31:
385:, and then down the Chinese coast. During August and September 1998 two survey circuits were conducted along most of the west and south coast of South Korea and provided some insight into the suspected autumn migration strategy, with around 475 Chinese egrets found between August 18 and September 2, increasing to 615 between September 13 and 28. Most were found in the northwestern Gyeonggi Bay, which also holds most of South Korea's breeding birds, but significant counts were made at several more southern sites, especially in the second survey circuit.
87:
209:
62:
565:
261:
553:
370:
therefore rather short, and most birds are thought to arrive in their Korean breeding colonies without staging anywhere along the Korean coast. The autumn migration is rather more leisurely with many egrets appearing to move southward along the west coast during August and
September, before departing Korea probably out through the southwest of the peninsula across the
340:
where between one third and a half of the world population are believed to winter, based on the results of a winter census undertaken in 2004/05. The total population is estimated at 2,600–3,400 individuals. During the decade from 2002 to 2012 there was no significant decline in the population of
369:
In South Korea the first returning
Chinese egrets, almost always already in full-breeding plumage, start to arrive back in mid-April. Their first appearance is in small numbers on offshore islands, especially in stormy weather, with immigration over by mid-May. The period of spring migration is
397:
for decorating hats. They had been used for this purpose since at least the 17th century but in the 19th century it became a major craze and the number of egret skins passing through dealers reached into the millions. This is thought to have contributed to the decline of all of the white
283:
and legs yellow green, while the iris is yellow. All individuals are similar in this season. In the breeding season the adults develop a luxuriant crest which is sometimes over 11 cm long. It also develops long
360:
Outside the breeding season the
Chinese egret occurs in shallow tidal estuaries, mudflats and bays, occasionally visiting rice fields and fish ponds. All recent breeding records have been from offshore islands.
341:
this species, and there are newly discovered colonies off the coast of southern China which may represent increased observer effort, but could also indicate a real growth in the population.
308:
although it is now only a non-breeding visitor or passage migrant to these countries. It is also a non-breeding passage migrant or winterer in Japan, the
Philippines, Vietnam, Thailand,
738:
292:
and similar to those of little egret. The bare parts change too, the bill becomes a bright, almost orange, yellow while the lores turn bright blue and the legs black with yellow feet.
300:
The
Chinese egret breeds on small islands off the coasts of far eastern Russia, North Korea, South Korea and mainland China. It formerly bred in Taiwan and the
826:
378:
878:
958:
577:
800:
839:
988:
844:
557:
774:
478:
983:
917:
883:
271:
The
Chinese egret averages 68 cm in height. The plumage is white throughout the bird's life and resembles the
787:
865:
668:
30:
639:
630:
978:
702:
707:
520:
448:
922:
681:
279:). Outside the breeding season the bill is dusky with the basal portion being tannish peach and the
86:
909:
973:
968:
569:
497:
831:
689:
592:
857:
181:
694:
655:
650:
8:
309:
245:
51:
425:
382:
345:
81:
66:
725:
474:
935:
743:
963:
730:
443:
405:
891:
792:
717:
317:
301:
870:
280:
249:
198:
138:
316:, Singapore, Indonesia and Brunei. The most important wintering areas are the
952:
852:
615:
434:
394:
71:
39:
779:
349:
272:
264:
904:
896:
813:
624:
288:
plumes on its breast and dorsal plumes extending beyond the tail, called
208:
766:
930:
805:
371:
285:
241:
305:
98:
818:
586:
756:
609:
564:
337:
289:
118:
676:
400:
393:
The nuptial plumes of the
Chinese egret, like other egrets, were
377:
Other
Chinese egrets probably move westward directly across from
333:
313:
158:
260:
663:
552:
108:
43:
408:
of tidal flats and estuarine habitats, and through pollution.
751:
325:
321:
237:
148:
417:
329:
128:
404:
species. The greatest modern threat is habitat loss and
216:
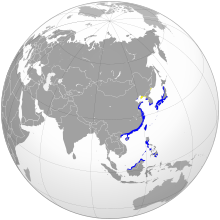
Yellow: breeding, green: year-round, blue: nonbreeding
423:
449:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22696977A93596047.en
950:
332:in the Philippines, and the Malaysian states of
295:
492:
490:
488:
486:
207:
60:
29:
447:
483:
259:
951:
518:
469:Hancock, J. & Kushlan, J. (1984).
