO
1511:FMR1
1485:and
499:MeSH
473:OMIM
432:PMID
368:Iraq
275:OPA3
260:OPA3
229:Xq28
163:Gene
159:OMIM
155:Type
1386:of
584:of
449:NLM
447:at
282:).
240:TAZ
225:TAZ
200:AUH
188:AUH
72:MGA
1746::
1669::
1643::
1641:E3
1632::
1630:E1
1549::
1538::
1503::
1390::
1299::
1273::
1177:G→
1110::
1008:G→
977:OA
973:BC
872:G→
780:G→
760::
714:G→
537::
513::
502::
491:,
487:,
483:,
476::
426:.
413:.
90:.
1474:e
1467:t
1460:v
1415:)
1411:(
1376:e
1369:t
1362:v
1260:/
1239:/
1204:)
1195:(
1190:/
1144:→
1128:)
1124:(
1118:)
1116:1
1114:(
1098:→
1084:/
1065:/
1021:/
975:/
876:→
849:/
784:→
756:→
718:→
706:G
596:→
594:K
574:e
567:t
560:v
465:D
417:.
298:?
295:?
70:(
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.