577:: An audit of backup processes determines if (a) they are effective, and (b) if they are actually being implemented by the involved personnel. The disaster recovery plan also includes information on how best to recover any data that has not been copied. Controls and protections are put in place to ensure that data is not damaged, altered, or destroyed during this process.
527:: When there is a disaster, an organization's data and business processes become vulnerable. As such, security can be more important than the raw speed involved in a disaster recovery plan's RTO. The most critical consideration then becomes securing the new data pipelines: from new VPNs to the connection from offsite backup services.
444:, off-site storage location equipment, telephones, etc.), distribution register, software and data files backup/retention schedules, temporary location specifications, any other such lists, materials, inventories, and documentation. Pre-formatted forms are often used to facilitate the data gathering process.
626:
and other research. Among the items that the auditor needs to verify are: the scope of the policy (including any stated exclusions), that the amount of coverage is sufficient to cover the organization's needs, and that the policy is current and in force. The auditor also ascertains, through a review
330:
The first three components (business resumption, occupant emergency, and continuity of operations plans) do not deal with the IT infrastructure. The incident management plan (IMP) does deal with the IT infrastructure, but since it establishes structure and procedures to address cyber attacks against
69:
Often used together, the terms business continuity (BC) and disaster recovery (DR) are very different. BC refers to the ability of a business to continue critical functions and business processes after the occurrence of a disaster, whereas DR refers specifically to the IT functions of the business,
647:
or any other unusual circumstance is minimized. Agreements pertaining to establishing support and assisting with recovery for the entity are also outlined. Techniques used for evaluating this area include an examination of the reasonableness of the plan, a determination of whether or not the plan
306:
of business continuity. Where DRP encompasses the policies, tools and procedures to enable recovery of data following a catastrophic event, BCP involves keeping all aspects of a business functioning regardless of potential disruptive events. As such, a business continuity plan is a comprehensive
159:
a specific individual within the organization, who may be referred to as the disaster recovery officer, the disaster recovery liaison, the DR coordinator, or some other similar title, has the technical skills, training, experience, and abilities to analyze the capabilities of the team members to
339:
The overall categorization of tests are functional- and discussion-based. Types of tests include: tabletop exercises, checklists, simulations, parallel processing (testing recovery site while primary site is in operation), and full interruption (fail over) tests. These apply to both BC and DR.
396:(BIA) that includes a range of possible disasters. Each functional area of the organization is analyzed to determine potential consequences. Traditionally, fire has posed the greatest threat. A thorough plan provides for "worst case" situations, such as destruction of the main building.
583:: Practice drills conducted periodically to determine how effective the plan is and to determine what changes may be necessary. The auditor's primary concern here is verifying that these drills are being conducted properly and that problems uncovered during these drills are addressed.
562:
Occasional tests and trials verify the viability and effectiveness of the plan. An auditor looks into the probability that operations of the organization can be sustained at the level that is assumed in the plan, and the ability of the entity to actually establish operations at the
511:: Failure to include each and every important business process or a block of data. Ripples can extend a disaster's impact. Payroll may not initially be mission-critical, but left alone for several days, it can become more important than any of your initial problems.
414:, any special security procedures, procedure for the notification of system changes, hours of operation, the specific hardware and other equipment required for processing, personnel requirements, definition of the circumstances constituting an
699:
programs and a clear definition of job responsibilities. A review of the readiness capacity of a plan often includes tasks such as inquires of personnel, direct physical observation, and examination of training records and any certifications.
517:: A third point of failure involves focusing only on DR without considering the larger business continuity needs. Corporate office space lost to a disaster can result in an instant pool of teleworkers which, in turn, can overload a company's
432:: This includes various lists (employee backup position listing, critical telephone numbers list, master call list, master vendor list, notification checklist), inventories (communications equipment, documentation, office equipment, forms,
209:. Man-made disasters could be intentional (for example, an act of a terrorist) or unintentional (that is, accidental, such as the breakage of a man-made dam or even "fat fingers" - or errant commands entered - on a computer system).