591:
590:
435:IUCN Red List of Threatened Species
13:
14:
1000:
545:
959:IUCN Red List vulnerable species
563:
551:
85:
502:) - BirdLife species factsheet"
424:BirdLife International (2016).
388:
512:
463:
255:
1:
411:
236:) is a threatened species of
989:Taxa named by Robert Swinhoe
7:
364:
296:Distribution and population
10:
1005:
519:Moores, Nial (July 2003).
355:
599:
521:"The "Tidal-flat" Egret:
215:
206:
187:
180:
82:Scientific classification
80:
58:
49:
37:
28:
23:
583:- BirdLife International
442:: e.T22696977A93596047.
984:Birds described in 1860
348:, mostly threatened by
344:It is classified as a
320:, i.e. the islands of
268:
263:
560:at Wikimedia Commons
471:The Herons Handbook
310:Peninsular Malaysia
52:Conservation status
979:Birds of Manchuria
936:Egretta-eulophotes
744:egretta-eulophotes
669:egretta-eulophotes
656:Egretta_eulophotes
631:Egretta eulophotes
601:Egretta eulophotes
580:Egretta eulophotes
558:Egretta eulophotes
523:Egretta eulophotes
500:Egretta eulophotes
428:Egretta eulophotes
383:Shandong Peninsula
346:vulnerable species
269:
233:Egretta eulophotes
191:Egretta eulophotes
173:E. eulophotes
946:
945:
593:Taxon identifiers
556:Media related to
220:
219:
75:
996:
939:
938:
926:
925:
913:
912:
900:
899:
887:
886:
874:
873:
871:NHMSYS0000533063
861:
860:
848:
847:
835:
834:
822:
821:
809:
808:
796:
795:
783:
782:
770:
769:
760:
759:
747:
746:
734:
733:
721:
720:
711:
710:
698:
697:
685:
684:
682:A8E3A3DA05EC77F2
672:
671:
659:
658:
646:
645:
635:
634:
633:
620:
619:
618:
588:
587:
568:Data related to
567:
555:
540:
539:
537:
535:
516:
510:
509:
506:www.birdlife.org
498:"Chinese Egret (
494:
481:
467:
461:
460:
458:
456:
451:
421:
277:Egretta garzetta
211:
193:
90:
89:
69:
64:
63:
33:
21:
20:
1004:
1003:
999:
998:
997:
995:
994:
993:
949:
948:
947:
942:
934:
929:
921:
916:
908:
903:
895:
892:Observation.org
890:
882:
877:
869:
864:
856:
851:
843:
838:
830:
825:
817:
812:
804:
799:
791:
786:
778:
773:
765:
763:
755:
750:
742:
737:
729:
724:
716:
714:
706:
701:
693:
688:
680:
675:
667:
662:
654:
649:
643:
638:
629:
628:
623:
614:
613:
608:
595:
548:
543:
533:
531:
517:
513:
496:
495:
484:
468:
464:
454:
452:
422:
418:
414:
391:
367:
358:
318:Eastern Visayas
302:New Territories
298:
258:
246:first described
228:Swinhoe's egret
202:
195:
189:
176:
84:
76:
65:
61:
54:
17:
16:Species of bird
12:
11:
5:
1002:
992:
991:
986:
981:
976:
974:Birds of Korea
971:
969:Birds of China
966:
961:
944:
943:
941:
940:
927:
914:
901:
888:
875:
862:
849:
836:
823:
810:
797:
784:
771:
761:
748:
735:
722:
712:
699:
686:
673:
660:
647:
636:
621:
605:
603:
597:
596:
585:
584:
578:Chinese Egret
575:
574:at Wikispecies
561:
547:
546:External links
544:
542:
541:
511:
482:
462:
415:
413:
410:
390:
387:
366:
363:
357:
354:
297:
294:
257:
254:
250:Robert Swinhoe
218:
217:
213:
212:
204:
203:
196:
185:
184:
178:
177:
170:
168:
164:
163:
156:
152:
151:
146:
142:
141:
139:Pelecaniformes
136:
132:
131:
126:
122:
121:
116:
112:
111:
106:
102:
101:
96:
92:
91:
78:
77:
59:
56:
55:
50:
47:
46:
35:
34:
26:
25:
24:Chinese egret
