239:, hatch as first-stage juveniles within the soil and develop to an infective third-stage juvenile. Infection occurs by direct penetration through the skin of the host. Although the two species differ, they are both susceptible to environmental hazards such as desiccation. This limits their distribution to warm, wet climates such as the tropics. The third-stage juvenile is also the infective stage of trichostrongyle nematodes, including those infecting sheep and cattle. Both the first-stage juvenile within the egg and the ensheathed infective juvenile are resistant to desiccation, chemicals, and low temperatures and the infective juvenile can survive on pasture for several months before infecting a host.
31:
53:
780:
723:
247:
The most appropriate control measures for hookworms and ascariasis are to concentrate chemotherapy on heavily infected individuals (taking advantage of overdispersion) and to improve sanitation to reduce the rate of transmission.
223:, draw a plug of intestinal mucosa into their buccal capsule. The tissue is broken down and blood is rapidly pumped through the intestine of the nematode so that most of it goes undigested.
30:
175:
633:
824:
646:
154:
182:
764:
607:
282:
817:
695:
586:
651:
858:
599:
810:
757:
52:
529:
516:
534:
848:
687:
853:
843:
700:
661:
750:
507:
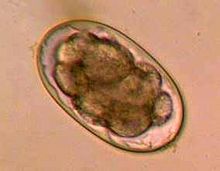
355:: Life history parameters and epidemiological implications of two sympatric hookworms of humans".
469:
638:
674:
555:
798:
738:
8:
521:
324:
299:
196:
47:
669:
542:
411:
372:
368:
329:
278:
114:
547:
438:
403:
364:
319:
311:
270:
137:
315:
390:
Wharton, D.A. (1982). "The survival of desiccation by the free-living stages of
794:
734:
594:
581:
492:
429:
Wharton, D.A.; Young, S.R.; Barrett, J. (1984). "Cold tolerance in nematodes".
407:
274:
837:
333:
415:
620:
501:
376:
161:
94:
779:
722:
787:
730:
442:
189:
168:
104:
625:
568:
203:
64:
612:
463:
573:
486:
141:
84:
560:
790:
74:
682:
300:"The diversity and impact of hookworm infections in wildlife"
428:
835:
297:
818:
758:
346:
147:
825:
811:
765:
751:
29:
323:
455:
389:
264:
836:
468:
467:
347:Hoagland, K.E.; Schad, G.A. (1978). "
774:
717:
688:6C7F87C1-FFED-E008-FF54-F9104CADFBEB
662:ba6bb263-ccd1-40e5-ba19-cae091d819c7
600:9b5a0945-ae0b-40d6-9dfc-b94946e60daa
298:Seguel, M.; Gottdenker, N. (2017).
13:
14:
870:
394:(Nematoda: Trichostrongylidae)".
267:A Functional Biology of Nematodes
778:
721:
269:. Functional Biology. Springer.
51:
733:roundworm-related article is a
304:Int J Parasitol Parasites Wildl
449:
422:
392:Trichostrongylus colubriformis
383:
340:
291:
258:
1:
251:
797:. You can help Knowledge by
737:. You can help Knowledge by
369:10.1016/0014-4894(78)90078-4
316:10.1016/j.ijppaw.2017.03.007
226:
7:
140:of worms that includes the
10:
875:
773:
716:
265:Wharton, David A. (1986).
242:
148:Genera of Ancylostomatidae
476:
408:10.1017/s0031182000052756
357:Experimental Parasitology
275:10.1007/978-1-4615-8516-9
48:Scientific classification
46:
37:
28:
23:
210:
859:Parasitic animal stubs
793:-related article is a
353:Ancylostoma duodenale
237:Ancylostoma duodenale
595:Fauna Europaea (new)
16:Family of roundworms
443:10.1007/BF00683218
349:Necator americanus
233:Necator americanus
849:Nematode families
806:
805:
746:
745:
711:
710:
670:Open Tree of Life
470:Taxon identifiers
284:978-1-4615-8516-9
130:
129:
115:Ancylostomatoidea
24:Ancylostomatidae
866:
854:Rhabditida stubs
844:Ancylostomatidae
827:
820:
813:
782:
775:
767:
760:
753:
725:
718:
704:
703:
691:
690:
678:
677:
665:
664:
655:
654:
642:
641:
629:
628:
616:
615:
603:
602:
590:
589:
577:
576:
564:
563:
551:
550:
538:
537:
525:
524:
522:Ancylostomatidae
512:
511:
510:
497:
496:
495:
478:Ancylostomatidae
465:
464:
458:
453:
447:
446:
431:J Comp Physiol B
426:
420:
419:
387:
381:
380:
344:
338:
337:
327:
295:
289:
288:
262:
176:Cyclodontostomum
134:Ancylostomatidae
125:Ancylostomatidae
56:
55:
33:
21:
20:
874:
873:
869:
868:
867:
865:
864:
863:
834:
833:
832:
831:
772:
771:
714:
712:
707:
699:
694:
686:
681:
673:
668:
660:
658:
650:
645:
637:
632:
624:
619:
611:
606:
598:
593:
585:
580:
572:
567:
559:
554:
546:
541:
533:
528:
520:
515:
506:
505:
500:
491:
490:
485:
472:
462:
461:
454:
450:
427:
423:
388:
384:
345:
341:
296:
292:
285:
263:
259:
254:
245:
231:The hookworms,
229:
215:The hookworms,
213:
150:
50:
17:
12:
11:
5:
872:
862:
861:
856:
851:
846:
830:
829:
822:
815:
807:
804:
803:
783:
770:
769:
762:
755:
747:
744:
743:
726:
709:
708:
706:
705:
692:
679:
666:
656:
643:
630:
617:
604:
591:
582:Fauna Europaea
578:
565:
552:
539:
526:
513:
508:Ancylostomidae
498:
482:
480:
474:
473:
460:
459:
448:
421:
382:
339:
310:(3): 177–194.
