17:
116:. Linear accelerations (such as that of gravity) should not in theory effect a movement of the cupula when it is neutrally buoyant. The Buoyancy Hypothesis assumes that alcohol, with a different specific gravity from that of the cupula/endolymph, diffuses at different rates into the cupula and the surrounding endolymph. The result is a temporary density gradient between the cupula and endolymph, and a consequent (erroneous) sensitivity to linear accelerations such as that of gravity by a system normally signalling rotational accelerations. This sensation is commonly referred to as "the spins" .
891:
60:
continual rotation however, the endolymph's acceleration normalizes with the rate of rotation of the semicircular ducts. As a result, the cupula returns to its resting position and the hair cells cease to be stimulated. This continues until the head stops rotating which simultaneously halts semicircular duct rotation. Due to inertia, however, the endolymph continues on. As the endolymph continues to move, the cupula is once again deflected resulting in the compensatory movements of the body when spun.
126:
59:
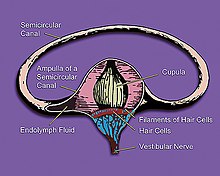
filling the semicircular ducts initially lags behind due to inertia. As a result, the cupula is deflected opposite the direction of head movement. As the endolymph pushes the cupula, the stereocilia is bent as well, stimulating the hair cells within the crista ampullaris. After a short time of
55:, the cupula has embedded within it hair cells that have several stereocilia associated with each kinocilium. The cupula itself is the gelatinous component of the crista ampullaris that extends from the crista to the roof of the ampullae. When the head rotates, the
911:
79:, respectively. When the endolymph moves in the opposite direction, the direction of stimulation is reversed accordingly, from depolarization to hyperpolarization or vice versa. The corresponding signal is transmitted to the brain by the
257:
99:
230:
201:"VEDA – Vestibular Disorders Association – Sensory Input." VEDA – Vestibular Disorders Association – Vestibular Disorders Home. Web. 09 Dec. 2011. <
86:
In their natural orientation within the head, the cupulae are located on the medial aspect of the semicircular canals. In this orientation, the
250:
243:
231:
https://web.archive.org/web/20070703152544/http://education.vetmed.vt.edu/curriculum/VM8054/Labs/Lab11/Ear/EXAMPLES/Excrista.htm
182:
192:
344:
675:
198:
Saladin, Kenneth S. Anatomy & Physiology: the Unity of Form and
Function. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2012. Print.
225:
220:
843:
396:
16:
838:
704:
451:
441:
202:
833:
468:
446:
386:
135:
72:
921:
881:
463:
391:
480:
719:
714:
411:
916:
692:
80:
191:
Mann, Michael D. "Vestibular System." The
Nervous System In Action. 2007. Web. 8 Dec. 2011. <
653:
495:
749:
546:
157:
8:
798:
193:
https://web.archive.org/web/20111126234002/http://www.unmc.edu/physiology/Mann/index.html
37:
890:
112:
by affecting the neutral buoyancy of the cupula within the surrounding fluid called the
825:
803:
791:
663:
596:
416:
215:
48:
858:
808:
774:
762:
740:
616:
329:
312:
287:
271:
140:
109:
52:
33:
912:
Knowledge articles incorporating text from the 20th edition of Gray's
Anatomy (1918)
164:. The University of Texas, Health Science Center at Houston, McGovern Medical School
853:
658:
490:
75:, depending on whether the endolymph moves them toward or away from their adjacent
44:
815:
680:
601:
581:
561:
365:
267:
235:
100:
Short-term effects of alcohol consumption § Alcohol consumption and balance
20:
The cupula is the onion shaped structure surrounded by endolymph in the ampulla.
895:
687:
631:
551:
517:
68:
905:
757:
726:
643:
626:
591:
507:
406:
131:
381:
302:
226:
http://www.anatomyatlases.org/MicroscopicAnatomy/Section16/Plate16314.shtml
221:
http://www.kumc.edu/instruction/medicine/anatomy/histoweb/eye_ear/ear04.htm
183:
Vertigo It's
Multisensory Syndromes Second Edition Thomas Brandt Chapter 17
586:
376:
292:
203:
http://www.vestibular.org/vestibular-disorders/balance/sensory-input.php
781:
356:
307:
339:
670:
611:
531:
324:
297:
279:
113:
87:
76:
64:
56:
697:
428:
786:
769:
576:
436:
334:
317:
475:
458:
158:"Chapter 10: Vestibular System: Structure and Function"
879:
216:
http://faculty.une.edu/com/abell/histo/CristaAmp.jpg
265:
903:
251:
90:rest on the posterior aspect of the cupula.