1106:
307:
organizational strategy that includes the DRP as well as threat prevention, detection, recovery, and resumption of operations should a data breach or other disaster event occur. Therefore, BCP consists of five component plans:
634:
Effective DR plans take into account the extent of a company's responsibilities to other entities and its ability to fulfill those commitments despite a major disaster. A good DR audit will include a review of existing
348:
Like every insurance plan, there are benefits that can be obtained from proper business continuity planning, including: Studies have shown a correlation between higher spending on auditing fees and lower rates of
293:
system. Copies of it are stored on and off site and are made available or accessible to those who require them. An auditor tests the procedures used to meet this objective and determine their effectiveness.
686:
Procedures to sustain staff during a round-the-clock disaster recovery effort are included in any good disaster recovery plan. Procedures for the stocking of food and water, capabilities of administering
92:
551:. A hot site is fully equipped to resume operations while a cold site does not have that capability. A warm site has the capability to resume some, but not all operations.
1079:
163:
more than one individual is trained and capable of doing a particular function during the DR exercise. Tests and inquiries of personnel can help achieve this objective.
1026:
1012:
84:
The primary objective is to protect the organization in the event that all or part of its operations and/or computer services are rendered partially or completely
486:
Initial testing can be plan is done in sections and after normal business hours to minimize disruptions. Subsequent tests occur during normal business hours.
331:
an organization's IT systems, it generally does not represent an agent for activating the DRP; thus DRP is the only BCP component of active interest to IT.
1130:
940:
381:
According to
Geoffrey H. Wold of the Disaster Recovery Journal, the entire process involved in developing a Disaster Recovery Plan consists of 10 steps:
803:
827:
505:: When executive management sees DR planning as "just another fake earthquake drill" or CEOs fail to make DR planning and preparation a priority
708:
The auditor must review procedures that take into account the possibility of power failures or other situations that are of a non-IT nature.
914:
648:
takes all factors into account, and a verification of the contracts and agreements reasonableness through documentation and outside research.
521:
overnight, overwork the IT support staff at the blink of an eye and cause serious bottlenecks and monopolies with the dial-in PBX system.
888:
482:" of the plan is performed by conducting a structured walk-through test. An actual test-run must be performed. Problems are corrected.
695:, and dealing with family emergencies are clearly written and tested. This can generally be accomplished by the company through good
671:
testing of procedures, interviewing employees, making comparison against the plans of other company and against industry standards,
197:. It is "a comprehensive statement of consistent actions to be taken before, during and after a disaster". The disaster could be
664:
hardware, contact information for both internal communication and external issues, such as business partners and key customers.
627:
of the ratings assigned by independent rating agencies, that the insurance company or companies providing the coverage have the
1197:
1083:
749:
360:
Guaranteeing the reliability of standby systems (even automating the failure detection and recovery in certain scenarios)
1131:
http://www.businessinsurance.com/article/20150309/ISSUE0401/303159991/constructing-a-successful-business-continuity-plan
1168:
1149:
787:
285:
to verify that records are being kept. One such record is a current list of the organization's hardware and software
970:
855:
17:
1013:"What is the difference between a tabletop exercise, a drill, a functional exercise, and a full-scale exercise?"
677:
direct observation that emergency telephone numbers are listed and easily accessible in the event of a disaster.
