40:
224:(more Na+ and less K+ compared to intracellular matrix). This depolarization will open voltage gated calcium channels. The influx of calcium then triggers the cell to release vesicles containing excitatory neurotransmitters into a synapse. The post-synaptic neurite then sends an action potential to the Spiral Ganglia of Gard. Unlike the hair cells of the
248:. One kinocilium is the longest cilium located on the hair cell next to 40–70 stereocilia. During movement of the body, the hair cell is depolarized when the stereocilia move toward the kinocilium. The depolarization of the hair cell causes neurotransmitter to be released and an increase in firing frequency of
211:
flow, will cause potassium channels on the stereocilia to open. This is mostly due to the pulling force stereocilia exerts on its neighboring stereocilia via interconnecting links that hold stereocilia together (usually from tallest to shortest) and this leads to the depolarization of the hair cell.
192:
of the hair bundle, the kinocilium is found in the center of the apical surface of the hair cell surrounded by 20-300 microvilli. During hair bundle morphogenesis, the kinocilium moves to the cell periphery dictating hair bundle orientation. As the kinocilium does not move, microvilli surrounding it
168:. Vibrations (either by movement or sound waves) cause displacement of the hair bundle, resulting in depolarization or hyperpolarization of the hair cell. The depolarization of the hair cells in both instances causes
212:
This pattern of depolarization should not be confused with the more common depolarization which involves the influx of Na+ into the cell while K+ channels stay closed. Endolymph composition resembles that of the
252:. When the stereocilia tilt away from the kinocilium, the hair cell is hyperpolarized, decreasing the amount of neurotransmitter released, which decreases the firing frequency of cranial nerve VIII.
152:. When the stereocilia and kinocilium move further apart, the cell hyperpolarizes. When they move closer together, the cell depolarizes and may fire an action potential.
497:
86:
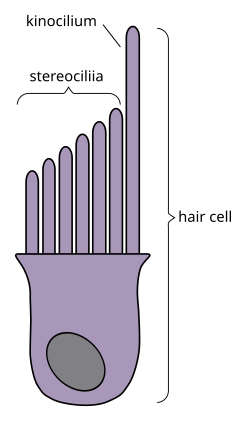
137:, which are numerous, there is only one kinocilium on each hair cell. The kinocilium can be identified by its apical position as well as its enlarged tip.
283:
Hair cells in fish and some frogs are used to detect water movements around their bodies. These hair cells are embedded in a jelly-like protrusion called
284:
490:
470:
483:
346:
584:
272:
of the stereocilia toward or away from the kinocilium causes an increase or decrease in the firing rate of the sensory
915:
1083:
636:
81:
1078:
944:
691:
681:
1073:
708:
686:
626:
141:
240:
Kinocilia are present in the crista ampullaris of the semicircular ducts and the sensory maculae of the
1129:
703:
631:
287:. The hair cells therefore can not be seen and do not appear on the surface of skin of fish and frogs.
74:
720:
17:
197:. In many mammals, but not in humans, the kinocilium will regress once the hair bundle has matured.
1134:
959:
954:
651:
471:
https://web.archive.org/web/20120414213627/http://www.unmc.edu/physiology/Mann/pix_4b/hair_cell.gif
269:
69:
932:
134:
893:
93:
1139:
735:
989:
786:
8:
1038:
221:
213:
169:
165:
1065:
1043:
1031:
903:
836:
656:
452:
391:
366:
249:
440:
1098:
1048:
1014:
1002:
980:
856:
569:
552:
527:
511:
444:
396:
342:
225:
456:
1093:
1088:
898:
730:
436:
386:
378:
337:
Mescher, Anthony L. (2021). "Chapter 23: The Eye & Ear: Special Sense Organs".
173:
149:
427:
Raphael Y, Altschuler RA (June 2003). "Structure and innervation of the cochlea".
1055:
920:
841:
821:
801:
605:
507:
475:
927:
871:
791:
757:
1123:
997:
966:
883:
866:
831:
747:
646:
301:
241:
229:
189:
621:
542:
448:
400:
296:
382:
826:
616:
532:
265:
194:
185:
99:
596:
547:
140:
Together with stereocilia, the kinocilium regulates depolarization and
127:
123:
579:
910:
851:
771:
564:
537:
519:
277:
217:
207:
161:
130:
119:
937:
668:
164:
and are involved in both the morphogenesis of the hair bundle and
1026:
1009:
816:
676:
574:
557:
306:
245:
216:(more K+ and less Na+) more closely compared to its counterpart,
715:
273:
145:
115:
341:. Lange medical books (16th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
698:
228:
or the maculae of the saccule and utricle, hair cells of the
57:
39:
261:
364:
179:
505:
426:
1121:
205:The movement of the hair bundle, as a result of
491:
365:Schwander M, Kachar B, Müller U (July 2010).
160:Kinocilia are found on the apical surface of
367:"Review series: The cell biology of hearing"
255:
339:Junqueira's basic histology: text and atlas
498:
484:
38:
390:
413:Ross. 2006. Histology: A Test and Atlas
336:
235:
14:
1122:
809:
268:and a single, much longer kinocilium.
