71:
91:
104:
289:
31:
or atom that has the ability to draw electron density toward itself and away from other adjacent atoms. This electron density transfer is often achieved by resonance or inductive effects. Electron-withdrawing groups have significant impacts on fundamental chemical processes such as
298:
is famously affected by EWGs. The effect is transmitted by inductive and resonance effects. Benzene with an EWG typically undergoes electrophilic substitution at meta positions. Overall the rates are diminished. thus EWGs are called deactivating.
432:
159:
216:
194:
238:
478:
417:
115:
581:
295:
303:
70:
90:
407:
62:
562:
361:
Electron-withdrawing groups are the opposite effect of electron-donating groups (EDGs). Both describe
586:
526:
Connelly, Neil G.; Geiger, William E. (1996). "Chemical Redox Agents for
Organometallic Chemistry".
103:
378:
241:
277:
265:
257:
253:
201:
170:
311:
223:
78:
8:
331:
33:
335:
98:
The impact of the EWG group on pKa decreases with distances from the carboxylic group.
543:
474:
413:
327:
269:
82:
535:
508:
466:
366:
362:
54:
28:
61:. The strength of the electron-withdrawing group is inversely proportional to the
346:
273:
37:
369:
away from a molecule, whereas EDGs push electron density onto a substituent.
575:
512:
339:
315:
58:
260:. For example, fluorine is a stronger electron-withdrawing substituent than
547:
459:"Non-conventional Lewis Acids and Bases in Frustrated Lewis Pair Chemistry"
458:
470:
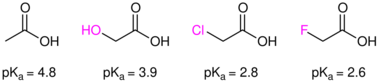
403:
307:
563:"Chapter 12: Reactions of Arenes. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution"
539:
350:
314:
is far more susceptible to reactions displacing chloride compared to
109:
For benzoic acids, the effect is quantified by the
Hammett equation:
288:
409:
Advanced
Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure
261:
499:
J. F. Bunnett, R. M. Conner (1960). "2,4-Dinitroiodobenzene".
283:
401:
498:
356:
345:
Oxidants with EWGs are stronger than the parent compound.
465:, Cham: Springer International Publishing, pp. 1–29,
334:
tendency of the attached species. For example,
226:
204:
173:
118:
457:
Caputo, Christopher B.; Stephan, Douglas W. (2015),
154:{\displaystyle \log {\frac {K}{K_{0}}}=\sigma \rho }
338:serves as an oxidant due to its attachment to four
276:. Electron-withdrawing groups also tend to reduce
232:
210:
188:
153:
573:
306:, electron-withdrawing groups are more prone to
525:
412:(6th ed.), New York: Wiley-Interscience,
48:
456:
321:
365:, however, electron-withdrawing groups pull
284:Effect on a aromatic substitution reactions
247:
102:
89:
69:
342:, which are electron-withdrawing groups.
357:Comparison with electron-donating groups
287:
43:
574:
433:"20.4: Substituent Effects on Acidity"
53:Electron-withdrawing groups exert an "
560:
397:
395:
393:
256:, making compounds more reactive as
77:The inductive effect is cumulative:
304:nucleophilic substitution reactions
296:Electrophilic aromatic substitution
13:
57:" or "electron-pulling" effect on
14:
598:
554:
425:
390:
519:
492:
450:
349:is 300 mV more oxidizing than
40:, and substitution reactions.
16:Class of chemical substituents
1:
384:
264:, resulting in an increased
7:
372:
330:, these groups enhance the
49:Effects on Bronsted acidity
10:
603:
582:Physical organic chemistry
322:Effects on redox potential
21:electron-withdrawing group
308:nucleophilic substitution
561:Hunt, Ian (2023-10-22).
513:10.15227/orgsyn.040.0034
65:of the carboxylic acid.
