272:
31:
388:
ganglia. Some send axons to the substantia nigra medially and to the medial and lateral nuclei of the pallidum laterally (3-target, 21.3%). Some are 2-target with the lateral pallidum and the substantia nigra (2.7%) or the lateral pallidum and the medial (48%). Less are single target for the lateral pallidum. In the pallidum, subthalamic terminals end in bands parallel to the pallidal border. When all axons reaching this target are added, the main efference of the subthalamic nucleus is, in 82.7% of the cases, clearly the
622:
408:
449:
was that, in the absence of current injection or synaptic stimulation, the majority of cells were spontaneously firing. The second observation is that these cells are capable of transiently firing at very high frequencies. The third observation concerns non-linear behaviors when cells are transiently depolarized after being hyperpolarized below –65mV. They are then able to engage voltage-gated calcium and sodium currents to fire bursts of action potentials.
63:
277:
276:
273:
278:
275:
387:
The axons of subthalamic nucleus neurons leave the nucleus dorsally. The efferent axons are glutamatergic (excitatory). Except for the connection to the striatum (17.3% in macaques), most of the subthalamic principal neurons are multitargets and directed to the other elements of the core of the basal
487:
system where the reduction between emitter/receiving elements is likely the strongest. In terms of volume, in humans, the lateral pallidum measures 808 mm, the subthalamic nucleus only 158 mm. This translated in numbers of neurons represents a strong compression with loss of map precision.
609:
The physiological role of the STN has been for long hidden by its pathological role. But lately, the research on the physiology of the STN led to the discovery that the STN is required to achieve intended movement, including locomotion, balance and motor coordination. It is involved in stopping or
307:
shape. The dimensions of these arbors (1200 μm, 600 μm, and 300 μm) are similar across many species—including rat, cat, monkey and human—which is unusual. However, the number of neurons increases with brain size as well as the external dimensions of the nucleus. The principal neurons
605:
control system that may perform action selection. It is plays a part in the so-called "hyperdirect" and "indirect" pathways of motor control, contrasting with the direct pathway which is thought to bypass the STN on its way from
Striatum to internal pallidum. STN dysfunction has been implicated in
448:
The first intracellular electrical recordings of subthalamic neurons were performed using sharp electrodes in a rat slice preparation. In these recordings three key observations were made, all three of which have dominated subsequent reports of subthalamic firing properties. The first observation
415:. Subthalamic nucleus is shown in red. Picture shows 2 coronal slices that have been superimposed to include the involved basal ganglia structures. + and - signs at the point of the arrows indicate respectively whether the pathway is excitatory or inhibitory in effect.
322:
The structure of the subthalamic nucleus has not yet been fully explored and understood, but it is likely composed of several internal domains. The primate subthalamic nucleus is often divided in three internal anatomical-functional domains. However, this so-called
274:
546:. The first to be stimulated are the terminal arborisations of afferent axons, which modify the activity of subthalamic neurons. However, it has been shown in thalamic slices from mice, that the stimulus also causes nearby astrocytes to release
565:
paper, the stereotactic field avoided lesioning the nucleus, since it was known that unilateral destruction or disruption of the subthalamic nucleus — which may result from naturally occurring strokes — may lead to
1727:
Martínez-Fernández R, Máñez-Miró JU, Rodríguez-Rojas R, Del Álamo M, Shah BB, Hernández-Fernández F, et al. (December 2020). "Randomized Trial of
Focused Ultrasound Subthalamotomy for Parkinson's Disease".
459:
Oscillatory and synchronous activity is likely to be a typical pattern of discharge in subthalamic neurons recorded from patients and animal models characterized by the loss of dopaminergic cells in the
945:
Canteras NS, Shammah-Lagnado SJ, Silva BA, Ricardo JA (April 1990). "Afferent connections of the subthalamic nucleus: a combined retrograde and anterograde horseradish peroxidase study in the rat".
491:
Some axons from the lateral pallidum go to the striatum. The activity of the medial pallidum is influenced by afferences from the lateral pallidum and from the subthalamic nucleus. The same for the
452:
Several recent studies have focused on the autonomous pacemaking ability of subthalamic neurons. These cells are often referred to as "fast-spiking pacemakers", since they can generate spontaneous
1618:
Benazzouz A, Gross C, Féger J, Boraud T, Bioulac B (April 1993). "Reversal of rigidity and improvement in motor performance by subthalamic high-frequency stimulation in MPTP-treated monkeys".
606:
motor symptoms such as rigidity, bradykinesia and tremor, behavioral features such as stopping of ongoing movements or impulsivity in individuals presented with two equally rewarding stimuli.
610:
interrupting on-going motor tasks. Moreover, STN excitation was generally correlated with significant reduction in locomotor activity, while in contrast, STN inhibition enhanced locomotion.
534:
and colleagues. This inspired
Benazzouz and colleagues to probe deep brain stimulation of the nucleus, which was known to exert similar effects as ablative lesions. Soon after, the team of
621:
1489:
Smith Y, Wichmann T, DeLong MR (May 1994). "Synaptic innervation of neurones in the internal pallidal segment by the subthalamic nucleus and the external pallidum in monkeys".
538:
showed that deep brain stimulation of the nucleus leads to symptom relief in human patients with
Parkinson disease, as well, which led to the establishment of the currently
578:
could recently show that, while some lesions that led to hemiballism were indeed in and around the STN, the majority of reported cases were in other regions of the brain.
1121:
Smith Y, Hazrati LN, Parent A (April 1990). "Efferent projections of the subthalamic nucleus in the squirrel monkey as studied by the PHA-L anterograde tracing method".
1684:
Bekar L, Libionka W, Tian GF, Xu Q, Torres A, Wang X, et al. (January 2008). "Adenosine is crucial for deep brain stimulation-mediated attenuation of tremor".
1532:
Bevan MD, Magill PJ, Terman D, Bolam JP, Wilson CJ (October 2002). "Move to the rhythm: oscillations in the subthalamic nucleus-external globus pallidus network".
319:
that participate in the local circuitry; however, the dendritic arbors of subthalamic neurons shy away from the border and primarily interact with one another.
187:
1911:
Lofredi R, Auernig GC, Irmen F, Nieweler J, Neumann WJ, Horn A, et al. (February 2021). "Subthalamic stimulation impairs stopping of ongoing movements".
570:. While this remains generally true, iatrogenic lesioning of the STN has been carried out numerous times and has recently gained new wind with the advent of
1446:
Sato F, Lavallée P, Lévesque M, Parent A (January 2000). "Single-axon tracing study of neurons of the external segment of the globus pallidus in primate".
898:"Confirmation of functional zones within the human subthalamic nucleus: patterns of connectivity and sub-parcellation using diffusion weighted imaging"
356:
360:
480:. Both are fast-spiking pacemakers. Together, they are thought to constitute the "central pacemaker of the basal ganglia" with synchronous bursts.
355:(entire frontal cortex with a predominance for motor, premotor and oculomotor input to the posterolateral part of the nucleus), and from the pars
2940:
163:
2992:
2895:
1164:
Kita H, Chang HT, Kitai ST (April 1983). "The morphology of intracellularly labeled rat subthalamic neurons: a light microscopic analysis".
853:
Alkemade A, Forstmann BU (July 2014). "Do we need to revise the tripartite subdivision hypothesis of the human subthalamic nucleus (STN)?".
3332:
3302:
554:(through a catabolic process). In turn, adenosine A1 receptor activation depresses excitatory transmission in the thalamus, thus mimicking
312:, which give them a particular functional position in the basal ganglia system. In humans there are also a small number (about 7.5%) of
1459:
988:
Alho EJ, Alho AT, Horn A, Martin MD, Edlow BL, Fischl B, et al. (January 2020). "The Ansa
Subthalamica: A Neglected Fiber Tract".
