1203:
252:
72:
1223:
any error of significance to make the nodes terminated is sufficient to accurately simulate the node. For example, the two internal nodes that were eliminated above could alternatively have had a 1e+09 ohm port attached to them, so instead of using Kron reduction to eliminate the nodes, the nodes could be accurately simulated with excessively large resistive ports.
158:
provided by mixed-mode simulators is general-purpose and supports non-digital types of data. For example, elements can use real or integer values to simulate DSP functions or sampled data filters. Because the event-driven algorithm is faster than the standard SPICE matrix solution, simulation time is
1231:
If the input source to the network is an ideal voltage source with no resistance, the example above may be made to work by including a port resistance small enough to not introduce any error of significance. For example, a port with a resistance of 1e-09 in a network that is terminated elsewhere by
1210:
The final validity test for the example is to simulate the
Chebyshev filter frequency response through the full useful range, which will be taken to be 100 MHz to 5 GHz for this case. This range should permit viewing of the equi-ripple |S12| of the pass band between 0 and -1 dB, somewhat steep stop
1121:
It may be useful to do some quick validity checks at this point. Since the example
Chebyshev filter design requirement is for -1dB attenuation at the cutoff frequency of 1GHz, |S12| at 1 GHz is expected to be -1dB. Furthermore, since all simulation elements are lossless, the well known relation,
1222:
Since S parameters require terminations on all nodes being simulated, simulating the S parameter value for unterminated nodes, such as the internal nodes of a network, are technically unsupported. However, placing a resistive termination on unterminated nodes that is large enough to not introduce
182:
problems where a close inspection of an IC’s I/O characteristics is needed. Boolean logic expressions are delay-less functions that are used to provide efficient logic signal processing in an analog environment. These two modeling techniques use SPICE to solve a problem while the third method,
183:
digital primitives, uses mixed mode capability. Each of these methods has its merits and target applications. In fact, many simulations (particularly those which use A/D technology) call for the combination of all three approaches. No one approach alone is sufficient.
410:
The table above provides a list of ideal elements to model along with a node attachments to simulate. Next, each non-port element must be converted into a 2X2 Y parameter model for each frequency to be simulated. For this example, a frequency of 1GHz is selected.
692:
To simulate the filter at 1GHz, or any frequency, the element Y parameters must be converted to numerical entries using Y parameter models appropriate for the element installed. For ideal inductors and capacitors, the well known Y11 = Y22 = -Y12 = -Y21 =
1349:
90:
display (see Figure 1), allowing designers to rapidly modify a simulated circuit and see what effect the changes have on the output. They also typically contain extensive model and device libraries. These models typically include IC specific
162:
Mixed-mode simulation is handled on three levels: with primitive digital elements that use timing models and the built-in 12 or 16 state digital logic simulator, with subcircuit models that use the actual transistor topology of the
43:
Simulating a circuit’s behavior before actually building it can greatly improve design efficiency by making faulty designs known as such, and providing insight into the behavior of electronic circuit designs. In particular, for
1071:
976:
Since the
Chebyshev frequency response is expected to be observable in |S12| as a 1dB equi-ripple response from 0 to 1GHz, the complex S parameter entries need to be converted to their respective magnitudes, using the standard
23:
to replicate the behavior of an actual electronic device or circuit. Simulation software allows for the modeling of circuit operation and is an invaluable analysis tool. Due to its highly accurate modeling capability, many
565:
It should be remembered that while Ideal inductor and capacitor modals consist of very simple 2x2 models where Y11 = Y22 = -Y12 = -Y21, most real world elements cannot be modeled so simply. With
869:. The table below shows the reduced Y parameter matrix of the Chebyshev filter example simulation after nodes 2 and 4 are eliminated. The nodes of the reduced table are renumbered to 1 and 2.
198:
switch changes its state. At this time a new analog model is calculated to be used for the next simulation period. This methodology both enhances simulation speed and stability significantly.
569:
and real world inductor and capacitor models, for example, Y11 != -Y12, and for some more complex passive asymmetric elements Y11 != Y22. For many active linear devices, such as
917:
Since the
Chebyshev frequency response is observed from the S parameter matrix, namely |S12|, the next step is to convert the Y parameter matrix to an S parameter matrix, using well known
573:, Y12 != Y21. Therefore, the example in this section uses independent Y11, Y12, Y21, and Y22 to illustrate the simulation processes that applies to more complex real world devices.