628:
122:
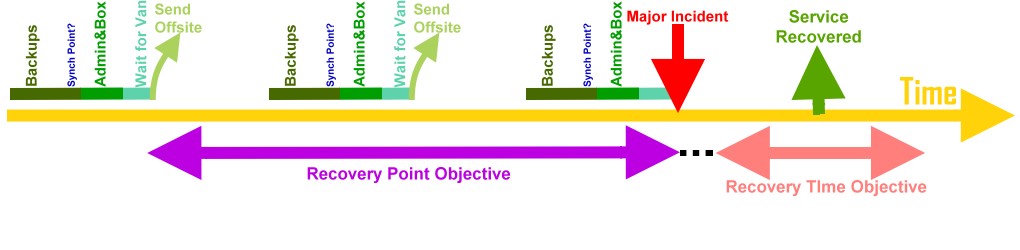
Minimizing downtime and data loss during disaster recovery is typically measured in terms of two key concepts:
991:
944:
744:
389:
754:
566:
The auditor can verify this through paper and paperless documentation and actual physical observation. The
32:
918:
289:. Such list is made and periodically updated to reflect changing business practices and as part of an
759:
594:
1187:
393:
136:
406:
for alternatives selected are prepared, with details specifying duration, termination conditions,
636:
126:
739:
419:
202:
190:
58:
28:
1044:
243:
To maximize their effectiveness, DRPs are most effective when updated frequently, and should:
555:
255:
79:
892:
498:
has identified five "common mistakes" organizations often make related to BCP/DR planning:
206:
50:
643:
to ensure that the organization's legal liability for lack of performance in the event of
8:
320:
290:
224:
detection, a byproduct of routine inspections, which may discover new (potential) threats
54:
1111:
1060:
623:
619:
615:
156:
the procedures stated in the BCP and DR plan are actually consistent with real practice
1202:
1164:
1145:
1064:
783:
479:
263:
248:
186:
36:
1052:
433:
232:
198:
139:(RPO), a measure of the ability to recover files by specifying a point in time the
458:
Determining the feasibility and compatibility of backup facilities and procedures.
91:
1192:
441:
274:
426:, non-mainframe resource requirements, priorities, and other contractual issues.
217:
Although there is no one-size-fits-all plan, there are three basic strategies:
407:
273:
Adequate records need to be retained by the organization. The auditor examines
259:
992:"Guide to Test, Training, and Exercise Programs for IT Plans and Capabilities"
1181:
661:
470:
Providing motivation for maintaining and updating the disaster recovery plan.
437:
185:) is a documented process or set of procedures to execute an organization's
85:
24:
221:
prevention, including proper backups, having surge protectors and generators
423:
402:: Critical needs of each department are evaluated and prioritized. Written
804:"What Is the Difference Between Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity"
1125:
Berman, Alan. : Constructing a
Successful Business Continuity Plan.
1056:
548:
1107:"Hurricane Joaquin Highlights the Importance of Plans to Keep Operating"
863:
780:
Business continuity and disaster recovery planning for IT professionals
712:
657:
692:
611:
415:
350:
282:
269:
be thoroughly tested, not just unpracticed bureaucratic documentation
862:. Adapted from Volume 5 #1. Disaster Recovery World. Archived from
696:
644:
640:
590:
567:
403:
194:
286:
278:
722:
716:
303:
140:
130:
1077:
1045:"Are External Auditors Concerned about Cyber Risk disclosure"
42:
1027:"Homeland Security Exercise and Evaluation Program (HSEEP)"
998:
726:
495:
411:
917:. Email Archiving and Remote Backup. 2010. Archived from
688:
518:
494:
Due to high cost, various plans are not without critics.
467:
Demonstrating the ability of the organization to recover.
464:
Providing training to the team managers and team members.
235:, and holding a "lessons learned" brainstorming session.
1142:
Auditing & Assurance
Services: A Systematic Approach
656:
The auditor must verify that planning ensures that both
418:, process to negotiate service extensions, guarantee of
1163:(4th ed.). Boca Raton, FL: Auerbach Publications.
674:
examining company manuals and other written procedures.
1080:"Five Mistakes That Can Kill a Disaster Recovery Plan"
1043:
Li, He; No, Won Gyun; Boritz, J. Efrim (24 Nov 2021).
47:
business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR) plans
828:"5 Tips to Build an Effective Disaster Recovery Plan"
610:
The auditor determines the adequacy of the company's
533:
Locking down or remotely wiping lost handheld devices
461:
Identifying areas in the plan that need modification.
400:
Establishing priorities for processing and operations
1078:Cormac Foster; Dell Corporation (25 October 2010).