2470:
1868:
Bergman H, Wichmann T, DeLong MR (September 1990). "Reversal of experimental parkinsonism by lesions of the subthalamic nucleus".
1575:
Bergman H, Wichmann T, DeLong MR (September 1990). "Reversal of experimental parkinsonism by lesions of the subthalamic nucleus".
2850:
2625:
2886:
2162:
1075:
Nauta HJ, Cole M (July 1978). "Efferent projections of the subthalamic nucleus: an autoradiographic study in monkey and cat".
2351:
1352:
Plenz D, Kital ST (August 1999). "A basal ganglia pacemaker formed by the subthalamic nucleus and external globus pallidus".
3341:
1255:"High-frequency synchronization of neuronal activity in the subthalamic nucleus of parkinsonian patients with limb tremor"
343:
as often said but by radiating 'comb' fibers crossing the medial pallidum first and the internal capsule (forming part of
1303:
724:
Rafols JA, Fox CA (July 1976). "The neurons in the primate subthalamic nucleus: a Golgi and electron microscopic study".
498:
The lateropallido-subthalamic system is thought to play a key role in the generation of the patterns of activity seen in
3768:
2005:"Triangulating a cognitive control network using diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and functional MRI"
3186:
3002:
2346:
2105:"Experimental investigation into the role of the subthalamic nucleus (STN) in motor control using optogenetics in mice"
1210:, Mercer JN, Chan CS (June 2005). "Autonomous pacemakers in the basal ganglia: who needs excitatory synapses anyway?".
3829:
2957:
2635:
2630:
2601:
582:
2701:
2518:
492:
194:
2407:
581:
As one of the STN's suspected functions is in impulse control, dysfunction in this region has been implicated in
327:
has been debated because it does not fully explain the complexity of the subthalamic nucleus in brain function.
3534:
3073:
2977:
2755:
2334:
643:
574:, which has also been probed for subthalamic nucleotomies to treat Parkinson disease. Curiously, a team around
461:
3892:
3866:
2981:
2596:
2525:
2330:
351:
are GABAergic, inhibiting neurons in the subthalamic nucleus. Excitatory, glutamatergic inputs come from the
182:
3897:
3871:
3834:
3800:
3795:
3700:
3667:
3631:
3581:
3446:
3203:
3061:
2271:
590:
539:
236:
2052:
Fife KH, Gutierrez-Reed NA, Zell V, Bailly J, Lewis CM, Aron AR, et al. (July 2017). Uchida N (ed.).
767:
Yelnik J, Percheron G (1979). "Subthalamic neurons in primates: a quantitative and comparative analysis".
3838:
3199:
3057:
2843:
2307:
627:
Coronal section of brain immediately in front of pons. Subthalamic nucleus labeled as "Nucleus of Luys".
3790:
3606:
3504:
3428:
3386:
2373:
2276:
2155:
3824:
3742:
3576:
3085:
3052:
2828:
2368:
2326:
681:
Afsharpour S (June 1985). "Light microscopic analysis of Golgi-impregnated rat subthalamic neurons".
138:
3621:
3508:
3432:
3242:
3094:
2812:
2738:
2587:
2317:
389:
376:
336:
121:
44:
40:
3113:
3722:
3709:
3681:
3614:
3589:
3496:
3464:
3420:
3190:
2961:
2733:
2673:
2321:
2296:
2140:
495:. The subthalamic nucleus sends axons to another regulator: the pedunculo-pontine complex (id).
428:
3034:
3936:
3643:
3610:
3601:
3480:
3476:
3468:
3404:
3209:
2836:
2750:
2513:
2447:
2442:
2424:
586:
547:
543:
523:
499:
465:
283:
220:
170:
158:
68:
3759:
3696:
3672:
3663:
3635:
3626:
3523:
3484:
3408:
3311:
3219:
3137:
2498:
2457:
2419:
2402:
2341:
2312:
2148:
638:
1827:
Mallet L, Polosan M, Jaafari N, Baup N, Welter ML, Fontaine D, et al. (November 2008).
3931:
3820:
3786:
3737:
3252:
3238:
3182:
3128:
3020:
2969:
2696:
2691:
2481:
2412:
2242:
2214:
1959:
1877:
1584:
1361:
515:
483:
The connection of the lateral pallidum with the subthalamic nucleus is also the one in the
476:
Strong reciprocal connections link the subthalamic nucleus and the external segment of the
348:
439:
pathways that are excitatory on the direct pathway and inhibitory on the indirect pathway.
8:
3704:
3492:
3416:
3336:
3247:
3133:
3123:
3099:
3069:
3064:
2951:
2775:
2620:
2488:
2462:
810:
Lévesque JC, Parent A (May 2005). "GABAergic interneurons in human subthalamic nucleus".
1963:
1881:
1588:
1365:
601:
The function of the STN is unknown, but current theories place it as a component of the
3887:
3861:
3692:
2922:
2918:
2904:
2779:
2642:
2503:
2388:
2383:
2378:
2080:
2053:
2029:
2004:
1985:
1948:"Hold your horses: impulsivity, deep brain stimulation, and medication in parkinsonism"
1789:
1764:
1709:
1631:
1557:
1514:
1471:
1428:
1385:
1334:
1279:
1270:
1254:
1235:
1189:
1146:
1100:
1054:
970:
922:
897:
878:
835:
792:
749:
706:
663:
535:
252:
30:
1655:"[Effects of the stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson disease]"
1545:
3875:
3804:
3747:
3733:
3571:
3488:
3412:
3360:
3306:
3281:
3081:
3044:
3006:
2908:
2493:
2452:
2209:
2126:
2085:
2034:
1977:
1928:
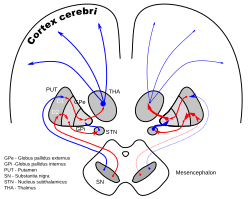
1893:
1850:
1794:
1745:
1701:
1666:
1635:
1600:
1549:
1506:
1463:
1420:
1377:
1326:
1284:
1227:
1207:
1181:
1138:
1092:
1046:
1041:
1024:
1005:
962:
958:
927:
913:
896:
Lambert C, Zrinzo L, Nagy Z, Lutti A, Hariz M, Foltynie T, et al. (March 2012).
870:
866:
827:
784:
780:
741:
698:
668:
Recherches sur le système cérébro-spinal, sa structure, ses fonctions et ses maladies
340:
151:
1726:
1518:
1475:
1432:
1338:
1304:"Dopamine deficiency increases synchronized activity in the rat subthalamic nucleus"
1239:
1193:
1104:
1058:
974:
882:
796:
753:
710:
3195:
3171:
3145:
2965:
2913:
2728:
2611:
2476:
2237:
2121:
2116:
2104:
2075:
2065:
2024:
2020:
2016:
1989:
1967:
1920:
1885:
1840:
1784:
1776:
1737:
1713:
1693:
1653:
Pollak P, Benabid AL, Gross C, Gao DM, Laurent A, Benazzouz A, et al. (1993).
