1755:
67:
31:
50:
that may be simultaneously accessed by multiple programs with an intent to provide communication among them or avoid redundant copies. Shared memory is an efficient means of passing data between programs. Depending on context, programs may run on a single processor or on multiple separate processors.
127:
A shared memory system is relatively easy to program since all processors share a single view of data and the communication between processors can be as fast as memory accesses to the same location. The issue with shared memory systems is that many CPUs need fast access to memory and will likely
418:
For programming languages with POSIX bindings (say, C/C++), shared memory regions can be created and accessed by calling the functions provided by the operating system. Other programming languages may have their own ways of using these operating facilities for similar effect. For example,
345:
is persistent. It stays in the system until explicitly removed by a process. This has a drawback in that if the process crashes and fails to clean up shared memory it will stay until system shutdown; that limitation is not present in an
Android-specific implementation dubbed
147:
lack of data coherence: whenever one cache is updated with information that may be used by other processors, the change needs to be reflected to the other processors, otherwise the different processors will be working with incoherent data. Such
291:
are generally held in memory once and mapped to multiple processes, and only pages that had to be customized for the individual process (because a symbol resolved differently there) are duplicated, usually with a mechanism known as
152:
protocols can, when they work well, provide extremely high-performance access to shared information between multiple processors. On the other hand, they can sometimes become overloaded and become a bottleneck to
266:). On the other hand, it is less scalable, as for example the communicating processes must be running on the same machine (of other IPC methods, only Internet domain sockets—not Unix domain sockets—can use a
338:. Unix System V provides an API for shared memory as well. This uses shmget from sys/shm.h. BSD systems provide "anonymous mapped memory" which can be used by several processes.
254:
Since both processes can access the shared memory area like regular working memory, this is a very fast way of communication (as opposed to other mechanisms of IPC such as
1081:
758:
238:
a method of conserving memory space by directing accesses to what would ordinarily be copies of a piece of data to a single instance instead, by using
366:, more specifically as a world-writable directory (a directory in which every user of the system can create files) that is stored in memory. Both the
299:
Compared to multiple address space operating systems, memory sharing -- especially of sharing procedures or pointer-based structures -- is simpler in
1171:
593:
The POSIX interprocess communication (IPC) is part of the POSIX:XSI Extension and has its origin in Unix System V interprocess communication.
1023:
270:), and care must be taken to avoid issues if processes sharing memory are running on separate CPUs and the underlying architecture is not
1805:
891:
751:
947:
193:
1152:
580:
514:
300:
1192:
1790:
1419:
744:
281:
on Unix systems, or inside the IStream object returned by CoMarshalInterThreadInterfaceInStream in the COM libraries under
485:
1442:
322:
from sys/mman.h. POSIX interprocess communication (part of the POSIX:XSI Extension) includes the shared-memory functions
727:, Ch. 12 from book by Richard Stevens "UNIX Network Programming, Volume 2, Second Edition: Interprocess Communications".
1331:
1187:
374:
based distributions include it by default. Support for this type of RAM disk is completely optional within the kernel
359:
API for mapping files into memory; a mapping can be shared, allowing the file's contents to be used as shared memory.
1437:
1414:
906:
666:
455:
177:
70:
1016:
296:
that transparently copies the page when a write is attempted, and then lets the write succeed on the private copy.
1409:
1224:
1780:
1516:
1430:
1379:
911:
120:
402:
Some C++ libraries provide a portable and object-oriented access to shared memory functionality. For example,
1795:
1740:
1574:
1425:
1112:
123:(COMA): the local memories for the processors at each node is used as cache instead of as actual main memory.