1247:
36:
programs. Electronics simulation software engages its users by integrating them into the learning experience. These kinds of interactions actively engage learners to analyze,
1544:
213:
and circuit simulators often do not take these variations into account. These variations can be small, but taken together, they can change the output of a chip significantly.
769:
151:
can be driven from one integrated schematic. All the digital models in mixed-mode simulators provide accurate specification of propagation time and rise/fall time delays.
723:
1633:
228:, or Y matrices. The technique involves modeling the individual linear components as an N port admittance matrix, inserting the component Y matrix into a circuits
1734:
143:
electronics circuit simulators, popular simulators often include both analog and event-driven digital simulation capabilities, and are known as mixed-mode or
980:
576:
Each element Y parameter is inserted into the nodal admittance matrix by summing in them into the nodes they are attached to following the rules below.
60:
relies heavily on simulation. The most well known analog simulator is SPICE. Probably the best known digital simulators are those based on
1409:
414:
Elements connected to node 0, the ground node, do not need their respective Y12 or Y21 calculated, and are shown as "n/a" in the table.
1585:
1869:
1548:
236:, converting the final Y matrix to an S or Z matrix as needed, and extracting desired measurements from the Y, Z, and/or S matrix.
128:
1214:
Since all simulation outputs conform to the expected results, the
Chebyshev filter example simulation is confirmed to be correct.
1600:
1404:
1864:
1630:
1211:
band |S12| falling off at 1GHz, and an equi-ripple |S12| at the expected peak values of 20log10(.4535...) = -6.86825 dB.
1694:
Proceedings of the IEEE 1999 International
Conference on Power Electronics and Drive Systems. PEDS'99 (Cat. No.99TH8475)
248:
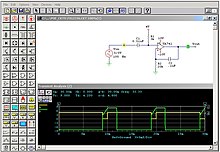
and subsequent impedance and frequency scaling produces the elements shown in the table and Micro-cap schematic below.
918:
1808:
1778:
1744:
1709:
244:
A fifth order, 50 ohm, Chebyshev filter with 1dB of pass band ripple and cutoff frequency of 1GHz designed using the
206:
210:
588:
Y22 is summed into the m x m node in the diagonal, where m is the node that the second pin, pin 2, is attached to.
580:
Y11 is summed into the n x n node in the diagonal, where n is the node that the first pin, pin 1, is attached to.
144:
56:
are impractical, and probing the behavior of internal signals is extremely difficult. Therefore, almost all
216:
Temperature variation can also be modeled to simulate the circuit's performance through temperature ranges.
1824:
1773:. Oxford, London, Edinburgh, New York, Toronto, Paris, Braunschweig: Pergamon Press, Ltd. pp. 45–58.
1344:{\displaystyle {\frac {V_{i}}{V_{j}}}={\frac {S_{ij}}{2}}{\sqrt {\frac {R_{j}}{R_{i}}}},{\text{ }}i\neq j}
925:
1414:
245:
921:
with the port impedance as the characteristic impedance (or characteristic admittance) for each node.
1840:
1803:. 610 Washington Street, Dedham, Massachusetts, US: Artech House, Inc. (published 1985). p. 44.
598:
The table below shows the
Chebyshev element 2x2 Y parameters summed in at the appropriate locations.
191:
57:
232:, installing port terminations at nodes that contain ports, eliminating ports without nodes though
728:
1651:"A new algorithm for simulation of power electronic systems using piecewise-linear device models"
1429:
229:
33:
1849:
29:
1240:
Since the example above simulates S parameters, another conversion is necessary to obtain the
696:
1845:
1469:
865:
Since ports are only attached to node 1 and node 4, nodes 2 and 3 need to be removed through
570:
120:
1768:
1369:
1662:
1364:
924:
Simulated S parameters also allow for useful post simulation processing for things such as
40:, organize, and evaluate content and result in learners constructing their own knowledge.
8:
1581:
45:
1666:
1568:
1818:
1798:
1715:
771:
for capacitors are sufficient. The numerical conversion are shown in the table below.
164:
20:
1607:
1804:
1774:
1740:
1719:
1705:
1374:
1241:
566:
560:
225:
195:
187:
175:
159:
greatly reduced for circuits that use event-driven models in place of analog models.
