27:
982:
1006:
970:
994:
957:
In 1950, 3 skulls from the Upper
Capsian of the Maghreb were measured, and based on indicators of the craniofacial form, considered to have been mixed in traits. The overall anthropological investigation highlighted that their dominant characteristics were conforming to a Mediterranean type, while
958:
the minority characteristics conformed to Mechta-Afalou (Iberomarusian) and "Negroid" type. It was suggested that this population was the product of Pre-Neolithic Mectha-Afalous, "White" immigrants from the east, and
African migrants from the south.
891:, and geographic association with modern speakers of the Afroasiatic languages, historical linguists have tentatively associated the industry with the Afroasiatic family's earliest speakers on the continent.
894:
Nothing is known about
Capsian religion, but their burial methods suggest a belief in an afterlife. Decorative art is widely found at their sites, including figurative and abstract
1477:
880:; there is little evidence concerning plants eaten. During the succeeding Neolithic of Capsian Tradition, there is evidence from one site, for domesticated, probably imported,
1463:
1200:
Jackes, Mary; Lubell, David (June 2008). "Early and Middle
Holocene Environments and Capsian Cultural Change: Evidence from the Télidjène Basin, Eastern Algeria".
946:
on the basis of cranial morphology and anthropological traits. Some have argued that they were associated with
Mediterranean immigrants from the east such as the
97:
89:
1364:
969:
101:
841:(6,200–5,300 BP) is also specified. They represent variants of one tradition, the differences between them being both typological and technological.
1123:
Rahmani, Noura (2004-03-01). "Technological and
Cultural Change Among the Last Hunter-Gatherers of the Maghreb: The Capsian (10,000–6000 B.P.)".
929:
which dates between 13,000 and 9,000 BC in East Africa, was formerly known as the "Kenya
Capsian" due to similarities in the stone blade shapes.
712:
105:
1527:
1507:
85:
109:
75:
1522:
1005:
981:
1458:
572:
1492:
1401:
1167:
1320:
Ferembach, Denise (May 1985). "On the origin of the iberomaurusians (Upper palaeolithic: North Africa). A new hypothesis".
1370:
1517:
1084:
769:
430:
26:
1032:
1094:
1067:
993:
328:
954:, whereas others argue for a population continuity based on physical skeletal characteristics and other criteria.
1512:
1497:
219:
629:
308:
1502:
1262:. XXIVe rencontres internationales d’archéologie et d’histoire d’Antibes, pp. 77–98. Antibes: Éditions APDCA.
423:
1285:
Bender, M. Lionel (1985). "Review of The
Archaeological and Linguistic Reconstruction of African History".
619:
373:
353:
837:(Upper Capsian), which are sometimes found in chronostratigraphic sequence. Sometimes, a third period,
664:
1355:
Sheppard, Peter; Lubell, David (1990). "Early
Holocene Maghreb prehistory: an evolutionary approach".
1109:
2005 D. Lubell. Continuité et changement dans l'Epipaléolithique du
Maghreb. In, M. Sahnouni (ed.)
1022:
762:
654:
193:
189:
1472:
907:
644:
418:
348:
1418:
393:
1057:
951:
826:
807:
185:
1329:
1037:
861:
853:
686:
557:
1273:Économie Pastorale Préagricole en Algérie Orientale: le Néolithique de Tradition Capsienne
298:
8:
1260:
Petits Animaux et Sociétés Humaines. Du Complément Alimentaire Aux Ressources Utilitaires
1136:
440:
368:
180:
1333:
1184:
Paleoenvironments and Epi Paleolithic economies in the Maghreb (ca. 20,000 to 5000 B.C.)
363:
323:
303:
1302:
1256:
Prehistoric edible land snails in the circum-Mediterranean: the archaeological evidence
1217:
1183:
1140:
939:
755:
727:
475:
465:
175:
1419:"On three skulls from Mechta‐el‐Arbi, Algeria. A reexamination of Cole's adult series"
1341:
1076:
413:
318:
1438:
1397:
1163:
1144:
1090:
1063:
732:
525:
490:
435:
278:
209:
1239:
Continuity in the Epipalaeolithic of northern Africa with an emphasis on the Maghreb
1238:
1221:
1430:
1389:
1337:
1294:
1255:
1209:
1132:
947:
926:
692:
639:
540:
530:
520:
515:
505:
500:
495:
333:
273:
266:
261:
251:
236:
165:
1113:, pp. 205–226. Paris: Guides de la Préhistoire Mondiale, Éditions Artcom’/Errance.