290:
283:
256:
255:
253:
250:
244:
241:
228:
225:
212:
209:
208:
207:
200:
193:
186:
179:
172:
165:
158:
149:
146:
128:
127:
122:
118:
117:
112:
108:
107:
102:
98:
97:
92:
88:
87:
82:
78:
77:
72:
68:
67:
62:
58:
57:
44:
43:
35:
34:
26:
25:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
871:
860:
857:
855:
852:
850:
847:
845:
842:
841:
839:
828:
823:
821:
816:
814:
809:
808:
802:
800:
796:
792:
789:
784:
781:
777:
776:
768:
763:
761:
756:
754:
749:
748:
742:
740:
736:
732:
727:
724:
720:
719:
715:
702:
697:
693:
689:
684:
680:
676:
671:
667:
663:
657:
653:
648:
644:
640:
635:
631:
627:
622:
618:
614:
609:
605:
601:
596:
592:
588:
583:
579:
575:
570:
566:
562:
557:
553:
549:
544:
540:
536:
531:
527:
523:
518:
514:
509:
503:
499:
494:
488:
484:
483:
481:
479:
475:
471:
466:
457:
452:
444:
440:
436:
432:
425:
417:
413:
409:
405:
402:(3): 455–62.
401:
397:
393:
386:
378:
374:
370:
366:
362:
358:
354:
350:
343:
335:
331:
326:
321:
317:
313:
309:
305:
301:
294:
286:
280:
276:
272:
268:
261:
257:
249:
240:
238:
234:
224:
222:
218:
206:
205:
201:
199:
198:
194:
192:
191:
187:
185:
184:
180:
178:
177:
173:
171:
170:
166:
164:
163:
159:
157:
156:
152:
151:
145:
143:
139:
135:
126:
123:
120:
119:
116:
113:
111:Superfamily:
110:
109:
106:
103:
100:
99:
96:
93:
90:
89:
86:
83:
80:
79:
76:
73:
70:
69:
66:
63:
60:
59:
54:
49:
45:
41:
36:
32:
27:
22:
19:
799:expanding it
785:
739:expanding it
728:
713:
477:
456:Wharton 1986
451:
434:
430:
424:
399:
396:Parasitology
395:
391:
385:
363:(1): 36–49.
360:
356:
352:
348:
342:
307:
303:
293:
266:
260:
246:
236:
232:
230:
220:
216:
214:
202:
195:
188:
181:
174:
167:
160:
153:
133:
131:
124:
39:
18:
621:iNaturalist
502:Wikispecies
217:Ancylostoma
162:Ancylostoma
155:Agriostomum
95:Chromadorea
40:Ancylostoma
838:Categories
731:Rhabditida
252:References
190:Monodontus
169:Bunostomum
105:Rhabditida
788:parasitic
437:: 73–77.
227:Lifecycle
204:Uncinaria
183:Galonchus
142:hookworms
71:Kingdom:
65:Eukaryota
493:Q3093248
487:Wikidata
334:28765810
121:Family:
85:Nematoda
81:Phylum:
75:Animalia
61:Domain:
561:4965449
416:7201628
325:5526439
243:Control
221:Necator
197:Necator
101:Order:
91:Class:
38:Egg of
791:animal
701:834871
675:168892
659:NZOR:
639:111297
626:341129
574:1ANCLF
414:
377:627275
375:
332:
322:
281:
138:family
136:are a
786:This
729:This
696:WoRMS
683:Plazi
652:33278
634:IRMNG
587:16897
548:8R3J7
535:26213
211:Habit
795:stub
735:stub
647:NCBI
613:5972
608:GBIF
569:EPPO
530:BOLD
412:PMID
373:PMID
351:and
330:PMID
279:ISBN
235:and
219:and
132:The
42:sp.
556:EoL
543:CoL
517:AFD
439:doi
435:154
404:doi
365:doi
320:PMC
312:doi
271:doi
840::
698::
685::
672::
649::
636::
623::
610::
597::
584::
571::
558::
545::
532::
519::
504::
489::
433:.
410:.
400:84
398:.
371:.
361:44
359:.
328:.
318:.
306:.
302:.
277:.
144:.
826:e
819:t
812:v
801:.
766:e
759:t
752:v
741:.
445:.
441::
418:.
406::
379:.
367::
336:.
314::
308:6
287:.
273::
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.