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1001:
990:
987:
985:
982:
980:
977:
975:
972:
970:
967:
965:
962:
960:
957:
956:
954:
937:
932:
928:
924:
919:
915:
911:
906:
902:
898:
893:
889:
885:
880:
876:
872:
867:
863:
859:
854:
850:
846:
841:
837:
833:
828:
824:
820:
815:
811:
807:
802:
798:
794:
789:
785:
781:
776:
772:
768:
762:
758:
753:
749:
745:
740:
736:
732:
727:
723:
719:
713:
709:
704:
700:
696:
691:
687:
683:
678:
674:
670:
665:
661:
657:
652:
648:
641:
637:
632:
626:
622:
617:
611:
607:
606:
604:
602:
598:
594:
589:
582:
581:
576:
573:
572:
571:Chinese egret
566:
562:
559:
554:
550:
549:
530:
526:
524:
515:
507:
503:
501:
493:
491:
489:
487:
480:
479:0-7099-3716-4
476:
473:. Croom Helm
472:
466:
450:
445:
441:
437:
436:
431:
429:
420:
416:
409:
407:
403:
402:
396:
386:
384:
380:
375:
373:
362:
353:
351:
347:
342:
339:
335:
331:
327:
323:
319:
315:
311:
307:
303:
293:
291:
287:
282:
278:
274:
266:
262:
253:
251:
247:
243:
239:
235:
234:
229:
225:
224:Chinese egret
214:
210:
205:
200:
194:
192:
186:
183:
182:Binomial name
179:
175:
174:
169:
166:
165:
162:
161:
157:
154:
153:
150:
147:
144:
143:
140:
137:
134:
133:
130:
127:
124:
123:
120:
117:
114:
113:
110:
107:
104:
103:
100:
97:
94:
93:
88:
83:
79:
73:
68:
57:
53:
48:
45:
41:
40:Zengwen River
36:
32:
27:
22:
19:
600:
579:
570:
532:. Retrieved
528:
522:
514:
505:
499:
470:
465:
453:. Retrieved
439:
433:
427:
419:
399:
392:
389:Conservation
379:Gyeonggi Bay
376:
368:
359:
350:habitat loss
343:
299:
276:
273:little egret
270:
265:Laem Pak Bia
232:
231:
227:
223:
221:
190:
188:
172:
171:
159:
18:
905:SeaLifeBase
814:iNaturalist
625:Wikispecies
529:Birds Korea
455:19 November
406:reclamation
381:toward the
256:Description
953:Categories
931:Xeno-canto
412:References
372:Yellow Sea
286:lanceolate
267:, Thailand
199:R. Swinhoe
67:Vulnerable
395:in demand
306:Hong Kong
290:aigrettes
252:in 1860.
242:east Asia
167:Species:
105:Kingdom:
99:Eukaryota
858:22696977
832:10717124
695:22696977
690:BirdLife
610:Wikidata
365:Behavior
338:Selangor
149:Ardeidae
145:Family:
119:Chordata
115:Phylum:
109:Animalia
95:Domain:
72:IUCN 3.1
964:Egretta
806:2480887
677:Avibase
616:Q392152
534:7 April
401:Egretta
356:Habitat
334:Sarawak
314:Sarawak
201:, 1860)
160:Egretta
155:Genus:
135:Order:
125:Class:
70: (
923:446492
910:172415
884:458089
845:174821
788:EURING
764:ECOS:
757:chiegr
718:chiegr
664:ARKive
644:chiegr
477:
44:Taiwan
918:WoRMS
897:73456
827:IRMNG
780:17225
775:EUNIS
752:eBird
731:6DYPK
715:BOW:
708:86966
326:Bohol
322:Leyte
281:lores
240:from
238:egret
879:NCBI
853:IUCN
840:ITIS
819:4949
801:GBIF
793:1160
767:8354
703:BOLD
536:2020
475:ISBN
457:2021
440:2016
336:and
330:Cebu
328:and
222:The
129:Aves
866:NBN
739:CMS
726:CoL
651:ADW
640:ABA
444:doi
304:of
248:by
226:or
38:In
955::
933::
920::
907::
894::
881::
868::
855::
842::
829::
816::
803::
790::
777::
754::
741::
728::
705::
692::
679::
666::
653::
642::
627::
612::
527:.
504:.
485:^
438:.
432:.
374:.
352:.
324:,
312:,
244:,
42:,
538:.
525:"
508:.
459:.
446::
430:"
426:"
275:(
230:(
197:(
74:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.