408:
1393:
1188:
From Hunters to Farmers: The Causes and Consequences of Food Production in Africa
1027:
915:
550:
455:
398:
293:
246:
199:
170:
649:
1468:
545:
535:
510:
480:
450:
445:
378:
358:
338:
313:
288:
241:
120:
1213:
1486:
1442:
943:
881:
594:
470:
460:
403:
388:
383:
283:
256:
214:
130:
1434:
934:
811:
745:
599:
485:
224:
37:
975:
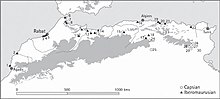
The main sites of the Iberomaurusian and Capsian cultures in north Africa
903:
849:
798:
that lasted from about 8,000 to 2,700 BC. It was named after the town of
41:
93:
16:
Culture centered in the Maghreb that lasted from about 8,000 to 2,700 BC
869:
787:
702:
589:
584:
562:
343:
150:
55:
1306:
791:
142:
70:
51:
887:
Given the Capsian culture's timescale, widespread occurrence in the
864:. The Capsian diet included a wide variety of animals, ranging from
1298:
911:
895:
857:
722:
624:
614:
604:
579:
567:
204:
1160:
Le Capsien de Hergla (Tunisie): culture, environnement et économie
1478:
L'Université de Genève – drawing of mircoliths from upper Capsian
1384:
Lubell, David (2001). "Late Pleistocene-Early Holocene Maghreb".
919:
865:
845:
822:
818:
803:
795:
697:
609:
888:
899:
877:
799:
717:
707:
844:
During this period, the environment of the Maghreb was open
873:
231:
1348:
817:
Capsian industry was concentrated mainly in what is now
1459:
Capsian African Neolithic Tools, Weapons and Artifacts
1190:. Berkeley: University of California Press, pp. 41–56.
1111:
Le Paléolithique en Afrique: l’histoire la plus longue
1062:. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 93.
1233:
1231:
1086:
Macmillan Dictionary of Archaeology – Google Książki
938:, traditionally classed into two variegate types:
1228:
1484:
1354:
1313:
932:Anatomically, Capsian populations were modern
1237:1984 D. Lubell, P. Sheppard & M. Jackes.
763:
1199:
860:; where the initial phase overlaps with the
1386:Encyclopedia of Prehistory Volume 1: Africa
1377:
1265:
1186:. In, J.D. Clark & S.A. Brandt (eds.),
1116:
1248:
1176:
1103:
1082:
922:continued sporadically, but became rarer.
902:is found coloring both tools and corpses.
770:
756:
25:
1423:American Journal of Physical Anthropology
1319:
1258:. In, J-J. Brugal & J. Desse (eds.),
1157:
1241:. In, F. Wendorf & A. Close (eds.),
1083:Whitehouse, Ruth D. (24 February 2016).
1122:
825:. It is traditionally divided into two
1485:
1416:
1383:
1284:
1059:Encyclopedic Dictionary of Archaeology
1055:
1243:Advances in World Archaeology, Vol. 3
1245:: 143–191. New York: Academic Press.
1528:6th-millennium BC disestablishments
918:practice of extracting the central
13:
1508:Archaeological cultures in Morocco
1162:(in French). Africa Magna Verlag.
1137:10.1023/B:JOWO.0000038658.50738.eb
1056:Kipfer, Barbara Ann (2000-04-30).
1033:Prehistory of Central North Africa
14:
1539:
1452:
1523:8th-millennium BC establishments
1004:
999:Typical Capsian burial (Tunisia)
992:
980:
968:
1417:Briggs, L. Cabot (1950-09-01).
1410:
1278:
220:Halaf-Ubaid Transitional period
1193:
1151:
1049:
1:
1493:Mesolithic cultures of Africa
1469:Prof. David Lubell' home page
1342:10.1016/S0047-2484(85)80047-6
1202:African Archaeological Review
1043:
914:were used for necklaces. The
424:Neolithic Southeastern Europe
1394:10.1007/978-1-4615-1193-9_11
987:A Capsian ostrich-egg bottle
7:
1125:Journal of World Prehistory
1016:
575: in the Gulf of Cambay
10:
1544:
1518:Hunter-gatherers of Africa
1322:Journal of Human Evolution
1158:Mulazzani, Simone (2013).
1089:. Macmillan Education UK.