1627:
1592:
1561:
1541:
1498:
1455:
1412:
1389:
1369:
1322:
1318:
1274:
1266:
1219:
1173:
1150:
1130:
1084:
1036:
997:
954:
917:
909:
862:
839:
819:
776:
733:
690:
453:
372:
248:
244:
52:
3659:
3355:
3103:
2930:
2926:
2816:
2767:
2663:
2568:
2563:
2554:
2508:
2356:
1780:
477:
352:
126:
3816:
3782:
3596:
3256:
2871:
2867:
2558:
2281:
2232:
1223:
575:
364:
344:
282:
Structural connectivity of the human subthalamic nucleus as visualized through
3925:
3639:
3376:
3048:
2668:
602:
567:
562:
531:
484:
420:
412:
309:
228:
175:
88:
36:
1972:
1947:
1924:
1889:
1596:
589:
has shown some promise in correcting severe impulsive behavior and has been
3726:
3685:
3512:
3456:
3436:
3396:
2807:
2715:
2539:
2434:
2363:
2199:
2172:
2130:
2089:
2038:
1981:
1932:
1854:
1798:
1749:
1705:
1553:
1467:
1424:
1381:
1330:
1288:
1231:
1050:
1009:
931:
874:
831:
368:
1897:
1845:
1828:
1741:
1670:
1654:
1639:
1604:
1510:
1502:
1460:
10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(20000131)417:1<17::AID-CNE2>3.0.CO;2-I
1185:
1177:
1142:
1134:
1088:
966:
737:
702:
694:
303:. In the more centrally located neurons, the dendritic arbors have a more
3714:
3276:
2863:
2859:
2794:
2651:
2578:
2291:
2224:
2184:
2176:
1829:"Subthalamic nucleus stimulation in severe obsessive-compulsive disorder"
1096:
788:
745:
511:
407:
316:
232:
84:
2070:
200:
3901:
3883:
3857:
3849:
3812:
3778:
3585:
3556:
133:
2858:
2102:
1416:
1001:
823:
551:
347:'s comb system, see figure), as well as the ansa subthalamica. These
304:
2103:
Guillaumin A, Serra GP, Georges F, Wallén-Mackenzie Å (March 2021).
399:
collaterals. However, there is little functional evidence for this.
3718:
3677:
3538:
3500:
3460:
3424:
3400:
3141:
3077:
2973:
2647:
2256:
2204:
1697:
944:
555:
436:
300:
240:
145:
2170:
2054:"Causal role for the subthalamic nucleus in interrupting behavior"
2003:
Aron AR, Behrens TE, Smith S, Frank MJ, Poldrack RA (April 2007).
1373:
2683:
1023:
Cragg SJ, Baufreton J, Xue Y, Bolam JP, Bevan MD (October 2004).
510:
Lesioning the STN leads to alleviation of motor symptoms such as
299:
found in the subthalamic nucleus has rather long, sparsely spiny
62:
1253:
Levy R, Hutchison WD, Lozano AM, Dostrovsky JO (October 2000).
519:
296:
235:. As suggested by its name, the subthalamic nucleus is located
1946:
Frank MJ, Samanta J, Moustafa AA, Sherman SJ (November 2007).
1252:
224:
101:
2051:
1403:
Yelnik J (2002). "Functional anatomy of the basal ganglia".
3025:
1945:
1910:
571:
527:
396:
313:
1445:
593:
approved for treatment resistant cases with the disorder.
227:
where it is, from a functional point of view, part of the
1617:
1025:"Synaptic release of dopamine in the subthalamic nucleus"
335:
The subthalamic nucleus receives its main input from the
231:
system. In terms of anatomy, it is the major part of the
1826:
1302:
Lintas A, Silkis IG, Albéri L, Villa AE (January 2012).
1301:
1531:
1022:
895:
2002:
1867:
1652:
1574:
1683:
1488:
471:
1765:"Network localization of hemichorea-hemiballismus"
1206:
1120:
987:
464:, which is the principal pathology that underlies
852:
3923:
1762:
411:Anatomical overview of the main circuits of the
375:pars compacta. It also receives inputs from the
766:
1163:
809:
2844:
2156:
1070:
1068:
674:
1116:
1114:
2851:
2837:
2163:
2149:
1763:Laganiere S, Boes AD, Fox MD (June 2016).
1351:
1065:
938:
680:
585:. Application of high frequency pulses by
456:at rates of 80 to 90 Hz in primates.
61:
35:Coronal slices of human brain showing the
29:
2602:Posterior (sympathetic/heat conservation)
2120:
2079:
2069:
2028:
1971:
1844:
1788:
1278:
1111:
1074:
1040:
921:
723:
3738:Flocculonodular lobe/vestibulocerebellum
406:
395:Some researchers have reported internal
363:. The subthalamic nucleus also receives
270:
3697:Intermediate hemisphere/spinocerebellum
3924:
3867:Ventral/anterior spinocerebellar tract
3796:Dorsal/posterior spinocerebellar tract
1402:
443:
16:Small lens-shaped nucleus in the brain
2832:
2144:
2597:Anterior (parasympathetic/heat loss)
1620:The European Journal of Neuroscience
1491:The Journal of Comparative Neurology
1448:The Journal of Comparative Neurology
1166:The Journal of Comparative Neurology
1123:The Journal of Comparative Neurology
1077:The Journal of Comparative Neurology
1029:The European Journal of Neuroscience
726:The Journal of Comparative Neurology
683:The Journal of Comparative Neurology
662:
613:
542:approved and widely applied form of
1833:The New England Journal of Medicine
1730:The New England Journal of Medicine
382:
13:
3664:Lateral hemisphere/pontocerebellum
3187:Posterior limb of internal capsule
3003:Posterior limb of internal capsule
1811:
1632:10.1111/j.1460-9568.1993.tb00505.x
1271:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-20-07766.2000
505:
14:
3948:
2958:Posterior external arcuate fibers
2636:Parvocellular neurosecretory cell
2631:Magnocellular neurosecretory cell
330:
2519:Anterior trigeminothalamic tract
1042:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03629.x
914:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.11.082
867:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.03.010
620:
493:substantia nigra pars reticulata
472:Lateropallido-subthalamic system
195:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
2096:
2045:
1996:
1939:
1904:
1861:
1820:
1805:
1756:
1720:
1677:
1646:
1611:
1568:
1525:
1482:
1439:
1396:
1345:
1295:
1246:
1212:Current Opinion in Neurobiology
1200:
1157:
1016:
339:(GPe), not so much through the
2756:Dorsal longitudinal fasciculus
2122:10.1016/j.brainres.2020.147226
2021:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0519-07.2007
1323:10.1016/j.brainres.2011.09.005
981:
889:
846:
803:
760:
717:
670:(in French). Paris: Baillière.
656:
644:Mesencephalic locomotor region
526:. This was first shown in the
462:substantia nigra pars compacta
1:
3893:Rostral spinocerebellar tract
1546:10.1016/S0166-2236(02)02235-X
649:
583:obsessive–compulsive disorder
402:
2272:Stria medullaris of thalamus
1781:10.1212/WNL.0000000000002741
959:10.1016/0006-8993(90)91087-W
781:10.1016/0306-4522(79)90030-7
572:MR guided focused ultrasound
558:of the subthalamic nucleus.
530:primate model in a paper by
290:
251:. It was first described by
7:
3839:Anterior lobe of cerebellum
2674:Suprachiasmatic (melatonin)
2009:The Journal of Neuroscience
1259:The Journal of Neuroscience
632:
596:
243:. It is also dorsal to the
10:
3953:
3791:Posterior thoracic nucleus
3505:Thalamocortical radiations
3429:Thalamocortical radiations
2277:Thalamic reticular nucleus
1224:10.1016/j.conb.2005.05.007
266:
3848:
3825:Accessory cuneate nucleus
3767:
3756:
3743:Vestibulocerebellar tract
3652:
3577:Vestibulocerebellar tract
3564:
3555:
3520:
3444:
3384:
3375:
3351:
3321:
3291:
3265:
3227:
3218:
3170:
3163:
3112:
3086:Posterior parietal cortex
3053:Anterior white commissure
3033:
3019:
2991:
2939:
2894:
2885:
2878:
2793:
2766:
2714:
2682:
2610:
2586:
2577:
2547:
2538:
2433:
2290:
2264:
2255:
2223:
2192:
2183:
263:is still sometimes used.