941:"Disaster Recovery & Business Continuity Plans"
376:
1158:
889:"Disaster Recovery Planning - Step by Step Guide"
372:Lowering unnecessarily stressful work environment
1179:
1104:
943:. Stone Crossing Solutions. 2012. Archived from
631:to cover the losses in the event of a disaster.
530:In disasters, planning for post-mortem forensics
436:, workgroup and data center computer hardware,
1159:Gallegos, F.; Senft, S.; Davis, A. L. (2012).
777:
729:or other such phenomena and PPE may be needed.
1144:(8th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill/Irwin.
189:processes and recover and protect a business
95:A DR plan illustrating the chronology of the
1049:Auditing: A Journal of Practice & Theory
849:
847:
845:
782:(2 ed.). Burlington: Elsevier Science.
366:Minimizing decision-making during a disaster
968:
891:. Michigan State University. Archived from
539:
1042:
825:
453:Developing testing criteria and procedures
842:
448:Organizing and documenting a written plan
363:Providing a standard for testing the plan
172:
1161:Information Technology Control and Audit
821:
819:
817:
489:
90:
1139:
703:
681:
651:
600:
297:
231:The latter may include securing proper
1180:
964:
962:
570:of the storage site is also confirmed.
35:covers the entire organization, while
883:
881:
814:
660:and the recovery team have effective
147:
49:provides a third-party validation to
45:documents covering an organization's
1105:Constance Gustke (October 7, 2015).
856:"Disaster Recovery Planning Process"
853:
750:Comparison of online backup services
622:) through a review of the company's
388:: The planning committee prepares a
369:Reducing potential legal liabilities
959:
605:
13:
878:
152:An auditor examines and assesses
14:
1214:
725:procedures in case of gas leaks,
238:
212:
193:infrastructure in the event of a
57:is complete and does not contain
16:For the Irish gauge railway, see
377:Planning and testing methodology
167:
1119:
1098:
1071:
1036:
1019:
1005:
18:Belfast and County Down Railway
1032:. Homeland Security. Jan 2020.
984:
933:
907:
796:
771:
455:: reasons for testing include
31:(IT) to run their operations,
1:
765:
745:Comparison of backup software
317:Continuity of operations plan
117:
1198:Information technology audit
971:"The Disaster Recovery Plan"
755:Information technology audit
597:, and personnel redundancy.
386:Performing a risk assessment
254:be revisited at every major
133:is completely up and running
33:business continuity planning
7:
1140:Messier, W. F. Jr. (2011).
1127:Business Insurance Magazine
826:Bill Abram (14 June 2012).
733:
343:
247:be an integral part of all
64:
27:' increasing dependency on
10:
1219:
915:"Backup Disaster Recovery"
854:Wold, Geoffrey H. (1997).
830:. Small Business Computing
667:Audit techniques include
334:
77:
73:
15:
969:Chad Bahan. (June 2003).
860:Disaster Recovery Journal
760:Vulnerability (computing)
357:Minimizing risk of delays
540:Decisions and strategies
509:Incomplete RTOs and RPOs
394:business impact analysis
311:Business resumption plan
137:Recovery point objective
778:Susan Snedaker (2013).
614:coverage (particularly
587:Backup of key personnel
440:hardware and software,
314:Occupant emergency plan
302:Disaster recovery is a
160:complete assigned tasks
127:Recovery time objective
70:albeit a subset of BC.
740:Backup rotation scheme
326:Disaster recovery plan
179:disaster recovery plan
173:Disaster recovery plan
114:
29:information technology
589:- including periodic
556:cost-benefit analysis
490:Caveats/controversies
256:corporate acquisition
143:copy will restore to.
94:
80:IT service continuity
78:Further information:
1057:10.2139/ssrn.2880928
704:Environmental issues
682:Emergency procedures
652:Communication issues
601:Other considerations
298:Relationship to BCPs
129:(RTO), time until a
61:misrepresentations.
629:financial viability
321:Incident management
291:IT asset management
110:major incident (MI)
1112:The New York Times
921:on 22 January 2013
624:insurance policies
620:casualty insurance
434:insurance policies
264:system development
233:insurance policies
148:The auditor's role
115:
107:with respect to a
1129:, March 9, 2015.