1011:Capsian culture, Arrowhead
961:
833:(Typical Capsian) and the
665:Savanna Pastoral Neolithic
329:Gumelnița–Karanovo culture
309:Cucuteni–Trypillia culture
1214:10.1007/s10437-008-9024-2
126:
116:
81:
69:
61:
47:
33:
24:
794:culture centered in the
1435:10.1002/ajpa.1330080311
655:Philippine jade culture
374:Shulaveri–Shomu culture
294:Cardium pottery culture
1513:Archaeology of Tunisia
1498:Archaeology of Algeria
1473:University of Waterloo
645:Jeulmun pottery period
419:Neolithic Transylvania
349:Linear Pottery culture
65:c. 8,000 – c. 2,700 BC
952:Pre-Pottery Neolithic
854:Mediterranean forests
806:, which was known as
1503:Archaeology of Libya
1464:Capsian North Africa
1388:. pp. 129–149.
1038:African humid period
1023:Ifri n'Amr or Moussa
862:African humid period
687:Neolithic Revolution
1334:1985JHumE..14..393F
940:Proto-Mediterranean
848:, much like modern
441:Pengtoushan culture
394:Tiszapolgár culture
369:San Ciriaco culture
181:Trihedral Neolithic
98:Khanguet El-Mouhaâd
21:
906:were used to make
728:Neolithic religion
573:Marine archaeology
476:Zhaobaogou culture
466:Xinglongwa culture
176:Shepherd Neolithic
159:Neolithic cultures
90:Dakhlat es-Saâdane
34:Geographical range
19:
1403:978-0-306-46255-9
1169:978-3-937248-36-3
904:Ostrich eggshells
839:Capsian Neolithic
835:Capsien supérieur
780:
779:
733:Neolithic decline
526:Qujialing culture
491:Majiabang culture
436:Peiligang culture
299:Cernavodă culture
279:Arzachena culture
210:Yarmukian culture
136:
135:
1535:
1447:
1446:
1414:
1408:
1407:
1381:
1375:
1374:
1369:
1352:
1346:
1345:
1317:
1311:
1310:
1282:
1276:
1271:1979 C. Roubet.
1269:
1263:
1252:
1246:
1235:
1226:
1225:
1197:
1191:
1182:1984 D. Lubell.
1180:
1174:
1173:
1155:
1149:
1148:
1120:
1114:
1107:
1101:
1100:
1080:
1074:
1073:
1053:
1008:
996:
984:
972:
927:Eburran industry
910:and containers;
772:
765:
758:
713:Circular ditches
693:Animal husbandry
680:Neolithic topics
640:Khiamian culture
636:Other locations
541:Shijiahe culture
531:Longshan culture
521:Majiayao culture
516:Liangzhu culture
506:Dawenkou culture
501:Hongshan culture
496:Yangshao culture
364:Petreşti culture
334:Hamangia culture
324:Gorneşti culture
304:Coțofeni culture
267:Amratian culture
262:Badarian culture
252:El Omari culture
237:Faiyum A culture
205:Tahunian culture
166:Fertile Crescent
138:
137:
29:
22:
18:
1543:
1542:
1538:
1537:
1536:
1534:
1533:
1532:
1483:
1482:
1455:
1450:
1415:
1411:
1404:
1382:
1378:
1367:
1353:
1349:
1318:
1314:
1283:
1279:
1270:
1266:
1254:2004 D. Lubell.
1253:
1249:
1236:
1229:
1198:
1194:
1181:
1177:
1170:
1156:
1152:
1121:
1117:
1108:
1104:
1097:
1081:
1077:
1070:
1054:
1050:
1046:
1028:Kelif el Boroud
1019:
1012:
1009:
1000:
997:
988:
985:
976:
973:
964:
916:Ibero-Maurusian
831:Capsien typique
784:Capsian culture
776:
739:
738:
737:
681:
673:
672:
671:
660:Capsian culture
574:
551:Neolithic Tibet
456:Dadiwan culture
414:Vučedol culture
399:Usatovo culture
319:Dudești culture
247:Merimde culture
200:Qaraoun culture
171:Heavy Neolithic
160:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1541:
1531:
1530:
1525:
1520:
1515:
1510:
1505:
1500:
1495:
1481:
1480:
1475:
1466:
1461:
1454:
1453:External links
1451:
1449:
1448:
1429:(3): 305–314.
1409:
1402:
1376:
1347:
1328:(4): 393–397.
1312:
1299:10.2307/414395
1293:(3): 694–698.
1277:
1275:. Paris: CNRS.
1264:
1247:
1227:
1208:(1–2): 41–55.