124:
92:
1066:{\displaystyle |S_{ij}|={\sqrt {S_{ij{\text{ real}}}^{2}+S_{ij{\text{ imag}}}^{2}}}}
111:, user defined models (such as controlled current and voltage sources, or models in
1697:
1670:
1494:
179:
83:
1637:
1202:
148:
37:
1514:
866:
233:
1689:
1650:
1858:
1701:
1484:
1394:
168:
140:
1509:
1434:
75:
108:
1800:
Microwave
Filters, Impudence-Matching Networks, and Coupling Structures
194:
algorithms. These algorithms use an analog (linear) simulation until a
53:
1674:
1479:
1454:
251:
155:
147:
simulators if they can simulate both simultaneously. An entire mixed
112:
100:
49:
1690:"PLECS-piece-wise linear electrical circuit simulation for Simulink"
1459:
116:
104:
96:
87:
25:
561:
Inserting the 2 port Y parameters into the nodal admittance matrix
1545:"Disadvantages and Advantages of Simulations in Online Education"
1464:
1449:
1439:
1389:
61:
1499:
1444:
1424:
71:
28:
and universities use this type of software for the teaching of
1569:
Mengue and Vignat, Entry in the
University of Marne, at Vallee
1232:
50 ohms would model an ideal source with sufficient accuracy.
224:
A common method of simulating linear circuits systems is with
1631:
L. Walken and M. Bruckner, Event-Driven
Multimodal Technology
1524:
1519:
1504:
1474:
687:
418:
Table of Chebyshev element Y parameters at 1GHz to simulate
1489:
1384:
65:
1797:
Matthaei, George L.; Young, Leo; Jones, E. M. T. (1984).
174:
Exact representations are used mainly in the analysis of
932:
Table of S parameters with 50 ohm terminations at 1GHz
123:(PCB) design requires specific models as well, such as
912:
1250:
1226:
983:
873:
Table of Kron Reduced numerical Y parameters at 1GHz
731:
699:
584:
If the second node is not 0, that is, not a ground:
219:
1235:
405:
1796:
1343:
1130:| = 1 applies at all frequencies, including 1GHz.
1065:
763:
717:
239:
1648:
1856:
1217:
1688:Allmeling, J.H.; Hammer, W.P. (July 13, 1999).
1687:
1601:"Entry in the Universidade de Aveiro, Portugal"
1077:S parameters with 50 ohm terminations at 1GHz
131:models for driving and receiving electronics.
1649:Pejovic, P.; Maksimovic, D. (May 13, 1995).
1197:
1410:List of free electronics circuit simulators
725:for inductors and Y11 = Y22 = -Y12 = -Y21 =
186:Another type of simulation used mainly for
1841:WCCA Simple Comparing of different Methods
860:
594:Y21 is summed into the m x n node location
591:Y12 is summed into the n x m node location
1598:
971:
688:Nodal admittance matrix numerical entries
95:such as BSIM, generic components such as
1766:
1201:
775:Table of numerical Y parameters at 1GHz
260:Table of Chebyshev elements to simulate
250:
86:, a simulation engine, and an on-screen
82:Some electronics simulators integrate a
70:
1696:. Vol. 1. pp. 355–360 vol.1.
1405:List of electrical engineering software
1244:from S parameters. The conversion is,
255:Chebyshev filter in Micro-cap schematic
1857:
1732:
1655:IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics
1792:
1790:
1582:"Entry in the University of Florida"
1579:
1116:
1770:Basic Matrix Analysis and Synthesis
1206:Chebyshev filter example simulation
913:Converting to an S parameter matrix
13:
1787:
1227:Simulating zero resistance sources
1134:Simulation validity Tests at 1GHz
14:
1881:
1834:
220:Simulation from admittance matrix
1870:Simulation programming languages
1588:from the original on 2000-05-19.
1236:Simulating the transfer function
919:Y matrix to S matrix conversions
406:Modeling the 2 port Y parameters
78:electronics simulation software.
240:Simple Chebyshev filter example
201:
1760:
1726:
1681:
1642:
1624:
1592:
1573:
1562:
1537:
1003:
985:
758:
743:
1:
1846:Electronic circuit simulation
1531:
1218:Simulating unterminated nodes
602:Table of Y parameter entries
17:Electronic circuit simulation
1865:Electronic design automation
764:{\displaystyle -j/(2\pi fC)}
7:
1354:
926:group delay and phase delay
167:, and finally, with inline
10:
1886:
1415:Comparison of EDA software
1188:0.45351050+0.89125104 = 1
1733:Ohnari, Mikihiko (1998).