219:) is a small lens-shaped
193:
181:
169:
157:
144:
132:
120:
112:
100:
95:
80:
75:
60:
28:
23:
3622:Inferior olivary nucleus
3509:Supplementary motor area
3433:Supplementary motor area
3243:Genu of internal capsule
3095:Spinomesencephalic tract
2813:Nuclei campi perizonalis
2739:Retinohypothalamic tract
390:internal globus pallidus
377:pedunculopontine nucleus
337:external globus pallidus
45:internal globus pallidus
41:external globus pallidus
3710:Cerebellothalamic tract
3191:Decussation of pyramids
2962:Internal arcuate fibers
2734:Medial forebrain bundle
2664:Arcuate (dopamine/GHRH)
1973:10.1126/science.1146157
1890:10.1126/science.2402638
1597:10.1126/science.2402638
1534:Trends in Neurosciences
3644:Deep cerebellar nuclei
3611:Deep cerebellar nuclei
3602:Pontocerebellar fibers
3477:Subthalamic fasciculus
3469:Subthalamic fasciculus
3210:Neuromuscular junction
2751:Mammillothalamic tract
2514:Subthalamic fasciculus
2448:Pallidothalamic tracts
2443:Mammillothalamic tract
2425:Interthalamic adhesion
587:deep brain stimulation
550:(ATP), a precursor to
548:adenosine triphosphate
544:deep brain stimulation
440:
295:The principal type of
287:
284:diffusion-weighted MRI
255:in 1865, and the term
3830:Cuneocerebellar tract
3673:Dentatothalamic tract
3627:Olivocerebellar tract
3524:nigrostriatal pathway
3485:Lenticular fasciculus
3409:Lenticular fasciculus
3312:Vestibulospinal tract
2778:is diencephalon, but
2499:Dentatothalamic tract
2458:Lenticular fasciculus
2420:Midline nuclear group
1925:10.1093/brain/awaa341
1846:10.1056/NEJMoa0708514
1742:10.1056/NEJMoa2016311
1503:10.1002/cne.903430209
1411:(Suppl. 3): S15–S21.
1178:10.1002/cne.902150302
1135:10.1002/cne.902940213
1089:10.1002/cne.901800102
738:10.1002/cne.901680105
695:10.1002/cne.902360102
639:Primate basal ganglia
410:
281:
107:nucleus subthalamicus
3342:Reticulospinal tract
3253:Facial motor nucleus
3239:Primary motor cortex
3183:Primary motor cortex
3129:Spinoreticular tract
2970:Trigeminal lemniscus
2909:Meissner's corpuscle
2482:Trigeminal lemniscus
2243:Subcommissural organ
2215:Habenular commissure
1814:The Human Brain Book
427:refer to inhibitory
419:refer to excitatory
3705:Reticular formation
3493:Thalamic fasciculus
3473:Subthalamic nucleus
3417:Thalamic fasciculus
3337:Reticular formation
3333:Vestibulocerebellum
3303:Vestibulocerebellum
3248:Corticobulbar tract
3196:Corticospinal tract
3134:Reticular formation
3124:Group C nerve fiber
3100:Superior colliculus
3065:Spinothalamic tract
2952:sensory decussation
2803:Subthalamic nucleus
2621:posterior pituitary
2489:Spinothalamic tract
2463:Thalamic fasciculus
2071:10.7554/eLife.27689
1964:2007Sci...318.1309F
1958:(5854): 1309–1312.
1882:1990Sci...249.1436B
1876:(4975): 1436–1438.
1816:. pp. 58, 233.
1589:1990Sci...249.1436B
1583:(4975): 1436–1438.
1366:1999Natur.400..677P
500:Parkinson's disease
466:Parkinson's disease
444:Subthalamic nucleus
213:subthalamic nucleus
69:Parkinson's disease
49:subthalamic nucleus
24:Subthalamic nucleus
3888:Golgi tendon organ
3862:Golgi tendon organ
3693:Interposed nucleus
2923:Cuneate fasciculus
2919:Gracile fasciculus
2905:Pacinian corpuscle
2504:Acoustic radiation
1659:Revue Neurologique
1405:Movement Disorders
990:Movement Disorders
812:Movement Disorders
536:Alim Louis Benabid
441:
288:
253:Jules Bernard Luys
247:and medial to the
3919:
3918:
3915:
3914:
3911:
3910:
3876:Cerebellar vermis
3805:Cerebellar vermis
3748:Vestibular nuclei
3734:Fastigial nucleus
3572:Vestibular nuclei
3551:
3550:
3547:
3546:
3489:Ansa lenticularis
3413:Ansa lenticularis
3371:
3370:
3364:→ muscles of neck
3361:Tectospinal tract
3307:Vestibular nuclei
3282:Rubrospinal tract
3159:
3158:
3155:
3154:
3082:Postcentral gyrus
3045:Free nerve ending
3015:
3014:
3007:Postcentral gyrus
2826:
2825:
2789:
2788:
2710:
2709:
2534:
2533:
2526:Medullary laminae
2494:Lateral lemniscus
2453:Ansa lenticularis
2251:
2250:
2210:Habenular trigone
2015:(14): 3743–3752.
1839:(20): 2121–2134.
1775:(23): 2187–2195.
1736:(26): 2501–2513.
1417:10.1002/mds.10138
1360:(6745): 677–682.
1265:(20): 7766–7775.
1002:10.1002/mds.27901
824:10.1002/mds.20374
775:(11): 1717–1743.
614:Additional images
524:Parkinson disease
454:action potentials
341:ansa lenticularis
279:
209:
208:
204:
3944:
3765:
3764:
3562:
3561:
3528:
3451:
3391:
3382:
3381:
3326:
3296:
3270:
3232:
3225:
3224:
3168:
3167:
3146:Cingulate cortex
3070:Spinal lemniscus
3031:
3030:
2966:Medial lemniscus
2914:Posterior column
2892:
2891:
2883:
2882:
2853:
2846:
2839:
2830:
2829:
2729:Stria terminalis
2584:
2583:
2545:
2544:
2477:Medial lemniscus
2262:
2261:
2238:Habenular nuclei
2190:
2189:
2165:
2158:
2151:
2142:
2141:
2135:
2134:
2124:
2100:
2094:
2093:
2083:
2073:
2049:
2043:
2042:
2032:
2000:
1994:
1993:
1975:
1943:
1937:
1936:
1908:
1902:
1901:
1865:
1859:
1858:
1848:
1824:
1818:
1817:
1809:
1803:
1802:
1792:
1760:
1754:
1753:
1724:
1718:
1717:
1681:
1675:
1674:
1650:
1644:
1643:
1615:
1609:
1608:
1572:
1566:
1565:
1529:
1523:
1522:
1486:
1480:
1479:
1443:
1437:
1436:
1400:
1394:
1393:
1349:
1343:
1342:
1308:
1299:
1293:
1292:
1282:
1250:
1244:
1243:
1204:
1198:
1197:
1161:
1155:
1154:
1118:
1109:
1108:
1072:
1063:
1062:
1044:
1035:(7): 1788–1802.