1192:
1175:
1168:
1150:
1115:
1102:
1095:
1075:
1068:
1047:
1045:
1042:
1041:
1040:
1035:
1030:
1025:
1018:
1015:
1014:
1013:
1010:
1003:
1001:
998:
991:
989:
986:
979:
977:
974:
967:
963:
960:
778:
777:
775:
774:
767:
760:
752:
749:
748:
741:
740:
736:
735:
730:
725:
720:
715:
710:
705:
700:
695:
690:
683:
682:
679:
678:
675:
674:
670:
669:
668:
667:
662:
657:
652:
647:
642:
634:
633:
632:
627:
622:
617:
612:
607:
602:
597:
592:
587:
582:
577:
570:
565:
555:
554:
553:
548:
546:Yueshi culture
543:
538:
536:Baodun culture
533:
528:
523:
518:
513:
511:Songze culture
508:
503:
498:
493:
488:
483:
481:Hemudu culture
478:
473:
468:
463:
458:
453:
451:Cishan culture
448:
446:Beixin culture
443:
438:
428:
427:
426:
421:
416:
411:
406:
401:
396:
391:
386:
381:
379:Sesklo culture
376:
371:
366:
361:
359:Ozieri culture
356:
351:
346:
341:
339:Kakanj culture
336:
331:
326:
321:
316:
314:Danilo culture
311:
306:
301:
296:
291:
289:Butmir culture
286:
281:
271:
270:
269:
264:
259:
254:
249:
244:
242:Tasian culture
239:
229:
228:
227:
222:
217:
212:
207:
202:
197:
183:
178:
173:
162:
161:
158:
157:
154:
153:
146:
145:
134:
133:
128:
124:
123:
121:Iberomaurusian
118:
114:
113:
102:Aïn Misteheyia
83:
79:
78:
73:
67:
66:
63:
59:
58:
49:
45:
44:
35:
31:
30:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1540:
1529:
1526:
1524:
1521:
1519:
1516:
1514:
1511:
1509:
1506:
1504:
1501:
1499:
1496:
1494:
1491:
1490:
1488:
1479:
1476:
1474:
1470:
1467:
1465:
1462:
1460:
1457:
1456:
1444:
1440:
1436:
1432:
1428:
1424:
1420:
1413:
1405:
1399:
1395:
1391:
1387:
1380:
1372:
1366:
1362:
1358:
1351:
1343:
1339:
1335:
1331:
1327:
1323:
1316:
1308:
1304:
1300:
1296:
1292:
1288:
1281:
1274:
1268:
1261:
1257:
1251:
1244:
1240:
1234:
1232:
1223:
1219:
1215:
1211:
1207:
1203:
1196:
1189:
1185:
1179:
1171:
1165:
1161:
1154:
1146:
1142:
1138:
1134:
1131:(1): 57–105.
1130:
1126:
1119:
1112:
1106:
1098:
1096:9781349075898
1092:
1088:
1087:
1079:
1071:
1069:9780306461583
1065:
1061:
1060:
1052:
1048:
1039:
1036:
1034:
1031:
1029:
1026:
1024:
1021:
1020:
1007:
1002:
995:
990:
983:
978:
971:
966:
965:
959:
955:
953:
949:
945:
944:Mechta-Afalou
941:
937:
936:
930:
928:
923:
921:
917:
913:
909:
905:
901:
897:
892:
890:
885:
883:
879:
875:
871:
867:
863:
859:
855:
851:
847:
842:
840:
836:
832:
828:
824:
820:
815:
813:
809:
805:
801:
797:
793:
789:
785:
773:
768:
766:
761:
759:
754:
753:
751:
750:
747:
743:
742:
734:
731:
729:
726:
724:
721:
719:
716:
714:
711:
709:
706:
704:
701:
699:
696:
694:
691:
688:
685:
684:
677:
676:
666:
663:
661:
658:
656:
653:
651:
648:
646:
643:
641:
638:
637:
635:
631:
628:
626:
623:
621:
618:
616:
613:
611:
608:
606:
603:
601:
598:
596:
595:Chopani Mando
593:
591:
588:
586:
583:
581:
578:
576:
571:
569:
566:
564:
561:
560:
559:
556:
552:
549:
547:
544:
542:
539:
537:
534:
532:
529:
527:
524:
522:
519:
517:
514:
512:
509:
507:
504:
502:
499:
497:
494:
492:
489:
487:
484:
482:
479:
477:
474:
472:
471:Xinle culture
469:
467:
464:
462:
461:Houli culture
459:
457:
454:
452:
449:
447:
444:
442:
439:
437:
434:
433:
432:
429:
425:
422:
420:
417:
415:
412:
410:
409:Vinča culture
407:
405:
404:Varna culture
402:
400:
397:
395:
392:
390:
389:Tisza culture
387:
385:
384:Sopot culture
382:
380:
377:
375:
372:
370:
367:
365:
362:
360:
357:
355:
354:Malta Temples
352:
350:
347:
345:
342:
340:
337:
335:
332:
330:
327:
325:
322:
320:
317:
315:
312:
310:
307:
305:
302:
300:
297:
295:
292:
290:
287:
285:
284:Boian culture
282:
280:
277:
276:
275:
272:
268:
265:
263:
260:
258:
257:Maadi culture
255:
253:
250:
248:
245:
243:
240:
238:
235:
234:
233:
230:
226:
225:Ubaid culture
223:
221:
218:
216:
215:Halaf culture
213:
211:
208:
206:
203:
201:
198:
195:
191:
187:
184:
182:
179:
177:
174:
172:
169:
168:
167:
164:
163:
156:
155:
152:
148:
147:
144:
140:
139:
132:
129:
125:
122:
119:
115:
111:
107:
103:
99:
95:
91:
87:
84:
80:
77:
74:
72:
68:
64:
60:
57:
53:
50:
46:
43:
39:
36:
32:
28:
23:
1426:
1422:
1412:
1385:
1379:
1360:
1356:
1350:
1325:
1321:
1315:
1290:
1286:
1280:
1272:
1267:
1259:
1250:
1242:
1205:
1201:
1195:
1187:
1178:
1159:
1153:
1128:
1124:
1118:
1110:
1105:
1085:
1078:
1058:
1051:
956:
935:Homo sapiens
933:
931:
924:
893:
886:
843:
838:
834:
830:
816:
783:
781:
746:Chalcolithic
659:
650:Jōmon period
486:Daxi culture
38:North Africa
850:East Africa
786:was a late
232:Nile valley
186:Pre-Pottery
127:Followed by
117:Preceded by
106:Kef Zoura D
82:Major sites
42:East Africa
40:, possibly
1487:Categories
1044:References
882:ovicaprids
870:hartebeest
856:at higher
788:Mesolithic
703:Metallurgy
630:Brahmagiri
590:Kalibangan
585:Rakhigarhi
563:Lahuradewa
558:South Asia
344:Khirokitia
151:Mesolithic
56:Bronze Age
1443:0002-9483
1363:: 63–69.
1145:162822759
948:Natufians
912:seashells
858:altitudes
792:Neolithic
723:Megaliths
689:(farming)
143:Neolithic
86:Medjez II
71:Type site
52:Neolithic
1371:11805152
1287:Language
1222:53678760
1017:See also
920:incisors
896:rock art
827:horizons
625:Mundigak
620:Burzahom
615:Koldihwa
605:Daimabad
580:Bhirrana
568:Mehrgarh
110:El Mekta
94:Aïn Naga
76:El Mekta
1330:Bibcode
962:Gallery
866:aurochs
852:, with
846:savanna
823:Algeria
819:Tunisia
814:times.
804:Tunisia
796:Maghreb
698:Pottery
610:Chirand
131:Libyans
20:Capsian
1441:
1400:
1368:
1357:Sahara
1307:414395
1305:
1220:
1166:
1143:
1093:
1066:
898:, and
889:Sahara
878:snails
829:, the
718:Henges
600:Jhukar
274:Europe
48:Period
1365:INIST
1303:JSTOR
1218:S2CID
1141:S2CID
908:beads
900:ochre
874:hares
812:Roman
808:Capsa
800:Gafsa
708:Wheel
431:China
62:Dates
1439:ISSN
1398:ISBN
1164:ISBN
1091:ISBN
1064:ISBN
942:and
925:The
876:and
868:and
821:and
790:and
782:The
141:The
1471:at
1431:doi
1390:doi
1338:doi
1295:doi
1210:doi
1133:doi
872:to
810:in
802:in
1489::
1437:.
1425:.
1421:.
1396:.
1359:.
1336:.
1326:14
1324:.
1301:.
1291:61
1289:.
1230:^
1216:.
1206:25
1204:.
1139:.
1129:18
1127:.
884:.
744:↓
192:,
149:↑
108:,
104:,
100:,
96:,
92:,
88:,
54:–
1445:.
1433::
1427:8
1406:.
1392::
1373:.
1361:3
1344:.
1340::
1332::
1309:.
1297::
1224:.
1212::
1172:.
1147:.
1135::
1099:.
1072:.
950:/
771:e
764:t
757:v
196:)
194:B
190:A
188:(
112:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.