379:Electron-donating group
248:Effect on Lewis acidity
211:{\displaystyle \sigma }
189:{\displaystyle {K}_{0}}
81:is 1000x stronger than
292:
242:Reaction rate constant
234:
218:= Substituent constant
212:
190:
155:
463:The Chemical Bond III
291:
235:
233:{\displaystyle \rho }
213:
191:
156:
471:10.1007/430_2015_177
437:Chemistry LibreTexts
312:chlorodinitrobenzene
224:
202:
196:= Reference constant
171:
116:
79:trichloroacetic acid
44:Consequences of EWGs
402:Smith, Michael B.;
34:acid-base reactions
340:cyano substituents
336:Tetracyanoethylene
326:In the context of
293:
230:
208:
186:
151:
540:10.1021/cr940053x
501:Organic Syntheses
480:978-3-319-35145-2
419:978-0-471-72091-1
363:functional groups
347:Acetylferrocenium
328:electron transfer
302:When it comes to
270:boron trifluoride
252:EWGs enhance the
140:
83:chloroacetic acid
594:
587:Chemical bonding
567:
566:
558:
552:
551:
528:Chemical Reviews
523:
517:
516:
496:
490:
489:
488:
487:
454:
448:
447:
445:
444:
429:
423:
422:
399:
367:electron density
239:
237:
236:
231:
217:
215:
214:
209:
195:
193:
192:
187:
185:
184:
179:
160:
158:
157:
152:
141:
139:
138:
126:
106:
93:
73:
38:redox potentials
602:
601:
597:
596:
595:
593:
592:
591:
572:
571:
570:
559:
555:
524:
520:
497:
493:
485:
483:
481:
455:
451:
442:
440:
431:
430:
426:
420:
400:
391:
387:
375:
359:
332:oxidizing power
324:
310:. For example,
286:
274:trimethylborane
250:
225:
222:
221:
203:
200:
199:
180:
175:
174:
172:
169:
168:
134:
130:
125:
117:
114:
113:
51:
46:
17:
12:
11:
5:
600:
590:
589:
584:
569:
568:
553:
534:(2): 877–910.
518:
491:
479:
449:
424:
418:
388:
386:
383:
382:
381:
374:
371:
358:
355:
323:
320:
285:
282:
278:Lewis basicity
249:
246:
245:
244:
229:
219:
207:
197:
183:
178:
162:
161:
150:
147:
144:
137:
133:
129:
124:
121:
100:
99:
95:
94:
75:
74:
59:covalent bonds
50:
47:
45:
42:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
599:
588:
585:
583:
580:
579:
577:
564:
557:
549:
545:
541:
537:
533:
529:
522:
514:
510:
506:
502:
495:
482:
476:
472:
468:
464:
460:
453:
438:
434:
428:
421:
415:
411:
410:
405:
398:
396:
394:
389:
380:
377:
376:
370:
368:
364:
354:
352:
348:
343:
341:
337:
333:
329:
319:
317:
316:chlorobenzene
313:
309:
305:
300:
297:
290:
281:
279:
275:
271:
267:
266:Lewis acidity
263:
259:
255:
254:Lewis acidity
243:
227:
220:
205:
198:
181:
176:
167:
166:
165:
148:
145:
142:
135:
131:
127:
122:
119:
112:
111:
110:
107:
105:
97:
96:
92:
88:
87:
86:
84:
80:
72:
68:
67:
66:
64:
60:
56:
41:
39:
35:
30:
26:
22:
556:
531:
527:
521:
504:
500:
494:
484:, retrieved
462:
452:
441:. Retrieved
439:. 2015-09-01
436:
427:
408:
404:March, Jerry
360:
344:
325:
301:
294:
272:relative to
251:
163:
108:
101:
76:
52:
24:
20:
18:
258:Lewis acids
576:Categories
486:2023-11-05
443:2023-12-07
385:References
351:ferrocene
228:ρ
206:σ
149:ρ
146:σ
123:
55:inductive
548:11848774
406:(2007),
373:See also
27:) is a
546:
507:: 34.
477:
416:
262:methyl
164:where
29:group
544:PMID
475:ISBN
414:ISBN
536:doi
509:doi
467:doi
268:of
120:log
63:pKa
25:EWG
19:An
578::
542:.
532:96
530:.
505:40
503:.
473:,
461:,
435:.
392:^
353:.
318:.
280:.
240:=
85:.
36:,
565:.
550:.
538::
515:.
511::
469::
446:.
182:0
177:K
143:=
136:0
132:K
128:K
23:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.