1020:
1014:
1013:
985:
979:
978:
942:
936:
935:
925:
893:
887:
886:
850:
844:
843:
807:
801:
800:
764:
758:
757:
721:
715:
714:
678:
672:
671:
660:
624:
434:
433:turquoise arrows
426:
418:
383:Efferent targets
373:substantia nigra
367:inputs, notably
357:parafascicularis
325:tripartite model
280:
249:internal capsule
245:substantia nigra
201:edit on Wikidata
198:
152:nlx_anat_1010002
65:
53:substantia nigra
33:
21:
20:
3952:
3951:
3947:
3946:
3945:
3943:
3942:
3941:
3922:
3921:
3920:
3907:
3844:
3817:muscle spindles
3783:muscle spindles
3770:
3760:Spinocerebellar
3758:
3752:
3660:Dentate nucleus
3648:
3543:
3521:
3516:
3445:
3440:
3385:
3367:
3356:Midbrain tectum
3347:
3322:
3317:
3292:
3287:
3266:
3261:
3228:
3214:
3151:
3108:
3104:Midbrain tectum
3024:
3011:
2987:
2954:/arcuate fibers
2935:
2931:Cuneate nucleus
2927:Gracile nucleus
2874:
2857:
2827:
2822:
2817:Fields of Forel
2785:
2762:
2706:
2678:
2669:Preoptic (GnRH)
2626:Paraventricular
2606:
2573:
2564:Mammillary body
2555:Median eminence
2530:
2509:Optic radiation
2429:
2357:Pulvinar nuclei
2295:
2286:
2247:
2219:
2179:
2171:Anatomy of the
2169:
2139:
2138:
2101:
2097:
2050:
2046:
2001:
1997:
1944:
1940:
1909:
1905:
1866:
1862:
1825:
1821:
1810:
1806:
1761:
1757:
1725:
1721:
1686:Nature Medicine
1682:
1678:
1651:
1647:
1616:
1612:
1573:
1569:
1540:(10): 525–531.
1530:
1526:
1487:
1483:
1444:
1440:
1401:
1397:
1350:
1346:
1306:
1300:
1296:
1251:
1247:
1205:
1201:
1162:
1158:
1119:
1112:
1073:
1066:
1021:
1017:
986:
982:
943:
939:
894:
890:
851:
847:
808:
804:
765:
761:
722:
718:
679:
675:
661:
657:
652:
635:
628:
625:
616:
599:
508:
506:Pathophysiology
478:globus pallidus
474:
446:
432:
424:
416:
405:
385:
371:axons from the
365:neuromodulatory
361:central complex
353:cerebral cortex
333:
293:
271:
269:
205:
71:
56:
17:
12:
11:
5:
3950:
3940:
3939:
3934:
3917:
3916:
3913:
3912:
3909:
3908:
3906:
3905:
3880:
3879:
3854:
3852:
3846:
3845:
3843:
3842:
3809:
3808:
3775:
3773:
3771:proprioception
3762:
3757:Bidirectional:
3754:
3753:
3751:
3750:
3730:
3729:
3689:
3688:
3656:
3654:
3650:
3649:
3647:
3646:
3618:
3617:
3597:Pontine nuclei
3593:
3592:
3568:
3566:
3559:
3553:
3552:
3549:
3548:
3545:
3544:
3542:
3541:
3531:
3529:
3518:
3517:
3454:
3452:
3442:
3441:
3394:
3392:
3379:
3373:
3372:
3369:
3368:
3366:
3365:
3352:
3349:
3348:
3346:
3345:
3329:
3327:
3319:
3318:
3316:
3315:
3299:
3297:
3289:
3288:
3286:
3285:
3273:
3271:
3263:
3262:
3260:
3259:
3257:Facial muscles
3235:
3233:
3222:
3220:Extrapyramidal
3216:
3215:
3213:
3212:
3176:
3174:
3165:
3161:
3160:
3157:
3156:
3153:
3152:
3150:
3149:
3119:
3117:
3110:
3109:
3090:
3089:
3040:
3038:
3028:
3017:
3016:
3013:
3012:
3010:
3009:
2998:
2996:
2989:
2988:
2986:
2985:
2946:
2944:
2937:
2936:
2934:
2933:
2901:
2899:
2889:
2880:
2876:
2875:
2856:
2855:
2848:
2841:
2833:
2824:
2823:
2821:
2820:
2810:
2805:
2799:
2797:
2791:
2790:
2787:
2786:
2784:
2783:
2772:
2770:
2764:
2763:
2761:
2760:
2759:
2758:
2753:
2743:
2742:
2741:
2736:
2731:
2720:
2718:
2712:
2711:
2708:
2707:
2705:
2704:
2699:
2694:
2688:
2686:
2680:
2679:
2677:
2676:
2671:
2666:
2657:
2656:
2655:
2654:
2640:
2639:
2638:
2633:
2616:
2614:
2608:
2607:
2605:
2604:
2599:
2593:
2591:
2581:
2575:
2574:
2572:
2571:
2566:
2561:
2559:Tuber cinereum
2551:
2549:
2542:
2536:
2535:
2532:
2531:
2529:
2528:
2522:
2521:
2516:
2511:
2506:
2501:
2496:
2491:
2486:
2485:
2484:
2479:
2467:
2466:
2465:
2460:
2455:
2445:
2439:
2437:
2431:
2430:
2428:
2427:
2422:
2417:
2416:
2415:
2405:
2396:
2395:
2394:
2393:
2392:
2391:
2386:
2381:
2371:
2361:
2360:
2359:
2354:
2349:
2339:
2338:
2337:
2324:
2310:
2301:
2299:
2288:
2287:
2285:
2284:
2282:Taenia thalami
2279:
2274:
2268:
2266:
2259:
2253:
2252:
2249:
2248:
2246:
2245:
2240:
2235:
2233:Pretectal area
2229:
2227:
2221:
2220:
2218:
2217:
2212:
2207:
2202:
2196:
2194:
2187:
2181:
2180:
2168:
2167:
2160:
2153:
2145:
2137:
2136:
2109:Brain Research
2095:
2044:
1995:
1938:
1903:
1860:
1819:
1804:
1755:
1719:
1698:10.1038/nm1693
1676:
1665:(3): 175–176.
1645:
1626:(4): 382–389.
1610:
1567:
1524:
1497:(2): 297–318.
1481:
1438:
1395:
1344:
1317:(3): 142–151.
1311:Brain Research
1294:
1245:
1218:(3): 312–318.
1199:
1172:(3): 245–257.
1156:
1129:(2): 306–323.
1110:
1064:
1015:
980:
947:Brain Research
937:
888:
845:
818:(5): 574–584.