258:
244:
15:
904:
569:
130:This article incorporates text in the
239:
93:
13:
14:
933:
209:
43:The cupula is located within the
889:
155:
124:
654:Reissner's/vestibular membrane
176:
149:
1:
397:promontory of tympanic cavity
119:
7:
387:secondary tympanic membrane
138:of the 20th edition of
108:posits that alcohol causes
10:
938:
392:prominence of facial canal
97:
824:
748:
739:
642:
560:
539:
530:
506:
427:
364:
355:
278:
36:, providing the sense of
412:aditus to mastoid antrum
63:With each rotation, the
32:, is a structure in the
81:vestibulocochlear nerve
21:
403:Posterior structures
98:Further information:
47:of each of the three
19:
644:Cochlear duct /
608:Perilymphatic space
508:Auditory tube /
826:Semicircular canals
799:Vestibular aqueduct
106:Buoyancy Hypothesis
49:semicircular canals
38:spatial orientation
804:endolymphatic duct
792:Otolithic membrane
705:Tectorial membrane
664:Reticular membrane
469:posterior ligament
417:pyramidal eminence
373:Medial structures
94:Effects of alcohol
22:
922:Vestibular system
877:
876:
873:
872:
869:
868:
859:crista ampullaris
809:endolymphatic sac
741:Vestibular system
735:
734:
617:Cochlear aqueduct
526:
525:
464:superior ligament
452:anterior ligament
442:superior ligament
330:Auricular muscles
313:intertragic notch
73:hyperpolarization
53:crista ampullaris
34:vestibular system
929:
894:
893:
885:
849:Ampullary cupula
746:
745:
676:Stria vascularis
659:Basilar membrane
567:
566:
537:
536:
481:annular ligament
447:lateral ligament
362:
361:
260:
253:
246:
237:
236:
185:
180:
174:
173:
171:
169:
153:
128:
127:
26:ampullary cupula
937:
936:
932:
931:
930:
928:
927:
926:
902:
901:
900:
888:
880:
878:
865:
820:
816:Ductus reuniens
731:
710:Sulcus spiralis
681:Spiral ligament
645:
638:
602:Cochlear cupula
582:Vestibular duct
562:Auditory system
556:
522:
510:Eustachian tube
509:
502:
423:
366:Tympanic cavity
351:
274:
264:
212:
188:
181:
177:
167:
165:
156:Gray, Lincoln.
154:
150:
125:
122:
102:
96:
67:undergo either
12:
11:
5:
935:
925:
924:
919:
917:Sensory organs
914:
899:
898:
875:
874:
871:
870:
867:
866:
864:
863:
862:
861:
851:
846:
841:
836:
830:
828:
822:
821:
819:
818:
813:
812:
811:
806:
796:
795:
794:
784:
779:
778:
777:
767:
766:
765:
754:
752:
743:
737:
736:
733:
732:
730:
729:
724:
723:
722:
717:
707:
702:
701:
700:
695:
688:Organ of Corti
684:
683:
678:
673:
667:
666:
661:
656:
650:
648:
640:
639:
637:
636:
635:
634:
629:
621:
620:
619:
614:
606:
605:
604:
599:
594:
589:
584:
573:
571:
564:
558:
557:
555:
554:
549:
543:
541:
534:
528:
527:
524:
523:
521:
520:
518:Torus tubarius
514:
512:
504:
503:
501:
500:
499:
498:
496:tensor tympani
493:
485:
484:
483:
473:
472:
471:
466:
456:
455:
454:
449:
444:
433:
431:
425:
424:
422:
421:
420:
419:
414:
409:
401:
400:
399:
394:
389:
384:
379:
370:
368:
359:
353:
352:
350:
349:
348:
347:
342:
332:
327:
322:
321:
320:
315:
310:
305:
300:
295:
284:
282:
276:
275:
263:
262:
255:
248:
240:
234:
233:
228:
223:
218:
211:
210:External links
208:
207:
206:
199:
196:
187:
186:
175:
147:
141:Gray's Anatomy
121:
118:
95:
92:
69:depolarization
51:. Part of the
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
934:
923:
920:
918:
915:
913:
910:
909:
907:
897:
892:
887:
886:
883:
860:
857:
856:
855:
852:
850:
847:
845:
842:
840:
837:
835:
832:
831:
829:
827:
823:
817:
814:
810:
807:
805:
802:
801:
800:
797:
793:
790:
789:
788:
785:
783:
780:
776:
773:
772:
771:
768:
764:
761:
760:
759:
756:
755:
753:
751:
747:
744:
742:
738:
728:
727:Spiral limbus
725:
721:
718:
716:
713:
712:
711:
708:
706:
703:
699:
696:
694:
691:
690:
689:
686:
685:
682:
679:
677:
674:
672:
669:
668:
665:
662:
660:
657:
655:
652:
651:
649:
647:
641:
633:
630:
628:
625:
624:
622:
618:
615:
613:
610:
609:
607:
603:
600:
598:
595:
593:
592:Tympanic duct
590:
588:
585:
583:
580:
579:
578:
575:
574:
572:
568:
565:
563:
559:
553:
550:
548:
545:
544:
542:
538:
535:
533:
529:
519:
516:
515:
513:
511:
505:
497:
494:
492:
489:
488:
486:
482:
479:
478:
477:
474:
470:
467:
465:
462:
461:
460:
457:
453:
450:
448:
445:
443:
440:
439:
438:
435:
434:
432:
430:
426:
418:
415:
413:
410:
408:
407:mastoid cells
405:
404:
402:
398:
395:
393:
390:
388:
385:
383:
380:
378:
375:
374:
372:
371:
369:
367:
363:
360:
358:
354:
346:
345:pars flaccida
343:
341:
338:
337:
336:
333:
331:
328:
326:
323:
319:
316:
314:
311:
309:
306:
304:
301:
299:
296:
294:
291:
290:
289:
286:
285:
283:
281:
277:
273:
269:
261:
256:
254:
249:
247:
242:
241:
238:
232:
229:
227:
224:
222:
219:
217:
214:
213:
204:
200:
197:
194:
190:
189:
184:
179:
163:
159:
152:
148:
146:
145:
142:
139:
137:
133:
132:public domain
117:
115:
111:
107:
101:
91:
89:
84:
82:
78:
74:
70:
66:
61:
58:
54:
50:
46:
41:
39:
35:
31:
27:
18:
848:
709:
382:round window
178:
166:. Retrieved
161:
151:
143:
129:
123:
105:
103:
85:
62:
42:
29:
25:
23:
693:stereocilia
646:scala media
587:Helicotrema
377:oval window
266:Anatomy of
83:(CN VIII).
906:Categories
844:Horizontal
782:Kinocilium
547:membranous
540:Labyrinths
357:Middle ear
308:antitragus
120:References
65:hair cells
839:Posterior
750:Vestibule
698:tip links
671:Endolymph
632:Boettcher
612:Perilymph
532:Inner ear
491:stapedius
325:Ear canal
298:antihelix
280:Outer ear
136:page 1051
114:endolymph
88:kinocilia
77:kinocilia
57:endolymph
854:Ampullae
834:Superior
720:internus
715:externus
627:Claudius
597:Modiolus
487:Muscles
429:Ossicles
168:7 August
162:UTHealth
45:ampullae
896:Anatomy
787:Otolith
770:Saccule
758:Utricle
577:Cochlea
570:General
437:Malleus
335:Eardrum
318:earlobe
288:Auricle
272:balance
268:hearing
110:vertigo
882:Portal
775:macula
763:macula
623:Cells
476:Stapes
303:tragus
144:(1918)
30:cupula
459:Incus
293:helix
205:>.
195:>.
134:from
28:, or
552:bony
340:umbo
270:and
170:2024
104:The
24:The
71:or
908::
160:.
40:.
884::
259:e
252:t
245:v
172:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.