479:
360:
358:
332:
330:
328:
326:
324:
322:
155:
24:
420:
200:
25:
1151:
464:
355:
319:
193:begin to elongate and form actin
180:Role in hair bundle morphogenesis
260:The apical surface of a sensory
264:hair cell usually has numerous
894:Reissner's/vestibular membrane
407:
13:
1:
637:promontory of tympanic cavity
441:10.1016/S0361-9230(03)00047-9
312:
184:Each hair cell has a single,
144:of the hair cell, which is a
27:Sensory hair in the inner ear
7:
627:secondary tympanic membrane
371:The Journal of Cell Biology
290:
10:
1156:
632:prominence of facial canal
232:do not possess kinocilia.
1064:
988:
979:
882:
800:
779:
770:
746:
667:
604:
595:
518:
256:Anatomy in fish and frogs
92:
80:
68:
56:
51:
46:
37:
32:
652:aditus to mastoid antrum
429:Brain Research Bulletin
122:located in the sensory
280:at its basal surface.
94:Anatomical terminology
643:Posterior structures
383:10.1083/jcb.201001138
114:is a special type of
884:Cochlear duct /
848:Perilymphatic space
748:Auditory tube /
236:Vestibular apparatus
220:which resembles the
1066:Semicircular canals
1039:Vestibular aqueduct
222:extracellular fluid
214:intracellular fluid
188:kinocilium. Before
170:signal transduction
166:mechanotransduction
133:. Contrasting with
1044:endolymphatic duct
1032:Otolithic membrane
945:Tectorial membrane
904:Reticular membrane
709:posterior ligament
657:pyramidal eminence
613:Medial structures
250:cranial nerve VIII
148:that can generate
75:H1.00.01.1.01015
1130:Vestibular system
1117:
1116:
1113:
1112:
1109:
1108:
1099:crista ampullaris
1049:endolymphatic sac
981:Vestibular system
975:
974:
857:Cochlear aqueduct
766:
765:
704:superior ligament
692:anterior ligament
682:superior ligament
570:Auricular muscles
553:intertragic notch
348:978-1-260-46298-2
226:crista ampullaris
156:Anatomy in humans
150:action potentials
142:hyperpolarization
108:
107:
103:
16:(Redirected from
1147:
1089:Ampullary cupula
986:
985:
916:Stria vascularis
899:Basilar membrane
807:
806:
777:
776:
721:annular ligament
687:lateral ligament
602:
601:
500:
493:
486:
477:
476:
460:
435:(5–6): 397–422.
414:
411:
405:
404:
394:
362:
353:
352:
334:
276:innervating the
174:neurotransmitter
100:edit on Wikidata
97:
42:
30:
29:
21:
1155:
1154:
1150:
1149:
1148:
1146:
1145:
1144:
1135:Auditory system
1120:
1119:
1118:
1105:
1060:
1056:Ductus reuniens
971:
950:Sulcus spiralis
921:Spiral ligament
885:
878:
842:Cochlear cupula
822:Vestibular duct
802:Auditory system
796:
762:
750:Eustachian tube
749:
742:
663:
606:Tympanic cavity
591:
514:
504:
467:
423:
421:Further reading
418:
417:
412:
408:
363:
356:
349:
335:
320:
315:
293:
258:
238:
203:
201:Auditory system
182:
158:
118:on the apex of
104:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1153:
1143:
1142:
1137:
1132:
1115:
1114:
1111:
1110:
1107:
1106:
1104:
1103:
1102:
1101:
1091:
1086:
1081:
1076:
1070:
1068:
1062:
1061:
1059:
1058:
1053:
1052:
1051:
1046:
1036:
1035:
1034:
1024:
1019:
1018:
1017:
1007:
1006:
1005:
994:
992:
983:
977:
976:
973:
972:
970:
969:
964:
963:
962:
957:
947:
942:
941:
940:
935:
928:Organ of Corti
924:
923:
918:
913:
907:
906:
901:
896:
890:
888:
880:
879:
877:
876:
875:
874:
869:
861:
860:
859:
854:
846:
845:
844:
839:
834:
829:
824:
813:
811:
804:
798:
797:
795:
794:
789:
783:
781:
774:
768:
767:
764:
763:
761:
760:
758:Torus tubarius
754:
752:
744:
743:
741:
740:
739:
738:
736:tensor tympani
733:
725:
724:
723:
713:
712:
711:
706:
696:
695:
694:
689:
684:
673:
671:
665:
664:
662:
661:
660:
659:
654:
649:
641:
640:
639:
634:
629:
624:
619:
610:
608:
599:
593:
592:
590:
589:
588:
587:
582:
572:
567:
562:
561:
560:
555:
550:
545:
540:
535:
524:
522:
516:
515:
503:
502:
495:
488:
480:
474:
473:
466:
465:External links
463:
462:
461:
422:
419:
416:
415:
406:
354:
347:
317:
316:
314:
311:
310:
309:
304:
299:
292:
289:
257:
254:
237:
234:
202:
199:
181:
178:
157:
154:
106:
105:
96:
90:
89:
84:
78:
77:
72:
66:
65:
60:
54:
53:
49:
48:
44:
43:
35:
34:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1152:
1141:
1138:
1136:
1133:
1131:
1128:
1127:
1125:
1100:
1097:
1096:
1095:
1092:
1090:
1087:
1085:
1082:
1080:
1077:
1075:
1072:
1071:
1069:
1067:
1063:
1057:
1054:
1050:
1047:
1045:
1042:
1041:
1040:
1037:
1033:
1030:
1029:
1028:
1025:
1023:
1020:
1016:
1013:
1012:
1011:
1008:
1004:
1001:
1000:
999:
996:
995:
993:
991:
987:
984:
982:
978:
968:
967:Spiral limbus
965:
961:
958:
956:
953:
952:
951:
948:
946:
943:
939:
936:
934:
931:
930:
929:
926:
925:
922:
919:
917:
914:
912:
909:
908:
905:
902:
900:
897:
895:
892:
891:
889:
887:
881:
873:
870:
868:
865:
864:
862:
858:
855:
853:
850:
849:
847:
843:
840:
838:
835:
833:
832:Tympanic duct
830:
828:
825:
823:
820:
819:
818:
815:
814:
812:
808:
805:
803:
799:
793:
790:
788:
785:
784:
782:
778:
775:
773:
769:
759:
756:
755:
753:
751:
745:
737:
734:
732:
729:
728:
726:
722:
719:
718:
717:
714:
710:
707:
705:
702:
701:
700:
697:
693:
690:
688:
685:
683:
680:
679:
678:
675:
674:
672:
670:
666:
658:
655:
653:
650:
648:
647:mastoid cells
645:
644:
642:
638:
635:
633:
630:
628:
625:
623:
620:
618:
615:
614:
612:
611:
609:
607:
603:
600:
598:
594:
586:
585:pars flaccida
583:
581:
578:
577:
576:
573:
571:
568:
566:
563:
559:
556:
554:
551:
549:
546:
544:
541:
539:
536:
534:
531:
530:
529:
526:
525:
523:
521:
517:
513:
509:
501:
496:
494:
489:
487:
482:
481:
478:
472:
469:
468:
458:
454:
450:
446:
442:
438:
434:
430:
425:
424:
410:
402:
398:
393:
388:
384:
380:
376:
372:
368:
361:
359:
350:
344:
340:
333:
331:
329:
327:
325:
323:
318:
308:
305:
303:
300:
298:
295:
294:
288:
286:
281:
279:
275:
271:
267:
263:
253:
251:
247:
243:
233:
231:
230:cochlear duct
227:
223:
219:
215:
210:
209:
198:
196:
191:
190:morphogenesis
187:
177:
175:
171:
167:
163:
153:
151:
147:
143:
138:
136:
132:
129:
125:
121:
117:
113:
101:
95:
91:
88:
85:
83:
79:
76:
73:
71:
67:
64:
61:
59:
55:
50:
45:
41:
36:
31:
19:
1140:Fish anatomy
1021:
949:
622:round window
432:
428:
409:
374:
370:
338:
297:Fish anatomy
282:
259:
239:
206:
204:
186:microtubular
183:
159:
139:
111:
109:
62:
933:stereocilia
886:scala media
827:Helicotrema
617:oval window
506:Anatomy of
377:(1): 9–20.
266:stereocilia
195:stereocilia
135:stereocilia
52:Identifiers
1124:Categories
1084:Horizontal
1022:Kinocilium
787:membranous
780:Labyrinths
597:Middle ear
548:antitragus
313:References
270:Deflection
162:hair cells
128:vertebrate
124:epithelium
120:hair cells
112:kinocilium
63:kinocilium
33:Kinocilium
1079:Posterior
990:Vestibule
938:tip links
911:Endolymph
872:Boettcher
852:Perilymph
772:Inner ear
731:stapedius
565:Ear canal
538:antihelix
520:Outer ear
278:hair cell
218:perilymph
208:endolymph
176:release.
131:inner ear
18:Kinocilia
1094:Ampullae
1074:Superior
960:internus
955:externus
867:Claudius
837:Modiolus
727:Muscles
669:Ossicles
457:26357578
449:12787864
401:20624897
291:See also
1027:Otolith
1010:Saccule
998:Utricle
817:Cochlea
810:General
677:Malleus
575:Eardrum
558:earlobe
528:Auricle
512:balance
508:hearing
392:2911669
307:Otolith
302:Utricle
246:saccule
242:utricle
126:of the
47:Details
1015:macula
1003:macula
863:Cells
716:Stapes
543:tragus
455:
447:
399:
389:
345:
285:cupula
274:neuron
146:neuron
116:cilium
699:Incus
533:helix
453:S2CID
98:[
87:67323
58:Latin
792:bony
580:umbo
510:and
445:PMID
397:PMID
343:ISBN
262:fish
244:and
172:via
437:doi
387:PMC
379:doi
375:190
82:FMA
1126::
451:.
443:.
433:60
431:.
395:.
385:.
373:.
369:.
357:^
321:^
110:A
70:TH
499:e
492:t
485:v
459:.
439::
403:.
381::
351:.
102:]
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.