802:
759:
716:
673:
654:
653:
651:
648:
647:
646:
641:
634:
631:
630:
629:
626:
619:
615:
612:
598:
595:
507:
504:
473:
470:
445:
442:
404:
401:
384:
381:
332:
331:Afferent axons
329:
292:
289:
268:
265:
207:
206:
197:
191:
190:
185:
179:
178:
173:
167:
166:
161:
155:
154:
149:
142:
141:
136:
130:
129:
124:
118:
117:
114:
110:
109:
104:
98:
97:
93:
92:
91:(functionally)
87:(physically);
82:
78:
77:
73:
72:
66:
58:
57:
34:
26:
25:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3949:
3938:
3937:Basal ganglia
3935:
3933:
3930:
3929:
3927:
3903:
3899:
3895:
3894:
3889:
3885:
3882:
3881:
3877:
3873:
3869:
3868:
3863:
3859:
3856:
3855:
3853:
3851:
3847:
3840:
3836:
3832:
3831:
3826:
3822:
3818:
3814:
3811:
3810:
3806:
3802:
3798:
3797:
3792:
3788:
3784:
3780:
3777:
3776:
3774:
3772:
3766:
3763:
3761:
3755:
3749:
3745:
3744:
3739:
3735:
3732:
3731:
3728:
3724:
3720:
3716:
3712:
3711:
3706:
3702:
3698:
3694:
3691:
3690:
3687:
3683:
3679:
3675:
3674:
3669:
3665:
3661:
3658:
3657:
3655:
3651:
3645:
3641:
3640:Purkinje cell
3637:
3633:
3629:
3628:
3623:
3620:
3619:
3616:
3612:
3608:
3604:
3603:
3598:
3595:
3594:
3591:
3587:
3583:
3579:
3578:
3573:
3570:
3569:
3567:
3563:
3560:
3558:
3554:
3540:
3536:
3535:Pars compacta
3533:
3532:
3530:
3527:
3525:
3519:
3514:
3510:
3506:
3502:
3498:
3494:
3490:
3486:
3482:
3478:
3474:
3470:
3466:
3462:
3458:
3453:
3450:
3449:
3443:
3438:
3434:
3430:
3426:
3422:
3418:
3414:
3410:
3406:
3402:
3398:
3393:
3390:
3389:
3383:
3380:
3378:
3377:Basal ganglia
3374:
3363:
3362:
3357:
3354:
3353:
3350:
3344:
3343:
3338:
3334:
3331:
3330:
3328:
3325:
3320:
3314:
3313:
3308:
3304:
3301:
3300:
3298:
3295:
3290:
3284:
3283:
3278:
3275:
3274:
3272:
3269:
3264:
3258:
3254:
3250:
3249:
3244:
3240:
3237:
3236:
3234:
3231:
3226:
3223:
3221:
3217:
3211:
3207:
3205:
3201:
3197:
3192:
3188:
3184:
3181:
3178:
3177:
3175:
3173:
3169:
3166:
3162:
3147:
3143:
3139:
3135:
3131:
3130:
3125:
3121:
3120:
3118:
3115:
3111:
3107:
3105:
3101:
3097:
3096:
3087:
3083:
3079:
3075:
3071:
3067:
3066:
3063:
3059:
3054:
3050:
3049:A delta fiber
3046:
3042:
3041:
3039:
3036:
3032:
3029:
3027:
3022:
3021:Anterolateral
3018:
3008:
3004:
3000:
2999:
2997:
2994:
2990:
2983:
2979:
2975:
2971:
2967:
2963:
2959:
2955:
2953:
2948:
2947:
2945:
2942:
2938:
2932:
2928:
2924:
2920:
2916:
2915:
2910:
2906:
2903:
2902:
2900:
2897:
2893:
2890:
2888:
2884:
2881:
2877:
2873:
2869:
2868:neural tracts
2865:
2861:
2854:
2849:
2847:
2842:
2840:
2835:
2834:
2831:
2818:
2814:
2811:
2809:
2806:
2804:
2801:
2800:
2798:
2796:
2792:
2781:
2777:
2774:
2773:
2771:
2769:
2765:
2757:
2754:
2752:
2749:
2748:
2747:
2744:
2740:
2737:
2735:
2732:
2730:
2727:
2726:
2725:
2722:
2721:
2719:
2717:
2713:
2703:
2700:
2698:
2695:
2693:
2690:
2689:
2687:
2685:
2681:
2675:
2672:
2670:
2667:
2665:
2662:
2659:
2658:
2653:
2649:
2646:
2645:
2644:
2641:
2637:
2634:
2632:
2629:
2628:
2627:
2624:
2622:
2618:
2617:
2615:
2613:
2609:
2603:
2600:
2598:
2595:
2594:
2592:
2589:
2585:
2582:
2580:
2576:
2570:
2567:
2565:
2562:
2560:
2556:
2553:
2552:
2550:
2546:
2543:
2541:
2537:
2527:
2524:
2523:
2520:
2517:
2515:
2512:
2510:
2507:
2505:
2502:
2500:
2497:
2495:
2492:
2490:
2487:
2483:
2480:
2478:
2475:
2474:
2473:
2472:
2468:
2464:
2461:
2459:
2456:
2454:
2451:
2450:
2449:
2446:
2444:
2441:
2440:
2438:
2436:
2432:
2426:
2423:
2421:
2418:
2414:
2411:
2410:
2409:
2406:
2404:
2401:
2398:
2397:
2390:
2387:
2385:
2382:
2380:
2377:
2376:
2375:
2372:
2370:
2367:
2366:
2365:
2362:
2358:
2355:
2353:
2350:
2348:
2345:
2344:
2343:
2340:
2336:
2332:
2328:
2325:
2323:
2319:
2316:
2315:
2314:
2311:
2309:
2306:
2303:
2302:
2300:
2298:
2293:
2289:
2283:
2280:
2278:
2275:
2273:
2270:
2269:
2267:
2263:
2260:
2258:
2254:
2244:
2241:
2239:
2236:
2234:
2231:
2230:
2228:
2226:
2222:
2216:
2213:
2211:
2208:
2206:
2203:
2201:
2198:
2197:
2195:
2191:
2188:
2186:
2182:
2178:
2174:
2166:
2161:
2159:
2154:
2152:
2147:
2146:
2143:
2132:
2128:
2123:
2118:
2114:
2110:
2106:
2099:
2091:
2087:
2082:
2077:
2072:
2067:
2063:
2059:
2055:
2048:
2040:
2036:
2031:
2026:
2022:
2018:
2014:
2010:
2006:
1999:
1991:
1987:
1983:
1979:
1974:
1969:
1965:
1961:
1957:
1953:
1949:
1942:
1934:
1930:
1926:
1922:
1918:
1914:
1907:
1899:
1895:
1891:
1887:
1883:
1879:
1875:
1871:
1864:
1856:
1852:
1847:
1842:
1838:
1834:
1830:
1823:
1815:
1808:
1800:
1796:
1791:
1786:
1782:
1778:
1774:
1770:
1766:
1759:
1751:
1747:
1743:
1739:
1735:
1731:
1723:
1715:
1711:
1707:
1703:
1699:
1695:
1691:
1687:
1680:
1672:
1668:
1664:
1660:
1656:
1649:
1641:
1637:
1633:
1629:
1625:
1621:
1614:
1606:
1602:
1598:
1594:
1590:
1586:
1582:
1578:
1571:
1563:
1559:
1555:
1551:
1547:
1543:
1539:
1535:
1528:
1520:
1516:
1512:
1508:
1504:
1500:
1496:
1492:
1485:
1477:
1473:
1469:
1465:
1461:
1457:
1453:
1449:
1442:
1434:
1430:
1426:
1422:
1418:
1414:
1410:
1406:
1399:
1391:
1387:
1383:
1379:
1375:
1374:10.1038/23281
1371:
1367:
1363:
1359:
1355:
1348:
1340:
1336:
1332:
1328:
1324:
1320:
1316:
1312:
1305:
1298:
1290:
1286:
1281:
1276:
1272:
1268:
1264:
1260:
1256:
1249:
1241:
1237:
1233:
1229:
1225:
1221:
1217:
1213:
1209:
1203:
1195:
1191:
1187:
1183:
1179:
1175:
1171:
1167:
1160:
1152:
1148:
1144:
1140:
1136:
1132:
1128:
1124:
1117:
1115:
1106:
1102:
1098:
1094:
1090:
1086:
1082:
1078:
1071:
1069:
1060:
1056:
1052:
1048:
1043:
1038:
1034:
1030:
1026:
1019:
1011:
1007:
1003:
999:
995:
991:
984:
976:
972:
968:
964:
960:
956:
952:
948:
941:
933:
929:
924:
919:
915:
911:
907:
903:
899:
892:
884:
880:
876:
872:
868:
864:
860:
856:
849:
841:
837:
833:
829:
825:
821:
817:
813:
806:
798:
794:
790:
786:
782:
778:
774:
770:
763:
755:
751:
747:
743:
739:
735:
732:(1): 75–111.