1198:Full frequency simulation
209:occur when the design is
139:While there are strictly
1823:: CS1 maint: location (
1722:– via IEEE Xplore.
1702:10.1109/PEDS.1999.794588
1677:– via IEEE Xplore.
718:{\displaystyle j2\pi fL}
246:Chebyshev Cauar topology
134:
1599:Pedro, J; Carvalho, N.
1430:Circuit design language
861:Removing internal nodes
230:nodal admittance matrix
34:electronics engineering
1850:Open Directory Project
1736:Simulation engineering
1345:
1207:
1067:
972:S parameter magnitudes
965:-0.356328 + j0.280539
951:-0.356328 + j0.280539
765:
719:
571:operational amplifiers
256:
79:
30:electronics technician
1767:Zelinger, G. (1966).
1470:NL5 Circuit Simulator
1346:
1205:
1068:
962:0.551322 + j0.700266
954:0.551322 + j0.700266
766:
720:
663:L2_Y22+C2_Y11+L3_Y11
645:L1_Y22+C1_Y11+L2_Y11
254:
121:Printed circuit board
74:
1365:Lumped element model
1248:
1166:(0.89125104) = -1dB
981:
729:
697:
1667:1995ITPE...10..340P
1141:required condition
1135:
1078:
1060:
1034:
933:
874:
776:
603:
426:admittance at 1GHz
419:
261:
226:admittance matrices
127:for the traces and
46:integrated circuits
21:mathematical models
1636:2007-05-05 at the
1370:System isomorphism
1341:
1208:
1133:
1076:
1063:
1038:
1012:
931:
872:
774:
761:
715:
601:
567:transmission lines
417:
259:
257:
207:Process variations
165:integrated circuit
125:transmission lines
80:
1675:10.1109/63.388000
1375:Transistor models
1330:
1322:
1321:
1296:
1273:
1242:transfer function
1195:
1194:
1117:Check the results
1114:
1113:
1061:
1052:
1026:
969:
968:
910:
909:
858:
857:
685:
684:
558:
557:
432:Y12, Y21 at 1GHz
429:Y11, Y22 at 1GHz
403:
402:
276:50 ohms and 1GHz
188:power electronics
176:transmission line
154:The event-driven
93:transistor models
1877:
1829:
1828:
1822:
1814:
1794:
1785:
1784:
1764:
1758:
1757:
1755:
1753:
1730:
1724:
1723:
1685:
1679:
1678:
1646:
1640:
1628:
1622:
1621:
1619:
1618:
1612:
1606:. Archived from
1605:
1596:
1590:
1589:
1577:
1571:
1566:
1560:
1559:
1557:
1556:
1547:. Archived from
1541:
1350:
1348:
1347:
1342:
1331:
1328:
1323:
1320:
1319:
1310:
1309:
1300:
1299:
1297:
1292:
1291:
1279:
1274:
1272:
1271:
1262:
1261:
1252:
1136:
1132:
1079:
1075:
1072:
1070:
1069:
1064:
1062:
1059:
1054:
1053:
1050:
1033:
1028:
1027:
1024:
1011:
1006:
1001:
1000:
988:
934:
930:
875:
871:
777:
773:
770:
768:
767:
762:
742:
724:
722:
721:
716:
604:
600:
420:
416:
262:
258:
196:power electronic
192:piecewise linear
180:signal integrity
84:schematic editor
52:) is expensive,
1885:
1884:
1880:
1879:
1878:
1876:
1875:
1874:
1855:
1854:
1837:
1832:
1816:
1815:
1811:
1795:
1788:
1781:
1765:
1761:
1751:
1749:
1747:
1731:
1727:
1712:
1686:
1682:
1647:
1643:
1638:Wayback Machine
1629:
1625:
1616:
1614:
1610:
1603:
1597:
1593:
1578:
1574:
1567:
1563:
1554:
1552:
1543:
1542:
1538:
1534:
1529:
1357:
1327:
1315:
1311:
1305:
1301:
1298:
1284:
1280:
1278:
1267:
1263:
1257:
1253:
1251:
1249:
1246:
1245:
1238:
1229:
1220:
1200:
1184:
1180:
1165:
1159:(|S12|) = -1dB
1158:
1144:actual results
1129:
1125:
1119:
1055:
1049:
1042:
1029:
1023:
1016:
1010:
1002:
993:
989:
984:
982:
979:
978:
974:
915:
863:
738:
730:
727:
726:
698:
695:
694:
690:
563:
531:-J0.0093682013
528:-J0.0093682013
497:-J0.0066646164
494:-J0.0066646164
463:-J0.0093682013
460:-J0.0093682013
408:
242:
222:
204:
149:signal analysis
137:
48:, the tooling (
12:
11:
5:
1883:
1873:
1872:
1867:
1853:
1852:
1843:
1836:
1835:External links
1833:
1831:
1830:
1809:
1786:
1779:
1759:
1745:
1725:
1710:
1680:
1661:(3): 340–348.