1800:
1759:
1705:
1165:
1009:
767:
288:
224:
1785:
1684:
1479:
1364:
1326:
1176:
1066:
362:
Linux distributions based on the 2.6 kernel and later offer /dev/shm as shared memory in the form of a
886:
1700:
1679:
1624:
1511:
1501:
1474:
1336:
901:
445:
204:
114:
55:
1654:
1280:
1219:
1132:
678:
604:
550:
136:
access time degradation: when several processors try to access the same memory location it causes
1715:
1710:
1569:
1160:
833:
643:
480:
403:
94:
572:
1454:
1386:
1290:
1182:
1137:
868:
450:
189:
74:
1546:
1506:
1459:
1449:
1244:
1107:
1046:
108:
17:
277:
IPC by shared memory is used for example to transfer images between the application and the
144:. Shared memory computers cannot scale very well. Most of them have ten or fewer processors;
1486:
1374:
1369:
1359:
1346:
1142:
530:
232:
90:
47:
242:
mappings or with explicit support of the program in question. This is most often used for
8:
1649:
1604:
1404:
1270:
962:
724:
228:
137:
1674:
1523:
1496:
1321:
1285:
1275:
1234:
1076:
1056:
1051:
1032:
967:
873:
856:
780:
565:
440:
375:
259:
200:
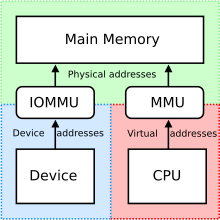
196:(IOMMU) of the GPU have to share certain characteristics, like a common address space.
690:
1720:
1396:
1354:
1249:
576:
510:
282:
617:
227:(IPC), i.e. a way of exchanging data between programs running at the same time. One
1730:
1529:
1464:
1311:
1127:
1122:
1117:
1086:
784:
534:
470:
267:
247:
39:
21:
117:(NUMA): memory access time depends on the memory location relative to a processor;
1594:
1534:
1469:
1316:
1306:
1239:
1229:
1071:
1061:
828:
808:
475:
460:
278:
271:
158:
149:
98:
54:
Using memory for communication inside a single program, e.g. among its multiple
1725:
1541:
1198:
1091:
851:
823:
407:
243:
239:
180:(processor architecture that integrates different types of processors, such as
170:
166:
736:
1774:
1614:
942:
813:
798:
703:
367:
293:
162:
141:
730:
718:
529:
Jeffrey S. Chase; Henry M. Levy; Michael J. Feeley; and Edward D. Lazowska.
1214:
843:
465:
129:
538:
1735:
881:
641:
990:
916:
818:
647:
394:
functions to map a region of a file into memory in multiple processes.
255:
1609:
1584:
1001:
1659:
1639:
1564:
980:
531:"Sharing and Protection in a Single Address Space Operating System"
363:
1664:
1644:
1619:
1254:
952:
921:
567:
Unix systems programming: communication, concurrency, and threads
66:
30:
1634:
1629:
371:
111:(UMA): all the processors share the physical memory uniformly;
985:
975:
926:
896:
428:
311:
263:
78:
34:
An illustration of a shared memory system of three processors
81:
of the GPU have an identical pageable virtual address space.
1669:
1599:
1589:
937:
932:
803:
776:
355:
27:
Computer memory that can be accessed by multiple processes
1579:
1556:
424:
420:
185:
181:
507:
Advanced
Computer Architecture and Parallel Processing
314:
provides a standardized API for using shared memory,
140:. Trying to access nearby memory locations may cause
504:
73:
defines a special case of memory sharing, where the
642:Christoph Rohland; Hugh Dickins; KOSAKI Motohiro.
564:
1772:
505:El-Rewini, Hesham; Abd-El-Barr, Mostafa (2005).
406:contains the Boost.Interprocess C++ Library and
93:(RAM) that can be accessed by several different
766:
413:
306:
562:
173:can be used to dampen the bottleneck-effects.
1017:
752:
733:, An open source, shared memory hash table.
1024:
1010:
759:
745:
571:(2 ed.). Prentice Hall PTR. p.
563:Robbins, Kay A.; Robbins, Steven (2003).
397:
65:
58:, is also referred to as shared memory.
29:
207:, each having a similar set of issues.
89:refers to a (typically large) block of
1773:
1031:
509:. Wiley-Interscience. pp. 77–80.
301:single address space operating systems
199:The alternatives to shared memory are
1005:
740:
381:
427:to create shared memory, similar to
607:from the Single Unix Specification.
486:Von Neumann Architecture Bottleneck
194:input–output memory management unit
13:
1806:Distributed computing architecture
704:Shared Memory Functions in PHP-API
553:from the Single Unix Specification
410:provides the QSharedMemory class.