731:
727:
720:
712:
708:
704:
700:
696:
692:
688:
684:
677:
669:
665:
659:
655:
645:
642:
640:
637:
636:
623:
618:
617:
611:
607:
604:
603:basal ganglia
594:
592:
588:
584:
579:
577:
573:
569:
568:hemiballismus
564:
559:
557:
553:
549:
545:
541:
537:
533:
529:
525:
521:
517:
513:
503:
501:
496:
494:
489:
486:
485:basal ganglia
481:
479:
469:
467:
463:
457:
455:
450:
438:
431:pathways and
430:
422:
421:glutamatergic
414:
413:basal ganglia
409:
400:
398:
393:
391:
380:
378:
374:
370:
366:
362:
358:
354:
350:
346:
342:
338:
328:
326:
320:
318:
315:
311:
310:glutamatergic
306:
302:
298:
285:
264:
262:
258:
254:
250:
246:
242:
238:
234:
230:
229:basal ganglia
226:
222:
218:
214:
202:
196:
192:
189:
186:
184:
180:
177:
174:
172:
168:
165:
162:
160:
156:
153:
150:
147:
143:
140:
137:
135:
131:
128:
125:
123:
119:
115:
111:
108:
105:
103:
99:
94:
90:
89:basal ganglia
86:
83:
79:
74:
70:
64:
59:
54:
50:
46:
42:
38:
37:basal ganglia
32:
27:
22:
19:
3891:
3865:
3828:
3794:
3741:
3727:Motor cortex
3708:
3686:Motor cortex
3671:
3625:
3615:Granule cell
3600:
3590:Granule cell
3575:
3522:
3513:Motor cortex
3472:
3457:Motor cortex
3447:
3437:Motor cortex
3397:Motor cortex
3387:
3359:
3340:
3323:
3310:
3293:
3280:
3267:
3246:
3229:
3194:
3179:
3127:
3093:
3091:
3056:
2950:
2912:
2808:Zona incerta
2802:
2782:is glandular
2745:
2723:
2716:White matter
2697:Ventromedial
2660:
2619:
2569:Infundibulum
2540:Hypothalamus
2469:
2435:White matter
2413:Centromedian
2408:Intralaminar
2399:
2364:Metathalamus
2304:
2200:Pineal gland
2173:diencephalon
2112:
2108:
2098:
2061:
2057:
2047:
2012:
2008:
1998:
1955:
1951:
1941:
1919:(1): 44–52.
1916:
1912:
1906:
1873:
1869:
1863:
1836:
1832:
1822:
1813:
1807:
1772:
1768:
1758:
1733:
1729:
1722:
1692:(1): 75–80.
1689:
1685:
1679:
1662:
1658:
1648:
1623:
1619:
1613:
1580:
1576:
1570:
1537:
1533:
1527:
1494:
1490:
1484:
1454:(1): 17–31.
1451:
1447:
1441:
1408:
1404:
1398:
1357:
1353:
1347:
1314:
1310:
1297:
1262:
1258:
1248:
1215:
1211:
1202:
1169:
1165:
1159:
1126:
1122:
1080:
1076:
1032:
1028:
1018:
996:(1): 75–80.
993:
989:
983:
953:(1): 43–59.
950:
946:
940:
908:(1): 83–94.
905:
901:
891:
858:
854:
848:
815:
811:
805:
772:
769:Neuroscience
768:
762:
729:
725:
719:
686:
682:
676:
667:
658:
608:
600:
580:
560:
509:
497:
490:
482:
475:
458:
451:
447:
437:dopaminergic
417:Green arrows
394:
386:
369:dopaminergic
334:
324:
321:
317:interneurons
294:
260:
257:corpus Luysi
256:
216:
212:
210:
164:A14.1.08.702
106:
67:DA-loops in
48:
18:
3932:Subthalamus
3769:Unconscious
3715:Red nucleus
3277:Red nucleus
2864:spinal cord
2795:Subthalamus
2702:Dorsomedial
2652:vasopressin
2579:Grey matter
2292:Grey matter
2225:Grey matter
2185:Epithalamus
2177:human brain
1208:Surmeier DJ
1083:(1): 1–16.
861:: 326–329.
689:(1): 1–13.
576:Michael Fox
561:Before the
305:ellipsoidal
233:subthalamus
96:Identifiers
85:Subthalamus
3926:Categories
3902:Cerebellum
3884:upper limb
3858:lower limb
3850:Reflex arc
3813:upper limb
3779:lower limb
3636:Hemisphere
3586:Cerebellum
3557:Cerebellar
3435:) → 5° (
3324:extension:
3294:extension:
2643:Supraoptic
2115:: 147226.
2064:: e27689.
1812:Carter R.
902:NeuroImage
855:NeuroImage
650:References
425:red arrows
423:pathways,
403:Physiology
261:Luys' body
134:NeuroNames
113:Acronym(s)
51:(STN) and
43:(GPe) and
3511:) → 7° (
3448:indirect:
3172:Pyramidal
2872:fasciculi
2776:Posterior
2768:Pituitary
2612:Endocrine
2588:Autonomic
1769:Neurology
552:adenosine
435:refer to
429:GABAergic
349:afferents
314:GABAergic
301:dendrites
291:Structure
3890:) → 2° (
3864:) → 2° (
3823:) → 2° (
3789:) → 2° (
3719:Thalamus
3678:Thalamus
3653:Efferent
3565:Afferent
3539:Striatum
3503:) → 6° (
3501:Thalamus
3483:) → 5° (
3475:) → 4° (
3467:) → 3° (
3463:) → 2° (
3461:Striatum
3427:) → 4° (
3425:Thalamus
3407:) → 3° (
3403:) → 2° (
3401:Striatum
3268:flexion:
3230:flexion:
3204:Anterior
3180:flexion:
3144:) → 3° (
3142:Thalamus
3136:) → 2° (
3084:) → 4° (
3080:) → 3° (
3078:Thalamus
3062:Anterior
3051:) → 2° (
3037:/lateral
2974:Thalamus
2780:anterior
2746:efferent
2724:afferent
2648:oxytocin
2400:midline:
2257:Thalamus
2205:Habenula
2131:33358727
2090:28742497
2039:17409238
1982:17962524
1933:33253351
1855:19005196
1799:27170566
1750:33369354
1706:18157140
1554:12220881
1519:24968074
1476:84665164
1468:10660885
1433:40925638
1425:11948751
1382:10458164
1339:14636489
1331:21959175
1289:11027240
1240:42900941
1232:15916893
1194:32152785
1105:43046462
1059:14698708
1051:15380000
1010:31758733
975:22996045
932:22173294
883:11010595
875:24642281
832:15645534
797:40909863
754:11962279
711:12482772
666:(1865).
633:See also
597:Function
556:ablation
516:rigidity
512:akinesia
241:thalamus
146:NeuroLex
47:(GPi)),
3707:, or →
3388:direct:
3200:Lateral
3116:/medial
3058:Lateral
2879:Sensory
2692:Lateral
2684:Emotion
2548:Surface
2342:Lateral
2313:Ventral
2305:paired:
2265:Surface
2193:Surface
2175:of the
2081:5526663
2030:6672420
1990:2718110
1960:Bibcode
1952:Science
1898:2402638
1878:Bibcode
1870:Science
1790:4898318
1714:7107064
1671:8235208
1640:8261116
1605:2402638
1585:Bibcode
1577:Science
1562:8127062
1511:8027445
1390:4356230
1362:Bibcode
1280:6772896
1186:6304154
1151:9667393
1143:2332533
967:2350684
923:3315017
840:9551517
703:4056088
664:Luys JB
563:Bergman
532:Bergman
392:(GPi).