1641:
1623:
1591:
1572:
1561:
1535:
1533:
1530:
1528:
1527:
1522:
1517:
1512:
1507:
1502:
1497:
1492:
1487:
1482:
1477:
1472:
1467:
1462:
1457:
1452:
1447:
1442:
1437:
1432:
1427:
1418:
1417:
1412:
1407:
1398:
1397:
1392:
1387:
1378:
1377:
1372:
1367:
1358:
1356:
1353:
1340:
1337:
1334:
1326:
1318:
1314:
1308:
1304:
1295:
1290:
1287:
1283:
1277:
1270:
1266:
1260:
1256:
1237:
1234:
1228:
1225:
1219:
1216:
1199:
1196:
1193:
1192:
1189:
1186:
1182:
1178:
1175:
1171:
1170:
1167:
1163:
1160:
1156:
1153:
1149:
1148:
1145:
1142:
1139:
1127:
1123:
1118:
1115:
1112:
1111:
1108:
1105:
1101:
1100:
1097:
1094:
1090:
1089:
1086:
1083:
1058:
1048:
1045:
1041:
1037:
1032:
1022:
1019:
1015:
1009:
1005:
999:
996:
992:
987:
973:
970:
967:
966:
963:
960:
956:
955:
952:
949:
945:
944:
941:
938:
914:
911:
908:
907:
904:
901:
897:
896:
893:
890:
886:
885:
882:
879:
867:Kron reduction
862:
859:
856:
855:
852:
849:
847:
845:
841:
840:
837:
834:
831:
829:
825:
824:
822:
819:
816:
813:
809:
808:
806:
804:
801:
798:
794:
793:
790:
787:
784:
781:
760:
757:
754:
751:
748:
745:
741:
737:
734:
714:
711:
708:
705:
702:
689:
686:
683:
682:
679:
676:
674:
672:
668:
667:
664:
661:
658:
656:
652:
651:
649:
646:
643:
640:
636:
635:
633:
631:
628:
625:
621:
620:
617:
614:
611:
608:
596:
595:
592:
589:
582:
581:
562:
559:
556:
555:
552:
549:
546:
543:
539:
538:
535:
534:J0.0093682013
532:
529:
526:
522:
521:
518:
515:
512:
509:
505:
504:
501:
500:J0.0066646164
498:
495:
492:
488:
487:
484:
481:
478:
475:
471:
470:
467:
466:J0.0093682013
464:
461:
458:
454:
453:
450:
447:
444:
441:
437:
436:
433:
430:
427:
424:
407:
404:
401:
400:
397:
394:
391:
388:
384:
383:
380:
379:1.6988847E-08
377:
374:
371:
367:
366:
363:
362:3.4731024E-12
360:
357:
354:
350:
349:
346:
345:2.3880586E-08
343:
340:
337:
333:
332:
329:
328:3.4731024E-12
326:
323:
320:
316:
315:
312:
311:1.6988847E-08
309:
306:
303:
299:
298:
295:
292:
289:
286:
282:
281:
278:
272:
269:
266:
241:
238:
234:Kron reduction
221:
218:
203:
200:
136:
133:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1882:
1871:
1868:
1866:
1863:
1862:
1860:
1851:
1847:
1844:
1842:
1839:
1838:
1826:
1820:
1812:
1810:0-89006-099-1
1806:
1802:
1801:
1793:
1791:
1782:
1780:9781483199061
1776:
1772:
1771:
1763:
1748:
1746:9784274902178
1742:
1738:
1737:
1729:
1721:
1717:
1713:
1711:0-7803-5769-8
1707:
1703:
1699:
1695:
1691:
1684:
1676:
1672:
1668:
1664:
1660:
1656:
1652:
1645:
1639:
1635:
1632:
1627:
1613:on 2012-02-07
1609:
1602:
1595:
1587:
1583:
1580:Fishwick, P.