14:
1817:
712:
456:Heterogeneous System Architecture
235:which other processes can access;
178:Heterogeneous System Architecture
1754:
1753:
1225:Analysis of parallel algorithms
697:
691:"QSharedMemory Class Reference"
683:
132:, which has two complications:
104:Shared memory systems may use:
679:Boost.Interprocess C++ Library
672:
660:
635:
610:
598:
556:
544:
523:
498:
210:
121:cache-only memory architecture
99:multiprocessor computer system
61:
1:
1172:Simultaneous and heterogenous
491:
341:The shared memory created by
1760:Category: Parallel computing
667:Creating Named Shared Memory
414:Programming language support
307:Support on Unix-like systems
7:
1791:Inter-process communication
768:Inter-process communication
434:
225:inter-process communication
188:, with shared memory), the
10:
1822:
1067:High-performance computing
725:Shared Memory Introduction
15:
1749:
1701:Automatic parallelization
1693:
1555:
1395:
1345:
1337:Application checkpointing
1299:
1263:
1207:
1151:
1100:
1039:
961:
867:
814:Message queue and mailbox
791:
774:
618:"Android Kernel Features"
551:Documentation of shm_open
446:Distributed shared memory
318:. This uses the function
205:distributed shared memory
192:(MMU) of the CPU and the
115:non-uniform memory access
386:On Windows, one can use
353:POSIX also provides the
95:central processing units
16:Not to be confused with
1716:Embarrassingly parallel
1711:Deterministic algorithm
481:Shared snapshot objects
231:will create an area in
1431:Associative processing
1387:Non-blocking algorithm
1193:Clustered multi-thread
605:Shared memory facility
451:Shared graphics memory
398:Cross-platform support
215:In computer software,
190:memory management unit
85:In computer hardware,
82:
35:
1781:Computer architecture
1547:Hardware acceleration
1460:Superscalar processor
1450:Dataflow architecture
1047:Distributed computing
539:10.1145/195792.195795
109:uniform memory access
69:
33:
18:Overlay (programming)
1796:Concurrent computing
1426:Pipelined processing
1375:Explicit parallelism
1370:Implicit parallelism
1360:Dataflow programming
91:random access memory
1650:Parallel Extensions
1455:Pipelined processor
316:POSIX Shared Memory
260:Unix domain sockets
77:of the CPU and the
1801:Parallel computing
1524:Massively parallel
1502:distributed shared
1322:Cache invalidation
1286:Instruction window
1077:Manycore processor
1057:Massively parallel
1052:Parallel computing
1033:Parallel computing
963:Software libraries
804:Memory-mapped file
441:Distributed memory
382:Support on Windows
376:configuration file
201:distributed memory
157:Technologies like
83:
36:
1786:Memory management
1768:
1767:
1721:Parallel slowdown
1355:Stream processing
1245:Karp–Flatt metric
999:
998:
929:(various methods)
785:computer programs
719:IPC:Shared Memory
582:978-0-13-042411-2
516:978-0-471-46740-3
388:CreateFileMapping
289:Dynamic libraries
159:crossbar switches
1813:
1757:
1756:
1731:Software lockout
1530:Computer cluster
1465:Vector processor
1420:Array processing
1405:Flynn's taxonomy
1312:Memory coherence
1087:Computer network
1026:
1019:
1012:
1003:
1002:
761:
754:
747:
738:
737:
721:by Dave Marshall
706:
701:
695:
694:
687:
681:
676:
670:
664:
658:
657:
655:
654:
639:
633:
632:
630:
628:
614:
608:
602:
596:
595:
590:
589:
570:
560:
554:
548:
542:
527:
521:
520:
502:
471:Execute in place
393:
389:
358:
349:
344:
337:
333:
329:
325:
321:
268:computer network
248:Execute in place
244:shared libraries
40:computer science
22:Overlapping code
1821:
1820:
1816:
1815:
1814:
1812:
1811:
1810:
1771:
1770:
1769:
1764:
1745:
1689:
1595:Coarray Fortran
1551:
1535:Beowulf cluster
1391:
1341:
1332:Synchronization
1317:Cache coherence
1307:Multiprocessing
1295:
1259:
1240:Cost efficiency
1235:Gustafson's law
1203:
1147:
1096:
1072:Multiprocessing
1062:Cloud computing
1035:
1030:
1000:
995:
965:
957:
871:
863:
809:Message passing
787:
779:exchange among
770:
765:
715:
710:
709:
702:
698:
689:
688:
684:
677:
673:
665:
661:
652:
650:
640:
636:
626:
624:
616:
615:
611:
603:
599:
587:
585:
583:
561:
557:
549:
545:
528:
524:
517:
503:
499:
494:
476:Shared register
461:Global variable
437:
416:
400:
391:
387:
384:
354:
347:
342:
335:
331:
327:
323:
319:
309:
213:
150:cache coherence
64:
28:
25:
12:
11:
5:
1819:
1809:
1808:
1803:
1798:
1793:
1788:
1783:
1766:
1765:
1763:
1762:
1750:
1747:
1746:
1744:
1743:
1738:
1733:
1728:
1726:Race condition
1723:
1718:
1713:
1708:
1703:
1697:
1695:
1691:
1690:
1688:
1687:
1682:
1677:
1672:
1667:
1662:
1657:
1652:
1647:
1642:
1637:
1632:
1627:
1622:
1617:
1612:
1607:
1602:
1597:
1592:
1587:
1582:
1577:
1572:
1567:
1561:
1559:
1553:
1552:
1550:
1549:
1544:
1539:
1538:
1537:
1527:
1521:
1520:
1519:
1514:
1509:
1504:
1499:
1494:
1484:
1483:
1482:
1477:
1470:Multiprocessor
1467:
1462:
1457:
1452:
1447:
1446:
1445:
1440:
1435:
1434:
1433:
1428:
1423:
1412:
1401:
1399:
1393:
1392:
1390:
1389:
1384:
1383:
1382:
1377:
1372:
1362:
1357:
1351:
1349:
1343:
1342:
1340:
1339:
1334:
1329:
1324:
1319:
1314:
1309:
1303:
1301:
1297:
1296:
1294:
1293:
1288:
1283:
1278:
1273:
1267:
1265:
1261:
1260:
1258:
1257:
1252:
1247:
1242:
1237:
1232:
1227:
1222:
1217:
1211:
1209:
1205:
1204:
1202:
1201:
1199:Hardware scout
1196:
1190:
1185:
1180:
1174:
1169:
1163:
1157:
1155:
1153:Multithreading
1149:
1148:
1146:
1145:
1140:
1135:
1130:
1125:
1120:
1115:
1110:
1104:
1102:
1098:
1097:
1095:
1094:
1092:Systolic array
1089:
1084:
1079:
1074:
1069:
1064:
1059:
1054:
1049:
1043:
1041:
1037:
1036:
1029:
1028:
1021:
1014:
1006:
997:
996:
994:
993:
988:
983:
978:
972:
970:
959:
958:
956:
955:
950:
945:
940:
935:
930:
924:
919:
914:
909:
904:
899:
894:
889:
884:
878:
876:
865:
864:
862:
861:
860:
859:
854:
846:
841:
836:
831:
826:
824:Anonymous pipe
821:
816:
811:
806:
801:
795:
793:
789:
788:
775:
772:
771:
764:
763:
756:
749:
741:
735:
734:
731:SharedHashFile
728:
722:
714:
713:External links
711:
708:
707:
696:
682:
671:
659:
634:
609:
597:
581:
555:
543:
522:
515:
496:
495:
493:
490:
489:
488:
483:
478:
473:
468:
463:
458:
453:
448:
443:
436:
433:
415:
412:
399:
396:
383:
380:
308:
305:
272:cache coherent
252:
251:
240:virtual memory
236:
212:
209:
171:front-side bus
167:HyperTransport
163:Omega networks
155:
154:
145:
125:
124:
118:
112:
63:
60:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1818:
1807:
1804:
1802:
1799:
1797:
1794:
1792:
1789:
1787:
1784:
1782:
1779:
1778:
1776:
1761:
1752:
1751:
1748:
1742:
1739:
1737:
1734:
1732:
1729:
1727:
1724:
1722:
1719:
1717:
1714:
1712:
1709:
1707:
1704:
1702:
1699:
1698:
1696:
1692:
1686:
1683:
1681:
1678:
1676:
1673:
1671:
1668:
1666:
1663:
1661:
1658:
1656:
1653:
1651:
1648:
1646:
1643:
1641:
1638:
1636:
1633:
1631:
1628:
1626:
1623:
1621:
1618:
1616:
1615:Global Arrays
1613:
1611:
1608:
1606:
1603:
1601:
1598:
1596:
1593:
1591:
1588:
1586:
1583:
1581:
1578:
1576:
1573:
1571:
1568:
1566:
1563:
1562:
1560:
1558:
1554:
1548:
1545:
1543:
1542:Grid computer
1540:
1536:
1533:
1532:
1531:
1528:
1525:
1522:
1518:
1515:
1513:
1510:
1508:
1505:
1503:
1500:
1498:
1495:
1493:
1490:
1489:
1488:
1485:
1481:
1478:
1476:
1473:
1472:
1471:
1468:
1466:
1463:
1461:
1458:
1456:
1453:
1451:
1448:
1444:
1441:
1439:
1436:
1432:
1429:
1427:
1424:
1421:
1418:
1417:
1416:
1413:
1411:
1408:
1407:
1406:
1403:
1402:
1400:
1398:
1394:
1388:
1385:
1381:
1378:
1376:
1373:
1371:
1368:
1367:
1366:
1363:
1361:
1358:
1356:
1353:
1352:
1350:
1348:
1344:
1338:
1335:
1333:
1330:
1328:
1325:
1323:
1320:
1318:
1315:
1313:
1310:
1308:
1305:
1304:
1302:
1298:
1292:
1289:
1287:
1284:
1282:
1279:
1277:
1274:
1272:
1269:
1268:
1266:
1262:
1256:
1253:
1251:
1248:
1246:
1243:
1241:
1238:
1236:
1233:
1231:
1228:
1226:
1223:
1221:
1218:
1216:
1213:
1212:
1210:
1206:
1200:
1197:
1194:
1191:
1189:
1186:
1184:
1181:
1178:
1175:
1173:
1170:
1167:
1164:
1162:
1159:
1158:
1156:
1154:
1150:
1144:
1141:
1139:
1136:
1134:
1131:
1129:
1126:
1124:
1121:
1119:
1116:
1114:
1111:
1109:
1106:
1105:
1103:
1099:
1093:
1090:
1088:
1085:
1083:
1080:
1078:
1075:
1073:
1070:
1068:
1065:
1063:
1060:
1058:
1055:
1053:
1050:
1048:
1045:
1044:
1042:
1038:
1034:
1027:
1022:
1020:
1015:
1013:
1008:
1007:
1004:
992:
989:
987:
984:
982:
979:
977:
974:
973:
971:
969:
964:
960:
954:
951:
949:
946:
944:
941:
939:
936:
934:
931:
928:
925:
923:
920:
918:
915:
913:
910:
908:
905:
903:
900:
898:
895:
893:
890:
888:
885:
883:
880:
879:
877:
875:
870:
866:
858:
855:
853:
850:
849:
847:
845:
842:
840:
839:Shared memory
837:
835:
832:
830:
827:
825:
822:
820:
817:
815:
812:
810:
807:
805:
802:
800:
797:
796:
794:
790:
786:
782:
778:
773:
769:
762:
757:
755:
750:
748:
743:
742:
739:
732:
729:
726:
723:
720:
717:
716:
705:
700:
692:
686:
680:
675:
668:
663:
649:
645:
638:
623:
619:
613:
606:
601:
594:
584:
578:
574:
569:
568:
559:
552:
547:
540:
536:
532:
526:
518:
512:
508:
501:
497:
487:
484:
482:
479:
477:
474:
472:
469:
467:
464:
462:
459:
457:
454:
452:
449:
447:
444:
442:
439:
438:
432:
430:
426:
422:
411:
409:
405:
395:
392:MapViewOfFile
379:
377:
373:
369:
365:
360:
357:
351:
339:
317:
313:
304:
302:
297:
295:
294:copy-on-write
290:
286:
284:
280:
275:
273:
269:
265:
261:
257:
249:
245:
241:
237:
234:
230:
226:
222:
221:
220:
218:
217:shared memory
208:
206:
202:
197:
195:
191:
187:
183:
179:
176:In case of a
174:
172:
168:
164:
160:
151:
146:
143:
142:false sharing
139:
135:
134:
133:
131:
122:
119:
116:
113:
110:
107:
106:
105:
102:
100:
96:
92:
88:
87:shared memory
80:
76:
72:
68:
59:
57:
52:
49:
45:
44:shared memory
41:
32:
23:
19:
1491:
1300:Coordination
1230:Amdahl's law
1166:Simultaneous
882:Apple events
838:
699:
685:
674:
662:
651:. Retrieved
637:
625:. Retrieved
621:
612:
600:
592:
586:. Retrieved
566:
558:
546:
525:
506:
500:
466:Nano-threads
423:provides an
417:
401:
385:
361:
352:
340:
315:
310:
298:
287:
276:
253:
223:a method of
216:
214:
198:
175:
156:
153:performance.