947:on 23 August 2012
866:on 15 August 2012
262:and at every new
249:business analysis
187:disaster recovery
37:disaster recovery
1210:
1174:
1155:
1133:
1123:
1117:
1116:
1102:
1096:
1095:
1093:
1091:
1082:. Archived from
1075:
1069:
1068:
1040:
1034:
1033:
1031:
1023:
1017:
1016:
1009:
1003:
1002:
996:
988:
982:
981:
979:
977:
966:
957:
956:
954:
952:
937:
931:
930:
928:
926:
911:
905:
904:
902:
900:
885:
876:
875:
873:
871:
851:
840:
839:
837:
835:
823:
812:
811:
800:
794:
793:
775:
606:Insurance issues
545:Site designation
476:Testing the plan
111:
105:
99:
1218:
1217:
1213:
1212:
1211:
1209:
1208:
1207:
1188:Data management
1178:
1177:
1171:
1152:
1136:
1124:
1120:
1103:
1099:
1089:
1087:
1076:
1072:
1041:
1037:
1029:
1025:
1024:
1020:
1011:
1010:
1006:
994:
990:
989:
985:
975:
973:
967:
960:
950:
948:
939:
938:
934:
924:
922:
913:
912:
908:
898:
896:
895:on 8 March 2014
887:
886:
879:
869:
867:
852:
843:
833:
831:
824:
815:
802:
801:
797:
790:
776:
772:
768:
736:
706:
684:
654:
608:
603:
542:
492:
430:Collecting data
379:
346:
337:
300:
258:, at every new
241:
215:
175:
170:
150:
120:
109:
103:
97:
82:
76:
67:
39:focuses on IT.
21:
12:
11:
5:
1216:
1206:
1205:
1200:
1195:
1190:
1176:
1175:
1169:
1156:
1150:
1135:
1134:
1118:
1097:
1070:
1035:
1018:
1004:
983:
958:
932:
906:
877:
841:
813:
795:
788:
769:
767:
764:
763:
762:
757:
752:
747:
742:
735:
732:
731:
730:
720:
719:may be needed.
705:
702:
683:
680:
679:
678:
675:
672:
653:
650:
607:
604:
602:
599:
595:cross-training
572:
571:
564:
547:: choice of a
541:
538:
537:
536:
535:
534:
531:
522:
515:Systems myopia
512:
506:
503:Lack of buy-in
491:
488:
484:
483:
478:: An initial "
473:
472:
471:
468:
465:
462:
459:
450:
445:
427:
408:system testing
397:
378:
375:
374:
373:
370:
367:
364:
361:
358:
345:
342:
336:
333:
328:
327:
324:
318:
315:
312:
299:
296:
271:
270:
267:
260:product launch
252:
240:
239:Best practices
237:
229:
228:
225:
222:
214:
213:Types of plans
211:
174:
171:
169:
166:
165:
164:
161:
157:
149:
146:
145:
144:
134:
119:
116:
75:
72:
66:
63:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1215:
1204:
1201:
1199:
1196:
1194:
1191:
1189:
1186:
1185:
1183:
1172:
1170:9781439893203
1166:
1162:
1157:
1153:
1151:9780077520151
1147:
1143:
1138:
1137:
1132:
1128:
1122:
1114:
1113:
1108:
1101:
1086:on 2013-01-16
1085:
1081:
1074:
1066:
1062:
1058:
1054:
1050:
1046:
1039:
1028:
1022:
1014:
1008:
1001:. p. 21.
1000:
993:
987:
972:
965:
963:
946:
942:
936:
920:
916:
910:
894:
890:
884:
882:
865:
861:
857:
850:
848:
846:
829:
822:
820:
818:
810:. 2019-11-25.