1576:
1570:
1565:
1551:on 2010-12-16
1550:
1546:
1540:
1536:
1526:
1523:
1521:
1518:
1516:
1513:
1511:
1508:
1506:
1503:
1501:
1498:
1496:
1493:
1491:
1488:
1486:
1483:
1481:
1478:
1476:
1473:
1471:
1468:
1466:
1463:
1461:
1458:
1456:
1453:
1451:
1448:
1446:
1443:
1441:
1438:
1436:
1433:
1431:
1428:
1426:
1423:
1422:
1421:
1416:
1413:
1411:
1408:
1406:
1403:
1402:
1401:
1396:
1395:SystemVerilog
1393:
1391:
1388:
1386:
1383:
1382:
1381:
1376:
1373:
1371:
1368:
1366:
1363:
1362:
1361:
1352:
1338:
1335:
1332:
1324:
1316:
1312:
1306:
1302:
1293:
1288:
1285:
1281:
1275:
1268:
1264:
1258:
1254:
1243:
1233:
1224:
1215:
1212:
1204:
1190:
1187:
1176:
1173:
1172:
1168:
1161:
1154:
1151:
1150:
1146:
1143:
1140:
1138:
1137:
1131:
1109:
1106:
1103:
1102:
1098:
1095:
1092:
1091:
1087:
1084:
1081:
1080:
1074:
1056:
1046:
1043:
1039:
1035:
1030:
1020:
1017:
1013:
1007:
997:
994:
990:
964:
961:
958:
957:
953:
950:
947:
946:
942:
939:
936:
935:
929:
927:
922:
920:
905:
902:
899:
898:
894:
891:
888:
887:
883:
880:
877:
876:
870:
868:
853:
850:
848:
846:
843:
842:
838:
835:
832:
830:
827:
826:
823:
820:
817:
814:
811:
810:
807:
805:
802:
799:
796:
795:
791:
788:
785:
782:
779:
778:
772:
755:
752:
749:
746:
739:
735:
732:
712:
709:
706:
703:
700:
680:
677:
675:
673:
670:
669:
665:
662:
659:
657:
654:
653:
650:
647:
644:
641:
638:
637:
634:
632:
629:
626:
623:
622:
618:
615:
612:
609:
606:
605:
599:
593:
590:
587:
586:
585:
579:
578:
577:
574:
572:
568:
553:
550:
547:
544:
541:
540:
536:
533:
530:
527:
524:
523:
519:
516:
514:j0.021822146
513:
511:j0.021822146
510:
507:
506:
502:
499:
496:
493:
490:
489:
485:
482:
480:j0.021822146
479:
477:j0.021822146
476:
473:
472:
468:
465:
462:
459:
456:
455:
451:
448:
445:
442:
439:
438:
434:
431:
428:
425:
422:
421:
415:
412:
398:
395:
392:
389:
386:
385:
381:
378:
375:
372:
369:
368:
364:
361:
358:
355:
352:
351:
347:
344:
341:
338:
335:
334:
330:
327:
324:
321:
318:
317:
313:
310:
307:
304:
301:
300:
296:
293:
290:
287:
284:
283:
279:
277:
273:
270:
267:
264:
263:
253:
249:
247:
237:
235:
231:
227:
217:
214:
212:
208:
199:
197:
193:
189:
184:
181:
177:
172:
171:expressions.
170:
169:Boolean logic
166:
160:
157:
152:
150:
146:
142:
132:
130:
126:
122:
118:
114:
110:
106:
102:
98:
94:
89:
85:
77:
73:
69:
67:
63:
59:
55:
51:
47:
41:
39:
35:
31:
27:
22:
18:
1799:
1769:
1762:
1750:. Retrieved
1735:
1728:
1693:
1683:
1658:
1654:
1644:
1626:
1615:. Retrieved
1608:the original
1594:
1575:
1564:
1553:. Retrieved
1549:the original
1539:
1510:TARGET 3001!