130:cache memory
126:
103:
97:(CPUs) in a
86:
84:
53:
43:
37:
1736:Scalability
1497:distributed
1380:Concurrency
1347:Programming
1188:Cooperative
1177:Speculative
1113:Instruction
644:"tmpfs.txt"
431:functions.
256:named pipes
211:In software
62:In hardware
1775:Categories
1741:Starvation
1480:asymmetric
1215:PRAM model
1183:Preemptive
968:frameworks
917:OpenBinder
819:Named pipe
669:from MSDN.
653:2010-03-16
648:kernel.org
622:elinux.org
588:2011-05-13
541:1993. p. 3
492:References
219:is either
138:contention
1475:symmetric
1220:PEM model
874:standards
869:Protocols
834:Semaphore
1706:Deadlock
1694:Problems
1660:pthreads
1640:OpenHMPP
1565:Ateji PX
1526:computer
1397:Hardware
1264:Elements
1250:Slowdown
1161:Temporal
1143:Pipeline
981:libevent
848:Sockets
435:See also
364:RAM disk
343:shm_open
320:shm_open
279:X server
246:and for
1665:RaftLib
1645:OpenACC
1620:GPUOpen
1610:C++ AMP
1585:Charm++
1327:Barrier
1271:Process
1255:Speedup
1040:General
953:XML-RPC
922:Sun RPC
852:Network
792:Methods
781:threads
283:Windows
229:process
56:threads
1758:
1635:OpenCL
1630:OpenMP
1575:Chapel
1492:shared
1487:Memory
1422:(SIMT)
1365:Models
1276:Thread
1208:Theory
1179:(SpMT)
1133:Memory
1118:Thread
1101:Levels
943:Thrift
844:Signal
627:12 Dec
579:
513:
372:Debian
368:RedHat
348:ashmem
336:shmget
328:shmctl
250:(XIP).
48:memory
1605:Dryad
1570:Boost
1291:Array
1281:Fiber
1195:(CMT)
1168:(SMT)
1082:GPGPU
986:SIMPL
976:D-Bus
927:POSIX
897:D-Bus
892:CORBA
429:POSIX
404:Boost
332:shmdt
324:shmat
312:POSIX
264:CORBA
79:IOMMU
1670:ROCm
1600:CUDA
1590:Cilk
1557:APIs
1517:COMA
1512:NUMA
1443:MIMD
1438:MISD
1415:SIMD
1410:SISD
1138:Loop
1128:Data
1123:Task
991:LINX
966:and
948:TIPC
938:REST
933:SOAP
887:COM+
872:and
857:Unix
829:Pipe
799:File
777:Data
629:2022
577:ISBN
511:ISBN
390:and
370:and
356:mmap
334:and
203:and
186:GPUs
184:and
182:CPUs
1685:ZPL
1680:TBB
1675:UPC
1655:PVM
1625:MPI
1580:HPX
1507:UMA
1108:Bit
912:ICE
907:DCE
902:DDS
783:in
573:512
535:doi
425:API
421:PHP
262:or
233:RAM
169:or
75:MMU
71:HSA
46:is
38:In
20:or
1777::
646:.
620:.
591:.
575:.
533:.
408:Qt
378:.
350:.
330:,
326:,
303:.
285:.
274:.
258:,
165:,
161:,
101:.
42:,
1025:e
1018:t
1011:v
760:e
753:t
746:v
693:.
656:.
631:.
537::
519:.
24:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.