359:of the
345:Edinger
267:Anatomy
239:to the
237:ventral
223:in the
221:nucleus
127:D020531
81:Part of
76:Details
3886:→ 1° (
3860:→ 1° (
3815:→ 1° (
3781:→ 1° (
2661:other:
2389:K cell
2384:M cell
2379:P cell
2297:nuclei
2129:
2088:
2078:
2037:
2027:
1988:
1980:
1931:
1896:
1853:
1797:
1787:
1748:
1712:
1704:
1669:
1638:
1603:
1560:
1552:
1517:
1509:
1474:
1466:
1431:
1423:
1388:
1380:
1354:Nature
1337:
1329:
1287:
1277:
1238:
1230:
1192:
1184:
1149:
1141:
1103:
1097:418083
1095:
1057:
1049:
1008:
973:
965:
930:
920:
881:
873:
838:
830:
795:
789:117397
787:
752:
746:819471
744:
709:
701:
520:tremor
518:, and
297:neuron
3164:Motor
2860:Brain
2590:zones
2058:eLife
1986:S2CID
1913:Brain
1710:S2CID
1558:S2CID
1515:S2CID
1472:S2CID
1429:S2CID
1386:S2CID
1335:S2CID
1307:(PDF)
1236:S2CID
1190:S2CID
1147:S2CID
1101:S2CID
1055:S2CID
971:S2CID
879:S2CID
836:S2CID
793:S2CID
750:S2CID
707:S2CID
225:brain
199:[
188:62035
102:Latin
55:(SN).
3725:) →
3684:) →
3455:1° (
3395:1° (
3122:1° (
3114:Slow
3092:2° (
3060:and
3043:1° (
3035:Fast
3026:pain
2964:) →
2925:) →
2887:DCML
2870:and
2862:and
2471:PCML
2127:PMID
2113:1755
2086:PMID
2035:PMID
1978:PMID
1929:PMID
1894:PMID
1851:PMID
1795:PMID
1746:PMID
1702:PMID
1667:PMID
1636:PMID
1601:PMID
1550:PMID
1507:PMID
1464:PMID
1421:PMID
1378:PMID
1327:PMID
1315:1434
1285:PMID
1228:PMID
1182:PMID
1139:PMID
1093:PMID
1047:PMID
1006:PMID
963:PMID
928:PMID
871:PMID
828:PMID
785:PMID
742:PMID
699:PMID
528:MPTP
397:axon
308:are
211:The
176:5709
159:TA98
122:MeSH
3898:ICP
3872:SCP
3835:ICP
3821:DRG
3801:ICP
3787:DRG
3736:in
3701:SCP
3695:in
3668:SCP
3662:in
3632:ICP
3624:→
3607:MCP
3582:ICP
3499:of
3481:GPi
3465:GPe
3423:of
3405:GPi
3305:→
3140:of
3102:of
3076:of
3074:VPL
2982:VPM
2978:VPL
2335:VPL
2331:VPM
2117:doi
2076:PMC
2066:doi
2025:PMC
2017:doi
1968:doi
1956:318
1921:doi
1917:144
1886:doi
1874:249
1841:doi
1837:359
1785:PMC
1777:doi
1738:doi
1734:383
1694:doi
1663:149
1628:doi
1593:doi
1581:249
1542:doi
1499:doi
1495:343
1456:doi
1452:417
1413:doi
1370:doi
1358:400
1319:doi
1275:PMC
1267:doi
1220:doi
1174:doi
1170:215
1131:doi
1127:294
1085:doi
1081:180
1037:doi
998:doi
955:doi
951:513
918:PMC
910:doi
863:doi
820:doi
777:doi
734:doi
730:168
691:doi
687:236
591:FDA
540:FDA
522:in
259:or
217:STN
183:FMA
171:TA2
139:435
116:STN
3928::
3900:→
3896:→
3874:→
3870:→
3837:→
3833:→
3827:→
3819:→
3803:→
3799:→
3793:→
3785:→
3746:→
3740:→
3723:VL
3717:→
3713:→
3703:→
3699:→
3682:VL
3676:→
3670:→
3666:→
3642:→
3638:→
3634:→
3630:→
3613:→
3609:→
3605:→
3599:→
3588:→
3584:→
3580:→
3574:→
3537:→
3507:→
3497:VL
3495:→
3491:→
3479:→
3471:→
3459:→
3431:→
3421:VL
3419:→
3415:→
3399:→
3358:→
3339:→
3335:→
3309:→
3279:→
3255:→
3251:→
3245:→
3241:→
3208:→
3202:,
3193:→
3189:→
3185:→
3138:MD
3132:→
3126:→
3106:)
3098:→
3072:→
3068:→
3055:→
3047:→
3005:→
3001:→
2993:3°
2980:,
2972:→
2960:,
2949:→
2941:2°
2911:→
2896:1°
2866::
2403:MD
2374:LG
2369:MG
2352:LP
2347:LD
2327:VP
2322:VL
2318:VA
2308:AN
2125:.
2111:.
2107:.
2084:.
2074:.
2060:.
2056:.
2033:.
2023:.
2013:27
2011:.
2007:.
1984:.
1976:.
1966:.
1954:.
1950:.
1927:.
1915:.
1892:.
1884:.
1872:.
1849:.
1835:.
1831:.
1793:.
1783:.
1773:86
1771:.
1767:.
1744:.
1732:.
1708:.
1700:.
1690:14
1688:.
1661:.
1657:.
1634:.
1622:.
1599:.
1591:.
1579:.
1556:.
1548:.
1538:25
1536:.
1513:.
1505:.
1493:.
1470:.
1462:.
1450:.
1427:.
1419:.
1409:17
1407:.
1384:.
1376:.
1368:.
1356:.
1333:.
1325:.
1313:.
1309:.
1283:.
1273:.
1263:20
1261:.
1257:.
1234:.
1226:.
1216:15
1214:.
1188:.
1180:.
1168:.
1145:.
1137:.
1125:.
1113:^
1099:.
1091:.
1079:.
1067:^
1053:.
1045:.
1033:20
1031:.
1027:.
1004:.
994:35
992:.
969:.
961:.
949:.
926:.
916:.
906:60
904:.
900:.
877:.
869:.
859:95
857:.
834:.
826:.
816:20
814:.
791:.
783:.
771:.
748:.
740:.
728:.
705:.
697:.
685:.
514:,
502:.
468:.
379:.
148:ID
3904:)
3878:)
3841:)
3807:)
3721:(
3680:(
3526::
3515:)
3487:/
3439:)
3411:/
3206:)
3198:(
3148:)
3088:)
3023:/
2995::
2984:)
2976:(
2968:/
2956:(
2943::
2929:/
2921:/
2917:(
2907:/
2898::
2852:e
2845:t
2838:v
2819:)
2815:(
2650:/
2623::
2557:/
2333:/
2329:/
2320:/
2294:/
2164:e
2157:t
2150:v
2133:.
2119::
2092:.
2068::
2062:6
2041:.
2019::
1992:.
1970::
1962::
1935:.
1923::
1900:.
1888::
1880::
1857:.
1843::
1801:.
1779::
1752:.
1740::
1716:.
1696::
1673:.
1642:.
1630::
1624:5
1607:.
1595::
1587::
1564:.
1544::
1521:.
1501::
1478:.
1458::
1435:.
1415::
1392:.
1372::
1364::
1341:.
1321::
1291:.
1269::
1242:.
1222::
1196:.
1176::
1153:.
1133::
1107:.
1087::
1061:.
1039::
1012:.
1000::
977:.
957::
934:.
912::
885:.
865::
842:.
822::
799:.
779::
773:4
756:.
736::
713:.
693::
286:.
215:(
203:]
39:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.