809:
805:
799:
791:
789:9780124114517
785:
781:
774:
770:
761:
758:
756:
753:
751:
748:
746:
743:
741:
738:
737:
728:
724:
721:
718:
714:
711:
710:
709:
701:
698:
694:
690:
676:
673:
670:
669:
668:
665:
663:
662:communication
659:
649:
646:
642:
638:
632:
630:
625:
621:
617:
613:
598:
596:
592:
588:
584:
582:
578:
576:
569:
565:
561:
560:
559:
557:
552:
550:
546:
532:
529:
528:
526:
523:
520:
516:
513:
510:
507:
504:
501:
500:
499:
497:
487:
481:
477:
474:
469:
466:
463:
460:
457:
456:
454:
451:
449:
446:
443:
442:office supply
439:
438:microcomputer
435:
431:
428:
425:
421:
420:compatibility
417:
413:
409:
405:
401:
398:
395:
391:
390:risk analysis
387:
384:
383:
382:
371:
368:
365:
362:
359:
356:
355:
354:
352:
341:
332:
325:
322:
319:
316:
313:
310:
309:
308:
305:
295:
292:
288:
284:
280:
276:
268:
265:
261:
257:
253:
250:
246:
245:
244:
236:
234:
226:
223:
220:
219:
218:
210:
208:
204:
203:environmental
200:
196:
192:
188:
184:
180:
168:Documentation
162:
158:
155:
154:
153:
142:
138:
135:
132:
128:
125:
124:
123:
112:
106:
100:
93:
89:
87:
81:
71:
62:
60:
56:
55:documentation
52:
48:
44:
40:
38:
34:
30:
26:
25:organizations
19:
1160:
1141:
1126:
1121:
1110:
1100:
1088:. Retrieved
1084:the original
1073:
1048:
1038:
1021:
1007:
986:
974:. Retrieved
949:. Retrieved
945:the original
935:
923:. Retrieved
919:the original
909:
897:. Retrieved
893:the original
868:. Retrieved
864:the original
859:
832:. Retrieved
807:
798:
779:
773:
707:
685:
666:
655:
633:
609:
586:
585:
580:
579:
574:
573:
553:
544:
543:
525:Lax security
524:
514:
508:
502:
493:
485:
475:
452:
447:
429:
424:availability
399:
385:
380:
347:
338:
329:
301:
272:
242:
230:
216:
182:
178:
176:
151:
121:
108:
102:
96:
83:
68:
51:stakeholders
46:
41:
22:
713:Flashlights
575:Data backup
558:is needed.
549:backup site
1182:Categories
766:References
658:management
404:agreements
266:milestone.
251:processes,
227:correction
118:DR metrics
1065:168198159
976:24 August
693:first aid
641:contracts
612:insurance
416:emergency
351:incidents
283:contracts
53:that the
1203:Planning
1090:8 August
951:9 August
870:8 August
834:9 August
808:Cloudian
734:See also
697:training
645:disaster
616:property
591:training
568:security
344:Benefits
279:billings
207:man-made
195:disaster
101:and the
86:unusable
65:Overview
59:material
43:Auditing
717:candles
480:dry run
335:Testing
287:vendors
275:records
199:natural
74:Metrics
1193:Backup
1167:
1148:
1063:
786:
723:Safety
581:Drills
392:and a
304:subset
281:, and
141:backup
131:system
23:Given
1061:S2CID
1030:(PDF)
995:(PDF)
925:9 May
899:9 May
727:fires
563:site.
1165:ISBN
1146:ISBN
1092:2012
999:NIST
978:2012
953:2012
927:2014
901:2014
872:2012
836:2012
784:ISBN
715:and
639:and
618:and
496:Dell
412:cost
323:plan
1053:doi
689:CPR
637:MOA
519:VPN
205:or
183:DRP
104:RTO
98:RPO
88:.
1184::
1109:.
1059:.
1051:.
1047:.
997:.
961:^
880:^
858:.
844:^
816:^
806:.
593:,
554:A
422:,
410:,
353:.
277:,
201:,
191:IT
177:A
1173:.
1154:.
1115:.
1094:.
1067:.
1055::
1015:.
980:.
955:.
929:.
903:.
874:.
838:.
792:.
691:/
181:(
113:.
20:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.