27:
81:) because of their unique structure, which consists of an aromatic moiety bridged by an aliphatic chain. The main difference between various derivatives of ansamycins is the aromatic moiety, which can be a
240:
Balerna, M.; Keller-Schierlein, W.; Martius, C.; Wolf, H.; Zähner, H. (1969). "Metabolic products of microorganisms. 72. Naphthomycin, an antimetabolite of vitamin K".
106:
128:
Rifamycins are a subclass of ansamycins with high potency against mycobacteria. This resulted in their widespread use in the treatment of
380:
205:
Prelog, V.; Oppolzer, W. (1973). "Rifamycins. 4. Ansamycins, a novel class of microbial metabolism products".
136:, and AIDS-related mycobacterial infections. Since then various analogues have been isolated from other
365:
283:
Sensi, P.; Margalith, P.; Timbal, M. T. (1959). "Rifomycin, a new antibiotic; preliminary report".
350:
61:. In addition, these compounds demonstrate antiviral activity towards bacteriophages and
8:
375:
355:
265:
323:
182:
157:
327:
310:
Floss, H. G.; Yu, T. (1999). "Lessons from the rifamycin biosynthetic gene cluster".
292:
257:
222:
187:
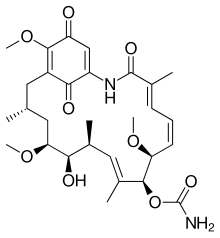
269:
360:
319:
249:
239:
214:
177:
173:
169:
370:
54:
86:
344:
218:
111:
50:
46:
42:
331:
296:
129:
117:
102:
98:
94:
31:
261:
226:
191:
137:
82:
253:
62:
58:
90:
20:
282:
133:
109:. Ansamycins were first discovered in 1959 by Sensi et al. from
26:
41:
is a family of bacterial secondary metabolites that show
155:
204:
53:
bacteria, and includes various compounds, including
309:
342:
97:. Another variation consists of benzene or a
73:They are named ansamycins (from the Latin
181:
25:
343:
34:, one of the benzoquinone ansamycins.
312:Current Opinion in Chemical Biology
13:
156:Wehrli, W.; Staehelin, M. (1971).
14:
392:
285:Il Farmaco, Edizione Scientifica
303:
276:
233:
198:
174:10.1128/MMBR.35.3.290-309.1971
149:
1:
324:10.1016/S1367-5931(99)00014-9
143:
68:
7:
158:"Actions of the rifamycins"
123:
16:Group of chemical compounds
10:
397:
18:
242:Archiv für Mikrobiologie
219:10.1002/hlca.19730560716
19:Not to be confused with
162:Bacteriological Reviews
381:Polyketide antibiotics
207:Helvetica Chimica Acta
45:activity against many
35:
29:
254:10.1007/bf00412210
101:ring system as in
36:
366:1,4-Benzoquinones
388:
336:
335:
307:
301:
300:
280:
274:
273:
237:
231:
230:
213:(7): 1179–1187.
202:
196:
195:
185:
153:
396:
395:
391:
390:
389:
387:
386:
385:
341:
340:
339:
308:
304:
281:
277:
238:
234:
203:
199:
154:
150:
146:
126:
71:
55:streptovaricins
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
394:
384:
383:
378:
373:
368:
363:
358:
353:
338:
337:
302:
275:
232:
197:
168:(3): 290–309.
147:
145:
142:
125:
122:
87:naphthoquinone
70:
67:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
393:
382:
379:
377:
374:
372:
369:
367:
364:
362:
359:
357:
354:
352:
349:
348:
346:
333:
329:
325:
321:
317:
313:
306:
298:
294:
290:
286:
279:
271:
267:
263:
259:
255:
251:
248:(4): 303–17.
247:
243:
236:
228:
224:
220:
216:
212:
208:
201:
193:
189:
184:
179:
175:
171:
167:
163:
159:
152:
148:
141:
139:
135:
131:
121:
119:
115:
113:
112:Amycolatopsis
108:
104:
100:
96:
95:naphthomycins
92:
88:
84:
80:
76:
66:
64:
60:
56:
52:
51:Gram-negative
48:
47:Gram-positive
44:
43:antimicrobial
40:
33:
30:Structure of
28:
22:
318:(5): 592–7.
315:
311:
305:
291:(2): 146–7.
288:
284:
278:
245:
241:
235:
210:
206:
200:
165:
161:
151:
130:tuberculosis
127:
118:actinomycete
114:mediterranei
110:
103:geldanamycin
99:benzoquinone
78:
74:
72:
38:
37:
32:geldanamycin
351:Polyketides
138:prokaryotes
120:bacterium.
107:ansamitocin
89:ring as in
83:naphthalene
376:Ansamycins
356:Carbamates
345:Categories
144:References
85:ring or a
63:poxviruses
59:rifamycins
39:Ansamycins
91:rifamycin
69:Structure
49:and some
21:Annamycin
332:10508670
297:13639988
270:31145406
124:Examples
93:and the
361:Lactams
262:4988744
227:4148590
192:5001420
134:leprosy
371:Ethers
330:
295:
268:
260:
225:
190:
183:378391
180:
79:handle
266:S2CID
116:, an
328:PMID
293:PMID
258:PMID
223:PMID
188:PMID
75:ansa
57:and
320:doi
250:doi
215:doi
178:PMC
170:doi
105:or
347::
326:.
314:.
289:14
287:.
264:.
256:.
246:65
244:.
221:.
211:56
209:.
186:.
176:.
166:35
164:.
160:.
140:.
132:,
77:,
65:.
334:.
322::
316:3
299:.
272:.
252::
229:.
217::
194:.
172::
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.