31:
39:
23:
277:
Măndescu, Dragoş. “Then and Now. The Limes
Transalutanus 130 Years after Its Discovery.” BEITRÄGE ZUM WELTERBE LIMES Bayerisches Landesamt für Denkmalpflege · Deutsche Limeskommission Limes XXIII Proceedings of the 23rd International Congress of Roman Frontier Studies Ingolstadt 2015, C. Sebastian
87:
advanced the province's eastern frontier by some 14 km (8.7 mi) east of the existing Limes
Alutanus although the road and many of the forts on the Limes date from the end of
287:
Teodor, Eugen & Ștefan, Maria-Magdalena. (2014). LANDSCAPE ARCHAEOLOGY ALONG LIMES TRANSALUTANUS. JOURNAL OF ANCIENT HISTORY AND ARCHAEOLOGY. 1. 10.14795/j.v1i3.68
268:
Eugen Teodor, The
Invisible Giant: Limes Transalutanus. An overview south of Argeş River ISBN 978-606-537-298-6 ©Editura Cetatea de Scaun, Târgoviște, 2015
118:
The frontier system was composed of a road linking military forts and towers and in the southern, less mountainous, part a 3 m high
349:
296:
TEODOR, E.S. 2013. Uriaşul invizibil: Limes
Transalutanus. O reevaluare la sud de râul Argeş. Târgovişte: Editura Cetatea de Scaun
103:) attacks, Philip the Arab abandoned the limes for some time. The Romans returned to the limes but closed the road to the
72:
The Limes
Transalutanus, of 235 km length, was needed to shorten the line of communication to the strategic fort at
359:
354:
328:
Dorin Bondoc (Repertoriul fortificaţiilor de pe ripa nordică a limesului Dunării de Jos în epoca romană)
314:
C. C. Petolescu, Auxilia dacica. Contribuție la istoria militară a Daciei Roma- ne (Bucharest 2002) p55
305:
E. S. Teodor et al. Roman frontier crossing
Mocanului Valley, Cercetări Arheologice 29.2, 2022, 543-556
112:
162:
88:
30:
344:
210:
193:
183:
8:
257:
220:
278:
Sommer, Suzana Matešic (Hrsg.) · In
Kommission: Nünnerich-Asmus Verlag · Mainz (2018)
188:
157:
84:
73:
225:
198:
173:
142:
54:
244:
Technological challenges on the Limes
Transalutanus, Eugen S. Teodor, Dan Ştefan,
245:
167:
108:
215:
92:
77:
338:
58:
50:
62:
327:
131:
178:
123:
104:
153:
66:
38:
134:
at a distance varying from 5 to 30 km east of the river.
119:
49:
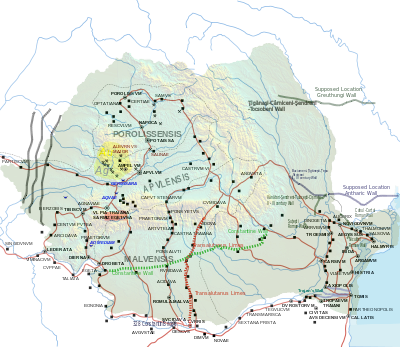
is the modern name given to a fortified frontier system of the
100:
96:
34:
76:
by almost 30 per cent compared to the earlier route via the
126:
on stone walls and also a ditch. In this southern part the
22:
258:
https://limesromania.ro/en/articole/about-the-project/
336:
246:https://www.antiquity.ac.uk/projgall/teodor342
16:Fortified frontier system of the Roman Empire
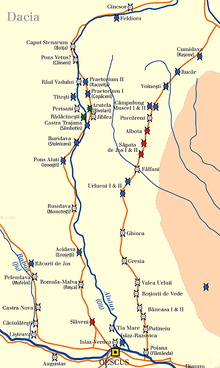
42:Forts on Limes Transalutanus (to the right)
111:pass starting from the modern village of
37:
29:
21:
91:(c.106 AD). Between 244–247, after the
337:
122:10–12 m wide reinforced with wooden
83:In first half of the 3rd century AD
13:
14:
371:
321:
141:was built in the area, known as
350:Roman fortifications in Romania
53:, built on the western edge of
308:
299:
290:
281:
271:
262:
250:
238:
1:
231:
170:also called Campulung Muscel
7:
204:
10:
376:
61:in the Roman province of
163:Castra of Drumul Carului
148:
57:forests as part of the
43:
35:
27:
41:
33:
25:
211:Limes (Roman Empire)
89:Trajan's Dacian Wars
360:Limes Transalutanus
355:History of Muntenia
221:Limes Porolissensis
47:Limes Transalutanus
44:
36:
28:
194:Castra of Băneasa
189:Gresia Roman fort
184:Castra of Fâlfani
158:Cumidava (castra)
85:Septimius Severus
367:
315:
312:
306:
303:
297:
294:
288:
285:
279:
275:
269:
266:
260:
254:
248:
242:
226:Brazda lui Novac
199:Castra of Poiana
174:Castra of Albota
143:Brazda lui Novac
130:was parallel to
375:
374:
370:
369:
368:
366:
365:
364:
335:
334:
324:
319:
318:
313:
309:
304:
300:
295:
291:
286:
282:
276:
272:
267:
263:
255:
251:
243:
239:
234:
207:
168:Jidava (castra)
151:
137:Later, another
19:
17:
12:
11:
5:
373:
363:
362:
357:
352:
347:
331:
330:
323:
322:External links
320:
317:
316:
307:
298:
289:
280:
270:
261:
249:
236:
235:
233:
230:
229:
228:
223:
218:
216:Limes Alutanus
213:
206:
203:
202:
201:
196:
191:
186:
181:
176:
171:
165:
160:
150:
147:
78:Limes Alutanus
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
372:
361:
358:
356:
353:
351:
348:
346:
343:
342:
340:
333:
329:
326:
325:
311:
302:
293:
284:
274:
265:
259:
253:
247:
241:
237:
227:
224:
222:
219:
217:
214:
212:
209:
208:
200:
197:
195:
192:
190:
187:
185:
182:
180:
177:
175:
172:
169:
166:
164:
161:
159:
156:
155:
154:
146:
144:
140:
135:
133:
129:
125:
121:
116:
114:
110:
106:
102:
98:
94:
90:
86:
81:
79:
75:
70:
68:
65:, modern-day
64:
60:
56:
52:
48:
40:
32:
24:
20:
332:
310:
301:
292:
283:
273:
264:
252:
240:
152:
138:
136:
127:
117:
82:
71:
59:Dacian Limes
51:Roman Empire
46:
45:
18:
345:Roman Dacia
55:Teleorman's
26:Roman Dacia
339:Categories
232:References
113:Băiculeşti
132:Olt river
124:palisades
205:See also
74:Angustia
93:Carpian
67:Romania
256:Limes
179:Săpata
120:vallum
149:Forts
139:limes
128:limes
105:Rucăr
101:Goths
97:Getae
63:Dacia
109:Bran
99:(or
95:and
69:.
341::
145:.
115:.
80:.
107:-
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.