1435:CircuitLogix
1419:
1399:
1379:
1359:
1239:
1230:
1221:
1213:
1209:
1120:
975:
923:
916:
903:-j0.0536574
895:-j0.0536574
864:
854:-j0.0093682
836:j0.00578933
833:j0.00666462
821:j0.00666462
818:j0.00578933
800:-j0.0093682
691:
597:
583:
575:
564:
413:
409:
275:
243:
223:
215:
205:
202:Complexities
185:
173:
161:
153:
145:mixed-signal
138:
109:transformers
81:
76:CircuitLogix
42:
16:
15:
1752:October 12,
1110:0.45351050
1107:0.89125104
1099:0.89125104
1096:0.45351050
906:j0.0372422
892:j0.0372422
274:scaled for
54:breadboards
1859:Categories
1739:. Ohmsha.
1617:2007-04-27
1555:2011-03-11
1532:References
1420:Software:
1360:Concepts:
1051: imag
1025: real
851:0.0093682
839:0.0093682
815:0.0093682
803:0.0093682
373:2.1348815
359:capacitor
356:1.0911073
339:3.0009229
325:capacitor
322:1.0911073
305:2.1348815
211:fabricated
190:represent
101:capacitors
50:photomasks
38:synthesize
1819:cite book
1720:111196369
1480:PowerEsim
1455:Micro-Cap
1336:≠
750:π
733:−
707:π
376:inductor
342:inductor
308:inductor
156:algorithm
113:Verilog-A
105:inductors
97:resistors
58:IC design
1634:Archived
1586:Archived
1460:Multisim
1355:See also
423:element
268:g-value
265:element
117:VHDL-AMS
88:waveform
26:colleges
1848:at the
1663:Bibcode
1465:ngspice
1450:LTspice
1440:EasyEDA
1400:Lists:
1390:Verilog
1147:Status
681:L3_Y22
678:L3_Y21
666:L3_Y12
660:L2_Y21
648:L2_Y12
642:L1_Y21
630:L1_Y12
627:L1_Y11
62:Verilog
1807:
1777:
1743:
1718:
1708:
1500:SapWin
1445:Gnucap
1425:Altium
1329:
1191:Valid
1185:| = 1
1169:Valid
435:nodes
280:nodes
141:analog
1716:S2CID
1611:(PDF)
1604:(PDF)
1525:Zuken
1520:Yenka
1505:SPICE
1495:Saber
1475:PLECS
1380:HDL:
1162:20log
1155:20log
1082:node
937:node
878:node
780:node
607:node
537:3, 4
520:3, 0
503:2, 3
486:2, 0
469:1, 2
393:port
382:3, 4
365:3, 0
348:2, 3
331:2, 0
314:1, 2
291:port
271:Type
135:Types
19:uses
1825:link
1805:ISBN
1775:ISBN
1754:2022
1741:ISBN
1706:ISBN
1515:TINA
1490:Qucs
1485:PSIM
1385:VHDL
1181:|+|S
1126:|+|S
551:n/a
548:n/a
545:n/a
517:n/a
483:n/a
449:n/a
446:n/a
443:n/a
178:and
129:IBIS
119:).
107:and
66:VHDL
64:and
32:and
1698:doi
1671:doi
542:P2
525:L3
508:C2
491:L2
474:C1
457:L1
440:P1
396:50
387:P2
370:L3
353:C2
336:L2
319:C1
302:L1
294:50
285:P1
115:or
1861::
1821:}}
1817:{{
1789:^
1714:.
1704:.
1692:.
1669:.
1659:10
1657:.
1653:.
1584:.
1351:.
1183:12
1179:12
1177:|S
1174:2
1164:10
1157:10
1152:1
1128:12
1124:11
1122:|S
1104:2
1093:1
1088:2
1085:1
1073:.
959:2
948:1
943:2
940:1
928:.
900:2
889:1
884:2
881:1
844:4
828:3
812:2
797:1
792:4
789:3
786:2
783:1
671:5
655:3
639:2
624:1
619:4
616:3
613:2
610:1
554:4
452:1
399:4
390:1
297:1
288:1
103:,
99:,
68:.
1827:)
1813:.
1783:.
1756:.
1700::
1673::
1665::
1620:.
1558:.
1339:j
1333:i
1325:,
1317:i
1313:R
1307:j
1303:R
1294:2
1289:j
1286:i
1282:S
1276:=
1269:j
1265:V
1259:i
1255:V
1057:2
1047:j
1044:i
1040:S
1036:+
1031:2
1021:j
1018:i
1014:S
1008:=
1004:|
998:j
995:i
991:S
986:|
759:)
756:C
753:f
747:2
744:(
740:/
736:j
713:L
710:f
704:2
701:j
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.